Comparative Noise Analysis of Readout Circuit in Hemispherical Resonator Gyroscope
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. HRG Detection Principle
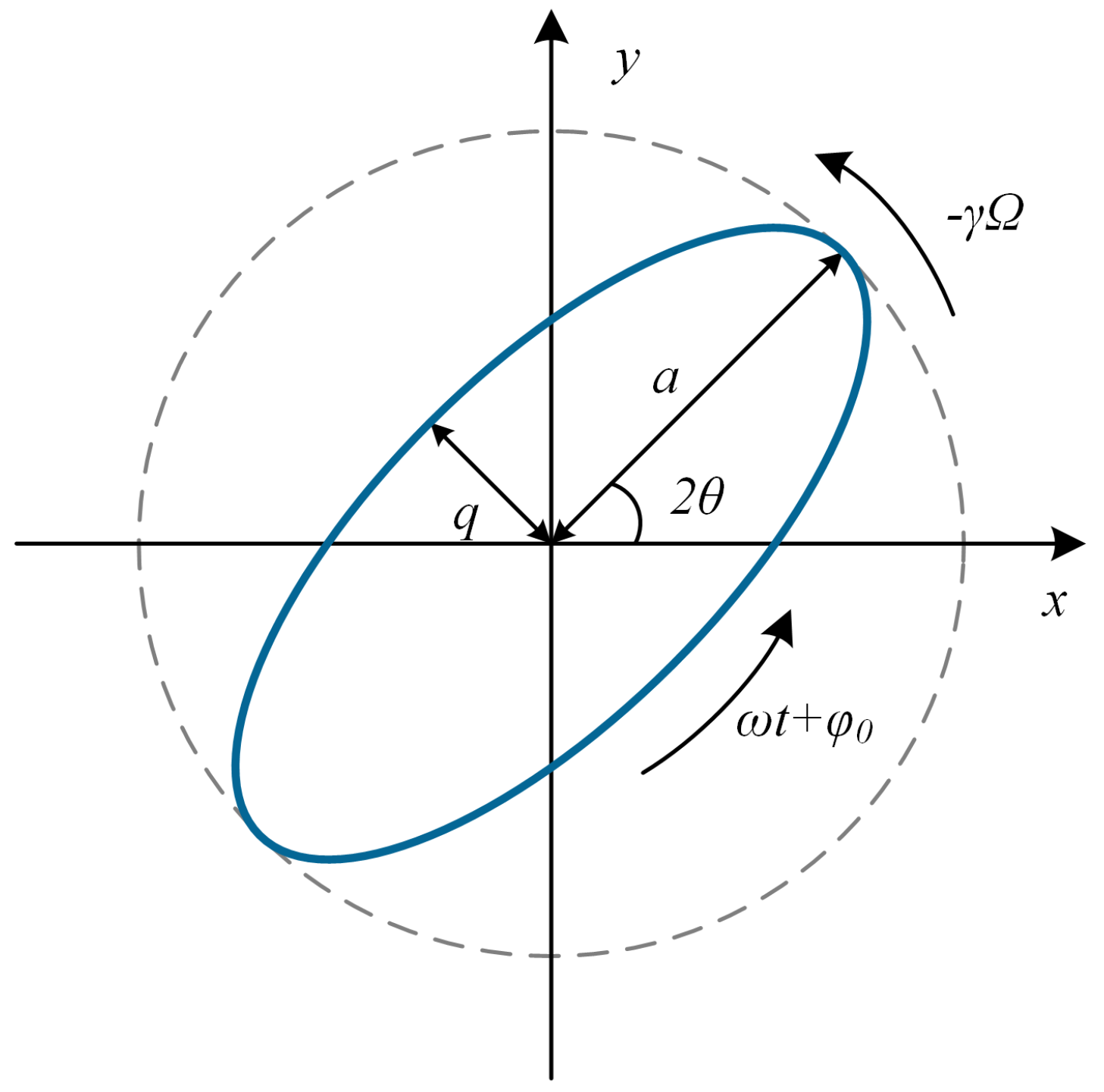
2.1. Dynamic Model of the HRG
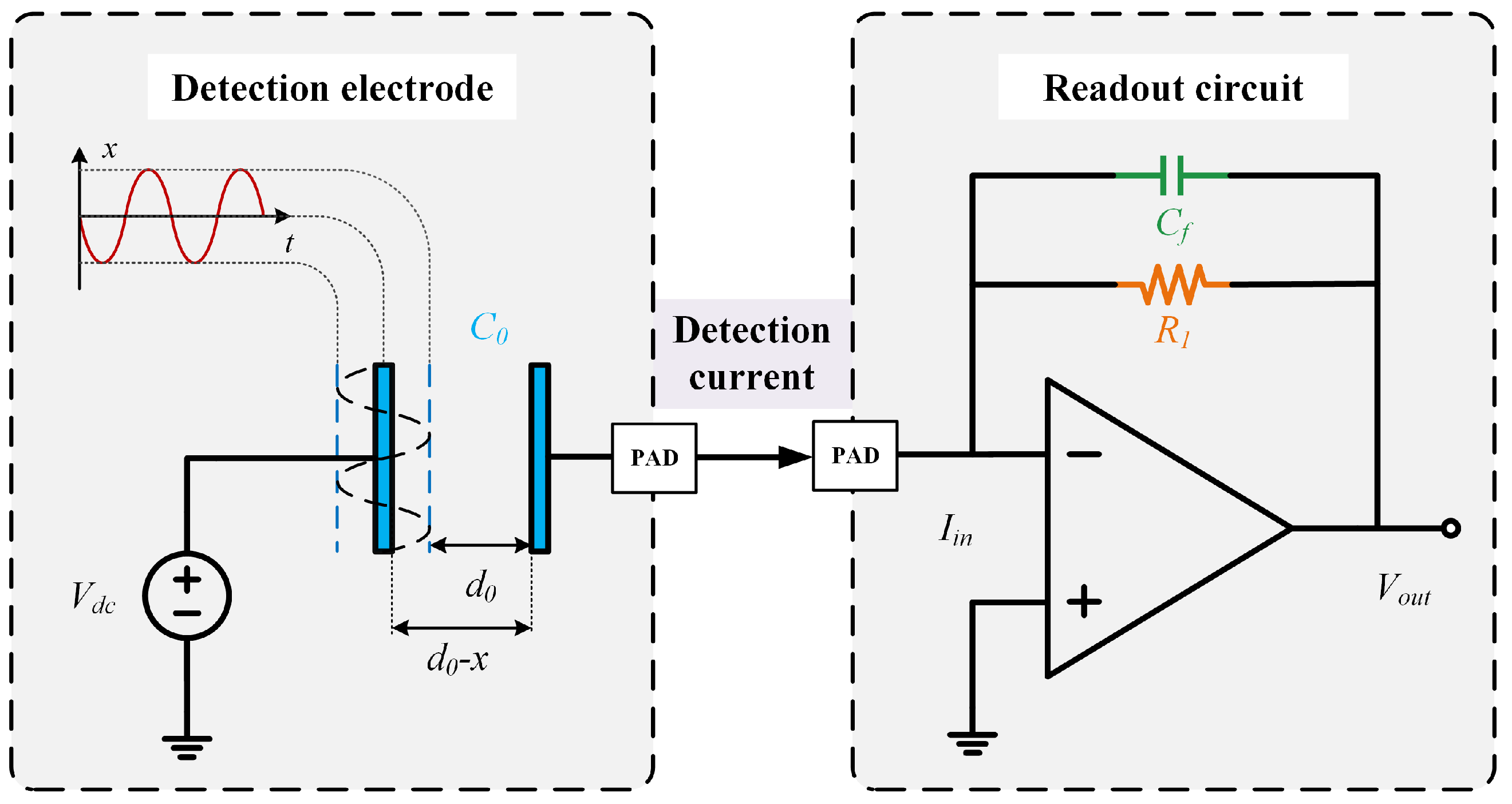
2.2. Detection Equation of the HRG
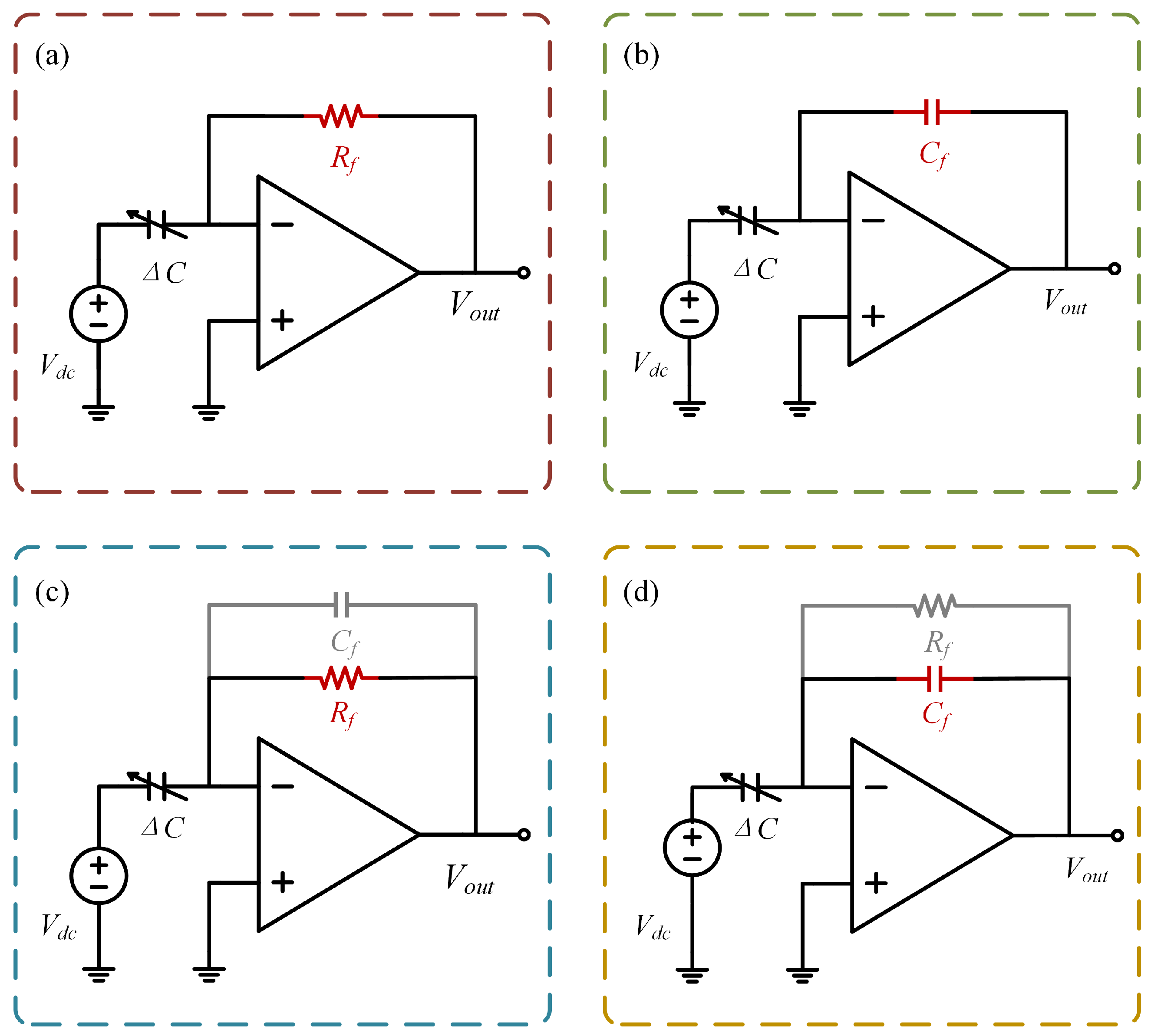
2.3. Readout Circuit Topologies and Operating Principle
3. Readout Circuit Noise Characteristics Analysis
3.1. Noise Model Construction and Characteristics Analysis
3.1.1. Operational Amplifier Input Voltage Noise
3.1.2. Operational Amplifier Input Current Noise
3.1.3. Resistor Thermal Noise
3.2. Gyroscope Detection Limit and Output Noise
4. Simulation Analysis Experimental
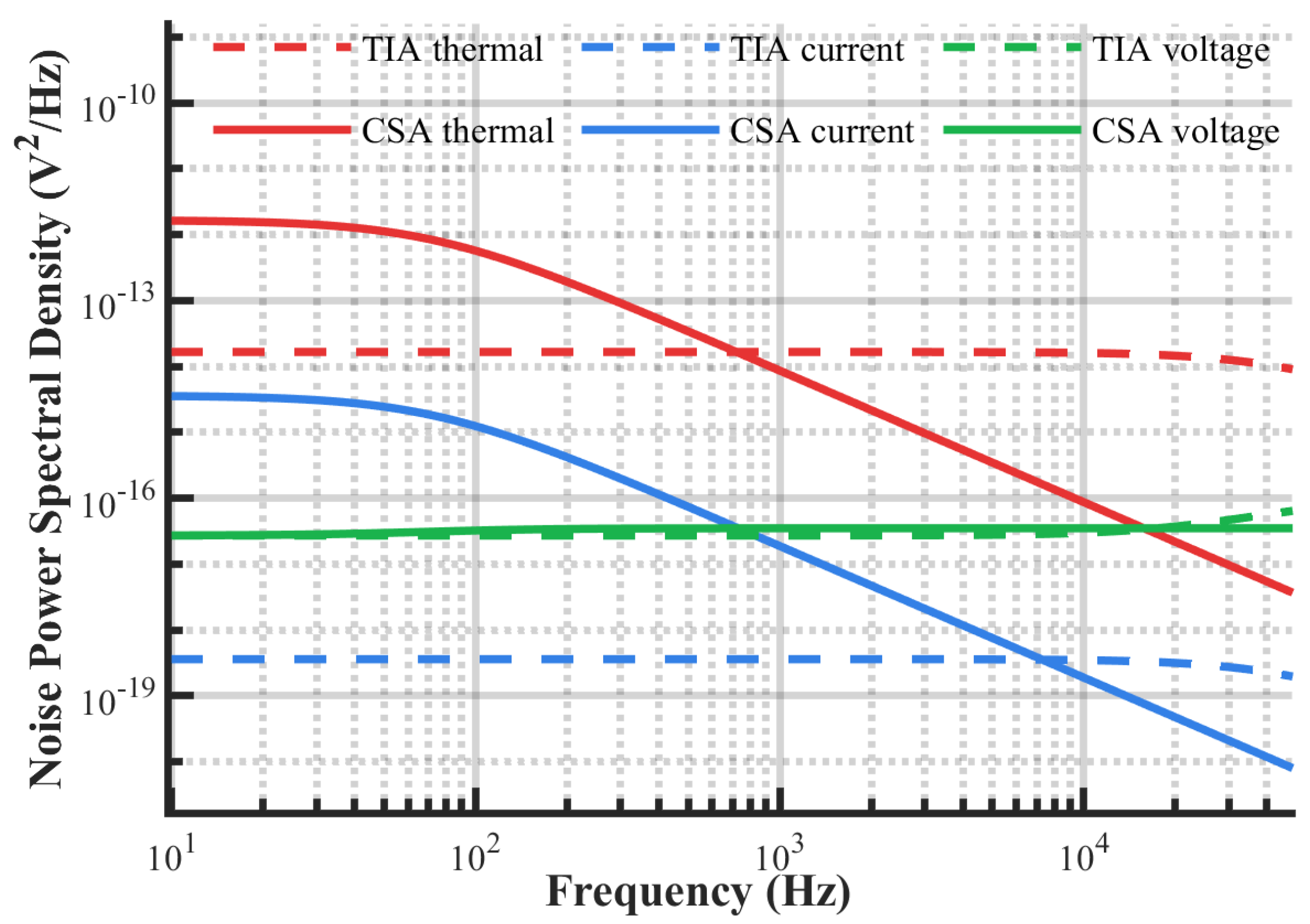
4.1. Noise Characteristics Simulation Analysis
4.2. Noise Measurement and Results Verification
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Delhaye, F. HRG by SAFRAN: The game-changing technology. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Inertial Sensors and Systems (INERTIAL), Lake Como, Italy, 26–29 March 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Rozelle, D.M. The hemispherical resonator gyro: From wineglass to the planets. In Proceedings of the 19th AAS/AIAA Space Flight Mechanics Meeting, Savannah, GA, USA, 8–12 February 2009; Volume 134, pp. 1157–1178. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.; Tang, X.; Li, J.; Xiao, P.; Xia, T.; Deng, K.; Yang, K.; Luo, H. Fast identification and compensation for actuation electrode errors of rate integrating gyroscopes. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 36433–36442. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.; Xu, R.; Nan, F.; Han, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y. Identification and Calibration of the Detection Signal Distortion in Whole Angle Mode Hemispherical Resonator Gyro. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 9515809. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Li, P.; Zhuang, X.; Sheng, Y.; Liu, J.; Gao, Z.; Yu, Z. Weak Capacitance Detection Circuit of Micro-Hemispherical Gyroscope Based on Common-Mode Feedback Fusion Modulation and Demodulation. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1161. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Minotti, P.; Dellea, S.; Mussi, G.; Bonfanti, A.; Facchinetti, S.; Tocchio, A.; Zega, V.; Comi, C.; Lacaita, A.L.; Langfelder, G. High scale-factor stability frequency-modulated MEMS gyroscope: 3-axis sensor and integrated electronics design. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 65, 5040–5050. [Google Scholar]
- Elsayed, A.; Elshennawy, A.; Elmallah, A.; Shaban, A.; George, B.; Elmala, M.; Ismail, A.; Wassal, A.; Sakr, M.; Mokhtar, A.; et al. A self-clocked ASIC interface for MEMS gyroscope with 1 m°/s/ noise floor. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (CICC), San Jose, CA, USA, 19–21 September 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Tirupathi, R.; Kar, S.K. Design and analysis of signal conditioning circuit for capacitive sensor interfacing. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Power, Control, Signals and Instrumentation Engineering (ICPCSI), Chennai, India, 21–22 September 2017; pp. 1717–1721. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.; Zaman, M.F.; Ayazi, F. A 104-dB dynamic range transimpedance-based CMOS ASIC for tuning fork microgyroscopes. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2007, 42, 1790–1802. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, P.; Zhu, J.; Liu, X.; Gu, K. A capacitance sensing method with trans-impedance based readout circuit and adaptive filtering for micro-gyro. Rev. Sci. Instruments 2023, 94, 075002. [Google Scholar]
- Rombach, S.; Marx, M.; Nessler, S.; De Dorigo, D.; Maurer, M.; Manoli, Y. An Interface ASIC for MEMS Vibratory Gyroscopes With a Power of 1.6 mW, 92 dB DR and 0.007°/s/ Noise Floor Over a 40 Hz Band. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2016, 51, 1915–1927. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Gu, K.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, P. A low noise capacitance to voltage readout circuit based on active feedback charge sensitive amplifier for micro-gyro. Rev. Sci. Instruments 2024, 95, 065001. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, C. Stability boundary and enhanced solution of dual-mode based micro gyroscope mode matching technology. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, F.; Gao, Z.; Xu, R.; Wu, H.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Stiffness Tuning of Hemispherical Shell Resonator Based on Electrostatic Force Applied to Discrete Electrodes. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 8505810. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Yuan, W.; Xue, Y.; Chang, H.; Shen, Q. Virtual Coriolis-Force-Based Mode-Matching Micromachine-Optimized Tuning Fork Gyroscope without a Quadrature-Nulling Loop. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1704. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, H. Transimpedance Amplifiers (TIA): Choosing the Best Amplifier for the Job. In Texas Instruments Application Report SNOA942A—Nov; Texas Instruments: Dallas, TX, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zargari, S.; Moezzi, M. A new readout circuit with robust quadrature error compensation for MEMS vibratory gyroscopes. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 41, 3050–3065. [Google Scholar]
- Kay, A. Operational Amplifier Noise: Techniques and Tips for Analyzing and Reducing Noise; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Ziel, A. Equivalent circuit and equipartition theorem in ideal dielectric and ferroelectric capacitors. J. Appl. Phys. 1973, 44, 1400–1401. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.; Zhu, K.; Li, H. A switch-bridge-based readout circuit for differential capacitance measurement in MEMS resonators. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 6978–6985. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.; M’Closkey, R.T. Spectral analysis of vibratory gyro noise. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 4361–4374. [Google Scholar]


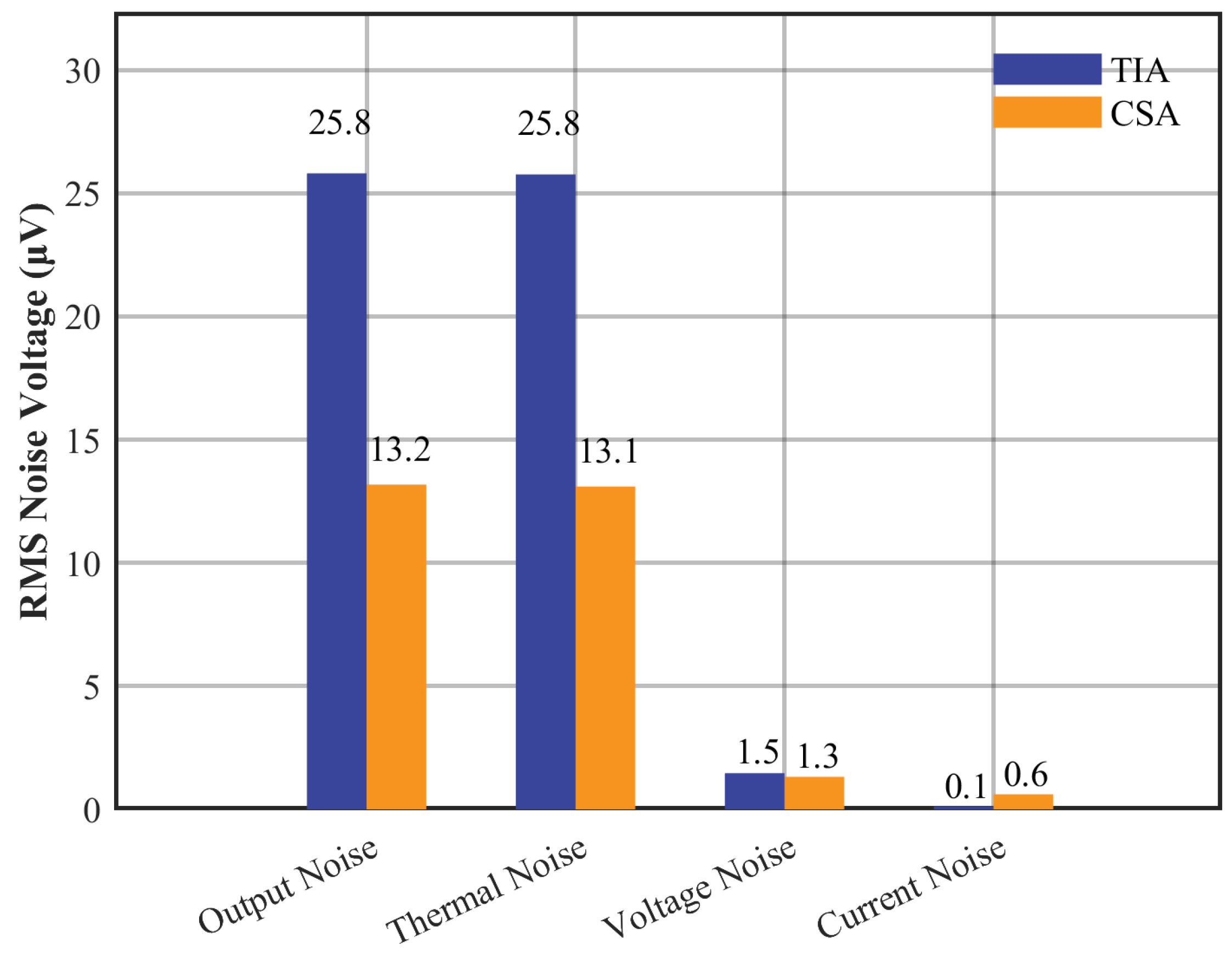
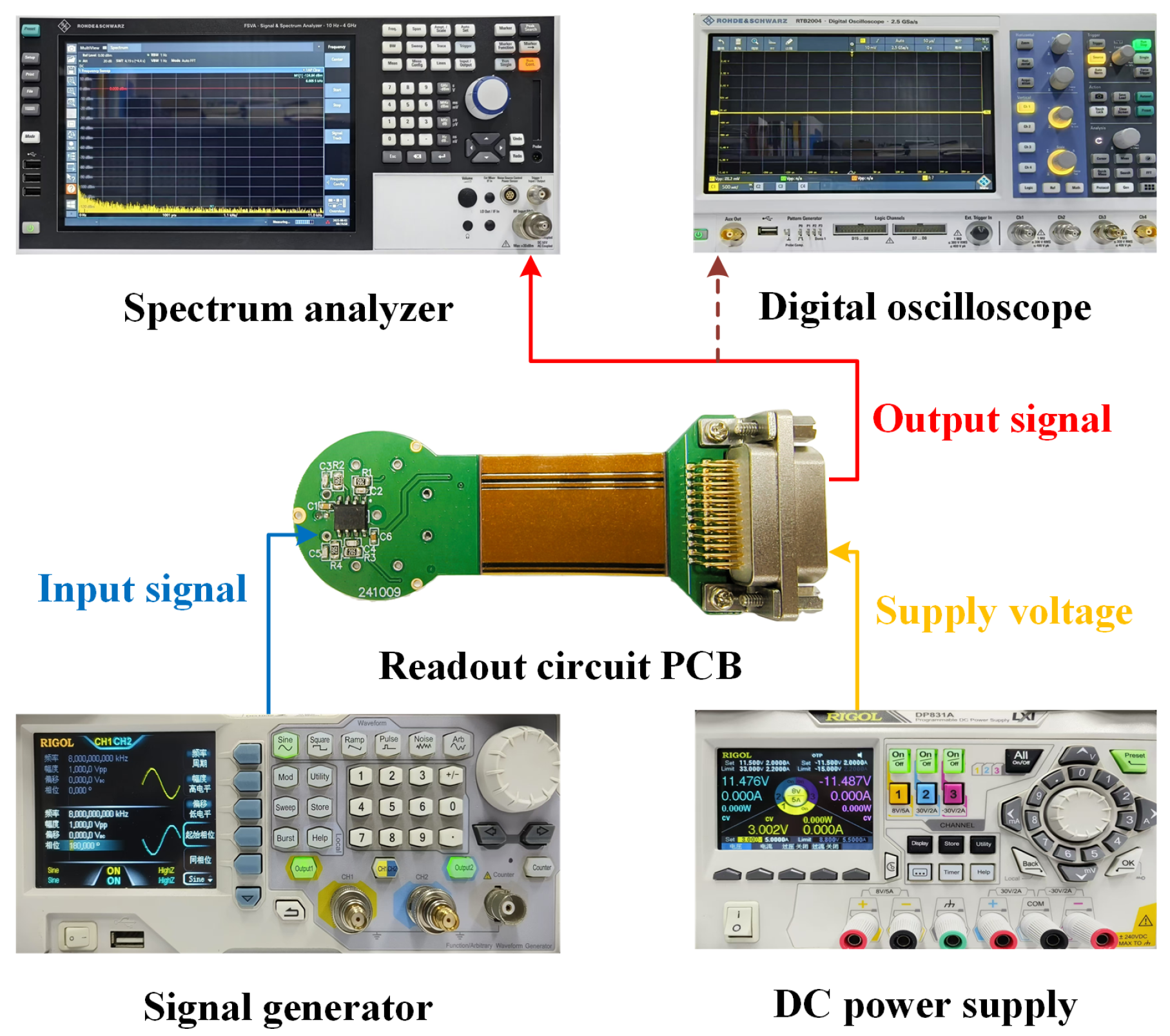
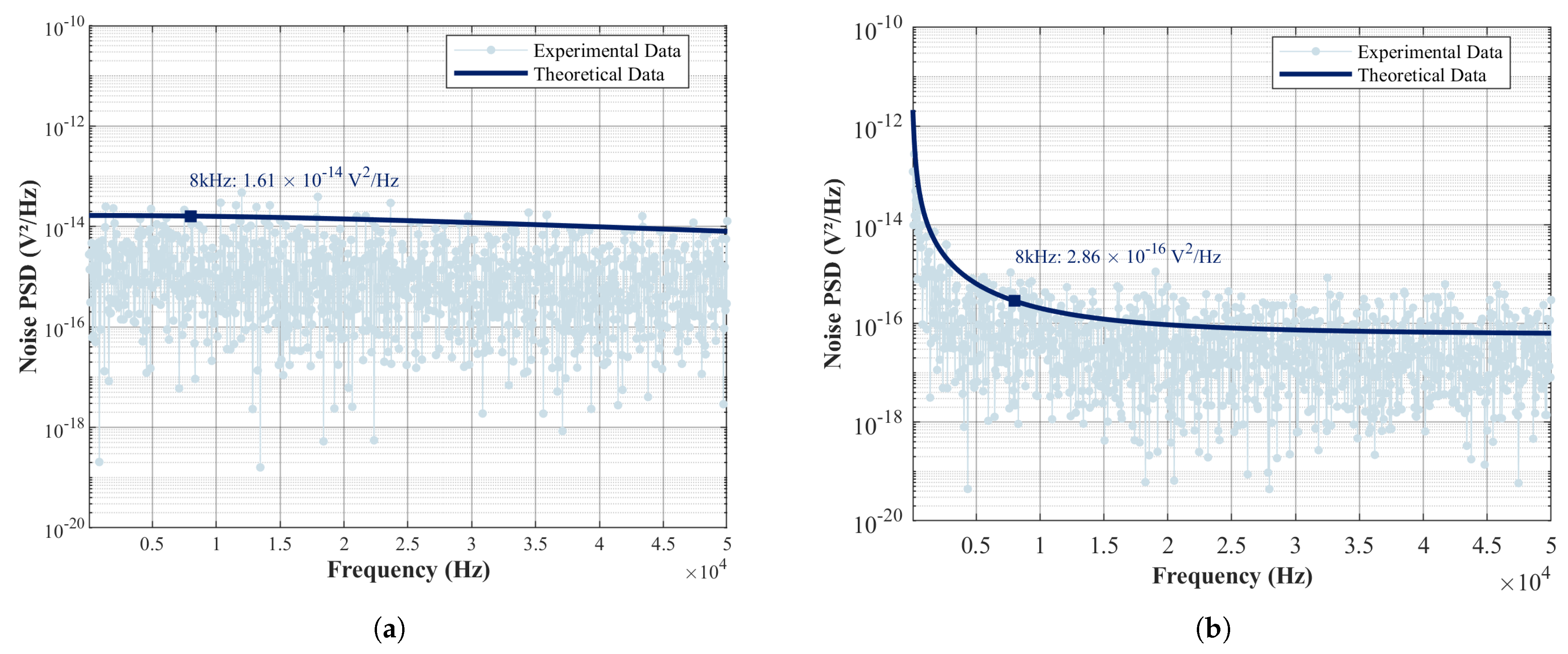
| Parameter | Setting Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| K | ||
| T | 300 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Z.; Zeng, L.; Xing, C.; Shang, L.; Yan, X.; Li, J. Comparative Noise Analysis of Readout Circuit in Hemispherical Resonator Gyroscope. Micromachines 2025, 16, 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16070802
Yu Z, Zeng L, Xing C, Shang L, Yan X, Li J. Comparative Noise Analysis of Readout Circuit in Hemispherical Resonator Gyroscope. Micromachines. 2025; 16(7):802. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16070802
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Zhihao, Libin Zeng, Changda Xing, Lituo Shang, Xiuyue Yan, and Jingyu Li. 2025. "Comparative Noise Analysis of Readout Circuit in Hemispherical Resonator Gyroscope" Micromachines 16, no. 7: 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16070802
APA StyleYu, Z., Zeng, L., Xing, C., Shang, L., Yan, X., & Li, J. (2025). Comparative Noise Analysis of Readout Circuit in Hemispherical Resonator Gyroscope. Micromachines, 16(7), 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16070802






