Laser Pulses for Studying Photoactive Spin Centers with EPR
Abstract
1. Introduction
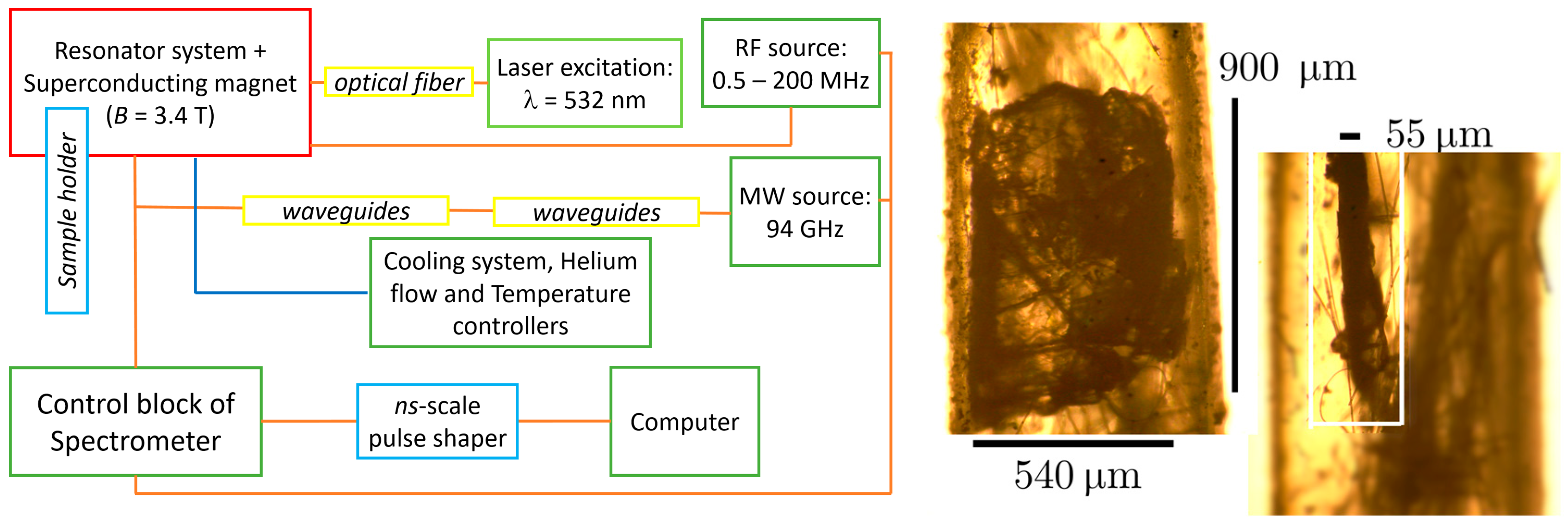
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Methodology
2.2. Samples
3. Results and Discussion
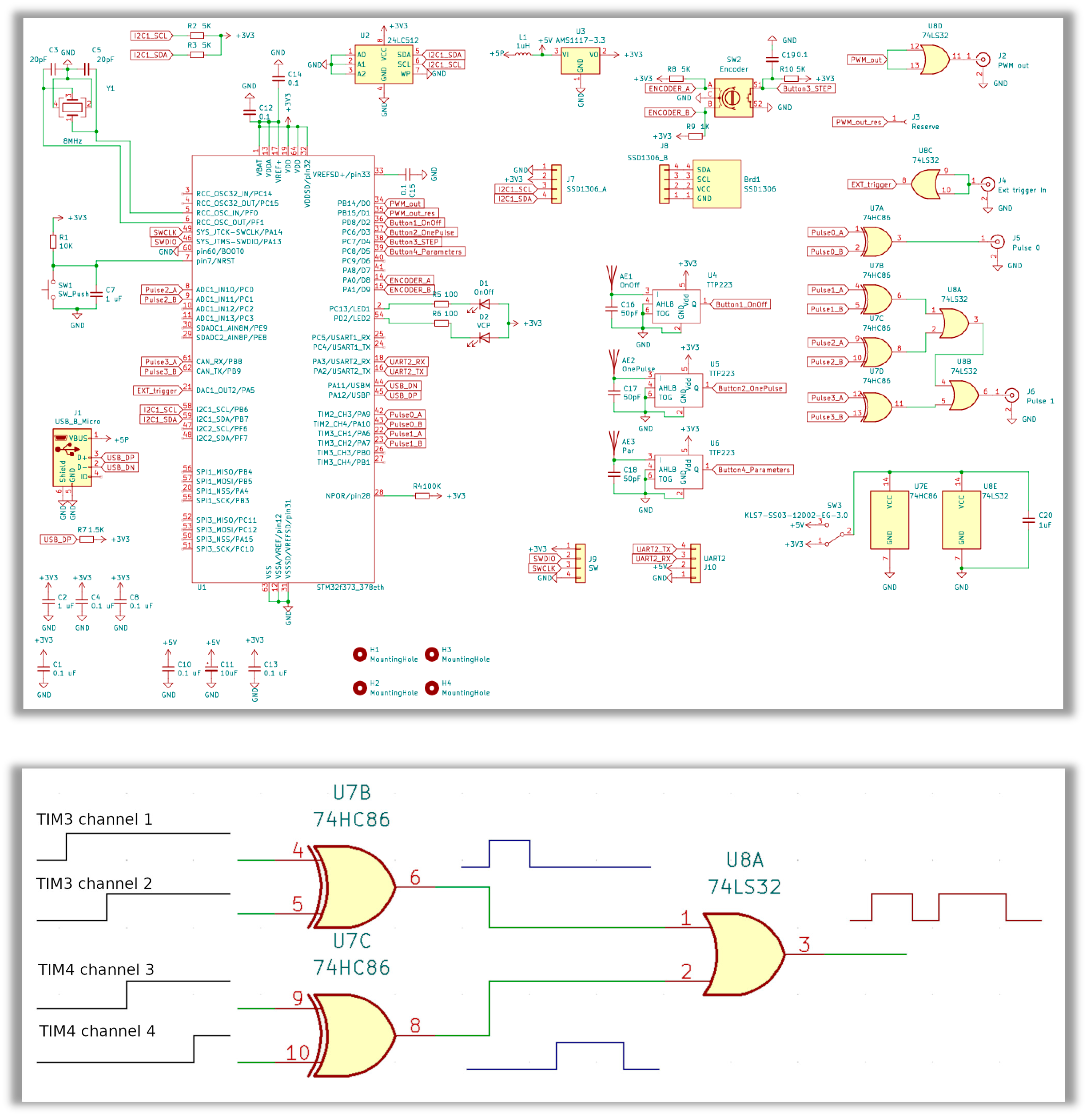
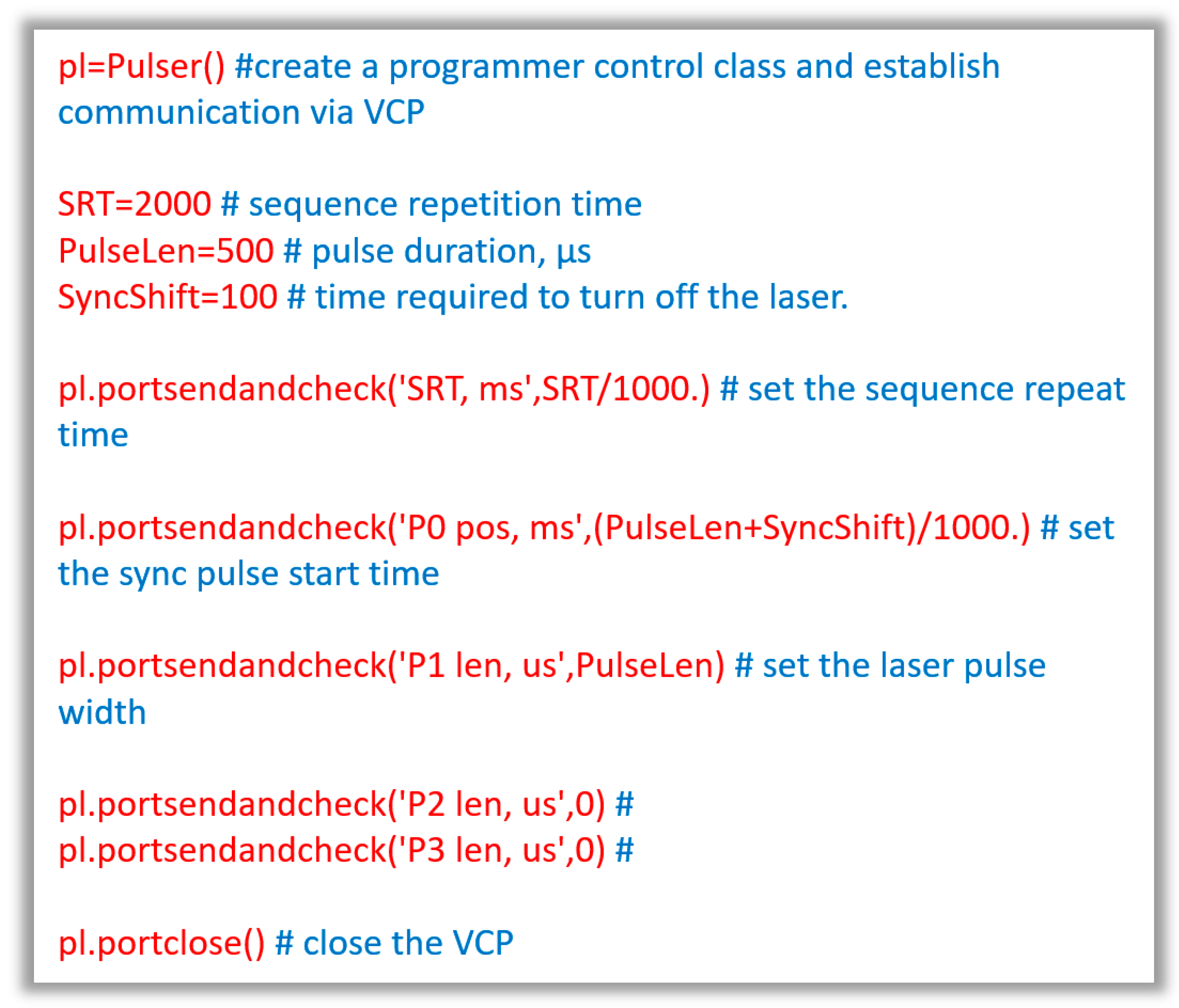
3.1. Implementation of a Pulse Sequence Programmer
3.2. Formation of Laser Diode Pulses
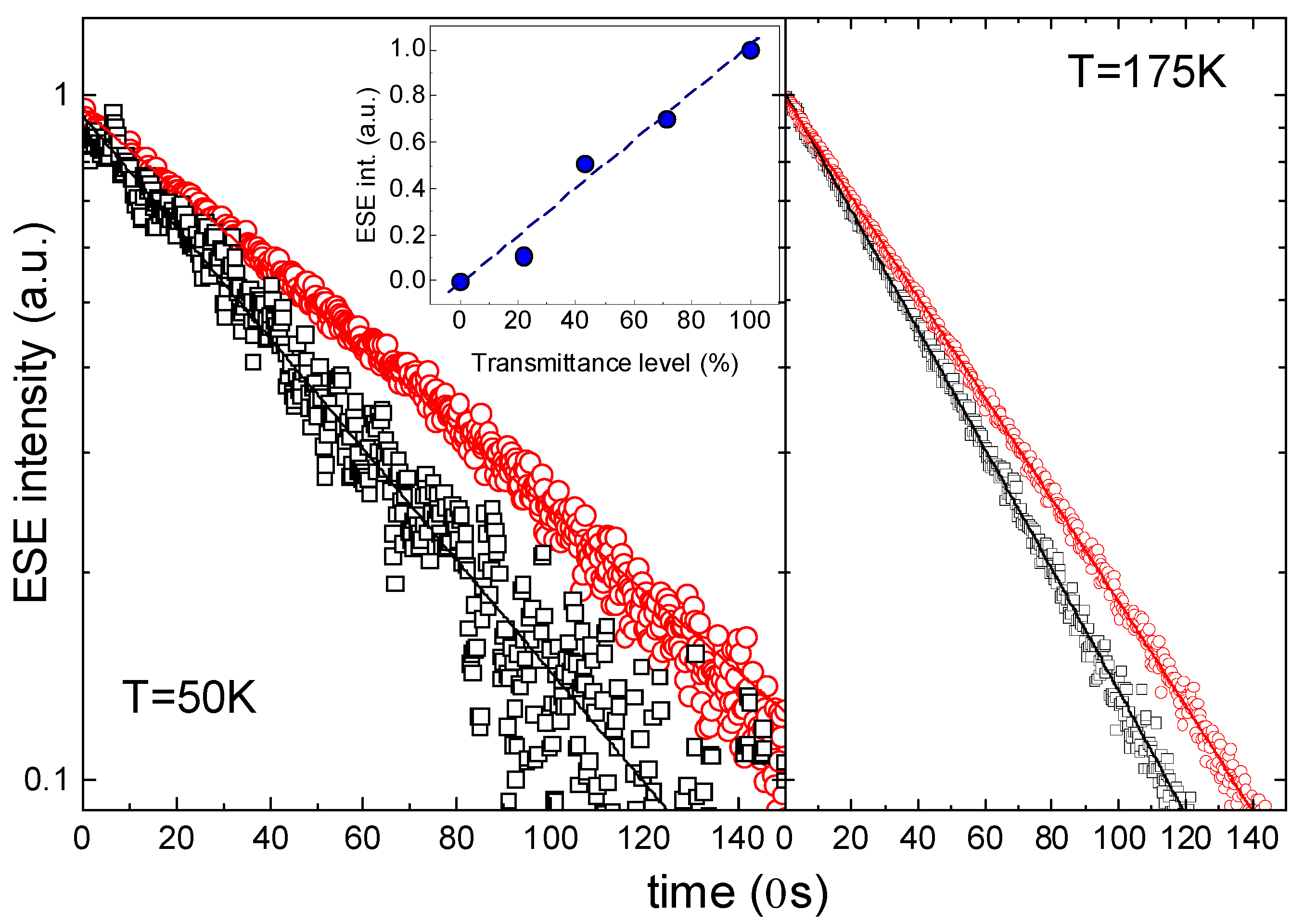
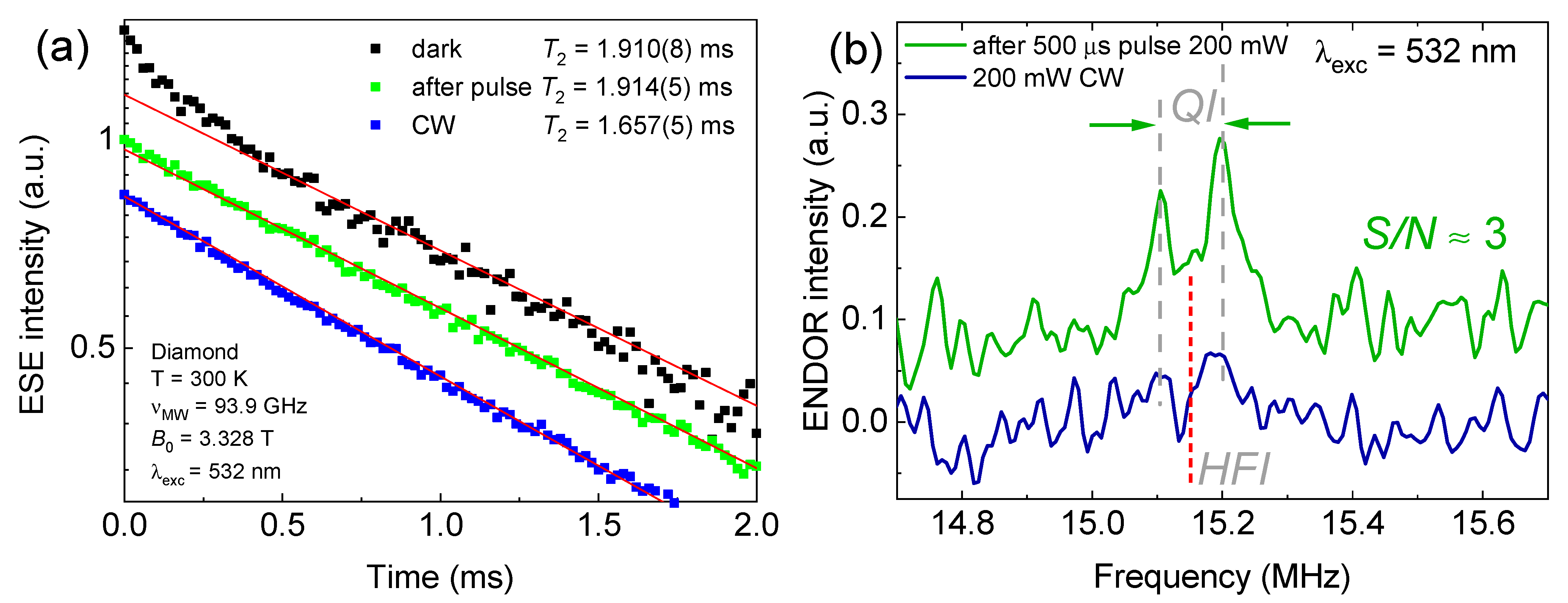
3.3. Experimental Applications
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EPR | Electron paramagnetic resonance |
| RF | Radio Frequency |
| MW | Microwave |
| NV | Nitrogen vacancy |
| ESE | Electron spin echo |
| PWM | Pulse-width modulation |
| DAF | Delay after flash |
References
- Atatüre, M.; Englund, D.; Vamivakas, N.; Lee, S.-Y.; Wrachtrup, J. Material Platforms for Spin-Based Photonic Quantum Technologies. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2018, 3, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaldini, A.; Cavallini, A.; Rigutti, L.; Nava, F. Low Temperature Annealing of Electron Irradiation Induced Defects in 4H-SiC. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 3780–3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rühl, M.; Ott, C.; Götzinger, S.; Krieger, M.; Weber, H.B. Controlled Generation of Intrinsic Near-Infrared Color Centers in 4H-SiC via Proton Irradiation and Annealing. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 113, 122102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nipoti, R.; Ayedh, H.M.; Svensson, B.G. Defects Related to Electrical Doping of 4H-SiC by Ion Implantation. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2018, 78, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, F.; Zheng, H.; Cheng, G.J. Ultrafast Pulsed Laser Stealth Dicing of 4H-SiC Wafer: Structure Evolution and Defect Generation. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 81, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazen, K.; von Bardeleben, H.J. NV-Centers in SiC: A Solution for Quantum Computing Technology? Front. Quantum Sci. Technol. 2023, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, M.K.; Taverne, M.P.C.; Huang, C.-C.; Mar, J.D.; Ho, Y.-L.D. Hexagonal Boron Nitride Based Photonic Quantum Technologies. Materials 2024, 17, 4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astakhov, G.V.; Simin, D.; Dyakonov, V.; Yavkin, B.V.; Orlinskii, S.B.; Proskuryakov, I.I.; Anisimov, A.N.; Soltamov, V.A.; Baranov, P.G. Spin Centres in SiC for Quantum Technologies. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2016, 47, 793–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelletto, S.; Peruzzo, A.; Bonato, C.; Johnson, B.C.; Radulaski, M.; Ou, H.; Kaiser, F.; Wrachtrup, J. Silicon Carbide Photonics Bridging Quantum Technology. ACS Photonics 2022, 9, 1434–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiering, G.; Gali, A. Chapter One—Color Centers in Diamond for Quantum Applications. In Semiconductors and Semimetals; Nebel, C.E., Aharonovich, I., Mizuochi, N., Hatano, M., Eds.; Diamond for Quantum Applications Part 1; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 103, pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Piparo, N.; Razavi, M.; Munro, W.J. Measurement-Device-Independent Quantum Key Distribution with Nitrogen Vacancy Centers in Diamond. Phys. Rev. A 2017, 95, 022338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rembold, P.; Oshnik, N.; Müller, M.M.; Montangero, S.; Calarco, T.; Neu, E. Introduction to Quantum Optimal Control for Quantum Sensing with Nitrogen-Vacancy Centers in Diamond. AVS Quantum Sci. 2020, 2, 024701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, G.; Lazariev, A.; Arumugam, S.R.; Duan, D. Nitrogen-Vacancy Color Center in Diamond—Emerging Nanoscale Applications in Bioimaging and Biosensing. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2014, 20, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childress, L.; Hanson, R. Diamond NV Centers for Quantum Computing and Quantum Networks. MRS Bull. 2013, 38, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latypova, L.R.; Gracheva, I.N.; Shurtakova, D.V.; Murzakhanov, F.F.; Sadovnikova, M.A.; Mamin, G.V.; Gafurov, M.R. Electron–Nuclear Interactions of NV Defects in an Isotopically Purified 6H-28SiC Crystal. J. Phys. Chem. C 2024, 128, 18559–18565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murzakhanov, F.F.; Mamin, G.V.; Orlinskii, S.B.; Gerstmann, U.; Schmidt, W.G.; Biktagirov, T.; Aharonovich, I.; Gottscholl, A.; Sperlich, A.; Dyakonov, V.; et al. Electron–Nuclear Coherent Coupling and Nuclear Spin Readout through Optically Polarized VB– Spin States in hBN. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 2718–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murzakhanov, F.; Mamin, G.; Sadovnikova, M.; Mokhov, E.; Nagalyuk, S.; Gafurov, M.; Soltamov, V. Coherence of NV Defects in Isotopically Enriched 6H-28SiC at Ambient Conditions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2024, 125, 204004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, N.T.; Ivanov, I.G. Charge State Control of the Silicon Vacancy and Divacancy in Silicon Carbide. J. Appl. Phys. 2021, 129, 215702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golter, D.A.; Lai, C.W. Optical Switching of Defect Charge States in 4H-SiC. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinherbers, E.; Mannel, H.; Kerski, J.; Geller, M.; Lorke, A.; König, J. Unraveling Spin Dynamics from Charge Fluctuations. Phys. Rev. Res. 2023, 5, 043103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favero, I.; Berthelot, A.; Cassabois, G.; Voisin, C.; Delalande, C.; Roussignol, P.; Ferreira, R.; Gérard, J.M. Temperature Dependence of the Zero-Phonon Linewidth in Quantum Dots: An Effect of the Fluctuating Environment. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 75, 073308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnusson, B.; Son, N.T.; Csóré, A.; Gällström, A.; Ohshima, T.; Gali, A.; Ivanov, I.G. Excitation Properties of the Divacancy in 4H-SiC. Phys. Rev. B 2018, 98, 195202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Das Sarma, S. Charge-Fluctuation-Induced Dephasing of Exchange-Coupled Spin Qubits. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 96, 100501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christle, D.J.; Klimov, P.V.; de las Casas, C.F.; Szász, K.; Ivády, V.; Jokubavicius, V.; Ul Hassan, J.; Syväjärvi, M.; Koehl, W.F.; Ohshima, T.; et al. Isolated Spin Qubits in SiC with a High-Fidelity Infrared Spin-to-Photon Interface. Phys. Rev. X 2017, 7, 021046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranov, P.G.; Il’in, I.V.; Mokhov, E.N.; Muzafarova, M.V.; Orlinskii, S.B.; Schmidt, J. EPR Identification of the Triplet Ground State and Photoinduced Population Inversion for a Si-C Divacancy in Silicon Carbide. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. Lett. 2005, 82, 441–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Bardeleben, H.J.; Cantin, J.L.; Csóré, A.; Gali, A.; Rauls, E.; Gerstmann, U. NV Centers in 3C,4H, and 6H Silicon Carbide: A Variable Platform for Solid-State Qubits and Nanosensors. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 94, 121202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazen, K.; von Bardeleben, H.J.; Zargaleh, S.A.; Cantin, J.L.; Zhao, M.; Gao, W.; Biktagirov, T.; Gerstmann, U. High-Resolution Resonant Excitation of NV Centers in 6H-SiC: A Matrix for Quantum Technology Applications. Phys. Rev. B 2019, 100, 205202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünsalan, C.; Gürhan, H.D.; Yücel, M.E. Microcontroller Architecture. In Embedded System Design with ARM Cortex-M Microcontrollers: Applications with C, C++ and MicroPython; Ünsalan, C., Gürhan, H.D., Yücel, M.E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 7–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishay. BPW34, BPW34S Photo Detectors. Available online: https://www.vishay.com/en/product/81521/ (accessed on 5 February 2025).
- Latypova, L.; Murzakhanov, F.; Mamin, G.; Sadovnikova, M.; von Bardeleben, H.J.; Rau, J.V.; Gafurov, M. Exploring High-Spin Color Centers in Wide Band Gap Semiconductors SiC: A Comprehensive Magnetic Resonance Investigation (EPR and ENDOR Analysis). Molecules 2024, 29, 3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, M.S.; Mohammed, Z.; Alip, R.I. The Effect of SiC Polytypes on the Heat Distribution Efficiency of a Phase Change Memory. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 340, 012013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, M.W.; Manson, N.B.; Delaney, P.; Jelezko, F.; Wrachtrup, J.; Hollenberg, L.C.L. The Nitrogen-Vacancy Colour Centre in Diamond. Phys. Rep. 2013, 528, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, M.W.; Dolde, F.; Fedder, H.; Jelezko, F.; Wrachtrup, J.; Manson, N.B.; Hollenberg, L.C.L. Theory of the Ground-State Spin of the NV- Center in Diamond. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 85, 205203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salikhov, K.M.; Khairuzhdinov, I.T. Theoretical Analysis of the EPR Spectrum Saturation Effect with Account for Spectral Diffusion in a System with a Gaussian Distribution of Spin Resonance Frequencies. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 2019, 128, 684–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzemsky, A.L. Statistical Theory of Spin Relaxation and Diffusion in Solids. J. Low Temp. Phys. 2006, 143, 213–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witzel, W.M.; Das Sarma, S. Nuclear Spins as Quantum Memory in Semiconductor Nanostructures. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 76, 045218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, S.K.; Kallinger, B.; Kaiser, F.; Berwian, P.; Dasari, D.B.R.; Friedrich, J.; Nagy, R. Scalable Quantum Memory Nodes Using Nuclear Spins in Silicon Carbide. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2023, 19, 034026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, C.E.; Randall, J.; Abobeih, M.H.; Berrevoets, R.C.; Degen, M.J.; Bakker, M.A.; Markham, M.; Twitchen, D.J.; Taminiau, T.H. A Ten-Qubit Solid-State Spin Register with Quantum Memory up to One Minute. Phys. Rev. X 2019, 9, 031045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubitz, W.; Lendzian, F. ENDOR Spectroscopy. In Biophysical Techniques in Photosynthesis; Amesz, J., Hoff, A.J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 255–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Description | Keywords | Increment | Min Value | Max Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PWM modulation frequency (kHz) | “PWM Freq, kHz” | 0.1 Hz | 0.1 Hz | 48 kHz |
| Power level (%) | “Power, %” | 0.1% | 0% | 100% |
| Sequence repetition time (ms) | “SRT, ms” | 0.1% | 0.02 | 2.3 × 109 |
| The position of the sync pulse in the sequence (ms) | “P0 pos, ms” | 0.1% | 0 | “SRT, ms” |
| Sync pulse duration (µs) | “P0 len, μs” | 0.1% | 0 | “SRT, ms”–“P0 pos, ms” |
| Position of the first pulse in the sequence (ms) | “P1 pos, μs” | 0.1% | 0 | 2.3 × 109 |
| Duration of the first pulse (µs) | “P1 len, μs” | 0.1% | 0 | 2.3 × 109 |
| Position of the second pulse in the sequence (ms) | “P2 pos, μs” | 0.1% | 0 | 2.3 × 109 |
| Duration of the second pulse (µs) | “P2 len, μs” | 0.1% | 0 | 2.3 × 109 |
| Position of the third pulse in the sequence (ms) | “P3 pos, μs” | 0.1% | 0 | 0.3 × 106 |
| Duration of the third pulse (ms) | “P3 len, μs” | 0.1% | 0 | 0.3 × 106 |
| Enable/disable synchronization on the “ExtTrig” input | “ExtTrig” | - | - | - |
| Maximum duty cycle for the “Pulse” output | “Max Duty” | - | 0 | 100 |
| Laser | Turn-On Delay Time, µs | Rise Time, µs | Decay Time, µs |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNI (CNI Laser, Changchun, China), 405 nm | 8 ± 0.1 | 4.5 ± 0.1 | 1.6 ± 0.1 |
| CNI (CNI Laser, Changchun, China), 532 nm | 10 ± 0.1 | 176 ± 0.5 | 41 ± 0.3 |
| CNI (CNI Laser, Changchun, China), 980 nm | 24 ± 0.1 | 53 ± 0.1 | 23.8 ± 0.1 |
| OXlasers (OXLasers Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China), 520 nm (driver on XL1583) | 2 | 2 ± 0.1 | 2 ± 0.1 |
| LPM-1845IR-TTL, 808 nm, driver with APM9410 (CNI Laser, Changchun, China) | 200 ± 0.1 | 68 ± 0.1 | 12 ± 0.1 |
| 1064T2W, 1064 nm, 2 W (CNI Laser, Changchun, China) | 9000 ± 10 | 3600 ± 100 | 100 ± 10 |
| Measured Value | 50 K | 175 K | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CW Laser Mode | Pulse Laser Mode | CW Laser Mode | Pulse Laser Mode | |
| Phase coherence time (T2) | 53.4 ± 0.2 μs | 73.9 ± 0.4 μs | 50.5 ± 0.1 μs | 60.1 ± 0.1 μs |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mamin, G.; Dmitrieva, E.; Murzakhanov, F.; Sadovnikova, M.; Nagalyuk, S.; Gafurov, M. Laser Pulses for Studying Photoactive Spin Centers with EPR. Micromachines 2025, 16, 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040396
Mamin G, Dmitrieva E, Murzakhanov F, Sadovnikova M, Nagalyuk S, Gafurov M. Laser Pulses for Studying Photoactive Spin Centers with EPR. Micromachines. 2025; 16(4):396. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040396
Chicago/Turabian StyleMamin, George, Ekaterina Dmitrieva, Fadis Murzakhanov, Margarita Sadovnikova, Sergey Nagalyuk, and Marat Gafurov. 2025. "Laser Pulses for Studying Photoactive Spin Centers with EPR" Micromachines 16, no. 4: 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040396
APA StyleMamin, G., Dmitrieva, E., Murzakhanov, F., Sadovnikova, M., Nagalyuk, S., & Gafurov, M. (2025). Laser Pulses for Studying Photoactive Spin Centers with EPR. Micromachines, 16(4), 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040396






