Abstract
To obtain more accurate information on using an inertial navigation system (INS)-based integrated localization system, an integrated filter with maximum correntropy criterion Kalman filter (mccKF) and finite impulse response (FIR) is proposed for the fusion of INS-based multisource sensor data in this work. In the realm of medical applications, precise localization is crucial for various aspects, such as tracking the movement of a medical instrument within the human body or monitoring its position in the human body during procedures. This study uses ultra-wideband (UWB) technology to rectify the position errors of the INS. In this method, the difference between the positions of the INS and UWB is used as the measurement of the filter. The main data fusion filter in this study is the mccKF, which utilizes the maximum correntropy criterion (mcc) method to enhance the robustness of the Kalman filter (KF). This filter is used for fusing data from multiple sources, including the INS. Moreover, we use the Mahalanobis distance to verify the performance of the mccKF. If the performance of the mccKF is lower than the preset threshold, the Allan Variance-assisted FIR filter is used to replace the mccKF, which is designed in this work. This adaptive approach ensures the resilience of the system in demanding medical environments. Two practical experiments were performed to evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed approach. The findings indicate that the mccKF/FIR integrated method reduces the localization error by approximately 32.43% and 37.5% compared with the KF and mccKF, respectively. These results highlight the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
1. Introduction
Nowadays, the inertial navigation system (INS)-based measurement is widely used in several fields [1]. For instance, in the research performed by [2], a design integrating multisensor fusion was suggested. This design includes an INS, a global navigation satellite system (GNSS), and light detection and ranging (LiDAR) for implementing 3D simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM; INS/GNSS/3D LiDAR-SLAM). Furthermore, the research performed in [3] delved into the utilization of GNSSs/INSs for assisted imaging systems in uncrewed aerial vehicles (UAVs). In addition, a method for analyzing gait in individuals with Parkinson’s disease using wearable technology based on the INS was designed to evaluate motor ability in [4]. Notably, INS-based measurement technology is gradually becoming a research hotspot.
In INS-based localization, reducing the position cumulative error of the INS is the most important issue that needs to be addressed [5]. Several approaches have been proposed to overcome this problem based on two aspects: integrated navigation methods and data fusion filters. The integrated navigation method has several approaches. For instance, in [6], a GNSS/INS integrated navigation system is supported by a back propagation (BP) neural network with motion constraints. This approach offers supplementary information to address the issue of rapid divergence in the positioning error of integrated navigation systems during GNSS outages. A new robust adaptive method, utilizing a tight real-time kinematic (RTK)/INS architecture, was proposed in [7]. It enhances the robust estimation method by considering two factors, including ambiguity variance, for RTK-related observations. To overcome the problem of inaccuracy in lateral velocity constraint parameters, a navigation method based on a BP neural network for an integrated GNSS/INS/odometer (OD) with nonholonomic constraints (NHCs) has been proposed [8], considering the state of vehicle motion. In the work by the authors of [9], the utilization of an adaptive model set aims to increase the effectiveness of an integrated navigation system compared to an INS with Doppler velocity log in challenging measurement environments. In [10], a microelectromechanical system (MEMS)–INS-based ultra-wideband (UWB) integrated method for indoor navigation was designed. Notably, the principle of the abovementioned examples is to employ different navigation and positioning technologies to continuously correct the calculation errors in INS navigation.
Based on the INS integrated navigation scheme, a data fusion filter can further improve the localization accuracy [11]. Meanwhile, several approaches have been proposed to deal with the data fusion problem. For example, in [12], one robust Kalman filter (KF) was proposed for loosely coupled global positioning system (GPS)/INS integration systems. A dual-rate KF has been devised for integrating time-differenced GPS measurements with INS data [13]. For nonlinear cases, the extended KF (EKF) was considered in [14]. In [15], the EKF was proposed for INS/GPS integrated navigation. Meanwhile, a locally weighted linear regression (LWLR)/long short-term memory (LSTM)-assisted EKF was designed for the integrated navigation of an INS/celestial navigation system [16]. Notably, Kalman-based approaches for data fusion have difficulty in overcoming the disadvantage of accurately capturing environmental noise. To overcome this problem, the finite impulse response (FIR) filter was developed in [17]. The FIR filter only uses the size of the data fusion window and state vector. Alternatively, the FIR filter only requires the size of the data fusion window because the data fusion model is already built. Simultaneously, several approaches have been suggested. For example, in [18], the extended FIR filter was introduced for the fusion of recent INS and UWB measurements. One self-tuning FIR filter has been proposed for processes with unknown measurement noise covariance [19]. Notably, the calculation of the size of the optimal data fusion window is considerably important.
Nowadays, both the mccKF and the FIR have been widely used in localization. However, is should be pointed out that there are many shortcomings. For mccKF, this method can improve the robustness; however, the matrix in the estimation process is prone to singularity, which can cause the mccKF to not work. Moreover, the accuracy of the noise will also affect the localization accuracy. The FIR filter has better robustness; however, if the noise of the filter affects the accuracy, we have to say that its performance is worse than that of the KF method. Thus, we propose an mccKF/FIR filtering approach; when the KF method cannot provide a stable solution, the FIR can. To obtain more accurate position information using the INS-based integrated localization system, a maximum correntropy criterion KF (mccKF)/FIR) integrated filter is proposed for the fusion of INS-based multisource sensor data in this work. Herein, UWB is used to correct the position error of the INS. In this method, the difference between the positions of the INS and UWB is used as the measurement of the filter. The main data fusion filter in this context is mccKF, which uses the mcc method to improve the robustness of the KF. Its application involves the fusion of INS-based multisource sensory data. Moreover, we use the Mahalanobis distance to verify the performance of the mccKF. If the performance of the mccKF is below the preset threshold, an Allan Variance-assisted FIR filter is used to replace the mccKF, which employs the Allan Variance method to improve the noise accuracy. Two practical tests were performed to evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed methodology. The results of these experiments verify the efficacy of the proposed strategy.
The remaining sections of this paper are organized as follows: Section 2 discusses the principle of indoor integrated localization system by fusing the INS and UWB. Section 3 presents the design of an mccKF/FIR integrated filter for INS-based integrated navigation. The analysis of the experimental tests is summarized in Section 4, and the conclusions are provided in Section 5.
2. Indoor Integrated Localization by Fusing INS and UWB
This subsection discusses the design of the indoor integrated localization scheme by combining INS and UWB data. Furthermore, we briefly introduce the state and measurement equations used by the proposed filter.
2.1. Indoor Integrated Localization Scheme
Figure 1 illustrates the indoor integrated localization scheme, which combines INS and UWB data. The figure shows that the integrated localization scheme uses UWB and the INS to obtain the position of UWB- and INS-based target drones and at time index k, respectively. Subsequently, the difference between and is used as the measurement of the mccKF/FIR integrated filter, which will be discussed in detail in the subsequent section. Meanwhile, the sampling time of the integrated localization scheme is used as the measurement of the mccKF/FIR integrated filter. With these measurements, the mccKF/FIR integrated filter outputs the estimation of the position , and this value is used to correct the .
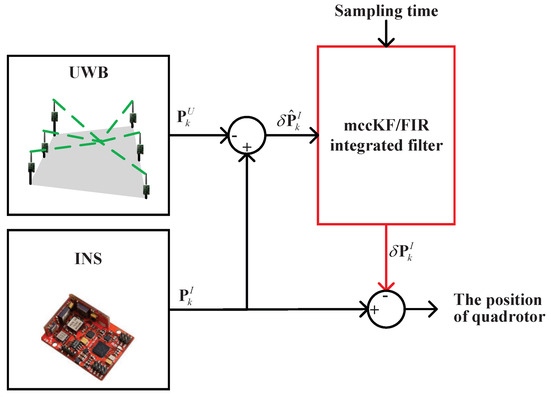
Figure 1.
Indoor integrated localization scheme obtained by fusing INS and UWB data.
2.2. State and Measurement Equations
Expanding on the integrated scheme described in Section 2.1, the state and measurement equations of the mccKF/FIR integrated filter are presented. The state equation used herein is presented as Equation (1).
where , , , , , , and represents the system noise, and , , and can be defined as follows:
where represents the sampling time. The measurement equation utilized herein can be expressed as follows:
where represents the position of the INS-based target drone at time index k, represents the position of the UWB-based target drone at time index k, and represents the measurement noise.
3. mccKF/FIR Integrated Filter
In this section, the mccKF/FIR integrated filter mentioned in Section 2.1 is presented. First, we provide a brief introduction to the mccKF method. Subsequently, the FIR filter based on the state and measurement equations mentioned in Section 2.2 is constructed. Finally, the mccKF/FIR integrated filter is proposed.
3.1. Maximum Correntropy Criterion
Correntropy quantifies the resemblance between two random variables :
where represents the joint distribution function. And represents its kernel, which is defined as follows:
Notably, obtaining is challenging. Therefore, we can estimate the correntropy using the following equation:
where . In this work, we set is available, and the mcc cost function can be written as follows:
3.2. mccKF Filter
With model (1) and (2), the data fusion filter, with the KF being the most famous example, has the potential to enhance localization accuracy. Based on model (1) and (2), the KF method initially uses one-step prediction, which can be written as follows:
Subsequently, with measurement , the KF uses the updated measurement to provide the estimated value using the following equations:
The KF algorithm based on model (1) and (2) can be listed as Algorithm 1.
| Algorithm 1: KF algorithm based on model (1) and (2) |
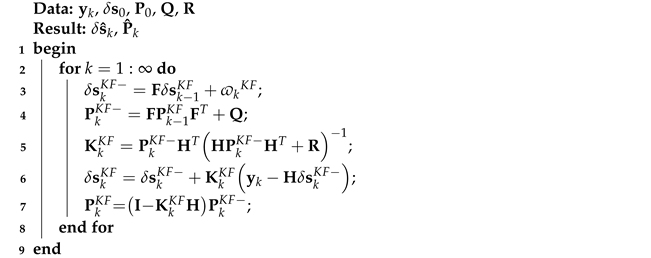 |
The mcc-KF employs the mcc as the optimization criterion to obtain the posterior estimates, which is robust against heavy-tailed non-Gaussian noises. We rewrite Equations (1) and (2) using Equations (8) and (9) as follows:
where
And we obtain the following equation:
where can be computed using Cholesky decomposition. In addition, Equation (13) can be rewritten as follows:
Thus, the optimal estimate of can be computed as follows:
Consequently, we can obtain one fixed-point iterative algorithm, and the steps of this method can be expressed as follows:
3.3. Allan Variance
In this work, we employ Allan Variance to assist the FIR filter, which is able to improve the accuracy of the noise estimation. Firstly, we are able to obtain the following equation with :
Based on Equation (25), we can obtain that
where N is the sum of the data groups. Then, we can obtain
3.4. FIR Filter
It is evident from the aforementioned section that the mccKF filter enhances robustness compared with the conventional KF method. However, the mccKF depends on noise statistics. Meanwhile, the FIR filter maintains the robustness of the proposed filter. Based on model (1) and (2), the FIR filter estimates the error of the INS using the measurement at time index . The FIR filter uses the KF to fuse the data in the dead zone. When the time index is , where is the size of the filtering window, the FIR performs one-step prediction, which is listed as follows:
Then, the measurement update can be performed using the following equations:
3.5. mccKF/FIR Integrated Filter
In this study, we used the mccKF/FIR integrated filter, which is shown in Figure 2. First, we performed the one-step prediction of the mccKF and with and . The Mahalanobis distance can be used to determine differences in the data distribution. Subsequently, the Mahalanobis distance is computed using the following equation:
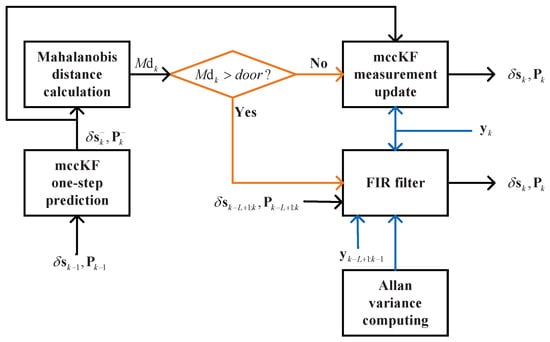
Figure 2.
Scheme of the mccKF/FIR integrated filter.
When , we used the FIR filter to provide the output, and when , we directly updated the measurement.
4. Results
In this study, a practical test was conducted to validate the efficacy of the proposed approach. First, we provide an overview of the test setup. Second, the localization accuracy of the proposed mccKF/FIR integrated filter is compared with that of a traditional filter.
4.1. The Design of the Testbed
In this subsection, the testbed used herein is presented. In this study, a practical test was conducted in building No. 1 of the University of Jinan, China. Figure 3 and Figure 4 illustrates the real test environment utilized for the experiment. In the test, we used crazyflie2.0 as the target drone, and six DW-1000-based UWB reference nodes (UWB RNs) with known coordinates and one UWB blind node fixed on the target drone to measure . Meanwhile, one IMU fixed on the target drone was used to measure the INS-derived position .
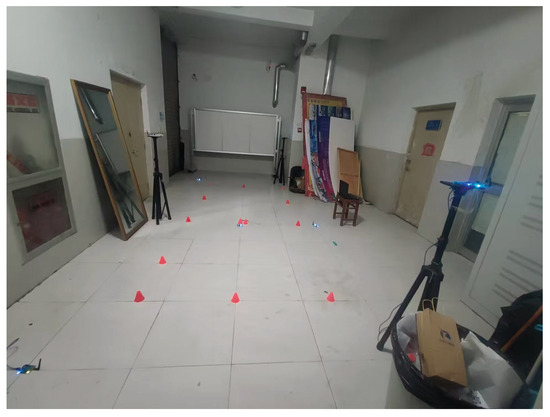

Figure 3.
Test environment used in this work.
Figure 4.
crazyflie2.0 used in the test.
4.1.1. Test 1
Herein, two practical tests were performed to demonstrate the enhancements achieved by the proposed method. In this subsection, the result of Test 1 is discussed. First, for the filter, we set , , , and , and then and were set as follows:
The reference path used in Test 1 is shown in Figure 5, and the positions measured by the KF, adaptive KF (AKF), mccKF, and mccKF/Allan-assisted FIR integrated filters in the east, north, and upward directions in Test 1 are compared in Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8. The figures reveal that the KF, mccKF, and proposed mccKF/Allan-assisted FIR integrated filters provide the position in the east, north, and upward directions, respectively. The AKF has big errors. The situations in Figure 7 and Figure 8 are similar. These figures show that the KF and mccKF exhibit weak divergence in the east and north directions. When compared with the KF and mccKF, the positions measured by the proposed mccKF/FIR integrated filter are closer to the reference position, indicating that the suggested approach is more effective in minimizing localization errors. Figure 8 shows that all solutions of the filters are similar, and the positions measured by the proposed have small fluctuations when compared with other filters.
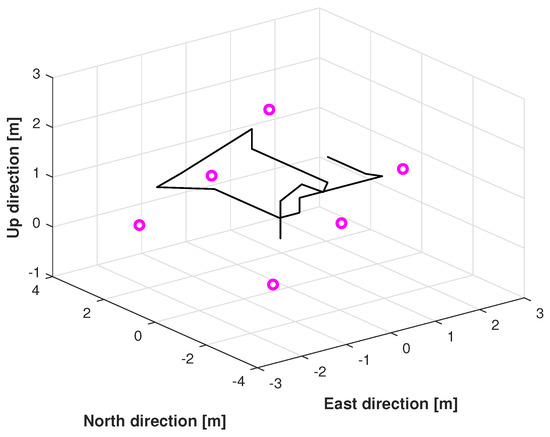
Figure 5.
Reference path used in Test 1.
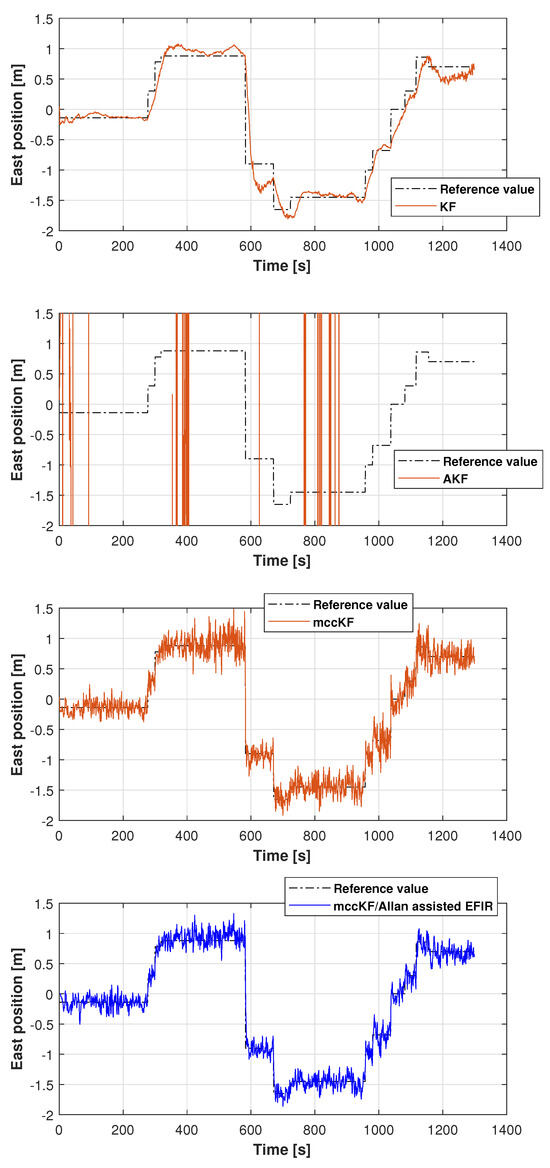
Figure 6.
East position measured by the KF, mccKF, and mccKF/Allan-assisted FIR integrated filter in Test 1.
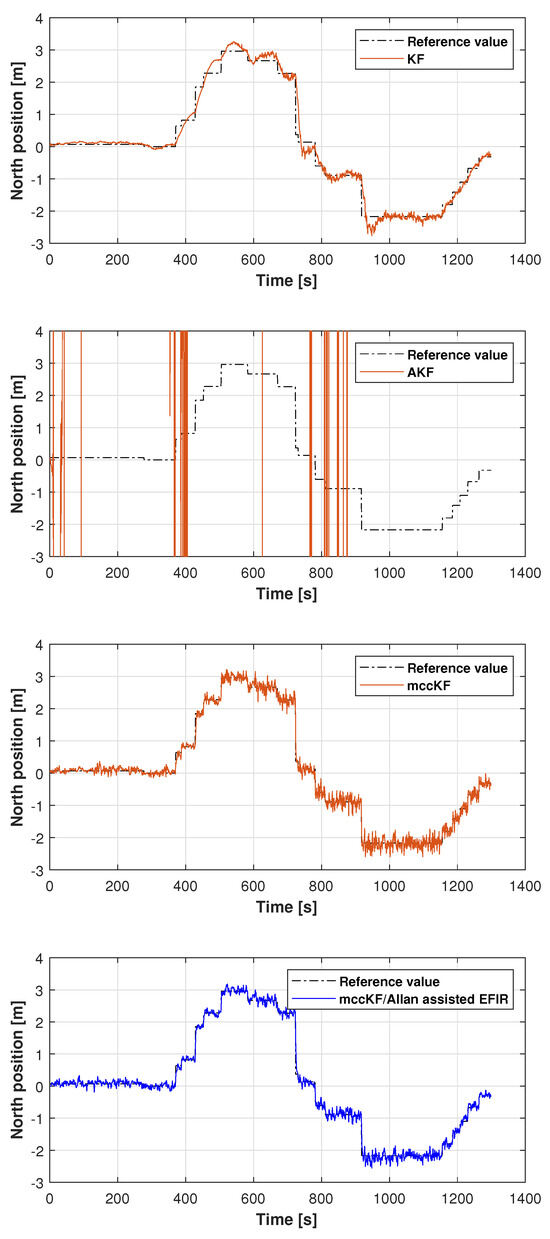
Figure 7.
North position measured by the KF, AKF, mccKF, and mccKF/FIR integrated filter in Test 1.
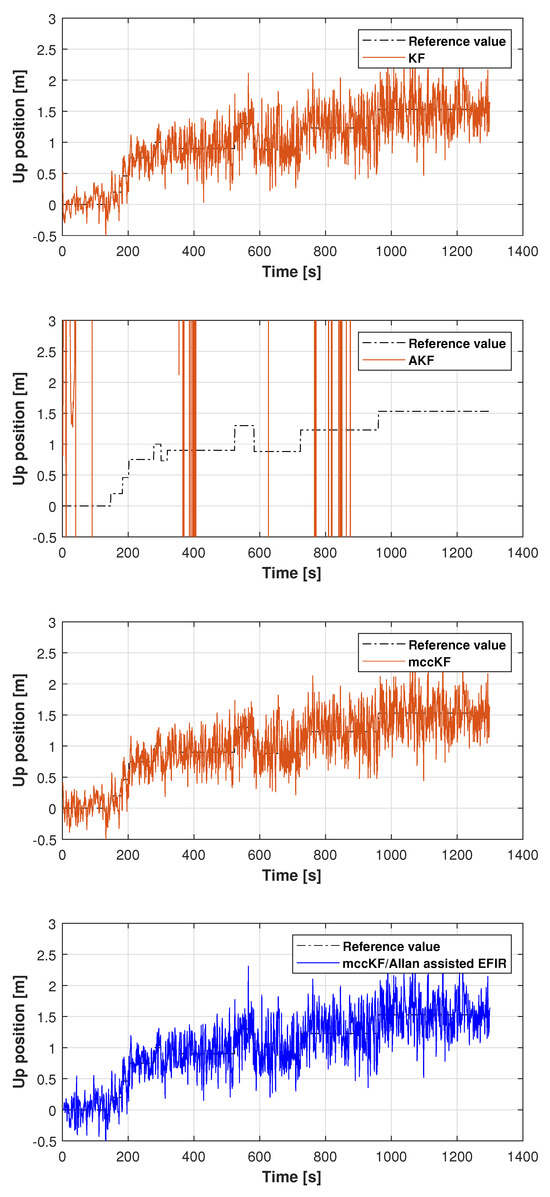
Figure 8.
Upward position measured by the KF, AKF, mccKF, and mccKF/Allan-assisted FIR integrated filter in Test 1.
The cumulative distribution function (CDF) of the position errors, as measured by the KF, AKF, mccKF, and mccKF/Allan-assisted FIR integrated filter in Test 1, are depicted in Figure 9. The figure shows that the localization error of the mccKF is less than that of the KF when the CDF is 0.9. Compared with the mccKF and KF, the proposed mccKF/FIR integrated filter exhibits minimal localization error when the CDF is 0.9. This highlights the efficacy of the suggested approach in minimizing localization errors.
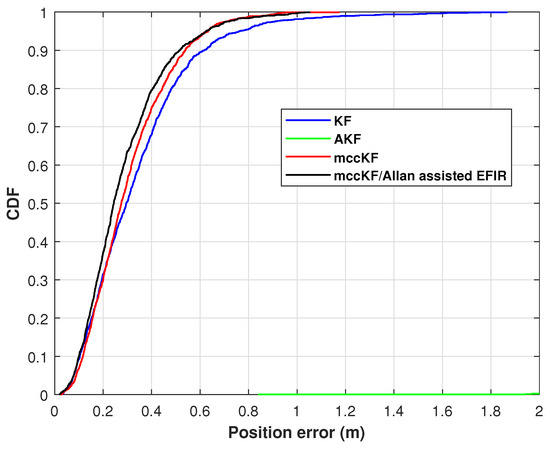
Figure 9.
CDF of the position errors measured by the KF, AKF, mccKF, and Allan-assisted mccKF/FIR integrated filter in Test 1.
To provide a more detailed demonstration of the effectiveness of the proposed approach, we use the position root mean square error (RMSE) in each time index, which is computed using the following equation:
where represents the measurement of at time index j. And Figure 10 shows the RMSE of the position errors measured by the KF, mccKF, and Allan-assisted mccKF/FIR integrated filter in Test 1. From this figure, we can see that the proposed method has the smallest RMSE errors.
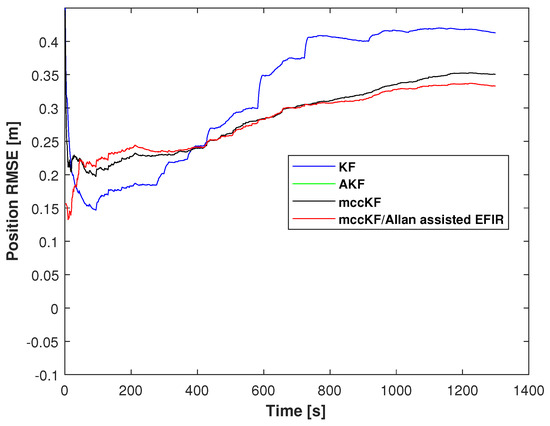
Figure 10.
RMSE of the position errors measured by the KF, AKF, mccKF, and Allan-assisted mccKF/FIR integrated filter in Test 1.
Table 1 lists the position RMSEs of the KF, mccKF, and mccKF/Allan-assisted FIR integrated filter in Test 1. The table shows that the mean RMSE of the mccKF is slightly lower than that of the KF. The mccKF/Allan-assisted FIR integrated filter reduces the localization error from 0.23 to 0.16 m when compared with the KF, which has the lowest localization error. All the figures and the table illustrate that, in Test 1, the proposed mccKF/Allan-assisted FIR filter is more efficient in minimizing localization errors when compared with the KF and mccKF.

Table 1.
Position RMSEs of the KF, mccKF, and mccKF/Allan-assisted FIR integrated filter in Test 1.
4.1.2. Test 2
In this study, the real test was performed following another reference path, which is shown in Figure 11. Figure 12, Figure 13 and Figure 14 display the positions measured by the KF, AKF, mccKF, and the mccKF/Allan-assisted FIR integrated filter in the east, north, and upward directions in Test 2. The figures show that the performances of the filters in the east and north directions are different from those in the upward direction. In Figure 12 and Figure 13, similar to Test 1, the KF and mccKF exhibit some divergence in the east and north directions, particularly when the position changes. When compared with the KF and mccKF, the position of the proposed mccKF/Allan-assisted FIR filter is more stable, and its solution is closer to the reference value. In the case of upward direction, the positions of all the filters are similar. In Test 2, the estimation of the position in the upward direction by all the filters is initially very accurate, and later, a small amplitude of vibration is observed. Overall, the estimations of the target aircraft position by all the filters are achieved in this direction. For the filter, we set the following:
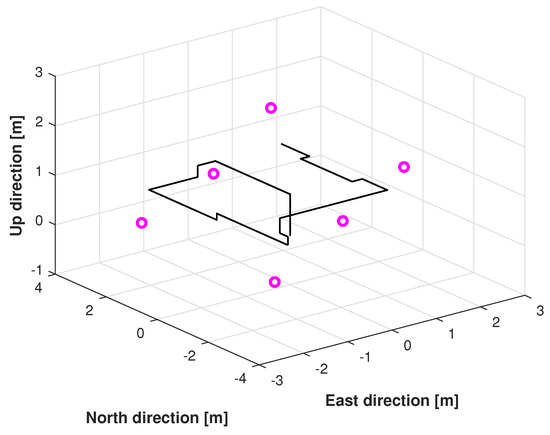
Figure 11.
Reference path used in Test 2.
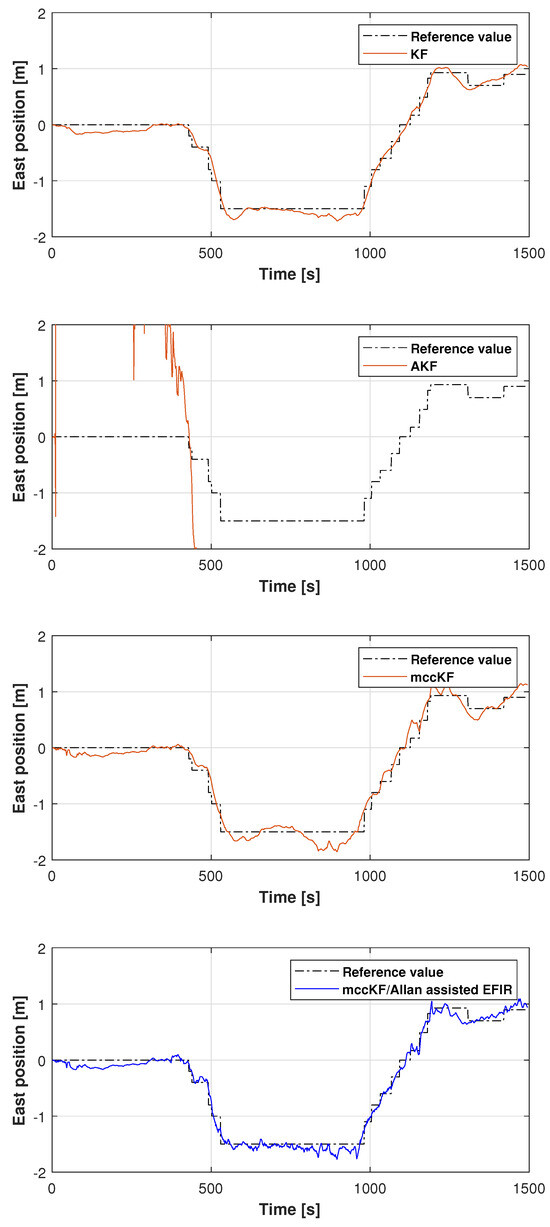
Figure 12.
East position measured by the KF, AKF, mccKF, and mccKF/Allan-assisted FIR integrated filter in Test 2.
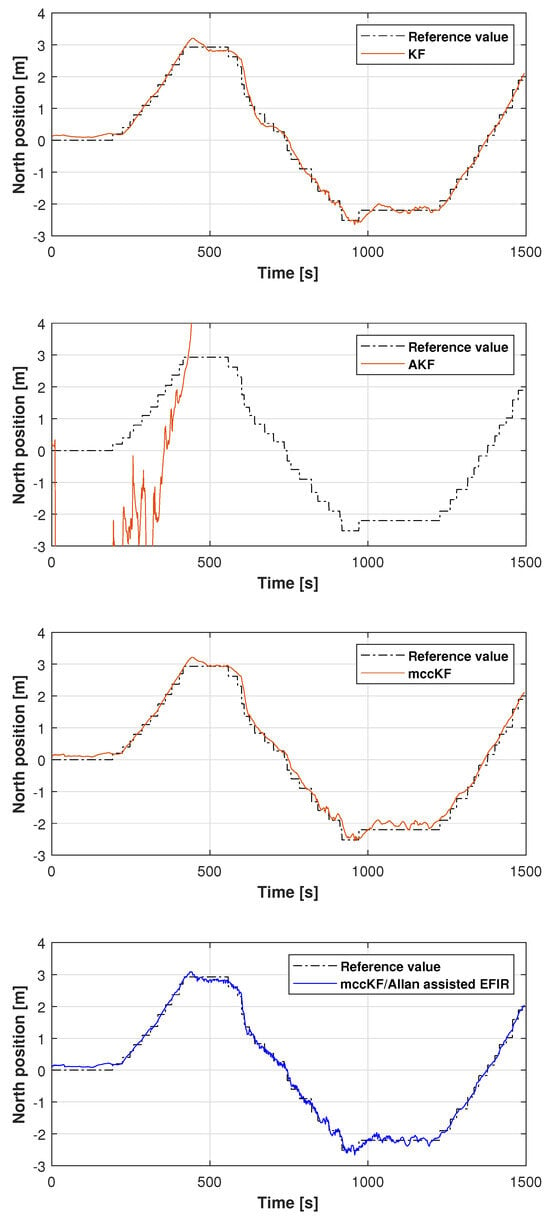
Figure 13.
North position measured by the KF, AKF, mccKF, and mccKF/Allan-assisted FIR integrated filter in Test 2.
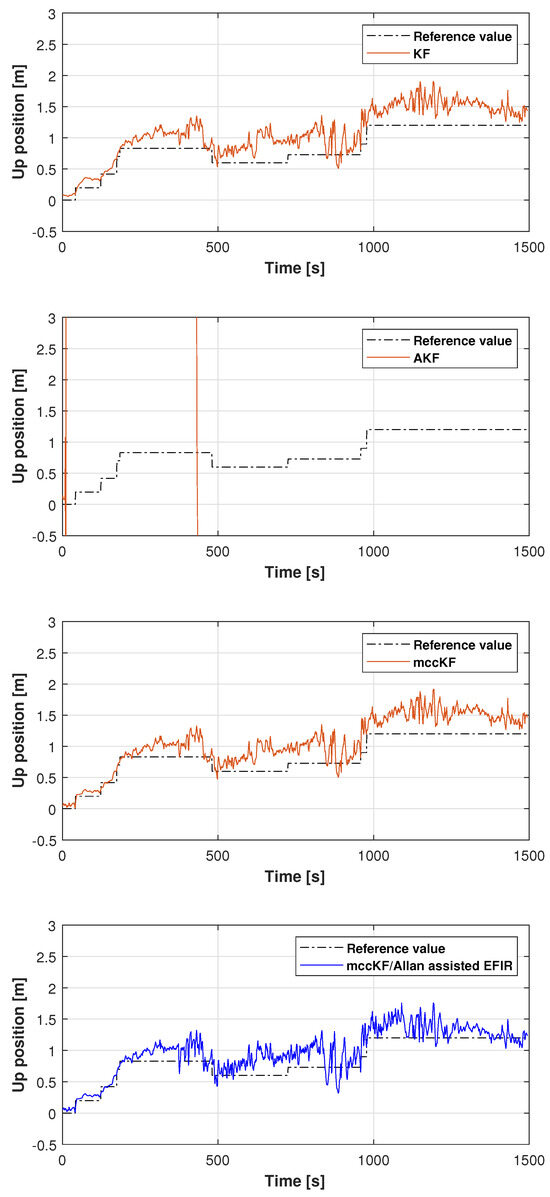
Figure 14.
Upward position measured by the KF, AKF, mccKF, and mccKF/Allan-assisted FIR integrated filter in Test 2.
The position RMSEs of the KF, mccKF, and mccKF/Allan-assisted FIR integrated filter in Test 2 are presented in Figure 15. The figure shows that the RMSEs of the mccKF and mccKF/Allan-assisted FIR are the same when the time index is <480 s. After 480 s, all the filters exhibit large differences. The localization error of the KF method rapidly increases, and this method has the largest RMSE when compared with the mccKF and proposed method. The increase in the RMSE of the mccKF is low compared with that of the KF. Compared with the KF and mccKF, although the RMSE of the proposed mccKF/Allan-assisted FIR integrated filter increases, it has the lowest value in all the filters. Table 2 lists the position RMSEs of the KF, mccKF, and mccKF/Allan-assisted FIR integrated filter in Test 2. The table reveals that, in comparison with the KF and mccKF, the proposed method exhibits the lowest RMSE. It reduces the localization error from the KF’s 0.18 m to 0.13 m, resulting in a reduction in the localization error by approximately 30%. The position CDFs of the KF, mccKF, and mccKF/Allan-assisted FIR integrated filter in Test 2 are shown in Figure 16. From the figure, we can see that the proposed method has the smallest localization error.
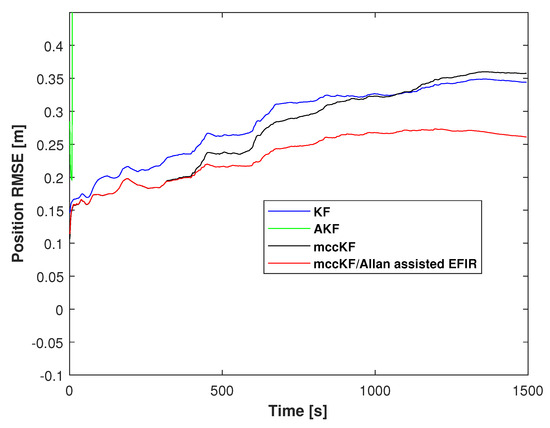
Figure 15.
Position RMSEs of the KF, AKF, mccKF, and mccKF/Allan-assisted FIR integrated filter in Test 2.

Table 2.
Position RMSEs of the KF, mccKF, and mccKF/Allan-assisted FIR integrated filter in Test 2.
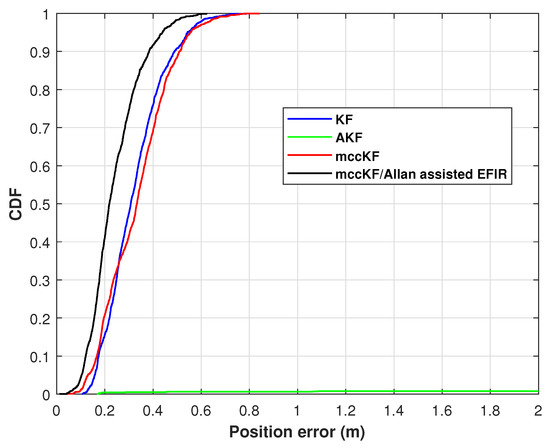
Figure 16.
Position CDF of the KF, AKF, mccKF, and mccKF/Allan-assisted FIR integrated filter in Test 2.
All the figures and the table indicate that, in Test 2, the proposed mccKF/Allan-assisted FIR filter is more efficient in minimizing localization errors when compared with the KF and mccKF. Tests 1 and 2 reveal that the proposed approach exhibits minimal localization error. Therefore, the suggested approach is the most effective.
5. Conclusions
To improve the robustness of the data fusion for INS-based integrated localization, an mccKF/FIR integrated filter was proposed herein. In this approach, the mccKF serves as the primary data fusion filter and is used for fusing data from multiple sources, including the INS. In this work, we used the Mahalanobis distance to verify the performance of the mccKF. If the performance of the mccKF is poor, the FIR filter is used to replace the mccKF. Two practical tests were performed to assess the performance of the suggested approach. The findings indicate that the mccKF/FIR integrated method is effective in minimizing localization errors when compared with the KF and mccKF. This observation emphasizes the efficacy of the proposed method.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.L. and Y.G.; methodology, L.D., Y.Z. and Y.X.; software, Y.Z. and Y.X.; validation, Y.Z. and Y.X.; formal analysis, M.L. and Y.G.; investigation, M.L. and Y.G.; resources, M.L. and Y.G.; data curation, Y.G.; writing—original draft preparation, M.L. and Y.G.; writing—review and editing, M.L., Y.X. and Y.G.; visualization, L.D. and Y.Z.; supervision, Y.G.; project administration, Y.G.; funding acquisition, Y.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Yuan Xu was employed by the company Jinan Chenhe Information Technology Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
This manuscript employs the following abbreviations:
| INS | Inertial Navigation System |
| KF | Kalman Filter |
| UWB | Ultra-Wideband |
| 3D-SLAM | 3D Simultaneous Localization and Mapping |
| UAVs | Unmanned Aerial Vehicles |
| PD | Parkinson’s Disease |
| ZUPT | Zero-velocity UPdaTe |
| MCC | Maximum Correntropy Criterion |
| GNSS | Global Navigation Satellite System |
| FIR | Finite Impulse Response |
| mccKF | Maximum Correntropy Criterion KF |
| LiDAR | Light Detection And Ranging |
| RTK | Real-Time Kinematics |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| OD | Odometer |
| NHC | Nonholonomic Constraint |
| DVL | Doppler Velocity Log |
| MEMS | Microelectormechanical System |
| GPS | Global Positioning System |
| DRKF | Dual-Rate Kalman Filter |
| CKF | Cubature Kalman Filter |
| LWLR | Locally Weighted Linear Regression |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| CNS | Celestial Navigation System |
| EFIR | Extended Finite Impulse Response |
References
- Xu, Y.; Wan, D.; Shmaliy, Y.S.; Chen, X.; Tao, S.; Bi, S. Dual Free-Size LS-SVM Assisted Maximum Correntropy Kalman Filtering for Seamless INS-Based Integrated Drone Localization. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 71, 9845–9854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, K.W.; Tsai, G.J.; Li, Y.H.; Li, Y.; El-Sheimy, N. Navigation Engine Design for Automated Driving Using INS/GNSS/3D LiDAR-SLAM and Integrity Assessment. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaForest, L.; Hasheminasab, S.M.; Zhou, T.; Flatt, J.E.; Habib, A. New Strategies for Time Delay Estimation during System Calibration for UAV-Based GNSS/INS-Assisted Imaging Systems. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wang, Z.; Qiu, S.; Zhao, H.; Wang, C.; Shi, X.; Lin, F. A Wearable Gait Analysis and Recognition Method for Parkinson’s Disease Based on Error State Kalman Filter. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2022, 26, 4165–4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sheimy, N.; Youssef, A. Inertial sensors technologies for navigation applications: State of the art and future trends. Satell. Navig. 2020, 1, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, K.; Jiang, C.; Li, Z.; Yang, C.; Liu, D.; Zhang, H. Motion-Constrained GNSS/INS Integrated Navigation Method Based on BP Neural Network. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Yan, P.; Meng, X. A Novel Optimal Robust Adaptive Scheme for Accurate GNSS RTK/INS Tightly Coupled Integration in Urban Environments. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, K.; Yang, C.; Li, Z.; Zhou, F.; Liu, D. GNSS/INS/OD/NHC Adaptive Integrated Navigation Method Considering the Vehicle Motion State. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 13511–13523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Zhang, R.; Wang, G.; Long, C.; Hu, M. Robust Interactive Multimodel INS/DVL Intergrated Navigation System With Adaptive Model Set. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 8568–8580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Sun, B.; Sun, Y.; Zhuang, X. Performance Enhancement of MEMS-Based INS/UWB Integration for Indoor Navigation Applications. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 3116–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Huang, B. Trial-and-error or avoiding a guess? Initialization of the Kalman filter. Automatica 2020, 121, 109184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Qiu, H.; Feng, Y. Analysis of a Robust Kalman filter in loosely coupled GPS/INS navigation system. Measurement 2015, 80, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Wang, J. Integrated GPS/INS navigation system with dual-rate Kalman Filter. GPS Solut. 2012, 16, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Hou, J.; Liu, L.; Sun, T.; Liu, J. Design and Simulation of the Integrated Navigation System based on Extended Kalman Filter. Open Phys. 2017, 15, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Shen, C.; Cao, H.; Yang, Y.; Liu, J. An Improved Strong Tracking Cubature Kalman Filter for GPS/INS Integrated Navigation Systems. Sensors 2018, 18, 1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Chen, X. An ANN-Based Data Fusion Algorithm for INS/CNS Integrated Navigation System. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 7846–7854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmaliy, Y.S. Linear optimal FIR estimation of discrete time-invariant state-space models. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2010, 58, 3086–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Shmaliy, Y.S.; Ahn, C.K.; Chen, X.; Guo, H.; Zhuang, Y. Blind Robust Multi-Horizon EFIR Filter for Tightly Integrating INS and UWB. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 23037–23045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Shmaliy, Y.S.; Ahn, C.K.; Liu, F. Self-tuning unbiased finite impulse response filtering algorithm for processes with unknown measurement noise covariance. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2020, 29, 1372–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).

