3D-Printed Microneedles with Controlled Structures for Drug Delivery Study in an Ex Vivo Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Microneedle Fabrication
2.2.1. Microneedle with Simple Structure
2.2.2. Microneedle with Channel Structures
2.3. Mechanical Testing of Microneedle Arrays in Ex Vivo Model
2.4. Cargo Release from Microneedles in Ex Vivo Model
3. Results
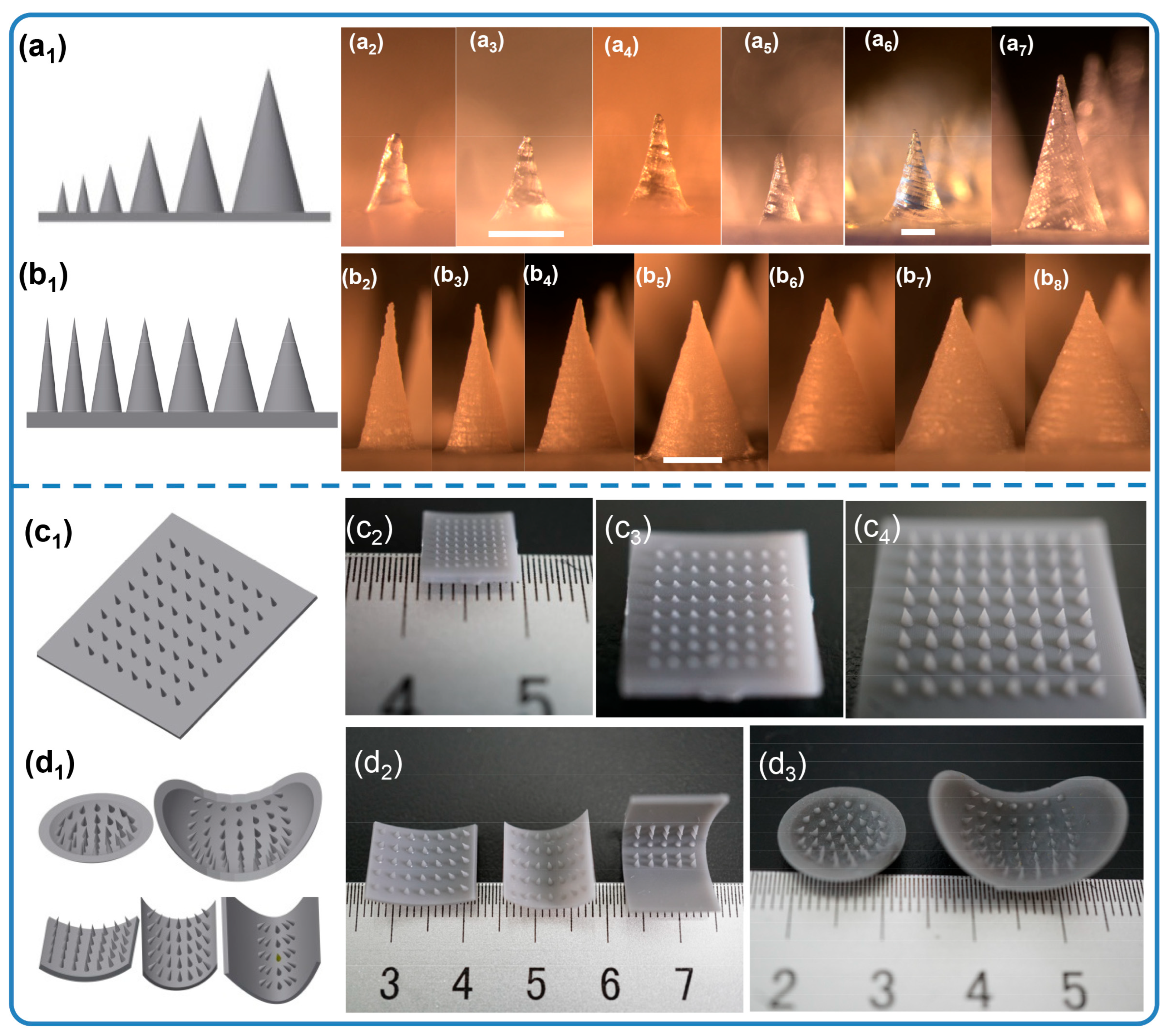
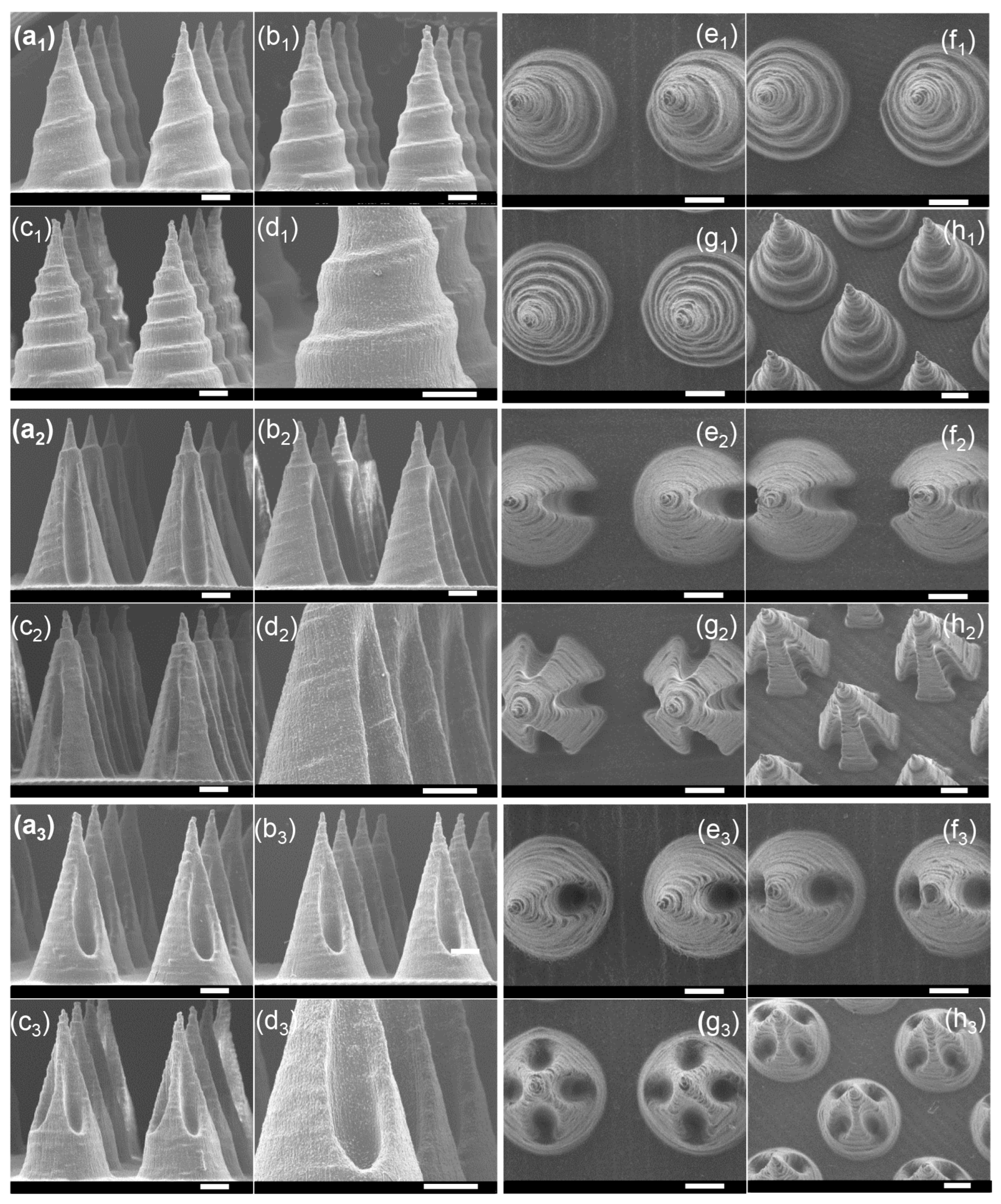
3.1. Microneedle Arrays Fabricated via Stereolithography Printing
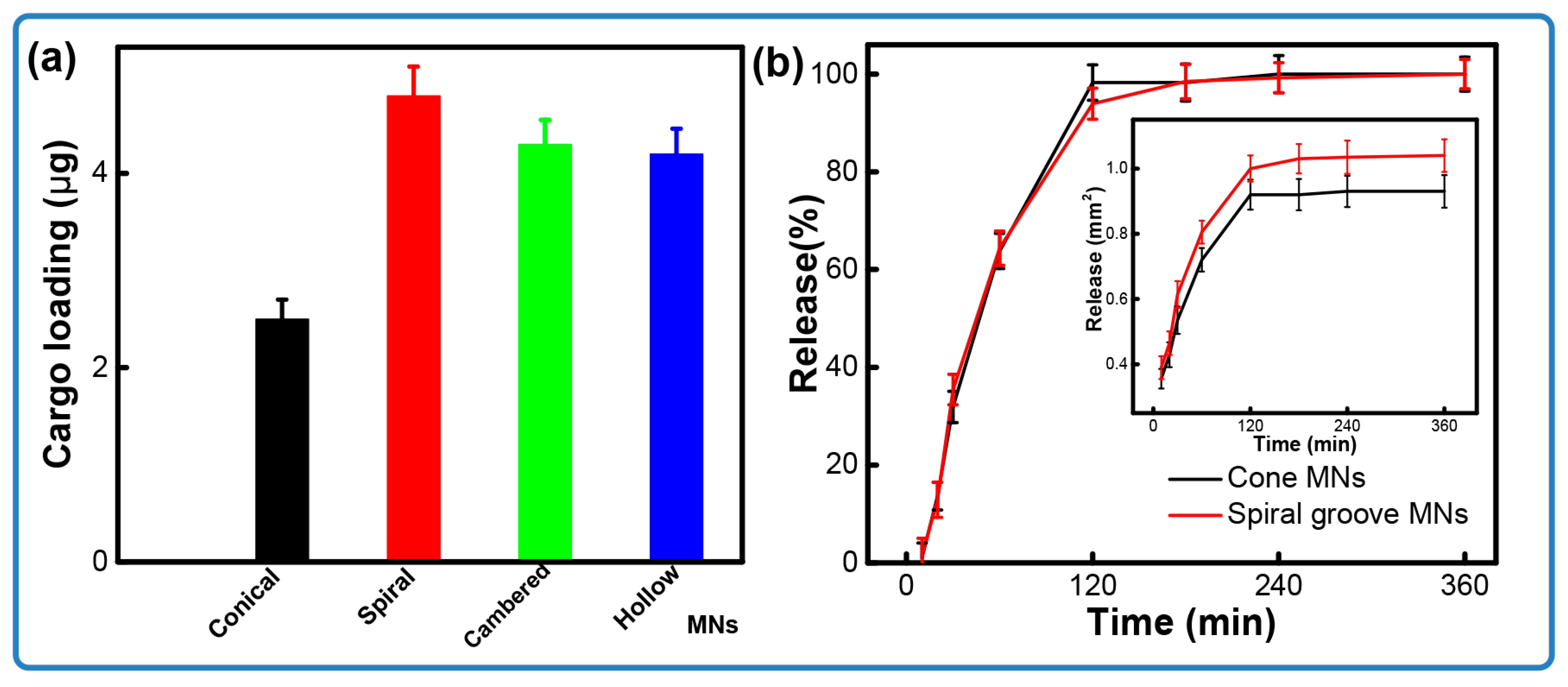
3.2. Mechanical Testing of Microneedle Arrays in Ex Vivo Model
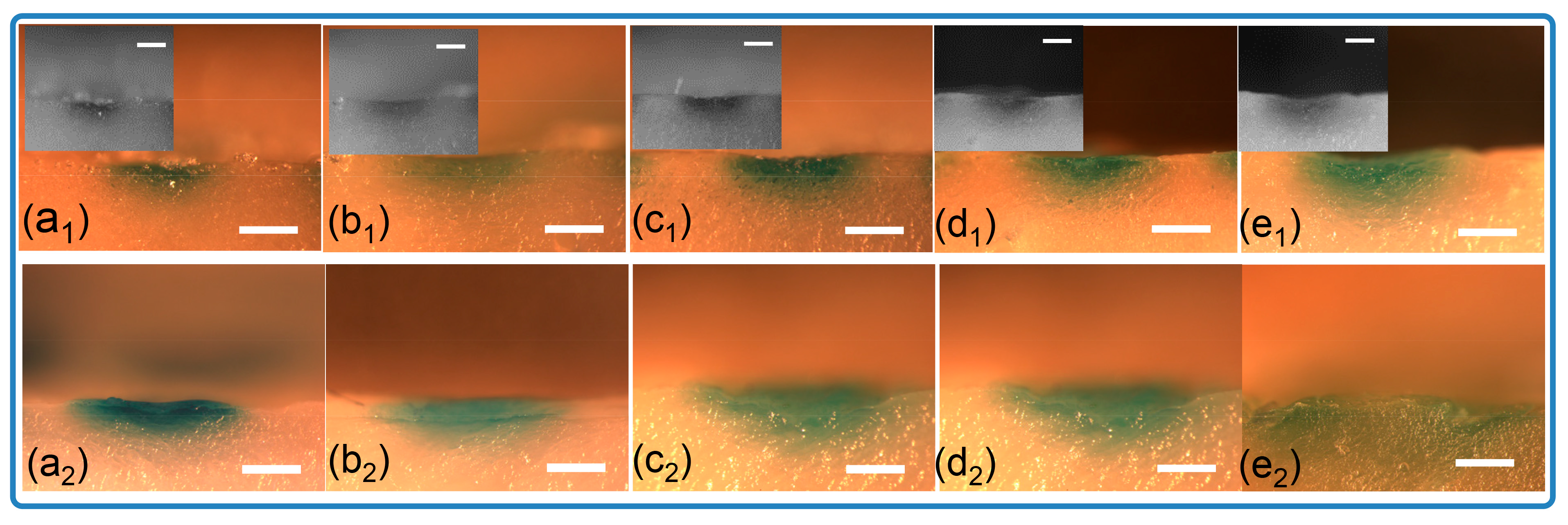
3.3. Cargo Release from Microneedles in Ex Vivo Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nestle, F.O.; Di Meglio, P.; Qin, J.-Z.; Nickoloff, B.J. Skin immune sentinels in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 679–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Liao, X.; Chen, D.; Jia, X.; Niu, X. Microneedles for non-transdermal drug delivery: Design strategies and current applications. Bio-Des. Manuf. 2025, 8, 243–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, A.; Baliga, V.; Shenoy, R.; Dessai, A.D.; Nayak, U.Y. 3D printed microneedles: Revamping transdermal drug delivery systems. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2025, 15, 436–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razzaghi, M.; Ninan, J.A.; Azimzadeh, M.; Askari, E.; Najafabadi, A.H.; Khademhosseini, A.; Akbari, M. Remote-Controlled Sensing and Drug Delivery via 3D-Printed Hollow Microneedles. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 13, 2400881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, M.R.; Vishwas, S.; Khursheed, R.; Harish, V.; Sravani, A.B.; Khan, F.; Alotaibi, B.; Binshaya, A.; Disouza, J.; Kumbhar, P.S.; et al. Unravelling the role of microneedles in drug delivery: Principle, perspectives, and practices. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2024, 14, 1393–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, B.H.; Wu, F.G. Hydrogel-based growth factor delivery platforms: Strategies and recent advances. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2210707. [Google Scholar]
- Walvekar, P.; Lulinski, P.; Kumar, P.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; Choonara, Y.E. A review of hyaluronic acid-based therapeutics for the treatment and management of arthritis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 264, 130645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugam, S.; Tade, R.; Dhole, R.; Nangare, S. Emerging era of microneedle array for pharmaceutical and biomedical applications: Recent advances and toxicological perspectives. Future J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacob, A.T.; Lupascu, F.G.; Apotrosoaei, M.; Vasincu, I.M.; Tauser, R.G.; Lupascu, D.; Giusca, S.E.; Caruntu, I.-D.; Profire, L. Recent biomedical approaches for chitosan based materials as drug delivery nanocarriers. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, S.; Dong, Z.; Xu, X.; Bei, H.-P.; Yuen, H.-Y.; Cheung, C.-W.J.; Wong, M.-S.; He, Y.; Zhao, X. Going below and beyond the surface: Microneedle structure, materials, drugs, fabrication, and applications for wound healing and tissue regeneration. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 27, 303–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Yang, L.; Cui, Y. Microneedles: Materials, fabrication, and biomedical applications. Biomed. Microdevices 2023, 25, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, R.Z.; Prewett, P.D.; Davies, G.J. High-resolution two-photon polymerization: The most versatile technique for the fabrication of microneedle arrays. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2021, 7, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, M.; Zhan, F.; Qiu, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, X.; Bu, P.; Zhou, B.; Serda, M.; Feng, Q. Research Progress of Hydrogel Microneedles in Wound Management, ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2024, 10, 4771–4790. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Dong, K.; Wei, M. Rolling stone gathers moss: Rolling microneedles generate meta microfluidic microneedles. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2316565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.X.; Kipping, T.; Banga, A.K. Enhancement of Transdermal Drug Delivery: Integrating Microneedles with Biodegradable Microparticles. Mol. Pharm. 2025, 2, 984–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.A.; Dhondale, M.R.; Agrawal, A.K.; Serrano, D.R.; Mishra, B.; Kumar, D. Advancements in microneedle fabrication techniques: Artificial intelligence assisted 3D-printing technology. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2024, 14, 1458–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lijnse, T.; Mendes, M.; Shu, W.; O’Cearbhaill, E.D. Low-cost fabrication of digital light processing 3D printed conical microneedles for biomedical applications. Appl. Mater. Today 2024, 41, 102482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pere, C.P.P.; Economidou, S.N.; Lall, G.; Ziraud, C.; Boateng, J.S.; Alexander, B.D.; Lamprou, D.A.; Douroumis, D. 3D printed microneedles for insulin skin delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 544, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzuriaga, M.A.; Berry, D.R.; Reagan, J.C.; Smaldone, R.A.; Gassensmith, J.J. Biodegradable 3D printed polymer microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 1223–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.H.; Ng, J.Y.; Kang, L. Three-dimensional printing of a microneedle array on personalized curved surfaces for dual-pronged treatment of trigger finger. Biofabrication 2017, 9, 015010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parhi, R. Recent advances in 3D printed microneedles and their skin delivery application in the treatment of various diseases. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 84, 104395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawre, S.; Suryavanshi, P.; Lalchandani, D.S.; Deka, M.K.; Porwal, P.K.; Kaity, S.; Roy, S.; Banerjee, S. Bioinspired labrum-shaped stereolithography (SLA) assisted 3D printed hollow microneedles (HMNs) for effectual delivery of ceftriaxone sodium. Eur. Polym. J. 2024, 204, 112702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Warner, K.S.; Zhang, J. Evaluation needle length and density of microneedle arrays in the pretreatment of skin for transdermal drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 391, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badnikar, K.; Jayadevi, S.N.; Pahal, S.; Vemula, P.K.; Nayak, M.M.; Subramanyam, D.N. Microscale engineering of hollow microneedle tips: Design, manufacturing, optimization and validation. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022, 12, 350–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detamornrat, U.; McAlister, E.; Hutton, A.R.J.; Larrañeta, E.; Donnelly, R.F. The role of 3D printing technology in microengineering of microneedles. Small 2022, 18, 2106392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, J.M.; Lim, Y.J.L.; Tay, J.T.; Cheng, H.M.; Tey, H.L.; Liang, K. Design and fabrication of customizable microneedles enabled by 3D printing for biomedical applications. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 32, 222–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahlabadi, M.; Hutapea, P. Novel design of honeybee-inspired needles for percutaneous procedure. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2018, 13, 036013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, J.; Scoutaris, N.; Klepetsanis, P.; Chowdhry, B.; Prausnitz, M.R.; Douroumis, D. Inkjet printing of transdermal microneedles for the delivery of anticancer agents. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 494, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economidou, S.N.; Pere, C.P.P.; Reid, A.; Uddin, J.; Windmill, J.F.; Lamprou, D.A.; Douroumis, D. 3D printed microneedle patches using stereolithography (SLA) for intradermal insulin delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 102, 743–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, S.; Scoutaris, N. Lamprou, Inkjet printing of insulin microneedles for transdermal delivery. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2015, 5, 451–461. [Google Scholar]
- Pailler-Mattei, C.; Bec, S.; Zahouani, H. In vivo measurements of the elastic mechanical properties of human skin by indentation tests. Med. Eng. Phys. 2008, 30, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagi, S.; Marshall, A.; Makdani, A. An ultrafast system for signaling mechanical pain in human skin. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, D.; Yang, W.; Song, X.; Liu, F. 3D-Printed Microneedles with Controlled Structures for Drug Delivery Study in an Ex Vivo Model. Micromachines 2025, 16, 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16111249
Wei D, Yang W, Song X, Liu F. 3D-Printed Microneedles with Controlled Structures for Drug Delivery Study in an Ex Vivo Model. Micromachines. 2025; 16(11):1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16111249
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Dong, Weixiong Yang, Xiang Song, and Fu Liu. 2025. "3D-Printed Microneedles with Controlled Structures for Drug Delivery Study in an Ex Vivo Model" Micromachines 16, no. 11: 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16111249
APA StyleWei, D., Yang, W., Song, X., & Liu, F. (2025). 3D-Printed Microneedles with Controlled Structures for Drug Delivery Study in an Ex Vivo Model. Micromachines, 16(11), 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16111249






