Interfacial Engineering-Free Microfluidics: Toward a Mild and Cost-Effective Strategy for Surfactant- and Demulsifier-Free Hydrogel Microsphere Fabrication
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Apparatus
2.2. The Fabrication of the PDMS Microfluidic Device
2.3. Characterization of Hydrogel Microspheres
3. Results and Discussion
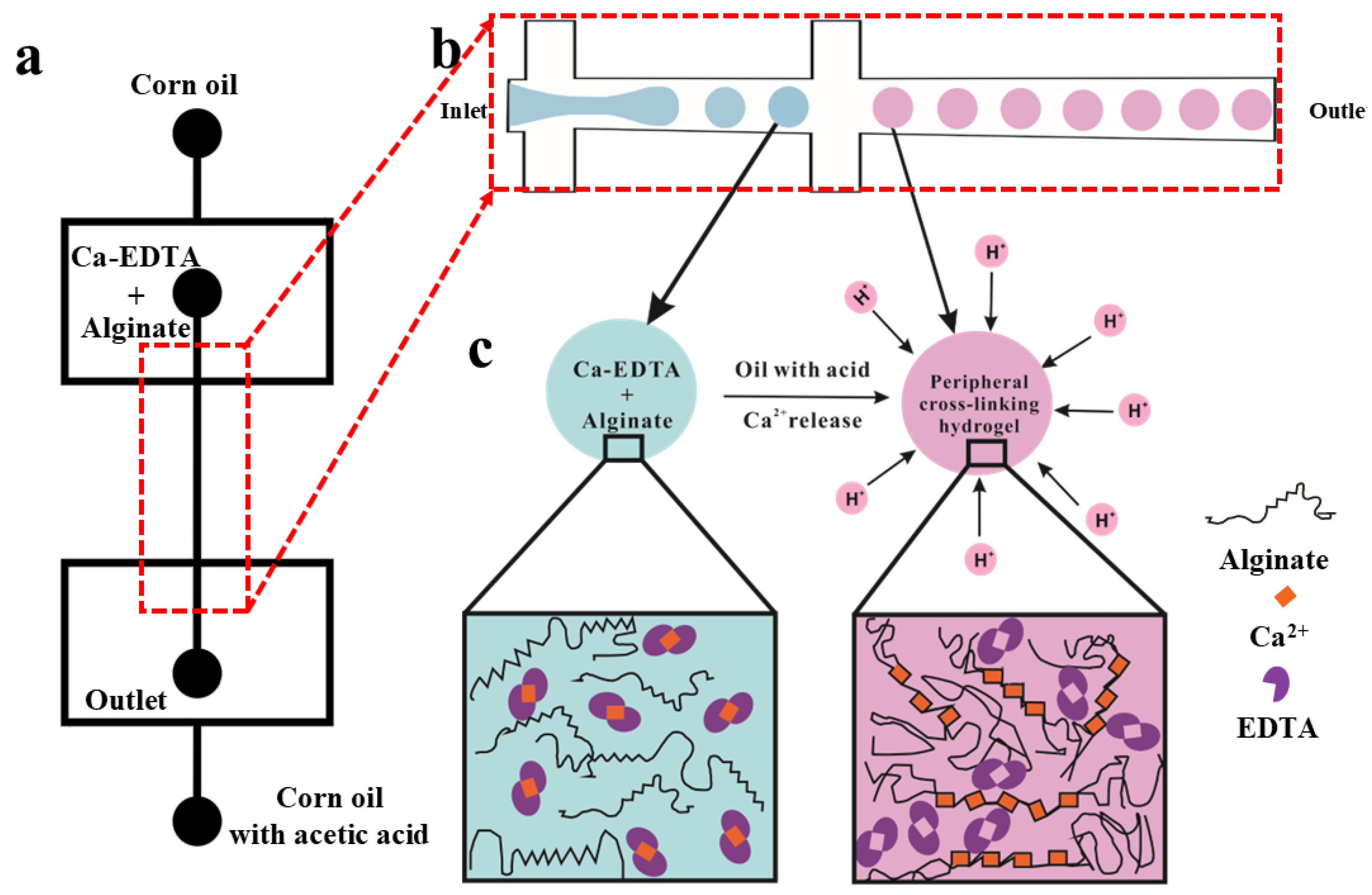
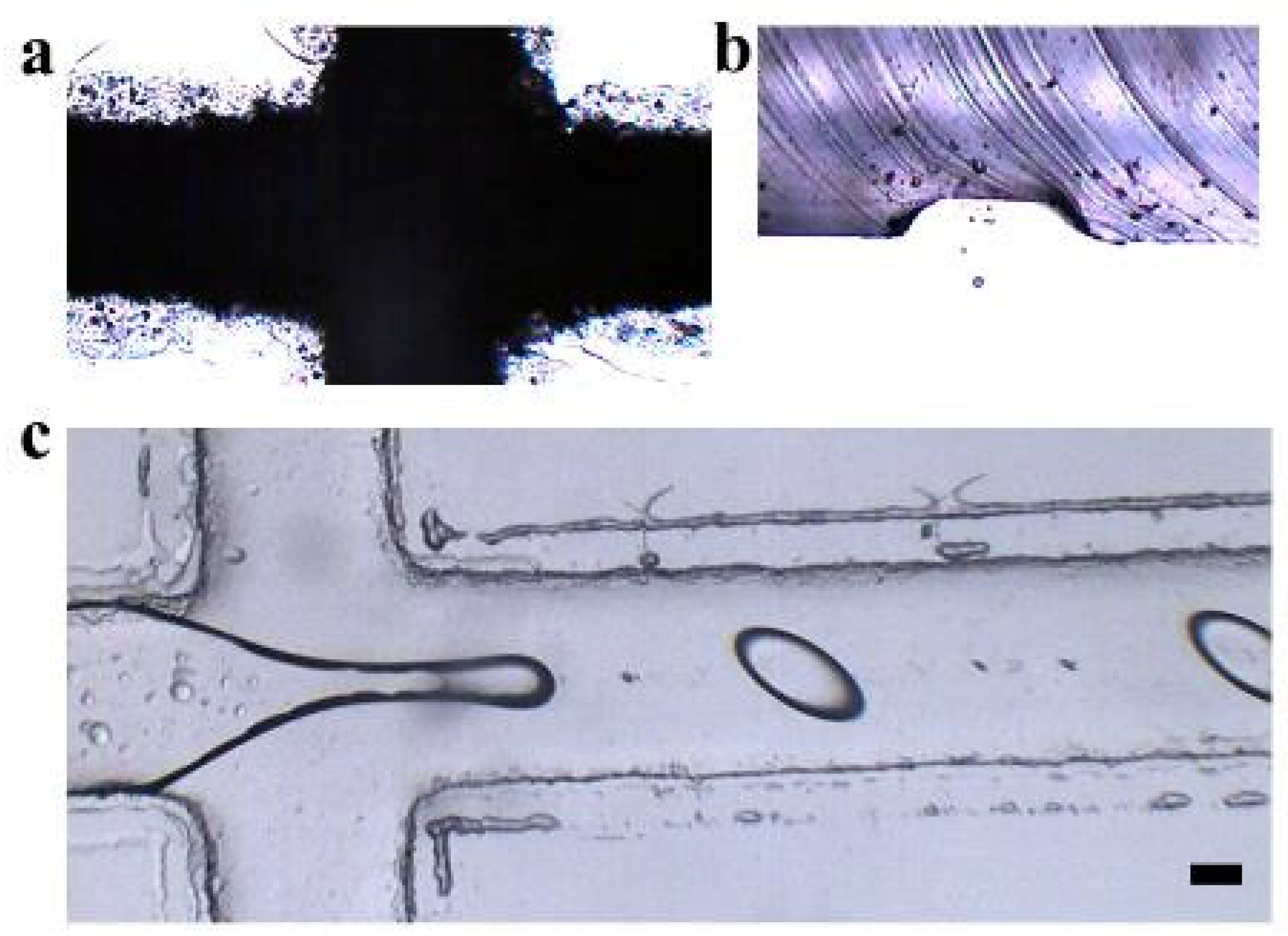
3.1. Formation of Hydrogel Microsphere
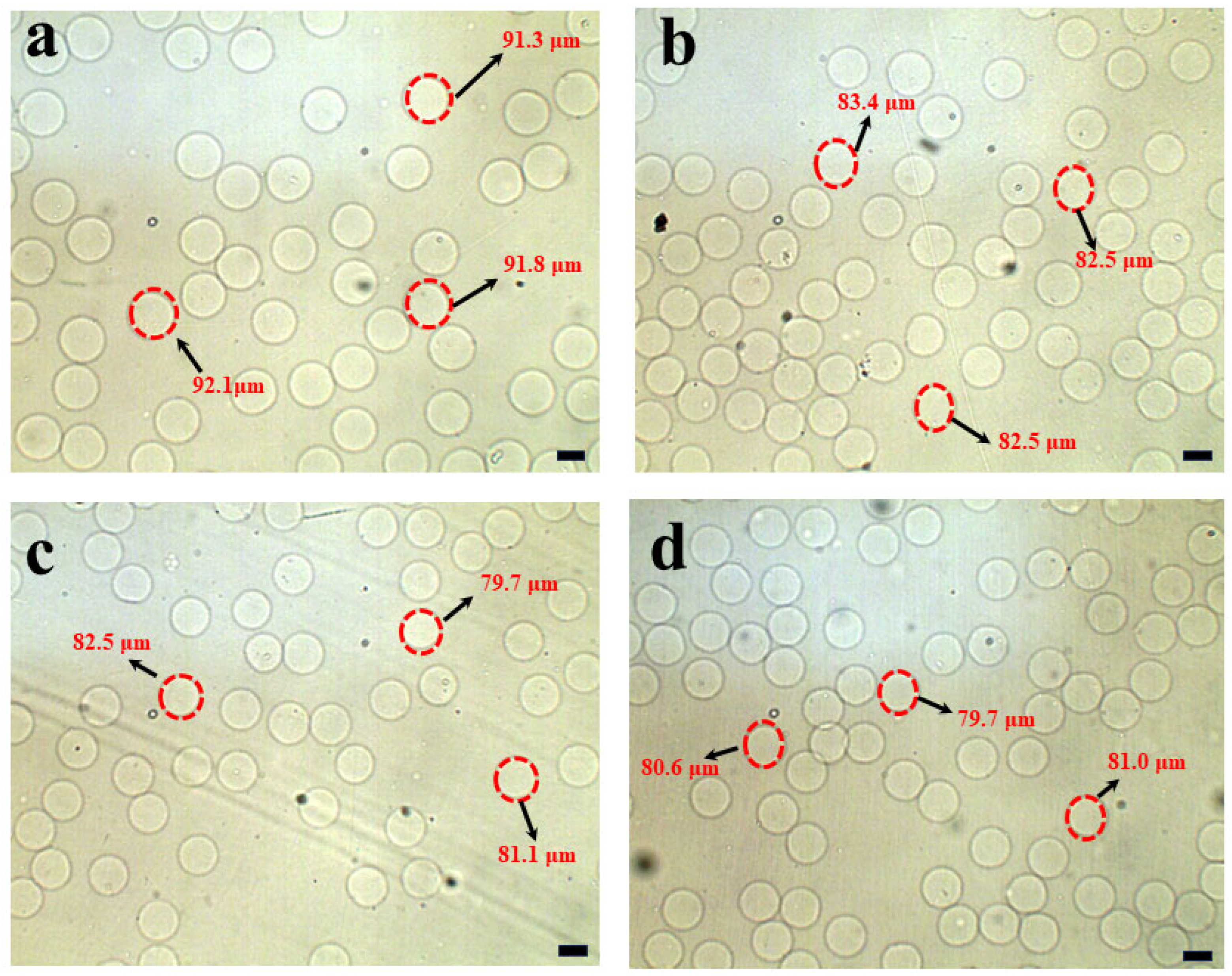
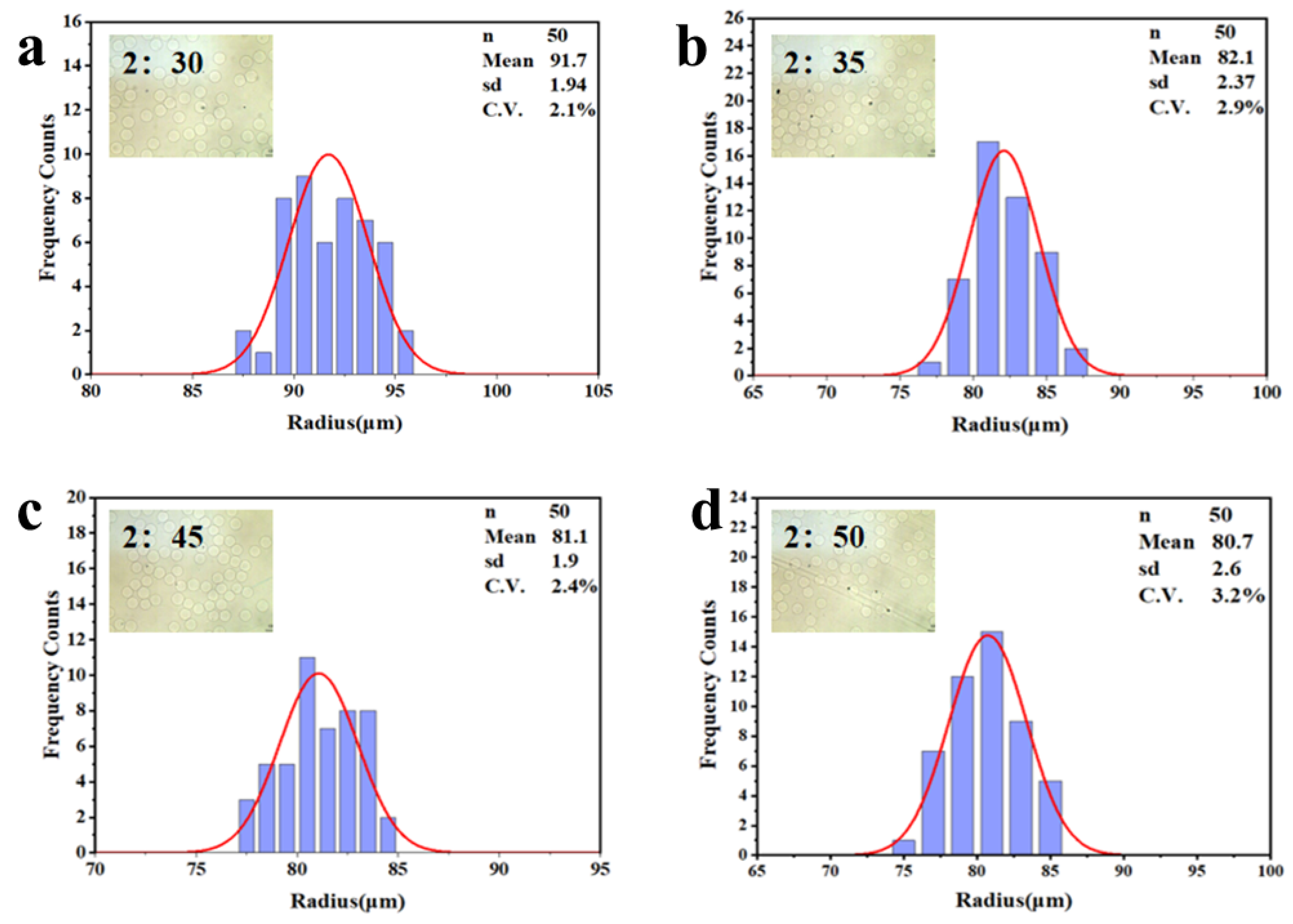
3.2. Separation of Hydrogel Microsphere
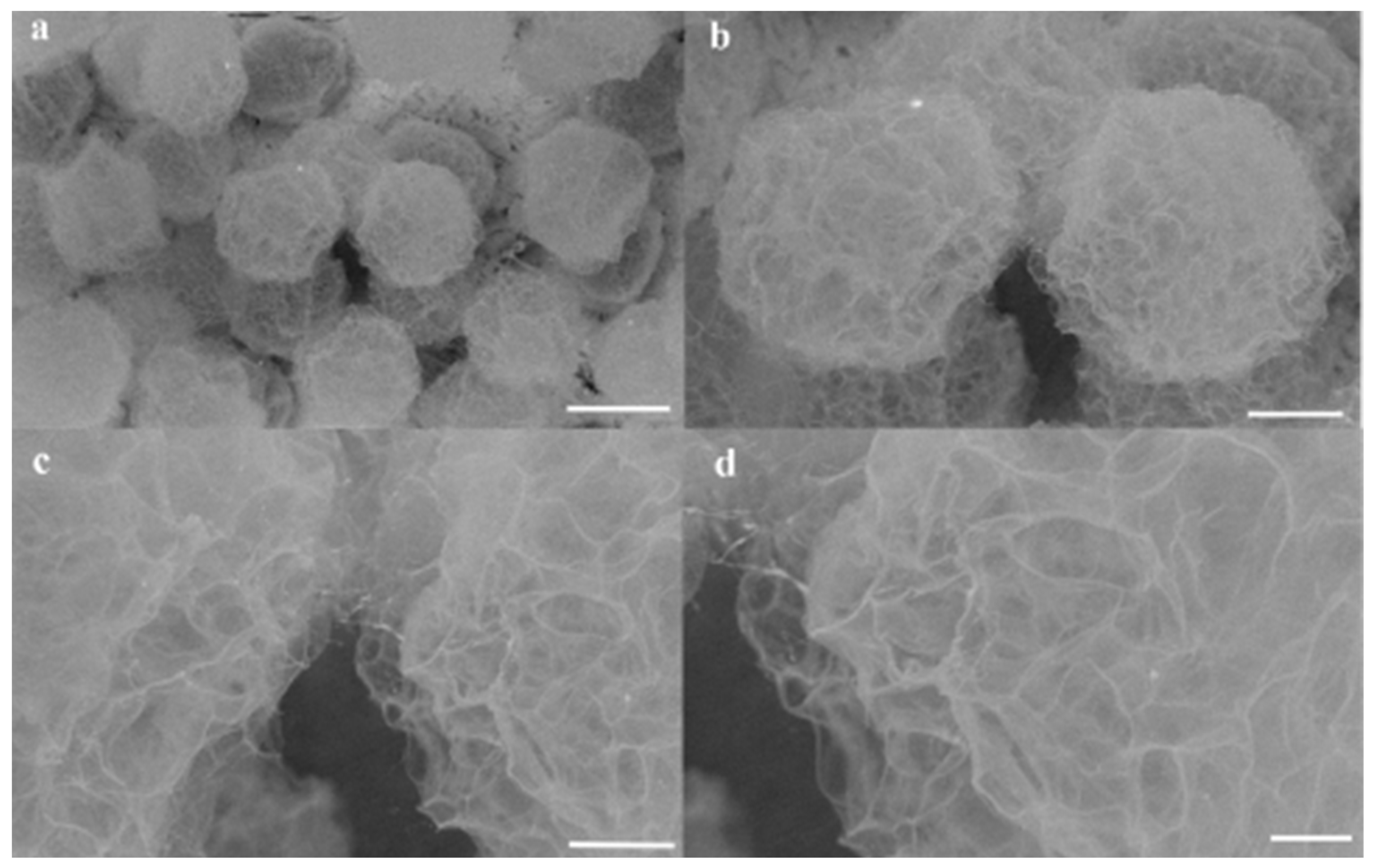
3.3. Surface Morphologies and Microstructures of Hydrogel Microsphere
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mou, C.-L.; Deng, Q.-Z.; Hu, J.-X.; Wang, L.-Y.; Deng, H.-B.; Xiao, G.; Zhan, Y. Controllable preparation of monodisperse alginate microcapsules with oil cores. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 569, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Jing, H.; Zhuang, Y.; Cui, J.; Fu, Z.; Li, D.; Zhao, C.; Liaqat, U.; Lin, K. BMSCs-laden mechanically reinforced bioactive sodium alginate composite hydrogel microspheres for minimally invasive bone repair. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 332, 121933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, I.M.; Barreiro, M.F.; Coelho, M.; Rodrigues, A.E. Microencapsulation of essential oils with biodegradable polymeric carriers for cosmetic applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 245, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, Y.; Onuki, M.; Takeuchi, S. Mass Production of Cell-Laden Calcium Alginate Particles with Centrifugal Force. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1601375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somo, S.I.; Langert, K.; Yang, C.-Y.; Vaicik, M.K.; Ibarra, V.; Appel, A.A.; Akar, B.; Cheng, M.-H.; Brey, E.M. Synthesis and evaluation of dual crosslinked alginate microbeads. Acta Biomater. 2018, 65, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.-H.; Takeuchi, S. Monodisperse Alginate Hydrogel Microbeads for Cell Encapsulation. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 2696–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.-H.; Jung, J.-H.; Rhee, Y.W.; Kim, D.-P.; Shim, S.-E.; Lee, C.-S. Generation of monodisperse alginate microbeads and in situ encapsulation of cell in microfluidic device. Biomed. Microdevices 2007, 9, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utech, S.; Prodanovic, R.; Mao, A.S.; Ostafe, R.; Mooney, D.J.; Weitz, D.A. Microfluidic generation of monodisperse, structurally homogeneous alginate microgels for cell encapsulation and 3D cell culture. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 1628–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojek, K.O.; Cwiklinska, M.; Kuczak, J.; Guzowski, J. Microfluidic Formulation of Topological Hydrogels for Microtissue Engineering. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 16839–16909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Utech, S.; Chen, D.; Prodanovic, R.; Lin, J.-M.; Weitz, D.A. Controlled assembly of heterotypic cells in a core–shell scaffold: Organ in a droplet. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 1346–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wu, Z.; Khan, M.; Mao, S.; Manibalan, K.; Li, N.; Lin, J.-M.; Lin, L. Multifunctional Regulation of 3D Cell-Laden Microsphere Culture on an Integrated Microfluidic Device. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 12283–12289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar, L.M.C.; Duchi, S.; Onofrillo, C.; O’Connell, C.D.; Di Bella, C.; Moulton, S.E. Formation of alginate microspheres prepared by optimized microfluidics parameters for high encapsulation of bioactive molecules. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 587, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Zhu, L.; Li, W.; Liu, Q. An integrated microfluidic chip for alginate microsphere generation and 3D cell culture. Anal. Methods 2022, 14, 1181–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yao, H.; Chen, S.; Xu, N.; Lin, J.-M. Effect of Tryptophan Metabolites on Cell Damage Revealed by Bacteria–Cell Interactions in Hydrogel Microspheres. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 1402–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, L.; Yin, Y.; Chen, A.; Seo, B.R.; Lou, J.; Mooney, D.J.; Weitz, D.A. Stiff hydrogel encapsulation retains mesenchymal stem cell stemness for regenerative medicine. Matter 2024, 7, 3447–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S.; Chen, W.; Zheng, X.; Ma, L. Preparation of pH-sensitive alginate-based hydrogel by microfluidic technology for intestinal targeting drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 254, 127649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Lang, Y.; He, J.; Cui, J.; Liu, X.; Yuan, H.; Li, L.; Zhou, M.; Wang, S. Phycocyanin-based multifunctional microspheres for treatment of infected radiation-induced skin injury. Biomaterials 2025, 317, 123061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Shahar, T.; Cohen, S. Thermo-controlled microfluidic generation of monodisperse alginate microspheres based on external gelation. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 32021–32028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wei, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, G. Rapid Fabrication of Diverse Hydrogel Microspheres for Drug Evaluation on a Rotating Microfluidic System. Langmuir 2025, 41, 8985–8997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.T.; Galeai, F.M.; Nguyen, N.-K.; Roshan, U.; Yadav, A.S.; Sreejith, K.R.; Nguyen, N.-T. Microfluidic Generation of Calcium Alginate Hydrogel Beads using External Gelation for Microalgae Cultivation. Chemnanomat 2025, 11, e202400549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marburger, J.; Vladisavljevic, G.T.; Leister, N. High-throughput millifluidics for monodisperse alginate milli-capsules filled with emulsions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2025, 714, 136541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Chen, D.; Wang, X.; Jiang, J. Milling Positive Master for Polydimethylsiloxane Microfluidic Devices: The Microfabrication and Roughness Issues. Micromachines 2017, 8, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, Y.; Irudayaraj, J. Multi-layered alginate hydrogel structures and bacteria encapsulation. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 8584–8587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Fluid | Density (ρ (g/mL−1)) | Dyn. Viscosity (η (mPa·s)) | Interfacial Tension (mN m−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corn oil | 0.96 | 1.4 | 85.5 |
| Acetic corn oil (2%) | 0.95 | 1.8 | - |
| Alginate solution (1%) | 1.68 | 4.4 | 72.0 |
| Master Type | Time (in Hour) | Price ($) | Minimum Width (in mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SU-8 | >24 | ~700 | ≥0.001 |
| Paper | ~2 | ~0.03 | ≥0.080 |
| Master Type | Width of Master (in µm) | PDMS Prototyping (in µm) |
|---|---|---|
| Designed size | 500 | 399.5 ± 4.7 |
| Fabricated size | 399.5 ± 4.7 | 339.8 ± 9.7 |
| Master | Surfactant | Demulsification | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glass tube | F-127 | Isopropyl alcohol | [1] |
| SU-8 | Span 80 | PFO | [2,16] |
| SU-8 | Lecithin | Hexane/Hexadecane | [6] |
| SU-8 | PFPE-PEG | PFO | [8,11,14] |
| SU-8 | PicosurfTM | 1H,1H-Perfluorooctan-1-ol | [12] |
| SU-8 | neat 008-uorosurfactant | PFO | [13] |
| SU-8 | Krytox–PEG–Krytox | PFO | [15] |
| Paper | Without addition | Without addition | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Lv, J.; Tian, M.; Sun, Y.; Fang, W.; Huang, X.; Li, J.; Su, Y.; et al. Interfacial Engineering-Free Microfluidics: Toward a Mild and Cost-Effective Strategy for Surfactant- and Demulsifier-Free Hydrogel Microsphere Fabrication. Micromachines 2025, 16, 733. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16070733
Qin Q, Zhang Y, Wei Y, Lv J, Tian M, Sun Y, Fang W, Huang X, Li J, Su Y, et al. Interfacial Engineering-Free Microfluidics: Toward a Mild and Cost-Effective Strategy for Surfactant- and Demulsifier-Free Hydrogel Microsphere Fabrication. Micromachines. 2025; 16(7):733. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16070733
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Qing, Yu Zhang, Yubei Wei, Jinnuo Lv, Meiling Tian, Yuanyuan Sun, Wei Fang, Xingjian Huang, Jianglin Li, Yifeng Su, and et al. 2025. "Interfacial Engineering-Free Microfluidics: Toward a Mild and Cost-Effective Strategy for Surfactant- and Demulsifier-Free Hydrogel Microsphere Fabrication" Micromachines 16, no. 7: 733. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16070733
APA StyleQin, Q., Zhang, Y., Wei, Y., Lv, J., Tian, M., Sun, Y., Fang, W., Huang, X., Li, J., Su, Y., Xiang, X., Hu, X., & Zhou, Z. (2025). Interfacial Engineering-Free Microfluidics: Toward a Mild and Cost-Effective Strategy for Surfactant- and Demulsifier-Free Hydrogel Microsphere Fabrication. Micromachines, 16(7), 733. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16070733





