Low-Temperature Electrospinning-Fabricated Three-Dimensional Nanofiber Scaffolds for Skin Substitutes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of PLGA-PCL-MAP 2D Nanofiber Scaffolds
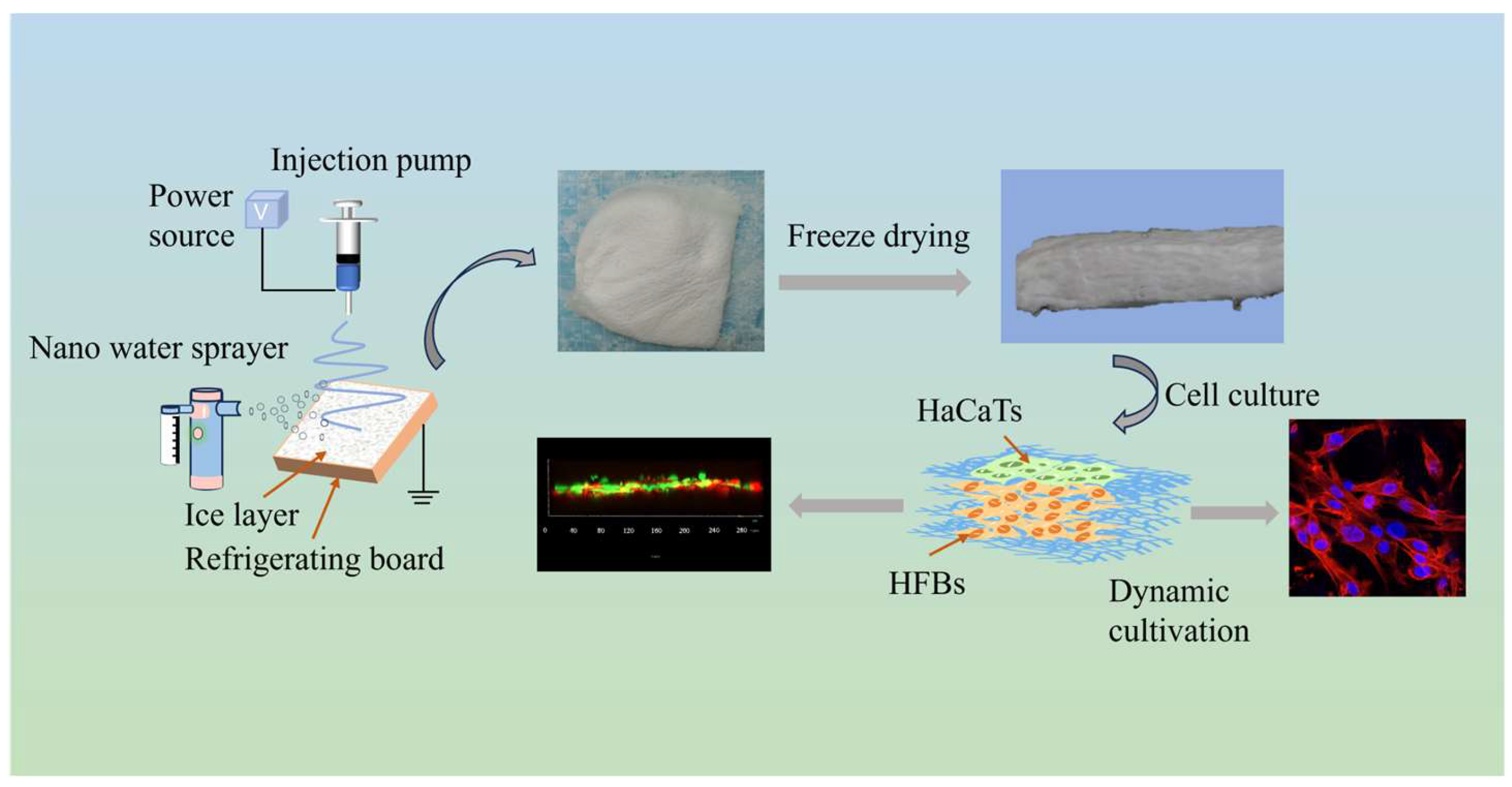
2.3. Preparation of PLGA-PCL-MAP 3D Nanofiber Scaffolds
2.4. Characterization of 2D and 3D Nanofiber Scaffolds
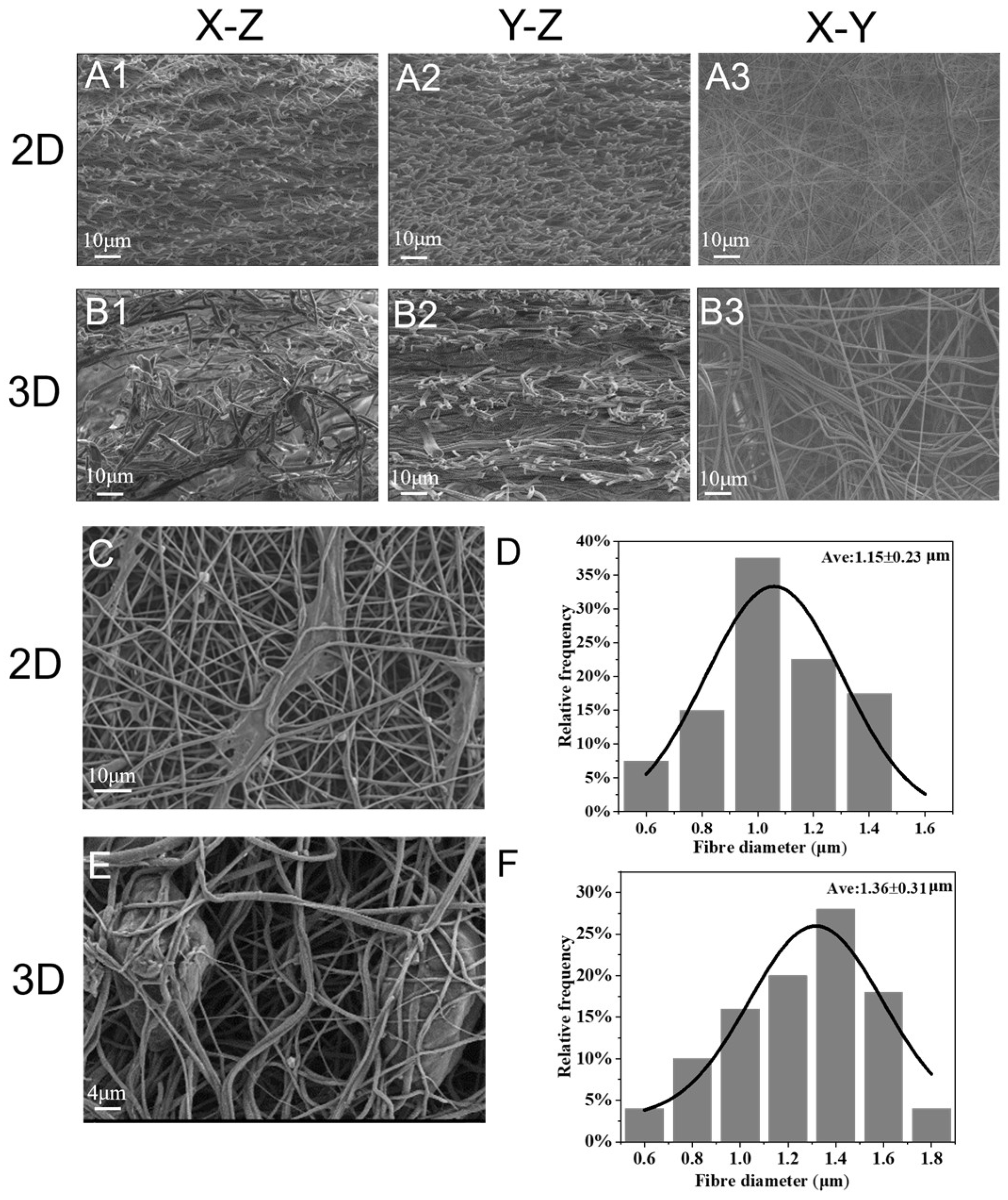
2.4.1. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
2.4.2. FTIR Test
2.4.3. Hydrophilicity
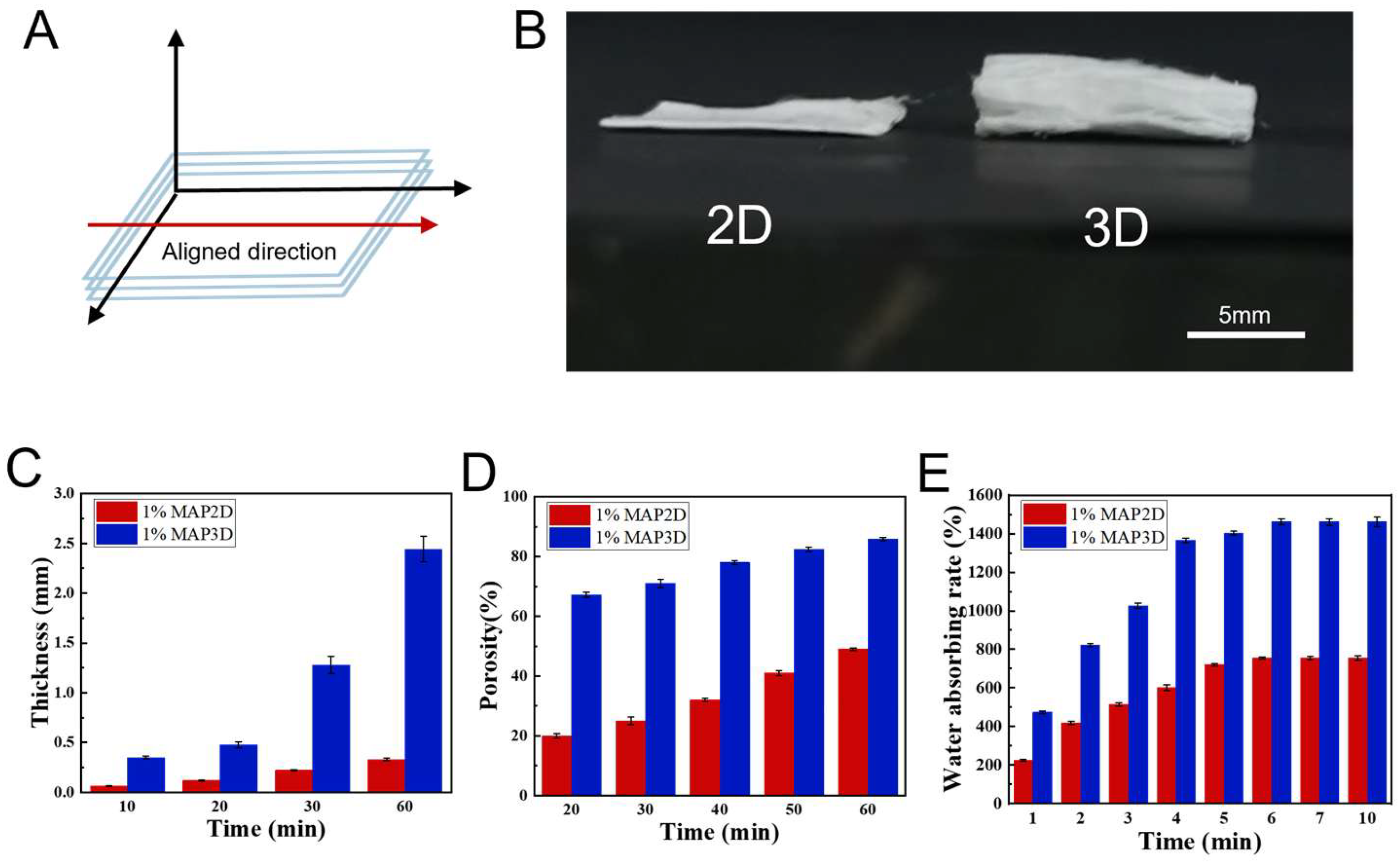
2.4.4. Porosity
2.4.5. Water Absorption
2.4.6. Tensile Test
2.5. Cell Preparation and Biological Characterization
2.5.1. Cell Culture
2.5.2. Cell Viability Stain
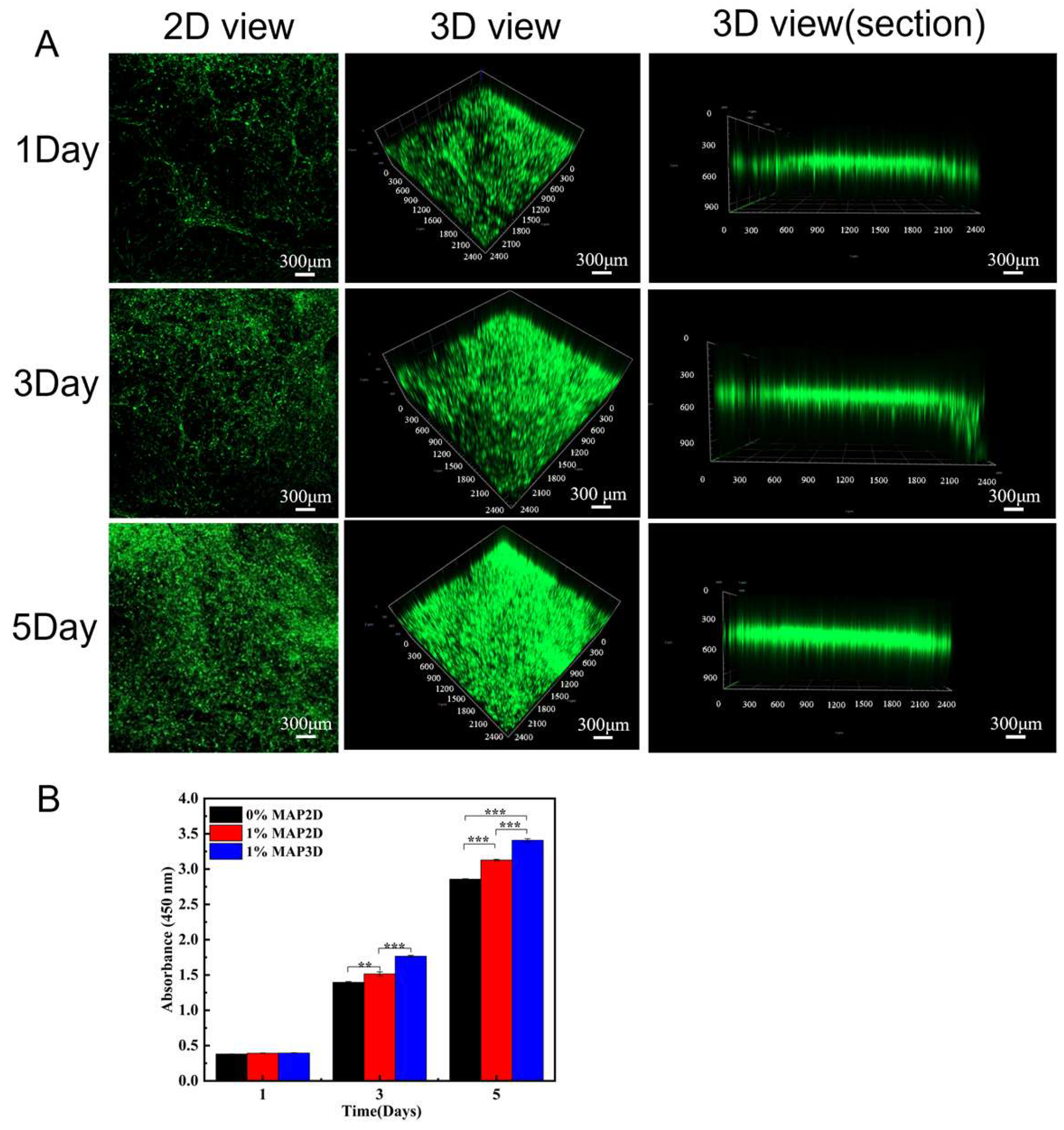
2.5.3. Cell Proliferation
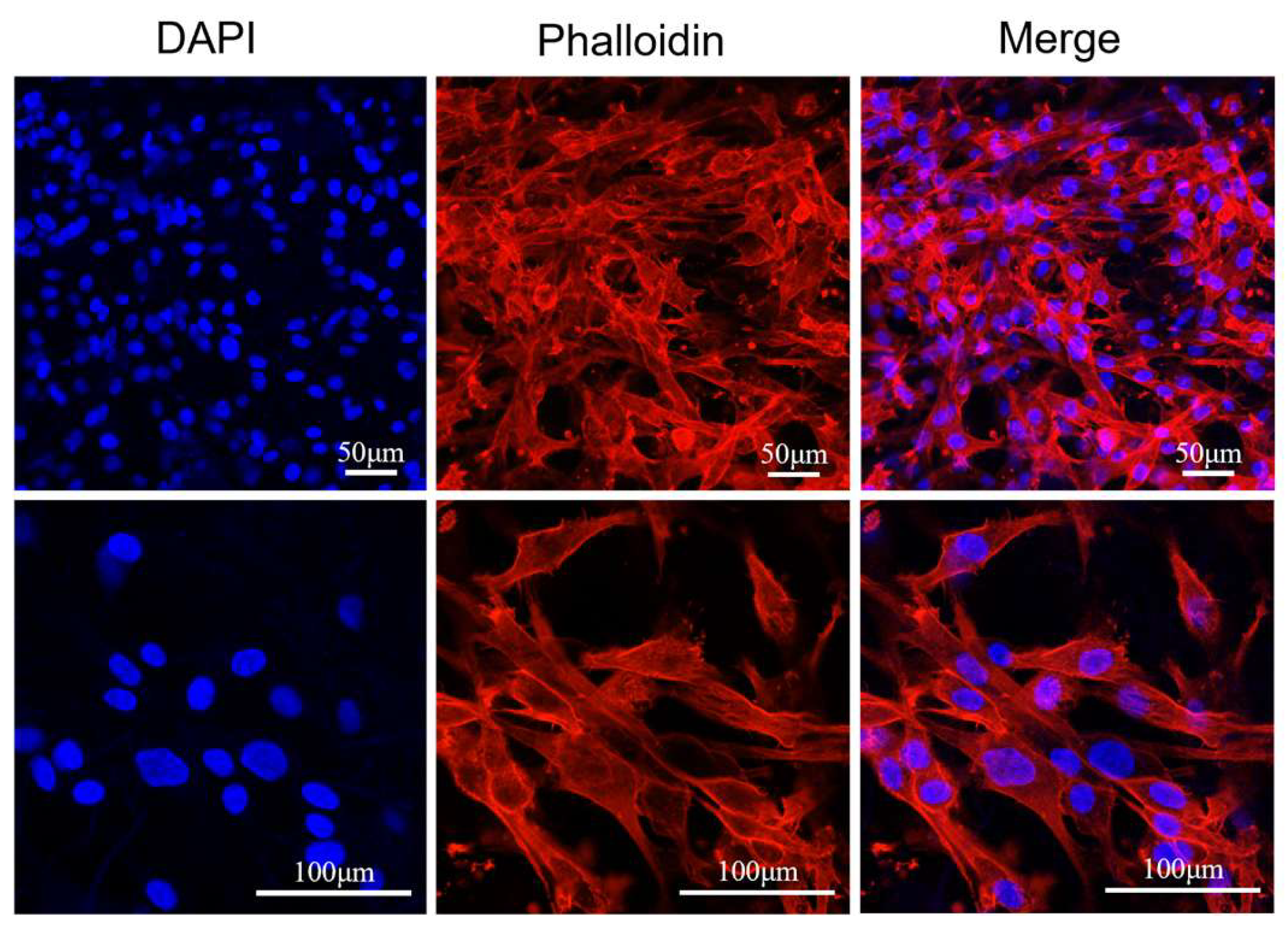
2.5.4. Cell Morphology
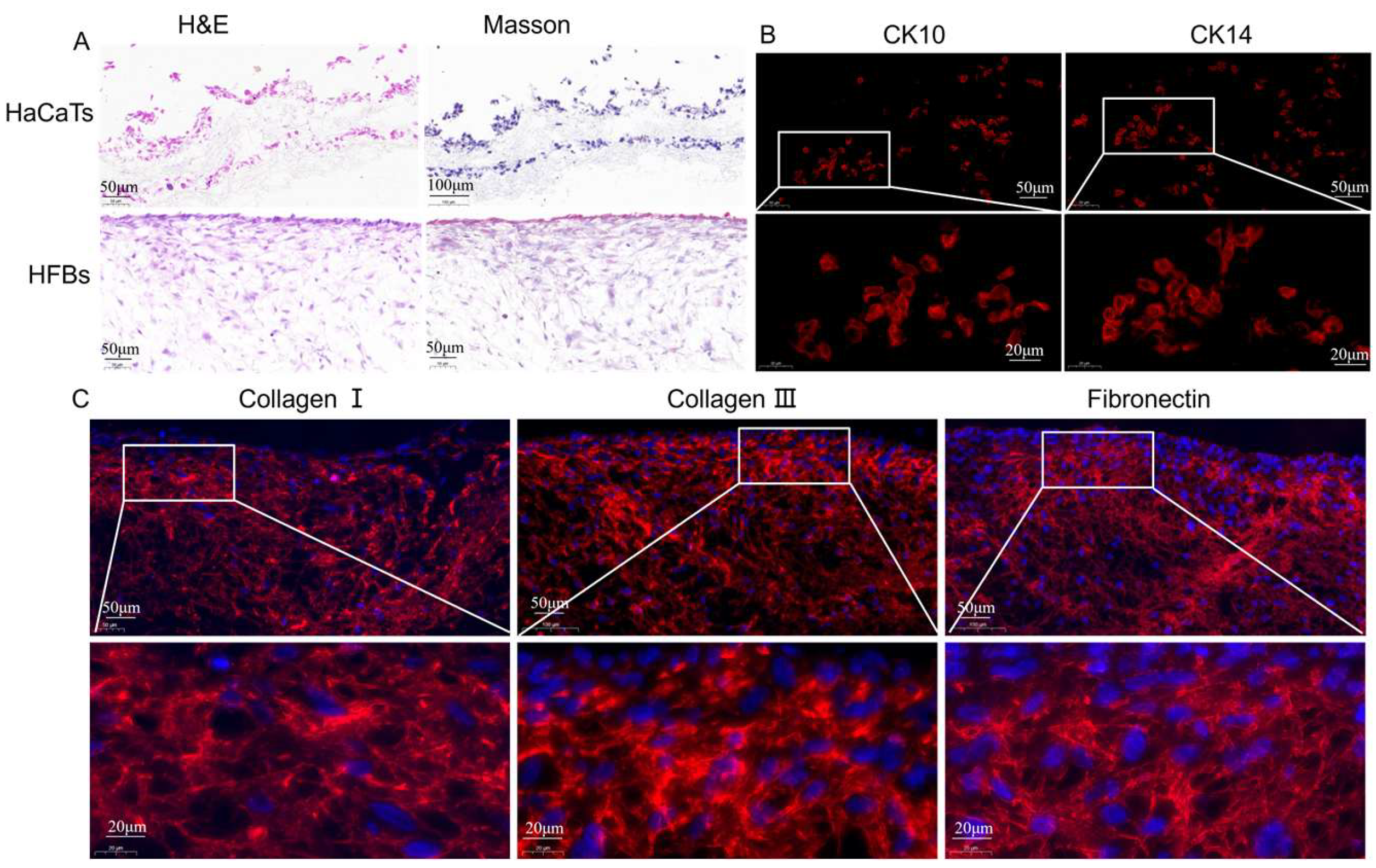
2.5.5. Histology and Immunofluorescence Staining
3. Results
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of 3D Nanofiber Scaffolds
3.1.1. Preparation of 3D Nanofiber Scaffolds
3.1.2. Microstructure
3.1.3. Characterization of 3D Nanofiber Scaffolds
3.2. Three-Dimensional Nanofiber Scaffolds Promote Cell Viability
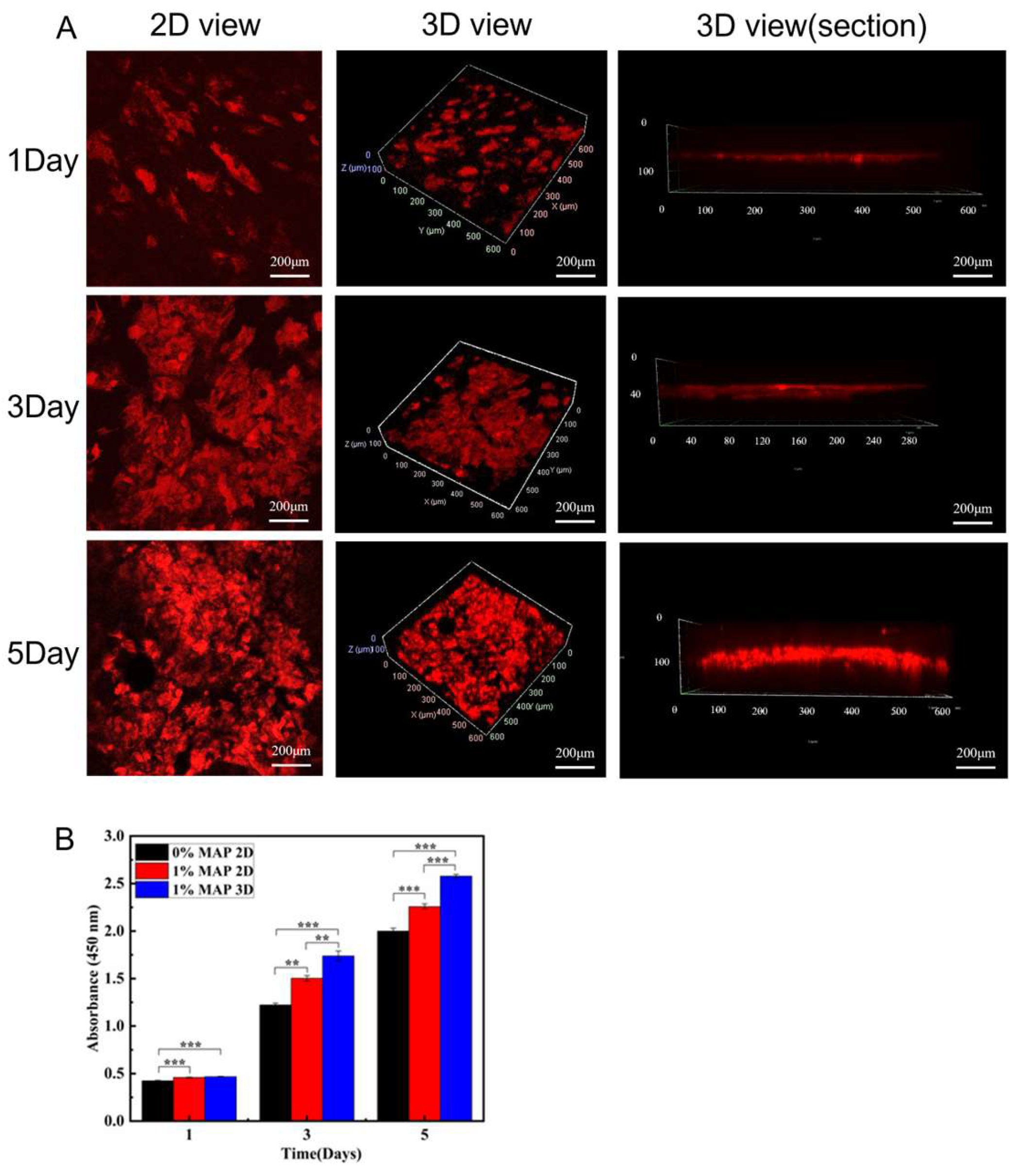
3.2.1. Promoted Cell Viability
3.2.2. Culture and Proliferation of Dermis
3.2.3. Culture and Proliferation of the Epidermis
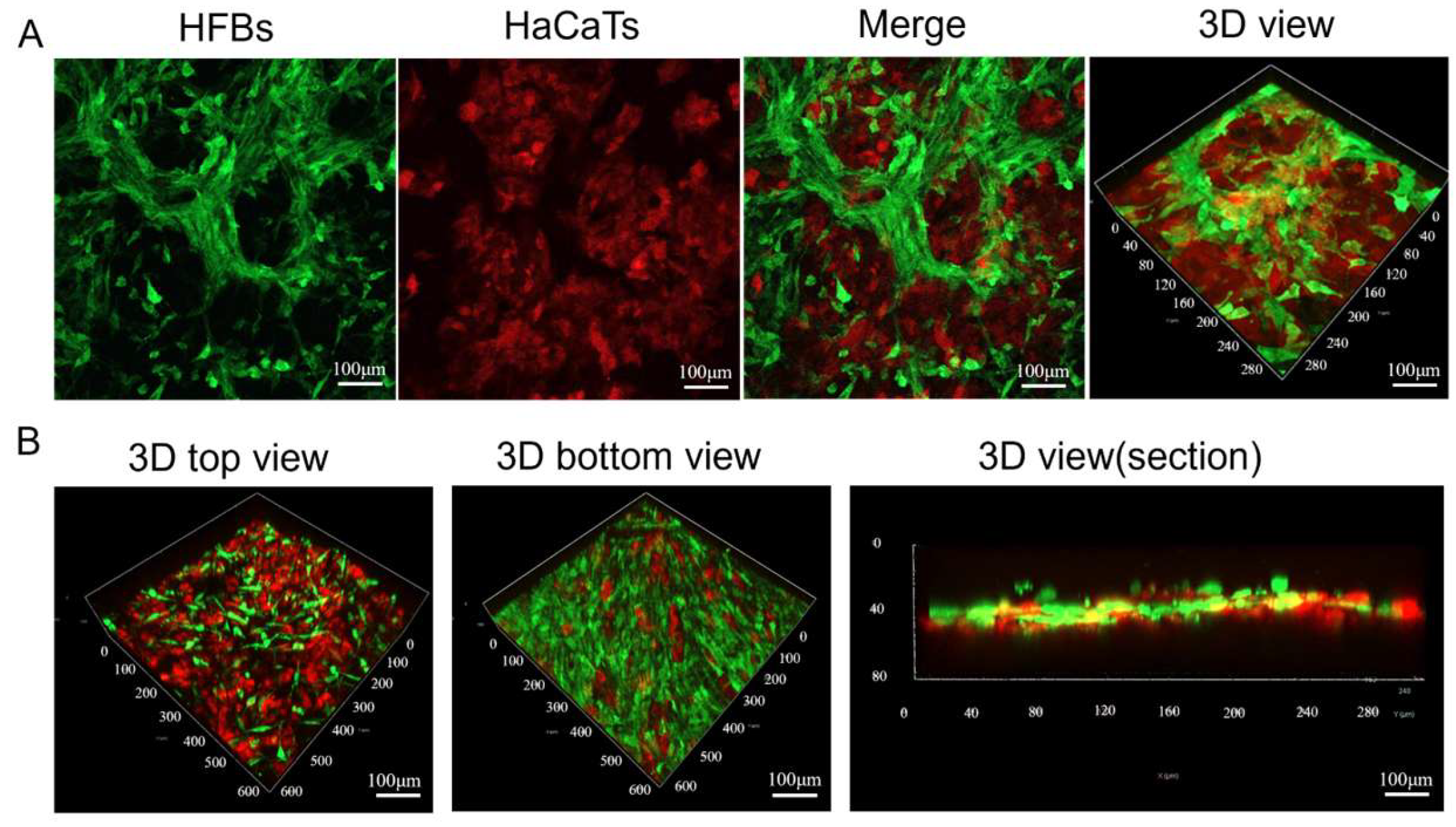
3.3. Construction of Skin Substitutes with a Double-Layer Structure of Composite Epidermis and Dermis
3.3.1. Construction of Skin Substitutes
3.3.2. Characteristics of Epidermis and Dermis in Skin Substitutes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, K.; Bai, X.; Yuan, Z.; Cao, X.; Jiao, X.; Li, Y.; Qin, Y.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, X. Layered nanofiber sponge with an improved capacity for promoting blood coagulation and wound healing. Biomaterials 2019, 204, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Q.; Liu, H.; Gao, C.; Sun, W.; Lu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, W.; Qiao, H.; Jin, A.; Wang, Y.; et al. Advances in Mussel Adhesion Proteins and Mussel-Inspired Material Electrospun Nanofibers for Their Application in Wound Repair. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2024, 10, 6097–6119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Fan, Y.; Dong, G.; Zhou, H.; Du, R.; Tang, X.; Ying, Y.; Li, J. Designing biomimetic scaffolds for skin tissue engineering. Biomater. Sci. 2023, 11, 3051–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, J.R.; Granja, P.L.; Bartolo, P.J. Advances in electrospun skin substitutes. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 84, 314–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhar, B.; Das, E.; Manikumar, K.; Mandal, B.B. 3D Bioprinted Human Skin Model Recapitulating Native-Like Tissue Maturation and Immunocompetence as an Advanced Platform for Skin Sensitization Assessment. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 13, e2303312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafari, R.; Jonoobi, M.; Amirabad, L.M.; Oksman, K.; Taheri, A.R. Fabrication and characterization of novel bilayer scaffold from nanocellulose based aerogel for skin tissue engineering applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 136, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, S.; Vilas-Boas, V.; Lebre, F.; Granjeiro, J.; Catarino, C.; Teixeira, L.M.; Loskill, P.; Alfaro-Moreno, E.; Ribeiro, A. Microfluidic-based skin-on-chip systems for safety assessment of nanomaterials. Trends Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 1282–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.H.; Chua, D.A.C.; Tang, J.R.J.; Bonnard, C.; Leavesley, D.; Liang, K. Design of hydrogel-based scaffolds for in vitro three-dimensional human skin model reconstruction. Acta Biomater. 2022, 153, 13–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.; Beak, J.W.; Sagong, M.; Ahn, S.; Nam, J.S.; Kim, I. Electrospinning and Nanofiber Technology: Fundamentals, Innovations, and Applications. Adv. Mater. 2025, 2025, e2500162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Ma, Y.; Yang, M.; Cheng, Y.; Ma, X.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, X.; Liu, M.; Long, Y.; et al. Wound dressings using electrospun nanofibers: Mechanisms, applications, and future directions. Eur. Polym. J. 2025, 2025, 113900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaramurthi, D.; Vasanthan, K.S.; Kuppan, P.; Krishnan, U.M.; Sethuraman, S. Electrospun nanostructured chitosan–poly(vinyl alcohol) scaffolds: A biomimetic extracellular matrix as dermal substitute. Biomed. Mater. 2012, 7, 045005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmick, S.; Rother, S.; Zimmermann, H.; Lee, P.S.; Moeller, S.; Schnabelrauch, M.; Scharnweber, D. Biomimetic electrospun scaffolds from main extracellular matrix com-ponents for skin tissue engineering application—The role of chondroitin sulfate and sulfated hyaluronan. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 79, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Huang, J.; Fang, Y.; Huang, H.; Wu, J. 1D, 2D, and 3D scaffolds promoting angiogenesis for enhanced wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 437, 134690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafari, R.; Jonoobi, M.; Naijian, F.; Ashori, A.; Mekonnen, T.H.; Taheri, A.R. Fabrication and characterization of bilayer scaffolds—Nanocellulosic cryogels—For skin tissue engineering by co-culturing of fibroblasts and keratinocytes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 223 Pt A, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Chen, X.; Cai, J.; Ye, D.; Wu, Y.; Fan, L.; Liu, P. Novel porous three-dimensional nanofibrous scaffolds for accelerating wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 369, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Chen, P.; Shi, X.; Zhang, G.; Wang, C. Multilevel structural stereocomplex polylactic acid/collagen membranes by pattern electro-spinning for tissue engineering. Polymer 2018, 156, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norzain, N.A.; Yu, Z.W.; Lin, W.C.; Su, H.H. Micropatterned Fibrous Scaffold Produced by Using Template-Assisted Electrospinning Technique for Wound Healing Application. Polymers 2021, 13, 2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liverani, L.; Lacina, J.; Roether, J.A.; Boccardi, E.; Killian, M.S.; Schmuki, P.; Schubert, D.W.; Boccaccini, A.R. Incorporation of bioactive glass nanoparticles in electrospun PCL/chitosan fibers by using benign solvents. Bioact. Mater. 2018, 3, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korniienko, V.; Husak, Y.; Radwan-Pragłowska, J.; Holubnycha, V.; Samokhin, Y.; Yanovska, A.; Varava, J.; Diedkova, K.; Janus, Ł.; Pogorielov, M. Impact of Electrospinning Parameters and Post-Treatment Method on Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Activity of Chitosan Nanofibers. Molecules 2022, 27, 3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.R.; Ju, H.W.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, D.K.; Lee, O.J.; Moon, B.M.; Park, C.H. Three-dimensional electrospun silk-fibroin nanofiber for skin tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93 Pt B, 1567–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; He, C.; Gao, Y.; Cen, L.; Cui, L.; Cao, Y. Preparation and cytocompatibility of PLGA scaffolds with controllable fiber morphology and diameter using electrospinning method. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2008, 87, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Murphy, E.J.; Cao, Z.; Buckley, C.; Cortese, Y.; Chee, B.S.; Scheibel, T. Electrospinning Recombinant Spider Silk Fibroin-Reinforced PLGA Membranes: A Bio-compatible Scaffold for Wound Healing Applications. ACS Biomater. Sci Eng. 2024, 10, 7144–7154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, H.; Gao, C.; Lu, C.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, A.; Dai, Q.; Yang, S.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Y. A Novel Method for Fabricating the Undulating Structures at Dermal—Epidermal Junction by Composite Molding Process. J. Funct. Biomater. 2024, 15, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado-Paula, M.; Corat, M.; Lancellotti, M.; Mi, G.; Marciano, F.; Vega, M.; Hidalgo, A.; Webster, T.; Lobo, A. A comparison between electrospinning and rotary-jet spinning to produce PCL fibers with low bacteria colonization. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 111, 110706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorramnezhad, M.; Akbari, B.; Akbari, M.; Kharaziha, M. Effect of surface modification on physical and cellular properties of PCL thin film. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 200, 111582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Zhang, M.; Zeng, Q.; Pan, W.; Huang, Y.; Qian, Y.; Dong, W.; Qi, X.; Shen, J. Mussel-inspired agarose hydrogel scaffolds for skin tissue engineering. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kim, E.; Kim, K.; Rhie, J.W.; Joo, K.I.; Cha, H.J. Protective Topical Dual-Sided Nanofibrous Hemostatic Dressing Using Mussel and Silk Proteins with Multifunctionality of Hemostasis and Anti-Bacterial Infiltration. Small 2024, 20, e2308833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, N.K.; Kaushik, N.; Pardeshi, S.; Sharma, J.G.; Lee, S.H.; Choi, E.H. Biomedical and Clinical Importance of Mussel-Inspired Polymers and Materials. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 6792–6817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhurakkat Perikamana, S.K.; Lee, J.; Lee, Y.B.; Shin, Y.M.; Lee, E.J.; Mikos, A.G.; Shin, H. Materials from Mussel-Inspired Chemistry for Cell and Tissue Engineering Applications. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 2541–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Ni, C.; Chen, Y.; Ma, X.; Cao, J.; Pan, J.; Li, C.; Zheng, Y. Construction and performance of PLA-COL@PU-COL@PLA-PU-COL electrospun vascular graft modified with chitosan/heparin. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 41, 111043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zou, H.; Liao, X.; Xiong, Y.; Hu, X.; Cao, J.; Pan, J.; Li, C.; Zheng, Y. Construction of PCL-collagen@PCL@PCL-gelatin three-layer small diameter artificial vascular grafts by electrospinning. Biomed. Mater. 2022, 18, 015008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, R.; Xu, T.; Ma, X.; Yao, Z.; Chi, B.; Xu, H. A mussel-inspired poly(γ-glutamic acid) tissue adhesive with high wet strength for wound closure. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 5668–5678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirtaghavi, A.; Baldwin, A.; Tanideh, N.; Zarei, M.; Muthuraj, R.; Cao, Y.; Luo, J. Crosslinked porous three-dimensional cellulose nanofibers-gelatine bio-composite scaffolds for tissue regeneration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 1949–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chantre, C.O.; Gonzalez, G.M.; Ahn, S.; Cera, L.; Campbell, P.H.; Hoerstrup, S.P.; Parker, K.K. Porous Biomimetic Hyaluronic Acid and Extracellular Matrix Protein Nanofiber Scaffolds for Accelerated Cutaneous Tissue Repair. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 45498–45510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Gu, H.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, C.; Cao, M.; Fu, J.; He, Y. Fabrication of electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds with 3D controllable geometric shapes. Mater. Des. 2018, 157, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.J.; Cheong, H.; Choi, E.S.; Yun, S.H.; Choi, B.H.; Park, K.S.; Cha, H.J. Accelerated skin wound healing using electrospun nanofibrous mats blended with mussel adhesive protein and polycaprolactone. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2017, 105, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, H.Y.; Jing, X.; Napiwocki, B.N.; Hagerty, B.S.; Chen, G.; Turng, L.S. Biocompatible, degradable thermoplastic polyurethane based on polycaprolac-tone-block-polytetrahydrofuran-block-polycaprolactone copolymers for soft tissue engineering. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 4137–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, H.Y.; Jing, X.; Napiwocki, B.N.; Li, Z.T.; Turng, L.S.; Huang, H.X. Fabrication of fibrous silica sponges by self-assembly electrospinning and their ap-plication in tissue engineering for three-dimensional tissue regeneration. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 331, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Predoi, D.; Iconaru, S.L.; Albu, M.; Petre, C.C.; Jiga, G. Physicochemical and antimicrobial properties of silver-doped hydroxyapatite collagen biocomposite. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2017, 57, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciobanu, C.S.; Popa, C.L.; Petre, C.C.; Jiga, G.; Trusca, R.; Predoi, D. Characterisations of collagen-silver-hydroxyapatite nanocomposites. AIP Conf. Proc. 2016, 1736, 20148. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Liu, X.; Tan, L.; Cui, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhu, S.; Li, Z.; Yuan, X.; Zheng, Y.; Yeung, K.W.K.; et al. Controlled-temperature photothermal and oxidative bacteria killing and acceleration of wound healing by polydopamine-assisted Au-hydroxyapatite nanorods. Acta Biomater. 2018, 77, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Fan, X.; Lu, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y. Mussel-Inspired Adhesive, Antibacterial, and Stretchable Composite Hydrogel for Wound Dressing. Macromol. Biosci. 2023, 23, e2200370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, G.; Chen, Y.; Mao, C.; Yang, M. Polydopamine-Coated Antheraea pernyi (A. pernyi) Silk Fibroin Films Promote Cell Ad-hesion and Wound Healing in Skin Tissue Repair. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 34736–34743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Nie, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, F.; Zheng, Y. Bilayer porous scaffold based on poly-(ɛ-caprolactone) nanofibrous membrane and gelatin sponge for favoring cell proliferation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 258, 1670–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Zhou, M.; Dong, W.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Y.; Yao, J.; Liu, Z.; Han, H.; Sun, D.; Zhang, M. A bi-layered scaffold of a poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanofiber mat and an alginate–gelatin hydrogel for wound healing. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 7492–7505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Li, Q.; Huang, Y.; Yang, S.; Ouyang, J.; Bu, S.; Zhong, W.; Liu, Z.; Xing, M.M.Q. Polydopamine-coated paper-stack nanofibrous membranes enhancing adipose stem cells′ adhesion and osteogenic differentiation. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 6917–6923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lan, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Tian, F.; Li, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, M.; Wang, W.; Tang, Y. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of ε-poly(L-lysine) immobilized poly(ε-caprolactone) nanofiber membrane by polydopamine-assisted decoration as a potential wound dressing material. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 220, 112945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shafiq, M.; Liu, M.; Morsi, Y.; Mo, X. Advanced fabrication for electrospun three-dimensional nanofiber aerogels and scaffolds. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 5, 963–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiri, A.; Saidin, S.; Sani, M.H.; Al-Ashwal, R.H. Epidermal and fibroblast growth factors incorporated polyvinyl alcohol electrospun nanofibers as biological dressing scaffold. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Tu, J.; Liu, Z.; Yao, F.; Xiong, G.; Wan, Y. Constructing three-dimensional nanofibrous bioglass/gelatin nanocomposite scaffold for enhanced mechanical and biological performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 326, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Nie, K.; Li, J.; Sun, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Li, Q. 3D Electrospun Nanofiber-Based Scaffolds: From Preparations and Properties to Tissue Regeneration Applications. Stem Cells Int. 2021, 2021, 8790143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, J.; He, Z.; Tang, Q. Moist exposed burn ointment accelerates diabetes-related wound healing by promoting re-epithelialization. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 1042015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinagawa, F.; Takata, S.; Toba, Y.; Ikuta, M.; Hioki, S.; Suzuki, T.; Nishimura, T.; Nakamura, R.; Kobayashi, K. Potential of Gouda cheese whey to improve epidermal conditions by regulating proliferation and differentiation of keratinocytes. Int. Dairy J. 2018, 87, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Rangel, A.; Martin-Martinez, E.S. Collagen based electrospun materials for skin wounds treatment. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2021, 109, 1751–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zollinger, A.J.; Smith, M.L. Fibronectin, the extracellular glue. Matrix Biol. 2017, 60–61, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yu, F.; Shao, M.; Zhang, T.; Lu, W.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y. Electrospun Nanofiber Scaffold for Skin Tissue Engineering: A Review. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2024, 7, 3556–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, R.; Patkar, S.; Maniar, D.; Pillai, M.M.; Tayalia, P. A bilayered skin substitute developed using an eggshell membrane crosslinked gela-tin-chitosan cryogel. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 7921–7933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Dong, X.; Shafiq, M.; Myles, G.; Radacsi, N.; Mo, X. Recent Advancements on Three-Dimensional Electrospun Nanofiber Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2022, 4, 959–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Mao, C.; Yang, M. Polydopamine modification of silk fibroin membranes significantly promotes their wound healing effect. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 5232–5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Chen, J.; Duan, X.; Guo, B. Mussel-inspired adhesive antioxidant antibacterial hemostatic composite hydrogel wound dressing via photo-polymerization for infected skin wound healing. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 8, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonet, M.; Schneider, O.D.; Neuenschwander, P.; Stark, W.J. Ultraporous 3D polymer meshes by low-temperature elec-trospinning: Use of ice crystals as a removable void template. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2007, 47, 2020–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarjargal, A.; Goudarzi, Z.M.; Cegielska, O.; Gradys, A.; Kolbuk, D.; Kalaska, B.; Sajkiewicz, P. A facile one-stone-two-birds strategy for fabricating multifunctional 3D nanofibrous scaffolds. Biomater. Sci. 2023, 11, 5502–5516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadelmann, K.; Weghofer, A.; Urbanczyk, M.; Maulana, T.I.; Loskill, P.; Jones, P.D.; Schenke-Layland, K. Development of a bi-layered cryogenic electrospun polylactic acid scaffold to study calcific aortic valve disease in a 3D co-culture model. Acta Biomater. 2022, 140, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, P.; Moskwa, N.; Hanchon, Z.; Koplas, A.; Nelson, D.A.; Mills, K.L.; Castracane, J.; Larsen, M.; Sharfstein, S.T.; Xie, Y. Engineering cryoelectrospun elastin-alginate scaffolds to serve as stromal extracellular matrices. Biofabrication 2022, 14, 035010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulysheva, A.A.; Bowlin, G.L.; Klingelhutz, A.J.; Yeudall, W.A. Low-temperature electrospun silk scaffold for in vitro mucosal modeling. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2012, 100, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moors, J.J.; Xu, Z.; Xie, K.; Rashad, A.; Egger, J.; Röhrig, R.; Puladi, B. Full-thickness skin graft versus split-thickness skin graft for radial forearm free flap donor site closure: Protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis. Syst. Rev. 2024, 13, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Sun, X.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.W.; Fu, X.; Leong, K.W. Advanced drug delivery systems and artificial skin grafts for skin wound healing. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 146, 209–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim, N.; Nallusamy, N.; Lakshminarayanan, R.; Ramakrishna, S.; Vigneswari, S. Electrospinning in Drug Delivery: Progress and Future Outlook. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2025, 2025, e2400903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Chang, Z.; Feng, Y.; Yao, X.; Wang, M.; Ju, Y.; Wang, K.; Jiang, J.; Li, P. Electrospinning and electrospun polysaccharide-based nanofiber membranes: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 263 Pt 2, 130335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Shi, L.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, X.; Ullah, I.; Ou, H.; Zhang, W.; Wu, T. Facile fabrication of porous polymer fibers via cryogenic electrospinning system. J. Mech. Work. Technol. 2019, 266, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.L.; Faraz, F.; Wang, J.X.; Radacsi, N. Combination of 3D Printing and Electrospinning Techniques for Biofabrication. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 7, 2101309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, Q.; Liu, H.; Sun, W.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, W.; Lu, C.; Luo, K.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y. Low-Temperature Electrospinning-Fabricated Three-Dimensional Nanofiber Scaffolds for Skin Substitutes. Micromachines 2025, 16, 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050552
Dai Q, Liu H, Sun W, Zhang Y, Cai W, Lu C, Luo K, Liu Y, Wang Y. Low-Temperature Electrospinning-Fabricated Three-Dimensional Nanofiber Scaffolds for Skin Substitutes. Micromachines. 2025; 16(5):552. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050552
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Qiqi, Huazhen Liu, Wenbin Sun, Yi Zhang, Weihuang Cai, Chunxiang Lu, Kaidi Luo, Yuanyuan Liu, and Yeping Wang. 2025. "Low-Temperature Electrospinning-Fabricated Three-Dimensional Nanofiber Scaffolds for Skin Substitutes" Micromachines 16, no. 5: 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050552
APA StyleDai, Q., Liu, H., Sun, W., Zhang, Y., Cai, W., Lu, C., Luo, K., Liu, Y., & Wang, Y. (2025). Low-Temperature Electrospinning-Fabricated Three-Dimensional Nanofiber Scaffolds for Skin Substitutes. Micromachines, 16(5), 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050552






