ELID Polishing of Glass Substrates Using a Grainless Iron-Bonded Wheel with Free Abrasive Particles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Polishing Principle of Grainless Iron Grinding Wheel
3. Experimental Equipment and Methods
4. Results and Discussion
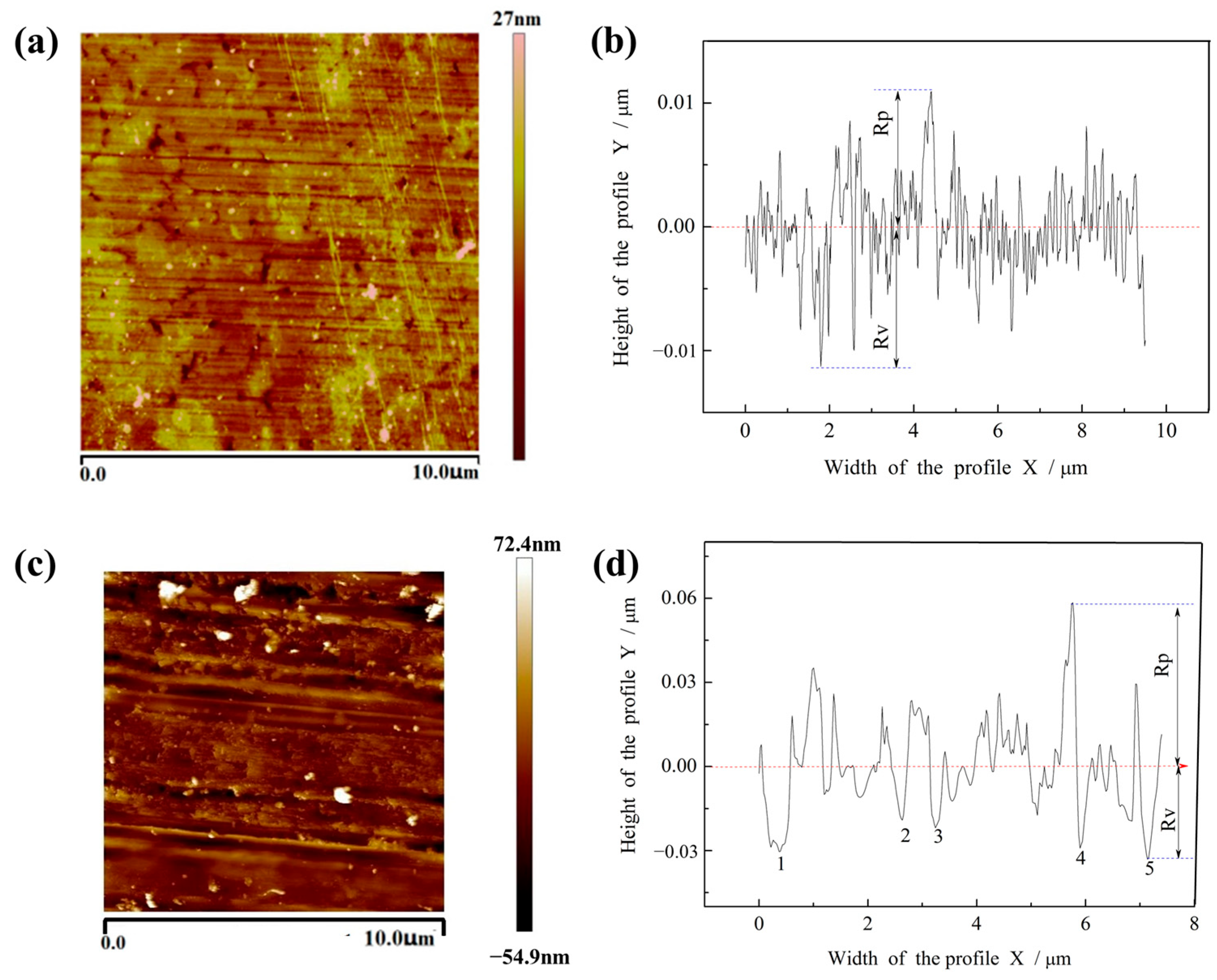
4.1. Polishing Surface Quality
4.2. Polishing Removal Rate
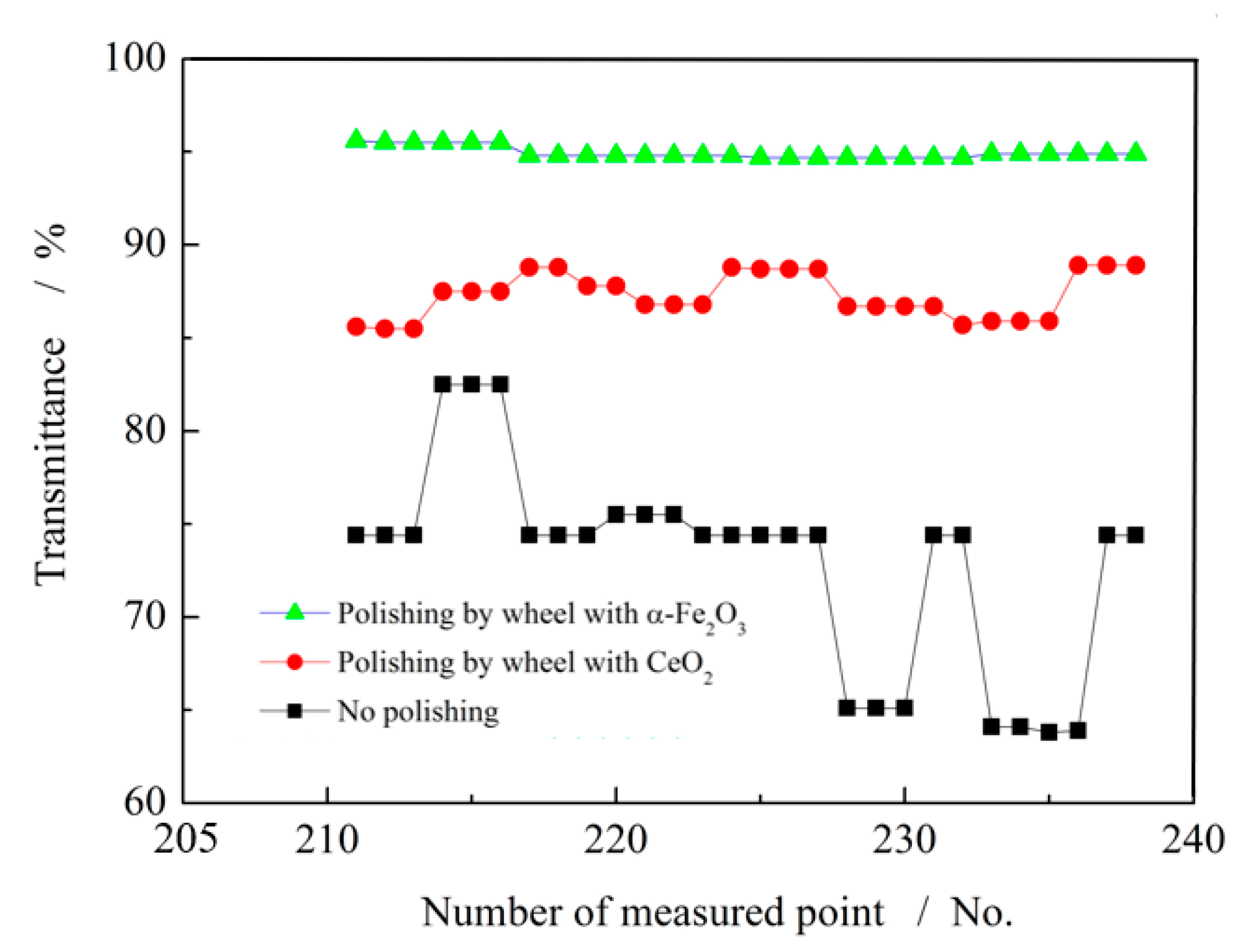
4.3. Optical Transmittance
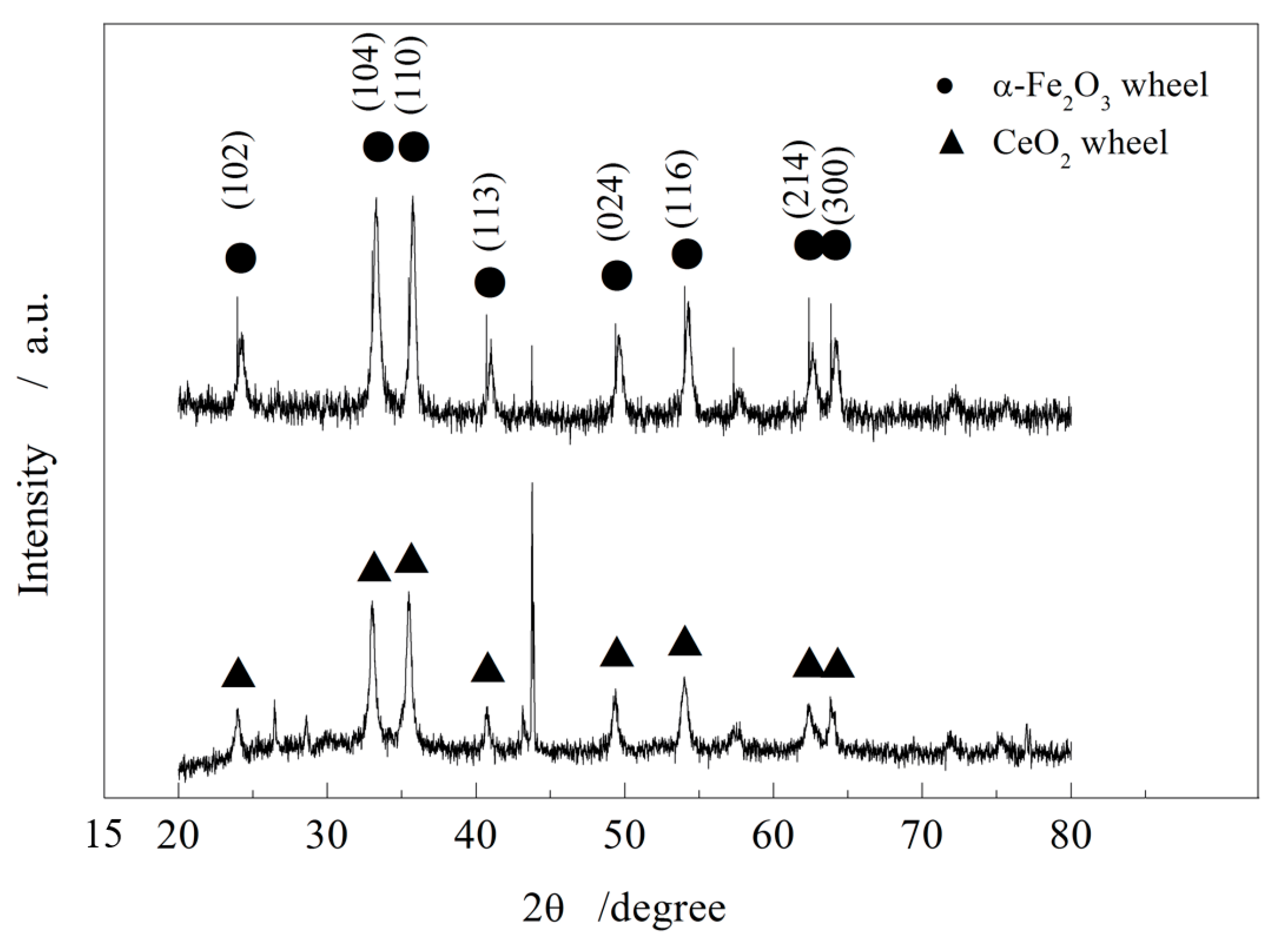
4.4. Thermal Effects and Oxide Film Transformation
4.5. Comparative Analysis of Abrasive Density and Oxide Film Composition
4.6. Analysis of Mechanical Properties of Grainless Iron-Based Grinding Wheel
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Polishing mechanism: High grinding temperatures during ELID electrolysis promote the transformation of iron oxides in the oxide film into α-Fe2O3 particles. The collaborative cutting action of these densely distributed nanoscale particles enables ultra-smooth surface accuracy.
- (2)
- Polishing efficiency: In super-fine polishing at low pressures, the process achieves high precision but low efficiency. With increasing polishing pressure, the material removal rate rises rapidly, reaching a maximum of 1.6 μm/min—nearly four times higher than that of the conventional CeO2 grinding wheel.
- (3)
- Surface quality: AFM analysis revealed that W0 achieves a surface roughness of Ra ≈ 2.1 nm, with no visible scratches or surface defects. This confirms the capability of W0 to produce ultra-precision surfaces.
- (4)
- Optical transmittance: After polishing with W0, glass substrates exhibited transmittance of 93–95%, approximately 5% higher than that obtained using CeO2 wheels. This improvement indicates superior potential for applications in display technologies, where enhanced image clarity and brightness are critical.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peng, S.; Qin, X.; Hong, W.; Wu, B.; Huang, Y. Development Strategy of Key Functional Glass Material System. Strateg. Study CAE 2024, 26, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, R. Application and Performance Requirements of Glass Substrates in Chip Packaging. Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2025, 44, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Min, J. Scratch control measures for TFT-LCD glass substrate. Glass 2023, 4, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zheng, C.; Wang, G.; Liang, B.; Zu, G. Analysis and Countermeasure of Grinding Scratch on the Convex Edge of TFT-LCD Glass. Glass 2025, 52, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C. Modeling and Simulation of Ultra-Precision Surface Grinding Scratch Formation. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, C.; Jing, L. Study on Surface Grinding Accuracy and Scratch Generation of Aluminum Alloy. Mech. Eng. 2016, 3, 222–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Liang, S.; Jiao, X.; Fan, Q.; Yin, J.; Zhu, J. Formation and control of scratches on optical components during polishing. Chin. J. Lasers 2019, 46, 1202009. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zheng, Z.; Peng, X.; Shi, F. Research on near-zero subsurface damage process of Magnetorheological polishing. Aeronaut. Precis. Manuf. Technol. 2010, 46, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wang, H.; Cheng, J.; Zhao, L.; Yang, H.; Liu, Q.; Tan, C.; Yin, Z.; Yang, Z.; Ding, W. Research progress on detection and suppression of subsurface Defects in fused Quartz optical Components. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2021, 57, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmori, H.; Kim, Y.J.; Uehara, Y.; Kasuga, H.; Ono-Kato, T.; Lin, W.M.; Kurokawa, S.; Umezu, S. Attempts on pico-precision machining via combination of ELID-grinding and polishing. J. Jpn. Soc. Precis. Eng. 2019, 85, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Kuai, J.; Ardashev, D.V. ELID Dressing Behaviors of Non-Abrasive Iron-Based Grinding Wheels. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, B.; Zhang, M.M.; Marinescu, I.; Bafakeeh, O.T.; Sofyani, S.A. Microscopic characterization and modeling of oxide layer for electrolytic in-process dressing (ELID) grinding with focus on voltage, electrode-wheel gap, and coolant flow. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 105, 4853–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.L.; Zhang, L.Y.; Liu, S.J.; Yang, Y. Research on ELID grinding mechanism and process parameter optimization of aluminum-based diamond composites for electronic packaging. Sci. Eng. Compos. Mater. 2019, 26, 550–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuai, J.C. Grinding point-temperature model of ELID oxide film and its heat transfer and formation mechanism of alpha-Fe2O3. Nanomater. Energy 2017, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuai, J.; Ardashev, D.V.; Zhang, H. Study of alpha-Fe2O3 formation and its measurement in oxide films of wheel surface during ELID grinding process. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2017, 31, 1750025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh Kumar, C.; Omkumar, M. Optimisation of Process Parameters of Chemical Mechanical Polishing of Soda Lime Glass. Silicon 2019, 11, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Karpuschewski, B.; Ohmori, H.; Riemer, O.; Wang, Y.; Dong, T. Adaptive shearing-gradient thickening polishing (AS-GTP) and subsurface damage inhibition. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2021, 160, 103651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wu, P.; Xie, M.; Li, Y.; Li, H. Research on High-Efficiency Rare Earth Polishing Slurry for CMP of Optical Glass. Lubr. Seal. 2019, 48, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeng, J.-H.; Kim, D.-H.; Park, S.-M.; Kim, H.-J. The effect of chemical treatment on the strength and transmittance of soda-lime cover glass for mobile. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2014, 15, 1779–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.B.; Komanduri, R. On the mechanics of the grinding process, Part II—Thermal analysis of fine grinding. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2004, 44, 247–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkin, S. Grinding Technology Theory and Application; Cai, G.; Gong, Y.; Song, G., Translators; Northeastern University Press: Shenyang, China, 2022; ISBN 7-81054-776-3. [Google Scholar]
- Kuai, J.; Zhang, H. Research on Generation and Polishing Mechanisms of Nano Grain α-Fe2O3 in Precision Electrolytic in Process Dressing (ELID) Grinding; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuai, J.; Duan, Y.; Ardashev, D.V. Oxidation Film Interface Reaction and Composite particle Formation Mechanism of On-line Electrolytic Grinding Wheel. Opt. Precis. Eng. 2023, 31, 2975–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zboril, R.; Mashlan, M.; Petridis, D. Iron (III) Oxides from Thermal ProcessessSynthesis, Structural and Magnetic Properties, Mossbauer Spectroscopy Characterization, and Applications. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 969–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorescu, M.; Brand, R.A.; Mihaila-Tarabasanu, D.; Diamandescu, L. The crucial role of particle morphology in the magnetic properties of haematite. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 85, 5546–5548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krbata, M.; Ciger, R.; Kohutiar, M.; Eckert, M.; Barenyi, I.; Trembach, B.; Dubec, A.; Escherova, J.; Gavalec, M.; Beronská, N. Microstructural Changes and Determination of a Continuous Cooling Transformation (CCT) Diagram Using Dilatometric Analysis of M398 High-Alloy Tool Steel Produced by Microclean Powder Metallurgy. Materials 2023, 16, 4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, J.; Zhang, F. Study on Calculation Model of Spring Stiffness of Passive Film for ELID Grinding. Tool Eng. 2008, 42, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathima, K.; Rahman, M.; Senthil Kumar, A.; Lim, H. Modeling of ultraprecision ELID grinding. Trans. ASME J. Manu. Sci. Eng. 2007, 129, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
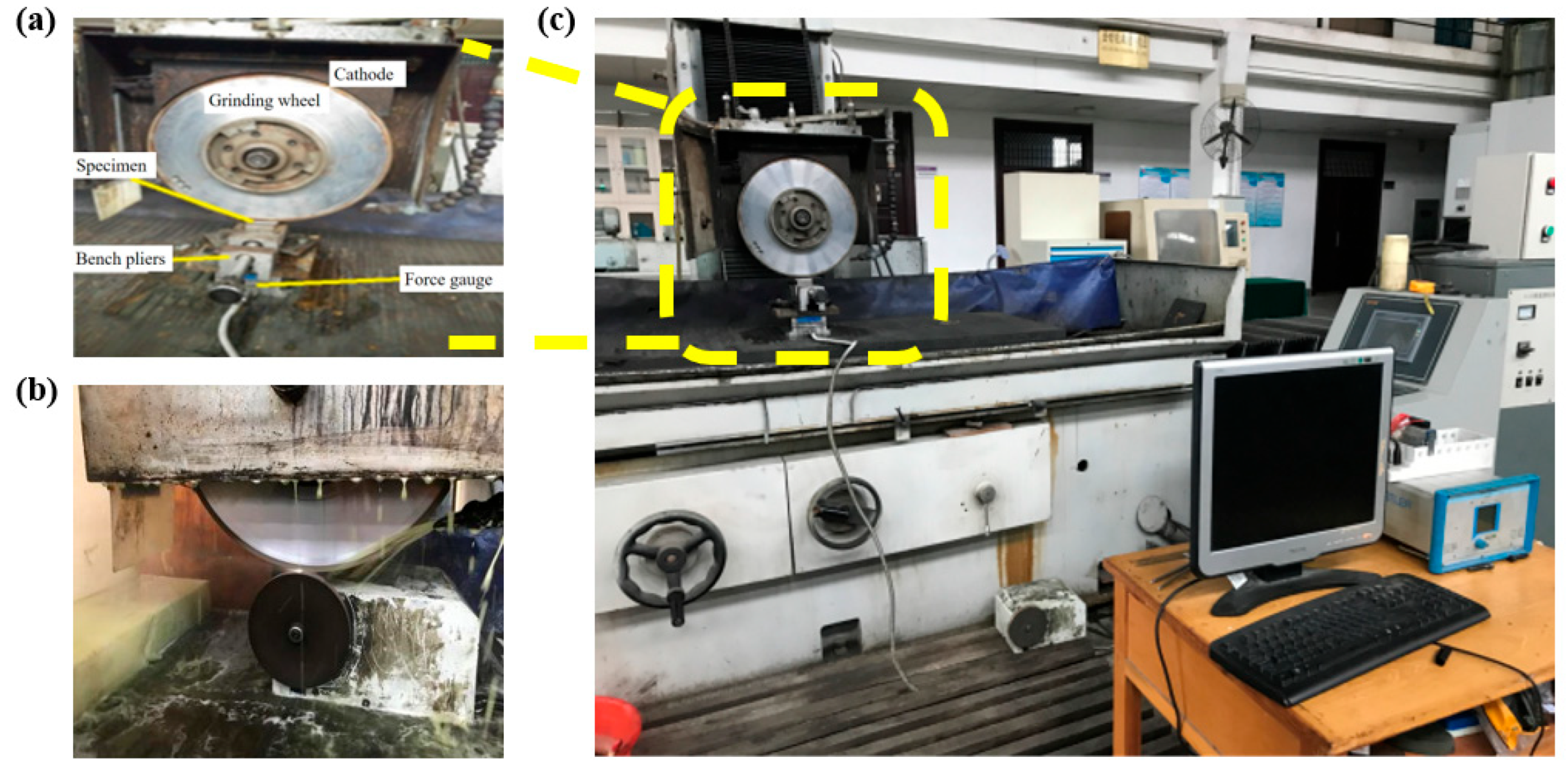


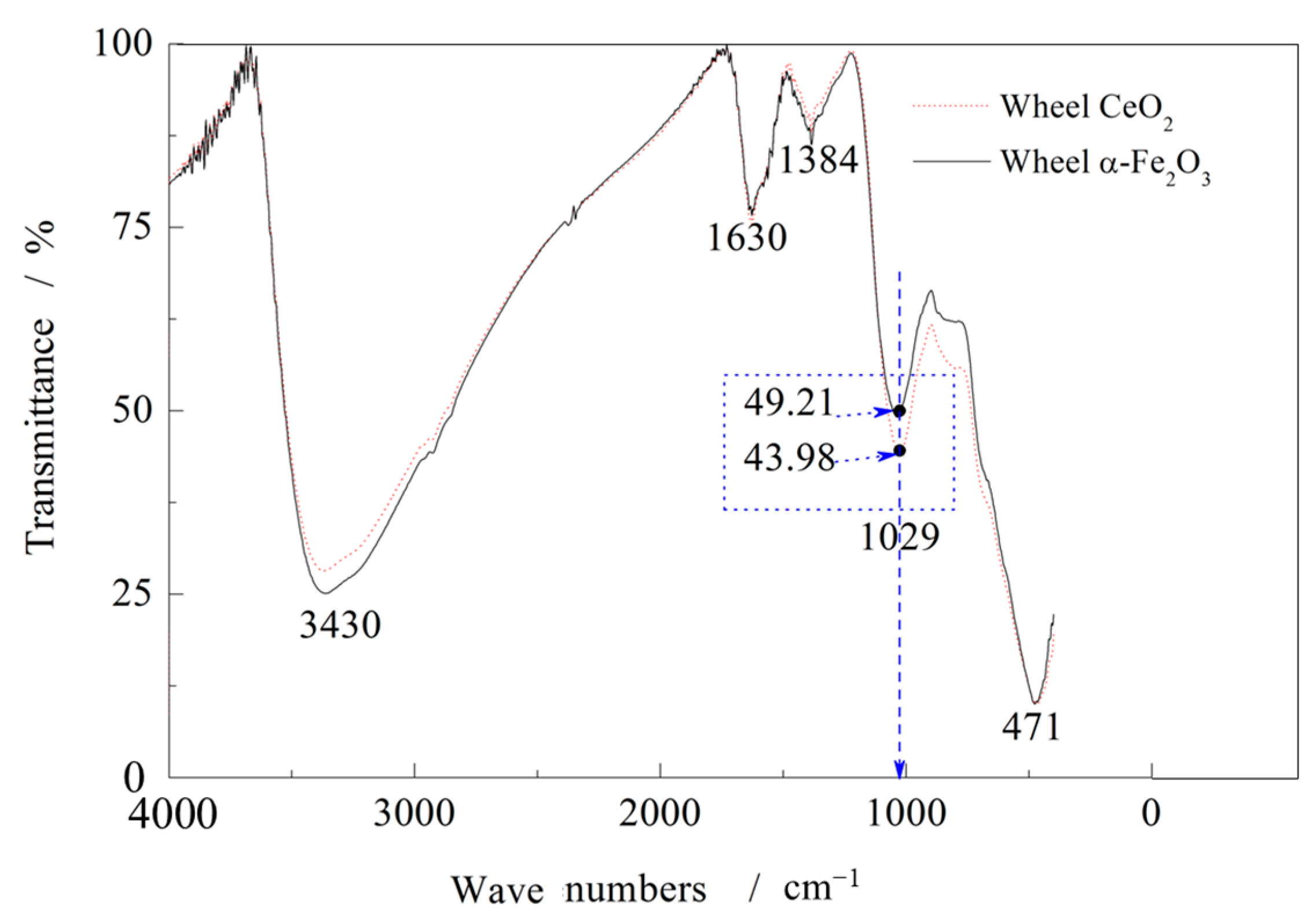
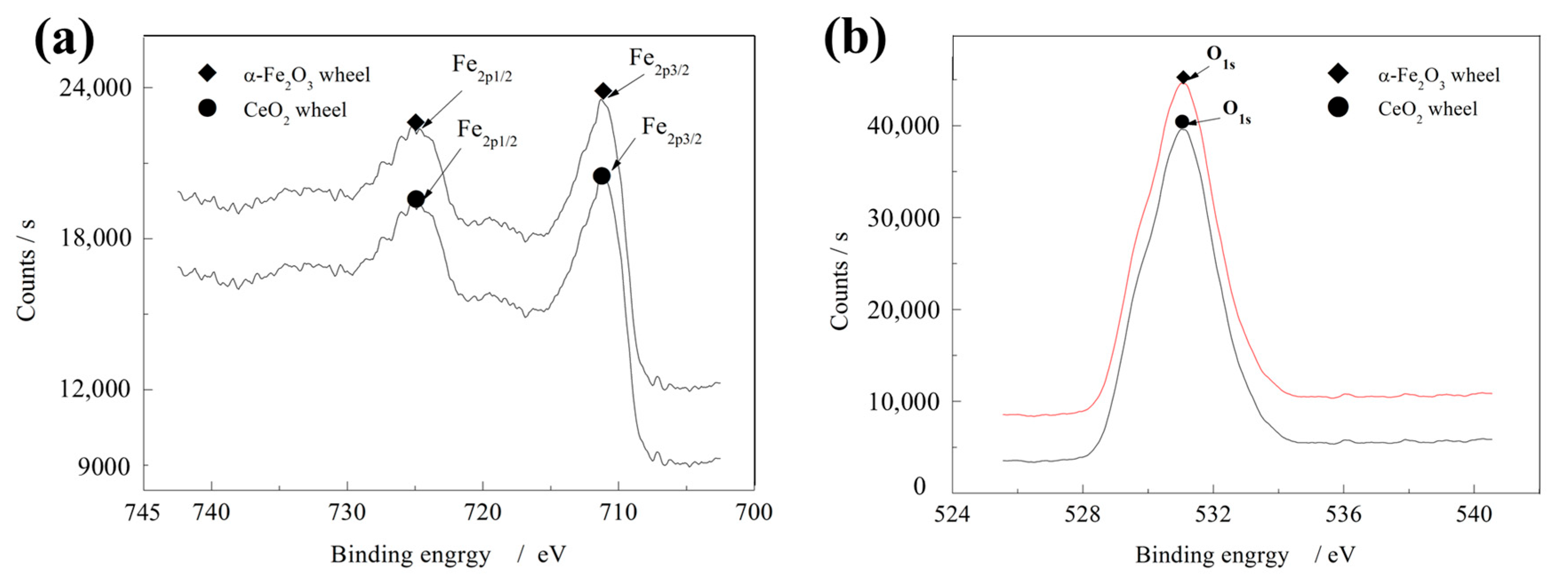
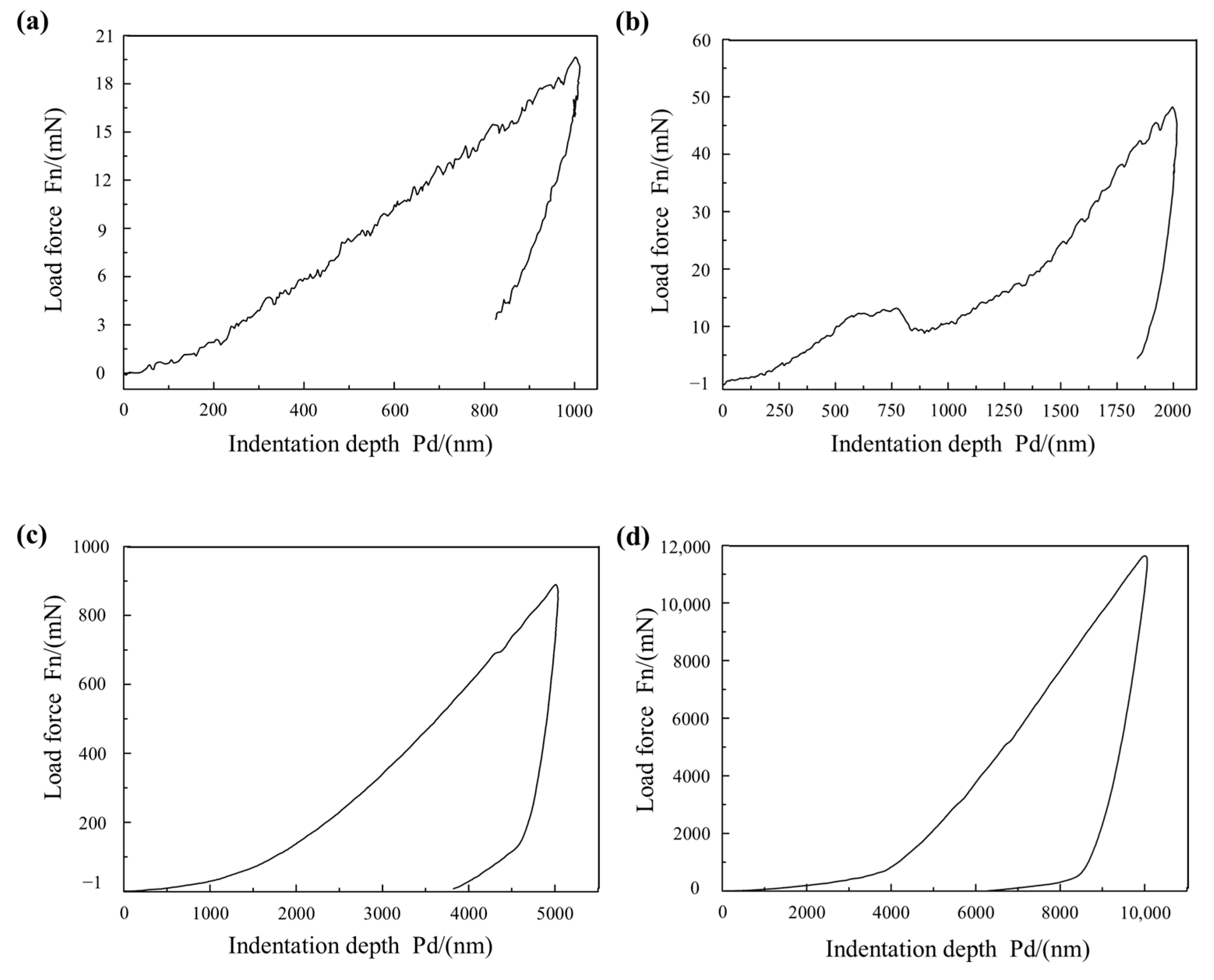
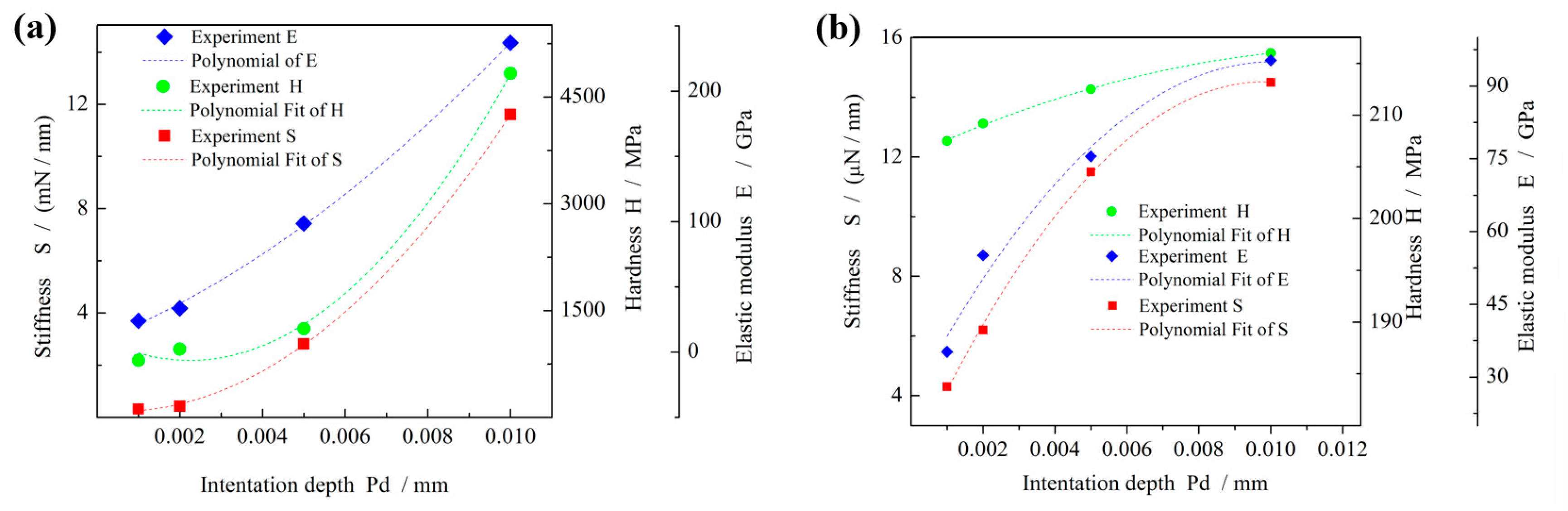
| Voltage U/V | Electric Current I/A | Pulse Width Ton/μs | Interpulse Width Toff /μs | Duty Cycle | Grinding Wheel Speed Vs/m/s | Feed Rate Vw /m/min | Polishing Depth ap /μm | Pre-Electrolysis Time t/min | Electrolyte pH Value | Circulation Method | Electrolyte Ratio | Grinding Wheel Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60, 90, 120 | 50−2 | 99−1 | 99−1 | 50% | 15.7 | 0.2−0.4 | 1−0.01 | 30−60 | 8−9 | pump circulation | 1:50 | W1 W0 |
| Grinding Wheel | Ra (nm) | Rz (nm) | Rp (nm) | Rv (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| W0 (Fe-based, grainless) | 2.1 | 12.2 | 6.99 | 11.56 |
| W1 (CeO2, conventional) | 9.4 | 62.1 | 42.1 | 38.5 |
| Polishing Method | Polishing Conditions | Removal Rate (μm/min) | Relative Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|
| W0(Fe-based, grainless) | 500 mN, 80% volume fraction, 1000 r/min, 10–30min | 1.6 | ~4× higher |
| W1(CeO2, conventional) | Standard conditions [18] | 0.409 | Baseline |
| Material | Hardness H (MPa) | Elastic Modulus E (GPa) | Stiffness S (mN/nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oxide film (intrinsic) | 700~900 | 21~25 | 0.2~0.4 |
| Grinding wheel substrate | 4800~5000 | 220~240 | 10~12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Yan, X.; Kuai, J.; Ardashev, D.V. ELID Polishing of Glass Substrates Using a Grainless Iron-Bonded Wheel with Free Abrasive Particles. Micromachines 2025, 16, 1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16111226
Zhang H, Yan X, Kuai J, Ardashev DV. ELID Polishing of Glass Substrates Using a Grainless Iron-Bonded Wheel with Free Abrasive Particles. Micromachines. 2025; 16(11):1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16111226
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Huali, Xu Yan, Jicai Kuai, and Dmitrii V. Ardashev. 2025. "ELID Polishing of Glass Substrates Using a Grainless Iron-Bonded Wheel with Free Abrasive Particles" Micromachines 16, no. 11: 1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16111226
APA StyleZhang, H., Yan, X., Kuai, J., & Ardashev, D. V. (2025). ELID Polishing of Glass Substrates Using a Grainless Iron-Bonded Wheel with Free Abrasive Particles. Micromachines, 16(11), 1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16111226





