Optimized Design of a Sub-Arc-Second Micro-Drive Rotary Mechanism Based on the Swarm Optimization Algorithm †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Design of the Micro-Drive Rotary Mechanism
2.1. Working Principle of the Micro-Drive Rotary Mechanism
2.1.1. Principle of Balanced Additional Force
2.1.2. The Transmission Conversion Principle
2.2. Design of the Initial Mechanism
3. Optimizing the Structure of the Micro-Drive Rotary Mechanism
3.1. Optimized Mathematical Model
3.2. Determination of the Design Variables
3.3. Establishment of the Objective Function
3.4. Establishment of Constraints
3.4.1. The Position Condition of the X-Direction Point
3.4.2. The Position Condition of the Y-Direction Point
3.4.3. Collinear Conditions
3.5. Optimized Micro-Drive Rotary Mechanism
4. Analysis and Experiment
4.1. Kinematic Analysis
4.2. Experiment Assessing the Drive Characteristics of Mechanism
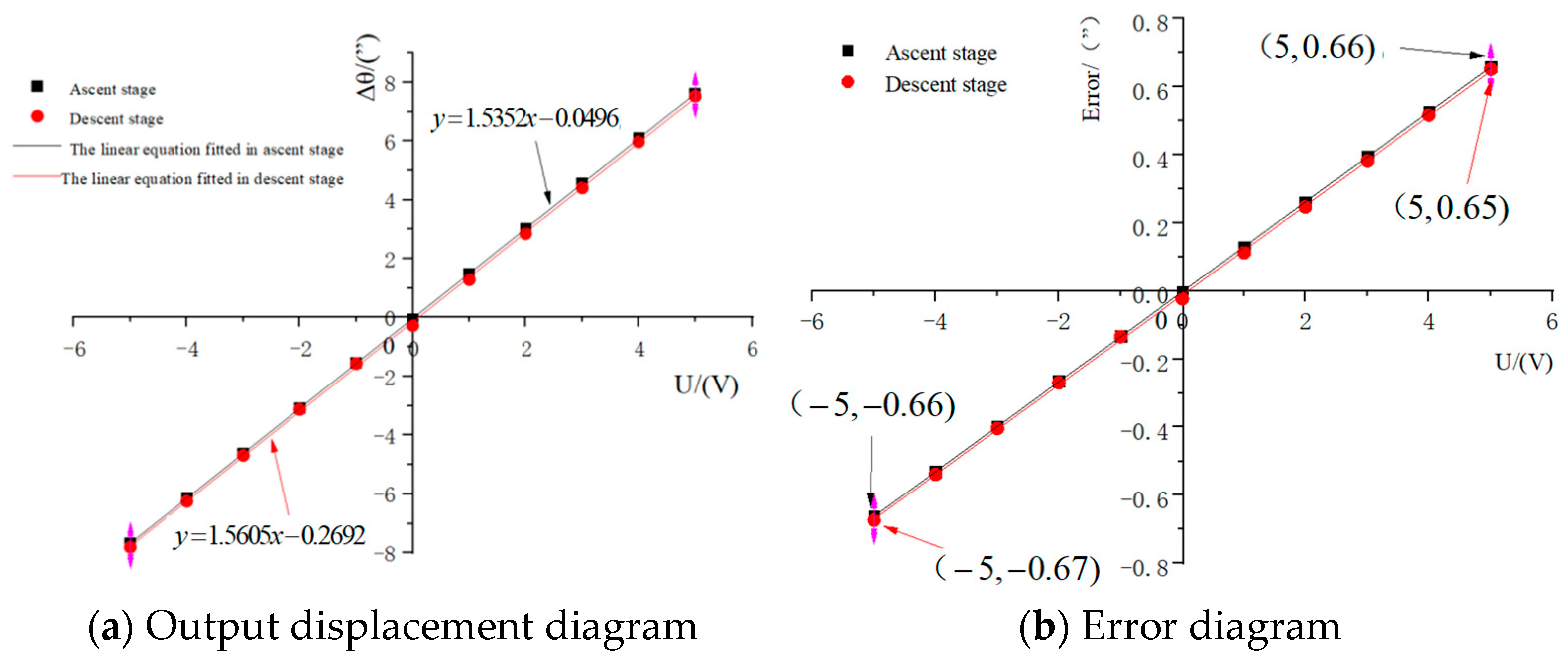
4.3. Experiment Assessing Positioning Performance
5. Performance Analysis and Discussion
5.1. Analysis of the Conversion Characteristics
5.2. Analysis of the Positioning Performance
5.3. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Variable | Interpretation | Unit |
| DOF | Degrees of freedom | \ |
| PSU | Prismatic–spherical–universal | \ |
| SPS | Spherical–prismatic–spherical | \ |
| PSO | Particle swarm optimization | \ |
| PZT | Piezoelectric actuator | \ |
| a | Connecting element | \ |
| b | Input motion element | \ |
| c | Flexure hinge | \ |
| d | Output motion element | \ |
| The velocity of the ith particle at the kth iteration | \ | |
| The position of the ith particle at the kth iteration | \ | |
| The velocity of the ith particle at the (k + 1)th iteration | \ | |
| The inertia weight factor | \ | |
| cn | The learning factor | \ |
| randn | A random number between 0 and 1 | \ |
| gbest | The best solution found by the population so far | \ |
| pbest | The optimal solution currently found by the population’s fitness | \ |
| xn | The x-coordinate of point n | mm |
| yn | The y-coordinate of point n | mm |
| Rn | The distance from point n to the origin o | mm |
| θn | The angle between the line connecting point n to the origin o and the X-axis | Angle (°) |
| lab | The length of rod AB before the change in motion | mm |
| La′b′ | The length of rod AB after the change in motion | mm |
| Δv | The input displacement of the piezoelectric ceramic | μm |
| Δu | Half of the input displacement of the piezoelectric ceramic | μm |
| Δθ | The rotational angle generated by the actuator input on the micro-motion output mechanism d | ) |
| kn | Process variable | mm |
| The abscissa values of flexure hinges 1, 2, and 3 | mm | |
| The ordinate values of flexure hinges 1, 2, and 3 | mm | |
| U | The driving voltage | V |
| δyn | The displacement variation of the side-mounted displacement sensor n along the Y-axis direction | μm |
| δxn | The displacement measured by the linear displacement sensor n in the X-axis direction | μm |
| Δθ1max, Δθ2max | The maximum output angular displacement during the ascending and descending phases of the optimized micro-motion rotary mechanism | ) |
| e1max, e2max | The maximum positioning error during the ascending and descending phases of the optimized micro-motion rotary mechanism | ) |
References
- Zhang, Z.; Xiao, H.; Bordia, R.K.; Peng, F. Elastic Modulus Measurement at High Temperatures for Miniature Ceramic Samples Using Laser Micro-Machining and Thermal Mechanical Analyzer. Materials 2024, 17, 4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinskier, J.; Shirinzadeh, B.; Ghafarian, M.; Das, T.K.; Al-Jodah, A.; Nowell, R. Topology optimization of stiffness constrained flexure-hinges for precision and range maximization. Mech. Mach. Theory 2020, 150, 103874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Cheng, T.; Zhang, N.; Bi, Q.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, C. Thermal-mechanical coupling simulation and experimental study of ultrasound-assisted laser cladding of Ni60 coating. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 7, 180270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.W.; Cho, N.G.; Lee, D.H. Fabrication of a piezoelectrically driven micropositioning 3-DOF stage with elastic body using a multi-material 3D printer. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2020, 26, 1579–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Dai, Y.; Sun, Z.; Guan, C.L.; Lai, T.; Xu, H.; Zhou, X. A sub-micron precision machining and measurement method of long travel metal guideways. J. Manuf. Process. 2025, 133, 947–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, H.; Yu, C.; Han, Z.; Wu, K. Prediction of nonlinear vibration characteristics for high-speed and ultra-precision mechanism with clearance joints. J. Sound Vib. 2024, 573, 118201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Liu, Y.; Tian, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, J. A precise rotary positioner driven by piezoelectric bimorphs: Design, analysis and experimental evaluation. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 313, 112197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabarianand, D.; Karthikeyan, P.; Muthuramalingam, T. A review on control strategies for compensation of hysteresis and creep on piezoelectric actuators based micro systems. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 140, 106634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Tian, D. Friction-Less Force Sensing of a Macro-Micro Manipulator With Large Stroke Based on RFOB for Bilateral Control. IEEE Sens. J. 2025, 25, 6095–6106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, Y.; Deng, S.; Jin, X.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, Z. Research on geometric error compensation of ultra-precision turning-milling machine tool based on macro–micro composite technology. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 132, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, B.; Li, D.; Yip, W.S.; To, S. Digital-twin-driven intelligent tracking error compensation of ultra-precision machining. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2024, 219, 111630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Xi, Y. Micro-vision super-resolution restoration and positioning based on ultra-precision machining topography guidance. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Yu, Y.; Cui, L.; Ji, N.; Deng, X. Research on micro-/nano-positioning system driven by a stepper motor. Actuators 2024, 13, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Liu, X.; Guo, X.; Lu, W.; Yao, Z.; Lei, Z. A method for simultaneously measuring 6DOF geometric motion errors of a precision rotary stage based on absolute position-distance measurement. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2021, 138, 106420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gräser, P.; Linß, S.; Harfensteller, F.; Torres, M.; Zentner, L.; Theska, R. High-precision and large-stroke XY micropositioning stage based on serially arranged compliant mechanisms with flexure hinges. Precis. Eng. 2021, 72, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Lv, Z.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Y.; Jing, G.; Guo, W.; Lu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Wei, K.; Li, L.; et al. Positioning Performance of a Sub-Arc-Second Micro-Drive Rotary System. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Wang, M.; Tu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Jiao, S.-Q. Reduction of residual stress in porous Ti6Al4V by in situ double scanning during laser additive manufacturing. Int. J. Min. Met. Mater. 2021, 28, 1844–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.D.; Zhang, W.M.; Li, Y.S.; Xue, F.; Fleischer, J. Chatter identification of thin-walled parts for intelligent manufacturing based on multi-signal processing. Adv. Manuf. 2021, 9, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Li, D.; Guo, W.; Ma, R.; Shan, Z.; Wang, F. Structural design and experimental research of a micro-feed tool holder based on topology optimization. Mech. Sci. 2024, 15, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, G.; Jiang, Y.; Cao, Q.; Gong, G.; Zhang, D.; Yang, H.; Han, D. A long-stroke lifetime piezo inertial actuation and its application in micro-nano observation. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2025, 235, 112921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iafolla, L.; Filipozzi, M.; Freund, S.; Zam, A.; Rauter, G.; Cattin, P.C. Machine learning-based method for linearization and error compensation of a novel absolute rotary encoder. Measurement 2021, 169, 108547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, D.; Lin, Y.; Chen, Z.; Shi, Z.; Li, C.; Zhao, L. Research on Output Characteristics of a Non-Contact Piezoelectric Actuator’s Micro-Displacement Amplifying Mechanism. Actuators 2024, 13, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Qi, C.; Gao, F.; Yue, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wu, Y. Integration modeling and control of a 12-degree-of-freedom macro–micro dual parallel manipulator. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2022, 236, 6064–6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.X.; Lin, R.W.; Li, R.J.; Li, J.; Cheng, Z.-Y.; Pan, Q.-S.; Huang, Q.-X.; Fan, K.-C. Nanopositioning X–Y stage with an embedded Six-DOF error compensation system based on Abbe and Bryan principles. Measurement 2024, 227, 114218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wen, Z.; Chen, G.; Liang, J.; Liu, P. A decoupled flexure-based rotary micropositioning stage with compact size. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2018, 232, 4167–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, B.; Cheng, R.; Zhang, L.; Li, H. Design and experiment of multidimensional and subnanometer stage driven by spatially distributed piezoelectric ceramics. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2024, 95, 053702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Huang, Q.; Liu, H.; Li, H.; Cheng, R.; Zhang, L. Design and Driving Control of Cross-scale Micro-nano Coordinate Measuring Machine. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2025, 74, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wen, Z.; Cao, T.; Lu, C.; Wang, B.; Wu, D.; Li, X. A precision positioning rotary stage driven by multilayer piezoelectric stacks. Precis. Eng. 2022, 76, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Li, S. Modeling and Prediction of Inter-System Bias for GPS/BDS-2/BDS-3 Combined Precision Point Positioning. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2022, 132, 823–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Huo, Z.; Wang, F.; Liang, C.; Shi, B.; Zhang, D. A novel friction-actuated 2-DOF high precision positioning stage with hybrid decoupling structure. Mech. Mach. Theory 2022, 167, 104511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooijschuur, R.; Saikumar, N.; HosseinNia, S.H.; van Ostayen, R.A.J. Air-Based Contactless Wafer Precision Positioning System. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.W.; Wang, X.; Meng, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Ren, M.; Zhu, L.-M. Design, modeling and control of high-bandwidth nano-positioning stages for ultra-precise measurement and manufacturing: A survey. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2024, 6, 062007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, W. Optimization Analysis of Vibration Characteristics for Precision Positioning Stage. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1939, 012072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhong, B.; Liu, B.; Jin, Z.; Wang, Z.; Sun, L. A Small Bipedal Trans-Scale Precision Positioning Stage Based on Inertial Stick-Slip Driving. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2021, 22, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wu, Y. Piezoelectric actuator for machining on macro-to-micro cylindrical components by a precision rotary motion control. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 114, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, X.; Jia, Z.; Li, H.; Ma, X.; Yan, H.; Ma, J. Binocular-vision-based error detection system and identification method for PIGEs of rotary axis in five-axis machine tool. Precis. Eng. 2018, 51, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Wu, H.; Yang, Y. Design and Performance Research of a Precision Micro-Drive Reduction System without Additional Motion. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latchoumi, T.P.; Balamurugan, K.; Dinesh, K.; Ezhilarasi, T.P. Particle Swarm Optimization approach for waterjetcavitation peening. Measurement 2019, 141, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhou, X.; Luo, Y. Simultaneously Optimizing lnertia Weight and Acceleration Coefficients viaIntroducing New Functions into PSO Algorithm. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1754, 012195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Li, S.; Li, Z.; Kong, X. A new global particle swarm optimization for the economic emission dispatch with or without transmission losses. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 139, 45–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
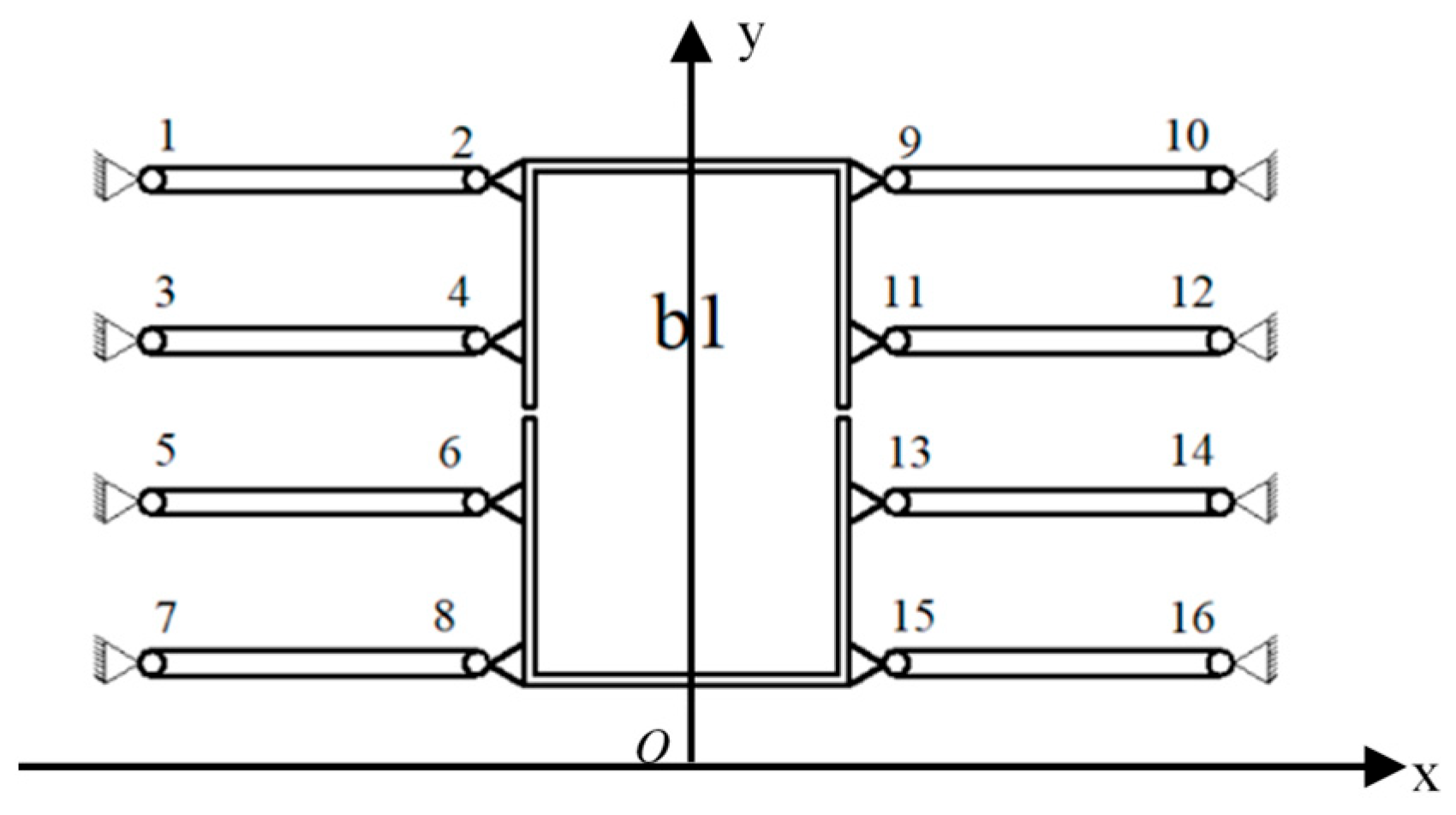









| Parameter | x1 | y1 | x4 | y4 | R2 | θ2 | R3 | θ3 | R5 | θ5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| value | 26.5 | 44.0 | −26.5 | 44.0 | 68.8 | 40.0 | 81.0 | 40.0 | 68.8 | 140.0 |
| Input Values Δu/μm | Theoretical Δθ/(″) | Rate of Increase/(%) | Finite Element Analysis Δθ/(″) | Rate of Increase/(%) | The Optimized Error/(%) (θ1 − θ2)/θ1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Optimization | After Optimization θ1 | Before Optimization | After Optimization θ2 | ||||
| 1.01 | 1.24 | 1.98 | 0.597 | 1.21 | 1.86 | 0.537 | 0.0606 |
| 1.67 | 2.06 | 3.27 | 0.587 | 2.00 | 3.07 | 0.535 | 0.0612 |
| 2.34 | 2.88 | 4.68 | 0.625 | 2.81 | 4.30 | 0.530 | 0.0812 |
| 3.21 | 3.95 | 6.12 | 0.549 | 3.85 | 5.90 | 0.532 | 0.0359 |
| 3.85 | 4.74 | 7.56 | 0.595 | 4.62 | 7.07 | 0.530 | 0.0648 |
| 4.51 | 5.55 | 8.64 | 0.557 | 5.41 | 8.28 | 0.530 | 0.0417 |
| 5.37 | 6.61 | 10.44 | 0.579 | 6.44 | 9.87 | 0.533 | 0.0546 |
| 6.14 | 7.56 | 11.88 | 0.571 | 7.37 | 11.28 | 0.531 | 0.0505 |
| 6.84 | 8.42 | 13.32 | 0.582 | 8.21 | 12.60 | 0.535 | 0.0541 |
| 7.43 | 9.15 | 14.40 | 0.574 | 8.91 | 13.75 | 0.543 | 0.0451 |
| Input Values Δu/μm | Output Values Δθ/(″) Pre-Optimization | Input Values Δu/μm | Output Values Δθ/(″) Post-Optimization |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.01 | 1.01 | 1.06 | 1.86 |
| 1.67 | 1.85 | 1.65 | 2.91 |
| 2.34 | 2.96 | 2.37 | 4.25 |
| 3.21 | 4.03 | 3.36 | 6.10 |
| 3.85 | 4.90 | 3.91 | 7.12 |
| 4.51 | 6.14 | 4.46 | 8.15 |
| 5.37 | 7.18 | 5.42 | 9.94 |
| 6.14 | 7.83 | 6.19 | 11.37 |
| 6.84 | 8.84 | 6.91 | 12.71 |
| 7.43 | 9.55 | 7.38 | 13.59 |
| Reference | Author | Year | Maximum Output Rotary Displacement (″) |
|---|---|---|---|
| [16] | Yang M. et al. | 2021 | 9.56 |
| This Paper | Na Zhang et al. | 2025 | 15.34 |
| Reference | Author | Year | Positioning Error Value (″) |
|---|---|---|---|
| [14] | Yang, W.J. et al. | 2021 | 2.98 |
| [15] | Graser Philipp et al. | 2021 | 1.3 (72.5 µrad) |
| [16] | Yang M. et al. | 2021 | 0.85 |
| [21] | Lorenzo, Iafolla et al. | 2021 | 10 |
| [36] | Liu, W.; Li, X. et al. | 2018 | 7.2 |
| This Paper | Na Zhang et al. | 2025 | 0.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, N.; Wang, D.; Li, K.; Lv, Z.; Gui, H.; Yang, Y.; Yang, M. Optimized Design of a Sub-Arc-Second Micro-Drive Rotary Mechanism Based on the Swarm Optimization Algorithm. Micromachines 2025, 16, 1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101190
Zhang N, Wang D, Li K, Lv Z, Gui H, Yang Y, Yang M. Optimized Design of a Sub-Arc-Second Micro-Drive Rotary Mechanism Based on the Swarm Optimization Algorithm. Micromachines. 2025; 16(10):1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101190
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Na, Dongmei Wang, Kai Li, Zhenyang Lv, Haochen Gui, Yizhi Yang, and Manzhi Yang. 2025. "Optimized Design of a Sub-Arc-Second Micro-Drive Rotary Mechanism Based on the Swarm Optimization Algorithm" Micromachines 16, no. 10: 1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101190
APA StyleZhang, N., Wang, D., Li, K., Lv, Z., Gui, H., Yang, Y., & Yang, M. (2025). Optimized Design of a Sub-Arc-Second Micro-Drive Rotary Mechanism Based on the Swarm Optimization Algorithm. Micromachines, 16(10), 1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101190







