An Optimization Method to Enhance the Accuracy of Noise Source Impedance Extraction Based on the Insertion Loss Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
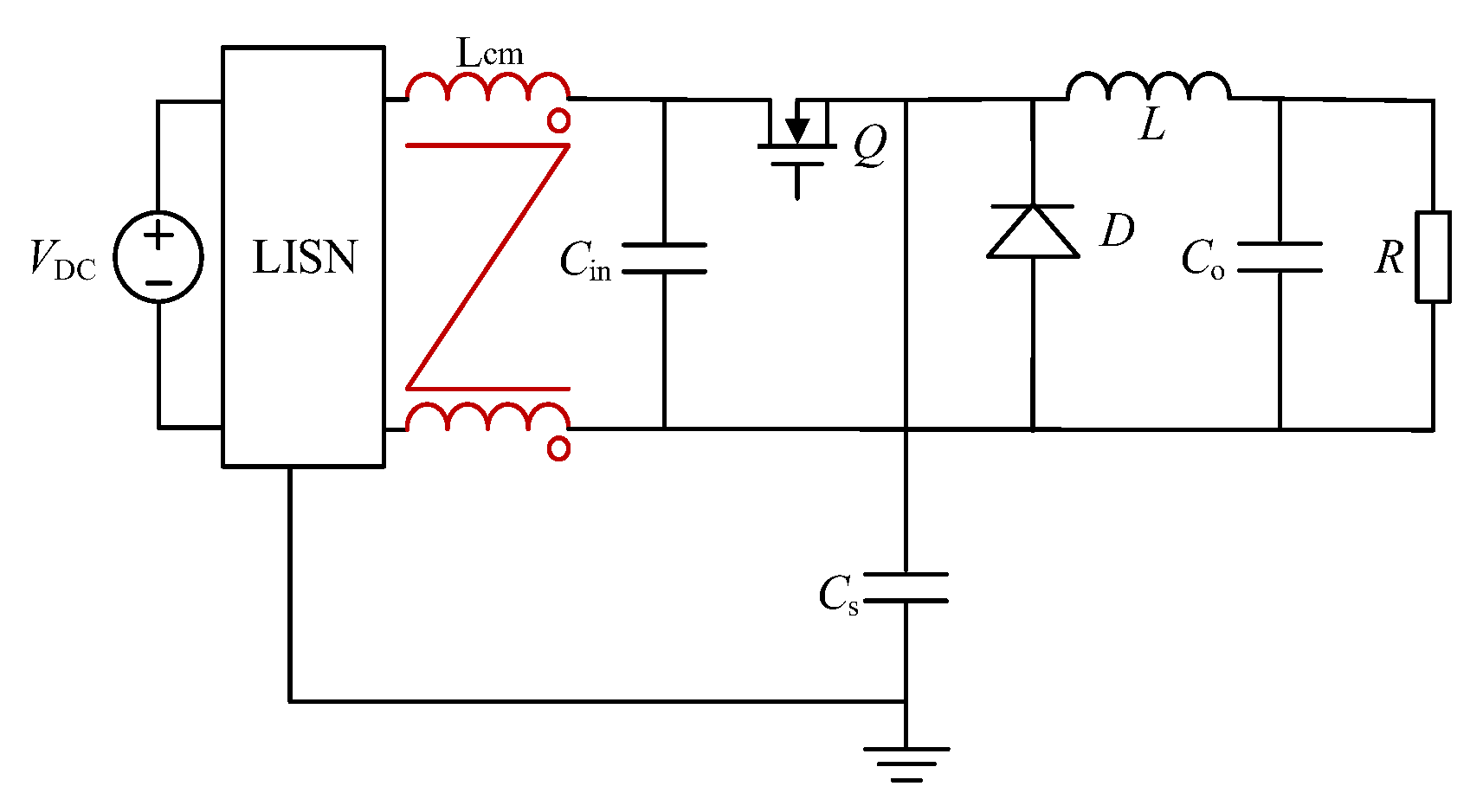
2. Principle of the Insertion Loss Method
3. Analyzing Ai Error Impact on Extraction Results
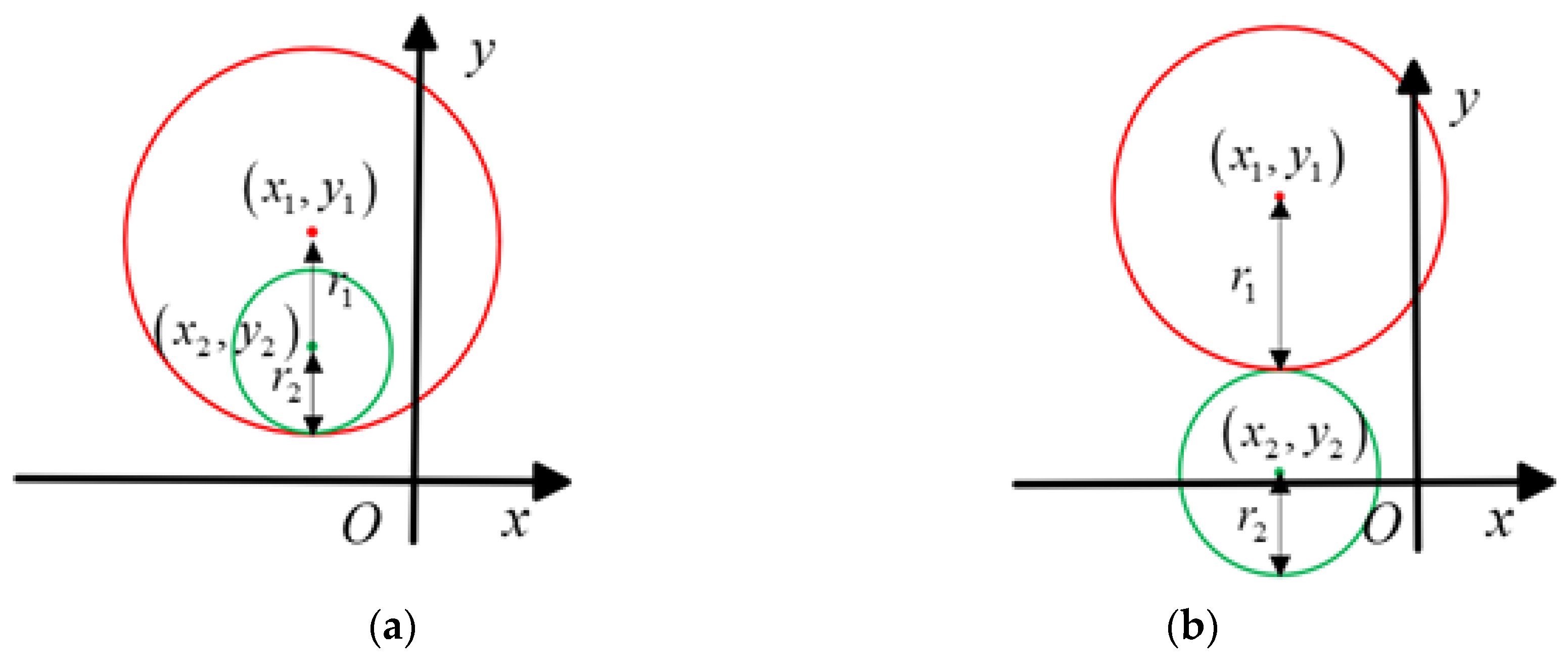
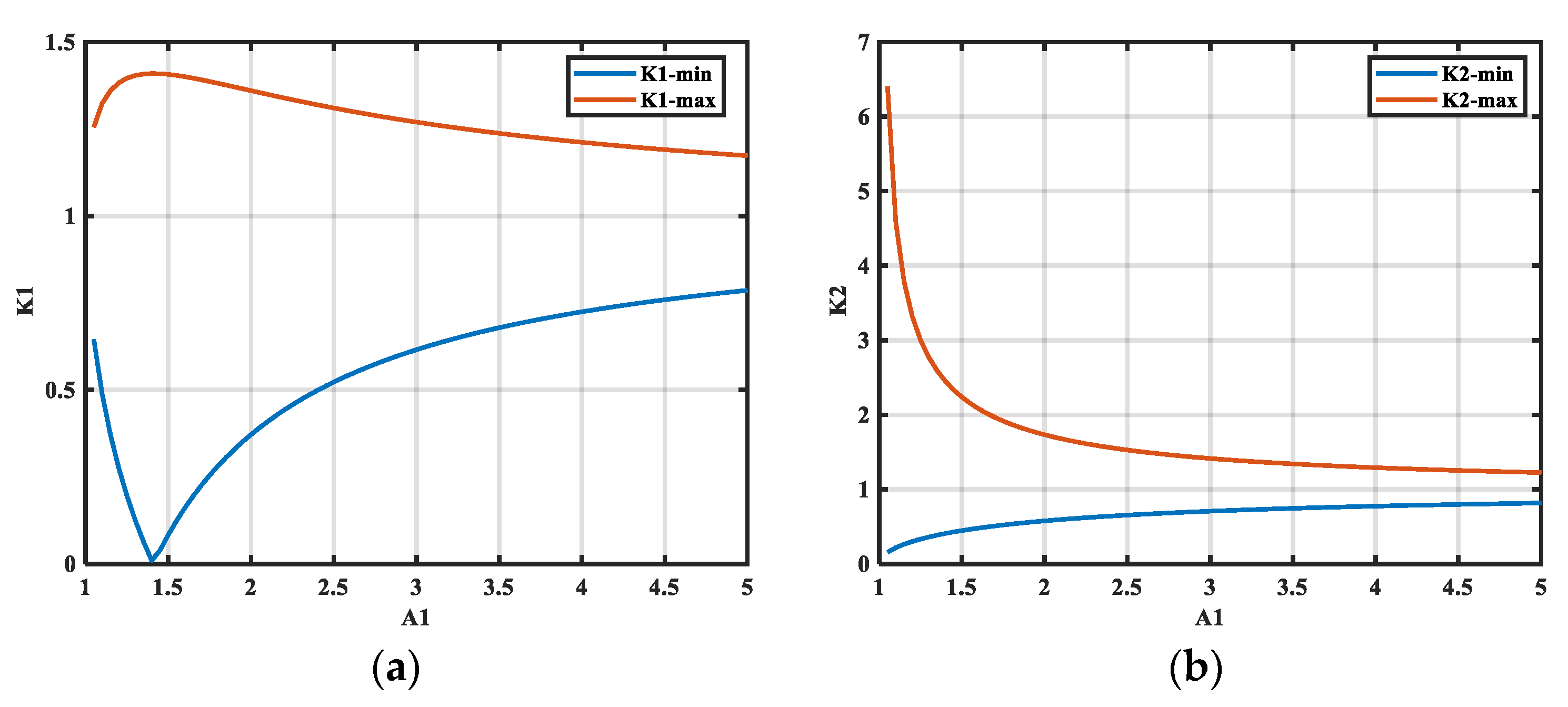
3.1. Constraints on the Solvable Equations
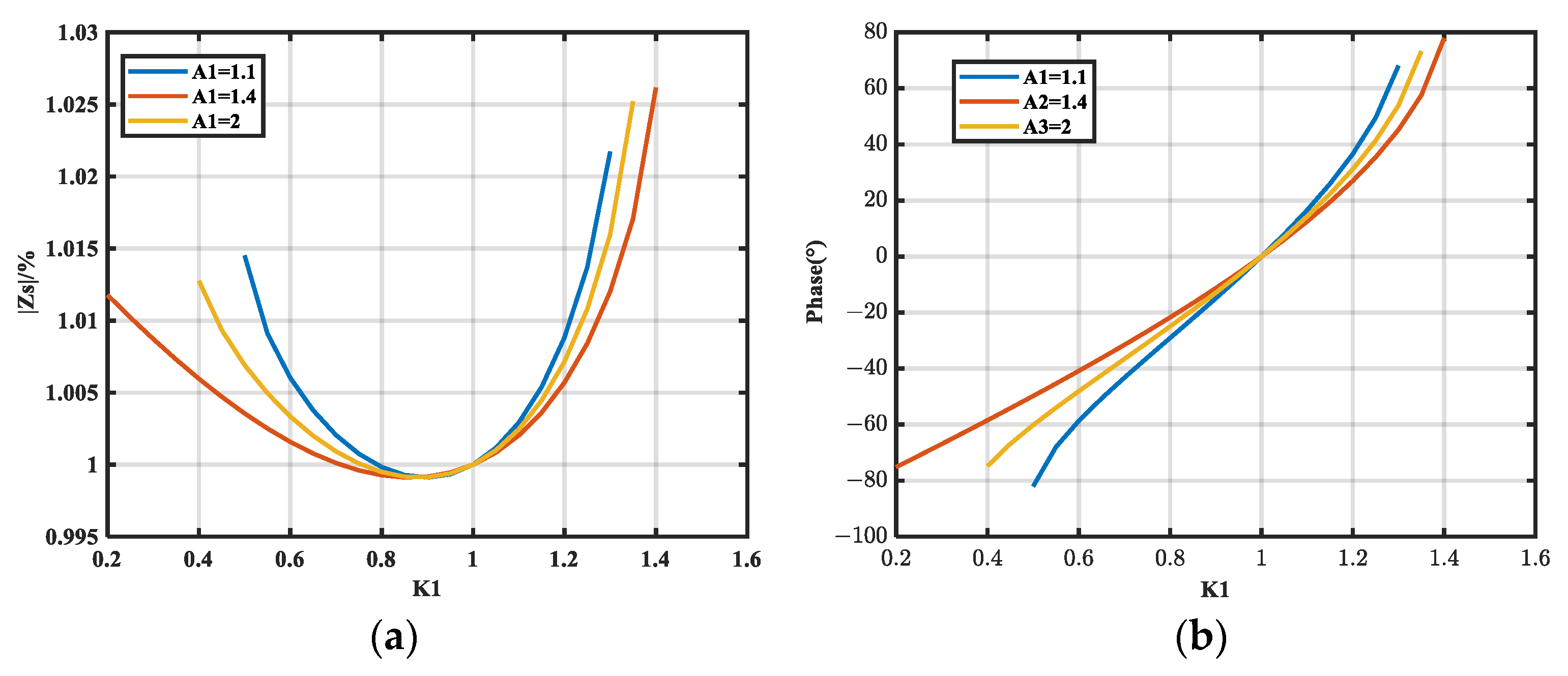
3.2. Effect of Insertion Loss Measurement Errors on Extraction Accuracy
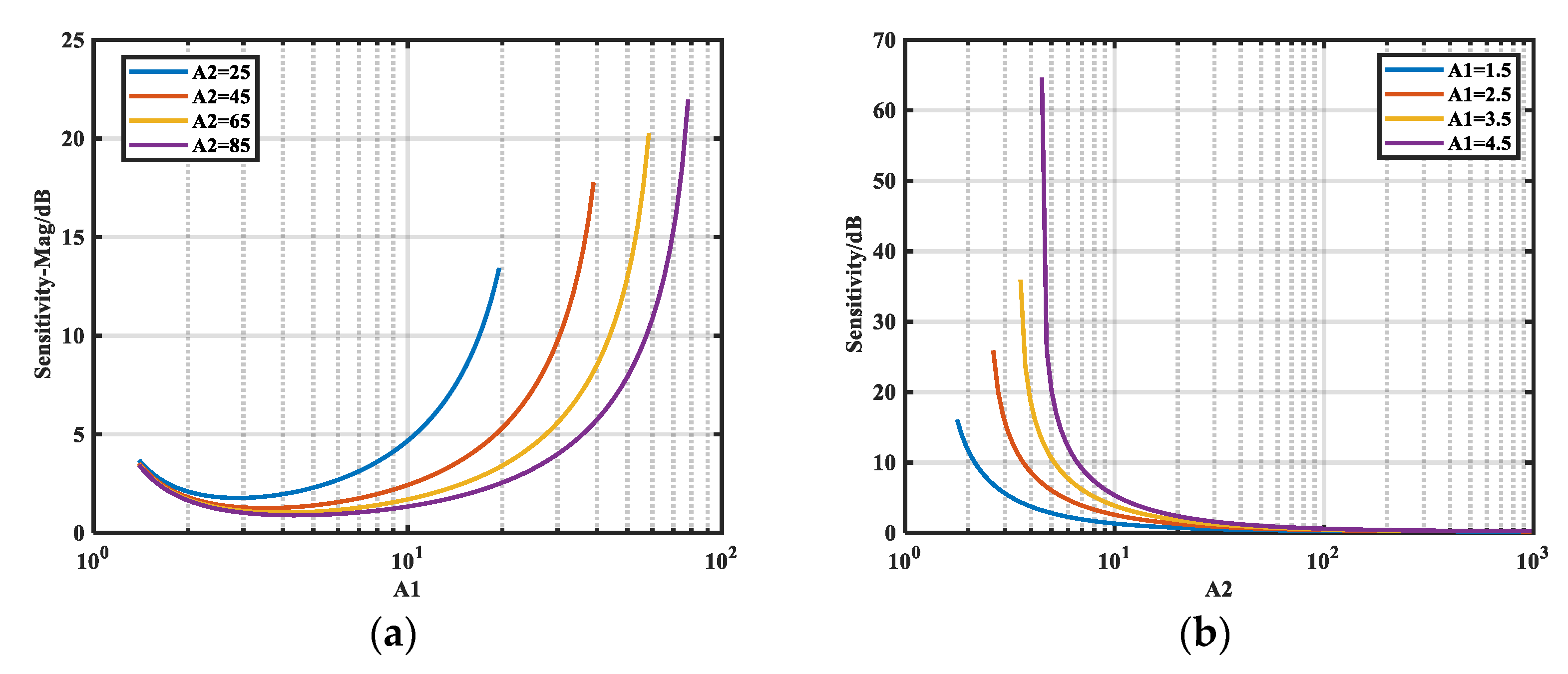
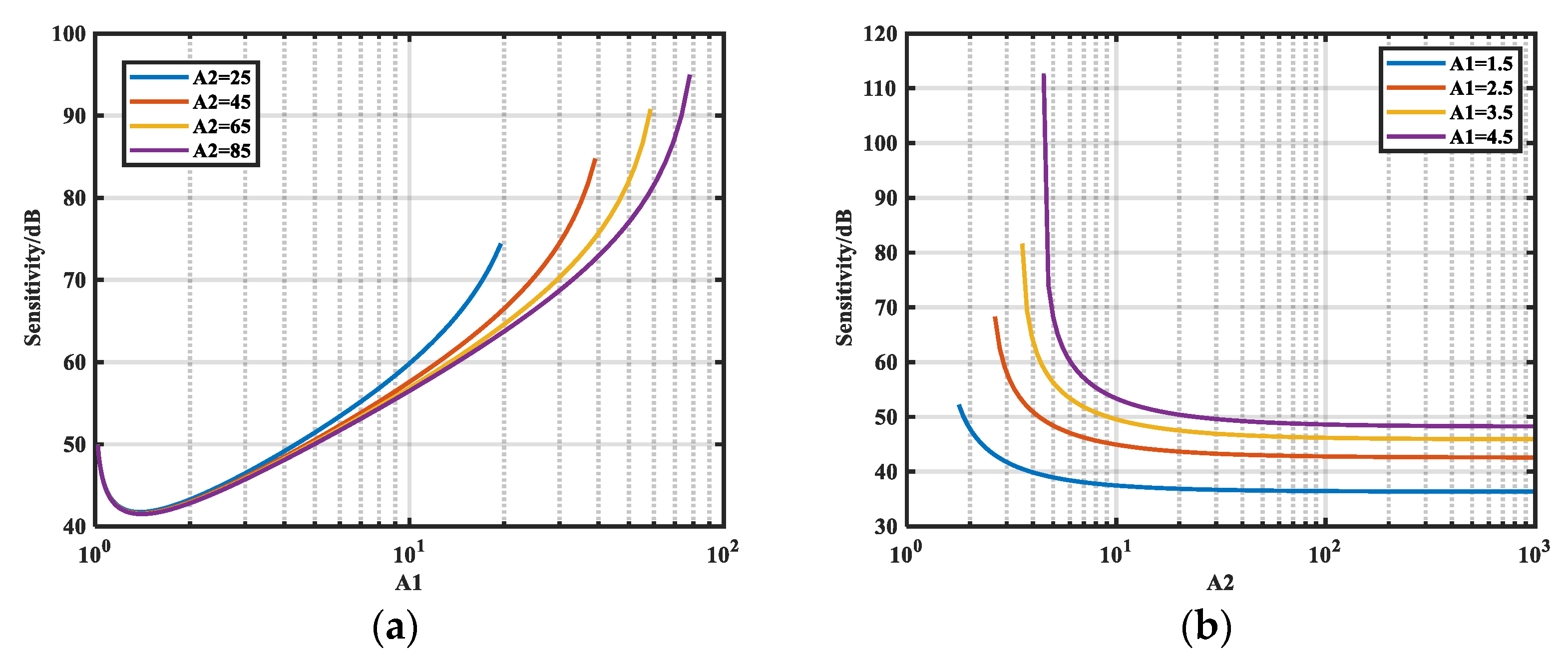
3.2.1. Sensitivity
3.2.2. Analyzing Si-M Under Resistive Noise Source Impedance
3.2.3. Analyzing Si-φ Under Resistive Noise Source Impedance
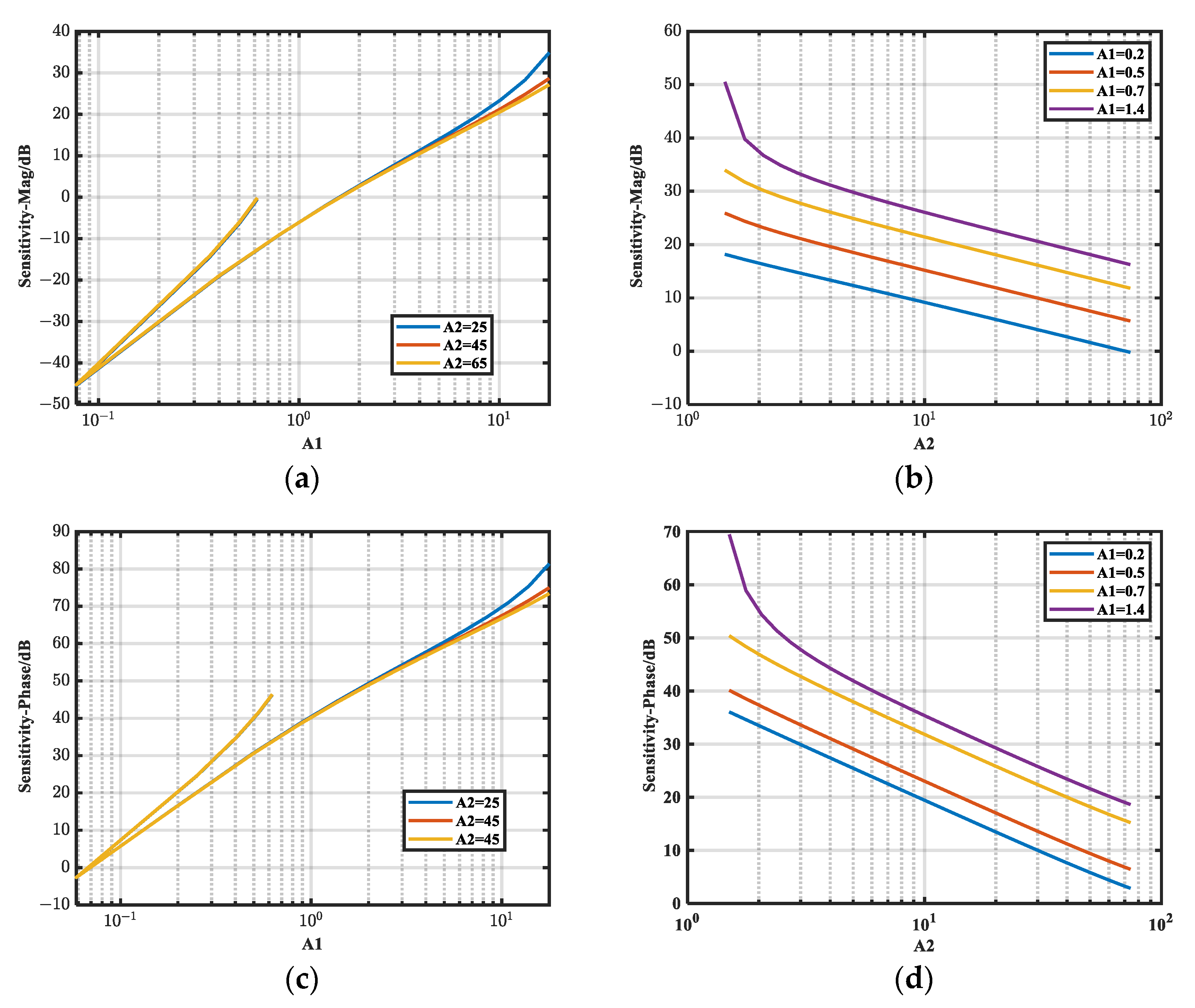
3.2.4. Analyzing Si-φ and Si-M Under Capacitive Noise Source Impedance
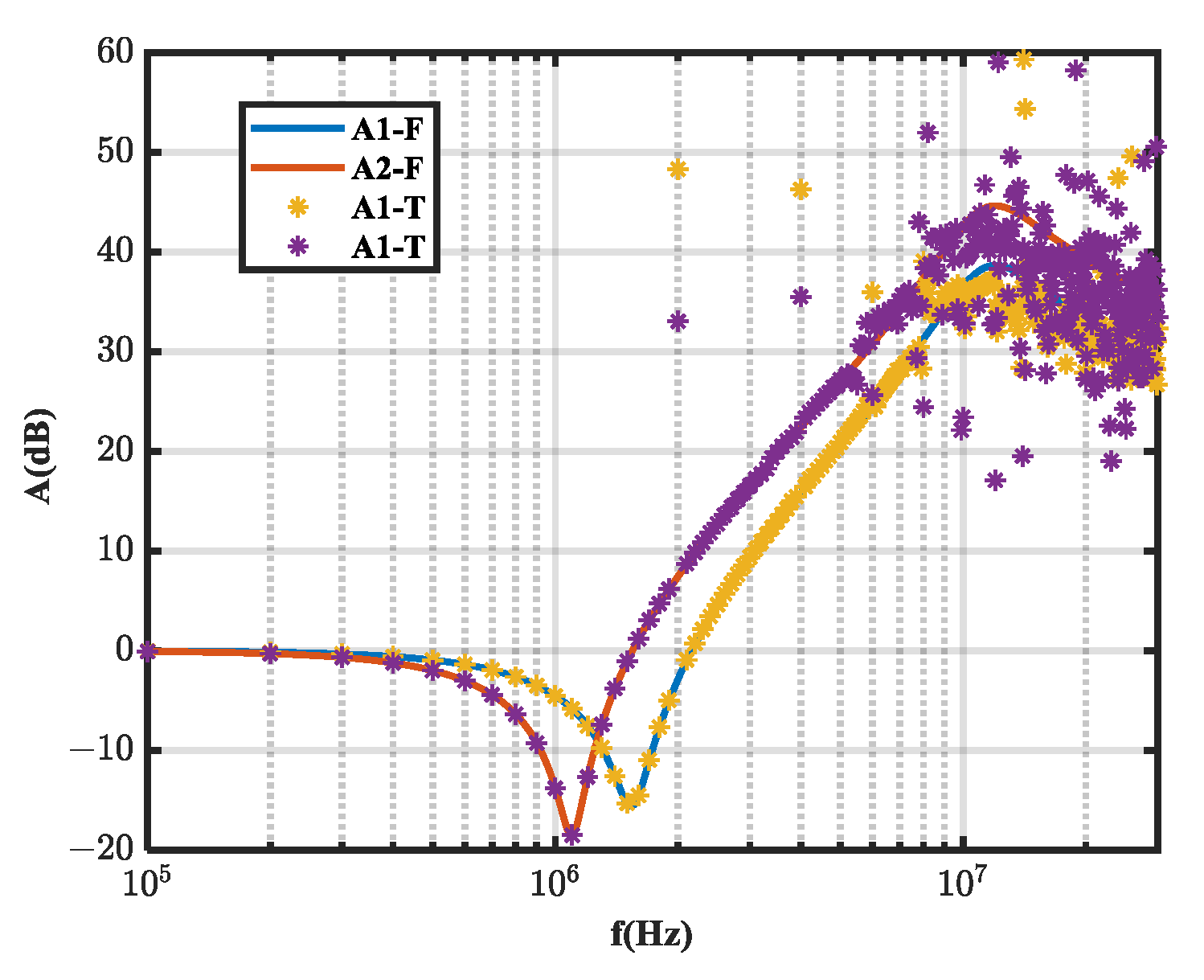
4. Optimization Methods to Improve Extraction Accuracy
- (1)
- Test the noise spectrum of the device under test within the frequency band of interest and select several frequency points with relatively high noise amplitude within each decade of the frequency range.
- (2)
- Select an inductor with any inductance value and insert it into the test to obtain the frequency characteristics of Ai under that inductor. Then, determine the magnitude of the noise source impedance in different frequency bands. Determine the frequency band suitable for extracting the noise source impedance based on the requirements that A must meet.
- (3)
- Based on the frequency band obtained in step 2, select L1 and L2 for the remaining frequency bands. Select inductors with higher inductance values for lower frequency bands and lower inductance values for higher frequency bands. Measure the impedance frequency characteristics of each inductor and the frequency characteristics of Ai after insertion testing. Then, determine L1 and L2 for the different frequency bands based on the requirements.
- (4)
- Substitute A1, A2, ZL-1, and ZL-2 into the analytical expressions for the magnitude and phase of the noise source impedance at each frequency point to calculate the impedance frequency characteristics of the noise source impedance.
- (5)
- To organize the data, remove singularities to fit a relatively accurate noise source impedance curve. Note that it is critical to remove frequency points where the initial noise is relatively small, since these frequency points are subject to larger testing errors.
5. Simulation and Experimental Validation
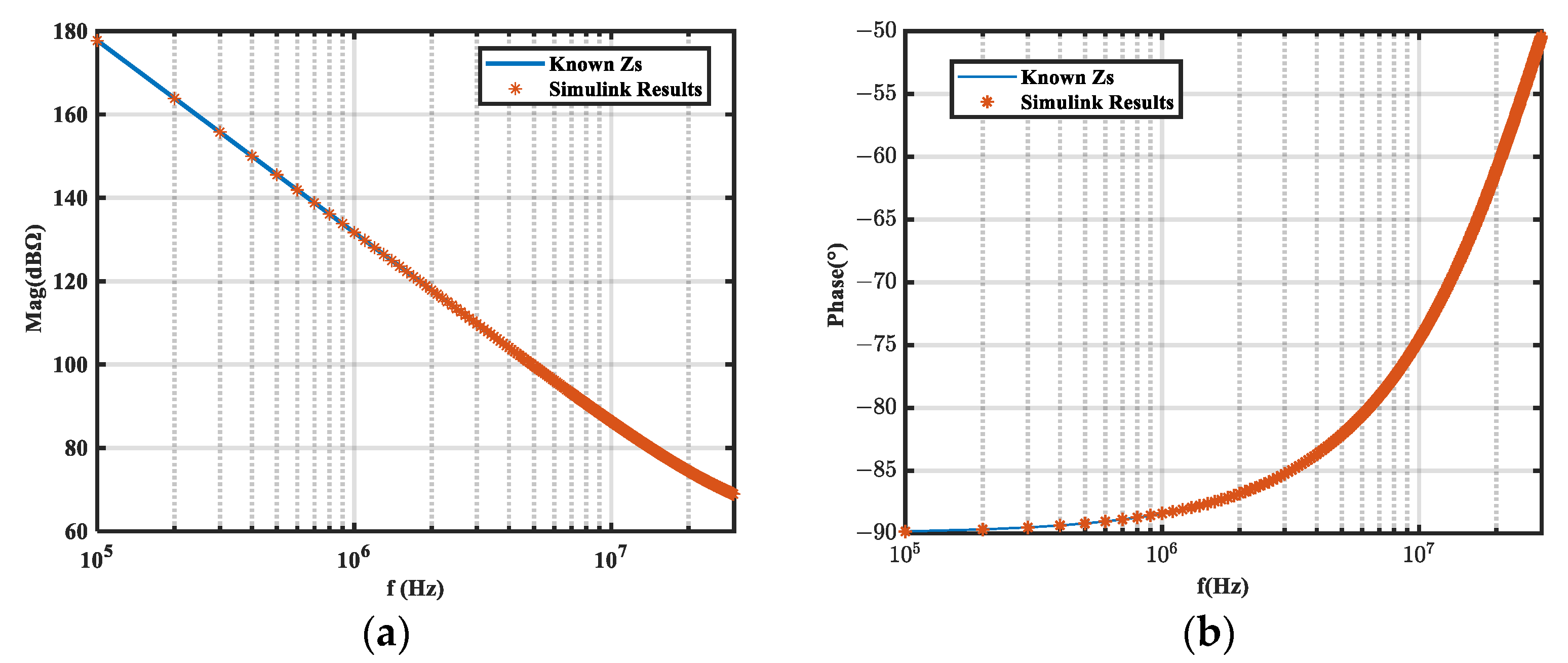
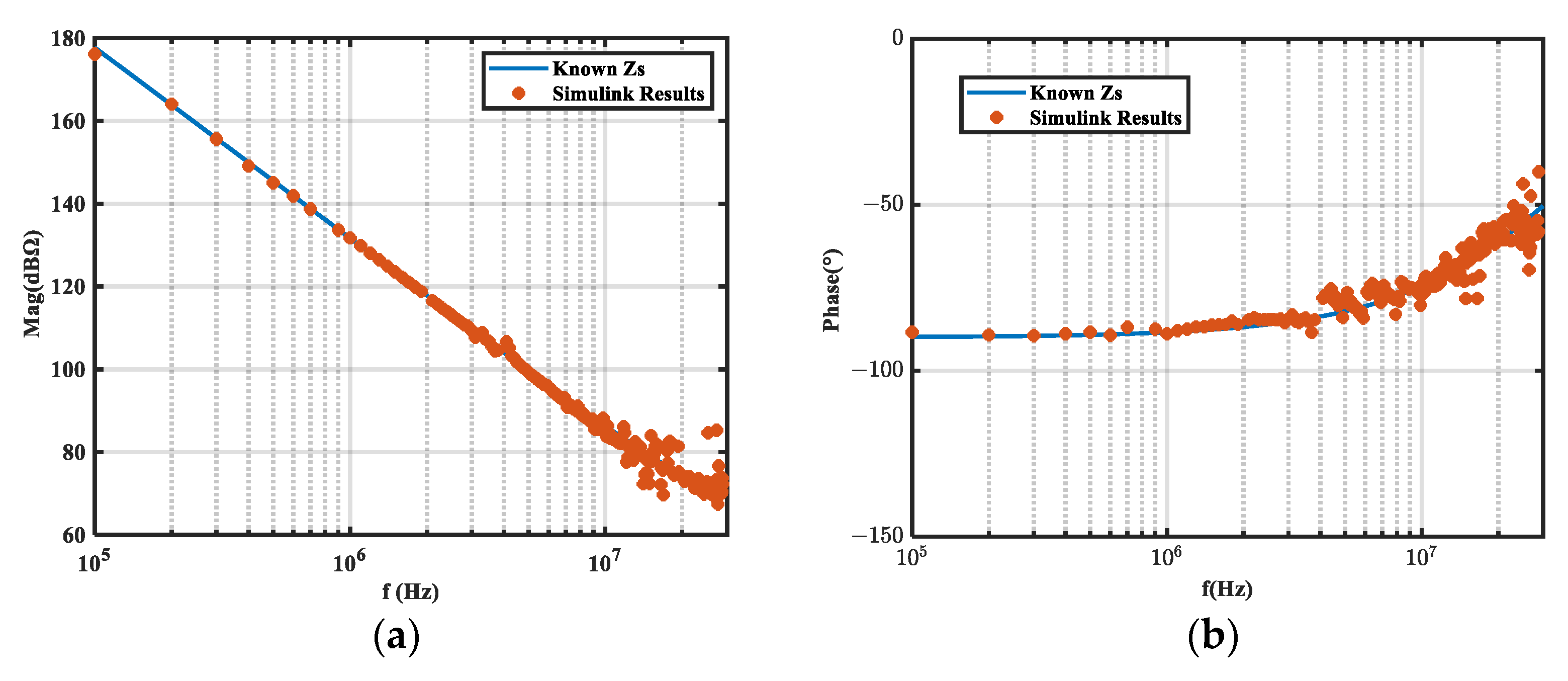
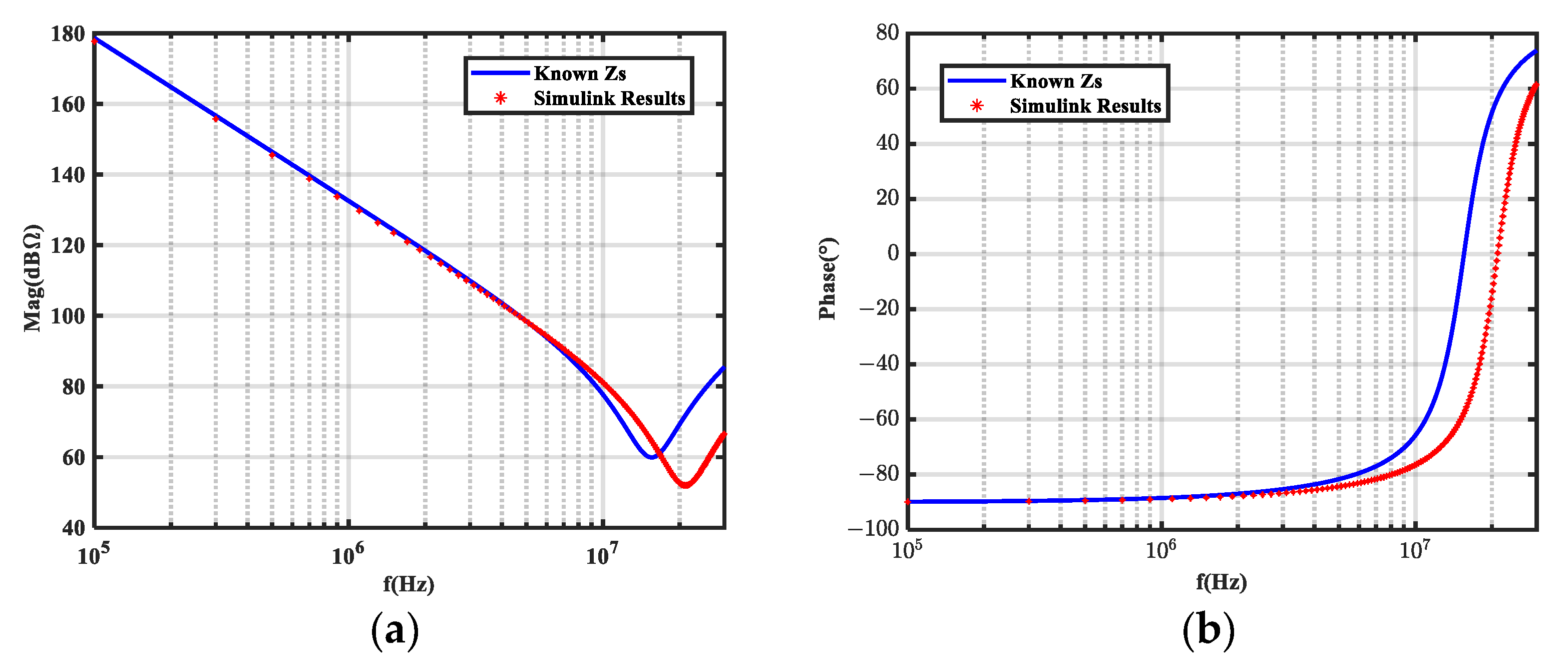
5.1. Simulation Validation
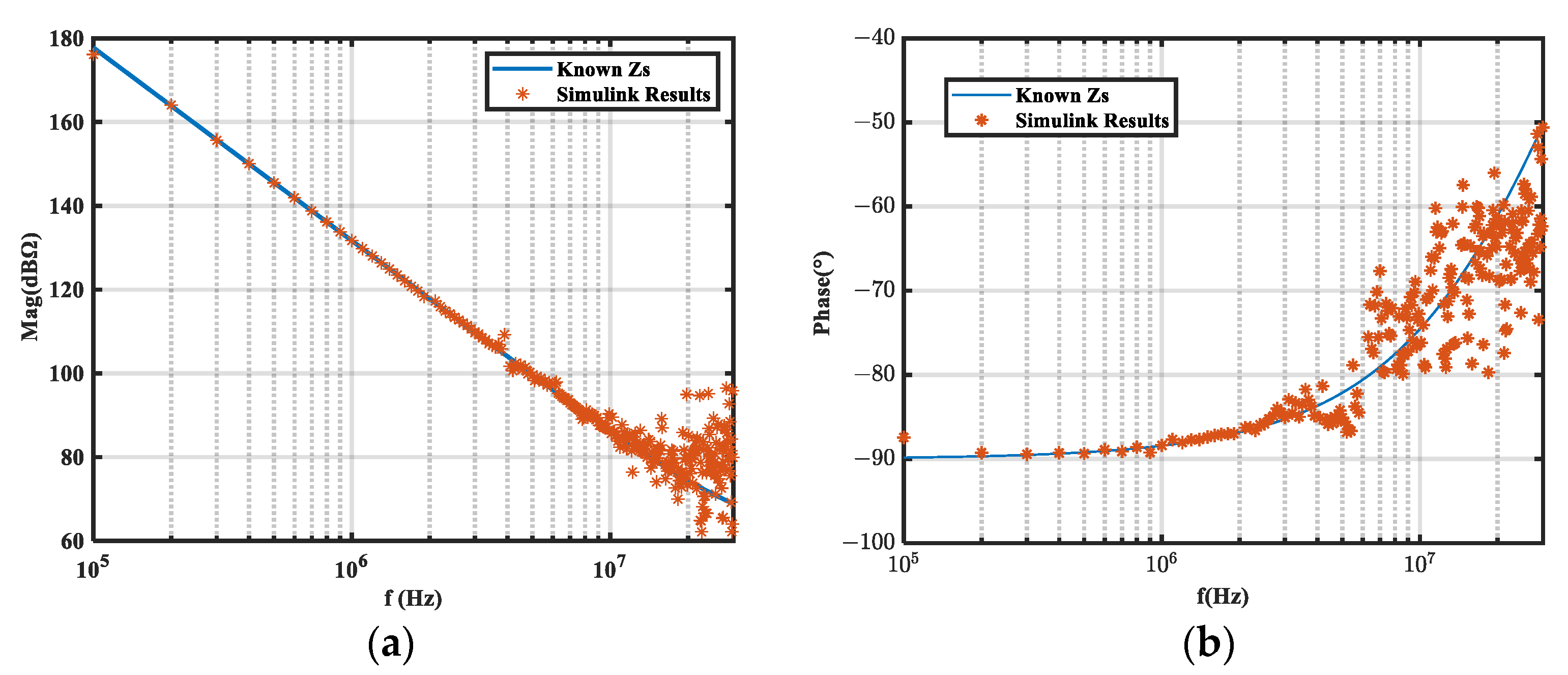
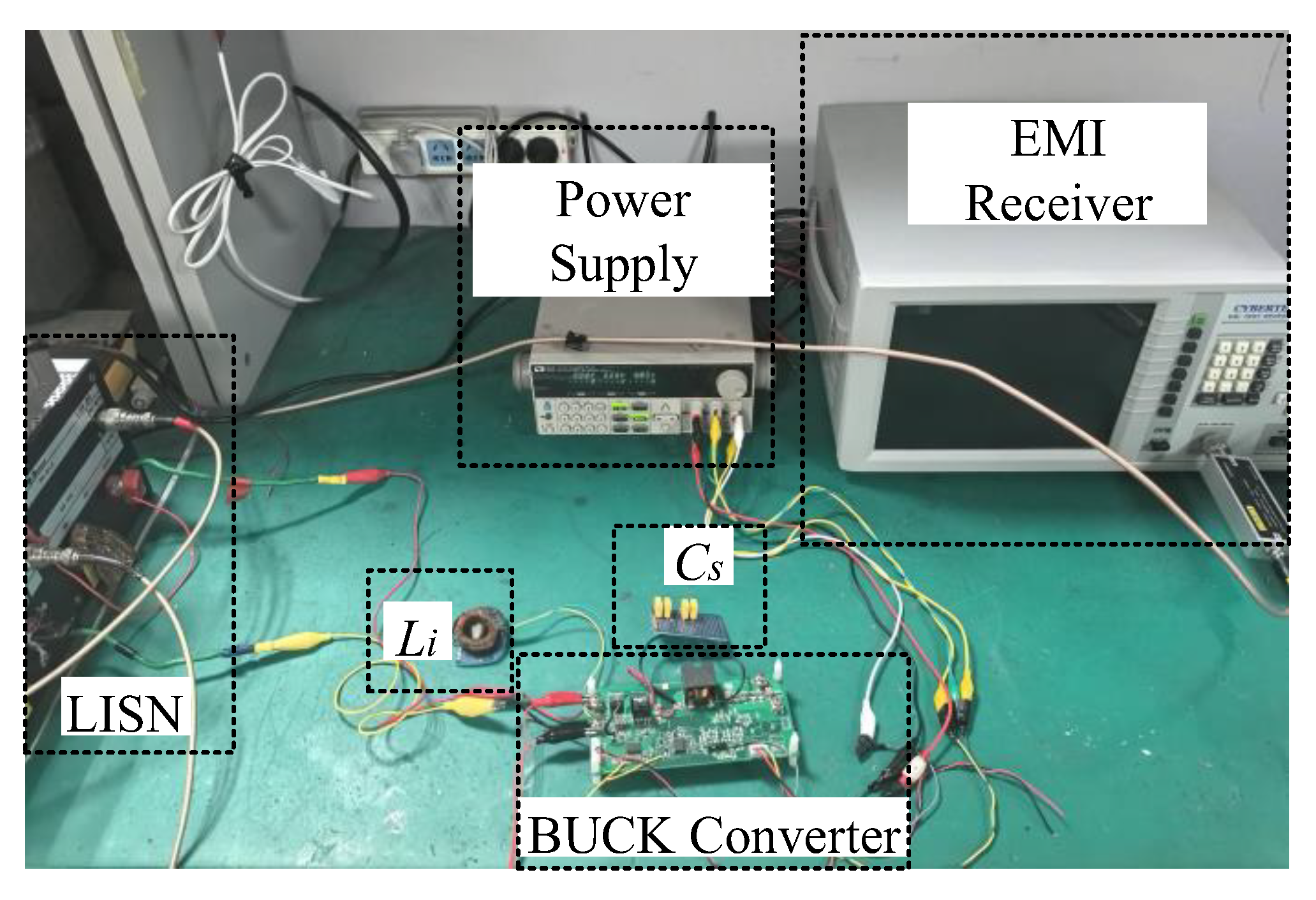
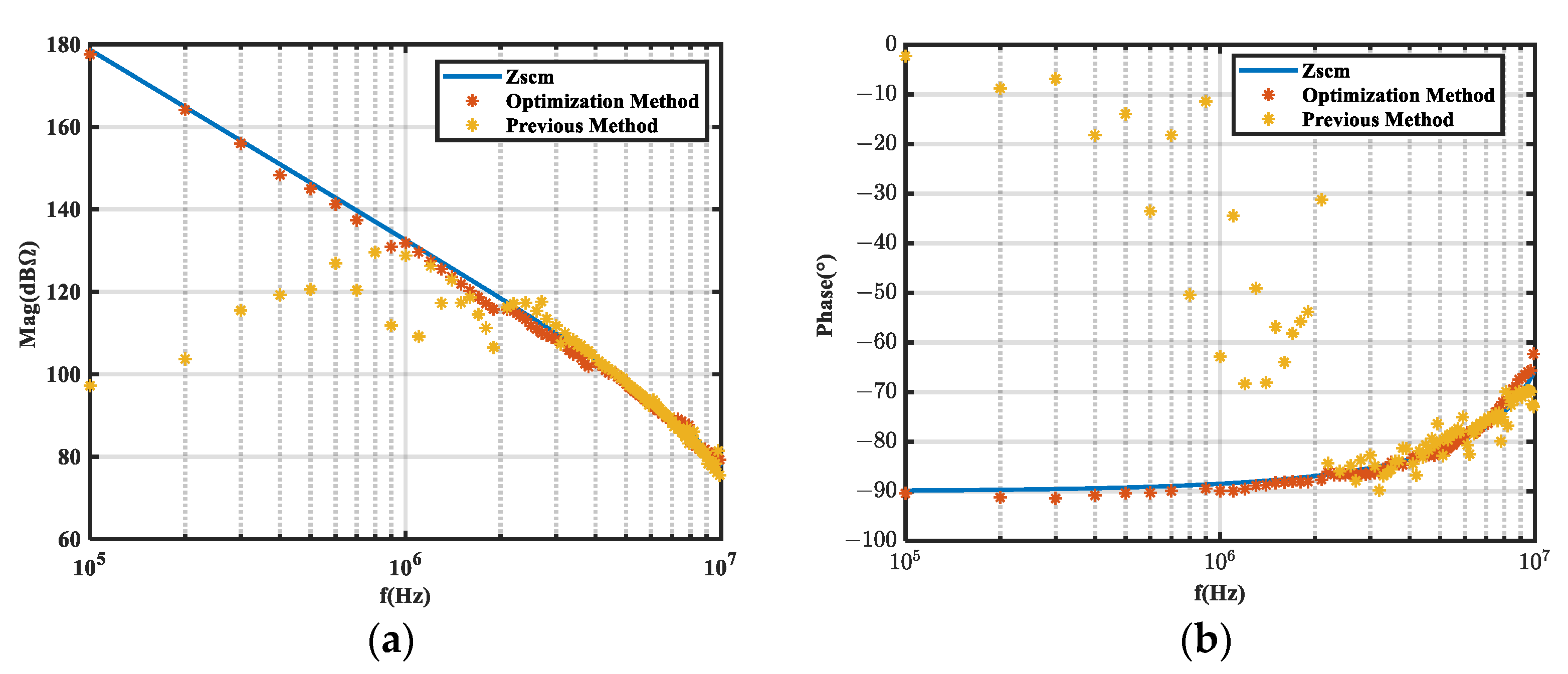
5.2. Experimental Validation
- The noise generated by this buck converter was relatively low above 10 MHz. This made it difficult for the insertion loss to fully meet the specified value conditions, thereby affecting the extraction results.
- At frequencies above 10 MHz, the noise source impedance was less than 75 Ω, making it difficult to fulfill the requirement for the noise source impedance to be significantly greater than the load impedance (25 Ω). This resulted in significantly increased sensitivity and a higher failure rate in the extraction results.
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The causes of insertion loss measurement error were investigated, revealing that excessively large errors lead to solution failure. A permissible range and rule for insertion loss deviation ensuring solution existence are provided. When A2 is significantly larger than A1, the deviation coefficient ensuring a solution is found to depend primarily on the value of A1.
- (2)
- The relative sensitivity of impedance magnitude and phase to insertion loss is analyzed. Analytical expressions for the limiting values of these relative sensitivities were theoretically deduced, and the relationship was established through simulation. Requirements for A1 and A2 are proposed to ensure higher extraction accuracy.
- (3)
- Variation in the relative sensitivity of magnitude and phase to insertion loss under capacitive noise source impedance was examined using a proven simulation technique.
- (4)
- An optimization method to enhance extraction accuracy is proposed. Its effectiveness was validated through simulations and experiments conducted on a buck converter.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
References
- Chen, H.; Feng, L.; Chen, W.; Qian, Z. Modeling and measurement of the impedance of common mode noise source of switching converters. In Proceedings of the Twenty-First Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition, APEC ‘06, Dallas, TX, USA, 19–23 March 2006; pp. 1165–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanasamy, B.; Luo, F.; Chua, Y. High density EMI mitigation solution using active approaches. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility & Signal/Power Integrity (EMCSI), Washington, DC, USA, 7–11 August 2017; pp. 813–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Chen, W.; Yang, Y.; Wang, R.; Yang, X. Design of active EMI filters with the integrated passive component. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), Anaheim, CA, USA, 17–21 March 2019; pp. 640–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z. Analysis of insertion loss and impedance compatibility of hybrid EMI filter based on equivalent circuit model. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2007, 54, 2057–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.; See, K.Y.; Li, K.; Liu, X.; Zagrodnik, M.A.; Gupta, A.K. In-circuit common-mode impedance measurement for motor drive system. In Proceedings of the 2017 Asia-Pacific International Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility (APEMC), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 20–23 June 2017; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Jeong, S.; Kim, J. Quantified Design Guidelines of a Compact Transformerless Active EMI Filter for Performance, Stability, and High Voltage Immunity. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 6723–6737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, M.; Palethorpe, B.; Thomas, D.W.P.; Zanchetta, P.; Di Piazza, M.C. A technique for power supply harmonic impedance estimation using a controlled voltage disturbance. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2002, 17, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, G.; Yin, J.; Peng, J. EMI filter design of single-phase SiC MOSFET inverter with extracted noise source impedance. IEEE Electromagn. Compat. Mag. 2019, 8, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Wang, W.; Zhao, X.; Cui, M.; Zhang, Q.; He, G. Identifying Electromagnetic Noise-Source Impedance Using Hybrid of Measurement and Calculation Method. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 9609–9618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Peng, J. Extraction of Noise Source Impedance under Operating Conditions Using a Two-Probe Approach. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 9th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference (IPEMC2020-ECCE Asia), Nanjing, China, 29 November–2 December 2020; pp. 1858–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, Z.; Min, Z.; Zhiming, F.; Limin, S.; Min, Y. An improved dual-probe approach to measure noise source impedance. In Proceedings of the 2010 Asia-Pacific International Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility, Beijing, China, 12–16 April 2010; pp. 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Su, D.; Xu, H.; Peng, Z. A Noise Source Impedance Extraction Method for Operating SMPS Using Modified LISN and Simplified Calibration Procedure. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 4132–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarateeraseth, V. EMI Filter design part II: Measurement of noise source impedances. IEEE Electromagn. Compat. Mag. 2012, 1, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Cheng, B.; Ma, H.; Xu, D. Study of Conducted Electromagnetic Interference Noise Source Impedance Extraction. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 3rd China International Youth Conference on Electrical Engineering (CIYCEE), Wuhan, China, 3–5 November 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D. Extraction of Noise Source Impedance of an operating high-power converter with high-EMI noises by increasing SNR using an amplifier. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility–EMC Europe, Brugge, Belgium, 2–5 September 2024; pp. 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, H.; Zhao, Z.; Fei, F.; See, K.Y.; Simanjorang, R.; Sasongko, F. A Survey of Impedance Measurement Methods in Power Electronics. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 16–19 May 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, G.; Yan, J.; Peng, J. Effective EMI Filter Design Method of Single-phase Inverter Based on Noise Source Impedance. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Power Electronics and Application Conference and Exposition (PEAC), Shenzhen, China, 4–7 November 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Gong, C. In-circuit Noise Source Impedance Using Double Impedances Insert Loss Approach. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Joint International Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility, Signal & Power Integrity: EMC Japan/Asia-Pacific International Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC Japan/APEMC Okinawa), Ginowan, Okinawa, Japan, 20–24 May 2024; pp. 673–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
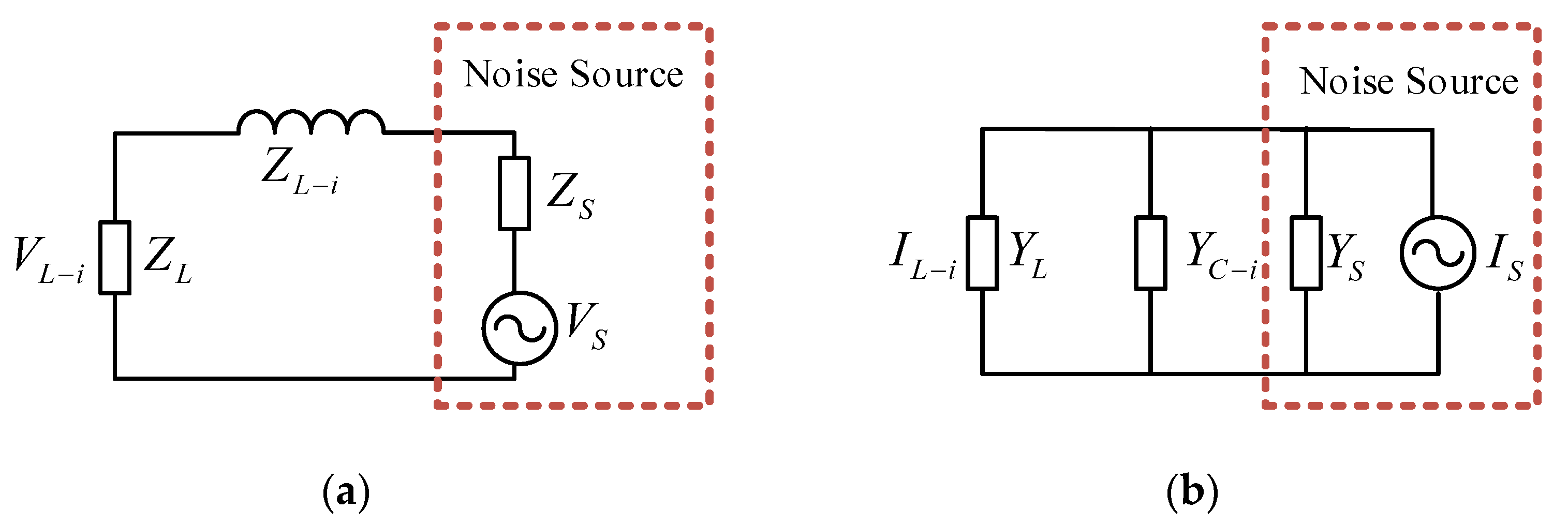

| Measurement Method | Principle | Advantages | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage injection method [7] | Shunt-inject voltage V, measure current response I, Z = V/I. | Noninterruptive to main circuit; effective for low impedance. | Large errors at high impedance; bandwidth limitations of current probe. |
| Insertion loss method [8] | Insert precision inductor ZL, measure insertion loss A, Z ≈ |ZL|/A. | Low cost; no specialized equipment required. | Highly sensitive to insertion loss measurement error; unreliable when insertion loss is minimal. |
| Network analyzer method [9] | Measure S parameter, derive impedance Z. | Broad frequency coverage. | Complex setup requiring specialized probes/custom fixtures. |
| Two-probe method [10] | Measure ΔV with differential probes and current I with current probe, Z = ΔV/I. | Real-time dynamic response; nonintrusive; wide impedance measurement range. | High-frequency CMRR degradation; probe-induced errors; propagation delay matching; HF probe modeling challenges; notoriously complex calibration. |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| VDC (V) | 30 |
| Switching frequency (kHz) | 100 |
| Duty cycle | 0.5 |
| Output power (W) | 5 |
| Cs (pF) | 220 |
| Frequency Band (MHz) | L1 (μH) | A1 | L2 (μH) | A2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1–0.3 | 1000 | 0.3–0.9 | 35,000 | 4–14 |
| 0.4–1 | 100 | 0.3–0.9 | 1000 | 1.2–7 |
| 1.1–4.1 | 10 | 0.3–0.8 | 1000 | 7.7–31 |
| 4.2–11 | 1 | 0.6–0.9 | 100 | 14–85 |
| 11.1–30 | 0.5 | 0.7–1.5 | 10 | 7–30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Zhan, J.; Gong, C. An Optimization Method to Enhance the Accuracy of Noise Source Impedance Extraction Based on the Insertion Loss Method. Micromachines 2025, 16, 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080864
Zhang R, Zhang Z, Zhan J, Gong C. An Optimization Method to Enhance the Accuracy of Noise Source Impedance Extraction Based on the Insertion Loss Method. Micromachines. 2025; 16(8):864. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080864
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Rongxuan, Ziliang Zhang, Jun Zhan, and Chunying Gong. 2025. "An Optimization Method to Enhance the Accuracy of Noise Source Impedance Extraction Based on the Insertion Loss Method" Micromachines 16, no. 8: 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080864
APA StyleZhang, R., Zhang, Z., Zhan, J., & Gong, C. (2025). An Optimization Method to Enhance the Accuracy of Noise Source Impedance Extraction Based on the Insertion Loss Method. Micromachines, 16(8), 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080864






