Molecular Dynamics Study on the Effect of Surface Films on the Nanometric Grinding Mechanism of Single-Crystal Silicon
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Simulation Models
2.2. Potential Functions
2.3. Simulation Parameters
3. Results and Discussion
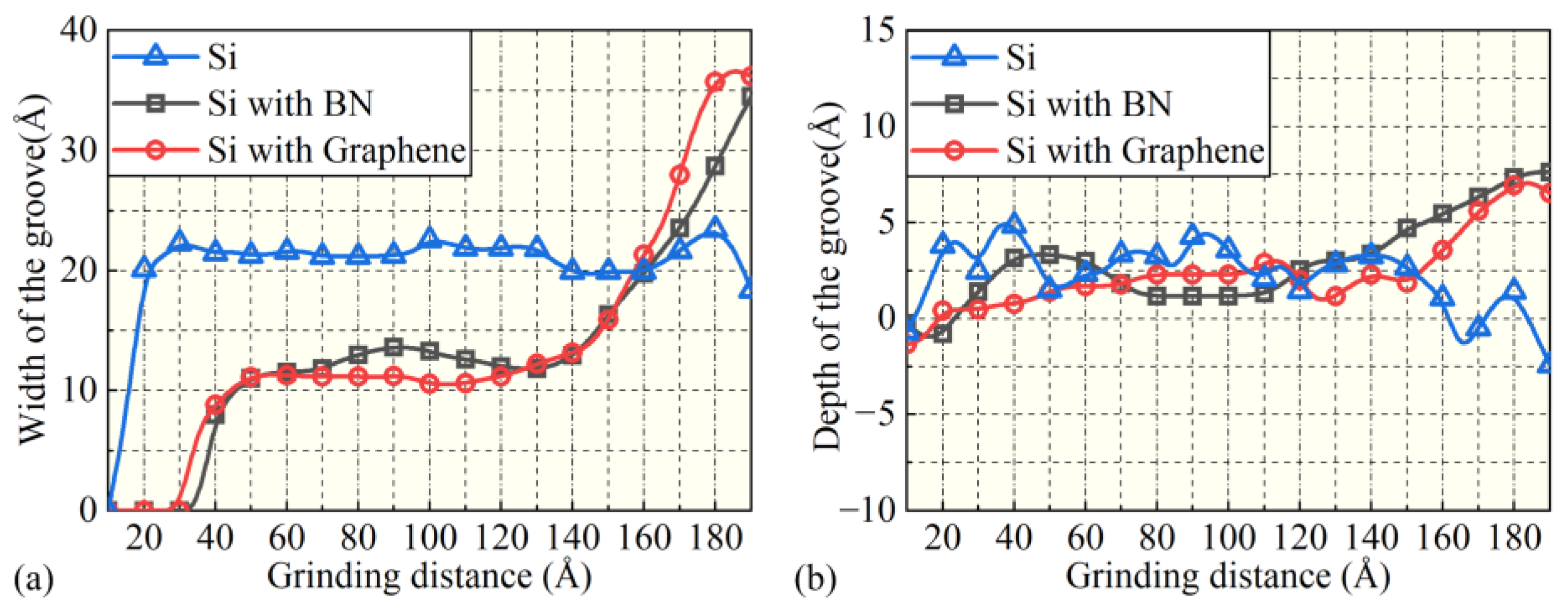
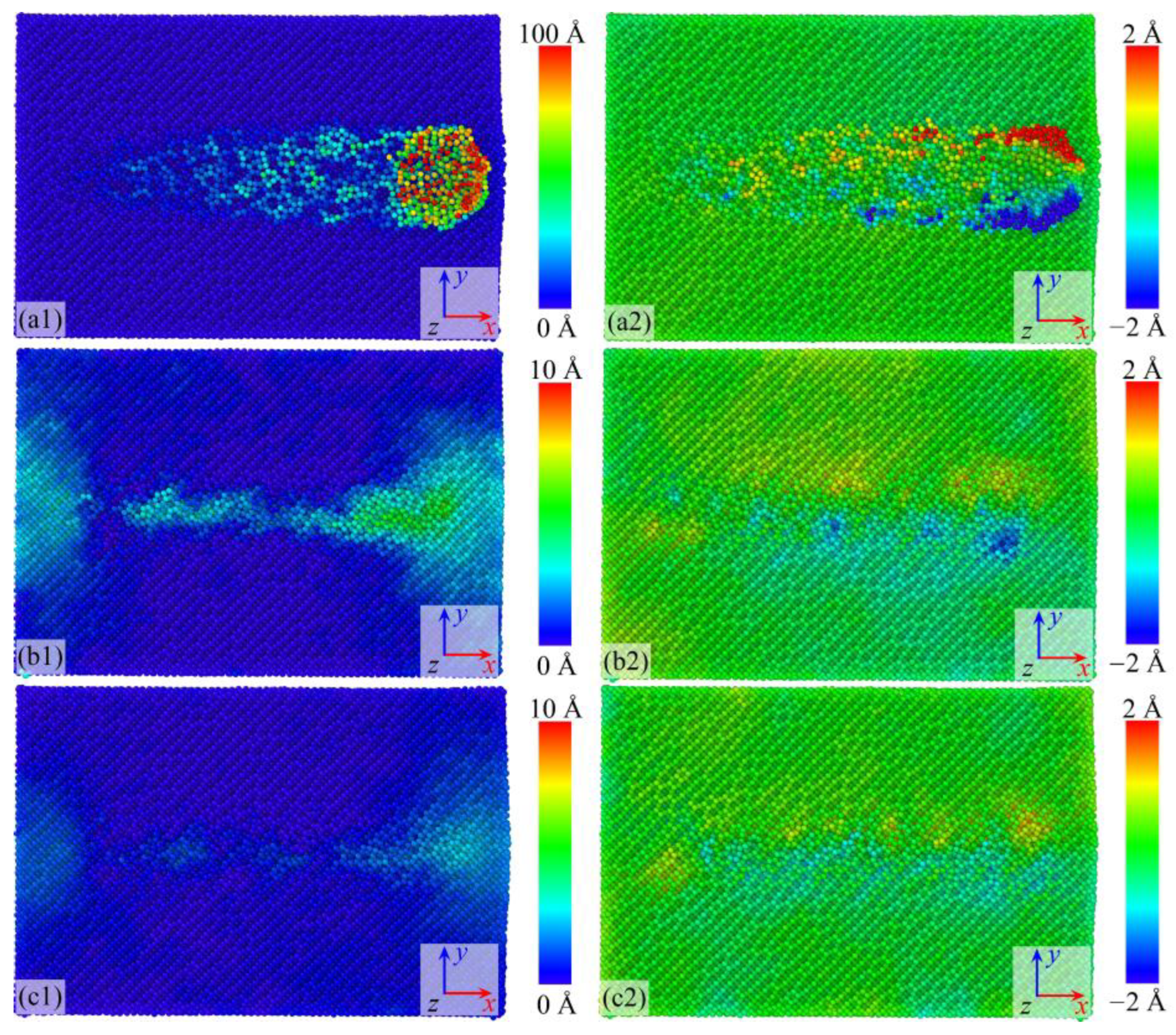
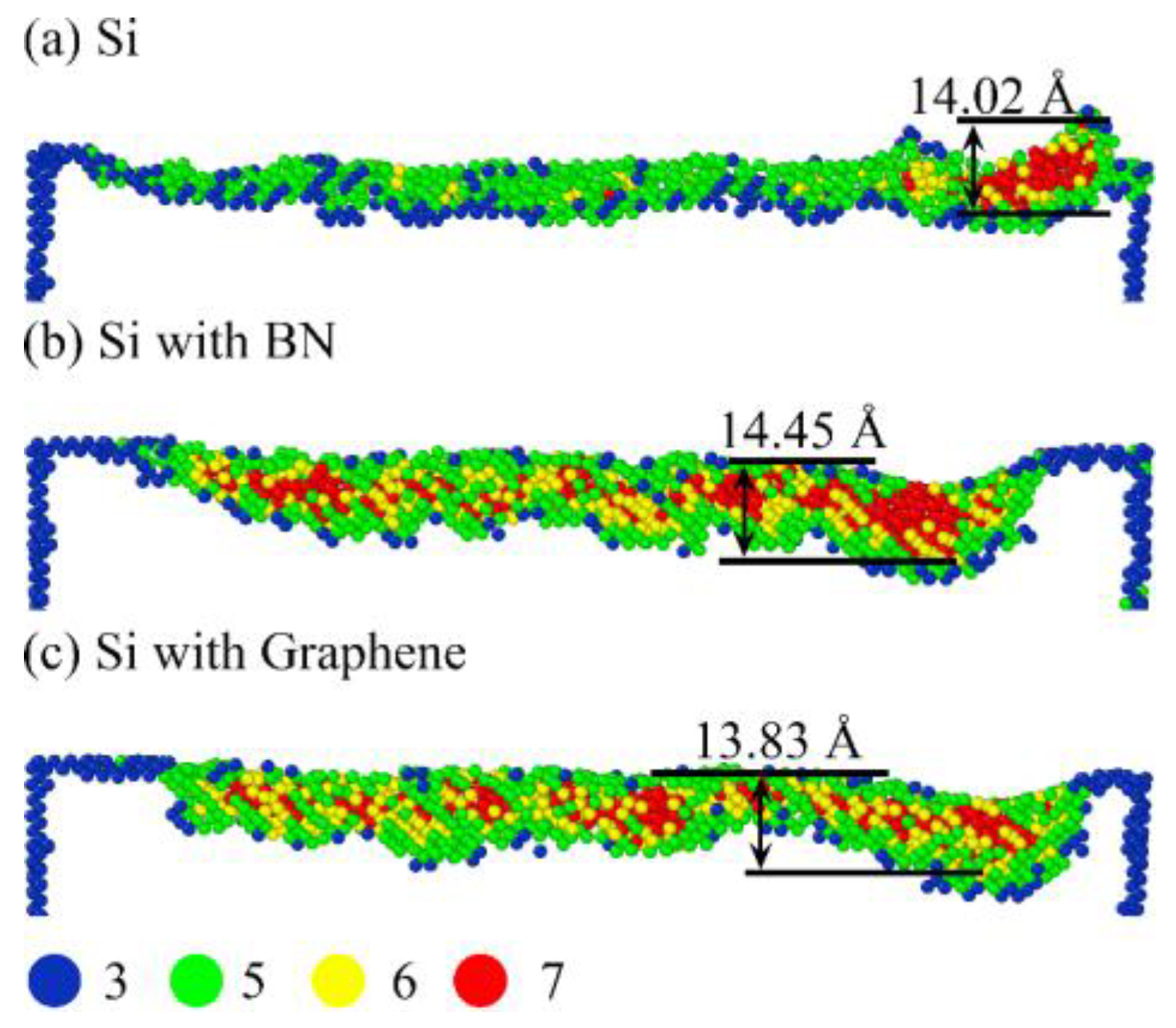
3.1. Surface Generation Mechanism
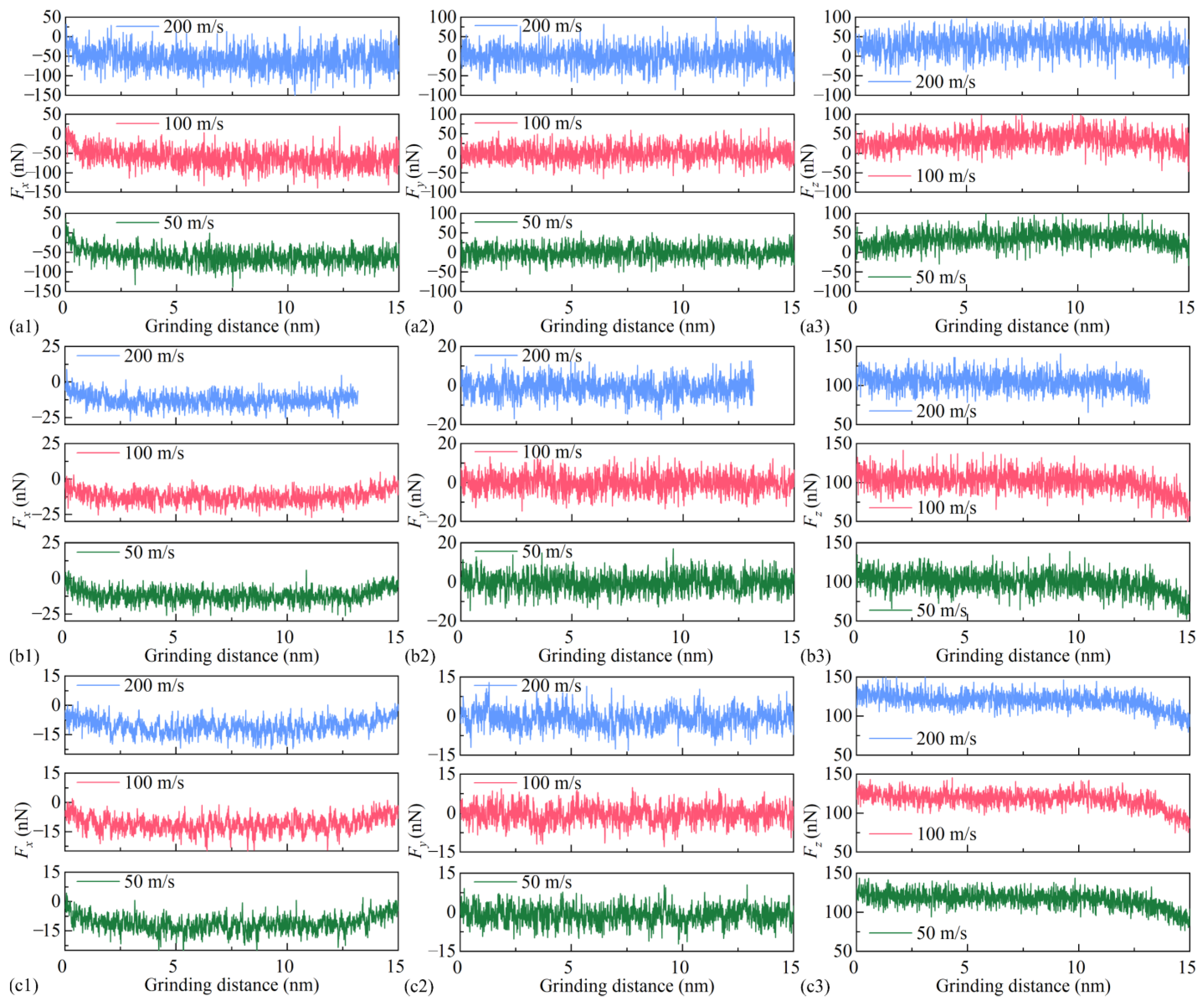
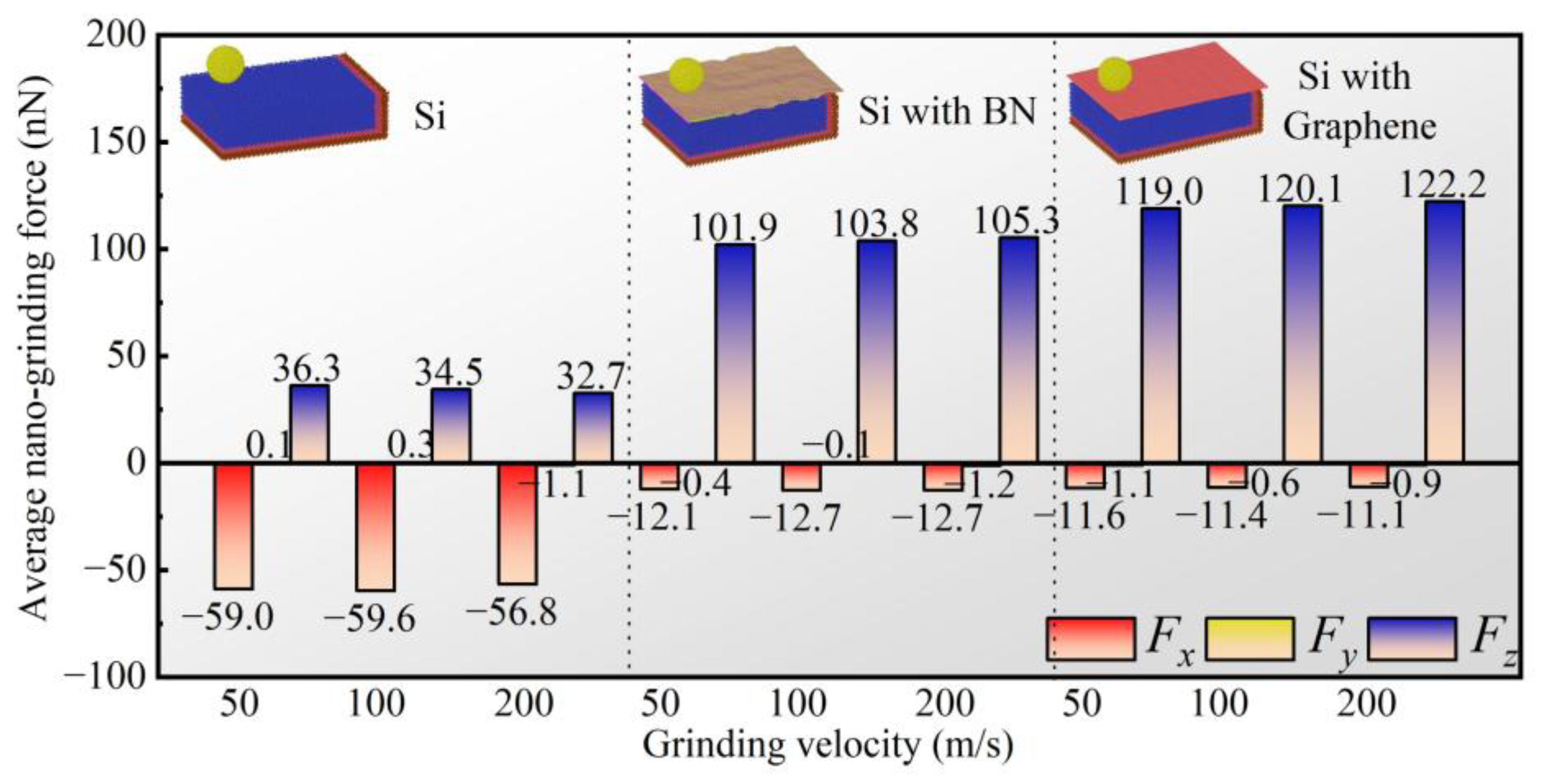
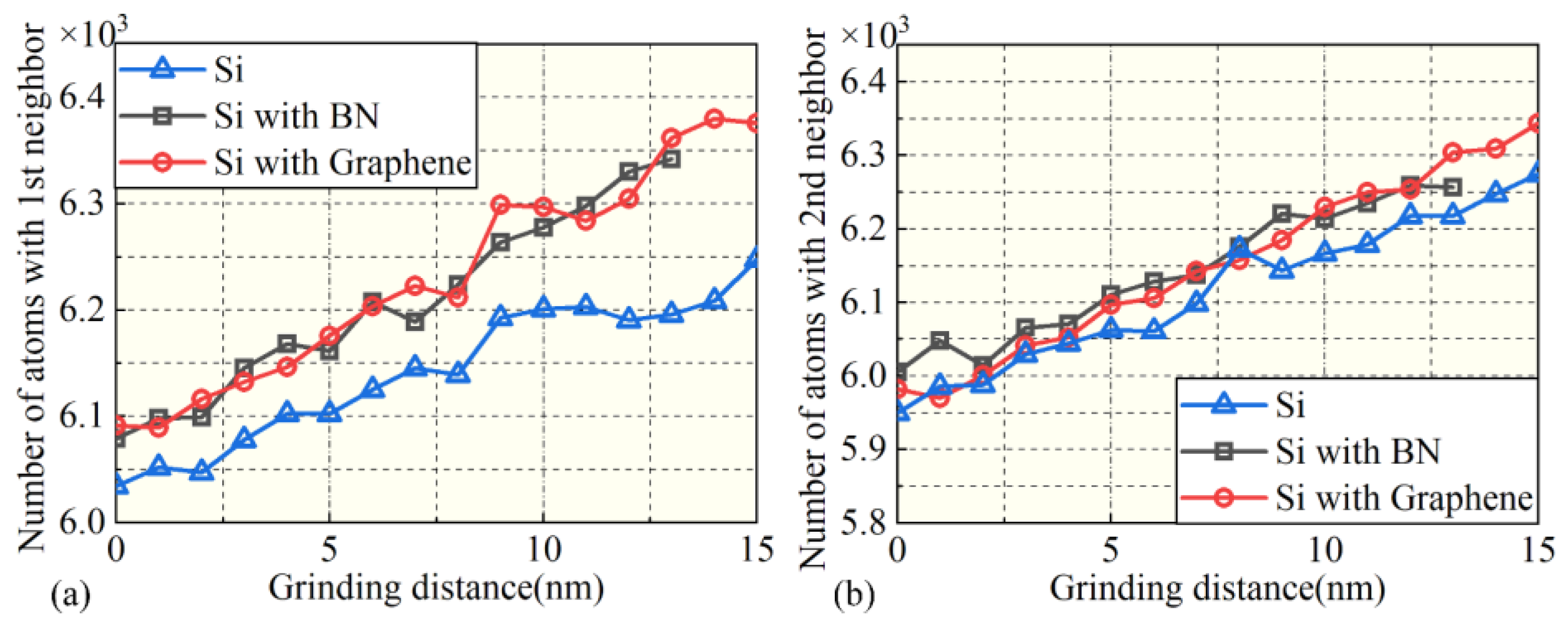
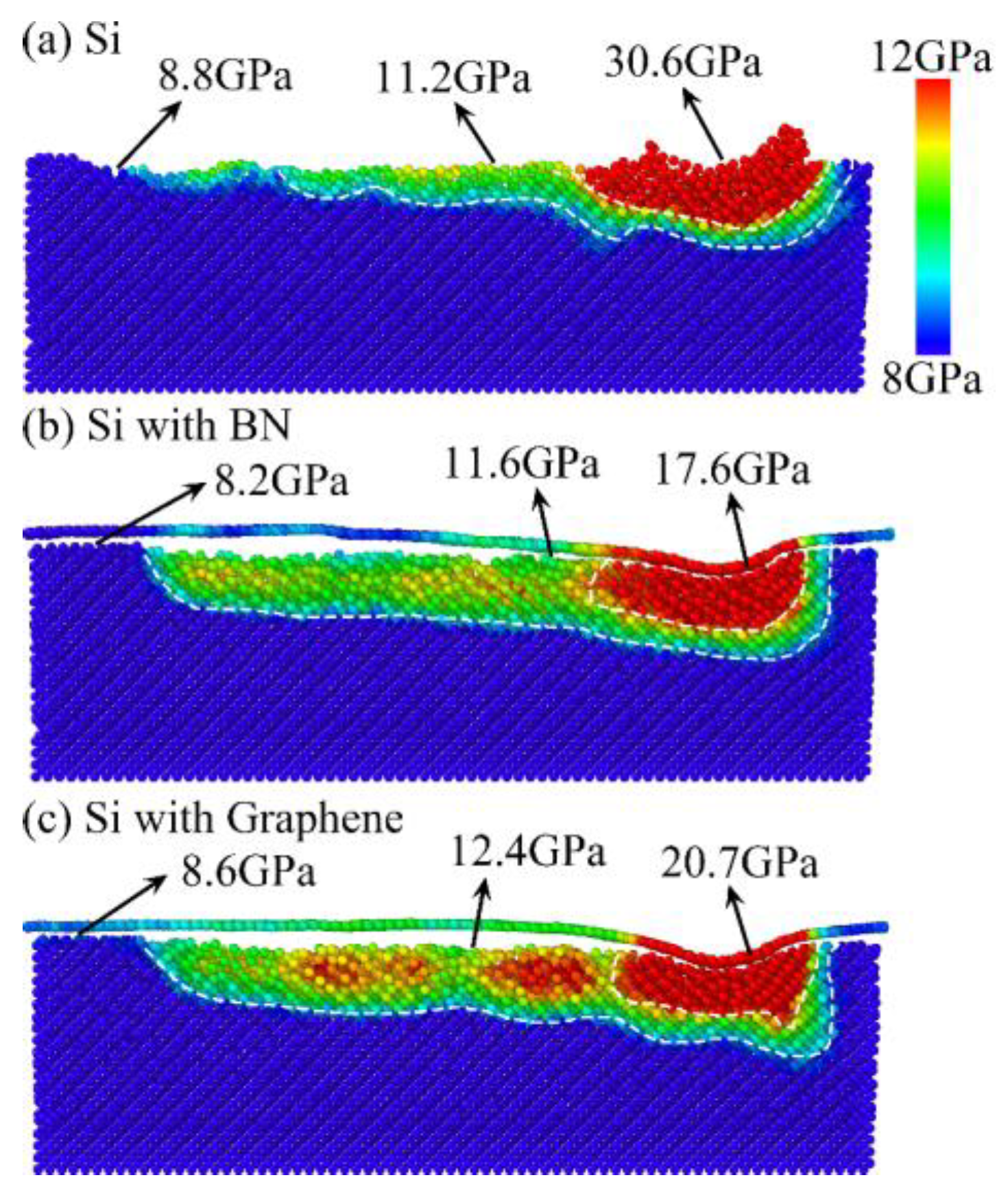
3.2. Analysis of Mechanical Properties
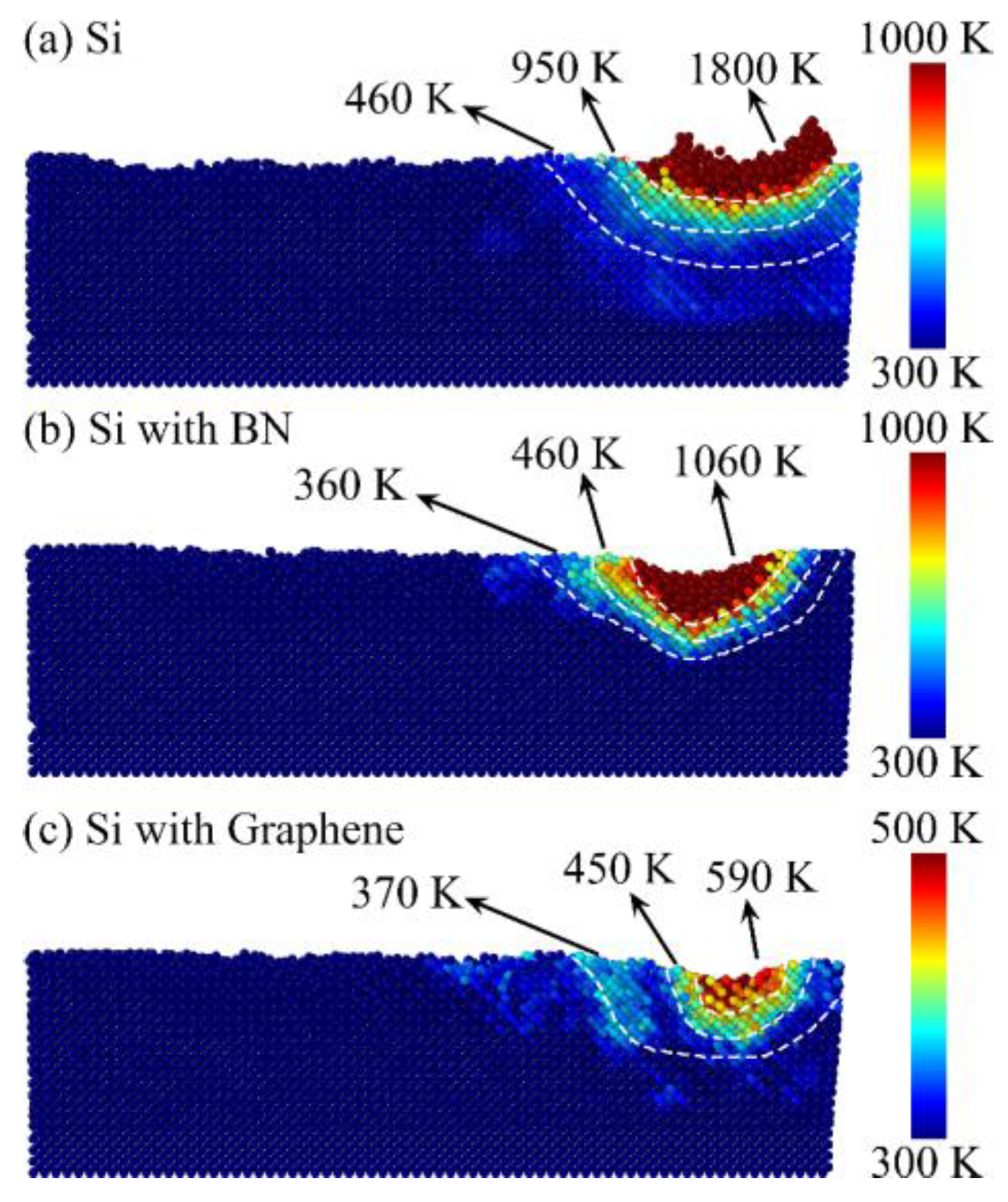
3.3. Analysis of Temperature Distribution
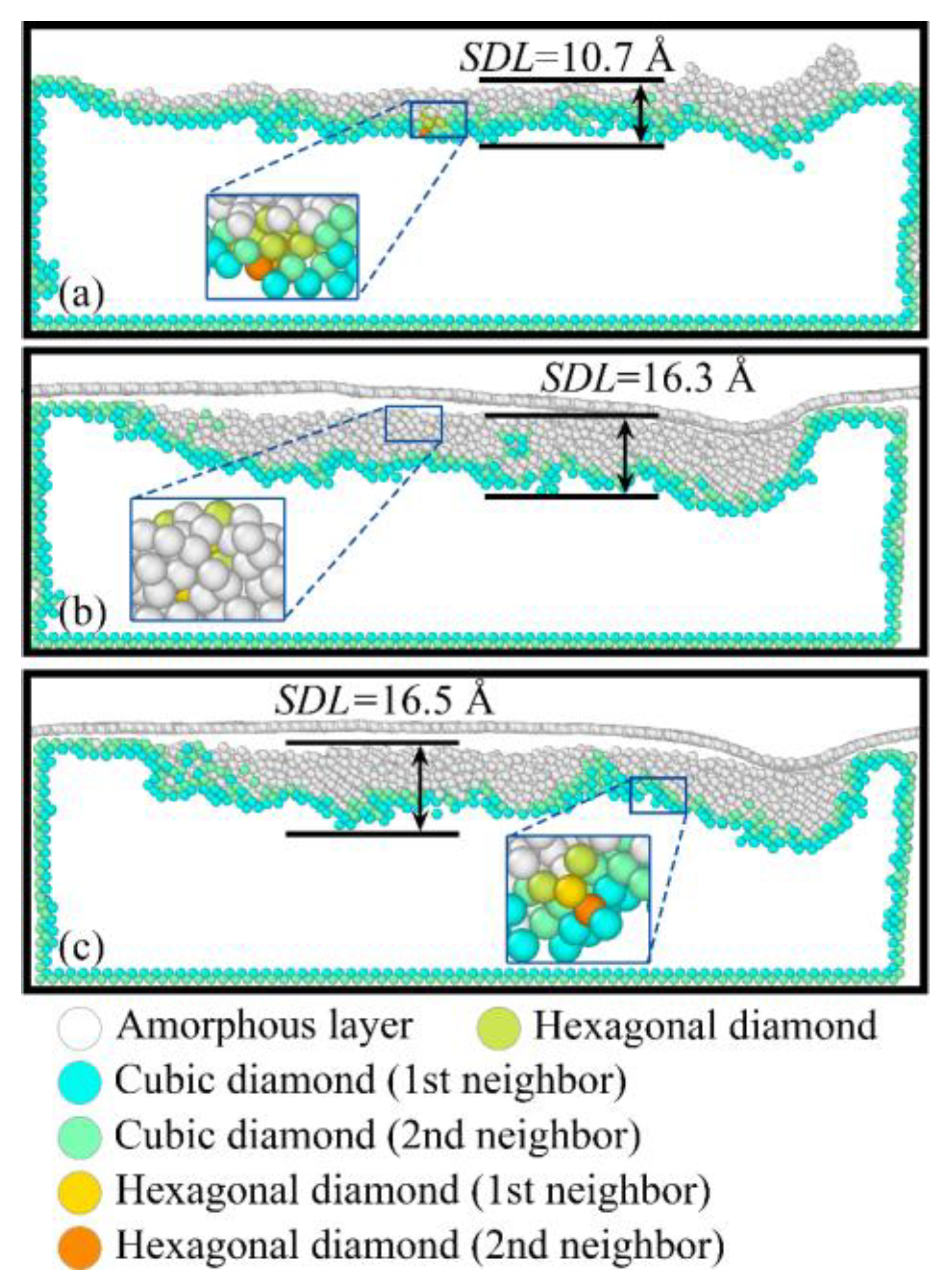
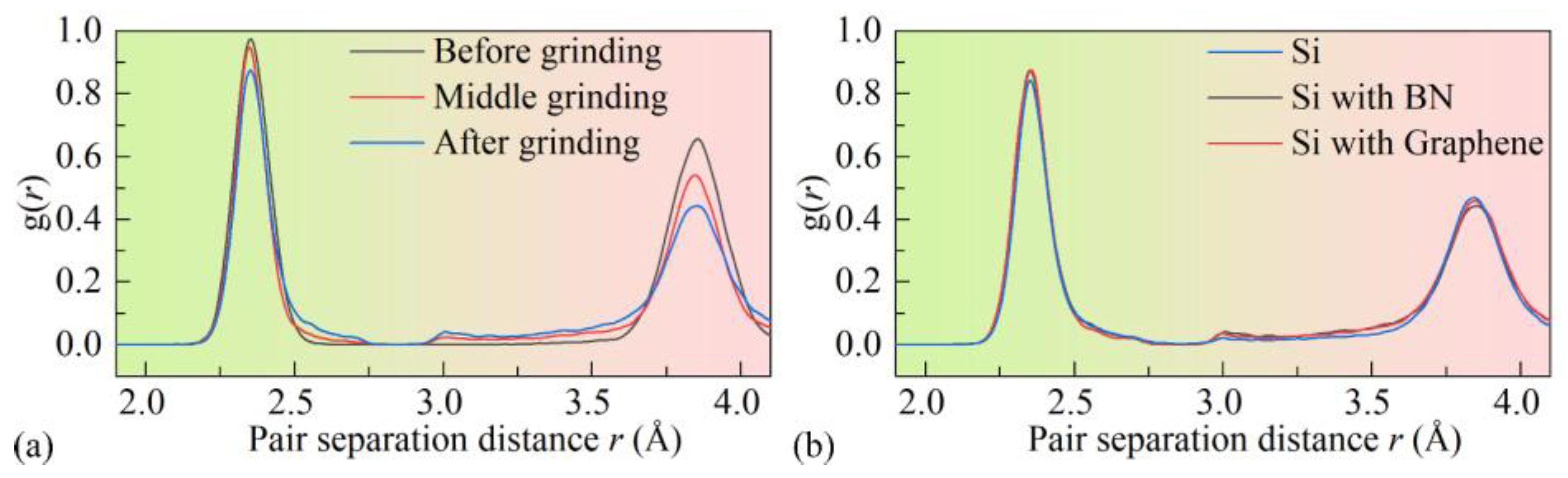
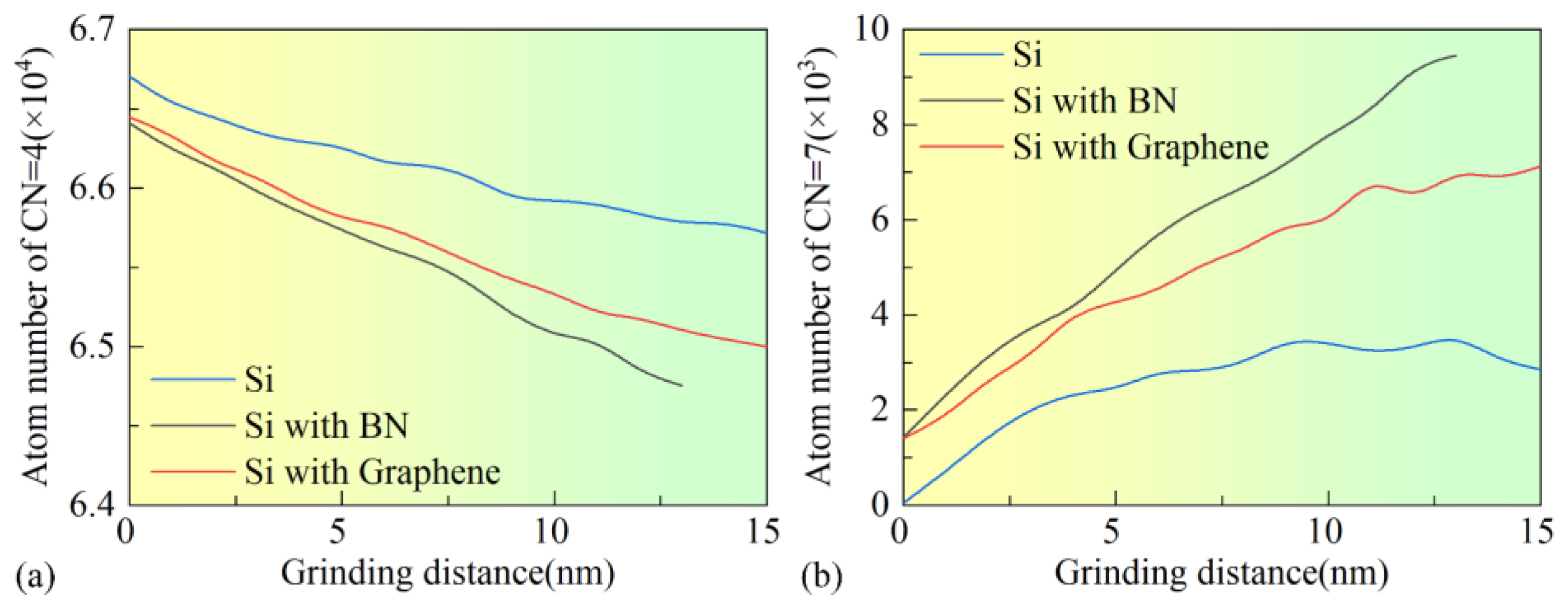
3.4. Analysis of Phase Transformation
3.5. Analysis of Residual Stress
3.6. General Discussion
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Different surface film conditions significantly affect machined surface morphology and subsurface damage. Without films, chip formation and groove-end pile-up dominate, whereas BN and graphene films suppress chip formation and promote groove expansion. Graphene provides stronger constraint on atomic displacements, leading to better surface quality.
- (2)
- Both BN and graphene films reduce the average tangential force by 77.64–80.87% while increasing the average normal force by 180.72–273.70%. Graphene shows a stronger suppression of tangential force but a higher increase in normal force. In addition, graphene effectively reduces force fluctuations, making it more suitable for high-speed nanogrinding. The effect of grinding speed on average forces is minimal under film-covered conditions, whereas without a film, higher speeds reduce the average forces.
- (3)
- The presence of surface films increases the SDL thickness by 52.34% (BN)–54.21% (graphene). However, their ability to inhibit phase transformation is limited. By slowing the release of surface pressure, high-coordination atoms (CN = 7) are partially retained, influencing the phase transformation process.
- (4)
- Both BN and graphene films decrease surface and subsurface temperatures, with graphene showing better heat dissipation due to its high thermal conductivity. Both films also reduce von Mises stress beneath the abrasive grain, and increasing the grinding depth further lowers the internal stress.
- (5)
- Uncoated Si workpieces are prone to chip formation and pile-up, favoring high-efficiency material removal. BN films reduce tangential force, friction, and temperature rise, making them suitable for conventional precision nanogrinding. Graphene films, with superior lubrication and heat conduction, perform better in improving surface quality, reducing temperature, and supporting high-speed grinding, but they also lead to higher normal force and more severe subsurface damage.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, P.; Pan, J.; Zhao, B.; Wu, J. Molecular dynamics study of crystal orientation effect on surface generation mechanism of single-crystal silicon during the nano-grinding process. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 74, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, S.; Luo, X.; Agrawal, A.; Reuben, R.L. Diamond machining of silicon: A review of advances in molecular dynamics simulation. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2015, 88, 131–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Zhang, F.; Chen, J. A study of ultraprecision mechanical polishing of single-crystal silicon with laser nano-structured diamond abrasive by molecular dynamics simulation. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2019, 157, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saga, T. Advances in crystalline silicon solar cell technology for industrial mass production. NPG Asia Mater. 2010, 2, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.N.; Yu, T.B.; Da Zhu, L.; Wang, W.S. Analytical modeling of grinding-induced subsurface damage in monocrystalline silicon. Mater. Des. 2017, 130, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Li, Q.; Liu, T.; Zhai, C.; Kang, R.; Jin, Z. Molecular dynamics study on the thickness of damage layer in multiple grinding of monocrystalline silicon. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2016, 51, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komanduri, R.; Ch and Rasekaran, N.; Raff, L. Molecular dynamics simulation of the nanometric cutting of silicon. Philos. Mag. B 2001, 81, 1989–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Zhao, B.; Pan, J.; Wu, J. Superimpose mechanism of surface generation process in grinding of monocrystalline silicon using molecular dynamics simulation. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2022, 147, 106684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Li, S.; Chen, G. Comparison of subsurface damages on mono-crystalline silicon between traditional nanoscale machining and laser-assisted nanoscale machining via molecular dynamics simulation. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2018, 414, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, D.; Zhang, H.; Wang, G. Study on the nano-cutting mechanism of monocrystalline silicon material with an amorphous layer by molecular dynamics simulations. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 132, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Sui, M.; Li, C.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, B.; Chen, Y.; Said, Z.; Debnath, S.; Sharma, S. Residual stress of grinding cemented carbide using MoS2 nano-lubricant. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 119, 5671–5685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, K.; Sinha, M.K.; Singh, A.; Archana; Gupta, M.K.; Korkmaz, M.E. A comprehensive review on the grinding process: Advancements, applications and challenges. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2022, 236, 10923–10952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, G.; Sidpara, A.; Bandyopadhyay, P. High efficiency chemical assisted nanofinishing of HVOF sprayed WC-Co coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 334, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Yan, Y.; Huang, N.; Wang, Z.; Kang, R.; Guo, D. Residual stress distribution in silicon wafers machined by rotational grinding. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2017, 139, 081012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Li, Y. The influence of crystal orientation on subsurface damage of mono-crystalline silicon by bound-abrasive grinding. Micromachines 2021, 12, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yan, Y.; Li, Z.; Geng, Y. Towards understanding the machining mechanism of the atomic force microscopy tip-based nanomilling process. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2021, 162, 103701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Dong, Z.; Kang, R.; Zhang, B.; Guo, D. Warping of silicon wafers subjected to back-grinding process. Precis. Eng. 2015, 40, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Zhao, P.; Liu, H.; Pan, J.; Wu, J. Investigation on surface generation mechanism of single-crystal silicon in grinding: Surface crystal orientation effect. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 34, 105125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhu, F.; Liu, X.; Chen, Q.; Hu, J.; Lu, Z.; Zeng, P.; Liu, Y. A molecular dynamic study of nano-grinding of a monocrystalline copper-silicon substrate. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 493, 933–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Liu, H.; Deng, Z. Atomistic simulation study of nanoparticle effect on nano-Cutting mechanisms of single-crystalline materials. Micromachines 2020, 11, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, P.; Qin, F.; An, T.; Yu, H. Mechanical properties of silicon in subsurface damage layer from nano-grinding studied by atomistic simulation. AIP Adv. 2018, 8, 055223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Guo, X.; Yuan, S.; Li, M.; Kang, R.; Guo, D. Effects of grinding speeds on the subsurface damage of single crystal silicon based on molecular dynamics simulations. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 554, 149668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhao, P.; Wu, D.; Li, D.; Wang, S.; Gao, X.; Wang, D.; Wu, X.; Huang, S.; Tan, J. Investigate on material removal of 3C-SiC crystals in nano-polishing via molecular dynamics. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 120, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y. The effect of rough surface on nanoscale high speed grinding by a molecular dynamics simulation. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2015, 98, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, J.; Zhu, F. Effect of abrasive particle shape on the development of silicon substrate during nano-grinding. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2021, 193, 110420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Sun, Y.; Wu, S. Molecular dynamics study of nano-grinding behavior for silicon wafer workpieces with nanoscale roughness under diamond abrasive rotation and translation. Tribol. Lett. 2024, 72, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Hu, Z.; Jin, J.; Li, L.; Yu, Y.; Peng, Q.; Xu, X. Molecular dynamics simulations of scratching characteristics in vibration-assisted nano-scratch of single-crystal silicon. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 551, 149451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Feng, Z.; Zheng, Q.; Li, B.; Zhou, H. Molecular dynamics simulation of nano-polishing of single crystal silicon on non-continuous surface. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2020, 118, 105168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkalos, N.E.; Markopoulos, A.P. Molecular dynamics study of the effect of abrasive grains orientation and spacing during nanogrinding. Micromachines 2020, 11, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Guo, X.; Kang, R.; Guo, D.; Zhou, P. Study on the transformation and control mechanism of amorphous damage during the grinding process of monocrystalline silicon considering grain shapes by MD method. Tribol. Int. 2023, 187, 108720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Kang, S.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Ren, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, L.; Li, D. Molecular dynamics study on burr formation mechanism during monocrystalline silicon nano-grinding process. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 131, 2505–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, J.; Liu, J.; Mei, M.; Chen, H.; Jiang, H.; Yu, D. Effect of gradient polishing depth on material removal mechanism of silicon wafer polishing by silicon dioxide abrasive based on molecular dynamics. J. Manuf. Process. 2025, 141, 746–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, Y. Numerical study of three-body diamond abrasive polishing single crystal Si under graphene lubrication by molecular dynamics simulation. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2020, 171, 109214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Fang, Q.; Li, J.; Tian, Y.; Liu, Y. Subsurface damage and material removal of Al-Si bilayers under high-speed grinding using molecular dynamics (MD) simulation. Appl. Phys. A 2019, 125, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Z.; Wu, W.; Dai, H. Quantitative analysis of grinding performance of cubic silicon carbide surface texture lubricated with water film. Tribol. Int. 2023, 180, 108267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Karkalos, N.; P Markopoulos, A. Modeling nano-metric manufacturing processes with molecular dynamics method: A review. Curr. Nanosci. 2017, 13, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Chen, G.; Zhou, C.; Fang, Q.; Fei, X. A numerical study of ultraprecision machining of monocrystalline silicon with laser nano-structured diamond tools by atomistic simulation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 393, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gunsteren, W.F.; Berendsen, H.J. Algorithms for macromolecular dynamics and constraint dynamics. Mol. Phys. 1977, 34, 1311–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, H.J.; Postma, J.v.; Van Gunsteren, W.F.; DiNola, A.; Haak, J.R. Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 81, 3684–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Sharma, K.; Dixit, A.R. A review on the mechanical and thermal properties of graphene and graphene-based polymer nanocomposites: Understanding of modelling and MD simulation. Mol. Simul. 2020, 46, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Srikanth, N.; Zhao, B.; Liu, B.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, K. Lubrication mechanisms of graphene for DLC films scratched by a diamond tip. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2016, 49, 485302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Diao, D.; Kubo, M. Nanoscratching of multi-layer graphene by molecular dynamics simulations. Tribol. Int. 2015, 88, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, L.; Mallick, G.; Sachdeva, G.; Shock, C.; Pandey, R. Orientation-dependent mechanical response of graphene/BN hybrid nanostructures. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 235703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Parashar, A. Atomistic modeling of BN nanofillers for mechanical and thermal properties: A review. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 22–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plimpton, S. Fast parallel algorithms for short-range molecular dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 1995, 117, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stukowski, A. Visualization and analysis of atomistic simulation data with OVITO—The Open Visualization Tool. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2009, 18, 015012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tersoff, J. Modeling solid-state chemistry: Interatomic potentials for multicomponent systems. Phys. Rev. B 1989, 39, 5566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaliwal, G.; Nair, P.B.; Singh, C.V. Uncertainty analysis and estimation of robust AIREBO parameters for graphene. Carbon 2019, 142, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo, S.L.; Olafson, B.D.; Goddard, W.A. DREIDING: A generic force field for molecular simulations. J. Phys. Chem. 1990, 94, 8897–8909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhi, A.; Behdinan, K. Identification of crystal structures in atomistic simulation by predominant common neighborhood analysis. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2017, 126, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, P.W.; Parr, R.G.; Nagy, A. Local kinetic energy and local temperature in the density-functional theory of electronic structure. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2002, 90, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Li, S.; Chen, G. Molecular dynamics simulation of subsurface damage mechanism during nanoscratching of single crystal silicon. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2019, 233, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Sun, Q.; Wang, C.; Yuan, X.; Li, X. Research on the Wear Suppression of Diamond Grain Enabled by Hexagonal Boron Nitride in Grinding Cast Steel. Molecules 2024, 29, 5925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, D.; Zhao, Y.; Li, R.; Cao, H. Tribological properties under the grinding wheel and workpiece interface by using graphene nanofluid lubricant. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 104, 3943–3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Zhao, B.; Pan, J.; Wu, J. Nano-grinding process of single-crystal silicon using molecular dynamics simulation: Nano-grinding parameters effect. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2022, 143, 106531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Element | σ(Å) | ε(meV) | r0 |
|---|---|---|---|
| C-Si | 4.0669 | 8.9092 | 3.0 |
| C-B | 3.9653 | 5.9615 | 3.0 |
| C-N | 3.7732 | 6.0089 | 3.0 |
| C-C | 3.8510 | 4.5532 | 3.0 |
| B-Si | 4.1876 | 11.6648 | 3.0 |
| N-Si | 3.9848 | 11.7575 | 3.0 |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Specimen materials | Silicon |
| Dimension of workpiece (nm3) | 25.0 × 14.0 × 10.5 |
| Surface crystal orientation of workpiece | {100} |
| Grinding directions | [100] |
| Material of grinding grit | Diamond |
| Radius of grinding grit (nm) | 4.0 |
| Potential function | Tersoff, L-J, AIREBO |
| Initial temperature (K) | 293 |
| Nano-grinding speed (m/s) | 50, 100, 200 |
| Nano-grinding depth (nm) | 1, 2, 3, 4 |
| Nano-grinding distance (nm) | 20 |
| Timestep (fs) | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.; Chang, D.; Zhao, P.; Tan, J. Molecular Dynamics Study on the Effect of Surface Films on the Nanometric Grinding Mechanism of Single-Crystal Silicon. Micromachines 2025, 16, 1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101141
Li M, Chang D, Zhao P, Tan J. Molecular Dynamics Study on the Effect of Surface Films on the Nanometric Grinding Mechanism of Single-Crystal Silicon. Micromachines. 2025; 16(10):1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101141
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Meng, Di Chang, Pengyue Zhao, and Jiubin Tan. 2025. "Molecular Dynamics Study on the Effect of Surface Films on the Nanometric Grinding Mechanism of Single-Crystal Silicon" Micromachines 16, no. 10: 1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101141
APA StyleLi, M., Chang, D., Zhao, P., & Tan, J. (2025). Molecular Dynamics Study on the Effect of Surface Films on the Nanometric Grinding Mechanism of Single-Crystal Silicon. Micromachines, 16(10), 1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101141







