Planar Two-Dimensional Vibration Isolator Based on Compliant Mechanisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
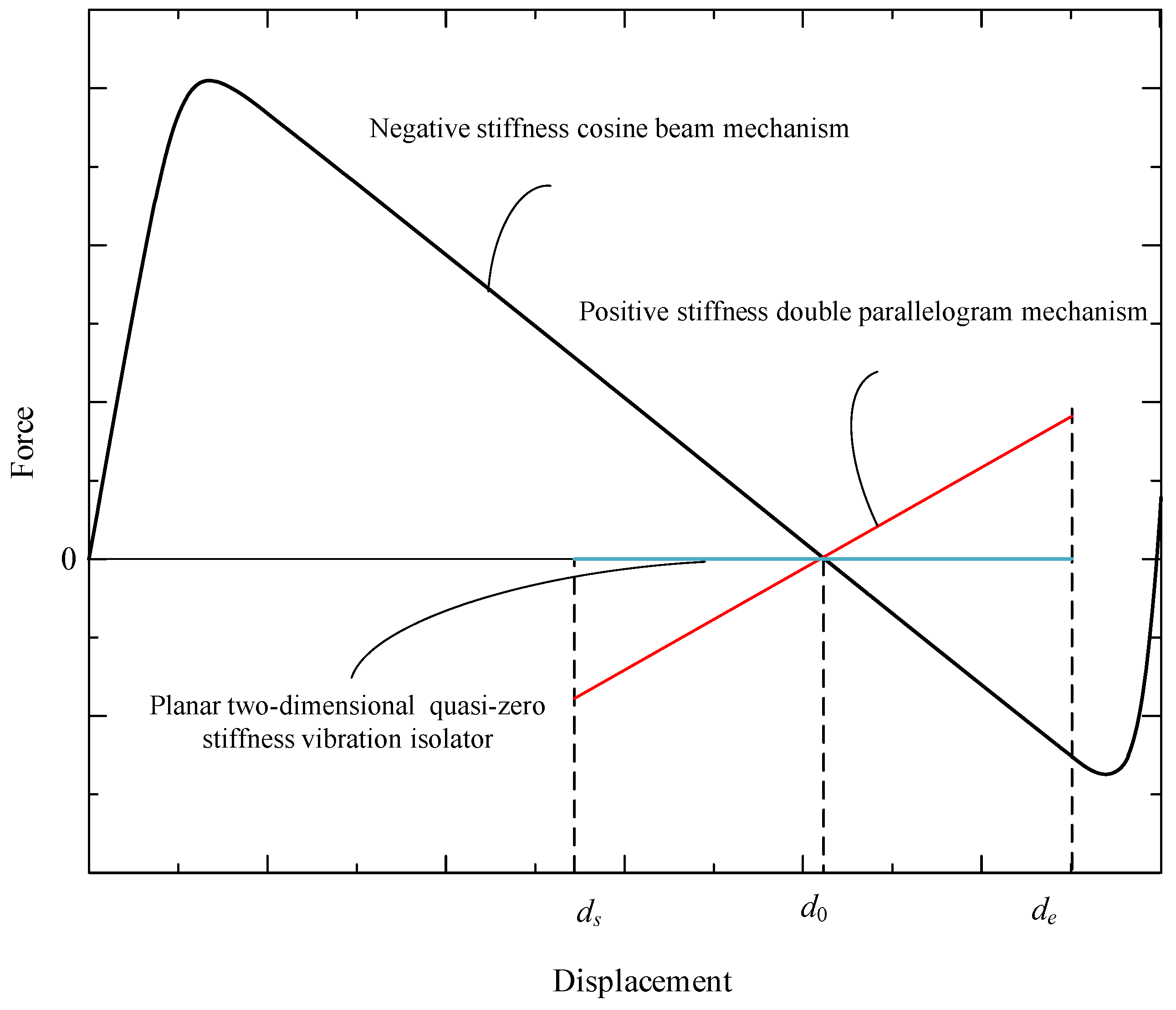
2. Design of Planar Two-Dimensional Quasi-Zero-Stiffness Vibration Isolator
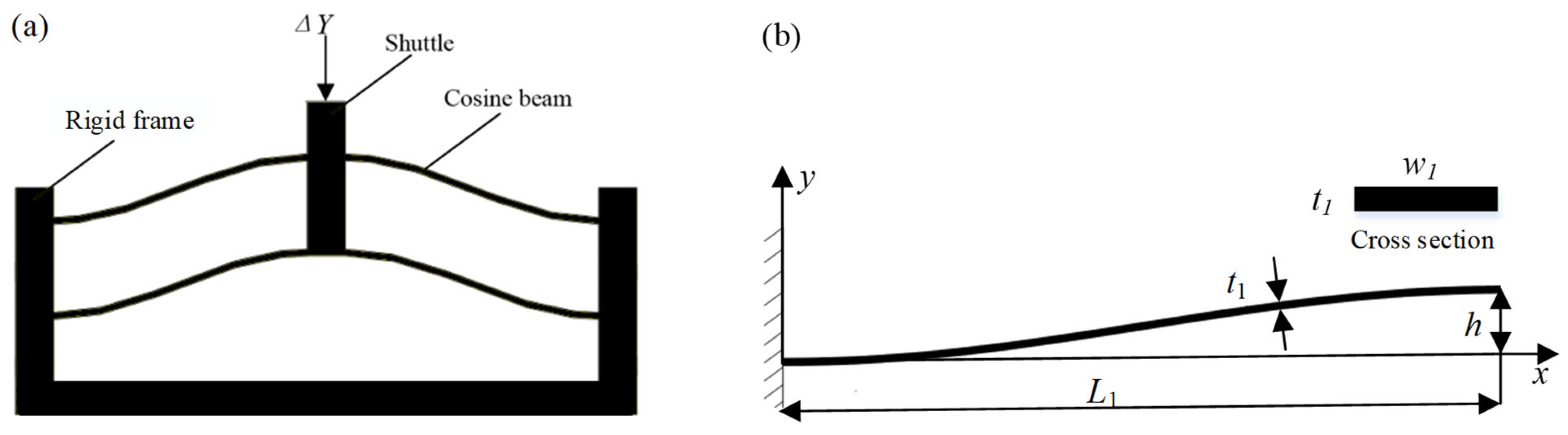
2.1. Negative Stiffness-Compliant Module Based on Cosine-Curve Beams
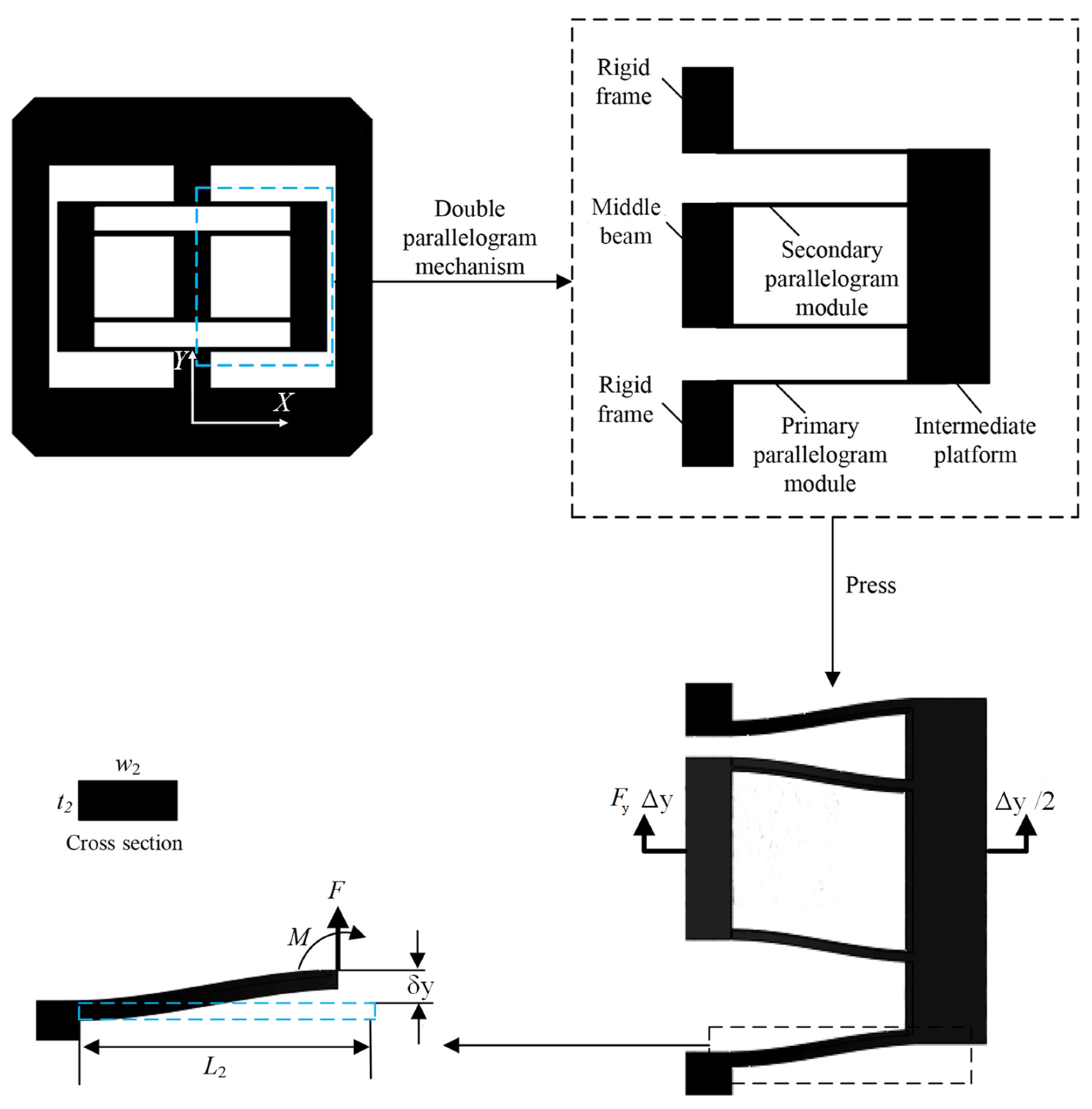
2.2. Positive Stiffness-Compliant Module Based on Parallelogram Mechanisms
2.3. Overall Design of Planar-Dimensional Quasi-Stiffness Vibration Isolator
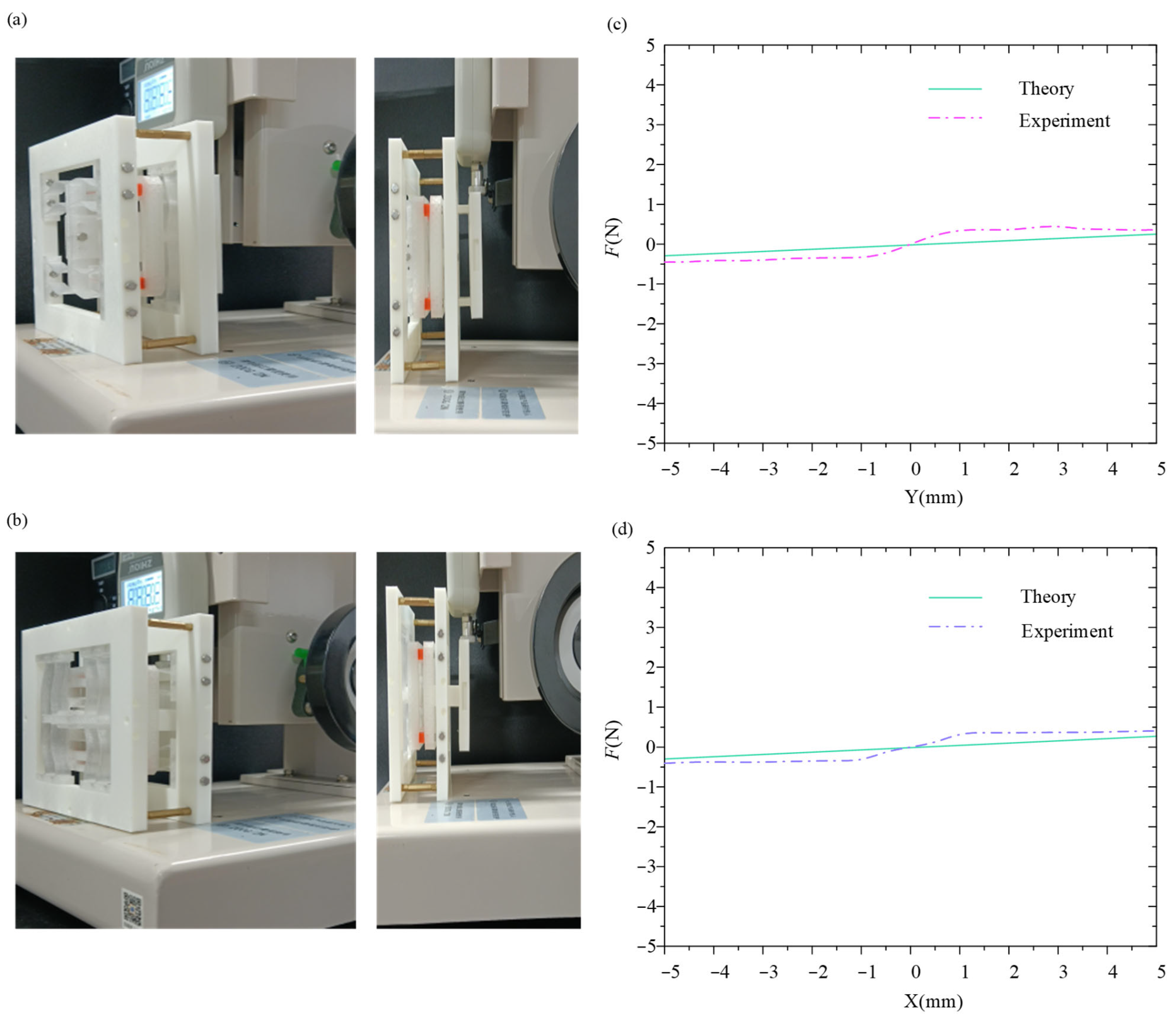
3. Static Experiments of Planar Two-Dimensional Vibration Isolator
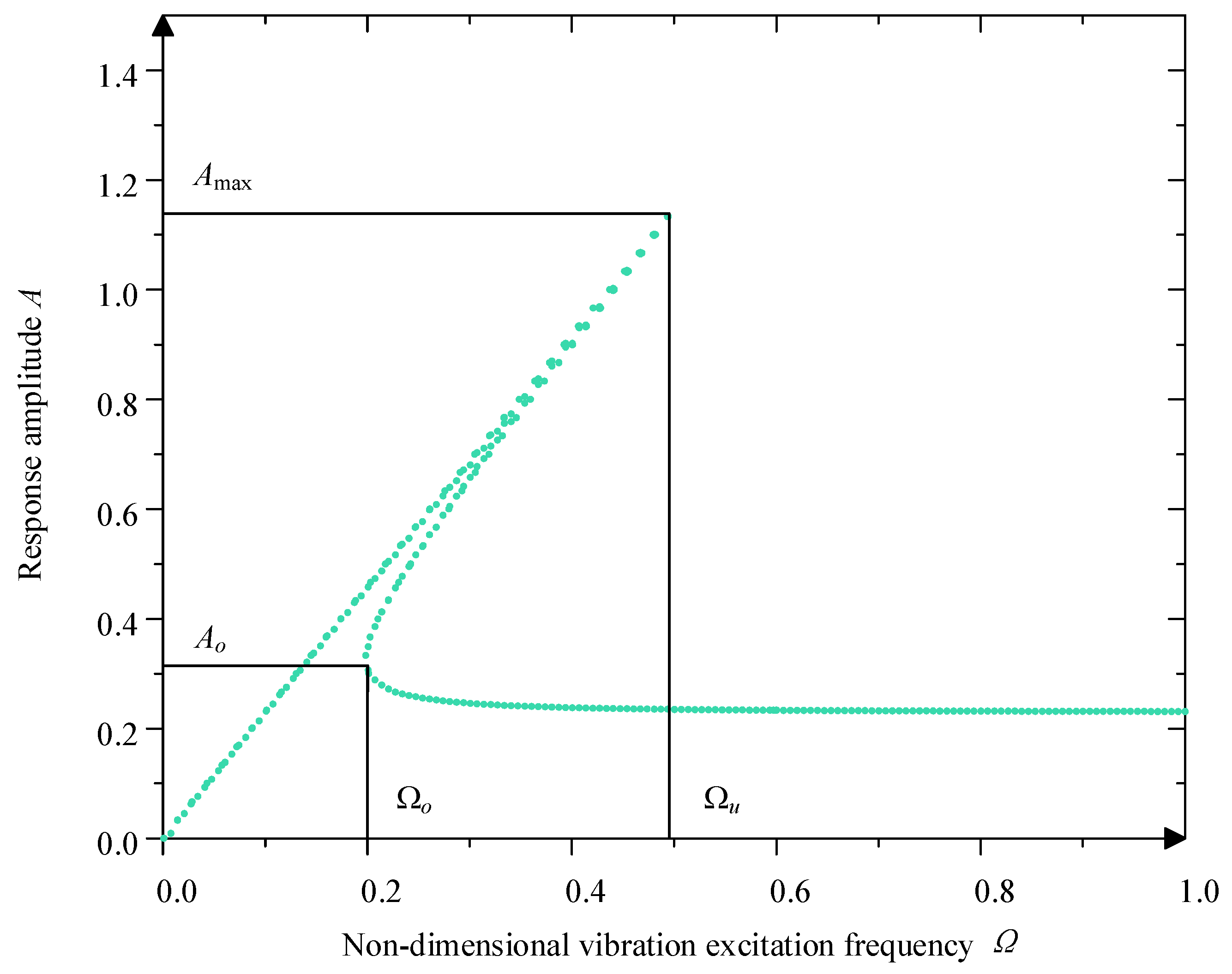
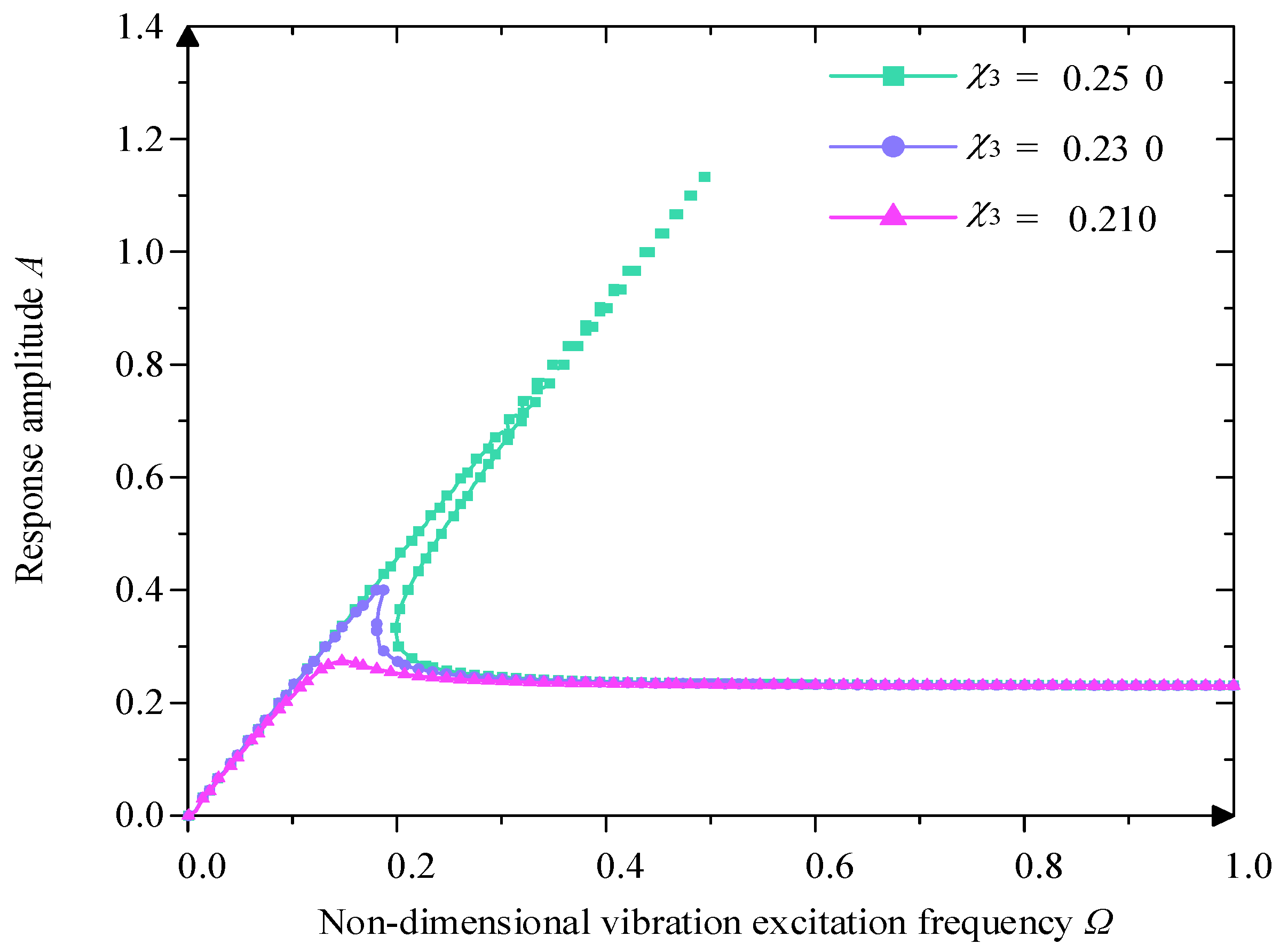
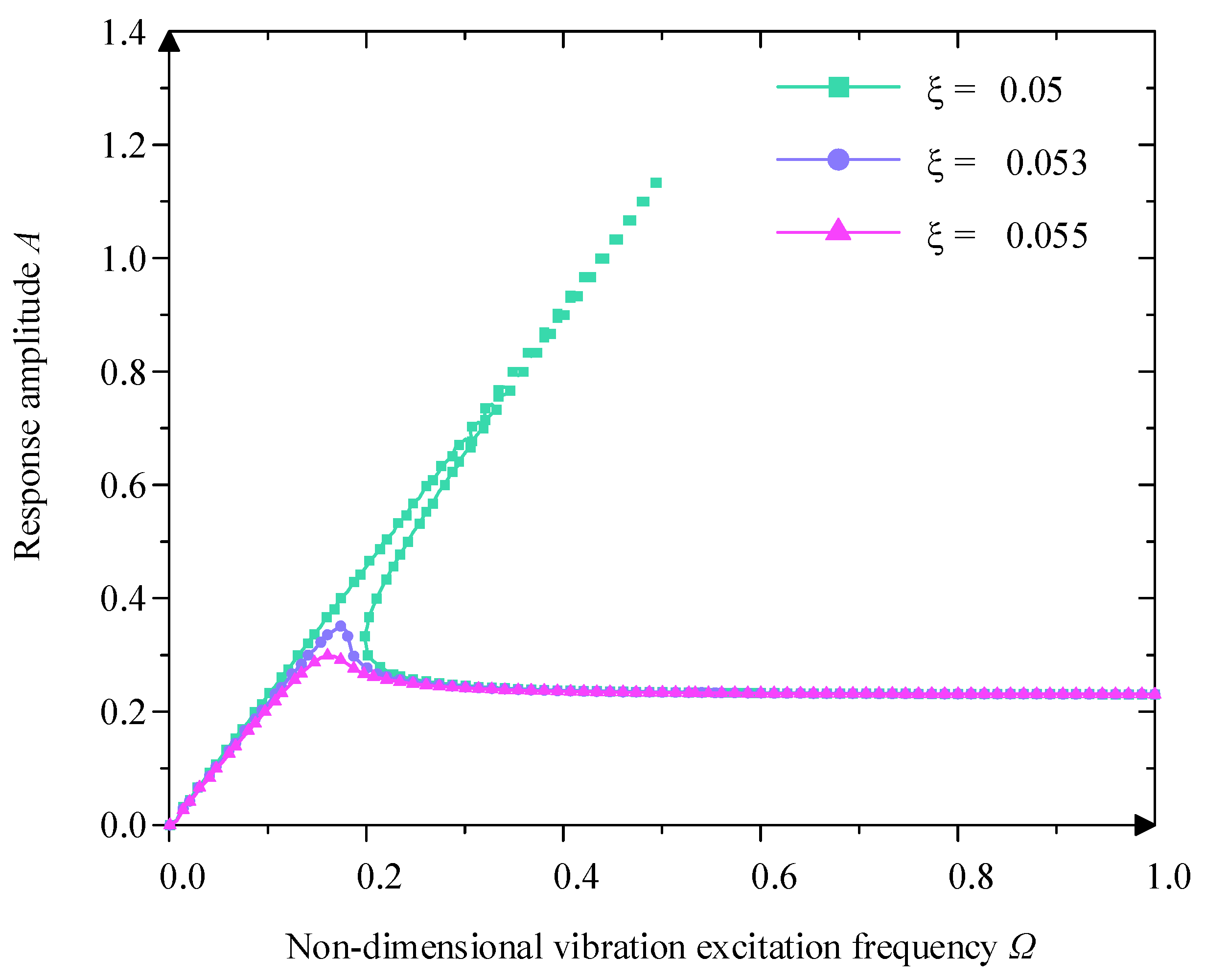
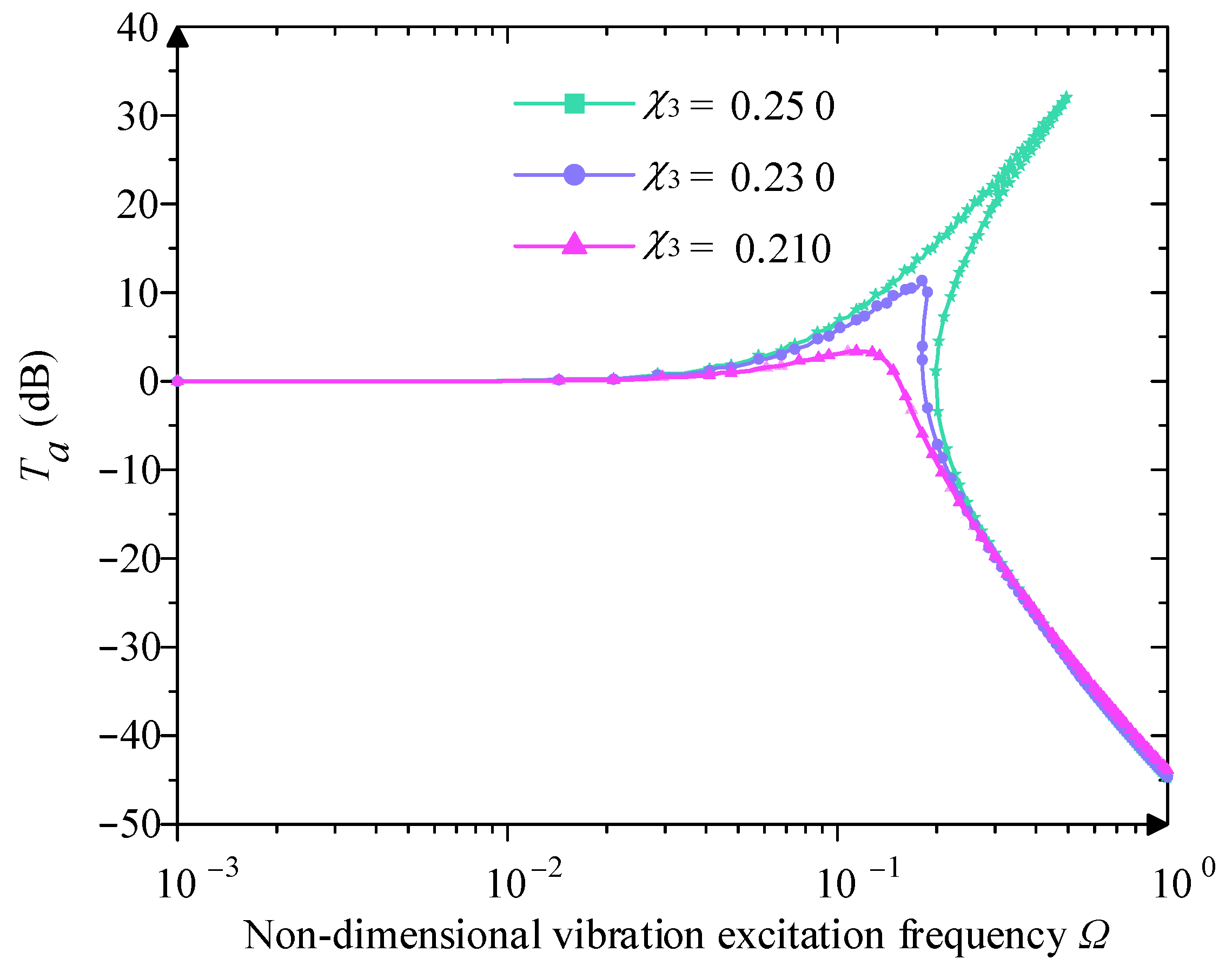
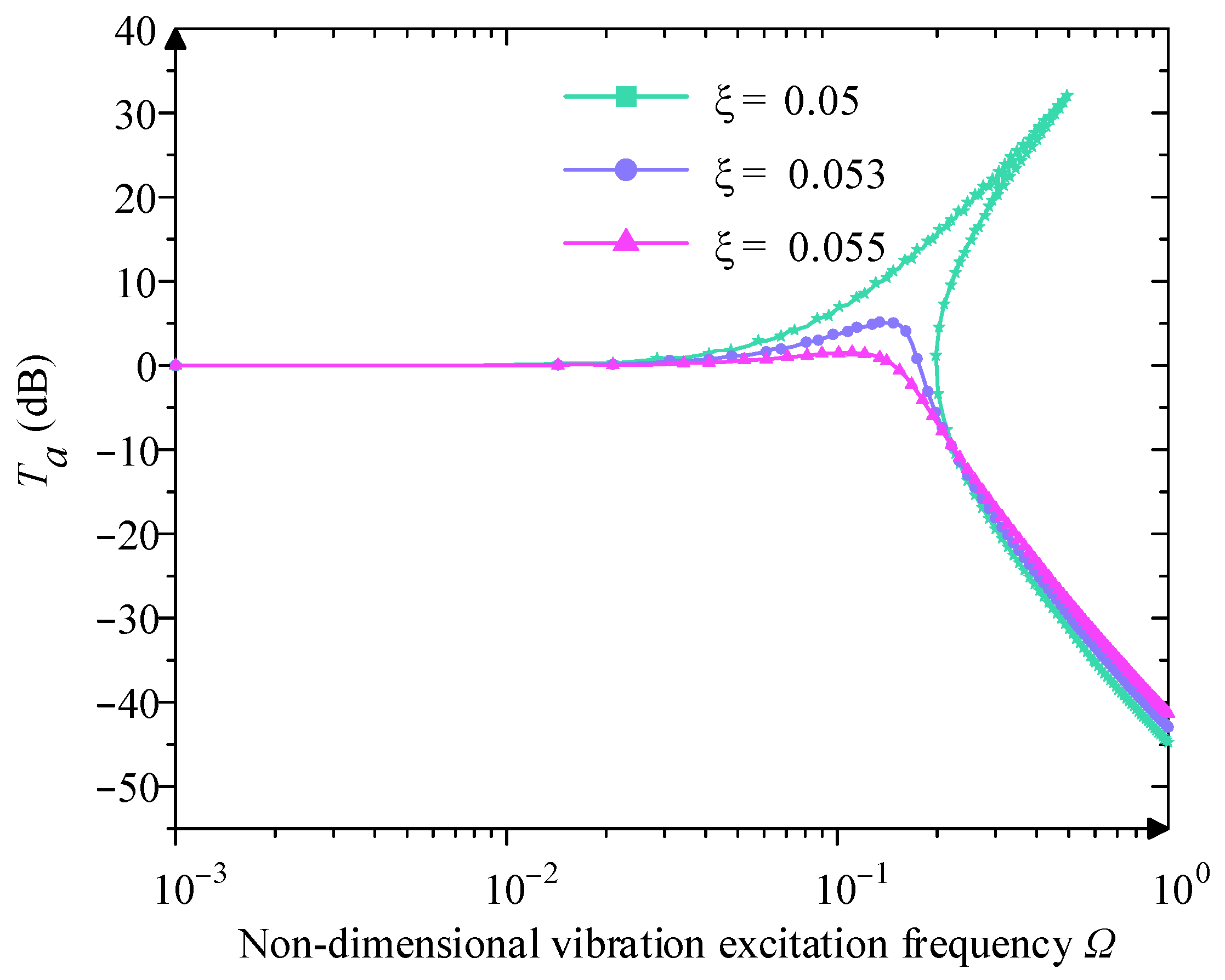
4. Dynamics of the Quasi-Zero-Stiffness Vibration Isolator
5. Vibration Experiments
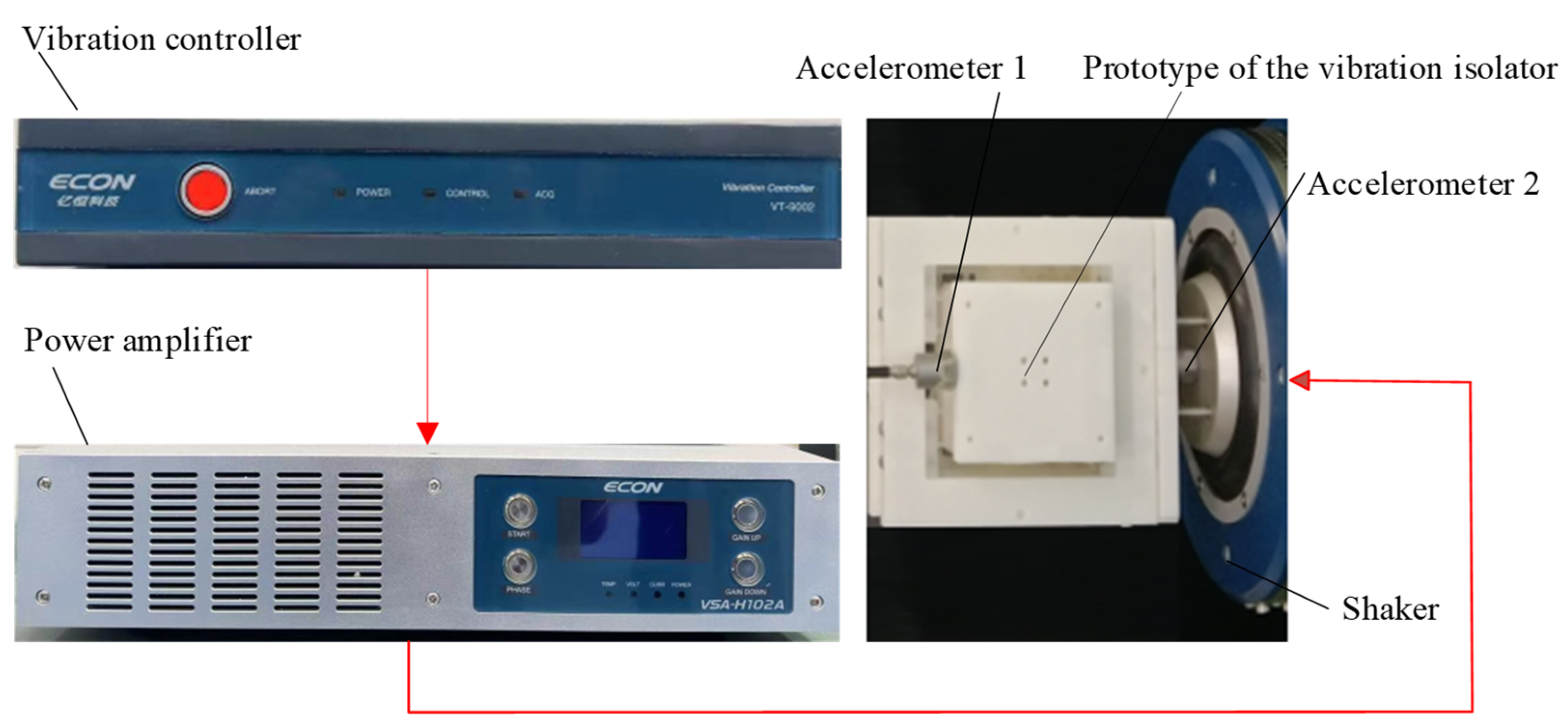
5.1. Experimental Setup
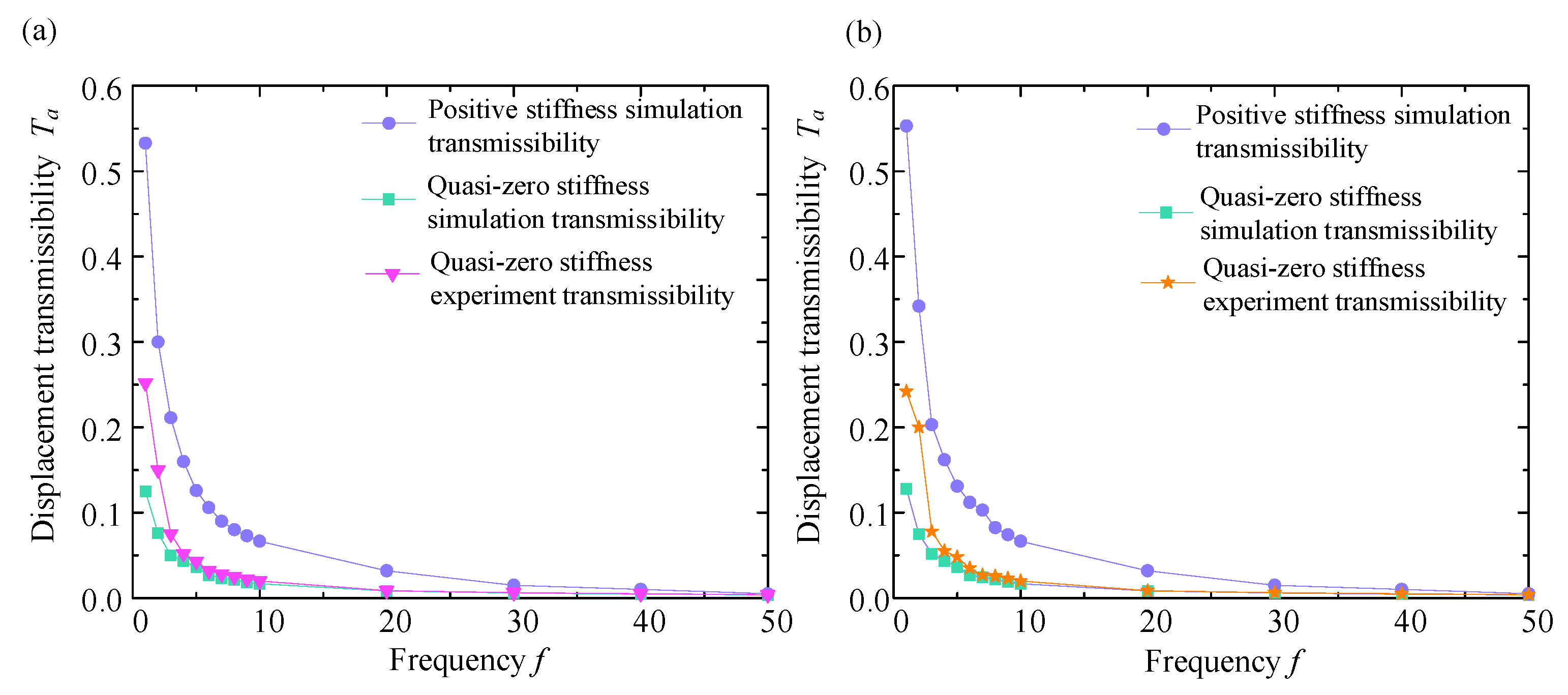
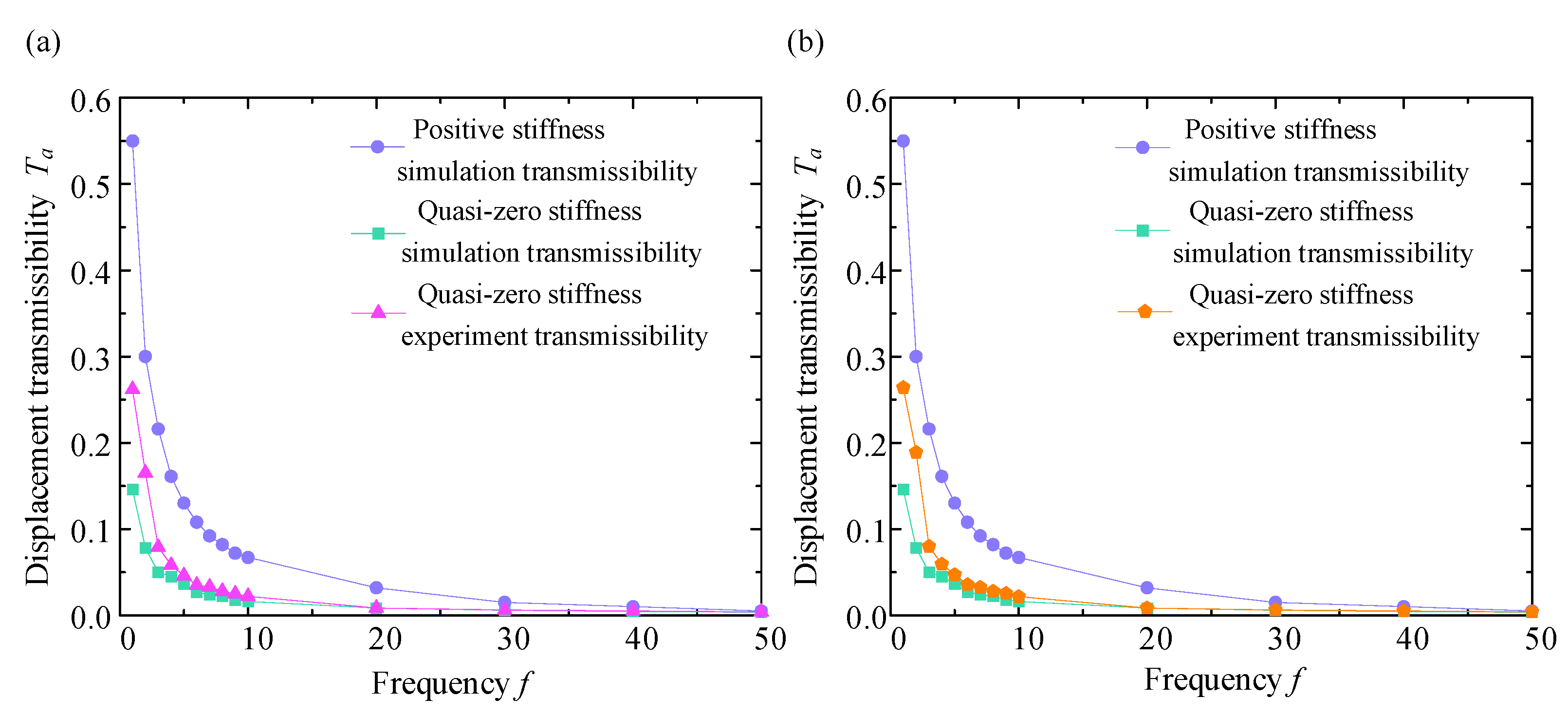
5.2. Experimental Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, C.; Zhang, W.; Yu, K.; Liu, T.; Zheng, Y. Quasi-zero-stiffness vibration isolation: Designs, improvements and applications. Eng. Struct. 2024, 301, 117282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zhou, R.; Yang, Q. Recent Advances in Quasi-Zero Stiffness Vibration Isolation Systems: An Overview and Future Possibilities. Machines 2022, 10, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrella, A.; Brennan, M.J.; Kovacic, I.; Waters, T.P. On the force transmissibility of a vibration isolator with quasi-zero-stiffness. J. Sound Vib. 2009, 322, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrella, A.; Brennan, M.J.; Waters, T.P. Static analysis of a passive vibration isolator with quasi-zero-stiffness characteristic. J. Sound Vib. 2007, 301, 678–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrella, A. Passive Vibration Isolators with High-Static-Low-Dynamic-Stiffness. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, C. Study on the performance of a novel 1DOF isolator with QZS characteristics. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2024, 2691, 012045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Lou, J. On the analytical and experimental assessment of the performance of a quasi-zero-stiffness isolator. J. Vib. Control 2013, 20, 2314–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; Xu, D.; Bishop, S. Nonlinear dynamic characteristics of a quasi-zero stiffness vibration isolator with cam–roller–spring mechanisms. J. Sound Vib. 2015, 346, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wei, G.; Wen, H.; Jin, D.; Hu, H. Design and analysis of a vibration isolation system with cam–roller–spring–rod mechanism. J. Vib. Control 2022, 28, 1781–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakadu, K.; Li, K. A passive vibration isolator integrated a dynamic vibration absorber with negative stiffness spring. J. Vib. Eng. Technol. 2022, 10, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Sun, X.; Zhao, D.; Yang, X.; Tang, K. The design and analysis of a novel passive quasi-zero stiffness vibration isolator. J. Vib. Eng. Technol. 2021, 9, 225–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Cheng, W.; Xie, R. A quasi-zero-stiffness vibration isolator using a cam mechanism with user-defined profile. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2021, 189, 105938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Cheng, W.; Xie, R. Design and experimental validation of a cam-based constant-force compression mechanism with friction considered. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2018, 233, 3873–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Cheng, W. Design and experimental validation of a large-displacement constant-force mechanism. J. Mech. Robot. 2018, 10, 051007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Liu, G.; Rao, Z.; Tan, T.; Zhang, W.; Liao, W.-H. A device capable of customizing nonlinear forces for vibration energy harvesting, vibration isolation, and nonlinear energy sink. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 147, 107101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Analytical and experimental investigation of a high-static-low-dynamic stiffness isolator with cam-roller-spring mechanism. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2020, 186, 105888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Song, G.; Li, Y.; Huang, Z. Effect of negative stiffness mechanism in a vibration isolator with asymmetric and high-static-low-dynamic stiffness. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 124, 388–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Xiao, Q.; Xu, D.; Ouyang, H.; Li, Y. A novel quasi-zero-stiffness strut and its applications in six-degree-of-freedom vibration isolation platform. J. Sound Vib. 2017, 394, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhou, J.; Xu, D. Sensitivity analysis of parametric errors on the performance of a torsion quasi-zero-stiffness vibration isolator. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2017, 134, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhou, J.; Xu, D.; Ouyang, H. Tunable low-frequency torsional-wave band gaps in a meta-shaft. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2019, 52, 055104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, G.; Zhang, X.; Hou, S.; Shan, X.; Hou, W.; Li, J. Quasi-Zero Stiffness Isolator Suitable for Low-Frequency Vibration. Machines 2023, 11, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Li, X.; Chen, S.-C.; Li, Y. Modular quasi-zero-stiffness isolator based on compliant constant-force mechanisms for low-frequency vibration isolation. J. Vib. Control 2023, 30, 3006–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; He, J.; Zhou, G.; Wang, K.; Xu, D.; Zhou, J. Compliant quasi-zero-stiffness isolator for low-frequency torsional vibration isolation. Mech. Mach. Theory 2023, 181, 105213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Liu, H.; Fan, D.; Xie, X. Design of quasi-zero stiffness compliant shock isolator under strong shock excitation. Precis. Eng. 2022, 78, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.-J.; Qi, W.-H.; Liu, F.-R.; Cao, Y.-B.; Zhao, T.-Y.; Cai, L.-Q.; Li, Y.; Yan, G.; Zhang, W.-M. Compliant curved beam support with flexible stiffness modulation for near-zero frequency vibration isolation. J. Sound Vib. 2025, 595, 118702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Yang, L.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Z. Design of metastructures with quasi-zero dynamic stiffness for vibration isolation. Compos. Struct. 2020, 243, 112244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Jing, X.; Guo, Y. A compact X-shaped mechanism based 3-DOF anti-vibration unit with enhanced tunable QZS property. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 168, 108651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Jing, X. Low-frequency multi-direction vibration isolation via a new arrangement of the X-shaped linkage mechanism. Nonlinear Dyn. 2022, 109, 2383–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Jing, X.; Chao, X. X-shaped mechanism based enhanced tunable QZS property for passive vibration isolation. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2022, 218, 107077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Cao, Q.; Chen, Y. An archetypal zero-or quasi-zero-stiffness model with three degrees of freedom based upon an inverse method. Nonlinear Dyn. 2023, 111, 2029–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yao, G. Multi-directional vibration isolation performances of a scissor-like structure with nonlinear hybrid spring stiffness. Nonlinear Dyn. 2024, 112, 8871–8888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ji, W.; Deng, E.; Wang, X.; Song, C. Dynamic characteristics of two degree-of-freedom quasi-zero stiffness vibration isolation system with nonlinear springs. Mech. Based Des. Struct. Mach. 2021, 51, 3100–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, K.; Xu, D.; Ouyang, H.; Li, Y. A six degrees-of-freedom vibration isolation platform supported by a hexapod of quasi-zero-stiffness struts. J. Vib. Acoust. 2017, 139, 034502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Huang, X.; Hua, H. On the characteristics of a quasi-zero stiffness isolator using Euler buckled beam as negative stiffness corrector. J. Sound Vib. 2013, 332, 3359–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Lang, J.H.; Slocum, A.H. A Curved-Beam Bistable Mechanism. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2004, 13, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awtar, S.; Slocum, A.H.; Sevincer, E. Characteristics of beam-based flexure modules. J. Mech. Des. 2007, 129, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameters of Negative Stiffness Beam | Parameters of Positive Stiffness Beam | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | h | L2 | ||||
| 40 mm | 10 mm | 1 mm | 10 mm | 13.5 mm | 10 mm | 1 mm |
| PP | 220 | 0.35 | 900 |
| PLA | 1400 | 0.2 | 1250 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, R.; Hu, J.; Huang, L.; Zhang, L.; Ren, G. Planar Two-Dimensional Vibration Isolator Based on Compliant Mechanisms. Micromachines 2025, 16, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16010010
Zhu R, Hu J, Huang L, Zhang L, Ren G. Planar Two-Dimensional Vibration Isolator Based on Compliant Mechanisms. Micromachines. 2025; 16(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Ruizhe, Jinpeng Hu, Long Huang, Leiyu Zhang, and Guangan Ren. 2025. "Planar Two-Dimensional Vibration Isolator Based on Compliant Mechanisms" Micromachines 16, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16010010
APA StyleZhu, R., Hu, J., Huang, L., Zhang, L., & Ren, G. (2025). Planar Two-Dimensional Vibration Isolator Based on Compliant Mechanisms. Micromachines, 16(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16010010






