Development of a Fluorescent Rapid Test Sensing System for Influenza Virus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
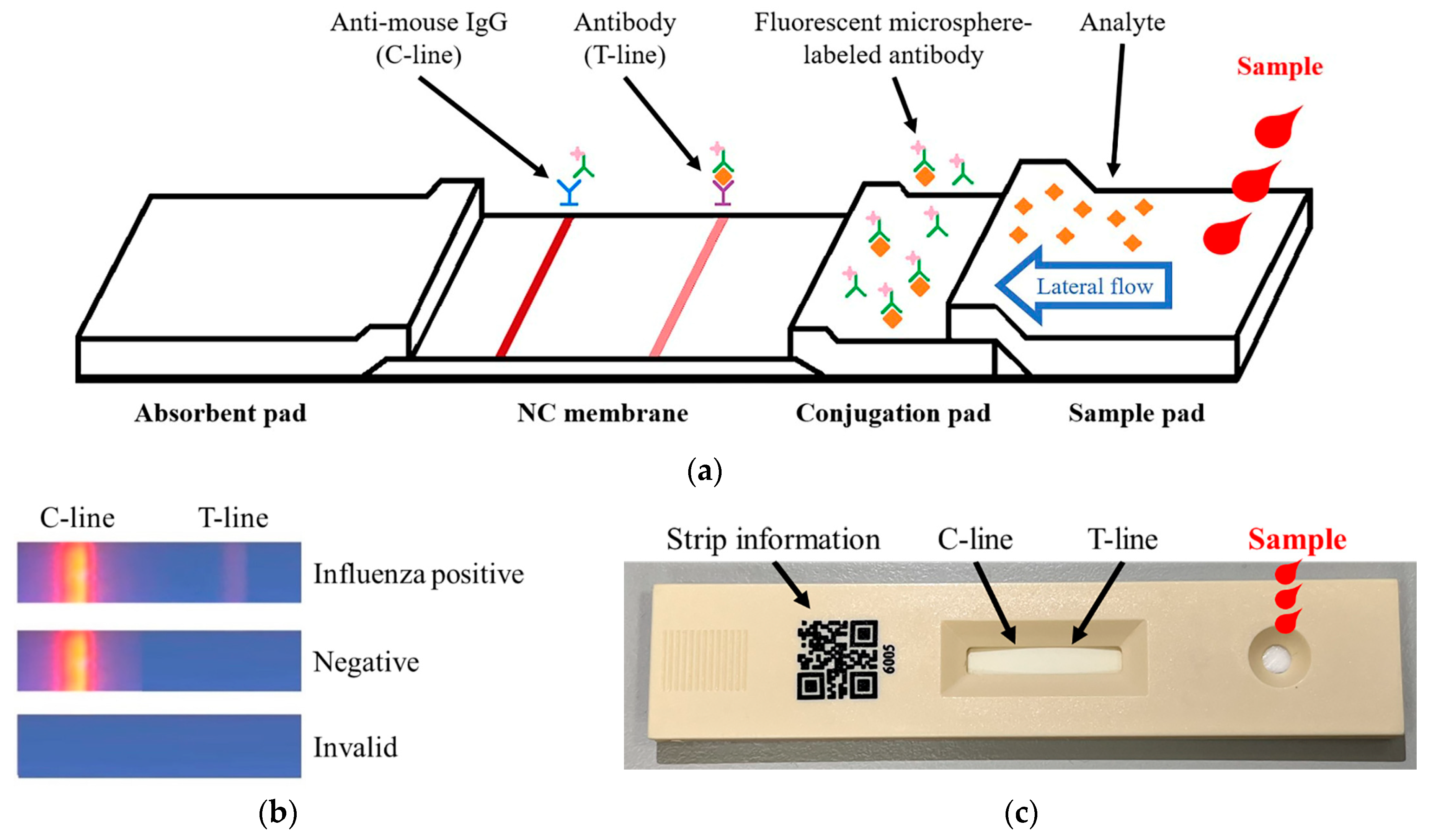
2.1. Fluorescence Strip
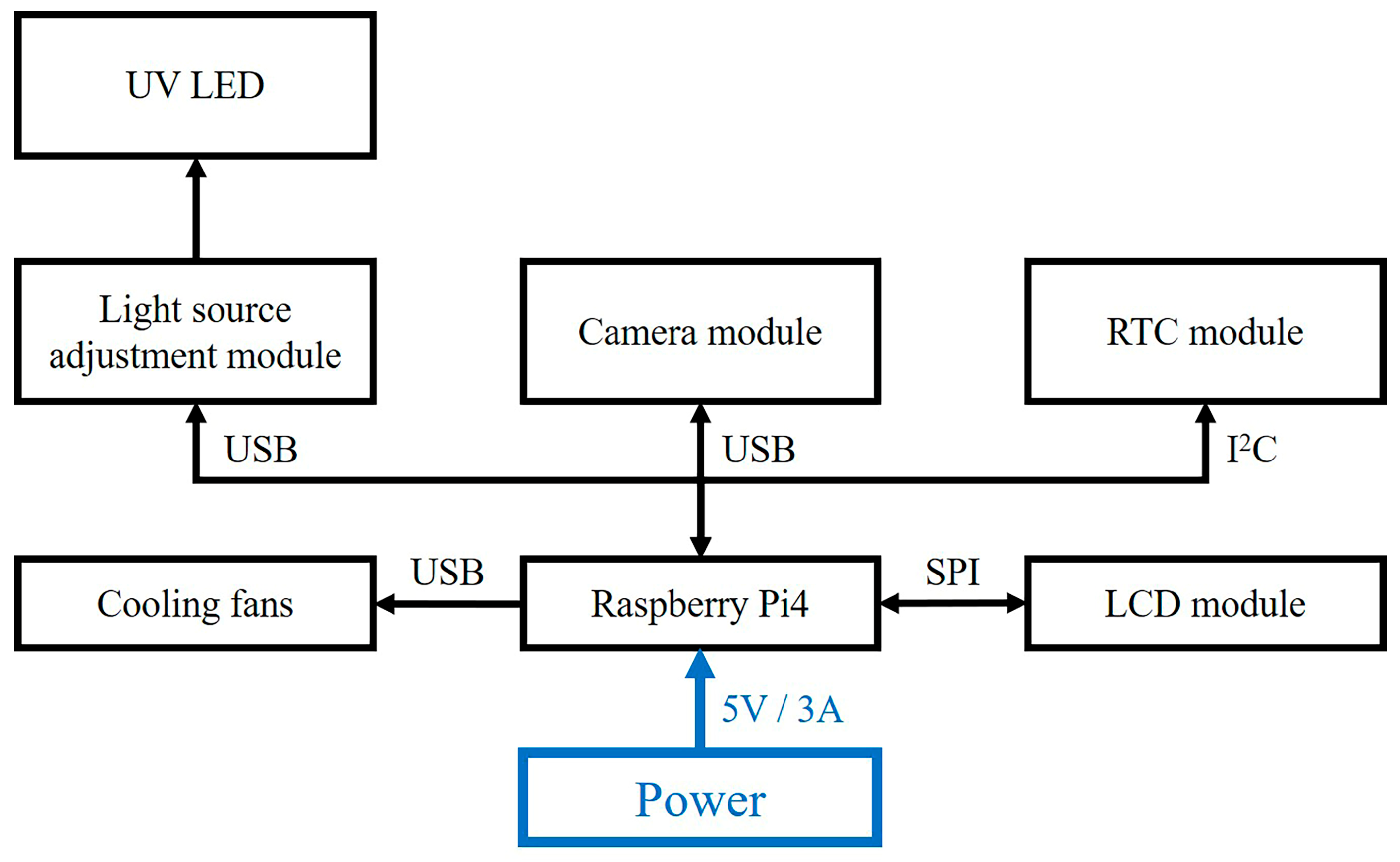
2.2. Hardware Architecture of the Detection Reader
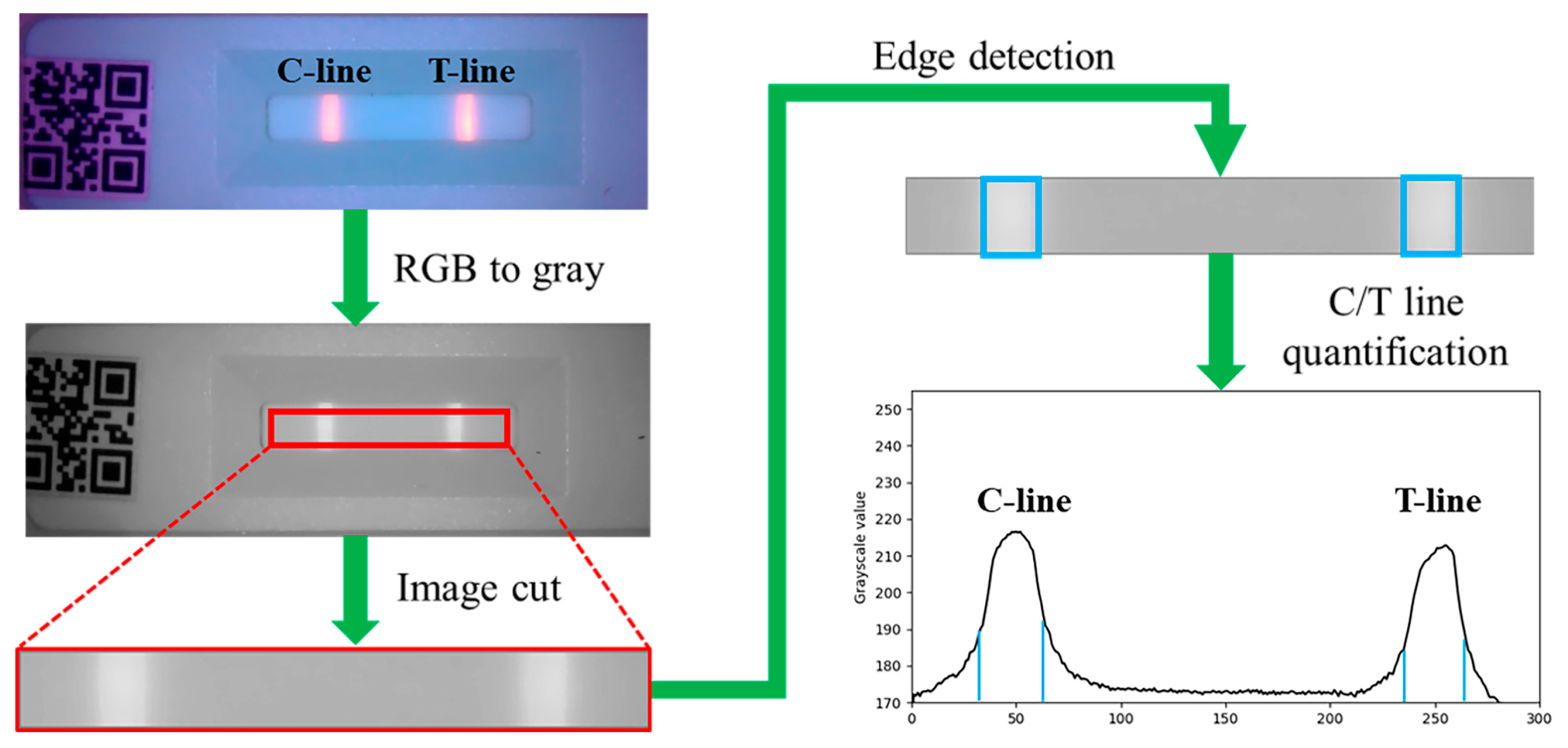
2.3. Image Processing
2.4. Quantitative Data Calculation (T/C Ratio)
3. Results and Discussion
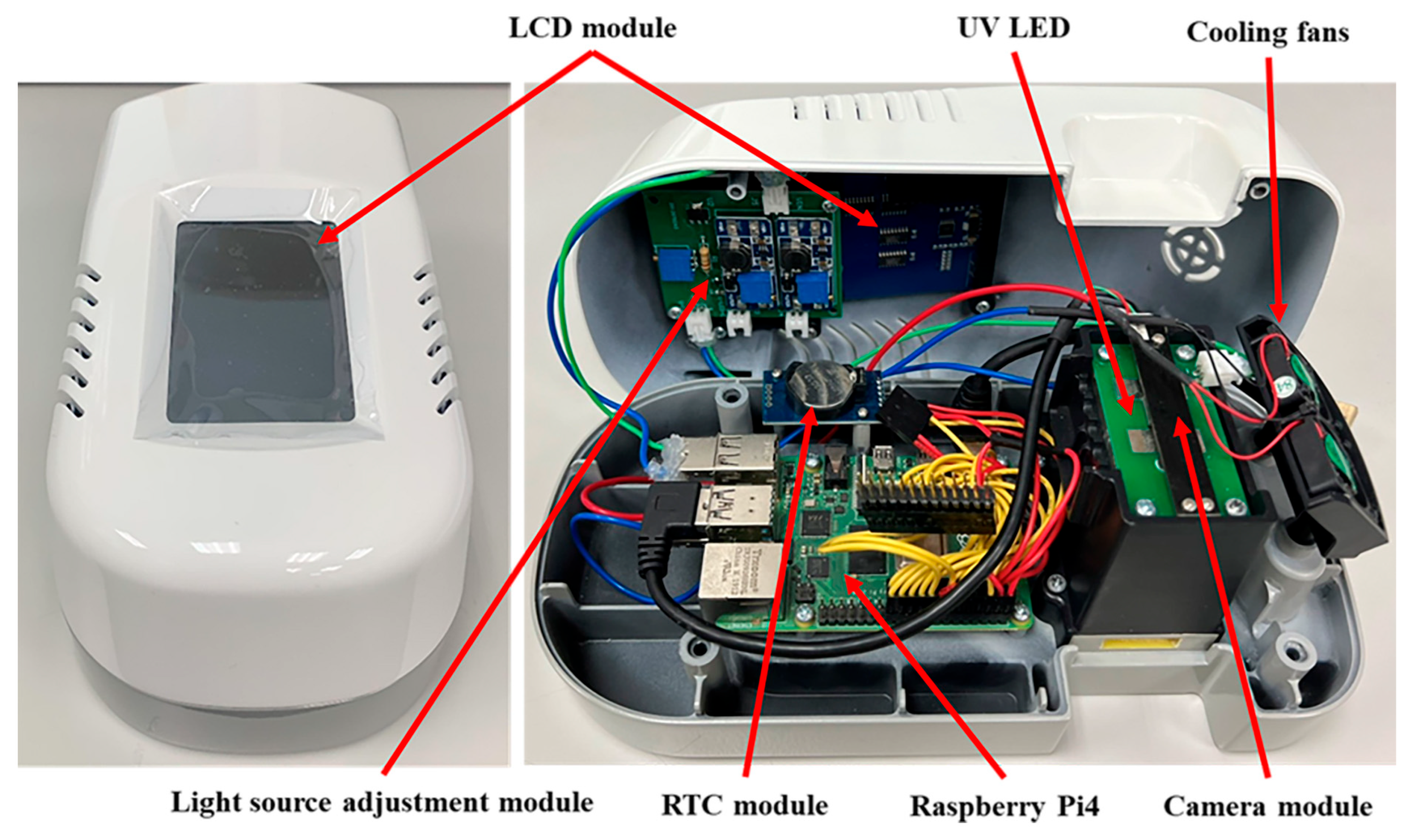
3.1. Fluorescence Rapid Test Detection Reader
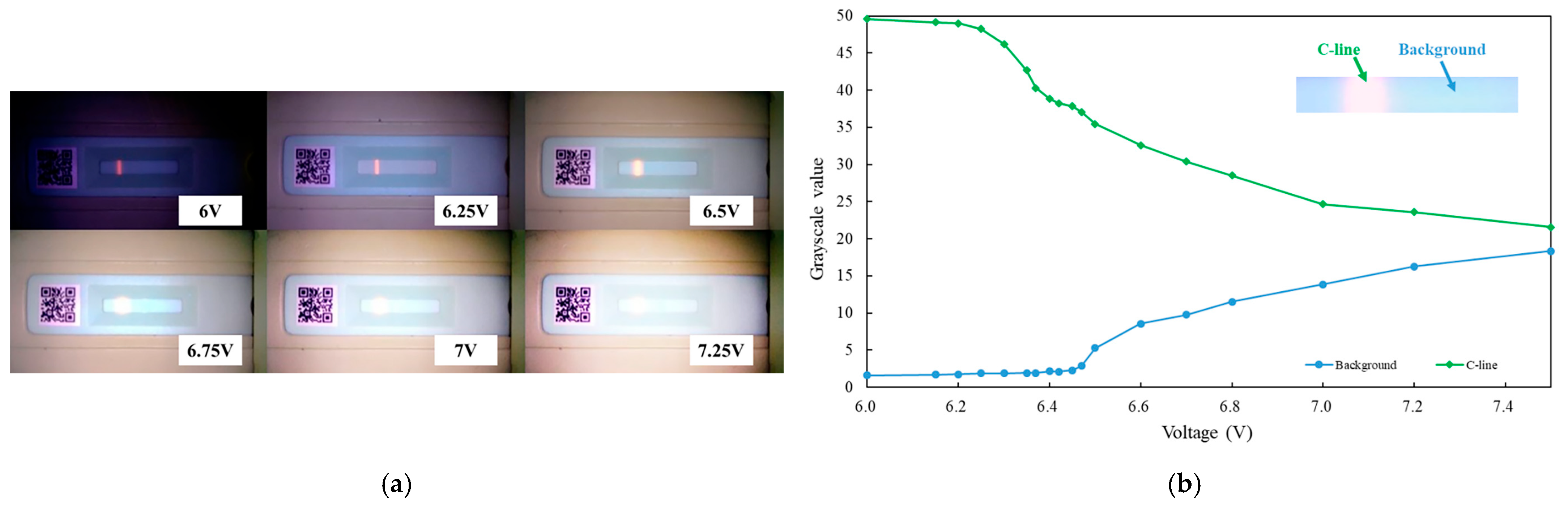
3.2. UV LED Light Intensity Testing
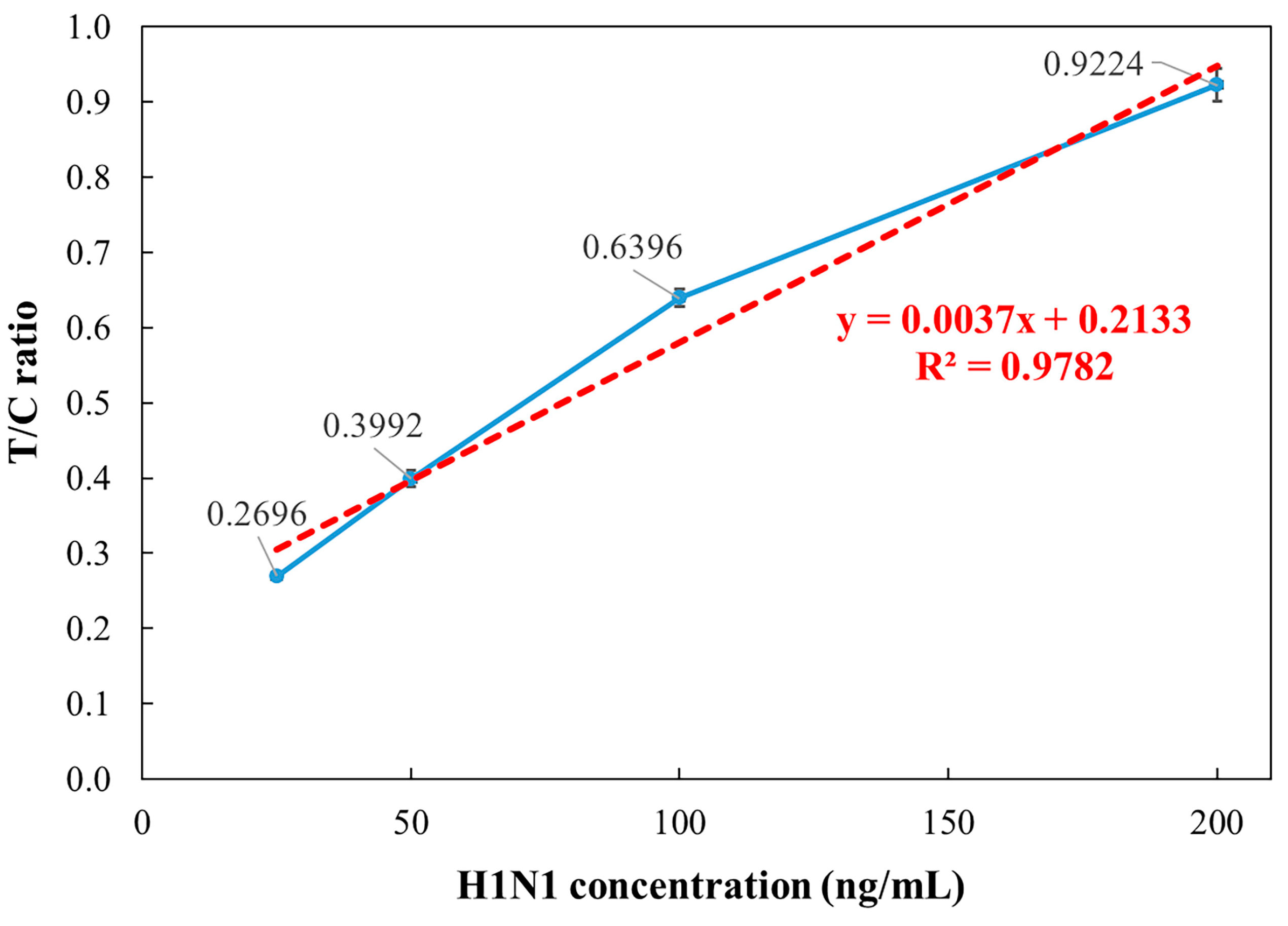
3.3. Influenza A Concentration Analysis
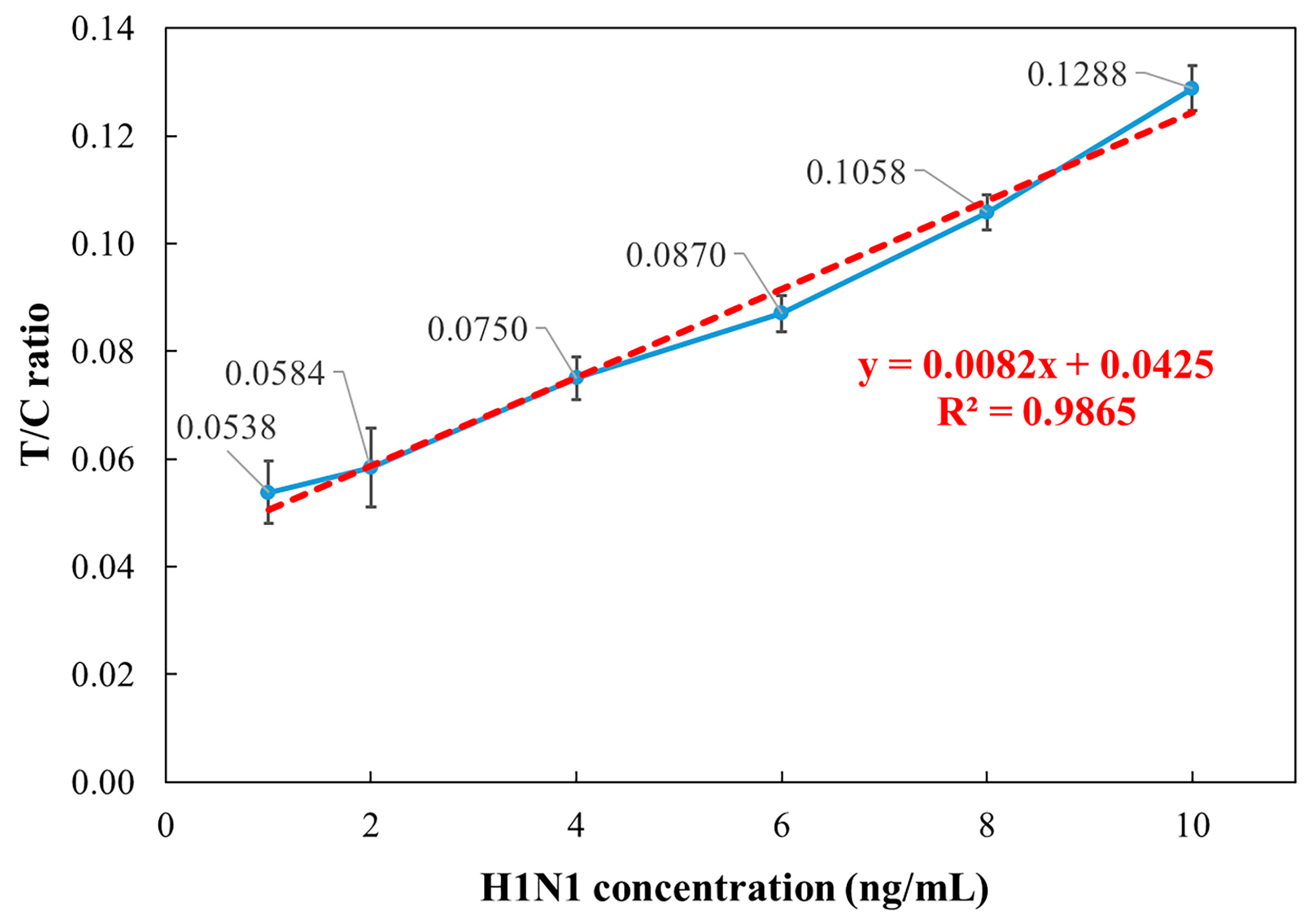
3.4. Influenza A Low-Concentration Analysis
3.5. Influenza B Low-Concentration Analysis
3.6. Comparison with Commercial Detection Systems
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Javanian, M.; Barary, M.; Ghebrehewet, S.; Koppolu, V.; Vasigala, V.; Vasigala, V. A brief review of influenza virus infection. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 4638–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, B.; Kirby, M.K.; Davis, W.G.; Warnes, C.; Liddell, J.; Liu, J.; Wu, K.; Hassell, N.; Benitez, A.J.; Wilson, M.M.; et al. Multiplex real-time reverse transcription PCR for influenza A virus, influenza B virus, and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 1821–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruning, A.H.; Leeflang, M.M.; Vos, J.M.; Spijker, R.; de Jong, M.D.; Wolthers, K.C.; Pajkrt, D. Rapid Tests for Influenza, Respiratory Syncytial Virus, and Other Respiratory Viruses: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, 1026–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.X.; Zhu, L.B.; Wu, S.T.; Ding, S.N. Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Influenza B Virus Employing Nanocomposite Spheres Based on Ag-Doped ZnIn2S4 Quantum Dots. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, A.; Takayama, K.; Nomura, N.; Kajiwara, N.; Okamatsu, M.; Yamamoto, N.; Tamura, T.; Yamada, J.; Hashimoto, M.; Sakoda, Y.; et al. Fluorescent Immunochromatography for Rapid and Sensitive Typing of Seasonal Influenza Viruses. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Cai, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, Q.; Piao, J.; Peng, W.; Gao, W.; Zhou, D.; Zhao, M.; Chang, J. A review of fluorescent signal-based lateral flow immunochromatographic strips. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 5079–5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sela-Culang, I.; Kunik, V.; Ofran, Y. The structural basis of antibody-antigen recognition. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thione, D. Insights into Antigen-Antibody Interactions: Mechanisms and Applications. J. Immunobiol. 2024, 9, 236. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, J.H.; Yalow, R.; Berson, S.A. Detection of Australia antigen and antibody by means of radioimmunoassay techniques. J. Infect. Dis. 1970, 121, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.A.N.G.; Hou, M.L.; Liu, L.P.; Jing, M.A.; Zhang, X.G.; Zhou, Z.X.; Cao, Y.X. A new method for ultra-sensitive P24 antigen assay based on near-infrared fluorescent microsphere immunochromatography. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2020, 33, 174–182. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Cheng, X.; Wei, H.; Tu, Z.; Rong, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, S. Fluorescence-enhanced dual signal lateral flow immunoassay for flexible and ultrasensitive detection of monkeypox virus. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wang, N.; Hou, Y.; Dong, H.; Liang, W.; Li, X.; Yuan, Y. A highly sensitive ratiometric fluorescence immunoassay based on bioorthogonal nanozymes. Chem. Commun. 2024, 60, 3978–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcon, S.; Talarmin, A.; Debruyne, M.; Falconar, A.; Deubel, V.; Flamand, M. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay Specific to Dengue Virus Type 1 Nonstructural Protein NS1 Reveals Circulation of the Antigen in the Blood during the Acute Phase of Disease in Patients Experiencing Primary or Secondary Infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Du, S.; Lai, L.; Wu, W.; Huang, X.; Li, A.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Wang, Q.; Sun, L.; et al. Development and evaluation of recombinant E2 protein based IgM capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and double antigen sandwich ELISA for detection of antibodies to Chikungunya virus. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahed Bel-Ochi, N.; Bouratbine, A.; Mousli, M. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay Using Recombinant SAG1 Antigen to Detect Toxoplasma gondii-Specific Immunoglobulin G Antibodies in Human Sera and Saliva. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2013, 20, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongpradit, S.; Prasongtanakij, S.; Srisala, S.; Chanprasertyothin, S.; Pasomsub, E.; Ongphiphadhanakul, B. The Detection of SARS-CoV2 Antigen in Wastewater Using an Automated Chemiluminescence Enzyme Immunoassay. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Wang, N.; Yu, F.; Yu, S.; Liu, L.; Tian, Y.; Wu, Y. Simultaneous detection of carcinoembryonic antigen and neuron-specific enolase in human serum based on time-resolved chemiluminescence immunoassay. Analyst 2019, 144, 4813–4819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.H.; Su, K.F.; Lin, Y.C. Development of an impedimetric immunobiosensor for measurement of carcinoembryonic antigen. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2016, 241, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhan, L.; Qin, Z.; Sackrison, J.; Bischof, J.C. Ultrasensitive and Highly Specific Lateral Flow Assays for Point-of-Care Diagnosis. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 3593–3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onnerfjord, P.; Eremin, S.; Emneus, J.; Marko-Varga, G. Fluorescence polarisation for immunoreagent characterization. J. Immunol. Methods 1998, 213, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNaught, R.W.; France, J.T. Studies of the biochemical basis of steroid sulphatase deficiency: Preliminary evidence suggesting a defect in membrane-enzyme structure. J. Steroid Biochem. 1980, 13, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilghaz, A.; Bagherbaigi, S.; Lam, C.L.; Mousavi, S.M.; Cόrcoles, E.P.; Wicaksono, D.H. Multiple semi-quantitative colorimetric assays in compact embeddable microfluidic cloth-based analytical device (μCAD) for effective point-of-care diagnostic. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2015, 19, 317–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, G.; Haffey, P.; Golub, E.E. A nanogram-level colloidal gold single reagent quantitative protein assay. Anal. Biochem. 2008, 380, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaimayo, C.; Kaewnaphan, B.; Tanlieng, N.; Athipanyasilp, N.; Sirijatuphat, R.; Chayakulkeeree, M.; Angkasekwinai, N.; Sutthent, R.; Puangpunngam, N.; Tharmviboonsri, T.; et al. Rapid SARS-CoV-2 antigen detection assay in comparison with real-time RT-PCR assay for laboratory diagnosis of COVID-19 in Thailand. Virol. J. 2020, 17, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gans, J.S.; Goldfarb, A.; Agrawal, A.K.; Sennik, S.; Stein, J.; Rosella, L. False-positive results in rapid antigen tests for SARS-CoV-2. JAMA 2022, 327, 485–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.W.; Wu, H.P.; Dong, L. Recent advances of photoacoustic imaging technology in biomedicine [Invited]. Acta Photonica Sin. 2023, 52, 0352105. [Google Scholar]
- Rong, J.; Liu, Y. Advances in medical imaging techniques. BMC Methods 2024, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manmana, Y.; Macka, M.; Nuchtavorn, N. Distance-based paper microfluidic devices for rapid visual quantification of heavy metals in herbal supplements and cosmetics. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 36142–36151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.K.; Mohanta, G.C.; Kumar, V.; Gupta, K. Diagnostic tools for rapid screening and detection of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Shrivas, A.; Soni, P.; Gupta, A.K.; Singh, S.; Bhattacharjee, M. Quantitative Image Sensing of Tuberculosis Biomarkers Using Rapid Diagnostic Test Kit. IEEE Sens. J. 2025, 4, 7242–7249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Hu, T.; Yan, L.; Le, Y.; Liu, L. A novel fluorescent probe for rapid and selective detection of fluoride ions in living cells. Anal. Methods 2025, 17, 939–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budri, M.B.; Gudasi, K.B.; Vadavi, R.S.; Patil, M.K.; Kumbar, V.M.; Inamdar, S.R. Tri-armed Schiff base fluorescent sensor for the rapid recognition of Zn (ii): Application in live cell imaging, test strips and TLC. Anal. Methods 2024, 16, 4743–4754. [Google Scholar]
- Thuy Tien, T.T.; Park, H.; Tuong, H.T.; Yu, S.T.; Choi, D.Y.; Yeo, S.J. Development of a rapid fluorescent immunochromatographic test to detect respiratory syncytial virus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Du, K.; Lin, S.; Wang, Y. Deep learning on lateral flow immunoassay for the analysis of detection data. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1091180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, S.; DeRosa, M.C.; Shah, M.I.; Jayaraj, J. Development and evaluation of a quantitative fluorescent lateral flow immunoassay for cystatin-C, a renal dysfunction biomarker. Sensors 2021, 21, 3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.J.; Ji, M.Q.; Huang, R.F.; Fan, Z.Y. Highly sensitive time-resolved fluorescent microspheres lateral flow immunoassay for the quantitative detection of triadimefon and its metabolite residues in fruits and vegetables. Microchim. Acta 2024, 19, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.; Peng, T.; Liang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Meng, B.; Zhao, Y.; Xie, J.; Gong, X.; Jiang, Y.; Fang, X.; et al. Lateral flow immunoassay based on time-resolved fluorescence microspheres for rapid and quantitative screening CA199 in human serum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.T.; Lin, C.P.; Fang, Y.Y.; Kao, M.H.; Shih, D.Y.C.; Lo, C.F.; Wang, D.Y. Sensitivity and specificity of in vitro diagnostic device used for influenza rapid test in Taiwan. J. Food Drug Anal. 2014, 22, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weng, W.-C.; Wu, Y.-L.; Lin, Z.-J.; Pan, W.-F.; Lin, Y.-C. Development of a Fluorescent Rapid Test Sensing System for Influenza Virus. Micromachines 2025, 16, 635. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16060635
Weng W-C, Wu Y-L, Lin Z-J, Pan W-F, Lin Y-C. Development of a Fluorescent Rapid Test Sensing System for Influenza Virus. Micromachines. 2025; 16(6):635. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16060635
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeng, Wei-Chien, Yu-Lin Wu, Zia-Jia Lin, Wen-Fung Pan, and Yu-Cheng Lin. 2025. "Development of a Fluorescent Rapid Test Sensing System for Influenza Virus" Micromachines 16, no. 6: 635. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16060635
APA StyleWeng, W.-C., Wu, Y.-L., Lin, Z.-J., Pan, W.-F., & Lin, Y.-C. (2025). Development of a Fluorescent Rapid Test Sensing System for Influenza Virus. Micromachines, 16(6), 635. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16060635







