Multidomain Molecular Sensor Devices, Systems, and Algorithms for Improved Physiological Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
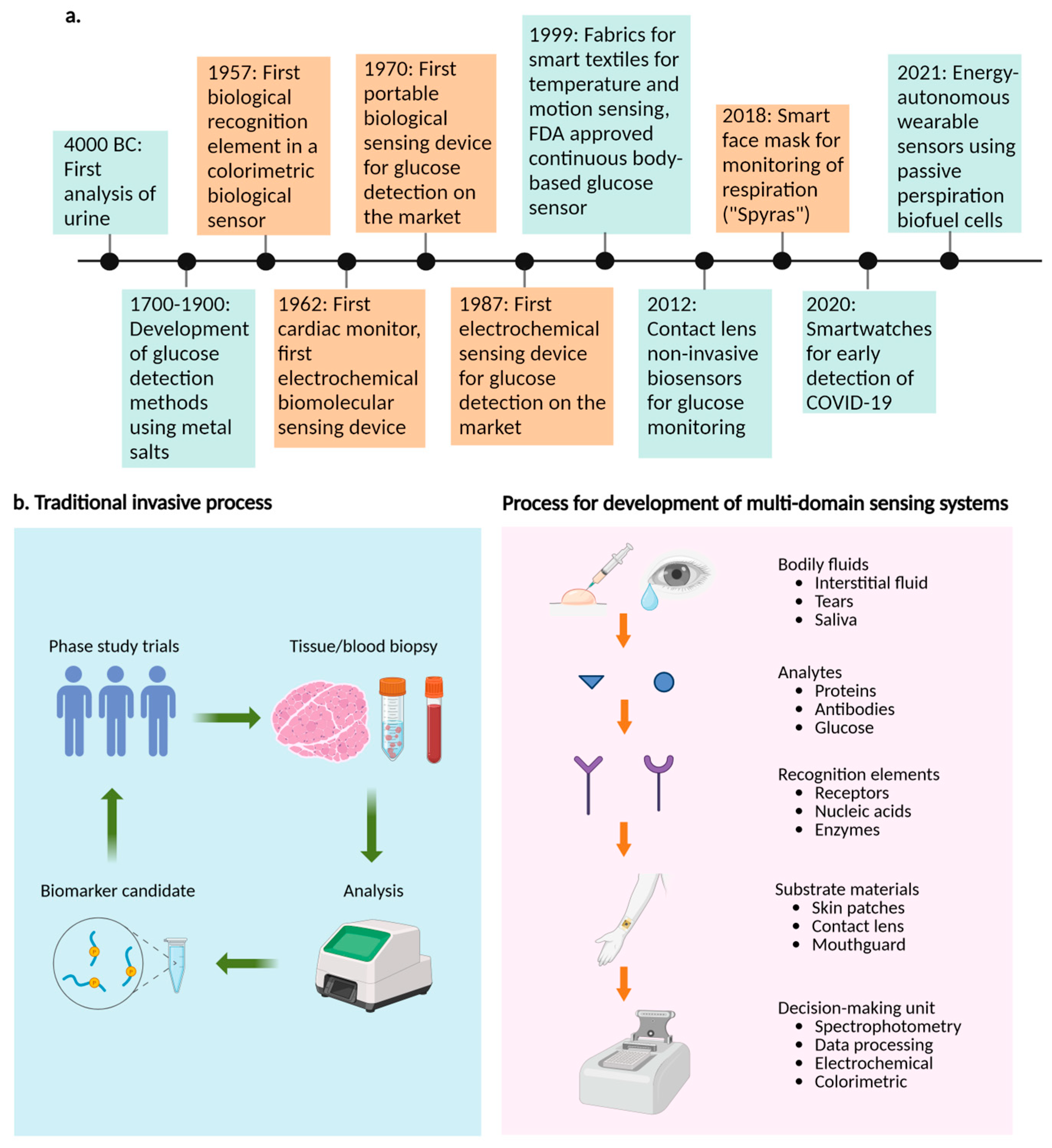
2. Multidomain Molecular Sensor Devices
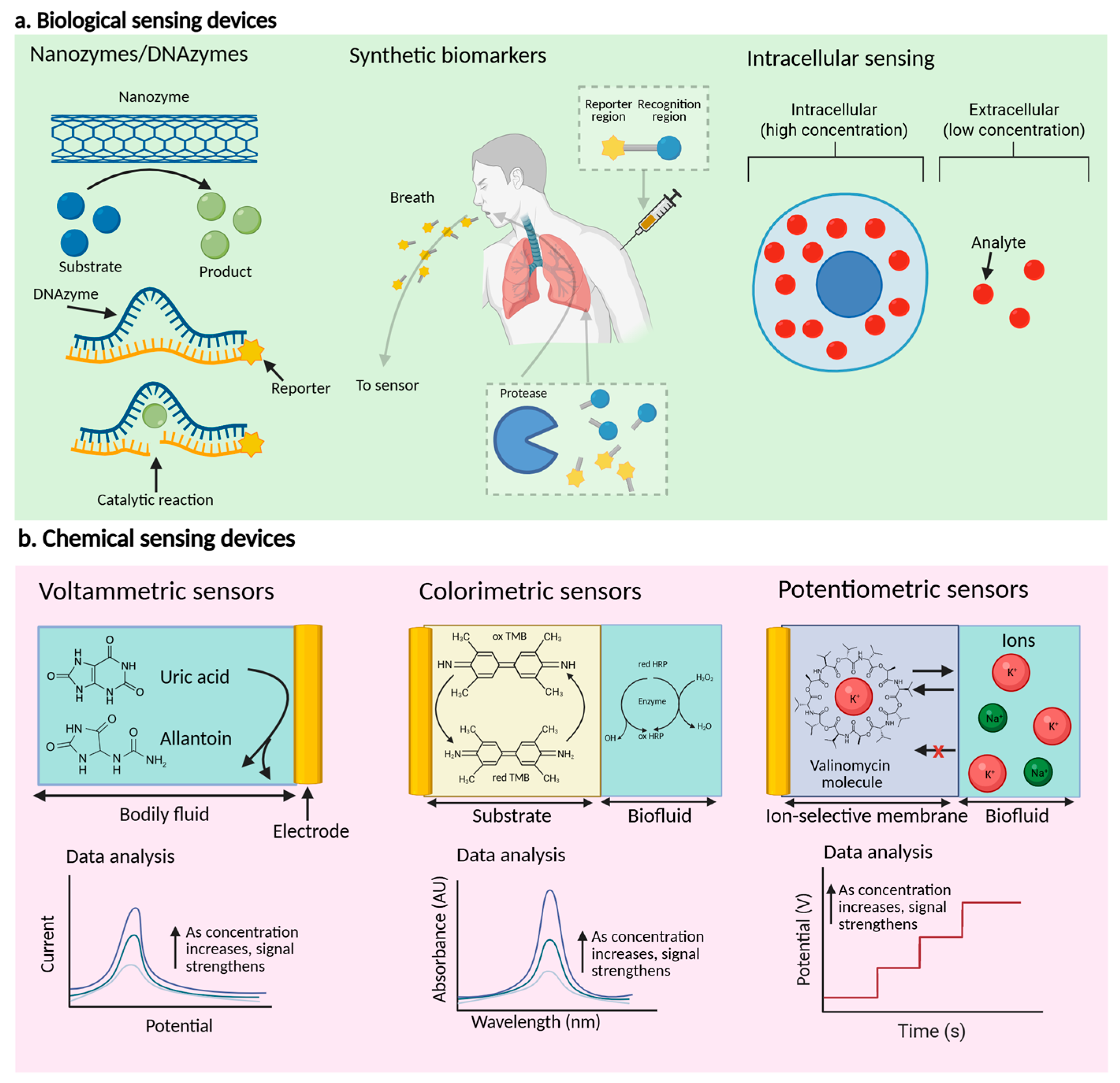
2.1. Biological-Based Sensor Devices
2.1.1. Signal Amplification Methods
2.1.2. Improvement Methodologies for Selectivity
2.1.3. Regentless, Real-Time Continuous Monitoring
2.2. Chemical-Based Sensor Devices
2.2.1. The Principal Recognition and Signal Transduction Methodologies
2.2.2. Methods for Improved Biomarker Detection
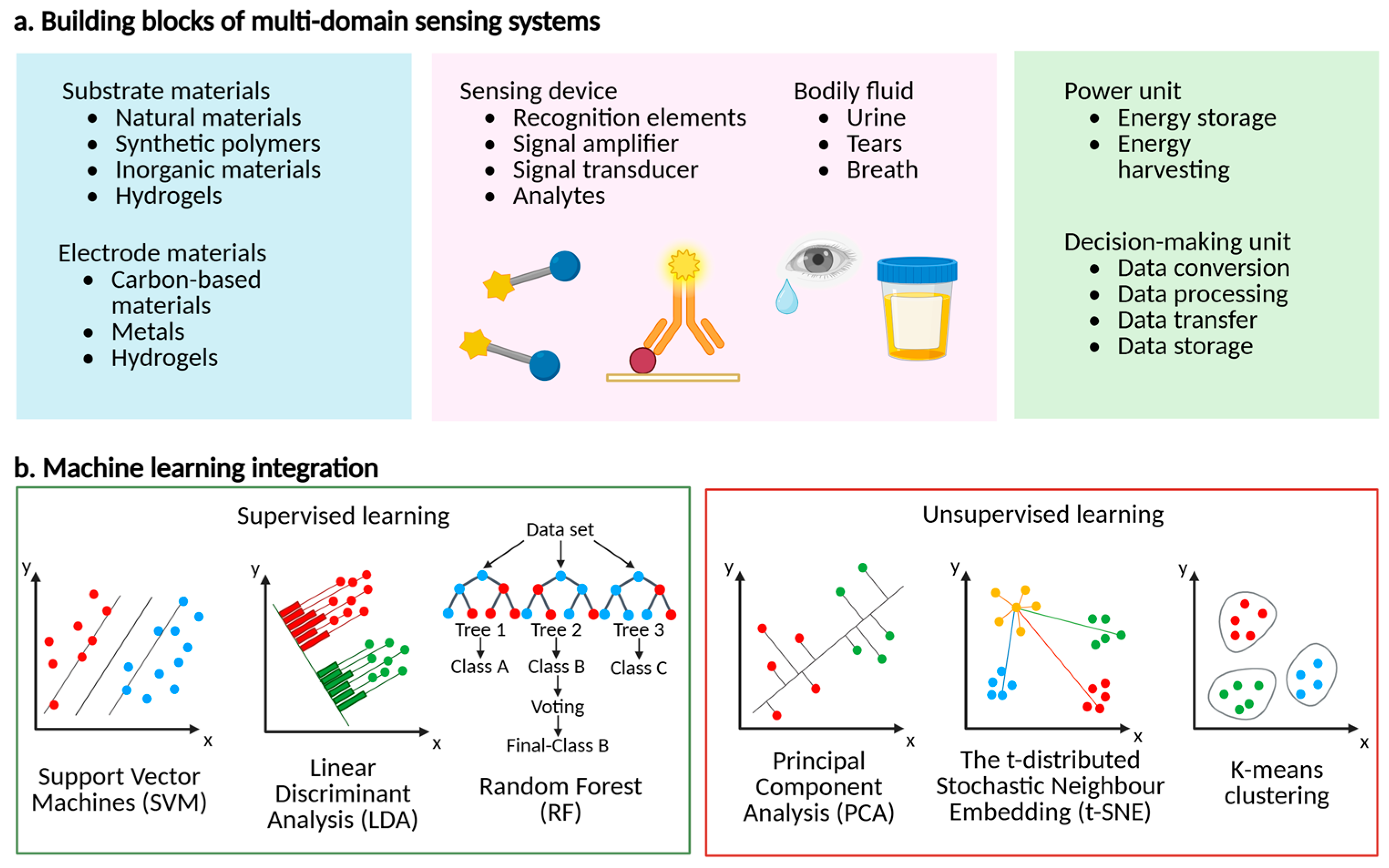
3. Multidomain Molecular Sensor Systems
3.1. Substrate Materials
3.2. The Bodily Fluids
3.3. The Power Units
3.4. Decision-Making [122,123] Units
4. Algorithms for Multidomain Molecular Sensor-Facilitated Data-Driven Biomarker Detection
4.1. Supervised Learning Algorithms
4.2. Unsupervised Learning Algorithms
4.3. Machine Learning for Disease Diagnosis Applications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flynn, C.D.; Chang, D.; Mahmud, A.; Yousefi, H.; Das, J.; Riordan, K.T.; Sargent, E.H.; Kelley, S.O. Biomolecular sensors for advanced physiological monitoring. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 2023, 1, 560–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyler, J.; Choi, S.W.; Tewari, M. Real-time, personalized medicine through wearable sensors and dynamic predictive modeling: A new paradigm for clinical medicine. Curr. Opin. Syst. Biol. 2020, 20, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.S.; Lee, D.; Meivita, M.P.; Li, L.; Tan, Y.S.; Bajalovic, N.; Loke, D.K. Ultrasensitive two-dimensional material-based MCF-7 cancer cell sensor driven by perturbation processes. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 6974–6983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Chan, S.S.-Y.; Naikar, J.S.; Meivita, M.P.; Teoh, W.-C.; Bajalovic, N.; Loke, D.K. Ultrasensitive low-probe-concentration PANC-1 and MCF-7 cancer cell sensors enabled by combined 2D-material-polymer-phage frameworks. Mater. Adv. 2023, 4, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterfield, D.A.; Halliwell, B. Oxidative stress, dysfunctional glucose metabolism and Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 20, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sempionatto, J.R.; Lasalde-Ramírez, J.A.; Mahato, K.; Wang, J.; Gao, W. Wearable chemical sensors for biomarker discovery in the omics era. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2022, 6, 899–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meivita, M.P.; Go, S.-X.; Mozar, F.S.; Li, L.; Tan, Y.S.; Bajalovic, N.; Loke, D.K. Shape complementarity processes for ultrashort-burst sensitive M13–PEG–WS 2-powered MCF-7 cancer cell sensors. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 16658–16668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, S.S.; Lee, D.; Meivita, M.P.; Li, L.; Tan, Y.S.; Bajalovic, N.; Loke, D.K. Ultrasensitive detection of MCF-7 cells with a carbon nanotube-based optoelectronic-pulse sensor framework. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 18459–18470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, S.; Jiang, B.; Hao, H.; Chen, Y.; Dong, J.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, R.; Chen, W.; Zhang, R. Matching the kinetics of natural enzymes with a single-atom iron nanozyme. Nat. Catal. 2021, 4, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ates, H.C.; Nguyen, P.Q.; Gonzalez-Macia, L.; Morales-Narváez, E.; Güder, F.; Collins, J.J.; Dincer, C. End-to-end design of wearable sensors. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2022, 7, 887–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ates, H.C.; Brunauer, A.; von Stetten, F.; Urban, G.A.; Güder, F.; Merkoçi, A.; Früh, S.M.; Dincer, C. Integrated devices for non-invasive diagnostics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2010388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, D.; Lazenby, R.A. Selective aptamer modification of Au surfaces in a microelectrode sensor array for simultaneous detection of multiple analytes. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 6828–6835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, B.D.; Soh, H.T. Re-evaluating the conventional wisdom about binding assays. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2020, 45, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, J.M.G.; Filho, N.R.A. The human volatilome meets cancer diagnostics: Past, present, and future of noninvasive applications. Metabolomics 2024, 20, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Beltagi, M.; Saeed, N.K.; Bediwy, A.S.; Elbeltagi, R. Insulin pumps in children-a systematic review. World J. Clin. Pediatr. 2022, 11, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Singh, V.; Sharma, R.; Koul, A.; McCarthy, E.T.; Savin, V.J.; Joshi, T.; Srivastava, T. Glomerular biomechanical stress and lipid mediators during cellular changes leading to chronic kidney disease. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleifel, M.; Fleifel, B.; El Alam, A. Diabetes Mellitus across the Arabo-Islamic World: A Revolution. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2023, 2023, 5541808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour-Haratbar, A.; Mohammadpour-Haratbar, S.; Zare, Y.; Rhee, K.Y.; Park, S.-J. A review on non-enzymatic electrochemical biosensors of glucose using carbon nanofiber nanocomposites. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fdez-Sanromán, A.; Bernárdez-Rodas, N.; Rosales, E.; Pazos, M.; González-Romero, E.; Sanromán, M.Á. Biosensor technologies for water quality: Detection of emerging contaminants and pathogens. Biosensors 2025, 15, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakata, T. Signal transduction interfaces for field-effect transistor-based biosensors. Commun. Chem. 2024, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freckmann, G.; Pleus, S.; Eichenlaub, M.; Eriksson Boija, E.; Fokkert, M.; Hinzmann, R.; Jendle, J.; Klonoff, D.C.; Makris, K.; Nichols, J.H. Recommendations on the collection of comparator measurement data in the performance evaluation of continuous glucose monitoring systems. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2025, 19, 19322968251336221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Steppe, P.L.; Kazman, M.W.; Styczynski, M.P. Point-of-care analyte quantification and digital readout via lysate-based cell-free biosensors interfaced with personal glucose monitors. ACS Synth. Biol. 2021, 10, 2862–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoaib, A.; Darraj, A.; Khan, M.E.; Azmi, L.; Alalwan, A.; Alamri, O.; Tabish, M.; Khan, A.U. A nanotechnology-based approach to biosensor application in current diabetes management practices. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, S.J.; Layouni, R.; Arshavsky-Graham, S.; Segal, E.; Weiss, S.M. Morlet wavelet filtering and phase analysis to reduce the limit of detection for thin film optical biosensors. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 2967–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Liu, G.; Han, Y.; Jin, W. Artificial channels for confined mass transport at the sub-nanometre scale. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 294–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, L. Intercomparison of PurpleAir sensor performance over three years indoors and outdoors at a home: Bias, precision, and limit of detection using an improved algorithm for calculating PM2.5. Sensors 2022, 22, 2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinhofer, I.; Rommer, P.; Zierfuss, B.; Altmann, P.; Foiani, M.; Heslegrave, A.; Zetterberg, H.; Gleiss, A.; Musolino, P.L.; Gong, Y. Neurofilament light chain as a potential biomarker for monitoring neurodegeneration in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesler, V.; Murmann, B.; Soh, H.T. Going beyond the Debye length: Overcoming charge screening limitations in next-generation bioelectronic sensors. Acs Nano 2020, 14, 16194–16201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrente-Rodríguez, R.M.; Lukas, H.; Tu, J.; Min, J.; Yang, Y.; Xu, C.; Rossiter, H.B.; Gao, W. SARS-CoV-2 RapidPlex: A graphene-based multiplexed telemedicine platform for rapid and low-cost COVID-19 diagnosis and monitoring. Matter 2020, 3, 1981–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ma, Q.; Li, M.; Chao, D.; Huang, L.; Wu, W.; Fang, Y.; Dong, S. Glucose-oxidase like catalytic mechanism of noble metal nanozymes. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, E.M.; Cozma, I.; Mou, Q.; Brennan, J.D.; Lu, Y.; Li, Y. Biosensing with dnazymes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 8954–8994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borggräfe, J.; Victor, J.; Rosenbach, H.; Viegas, A.; Gertzen, C.G.; Wuebben, C.; Kovacs, H.; Gopalswamy, M.; Riesner, D.; Steger, G. Time-resolved structural analysis of an RNA-cleaving DNA catalyst. Nature 2022, 601, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Lat, P.K.; Yu, H.-Z.; Sen, D. CLICK-17, a DNA enzyme that harnesses ultra-low concentrations of either Cu+ or Cu2+ to catalyze the azide-alkyne ‘click’ reaction in water. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 7356–7370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sero, J.E.; Stevens, M.M. Nanoneedle-based materials for intracellular studies. In Bio-Nanomedicine for Cancer Therapy; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 191–219. [Google Scholar]
- Terse-Thakoor, T.; Punjiya, M.; Matharu, Z.; Lyu, B.; Ahmad, M.; Giles, G.E.; Owyeung, R.; Alaimo, F.; Shojaei Baghini, M.; Brunyé, T.T. Thread-based multiplexed sensor patch for real-time sweat monitoring. npj Flex. Electron. 2020, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, L.W.; Anahtar, M.N.; Ong, T.-H.; Hern, K.E.; Kunz, R.R.; Bhatia, S.N. Engineering synthetic breath biomarkers for respiratory disease. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Chan, S.S.; Aksic, N.; Bajalovic, N.; Loke, D.K. Ultralong-time recovery and low-voltage electroporation for biological cell monitoring enabled by a microsized multipulse framework. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 35325–35333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Naikar, J.S.; Chan, S.S.; Meivita, M.P.; Li, L.; Tan, Y.S.; Bajalovic, N.; Loke, D.K. Ultralong recovery time in nanosecond electroporation systems enabled by orientational-disordering processes. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 7934–7942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiber, T.; Zavoiura, O.; Dose, C.; Yushchenko, D.A. Fluorophore multimerization as an efficient approach towards bright protein labels. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 2021, 2817–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanbhag, M.M.; Manasa, G.; Mascarenhas, R.J.; Mondal, K.; Shetti, N.P. Fundamentals of bio-electrochemical sensing. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2023, 16, 100516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaloo, S.; Zand, M.M. Wearable electrochemical flexible biosensors: With the focus on affinity biosensors. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2021, 32, 100403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Alkhamis, O.; Canoura, J.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, Y. Advances and challenges in small-molecule DNA aptamer isolation, characterization, and sensor development. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 16800–16823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Z.; Yang, K.-A.; Cheng, X.; Liu, W.; Yu, W.; Lin, S.; Zhao, Y.; Cheung, K.M. Wearable aptamer-field-effect transistor sensing system for noninvasive cortisol monitoring. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabk0967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frutiger, A.; Tanno, A.; Hwu, S.; Tiefenauer, R.F.; Voros, J.; Nakatsuka, N. Nonspecific binding—Fundamental concepts and consequences for biosensing applications. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 8095–8160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, A.; Haag, R.; Schedler, U. Hydrogels and their role in biosensing applications. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2100062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Yao, B.; Qiu, Y.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Alsaid, Y.; Frenkel, I.; Youssef, K.; Pei, Q. Hierarchically structured stretchable conductive hydrogels for high-performance wearable strain sensors and supercapacitors. Matter 2020, 3, 1196–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, D.; Chien, J.C.; Axpe, E.; Blankemeier, L.; Baker, S.W.; Swaminathan, S.; Piunova, V.A.; Zubarev, D.Y.; Maikawa, C.L.; Grosskopf, A.K. Combinatorial polyacrylamide hydrogels for preventing biofouling on implantable biosensors. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2109764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, L.; Yamazaki, H.; Ren, R.; Wanunu, M.; Ivanov, A.P.; Edel, J.B. Solid-state nanopore sensors. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 5, 931–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bariya, M.; Li, L.; Ghattamaneni, R.; Ahn, C.H.; Nyein, H.Y.Y.; Tai, L.-C.; Javey, A. Glove-based sensors for multimodal monitoring of natural sweat. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabb8308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhao, F.; Bai, Y.; Ye, Z.; Feng, Z.; Liu, X.; Gao, S.; Pang, X.; Sun, M.; Zhang, J. Slippery liquid-infused microphase separation surface enables highly robust anti-fouling, anti-corrosion, anti-icing and anti-scaling coating on diverse substrates. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 133945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Jiang, X.; Fang, X.; Kong, J. Wearable chem-biosensing devices: From basic research to commercial market. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 4285–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleman, J.; Kilic, T.; Mille, L.S.; Shin, S.R.; Zhang, Y.S. Microfluidic integration of regeneratable electrochemical affinity-based biosensors for continual monitoring of organ-on-a-chip devices. Nat. Protoc. 2021, 16, 2564–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, A.; Das, J.; Yousefi, H.; Mahmud, A.; Chen, J.B.; Kelley, S.O. Strategies for biomolecular analysis and continuous physiological monitoring. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 5281–5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dauphin-Ducharme, P.; Ploense, K.L.; Arroyo-Currás, N.; Kippin, T.E.; Plaxco, K.W. Electrochemical aptamer-based sensors: A platform approach to high-frequency molecular monitoring in situ in the living body. Biomed. Eng. Technol. 2022, 1, 479–492. [Google Scholar]
- Idili, A.; Gerson, J.; Kippin, T.; Plaxco, K.W. Seconds-resolved, in situ measurements of plasma phenylalanine disposition kinetics in living rats. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 4023–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.-W.; Fu, K.; Correa, S.; Eisenstein, M.; Appel, E.A.; Soh, H.T. Real-time monitoring of drug pharmacokinetics within tumor tissue in live animals. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabk2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurnik, M.; Pang, E.Z.; Plaxco, K.W. An electrochemical biosensor architecture based on protein folding supports direct real-time measurements in whole blood. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 18442–18445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Jin, T.; Dai, Y.; Liu, C.C. Surpassing the detection limit and accuracy of the electrochemical DNA sensor through the application of CRISPR Cas systems. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 155, 112100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parolo, C.; Greenwood, A.S.; Ogden, N.E.; Kang, D.; Hawes, C.; Ortega, G.; Arroyo-Currás, N.; Plaxco, K.W. E-DNA scaffold sensors and the reagentless, single-step, measurement of HIV-diagnostic antibodies in human serum. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2020, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Cui, H.; Hong, N.; Shu, Q.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; Wei, G.; Fan, H.; Zhang, J. A reagentless triplex DNA junctions-based electrochemical DNA sensor using signal amplification strategy of CHA and tetraferrocene. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 358, 131496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Yang, Y.; Gao, W. Skin-interfaced sensors in digital medicine: From materials to applications. Matter 2020, 2, 1414–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, C.; Lukas, H.; Wang, M.; Lee, Y.; Gao, W. Nucleic acid-based wearable and implantable electrochemical sensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 7960–7982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkinos, C.; Economou, A. Recent advances in voltammetric, amperometric and ion-selective (bio) sensors fabricated by microengineering manufacturing approaches. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2020, 23, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baracu, A.M.; Gugoasa, L.A.D. Recent advances in microfabrication, design and applications of amperometric sensors and biosensors. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 037503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhao, C. Wearable electrochemical sensors for noninvasive monitoring of health—A perspective. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2020, 23, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.; Sempionatto, J.R.; Teymourian, H.; Wang, J.; Gao, W. Wearable electrochemical biosensors in North America. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 172, 112750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Nyein, H.Y.Y.; Hou, L.; Lin, Y.; Bariya, M.; Ahn, C.H.; Ji, W.; Fan, Z.; Javey, A. A wearable nutrition tracker. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2006444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, B.; Roghani-Mamaqani, H.; Salami-Kalajahi, M. Colorimetric/fluorometric optical chemosensors based on oxazolidine for highly selective detection of Fe3+ and Ag+ in aqueous media: Development of ionochromic security papers. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1271, 134021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuhara, G. Analytical supramolecular chemistry: Colorimetric and fluorimetric chemosensors. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2020, 42, 100340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdrachek, E.; Bakker, E. Potentiometric sensing. Anal. Chem. 2020, 93, 72–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Qin, W. Recent advances in potentiometric biosensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 124, 115803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolkowicz, K.L.; Aiello, E.M.; Vargas, E.; Teymourian, H.; Tehrani, F.; Wang, J.; Pinsker, J.E.; Doyle, F.J., III; Patti, M.E.; Laffel, L.M. A review of biomarkers in the context of type 1 diabetes: Biological sensing for enhanced glucose control. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2021, 6, e10201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teymourian, H.; Barfidokht, A.; Wang, J. Electrochemical glucose sensors in diabetes management: An updated review (2010–2020). Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 7671–7709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, Y.-H.; Gutierrez-Wing, M.T.; Choi, J.-W. Recent progress in portable fluorescence sensors. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 017502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambaye, A.D.; Kefeni, K.K.; Mishra, S.B.; Nxumalo, E.N.; Ntsendwana, B. Recent developments in nanotechnology-based printing electrode systems for electrochemical sensors. Talanta 2021, 225, 121951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamun, M.A.A.; Yuce, M.R. Recent progress in nanomaterial enabled chemical sensors for wearable environmental monitoring applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2005703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, P.; Mishra, R.; Narayan, R.J. Biosensing applications of carbon-based materials. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 18, 100274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yang, Y.; Gao, W. Laser-engraved graphene for flexible and wearable electronics. Trends Chem. 2021, 3, 969–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, D.; Bai, X.; He, X. Research progress on hydrogel materials and their antifouling properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 181, 111665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Han, S.-T.; Gao, W.; Pan, C. Flexible and stretchable strategies for electronic skins: Materials, structure, and integration. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2021, 4, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Cheung, K.M.; Huang, I.-W.; Yang, H.; Nakatsuka, N.; Liu, W.; Cao, Y.; Man, T.; Weiss, P.S.; Monbouquette, H.G. Implantable aptamer–field-effect transistor neuroprobes for in vivo neurotransmitter monitoring. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabj7422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Agate, S.; Salem, K.S.; Lucia, L.; Pal, L. Hydrogel-based sensor networks: Compositions, properties, and applications—A review. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 4, 140–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, L.; Lin, G.; Feng, Y. Recent progress in the fabrication of flexible materials for wearable sensors. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 10, 614–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thadepalli, S. Review of multifarious applications of polymers in medical and health care textiles. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 55, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allafi, F.; Hossain, M.S.; Lalung, J.; Shaah, M.; Salehabadi, A.; Ahmad, M.I.; Shadi, A. Advancements in applications of natural wool fiber. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 497–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wang, G.; Zhu, M. Optoelectronic functional fibers: Materials, fabrication, and application for smart textiles. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 439–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-M.; Yuan, T.-Q.; Song, G.-Y.; Sun, R.-C. Advanced and versatile lignin-derived biodegradable composite film materials toward a sustainable world. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 3790–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzopoulou, Z.; Zamboulis, A.; Koumentakou, I.; Michailidou, G.; Noordam, M.J.; Bikiaris, D.N. Biocompatible synthetic polymers for tissue engineering purposes. Biomacromolecules 2022, 23, 1841–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, X.; Fitzpatrick, V.; Kaplan, D.L. From silk spinning to 3D printing: Polymer manufacturing using directed hierarchical molecular assembly. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2020, 9, 1901552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshammari, B.H.; Lashin, M.M.; Mahmood, M.A.; Al-Mubaddel, F.S.; Ilyas, N.; Rahman, N.; Sohail, M.; Khan, A.; Abdullaev, S.S.; Khan, R. Organic and inorganic nanomaterials: Fabrication, properties and applications. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 13735–13785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terna, A.D.; Elemike, E.E.; Mbonu, J.I.; Osafile, O.E.; Ezeani, R.O. The future of semiconductors nanoparticles: Synthesis, properties and applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2021, 272, 115363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La, T.G.; Le, L.H. Flexible and wearable ultrasound device for medical applications: A review on materials, structural designs, and current challenges. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 7, 2100798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wu, R.S.; Lin, M.; Xu, S. Emerging wearable ultrasound technology. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2023, 71, 713–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Fang, Y.; Chen, J. Wearable biosensors for non-invasive sweat diagnostics. Biosensors 2021, 11, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, S.M.; Kim, M.; Kwon, Y.W.; Kim, H.; Kim, M.J.; Park, Y.-G.; Park, J.-U. Recent advances in wearable devices for non-invasive sensing. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Park, W.; Lee, C.H. Electrochemically active materials and wearable biosensors for the in situ analysis of body fluids for human healthcare. NPG Asia Mater. 2021, 13, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senf, B.; Yeo, W.-H.; Kim, J.-H. Recent advances in portable biosensors for biomarker detection in body fluids. Biosensors 2020, 10, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, C.; Yang, B.; Fu, L.; Hou, H.; Qiang, J.; Zhou, C.; Gao, Y.; Mao, Z. Urine biomarkers can outperform serum biomarkers in certain diseases. Urine 2023, 5, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.; Stenzl, A.; Sharma, A.; Vasdev, N. Urinary biomarkers in bladder cancer: A review of the current landscape and future directions. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2021, 31, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitekenov, S.; Gaipov, A.; Bukasov, R. Detection and quantification of proteins in human urine. Talanta 2021, 223, 121718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, K.H.; Desai, D.T.; Patel, H.P.; Shah, D.O.; Willcox, M.D.; Maulvi, F.A. Contact lens as an emerging platform for non-invasive bio-sensing: A review. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2024, 376, 115617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Tao, X.; Liu, X.; Yang, L. Wearable eye patch biosensor for noninvasive and simultaneous detection of multiple biomarkers in human tears. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 8659–8667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, P.C.; Raposo, M.; Vassilenko, V. Breath volatile organic compounds (VOCs) as biomarkers for the diagnosis of pathological conditions: A review. Biomed. J. 2023, 46, 100623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratiu, I.A.; Ligor, T.; Bocos-Bintintan, V.; Mayhew, C.A.; Buszewski, B. Volatile organic compounds in exhaled breath as fingerprints of lung cancer, asthma and COPD. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijakowski, K.; Surdacka, A. Salivary biomarkers for diagnosis of inflammatory bowel diseases: A systematic review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinarov, Z.; Abdallah, M.; Agundez, J.A.; Allegaert, K.; Basit, A.W.; Braeckmans, M.; Ceulemans, J.; Corsetti, M.; Griffin, B.T.; Grimm, M. Impact of gastrointestinal tract variability on oral drug absorption and pharmacokinetics: An UNGAP review. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 162, 105812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashaninejad, N.; Munaz, A.; Moghadas, H.; Yadav, S.; Umer, M.; Nguyen, N.-T. Microneedle arrays for sampling and sensing skin interstitial fluid. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Qiao, Z.; Chen, S.; Fan, S.; Liu, Y.; Qi, J.; Lim, C.T. Interstitial fluid-based wearable biosensors for minimally invasive healthcare and biomedical applications. Commun. Mater. 2024, 5, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhang, F.; Wang, K.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Sun, X.; Li, C.; Dong, B.; Wang, L. Smart biosensors and intelligent devices for salivary biomarker detection. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 140, 116281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melguizo-Rodríguez, L.; Costela-Ruiz, V.J.; Manzano-Moreno, F.J.; Ruiz, C.; Illescas-Montes, R. Salivary biomarkers and their application in the diagnosis and monitoring of the most common oral pathologies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, M.; Tu, D.; Tong, L.; Sarwar, M.; Bhimaraj, A.; Li, C.; Cote, G.L.; Di Carlo, D. A review of biosensor technologies for blood biomarkers toward monitoring cardiovascular diseases at the point-of-care. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 171, 112621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Chen, J.; Xu, B.B.; Huang, Y. Flexible plasmonic biosensors for healthcare monitoring: Progress and prospects. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 18822–18847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, T.; Del Caño, R.; De la Paz, E.; Sandhu, S.S.; Wang, J. Access and management of sweat for non-invasive biomarker monitoring: A comprehensive review. Small 2023, 19, 2206064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Sun, J. Sweat detection theory and fluid driven methods: A review. Nanotechnol. Precis. Eng. 2020, 3, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lino, C.; Barrias, S.; Chaves, R.; Adega, F.; Martins-Lopes, P.; Fernandes, J. Biosensors as diagnostic tools in clinical applications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2022, 1877, 188726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, T.; Wen, J.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Qin, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X. Plasmonic biosensors with nanostructure for healthcare monitoring and diseases diagnosis. Sensors 2022, 23, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Kim, K.N.; Trifonov, A.; Podhajny, T.; Wang, J. Designing wearable microgrids: Towards autonomous sustainable on-body energy management. Energy Environ. Sci. 2022, 15, 82–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Kim, K.N.; Lv, J.; Tehrani, F.; Lin, M.; Lin, Z.; Moon, J.-M.; Ma, J.; Yu, J.; Xu, S. A self-sustainable wearable multi-modular E-textile bioenergy microgrid system. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, N.; Song, Y.; Tan, C.-H.; Zhang, K.; Yang, X.; Dong, S.; Xie, B.; Huang, F. Stretchable transparent electrodes for conformable wearable organic photovoltaic devices. npj Flex. Electron. 2021, 5, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Huang, F.; Zhao, S.; Lv, X.; Zhou, Y.; Xiang, S.; Xu, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, G.; Tao, C. Photo-rechargeable fabrics as sustainable and robust power sources for wearable bioelectronics. Matter 2020, 2, 1260–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, D.; Aili, A.; Zhang, S.; Shi, C.; Zhang, J.; Geng, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L. High-performance wearable thermoelectric generator with self-healing, recycling, and Lego-like reconfiguring capabilities. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe0586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Fu, R.; Zhong, X.; Yu, P.; Tan, G.; Li, W.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhou, L.; Ning, C. Wearable sensors and devices for real-time cardiovascular disease monitoring. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2021, 2, 100541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotur, Y.; Kasimatis, M.; Kaisti, M.; Olenik, S.; Georgiou, C.; Güder, F. Stretchable composite acoustic transducer for wearable monitoring of vital signs. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1910288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Yue, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, H.S. Advancing biosensors with machine learning. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 3346–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faes, L.; Liu, X.; Wagner, S.K.; Fu, D.J.; Balaskas, K.; Sim, D.A.; Bachmann, L.M.; Keane, P.A.; Denniston, A.K. A clinician’s guide to artificial intelligence: How to critically appraise machine learning studies. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjakkal, L.; Yin, L.; Nathan, A.; Wang, J.; Dahiya, R. Energy autonomous sweat-based wearable systems. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2100899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Kong, X.; Yan, S.; Gai, P.; Li, F. Glucose dehydrogenase-like nanozyme based on black phosphorus nanosheets for high-performance biofuel cells. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 16549–16554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Yin, L.; Chen, X.; Jeerapan, I.; Silva, C.A.; Li, Y.; Le, M.; Lin, Z.; Wang, L.; Trifonov, A. Wearable biosupercapacitor: Harvesting and storing energy from sweat. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2102915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, T.; Ghosh, I. Real-time forecasts and risk assessment of novel coronavirus (COVID-19) cases: A data-driven analysis. Chaos Solit. Fractals 2020, 135, 109850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benvenuto, D.; Giovanetti, M.; Vassallo, L.; Angeletti, S.; Ciccozzi, M. Application of the ARIMA model on the COVID-2019 epidemic dataset. Data Br. 2020, 29, 105340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GitLab. 2021. Available online: https://gitlab.kit.edu/cihan.ates/data-driven-engineering (accessed on 12 June 2025).
- Ates, H.C.; Yetisen, A.K.; Güder, F.; Dincer, C. Wearable devices for the detection of COVID-19. Nat. Electron. 2021, 4, 13–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laguarta, J.; Hueto, F.; Subirana, B. COVID-19 artificial intelligence diagnosis using only cough recordings. IEEE Open J. Eng. Med. Biol. 2020, 1, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hssayeni, M.D.; Jimenez-Shahed, J.; Burack, M.A.; Ghoraani, B. Ensemble deep model for continuous estimation of Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale III. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 20, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasseri, M.; Attia, T.P.; Joseph, B.; Gregg, N.M.; Nurse, E.S.; Viana, P.F.; Schulze-Bonhage, A.; Dümpelmann, M.; Worrell, G.; Freestone, D.R. Non-invasive wearable seizure detection using long–short-term memory networks with transfer learning. J. Neural Eng. 2021, 18, 056017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarafdar, P.; Bose, I. Recognition of human activities for wellness management using a smartphone and a smartwatch: A boosting approach. Decis. Support Syst. 2021, 140, 113426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthi, R.; Kumar, A.; Gopinathan, D.; Nayyar, A.; Qureshi, B. An overview of IoT sensor data processing, fusion, and analysis techniques. Sensors 2020, 20, 6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haensch, W.; Raghunathan, A.; Roy, K.; Chakrabarti, B.; Phatak, C.M.; Wang, C.; Guha, S. Compute in-memory with non-volatile elements for neural networks: A review from a co-design perspective. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2204944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macías-García, L.; Martínez-Ballesteros, M.; Luna-Romera, J.M.; García-Heredia, J.M.; García-Gutiérrez, J.; Riquelme-Santos, J.C. Autoencoded DNA methylation data to predict breast cancer recurrence: Machine learning models and gene-weight significance. Artif. Intell. Med. 2020, 110, 101976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamamoto, R.; Komatsu, M.; Takasawa, K.; Asada, K.; Kaneko, S. Epigenetics analysis and integrated analysis of multiomics data, including epigenetic data, using artificial intelligence in the era of precision medicine. Biomolecules 2019, 10, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Park, S.; Jeong, I.G.; Song, S.H.; Jeong, Y.; Kim, C.-S.; Lee, K.H. Noninvasive precision screening of prostate cancer by urinary multimarker sensor and artificial intelligence analysis. ACS Nano 2020, 15, 4054–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Cui, D.; Kong, L.; Chen, S.; Xie, W.; Zhang, C. Classification and identification of archaea using single-cell Raman ejection and artificial intelligence: Implications for investigating uncultivated microorganisms. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 17012–17019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Ai, W.; Huang, J.; Ma, L.; Geng, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Z. Mitochondria-targeted sensor array with aggregation-induced emission luminogens for identification of various cells. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 14444–14451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, Y.; Zhang, N.; Liu, T.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, D.; Dong, H.; Guo, L.; Qu, D.; Jiang, X.; Du, T. Artificially intelligent olfaction for fast and noninvasive diagnosis of bladder cancer from urine. ACS Sens. 2022, 7, 1720–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.P.D.; Brito, P. Linear discriminant analysis for interval data. Comput. Stat. 2006, 21, 289–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.-X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.-W.; Chen, S.; Yu, Y.-L.; Wang, J.-H. Nanozyme sensor array plus solvent-mediated signal amplification strategy for ultrasensitive ratiometric fluorescence detection of exosomal proteins and cancer identification. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 9002–9010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, J.; Khan, R.; Ahmad, N.; Maqsood, I. Random forests and decision trees. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Issues 2012, 9, 272. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, H.; Oh, S.; Hong, S.; Kang, M.; Kang, D.; Ji, Y.-g.; Choi, B.H.; Kang, K.-W.; Jeong, H.; Park, Y. Early-stage lung cancer diagnosis by deep learning-based spectroscopic analysis of circulating exosomes. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 5435–5444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alalayah, K.M.; Senan, E.M.; Atlam, H.F.; Ahmed, I.A.; Shatnawi, H.S.A. Effective early detection of epileptic seizures through EEG signals using classification algorithms based on t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding and K-means. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Fan, Y.Z.; Du, S.Z.; Yang, Y.Z.; Ling, Y.; Li, N.B.; Luo, H.Q. Conversion of fluorescence signals into optical fingerprints realizing high-throughput discrimination of anionic sulfonate surfactants with similar structure based on a statistical strategy and luminescent metal–organic frameworks. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 7273–7281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moisoiu, T.; Iancu, S.D.; Burghelea, D.; Dragomir, M.P.; Iacob, G.; Stefancu, A.; Cozan, R.G.; Antal, O.; Bálint, Z.; Muntean, V. SERS liquid biopsy profiling of serum for the diagnosis of kidney cancer. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yi, X.; Jin, G.; Peng, D.; Fan, G.; Xu, X.; Chen, X.; Yin, H.; Cooper, J.M.; Huang, W.E. High-speed diagnosis of bacterial pathogens at the single cell level by Raman microspectroscopy with machine learning filters and denoising autoencoders. ACS Chem. Biol. 2022, 17, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelmoula, W.M.; Balluff, B.; Englert, S.; Dijkstra, J.; Reinders, M.J.; Walch, A.; McDonnell, L.A.; Lelieveldt, B.P. Data-driven identification of prognostic tumor subpopulations using spatially mapped t-SNE of mass spectrometry imaging data. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 12244–12249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z. Extensions to the k-means algorithm for clustering large data sets with categorical values. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 1998, 2, 283–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Yang, J.; Xing, H.; Chang, Y.; Sun, J.; Guo, C.; Yang, X. FRET cascade miRNA addition probe from non-crosstalk DNA photonic wire assisted with clustering algorithm for early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 224, 115080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Chen, C.; Wang, P.; Mulvey, J.J.; Yang, Y.; Wun, C.; Antman-Passig, M.; Luo, H.-B.; Cho, S.; Long-Roche, K. Detection of ovarian cancer via the spectral fingerprinting of quantum-defect-modified carbon nanotubes in serum by machine learning. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 6, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Xia, J.; Li, X.; Yang, T.; Wang, J.-H. Ratiometric 3D DNA machine combined with machine learning algorithm for ultrasensitive and high-precision screening of early urinary diseases. Acs Nano 2021, 15, 19522–19534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Zong, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, B.; Cui, Y. Profiling of exosomal biomarkers for accurate cancer identification: Combining DNA-PAINT with machine-learning-based classification. Small 2019, 15, 1901014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, J.; Tian, F.; Chang, J.; Zhang, W.; Sun, J. λ-DNA-and aptamer-mediated sorting and analysis of extracellular vesicles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 3817–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Uriarte, R.; Gómez de Lope, E.; Giugno, R.; Fröhlich, H.; Nazarov, P.V.; Nepomuceno-Chamorro, I.A.; Rauschenberger, A.; Glaab, E. Ten quick tips for biomarker discovery and validation analyses using machine learning. PLoS Comp. Biol. 2022, 18, e1010357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echle, A.; Rindtorff, N.T.; Brinker, T.J.; Luedde, T.; Pearson, A.T.; Kather, J.N. Deep learning in cancer pathology: A new generation of clinical biomarkers. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 686–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, C.; Chawla, S.; Thakral, D.; Pant, H.; Verma, P.; Malik, P.S.; Jayadeva; Gupta, R.; Ahuja, G.; Sengupta, D. Molecular signature comprising 11 platelet-genes enables accurate blood-based diagnosis of NSCLC. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 744. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; LaRiviere, M.J.; Ko, J.; Till, J.E.; Christensen, T.; Yee, S.S.; Black, T.A.; Tien, K.; Lin, A.; Shen, H. A multianalyte panel consisting of extracellular vesicle miRNAs and mRNAs, cfDNA, and CA19-9 shows utility for diagnosis and staging of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer. Res. 2020, 26, 3248–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghayegh, F.; Norouziazad, A.; Haghani, E.; Feygin, A.A.; Rahimi, R.H.; Ghavamabadi, H.A.; Sadighbayan, D.; Madhoun, F.; Papagelis, M.; Felfeli, T. Revolutionary point-of-care wearable diagnostics for early disease detection and biomarker discovery through intelligent technologies. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2400595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, J.; Tian, F.; Cai, L.; Zhang, W.; Feng, Q.; Chang, J.; Wan, F.; Yang, Y.; Dai, B. Low-cost thermophoretic profiling of extracellular-vesicle surface proteins for the early detection and classification of cancers. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asif, S.; Yi, W.; ur-Rehman, S.; ul-ain, Q.; Amjad, K.; Yi, Y.; Si, J.; Awais, M. Advancements and prospects of machine learning in medical diagnostics: Unveiling the future of diagnostic precision. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2025, 32, 853–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahi, O. Deep Learning in Diagnostics. J. Med. Discov. 2025, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Meivita, M.P.; Chan, S.S.; Go, S.X.; Lee, D.; Bajalovic, N.; Loke, D.K. WS2/polyethylene glycol nanostructures for ultra-efficient MCF-7 cancer cell ablation and electrothermal therapy. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 23075–23082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.S.; Go, S.X.; Meivita, M.P.; Lee, D.; Bajalovic, N.; Loke, D.K. Ultra-efficient highly-selective MFC-7 cancer cell therapy enabled by combined electric-pulse carbon 1D-nanomaterials platforms. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 3915–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozar, F.S.; Meivita, M.P.; Go, S.-X.; Li, L.; Bajalovic, N.; Loke, D.K. Ultra-efficient MCF-7 cell ablation and chemotherapy-integrated electrothermal therapy with DOX–WS2–PEG–M13 nanostructures. Discov. Mater. 2024, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedir, W.M.; Li, L.; Tan, Y.S.; Bajalovic, N.; Loke, D.K. Nanomaterials and methods for cancer therapy: 2D materials, biomolecules, and molecular dynamics simulations. J. Mater. Chem. B 2024, 12, 12141–12173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soriano, L.D.; Go, S.-X.; Li, L.; Bajalovic, N.; Loke, D.K. Multidomain Molecular Sensor Devices, Systems, and Algorithms for Improved Physiological Monitoring. Micromachines 2025, 16, 900. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080900
Soriano LD, Go S-X, Li L, Bajalovic N, Loke DK. Multidomain Molecular Sensor Devices, Systems, and Algorithms for Improved Physiological Monitoring. Micromachines. 2025; 16(8):900. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080900
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoriano, Lianna D., Shao-Xiang Go, Lunna Li, Natasa Bajalovic, and Desmond K. Loke. 2025. "Multidomain Molecular Sensor Devices, Systems, and Algorithms for Improved Physiological Monitoring" Micromachines 16, no. 8: 900. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080900
APA StyleSoriano, L. D., Go, S.-X., Li, L., Bajalovic, N., & Loke, D. K. (2025). Multidomain Molecular Sensor Devices, Systems, and Algorithms for Improved Physiological Monitoring. Micromachines, 16(8), 900. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080900






