A Novel Nano-Scale Biosensor for Measuring Hemoglobin Oxygen Saturation Using Carbon Quantum Dots
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
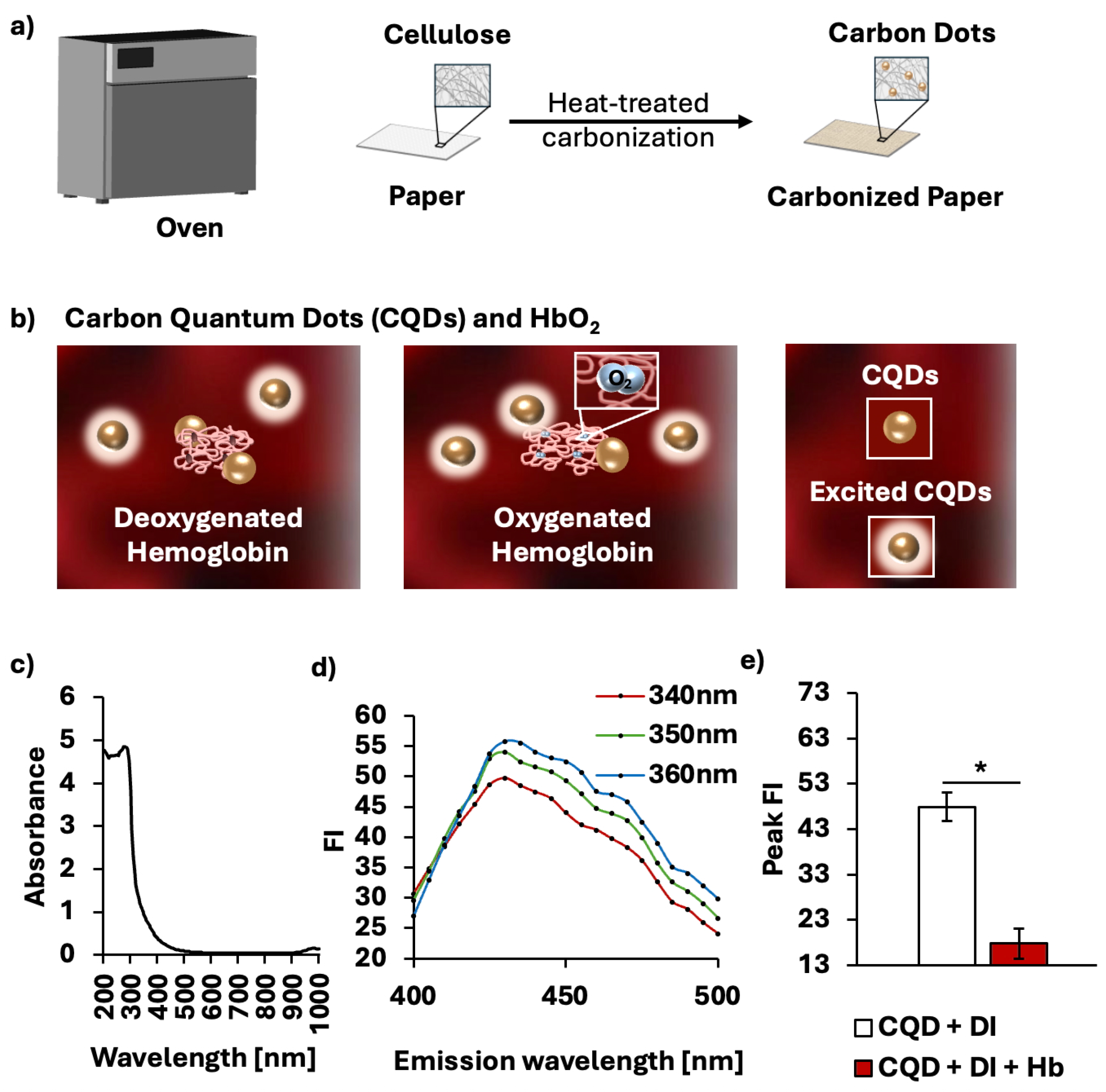
2.1. Carbon Quantum Dot (CQD)
2.2. Characterization of CQDs
2.3. Blood Sample Preparation
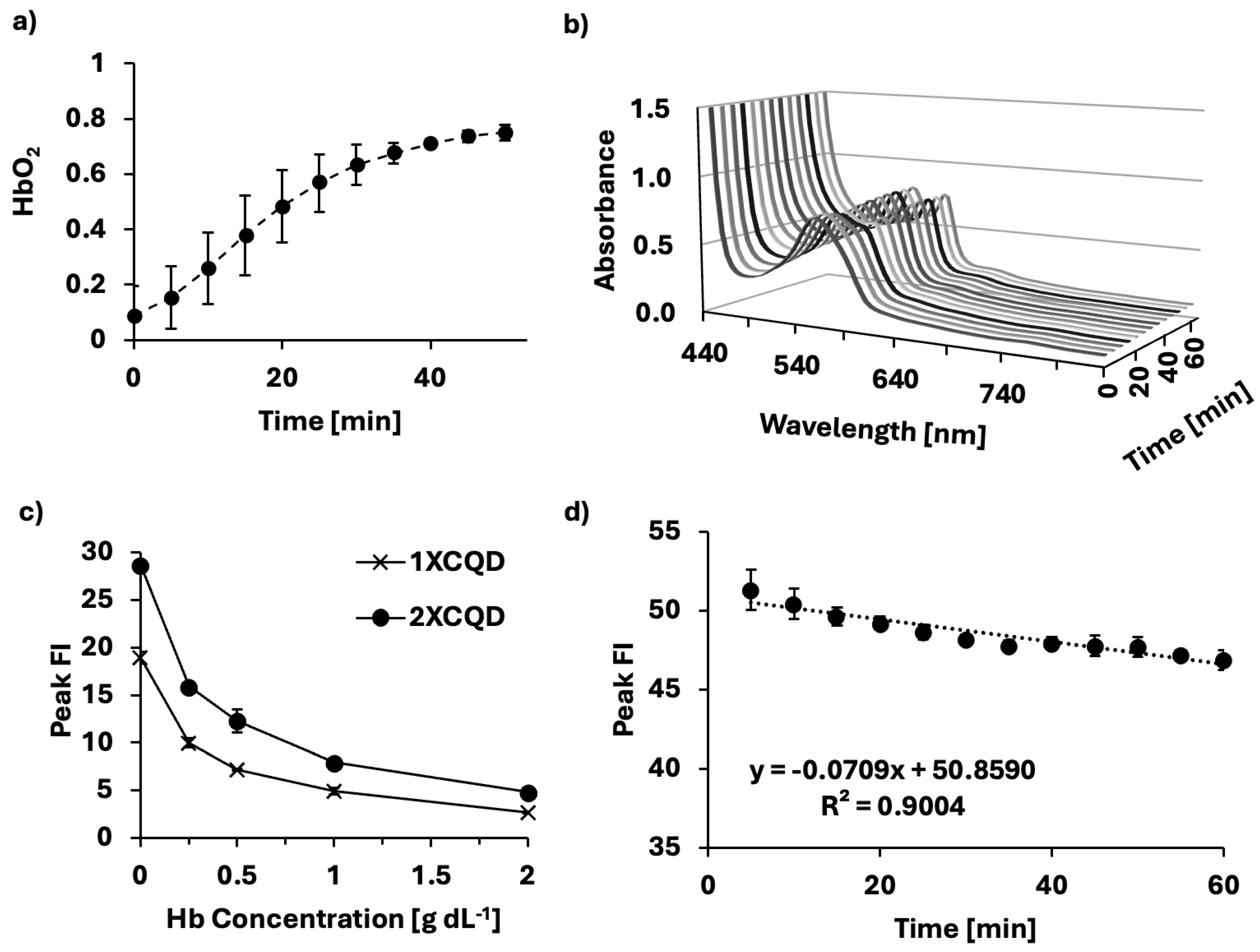
2.4. HbO2 Saturation Level Control
2.5. HbO2 Saturation Level Measurement
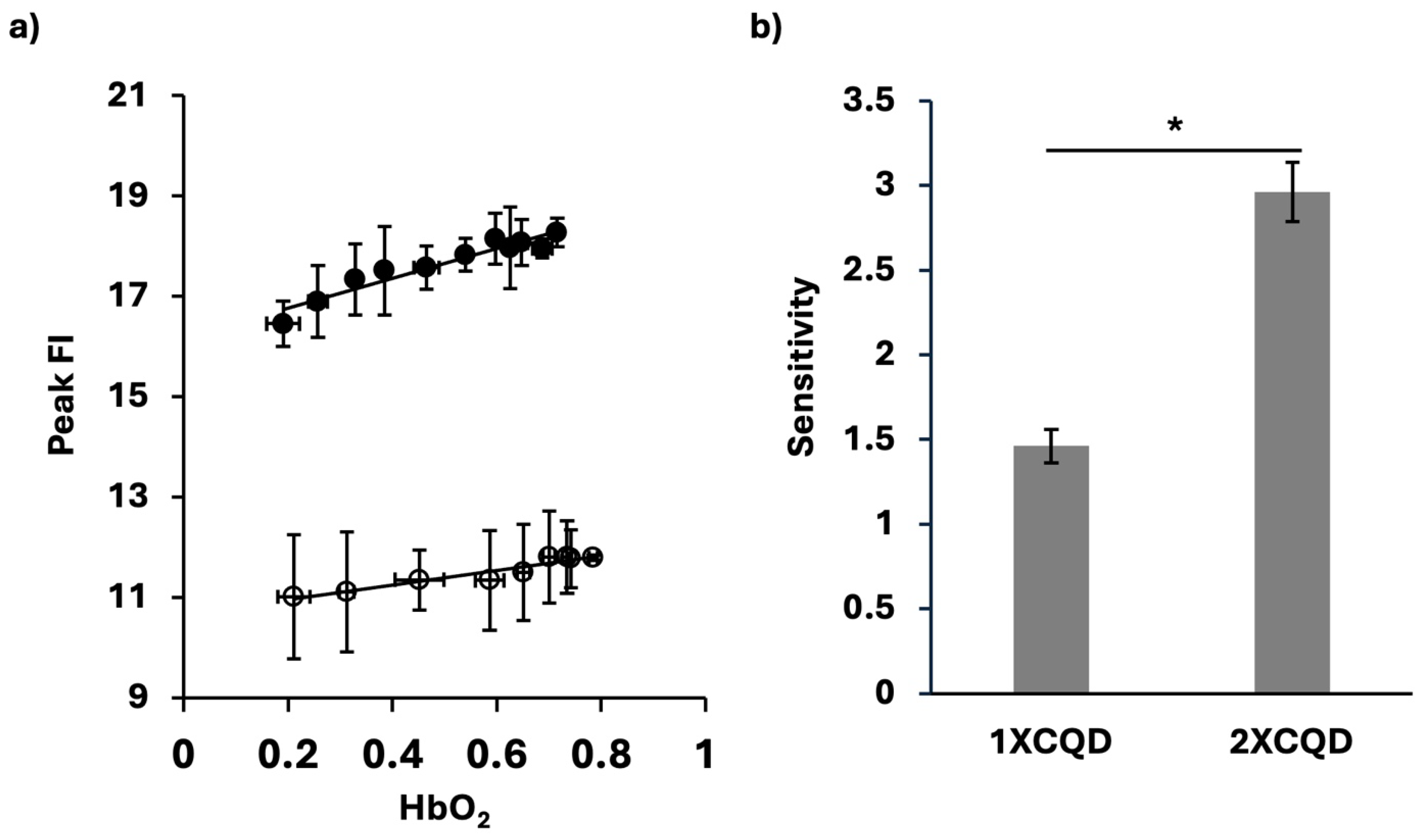
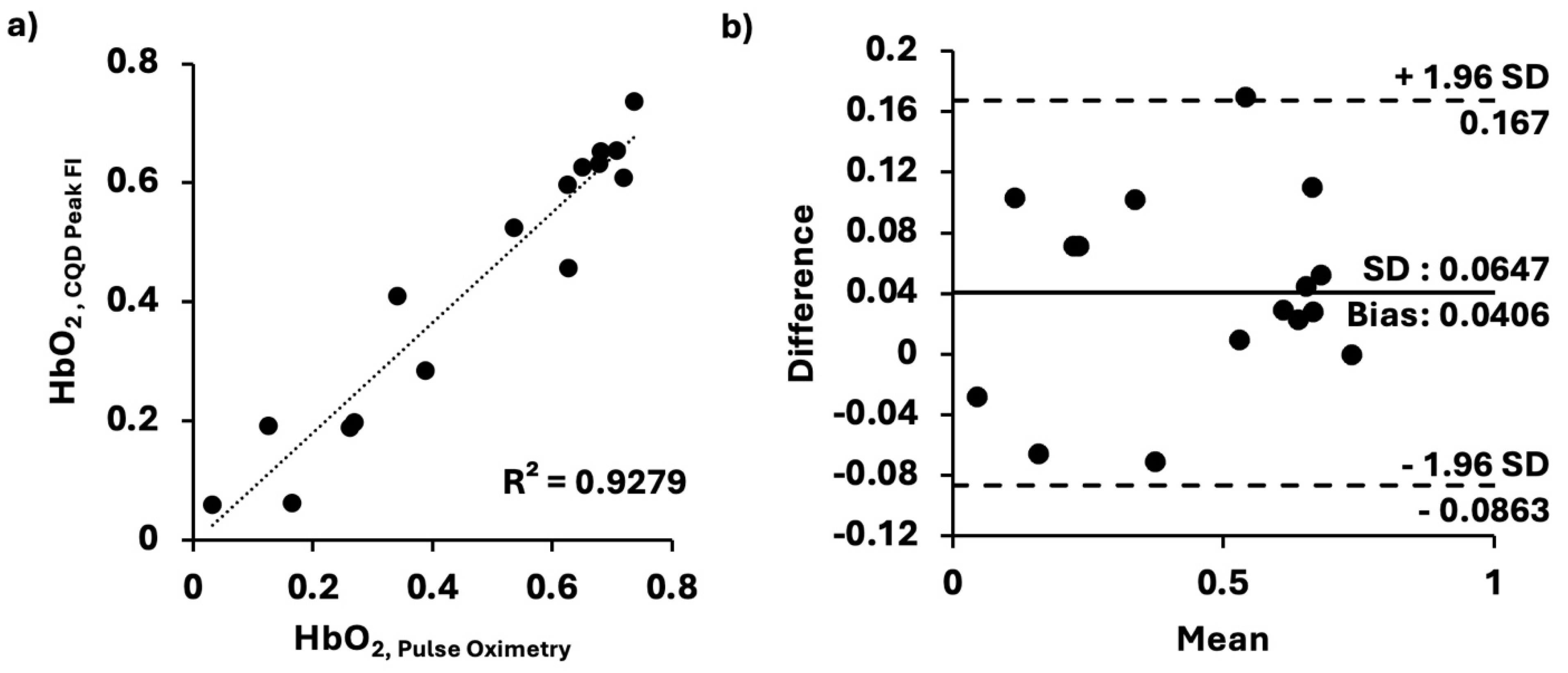
2.6. Validation of CQDs for Oxygen Sensing
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CQDs | Carbon Quantum Dots |
| HbO2 | Hemoglobin oxygen |
| FI | Fluorescence Intensity |
| DI | Deionized (water) |
| PRBC | Packed Red Blood Cell |
| OxyHb | Oxyhemoglobin |
| DeoxyHb | Deoxyhemoglobin |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| ANCOVA | Analysis of Covariance |
| R2 | Coefficient of determination |
| p | p-value |
| Na2S2O4 | Sodium Dithionite |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
References
- Hafen, B.B.; Sharma, S. Oxygen Saturation. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, B.K. In Physical Rehabilitation; Cameron, M.H., Monroe, L.G., Eds.; Vital Signs. Chapter 22; W.B. Saunders: Saint Louis, MO, USA, 2007; pp. 598–624. [Google Scholar]
- Samuel, J.; Franklin, C. In Common Surgical Diseases: An Algorithmic Approach to Problem Solving; Myers, J.A., Millikan, K.W., Saclarides, T.J., Eds.; Hypoxemia and Hypoxia. Springer New York: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 391–394. [Google Scholar]
- American Thoracic Society. ATS/ACCP Statement on cardiopulmonary exercise testing. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 167, 211–277. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premasiri, W.R.; Lee, J.C.; Ziegler, L.D. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering of whole human blood, blood plasma, and red blood cells: Cellular processes and bioanalytical sensing. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 9376–9386. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfbeis, O.S. Luminescent sensing and imaging of oxygen: Fierce competition to the Clark electrode. BioEssays 2015, 37, 921–928. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johny, V.; Chinmaya, K.V.; Nihal, C.V.M.; Kurian, V.; Rao, G.M.; Ghosh, M.; Ghosh, S. Towards Real-Time Oxygen Sensing: From Nanomaterials to Plasma. Front. Sens. 2022, 2, 826403. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Zhu, S.; Feng, T.; Yang, M.; Yang, B. Evolution and Synthesis of Carbon Dots: From Carbon Dots to Carbonized Polymer Dots. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1901316. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elugoke, S.E.; Uwaya, G.E.; Quadri, T.W.; Ebenso, E.E. Carbon Quantum Dots: Basics, Properties, and Fundamentals. In Carbon Dots: Recent Developments and Future Perspectives; Chapter 1; ACS Symposium Series, No. 1465; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2024; Volume 1465, pp. 3–42. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.Y.; Tan, J.K.S.; Mo, X.; Song, Y.; Lim, J.; Liew, X.R.; Chung, H.; Kim, S. Carbon Quantum Dots with Tunable Size and Fluorescence Intensity for Development of a Nano-biosensor. Small 2025, 21, e2404524. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briely-Sabo, K.; Bjornerud, A. Accurate de-oxygenation of ex vivo whole blood using sodium Dithionite. Proc. Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med. 2000, 8, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, F.; Alayash, A.I. Determination of extinction coefficients of human hemoglobin in various redox states. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 521, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benesch, R.E.; Benesch, R.; Yung, S. Equations for the spectrophotometric analysis of hemoglobin mixtures. Anal. Biochem. 1973, 55, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winterbourn, C.C. Oxidative reactions of hemoglobin. Methods Enzymol. 1990, 186, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, T.J. The oxyhaemoglobin dissociation curve in critical illness. Crit. Care Resusc. 1999, 1, 93–100. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prahl, S. Tabulated Molar Extinction Coefficient for Hemoglobin in Water; Oregon Medical Laser Center: Portland, OR, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, M.P.; Siu, V.; Silva-Garcia, A.; Xu, Q.; Li, Z.; Oksenberg, D. Development and validation of an oxygen dissociation assay, a screening platform for discovering, and characterizing hemoglobin-oxygen affinity modifiers. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2018, 12, 1599–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, D.; Patil, S.M.; Zubair, M.; Keenaghan, M. Arterial Blood Gas. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, E.D.; Chan, M.M.; Chan, M.M. Pulse oximetry: Understanding its basic principles facilitates appreciation of its limitations. Respir. Med. 2013, 107, 789–799. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, E.A.; Verma, G.; Arafat, Y.; Acharya, S.; Kumar, S.; Pantbalekundri, N. Comparative Analysis of Oxygen Saturation by Pulse Oximetry and Arterial Blood Gas in Hypoxemic Patients in a Tertiary Care Hospital. Cureus 2023, 15, e42447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, P.; Blatt, S.; Pabst, A.; Heimes, D.; Al-Nawas, B.; Kammerer, P.W.; Thiem, D.G.E. Comparison of Hyperspectral Imaging and Microvascular Doppler for Perfusion Monitoring of Free Flaps in an In Vivo Rodent Model. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calin, M.A.; Boiangiu, I.C.; Parasca, S.V.; Miclos, S.; Savastru, D.; Manea, D. Blood oxygenation monitoring using hyperspectral imaging after flap surgery. Spectrosc. Lett. 2017, 50, 150–155. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicher, C.; Rutkowski, R.; Lutze, S.; von Podewils, S.; Wild, T.; Kretching, M.; Daeschlein, G. Hyperspectral imaging as a possible tool for visualization of changes in hemoglobin oxygenation in patients with deficient hemodynamics—Proof of concept. Biomed. Eng./Biomed. Tech. 2018, 63, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J. Hyperspectral imaging for non-invasive blood oxygen saturation assessment. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2024, 45, 104003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serianni, R.; Barash, J.; Bentley, T.; Sharma, P.; Fontana, J.L.; Via, D.; Duhm, J.; Bunger, R.; Mongan, P.D. Porcine-specific hemoglobin saturation measurements. J. Appl. Physiol. 2003, 94, 561–566. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guensch, D.P.; Michel, M.C.; Huettenmoser, S.P.; Jung, B.; Gulac, P.; Segiser, A.; Longnus, S.L.; Fischer, K. The blood oxygen level dependent (BOLD) effect of in-vitro myoglobin and hemoglobin. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid, M.A.; Ullah, H.; Alshehri, A.M.; Tabassum, R.; Aleem, A.; Khan, A.R.; Batool, Z.; Nazir, A.; Bibi, I. Development of novel polymer haemoglobin based particles as an antioxidant, antibacterial and an oxygen carrier agents. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzfeld, J.; Seidel, N.E.; Taylor, M.P.; Droupadi, P.R.; Wang, N.E. Gentle Chemical Deoxygenation of Hemoglobin Solutions. Hemoglobin 1990, 14, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, I.S.; Belcher, D.A.; Palmer, A.F. Quantification of Active Apohemoglobin Heme-Binding Sites via Dicyanohemin Incorporation. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 5245–5259. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, K.; Okazaki, T.; Shukuya, R.; Kaziro, K. The deoxygenation of dilute oxyhemoglobin by sodium dithionite. J. Biochem. 1962, 52, 374–376. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, H.K.; Hall, W.D.; Hurst, J.W. Clinical Methods: The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations, (In English), 3rd ed.; Butterworths: Boston, MA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Nitzan, M.; Nitzan, I.; Arieli, Y. The Various Oximetric Techniques Used for the Evaluation of Blood Oxygenation. Sensors 2020, 20, 4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Tang, Y.; Yao, J. Photoacoustic tomography of blood oxygenation: A mini review. Photoacoustics 2018, 10, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.; Liew, X.R.; Tan, J.K.S.; Kim, S. A Novel Nano-Scale Biosensor for Measuring Hemoglobin Oxygen Saturation Using Carbon Quantum Dots. Micromachines 2025, 16, 1261. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16111261
Lee J, Liew XR, Tan JKS, Kim S. A Novel Nano-Scale Biosensor for Measuring Hemoglobin Oxygen Saturation Using Carbon Quantum Dots. Micromachines. 2025; 16(11):1261. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16111261
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jeehyun, Xuan Ru Liew, Justin Kok Soon Tan, and Sangho Kim. 2025. "A Novel Nano-Scale Biosensor for Measuring Hemoglobin Oxygen Saturation Using Carbon Quantum Dots" Micromachines 16, no. 11: 1261. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16111261
APA StyleLee, J., Liew, X. R., Tan, J. K. S., & Kim, S. (2025). A Novel Nano-Scale Biosensor for Measuring Hemoglobin Oxygen Saturation Using Carbon Quantum Dots. Micromachines, 16(11), 1261. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16111261





