Modular Flow Synthesis of Citric Acid-Coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Preliminary Results
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
- −
- Iron(II) chloride, tetrahydrate, 98%,
- −
- Iron(III) chloride,
- −
- Sodium hydroxide,
- −
- Hydochloric acid, 37%,
- −
- CA,
- −
- Purified water,
- −
- Absolute ethanol (CH3CH2OH).
- (i)
- 3 M NaOH solution,
- (ii)
- Iron salt precursor solution (ISPS) that contained 366 mg FeCl2·4H2O and 566 mg FeCl3 in 36 mL 1 M HCl,
- (iii)
- 1 M CA.
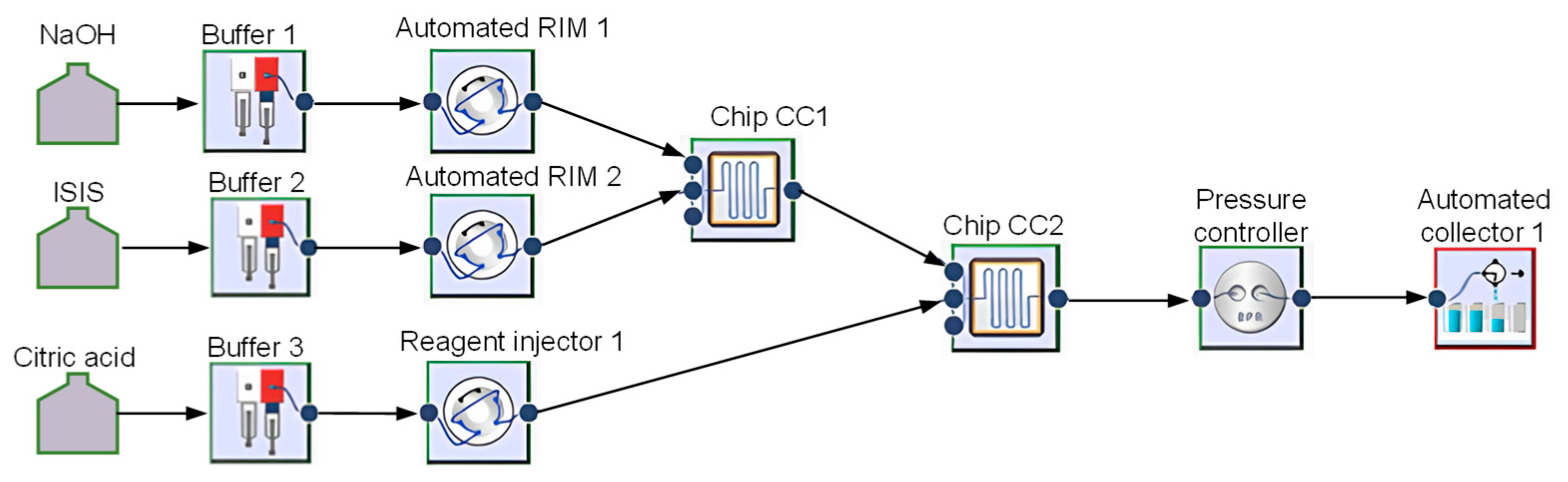
2.2. Modular Flow Microreactor System Setup
- −
- Asia pump,
- −
- Asia Automated RIM,
- −
- Chip reactor 250 µL and 1 mL,
- −
- Back pressure controller,
- −
- Automated collector.
2.3. Experimental Setup
2.4. Analysis/Characterization of Fe3O4@CA
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. X-Ray Powder Diffraction
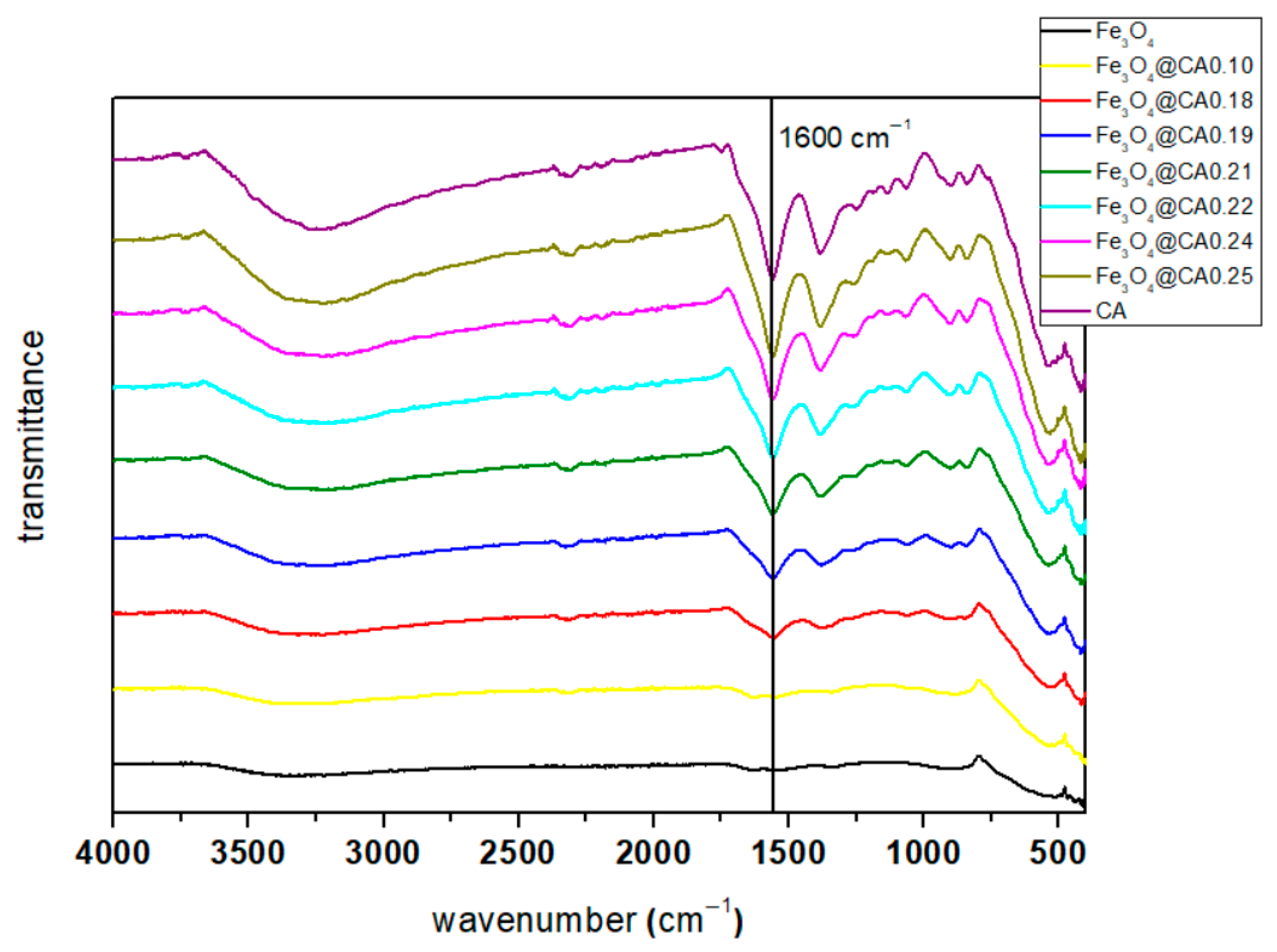
3.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
3.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis
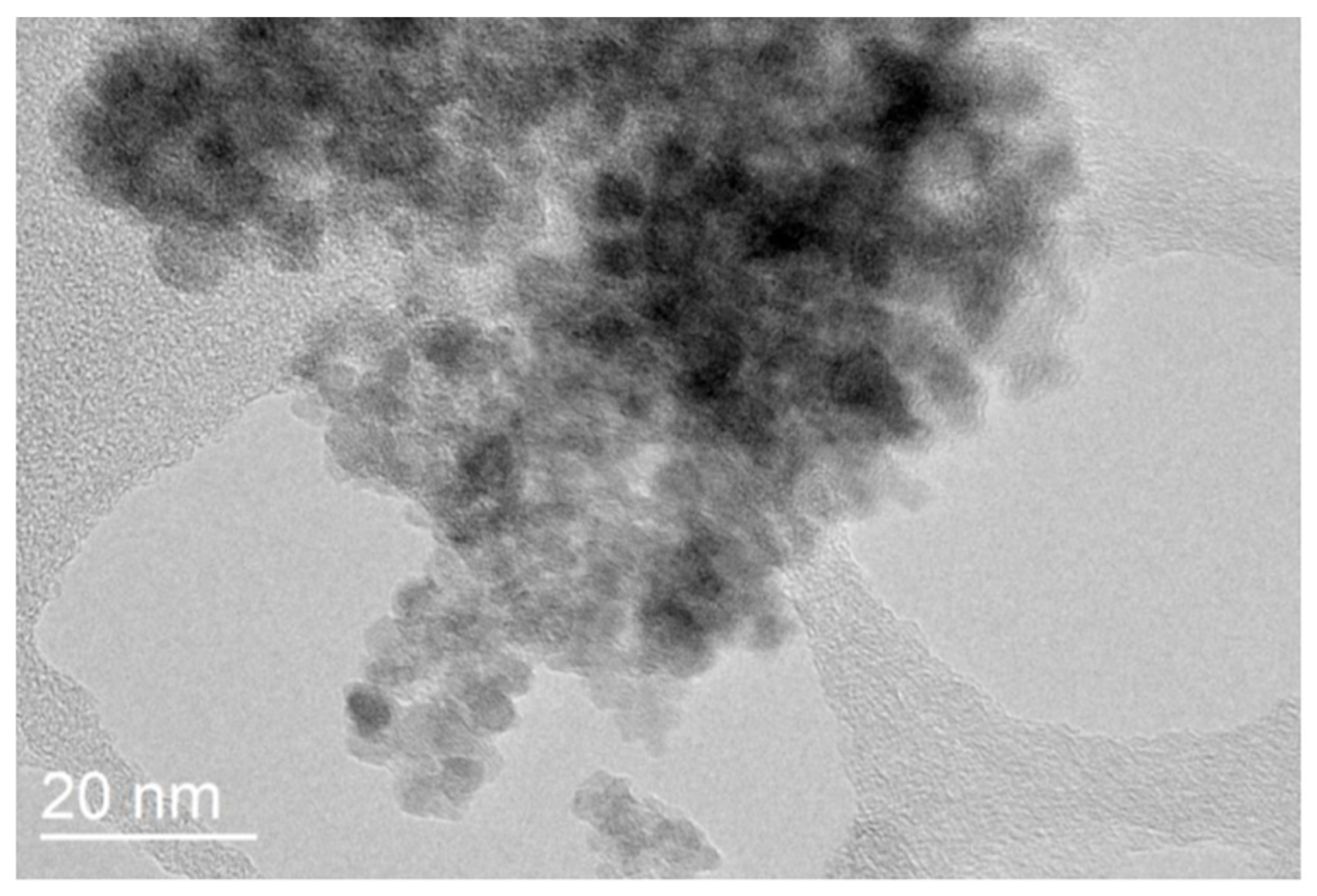
3.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy
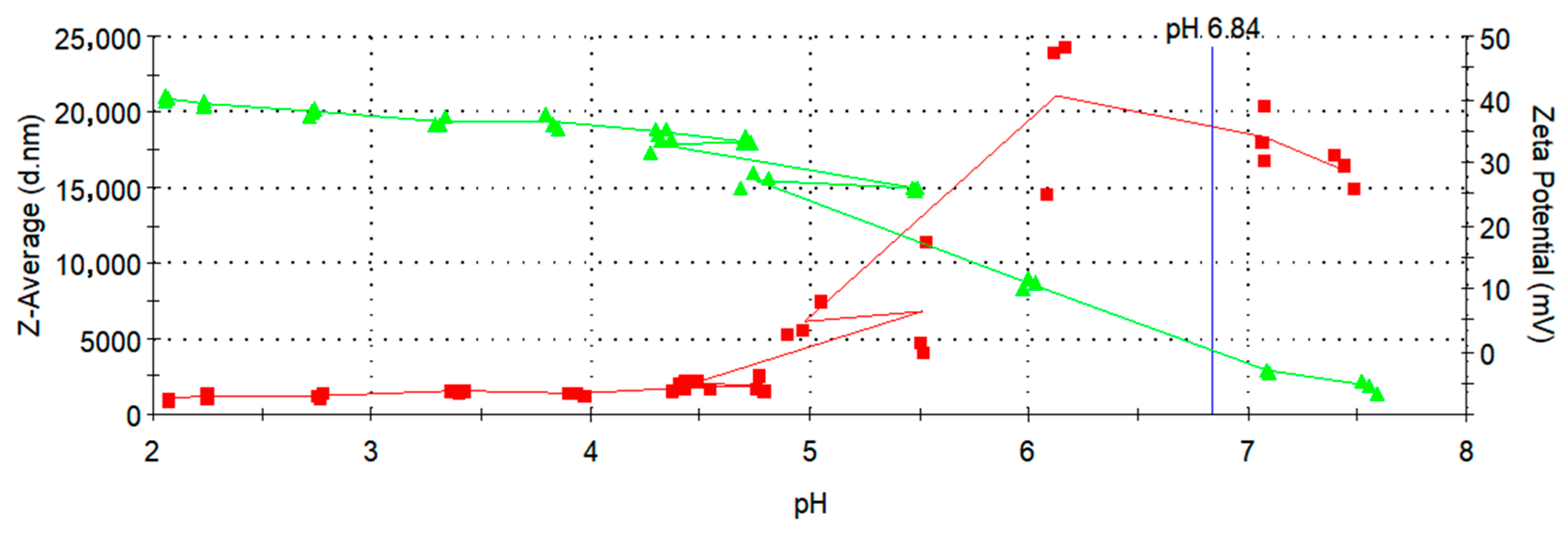
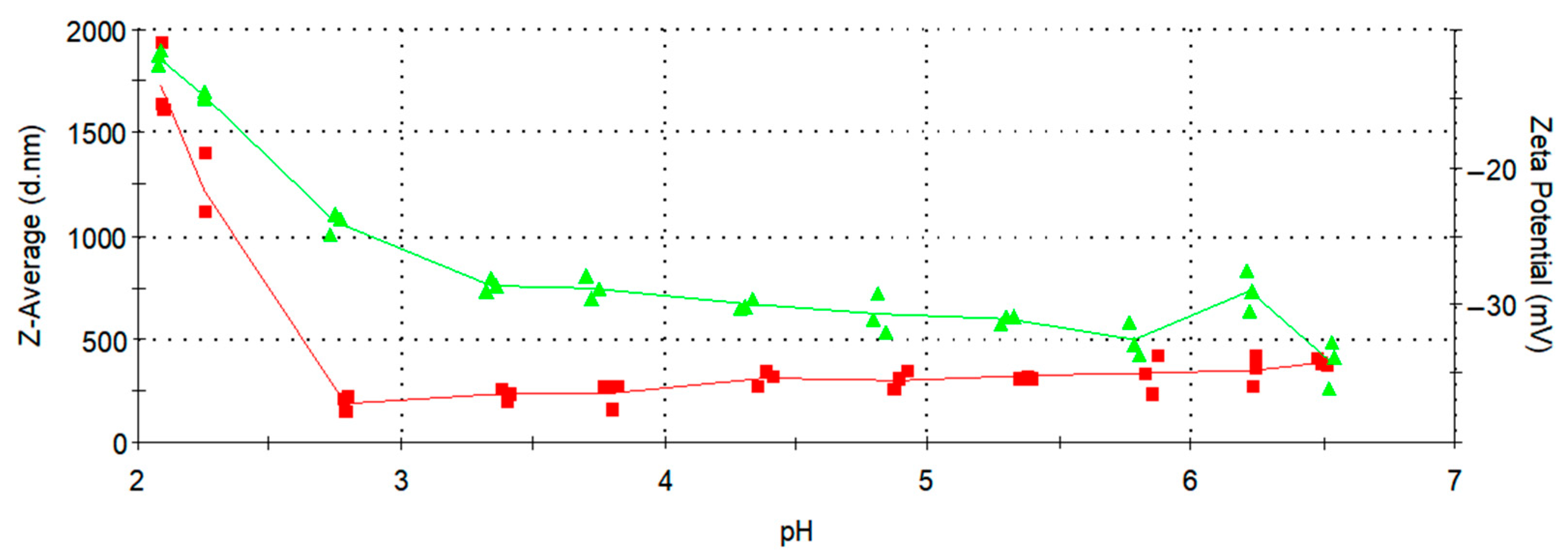
3.5. Zeta Potential Measurements
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CA | Citric acid |
| DLS | Dynamic light scattering |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| IEP | Isoeletric point |
| ISPS | Iron salt precursor solution |
| MH | Magnetic hyperthermia |
| MNPs | Magnetic nanoparticles |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| SPION | Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| TGA | Thermogravimetric analysis |
| XRD | X-ray powder diffraction |
References
- Dias, A.M.M.; Courteau, A.; Bellaye, P.-S.; Kohli, E.; Oudot, A.; Doulain, P.-E.; Petitot, C.; Walker, P.-M.; Decréau, R.; Collin, B. Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Immunotherapy of Cancers Through Macrophages and Magnetic Hyperthermia. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Hu, Y.; Wang, J.; Gao, X.; Qian, X.; Tang, M. Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Cytotoxicity, Metabolism, and Cellular Behavior in Biomedicine Applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 6097–6113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, P.M.; Lima, A.C.; Ribeiro, S.; Lanceros-Mendez, S.; Martins, P. Magnetic Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications: From the Soul of the Earth to the Deep History of Ourselves. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 5839–5870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Roy, I.; Gandhi, S. Magnetic Nanoparticles: An Overview for Biomedical Applications. Magnetochemistry 2022, 8, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rümenapp, C.; Gleich, B.; Haase, A. Magnetic Nanoparticles in Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Diagnostics. Pharm. Res. 2012, 29, 1165–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avasthi, A.; Caro, C.; Pozo-Torres, E.; Leal, M.P.; García-Martín, M.L. Magnetic Nanoparticles as MRI Contrast Agents. Top. Curr. Chem. 2020, 378, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caspani, S.; Magalhães, R.; Araújo, J.P.; Sousa, C.T. Magnetic Nanomaterials as Contrast Agents for MRI. Materials 2020, 13, 2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.L. 9-Magnetic nanoparticles as contrast agents in magnetic resonance imaging and radiosensitizers in radiotherapy. In Fundamentals and Industrial Applications of Magnetic Nanoparticles; Hussain, C.M., Patankar, K.K., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2022; pp. 291–316. [Google Scholar]
- Neuberger, T.; Schöpf, B.; Hofmann, H.; Hofmann, M.; von Rechenberg, B. Superparamagnetic nanoparticles for biomedical applications: Possibilities and limitations of a new drug delivery system. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 293, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, D.; Kandasamy, G. Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles for Cancer Hyperthermia Treatment. In Nanotechnology Characterization Tools for Tissue Engineering and Medical Therapy; Kumar, C.S.S.R., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 299–332. [Google Scholar]
- Fatima, H.; Charinpanitkul, T.; Kim, K.-S. Fundamentals to Apply Magnetic Nanoparticles for Hyperthermia Therapy. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, I. Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedical separation and purification. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2016, 5, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, A.; Xue, J.; Deb, S. Magnetic Nanoparticles in Bone Tissue Engineering. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, T.; Wang, H.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Fan, D.; Wang, X. Recent Advances of Magnetic Nanomaterials in Bone Tissue Repair. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- kianfar, E. Magnetic Nanoparticles in Targeted Drug Delivery: A Review. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2021, 34, 1709–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.F.; Jang, B.; Issadore, D.; Tsourkas, A. Use of magnetic fields and nanoparticles to trigger drug release and improve tumor targeting. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 11, e1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhong, X.; Wang, L.; Yang, L.; Mao, H. Improving the magnetic resonance imaging contrast and detection methods with engineered magnetic nanoparticles. Theranostics 2012, 2, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulińska-Litewka, J.; Łazarczyk, A.; Hałubiec, P.; Szafrański, O.; Karnas, K.; Karewicz, A. Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles—Current and Prospective Medical Applications. Materials 2019, 12, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritika; Roy, I. Therapeutic applications of magnetic nanoparticles: Recent advances. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 7425–7444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, G.; Hapuarachchige, S.; Artemov, D. Ultrasmall Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as Nanocarriers for Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Development and In Vivo Characterization. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 9625–9632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Shah, T.; Ullah, R.; Zhou, P.; Guo, M.; Ovais, M.; Tan, Z.; Rui, Y. Review on Recent Progress in Magnetic Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Diverse Applications. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 629054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiufiuc, G.F.; Stiufiuc, R.I. Magnetic Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Their Use in Biomedical Field. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dheyab, M.A.; Aziz, A.A.; Jameel, M.S.; Abu Noqta, O.; Khaniabadi, P.M.; Mehrdel, B. Simple rapid stabilization method through citric acid modification for magnetite nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikelashvili, V.; Kekutia, S.; Markhulia, J.; Saneblidze, L.; Maisuradze, N.; Kriechbaum, M.; Almásy, L. Synthesis and Characterization of Citric Acid-Modified Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Prepared with Electrohydraulic Discharge Treatment. Materials 2023, 16, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieciecka, D.; Rękorajska, A.; Cichy, D.; Końska, P.; Żuk, M.; Krysiński, P. Synthesis and Characterization of Magnetic Drug Carriers Modified with Tb(3+) Ions. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, T.; Liang, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Qiang, J.; Yuan, S. Investigation of geometric modifications in T-type micromixers for enhanced microfluidic mixing and ZIF-8 synthesis. Results Eng. 2025, 26, 105233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Shi, H.; Zheng, Y.; Cao, Y. A 3D homogeneous microreactor with high mixing intensity at wide Re range for MOF preparation and POCT application. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 476, 146481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Miyahara, M.T. Synthesis of Functional Nanoparticles Using a Microreactor. KONA Powder Part J. 2025, 42, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, L.; Gomez, L.; Irusta, S.; Arruebo, M.; Santamaria, J. Comparative study of the synthesis of silica nanoparticles in micromixer–microreactor and batch reactor systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 171, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.Y.; Bu, Z.Q.; Lei, Y.Q.; Wang, D.; He, B.; Wang, J.; Huang, W.T. Facile microwave-assisted synthesis of Sb2O3-CuO nanocomposites for catalytic degradation of p-nitrophenol. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 409, 125503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Xiao, L.; Ling, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhong, S. Preparation of artificial substrate binding sites of nanozyme with “modular structure” strategy used for the construction of visual sensing analysis platform for levodopa. Microchem. J. 2025, 212, 113292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Dai, C.; Hu, Y. Aqueous aggregation behavior of citric acid coated magnetite nanoparticles: Effects of pH, cations, anions, and humic acid. Environ. Res. 2018, 161, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzoubi, F.; Jabaly, A.; Noqta, A.; Al-Khateeb, H.M.; Alqadi, M.K.; Bououdina, M. Citric Acid Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as Contrast Agent for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Res. Sq. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Gautam, R.K.; Kumar, R.; Shukla, B.K.; Shankar, V.; Krishna, V. Citric acid coated magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and application in removal of Cd(II) ions from aqueous solution. J. Water Process Eng. 2014, 4, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajdú, A.; Tombácz, E.; Illés, E.; Bica, D.; Vékás, L. Magnetite nanoparticles stabilized under physiological conditions for biomedical application. In Colloids for Nano-and Biotechnology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Campelj, S.; Makovec, D.; Drofenik, M. Preparation and properties of water-based magnetic fluids. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2008, 20, 204101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boosz, P.; Pfister, F.; Stein, R.; Friedrich, B.; Fester, L.; Band, J.; Mühlberger, M.; Schreiber, E.; Lyer, S.; Dudziak, D.; et al. Citrate-Coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Enable a Stable Non-Spilling Loading of T Cells and Their Magnetic Accumulation. Cancers 2021, 13, 4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lattuada, M.; Hatton, T.A. Functionalization of monodisperse magnetic nanoparticles. Langmuir 2007, 23, 2158–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrinic, I.; Stergar, J.; Bukšek, H.; Drofenik, M.; Gyergyek, S.; Hélix-Nielsen, C.; Ban, I. Superparamagnetic Fe3O4@CA nanoparticles and their potential as draw solution agents in forward osmosis. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che Mohamed Hussein, S.N.; Amir, Z.; Jan, B.M.; Khalil, M.; Azizi, A. Colloidal Stability of CA, SDS and PVA Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (IONPs): Effect of Molar Ratio and Salinity. Polymers 2022, 14, 4787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estévez, M.; Cicuéndez, M.; Crespo, J.; Serrano-López, J.; Colilla, M.; Fernández-Acevedo, C.; Oroz-Mateo, T.; Rada-Leza, A.; González, B.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; et al. Large-scale production of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles by flame spray pyrolysis: In vitro biological evaluation for biomedical applications. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 650, 560–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Name of Sample | Amount of MNPs [mol] | Amount of CA [mol] |
|---|---|---|
| Fe3O4@CA0.10 | 1 | 0.10 |
| Fe3O4@CA0.18 | 1 | 0.18 |
| Fe3O4@CA0.19 | 1 | 0.19 |
| Fe3O4@CA0.21 | 1 | 0.21 |
| Fe3O4@CA0.22 | 1 | 0.22 |
| Fe3O4@CA0.24 | 1 | 0.24 |
| Fe3O4@CA0.25 | 1 | 0.25 |
| Sample | Mass Loss of CA (%) |
|---|---|
| Fe3O4@CA0.18 | 4.4 |
| Fe3O4@CA0.19 | 4.9 |
| Fe3O4@CA0.21 | 5.0 |
| Fe3O4@CA0.22 | 5.3 |
| Fe3O4@CA0.24 | 15.0 |
| Fe3O4@CA0.25 | 19.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vohl, S.; Nemet, A.; Stergar, J. Modular Flow Synthesis of Citric Acid-Coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Preliminary Results. Micromachines 2025, 16, 1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16111228
Vohl S, Nemet A, Stergar J. Modular Flow Synthesis of Citric Acid-Coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Preliminary Results. Micromachines. 2025; 16(11):1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16111228
Chicago/Turabian StyleVohl, Sabina, Andreja Nemet, and Janja Stergar. 2025. "Modular Flow Synthesis of Citric Acid-Coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Preliminary Results" Micromachines 16, no. 11: 1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16111228
APA StyleVohl, S., Nemet, A., & Stergar, J. (2025). Modular Flow Synthesis of Citric Acid-Coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Preliminary Results. Micromachines, 16(11), 1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16111228






