In-Plane MEMS Shallow Arch Beam for Mechanical Memory
Abstract
:1. Introduction
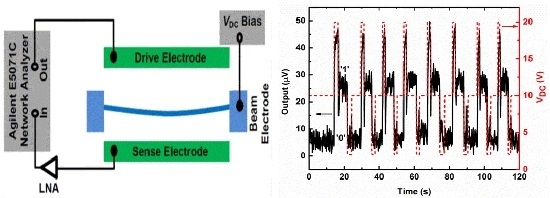
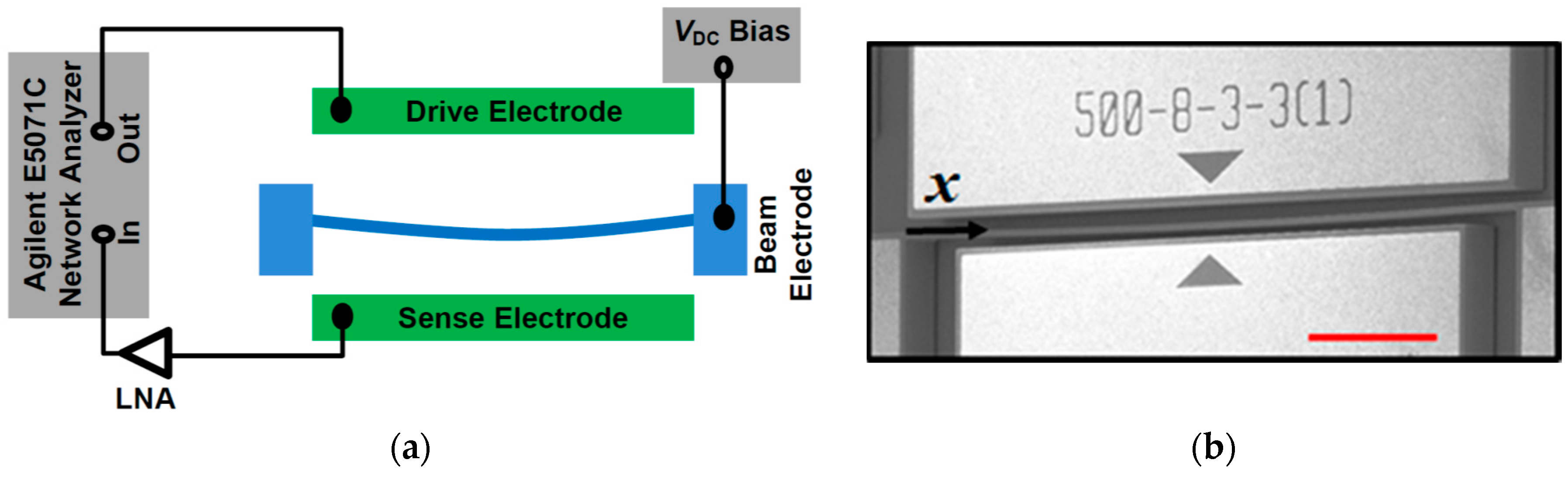
2. Device and Experimental Setup
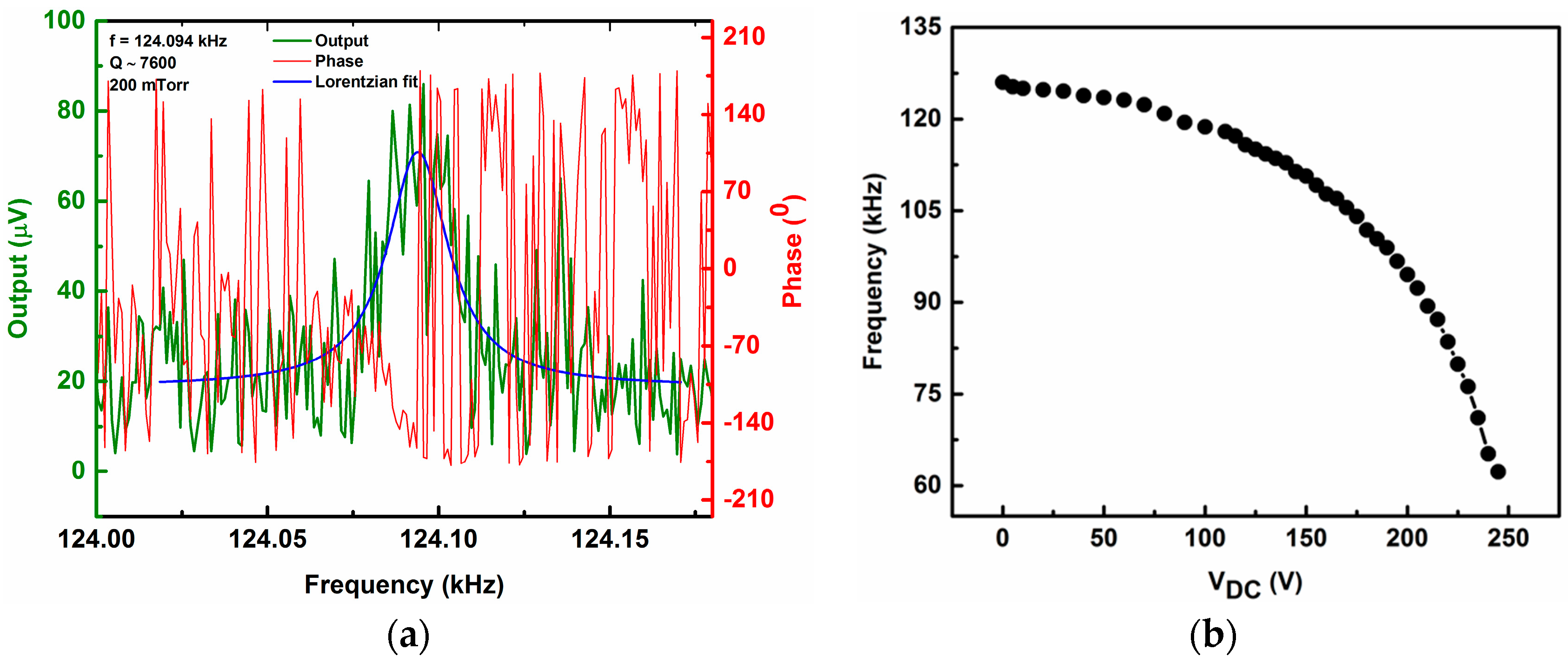
3. Softening Nonlinearity in Arch Microbeam
4. Results and Discussion
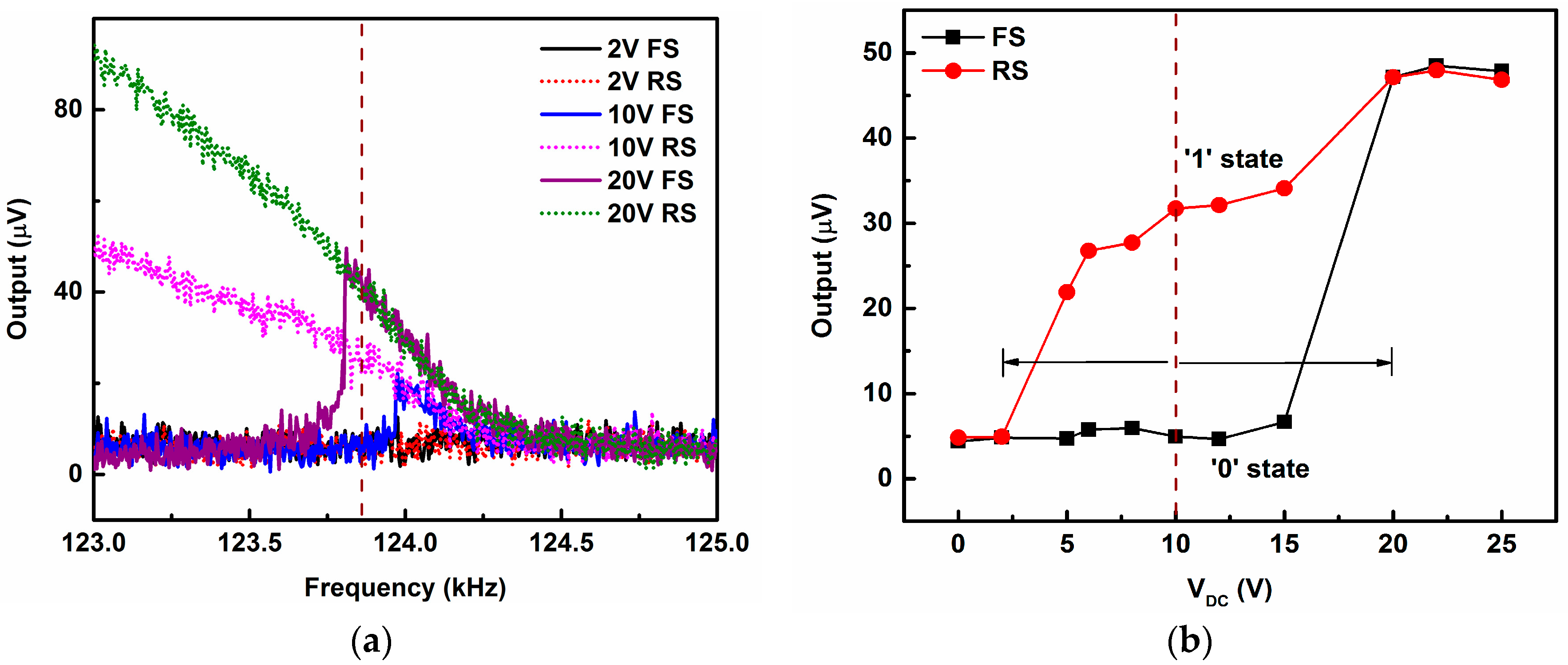
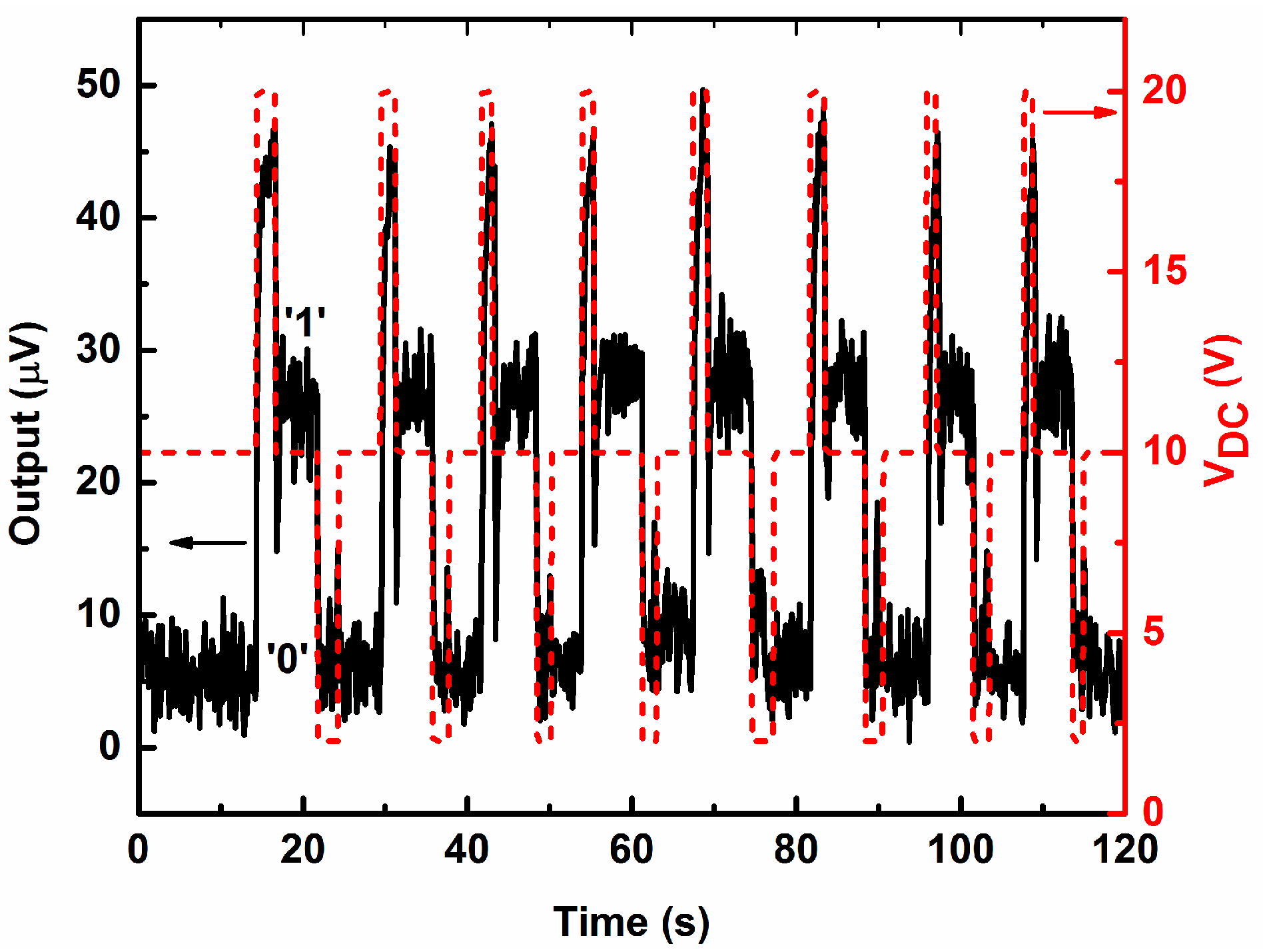
4.1. Switching from Low Vibration Amplitude (“0”) to High Vibration Amplitude (“1”)
4.2. Switching from High Vibration Amplitude (“1”) to Low Vibration Amplitude (“0”)
4.3. Sequential Switching Operation between the Memory States
4.4. Maximum Operating Speed and Energy Cost Per Switching between the Memory States
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Babbage, H.P. Babbage’s Calculating Engines; Tomash: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, M. The Universal Computer; Norton: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Theis, T.N.; Horn, P.M. Basic research in the information technology industry. Phys. Today 2003, 56, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swade, D.D. Redeeming Charles Babbage’s mechanical computer. Sci. Am. 1993, 268, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badzey, R.L.; Zolfagharkhani, G.; Gaidarzhy, A.; Mohanty, P. A controllable nanomechanical memory element. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 3587–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, D.N.; Imboden, M.; Mohanty, P. Electrostatically actuated silicon-based nanomechanical switch at room temperature. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 033515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, H.; Shim, S.B.; Jung, M.; Khim, Z.G.; Kim, J. A mechanical memory with a DC modulation of nonlinear resonance. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 033116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestra, W.J.; Westra, H.J.R.; Vander Zant, H.S.J. Mechanical stiffening, bistability and bit operation in a microcantilever. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 193107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uranga, A.; Verd, J.; Marigo, E.; Giner, J.; Munoz-Gamarra, J.L.; Narinol, N. Exploitation of non-linearities in CMOS-NEMS electrostatic resonators for mechanical memories. Sens. Actuators A 2013, 197, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahboob, I.; Yamaguchi, H. Bit storage and bit flip operations in an electromechanical oscillator. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, A.; Hikihara, T. Logic-memory device of a mechanical resonator. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 123104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halg, B. On a micro-electro-mechanical nonvolatile memory cell. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 1990, 37, 2230–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueckes, T.; Kim, K.; Joselevich, E.; Tseng, G.Y.; Cheung, C.L.; Liever, C.M. Carbon nanotube-based nonvolatile random access memory for molecular computing. Science 2000, 289, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlot, B.; Sun, W.; Yamashita, K.; Fujita, H.; Toshiyo, H. Bistable nanowire for micromechanical memory. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2008, 18, 045005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roodenburg, D.; Spronck, J.W.; van der Zant, H.S.J.; Venstra, W.J. Buckling beam micromechanical memory with on-chip readout. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 183501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, M.I. MEMS Linear and Nonlinear Statics and Dynamics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, L.C.; Palaniapan, M.; Tan, W.W.; Khine, L. Nonlinearity in micromechanical free-free beam resonators: Modeling and experimental verification. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2008, 18, 025017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoads, J.F.; Shaw, S.W.; Turner, K.L. Nonlinear dynamics and its applications in micro and nanoresonators. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2010, 132, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaajakari, V.; Mattila, T.; Oja, A.; Seppa, H. Nonlinear limits for single crystal silicon microresonators. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2004, 13, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, K.L.; Miller, S.A.; Hartwell, P.G.; MacDonald, N.C.; Strogatz, S.H.; Adams, S.G. Five parametric resonances in a microelectromechanicalsystem. Nature 1998, 396, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Baskaran, R.; Turner, K.L. Effect of cubic nonlinearity on auto-parametrically amplified resonant MEMS mass sensor. Sens. Actuators A 2002, 102, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trusov, A.A.; Shkel, A.M. The effect of high order non-linearities on sub-harmonic excitation with parallel plate capacitive actuators. In Proceedings of the ASME 2007 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 4–7 September 2007.
- Mestrom, R.M.C.; Fey, R.H.B.; Phan, K.L.; Nijmeijer, H. Simulations and experiments of hardening and softening resonances in a clamped-clamped beam MEMS resonator. Sens. Actuators A 2010, 162, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rahman, E.M.; Nayfeh, A.H. Secondary resonances of electrically actuated resonant microsensors. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2003, 13, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayfeh, A.H.; Younis, M.I. Dynamics of MEMS resonators under superharmonic and subharmonic excitations. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2005, 15, 1840–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaterjee, S.; Pohit, G. A large deflection model for the pull-in analysis of electrostatically actuated microcantilever beams. J. Sound Vib. 2009, 322, 969–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.L.; Yang, J.; Kitipornchai, S.; Lim, C.W. Resonance frequency response of geometrically nonlinear micro-switches under electrical actuation. J. Sound Vib. 2012, 331, 3397–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghimi Zand, M.; Ahmadian, M.T. Vibrational analysis of electrostatically actuated microstructures considering nonlinear effects. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2009, 14, 1664–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghayesh, M.H.; Farokhi, H.; Ambili, M. Nonlinear behavior of electrically actuated MEMS resonators. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2013, 71, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mindlin, R.; Tiersten, H. Effects of couple-stresses in linear elasticity. Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal. 1962, 11, 415–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, S. A micro scale Timoshenko beam model based on strain gradient elasticity theory. Eur. J. Mech. A Solids 2010, 29, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farokhi, H.; Ghayesh, M.H. Thermo-mechanical dynamics of perfect and imperfect Timoshenko microbeams. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2015, 91, 12–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farokhi, H.; Ghayesh, M.H.; Amabili, M. Nonlinear dynamics of a geometrically imperfect microbeam based on the modified couple stress theory. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2013, 68, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghayesh, M.H.; Farokhi, H.; Ambili, M. In-plane and out-of-plane motion characteristics of microbeams with modal interactions. Compos. B Eng. 2014, 60, 423–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghayesh, M.H.; Amabili, M. Coupled longitudinal-transverse behaviour of a geometrically imperfect microbeam. Compos. B Eng. 2014, 60, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghayesh, M.H.; Farokhi, H. Nonlinear dynamics of microplates. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2015, 86, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghir, S.; Younis, M.I. An investigation of the static and dynamic behavior of electrically actuated rectangular microplates. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 2016, 85, 81–93. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, J.; He, L.; Du, J.; Wu, H. Nonlinear analysis of functionally graded microplates based on a general four variable refined plate model and the modified couple stress theory. Compos. Struct. 2016, 152, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehrouyeh-Semnani, A.M.; Mostafaei, H.; Bahrami, M.N. Free flexural vibration of geometrically imperfect functionally graded microbeams. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2016, 105, 56–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiei, N.; Mousavi, A.; Ghadiri, M. On size-dependent nonlinear vibration of porous and imperfect functionally graded tapered microbeams. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2016, 106, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouakad, H.M.; Younis, M.I. The dynamic behavior of MEMS arch resonators actuated electrically. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 2010, 45, 704–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouakad, H.M.; Younis, M.I. On using the dynamic snap-through motion of MEMS initially curved microbeams for filtering applications. J. Sound Vib. 2014, 333, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramini, A.; Hennawi, Q.; Younis, M.I. Theoretical and experimental investigation of the nonlinear behavior of an electrostatically-actuated in-plane MEMS arch. J. MEMS 2016, 25, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkharabsheh, S.; Younis, M.I. Dynamics of MEMS arches of flexible supports. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2013, 22, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bataineh, A.; Younis, M.I. Dynamics of a clamped-clamped microbeam resonator considering fabrication imperfections. Microsyst. Technol. 2015, 21, 2425–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzziconi, L.; Bataineh, A.; Younis, M.I.; Cui, W.; Lenci, S. Nonlinear dynamics of an electrically actuated imperfect microbeam resonator: Experimental investigation and reduced-order modeling. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2013, 23, 075012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafiz, M.A.A.; Kosuru, L.; Younis, M.I. Microelectromechanical reprogrammable logic device. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayfeh, A.H.; Kreider, W.; Anderson, T.J. Investigation of natural frequencies and mode shapes of buckled beams. AIAA J. 1995, 33, 1121–1126. [Google Scholar]
- Nayfeh, A.H.; Mook, D.T. Nonlinear Oscillations; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hafiz, M.A.A.; Kosuru, L.; Ramini, A.; Chappanda, K.N.; Younis, M.I. In-Plane MEMS Shallow Arch Beam for Mechanical Memory. Micromachines 2016, 7, 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7100191
Hafiz MAA, Kosuru L, Ramini A, Chappanda KN, Younis MI. In-Plane MEMS Shallow Arch Beam for Mechanical Memory. Micromachines. 2016; 7(10):191. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7100191
Chicago/Turabian StyleHafiz, Md Abdullah Al, Lakshmoji Kosuru, Abdallah Ramini, Karumbaiah N. Chappanda, and Mohammad I. Younis. 2016. "In-Plane MEMS Shallow Arch Beam for Mechanical Memory" Micromachines 7, no. 10: 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7100191
APA StyleHafiz, M. A. A., Kosuru, L., Ramini, A., Chappanda, K. N., & Younis, M. I. (2016). In-Plane MEMS Shallow Arch Beam for Mechanical Memory. Micromachines, 7(10), 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7100191