Characterization of Shrink Film Properties for Rapid Microfluidics Lab-on-Chip Fabrication
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Heating Method
2.3. Baseplate Material
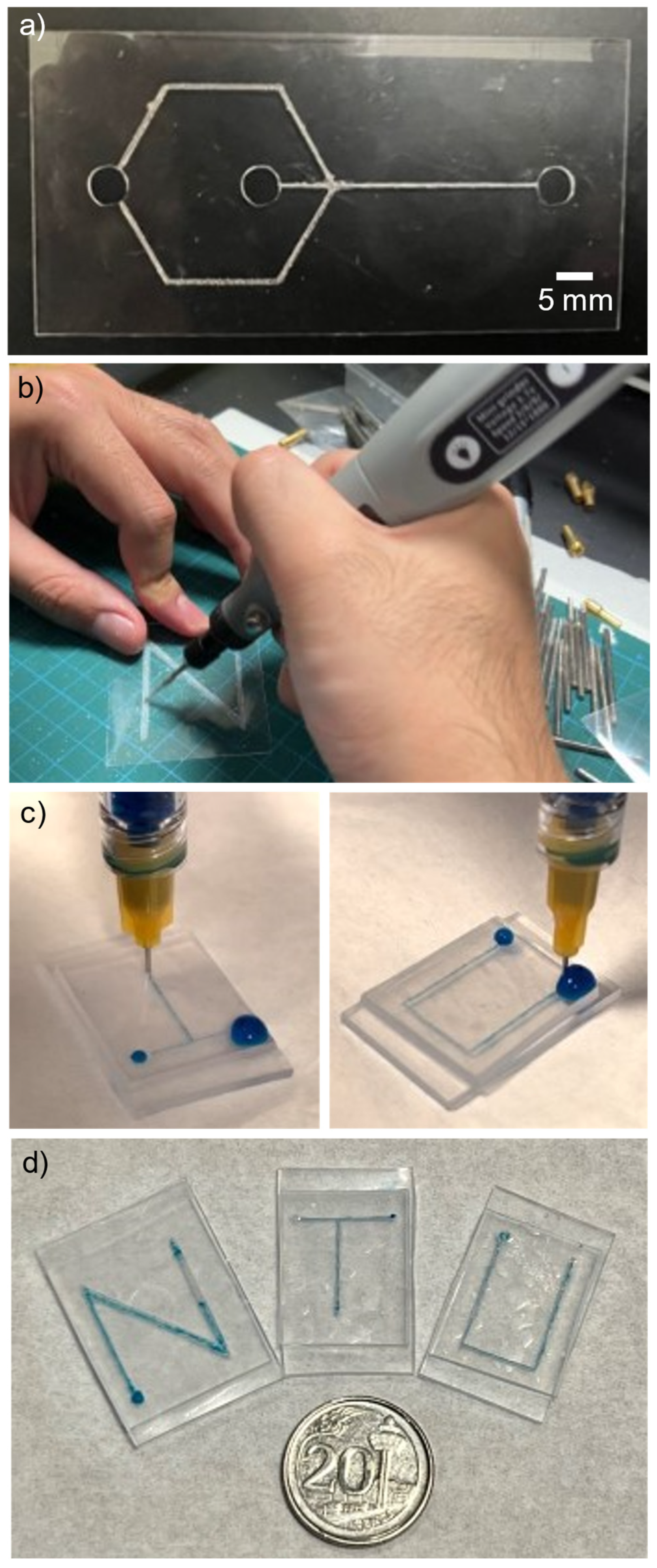
2.4. Fabrication of Shrink Film Microfluidic Chip
2.5. Alternative Method of Using Shrink Film as Mold for PDMS Microfluidic Chip Fabrication
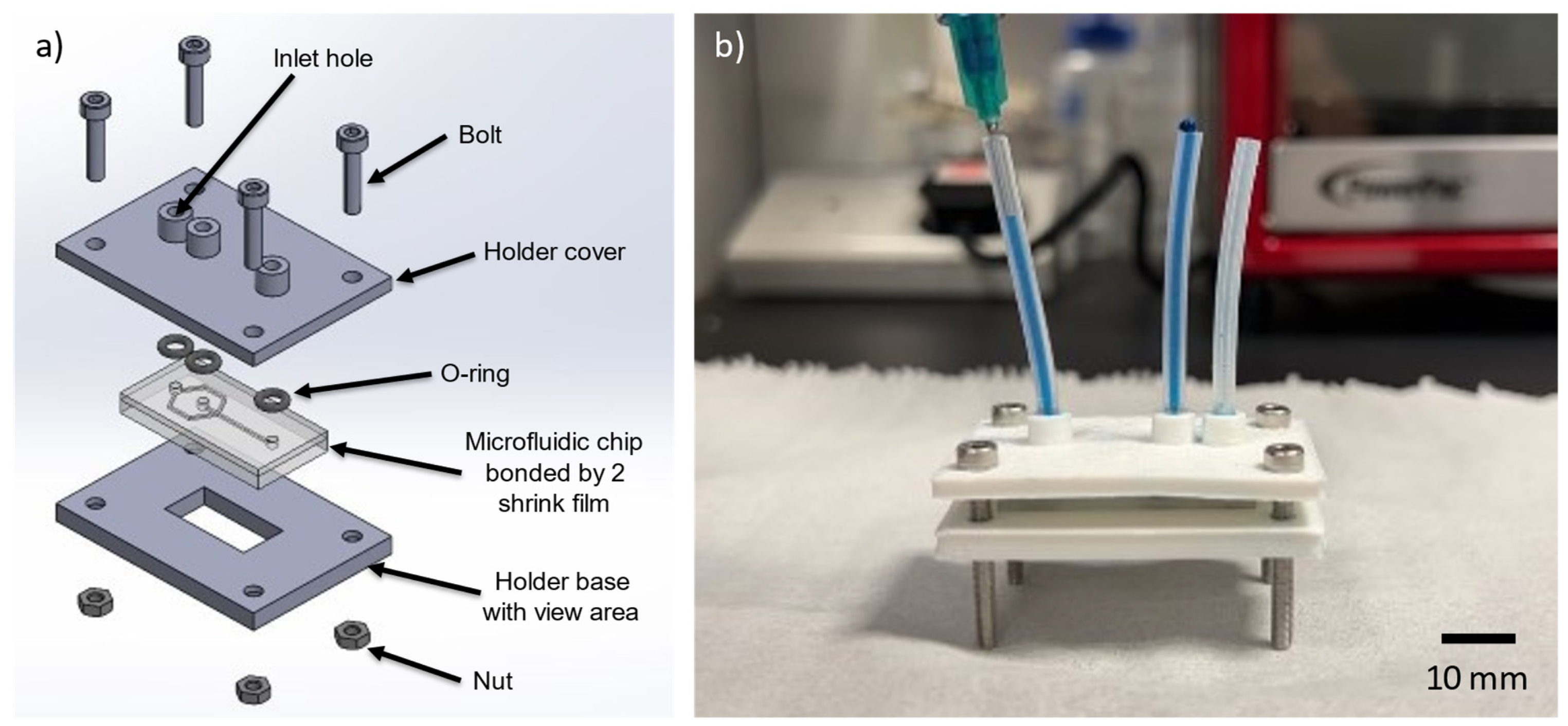
2.6. Creating of Chip Holder for Mounting of Microfluidic Device
3. Results and Discussion
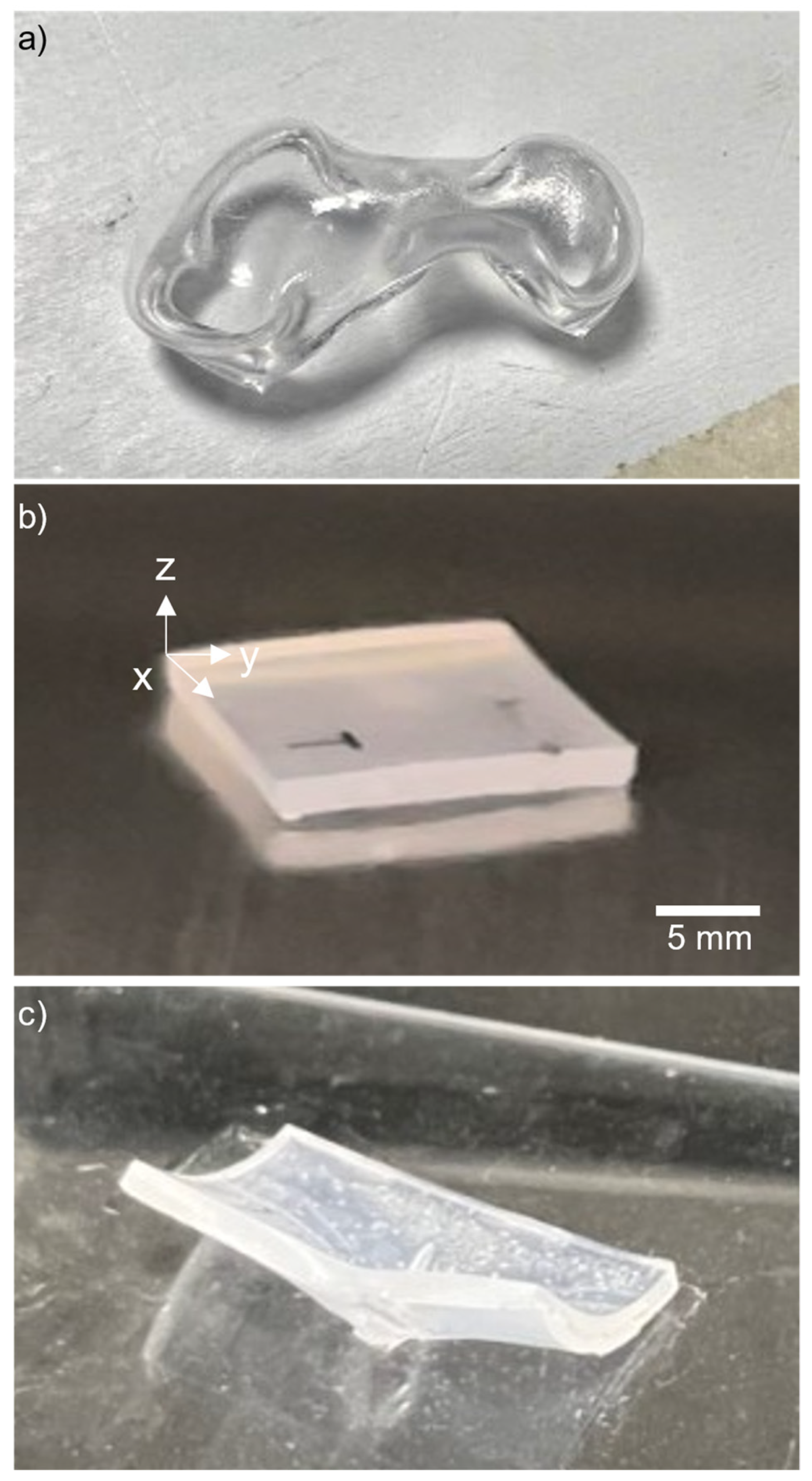
3.1. Heating Method
3.2. Base Plate Material
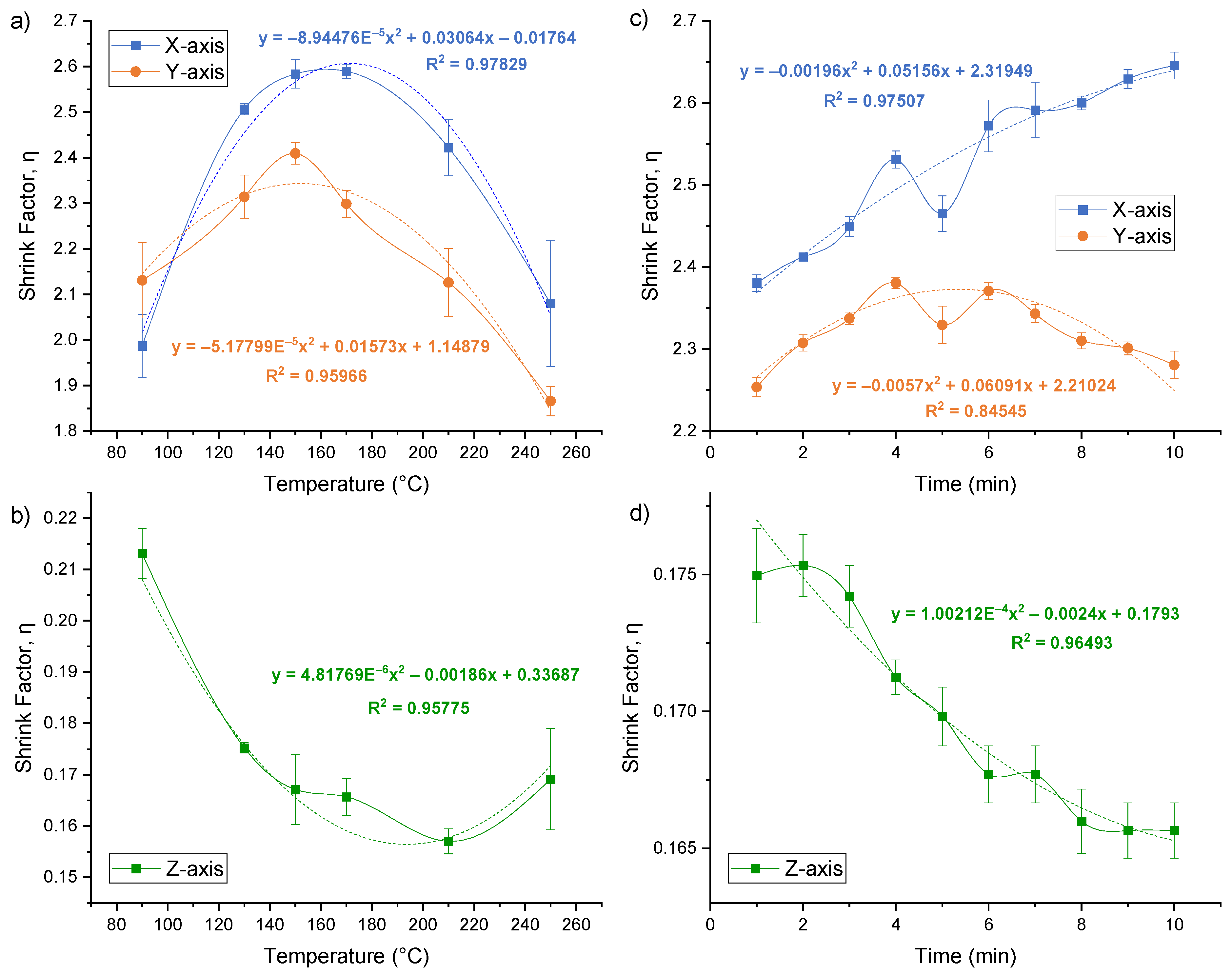
3.3. Shrinking Temperature
3.4. Shrinking Time
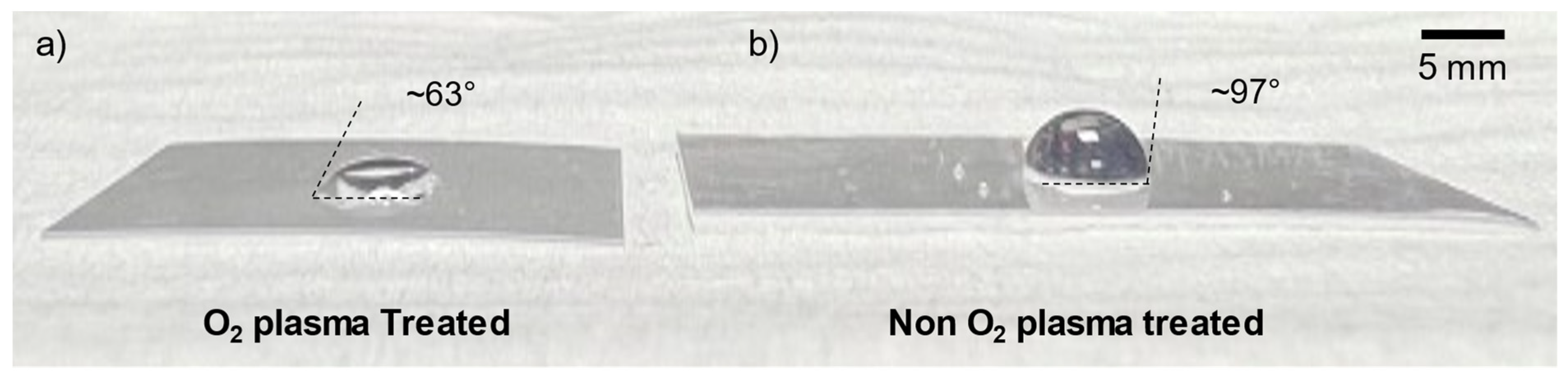
3.5. Shrink Film Wettability
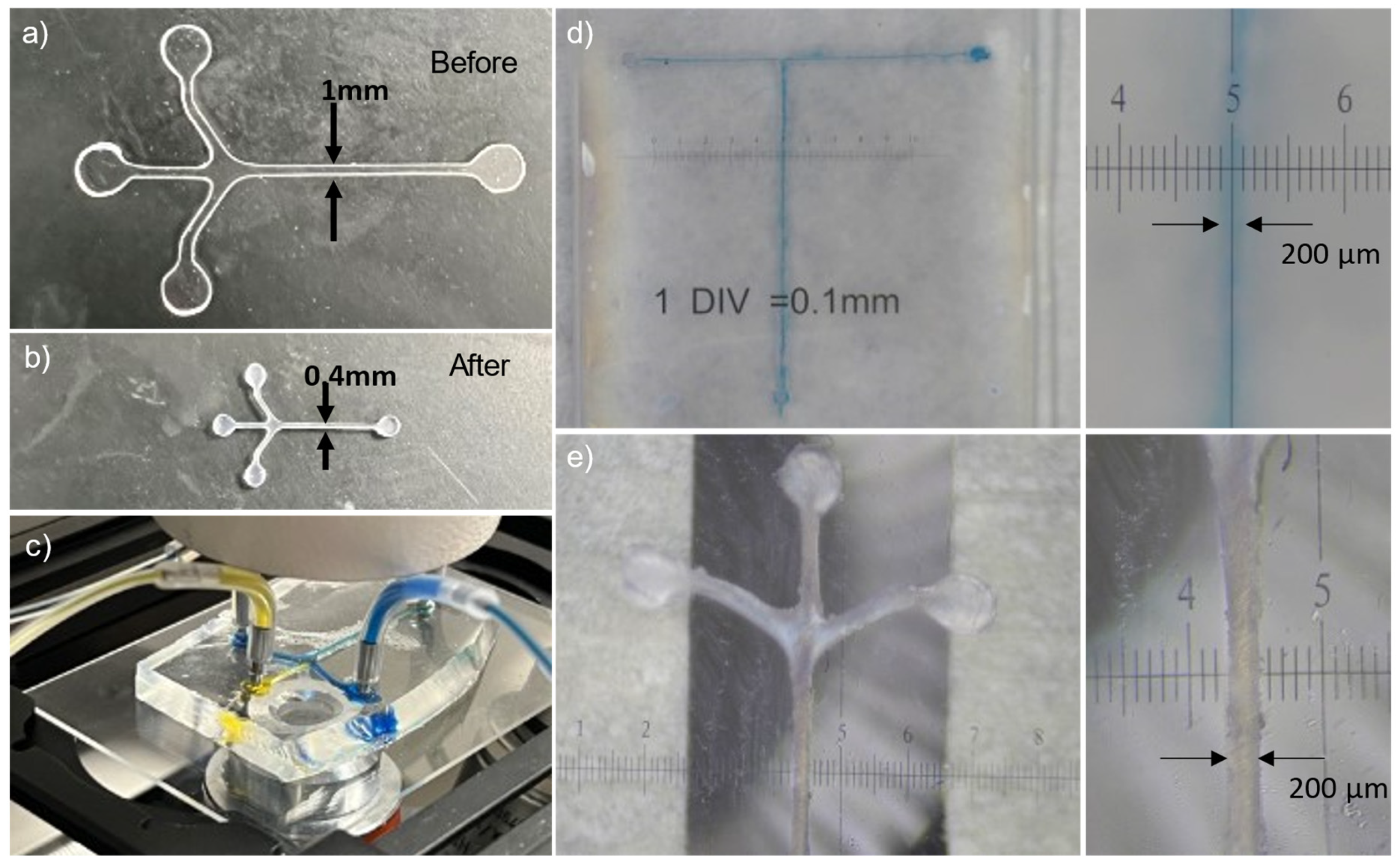
3.6. Shrink Film Microfluidic Chip
3.7. Chip Holder
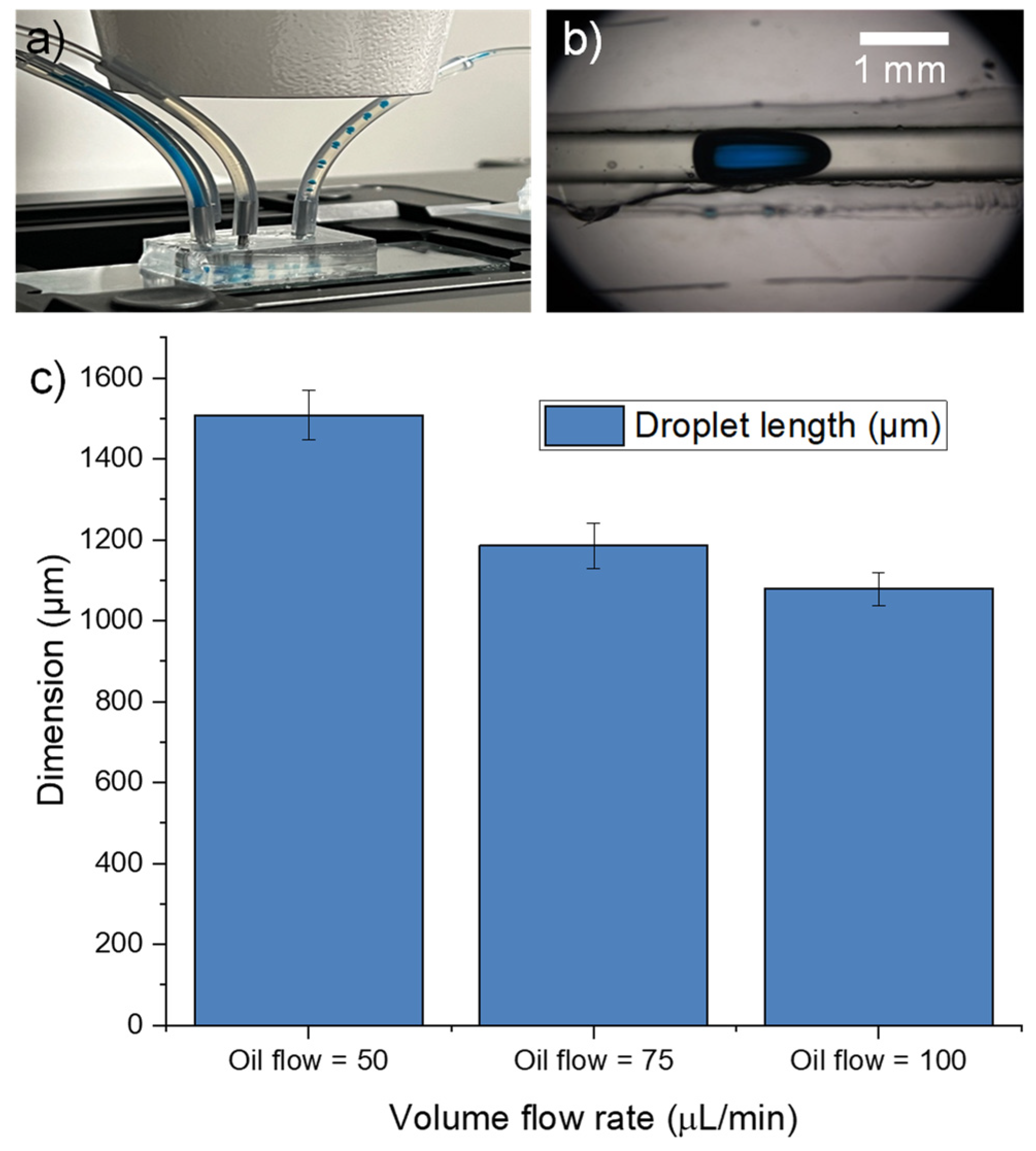
3.8. Shrink Film as Mold for PDMS Microfluidic Chip Fabrication
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ren, K.; Zhou, J.; Wu, H. Materials for Microfluidic Chip Fabrication. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2396–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Cole, T.; Zhang, Y.; Bayinqiaoge; Yuan, D.; Tang, S.-Y. An Automated and Intelligent Microfluidic Platform for Microalgae Detection and Monitoring. Lab Chip 2024, 24, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, T.F.; Tan, P.Y.; Tay, B.Z.; Shen, X.; Marcos. Bacteria and Cancer Cell Pearl Chain under Dielectrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2021, 42, 1070–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.-W.; Wei, K.; Liu, Q.-Q.; Sun, X.-G.; Su, N.; Li, W.-M.; Shang, M.-Y.; Li, J.-M.; Liao, D.; Li, J.; et al. Enhanced Separation Efficiency and Purity of Circulating Tumor Cells Based on the Combined Effects of Double Sheath Fluids and Inertial Focusing. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 750444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, T.F.; Shen, X.; Marcos; Yang, C.; Ibrahim, I.H. Dielectrophoretic Trapping and Impedance Detection of Escherichia Coli, Vibrio Cholera, and Enterococci Bacteria. Biomicrofluidics 2020, 14, 054105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omrani, V.; Targhi, M.Z.; Rahbarizadeh, F.; Nosrati, R. High-Throughput Isolation of Cancer Cells in Spiral Microchannel by Changing the Direction, Magnitude and Location of the Maximum Velocity. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadali, R.; Bayareh, M. Deformability-Based Isolation of Circulating Tumor Cells in Spiral Microchannels. Micromachines 2023, 14, 2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, T.F.; Shen, X.; Marcos; Yang, C. Lab-on-Chip Microfluidic Impedance Measurement for Laminar Flow Ratio Sensing and Differential Conductivity Difference Detection. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 110, 233501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, J.B.Y.; Marcos. Effect of Dielectrophoresis on Spermatozoa. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2014, 17, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Wong, T.N.; Marcos. Pair Interactions in Induced Charge Electrophoresis of Conducting Cylinders. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 88, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, J.B.Y.; Shen, X.; Marcos. Supervised Learning to Predict Sperm Sorting by Magnetophoresis. Magnetochemistry 2018, 4, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Shi, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lam, R.H.W.; Lim, C.T.; Hu, J. Recent Progress of Organ-on-a-Chip towards Cardiovascular Diseases: Advanced Design, Fabrication, and Applications. Biofabrication 2023, 15, 042001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hu, D.; Zhang, R.; Huang, S.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, Y.; et al. A Microfluidic Platform Revealing Interactions between Leukocytes and Cancer Cells on Topographic Micropatterns. Biosensors 2022, 12, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, T.F.; Nguyen, N.-T. Liquid Metal Microcoils for Sensing and Actuation in Lab-on-a-Chip Applications. Microsyst. Technol. 2015, 21, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Liu, Y.; Huang, W.; Lam, R.H.W. A Narrow Straight Microchannel Array for Analysis of Transiting Speed of Floating Cancer Cells. Micromachines 2022, 13, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimes, A.; Breslauer, D.N.; Long, M.; Pegan, J.; Lee, L.P.; Khine, M. Shrinky-Dink Microfluidics: Rapid Generation of Deep and Rounded Patterns. Lab Chip 2007, 8, 170–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-S.; Breslauer, D.N.; Luna, J.I.; Grimes, A.; Chin, W.; Lee, L.P.; Khine, M. Shrinky-Dink Microfluidics: 3D Polystyrene Chips. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 622–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morbioli, G.G.; Speller, N.C.; Stockton, A.M. A Practical Guide to Rapid-Prototyping of PDMS-Based Microfluidic Devices: A Tutorial. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1135, 150–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.Y.; Gao, N.; Barthlott, W. Mimicking Natural Superhydrophobic Surfaces and Grasping the Wetting Process: A Review on Recent Progress in Preparing Superhydrophobic Surfaces. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 169, 80–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.W.; Garvin, T.P.; Alvarado, J.L.; Jacobi, A.M.; Jones, B.G.; Marsh, C.P. Droplet Contact Angle Behavior on a Hybrid Surface with Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic Properties. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 111605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, K.-Y. Definitions for Hydrophilicity, Hydrophobicity, and Superhydrophobicity: Getting the Basics Right. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 686–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voronov, R.S.; Papavassiliou, D.V.; Lee, L.L. Review of Fluid Slip over Superhydrophobic Surfaces and Its Dependence on the Contact Angle. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 2455–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-M.; Reinhoudt, D.; Crego-Calama, M. What Do We Need for a Superhydrophobic Surface? A Review on the Recent Progress in the Preparation of Superhydrophobic Surfaces. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 1350–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodas, D.; Khan-Malek, C. Formation of More Stable Hydrophilic Surfaces of PDMS by Plasma and Chemical Treatments. Microelectron. Eng. 2006, 83, 1277–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.H.; Nguyen, N.-T.; Chua, Y.C.; Kang, T.G. Oxygen Plasma Treatment for Reducing Hydrophobicity of a Sealed Polydimethylsiloxane Microchannel. Biomicrofluidics 2010, 4, 032204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, S.; Bijwe, J. Surface Treatment of Carbon Fibers-A Review. Procedia Technol. 2014, 14, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, P. Investigations on the Flow Behaviour in Microfluidic Device Due to Surface Roughness: A Computational Fluid Dynamics Simulation. Microsyst. Technol. 2019, 25, 3779–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croce, G.; D’Agaro, P. Numerical Simulation of Roughness Effect on Microchannel Heat Transfer and Pressure Drop in Laminar Flow. J. Phys. Appl. Phys. 2005, 38, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikanth, S.; Raut, S.; Dubey, S.K.; Ishii, I.; Javed, A.; Goel, S. Experimental Studies on Droplet Characteristics in a Microfluidic Flow Focusing Droplet Generator: Effect of Continuous Phase on Droplet Encapsulation. Eur. Phys. J. E 2021, 44, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, S.; Solvas, X.C.I.; Bashir, M.; Rees, J.M.; Zimmerman, W.B.J. Dynamic Wetting in Microfluidic Droplet Formation. BioChip J. 2014, 8, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Cost effective | Thermal sensitivity |
| Easy to fabricate | Limited mechanical strength |
| Optical transparency | Limited scalability |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, T.F.; Ang, A.W.J.; Marcos. Characterization of Shrink Film Properties for Rapid Microfluidics Lab-on-Chip Fabrication. Micromachines 2024, 15, 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15030308
Kong TF, Ang AWJ, Marcos. Characterization of Shrink Film Properties for Rapid Microfluidics Lab-on-Chip Fabrication. Micromachines. 2024; 15(3):308. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15030308
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Tian Fook, Alger Wai Jiat Ang, and Marcos. 2024. "Characterization of Shrink Film Properties for Rapid Microfluidics Lab-on-Chip Fabrication" Micromachines 15, no. 3: 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15030308
APA StyleKong, T. F., Ang, A. W. J., & Marcos. (2024). Characterization of Shrink Film Properties for Rapid Microfluidics Lab-on-Chip Fabrication. Micromachines, 15(3), 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15030308






