Nanostructured Oxide (SnO2, FTO) Thin Films for Energy Harvesting: A Significant Increase in Thermoelectric Power at Low Temperature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
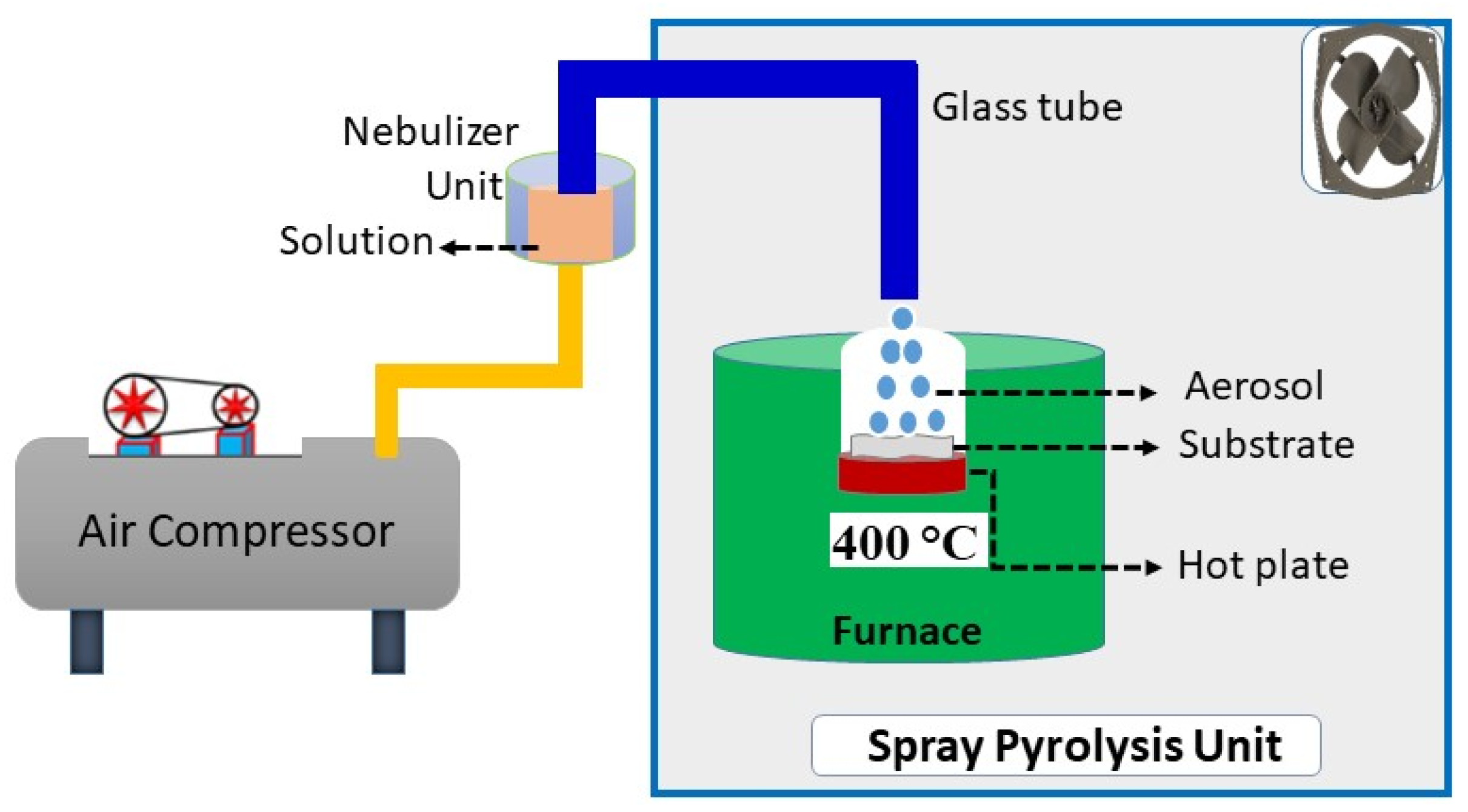
2.1. Thin Film Synthesis by Nebulizer-Assisted Spray Pyrolysis
2.2. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Properties
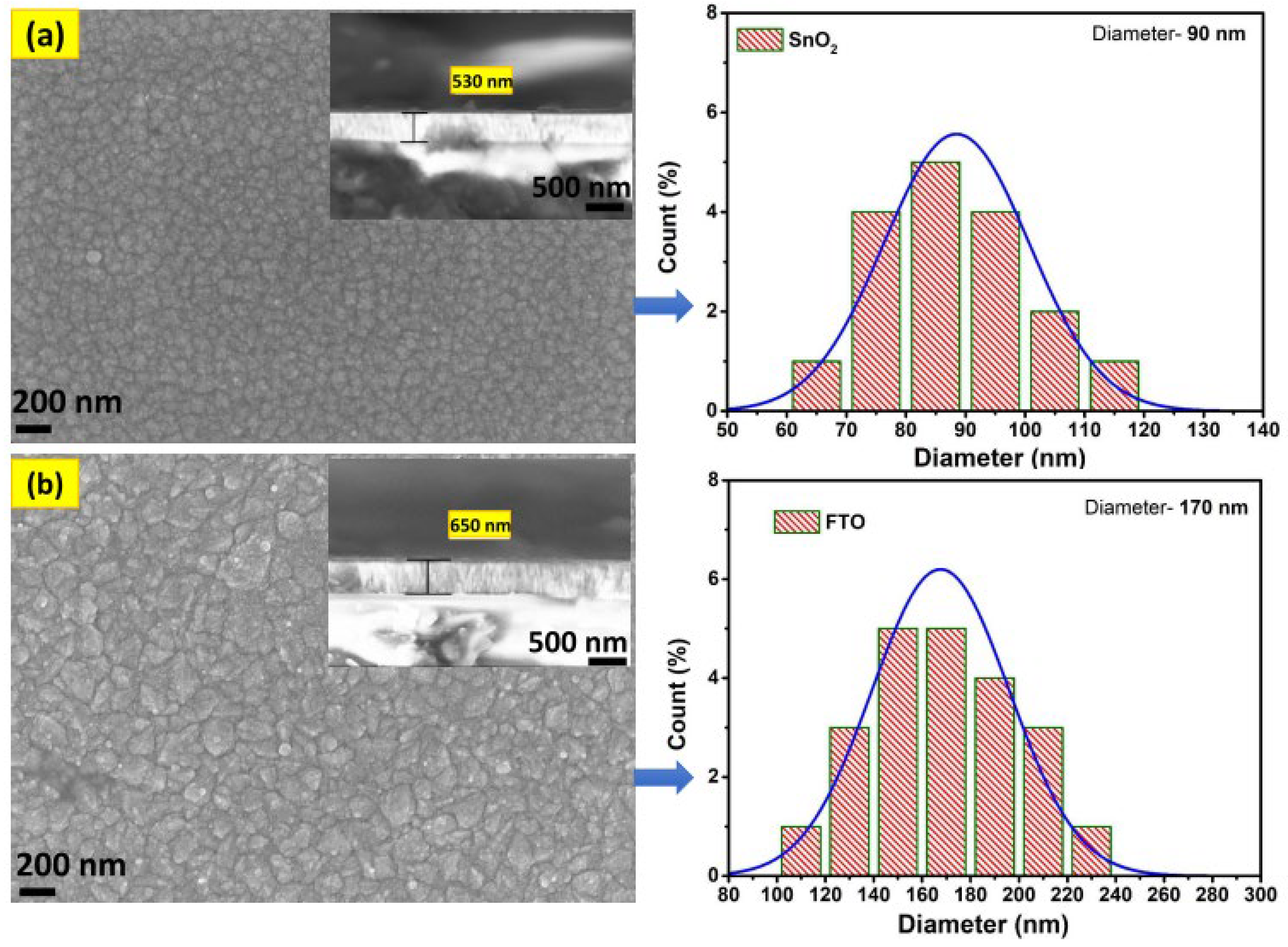
3.2. SEM Analyses
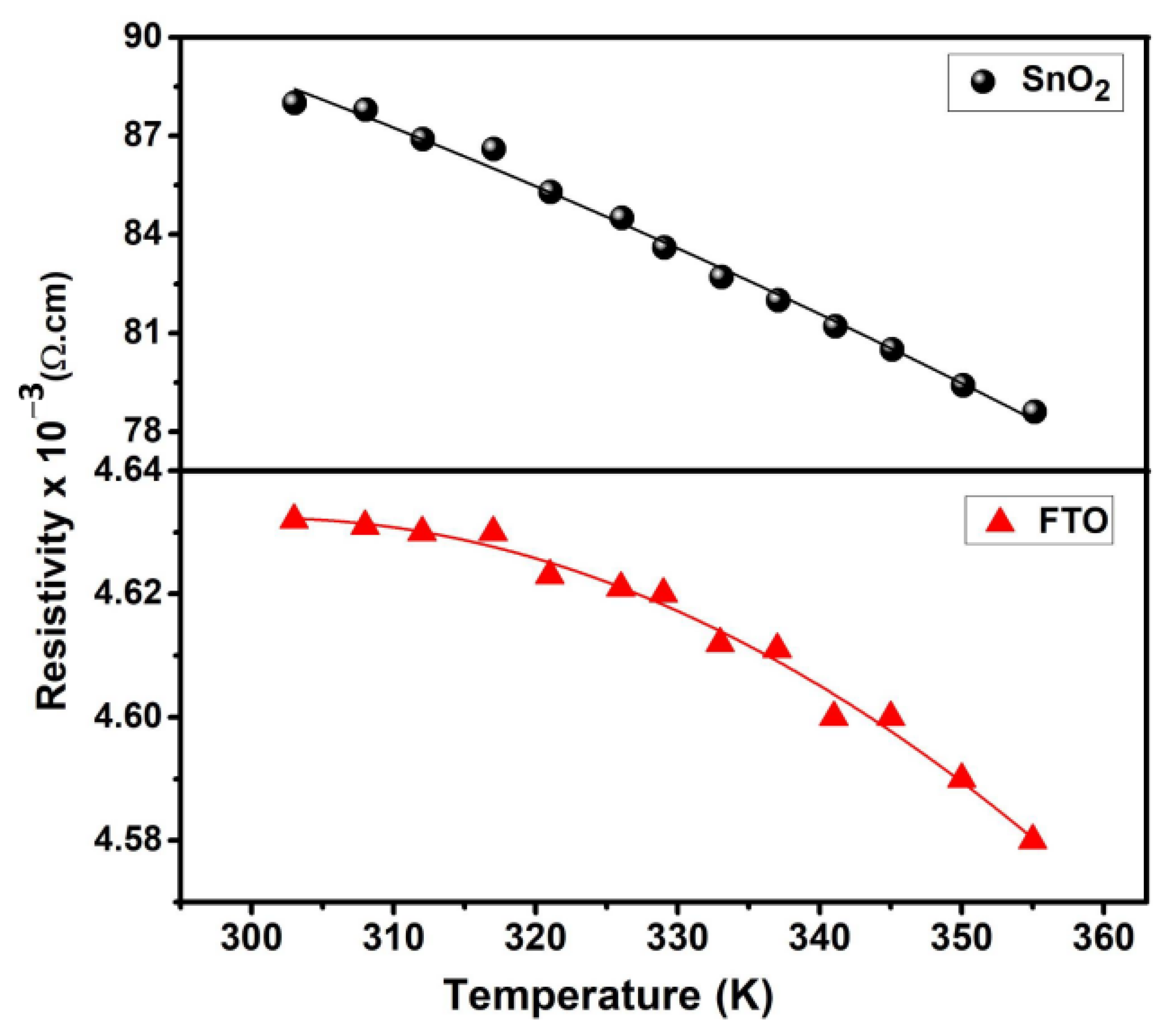
3.3. Hall Effect Measurements
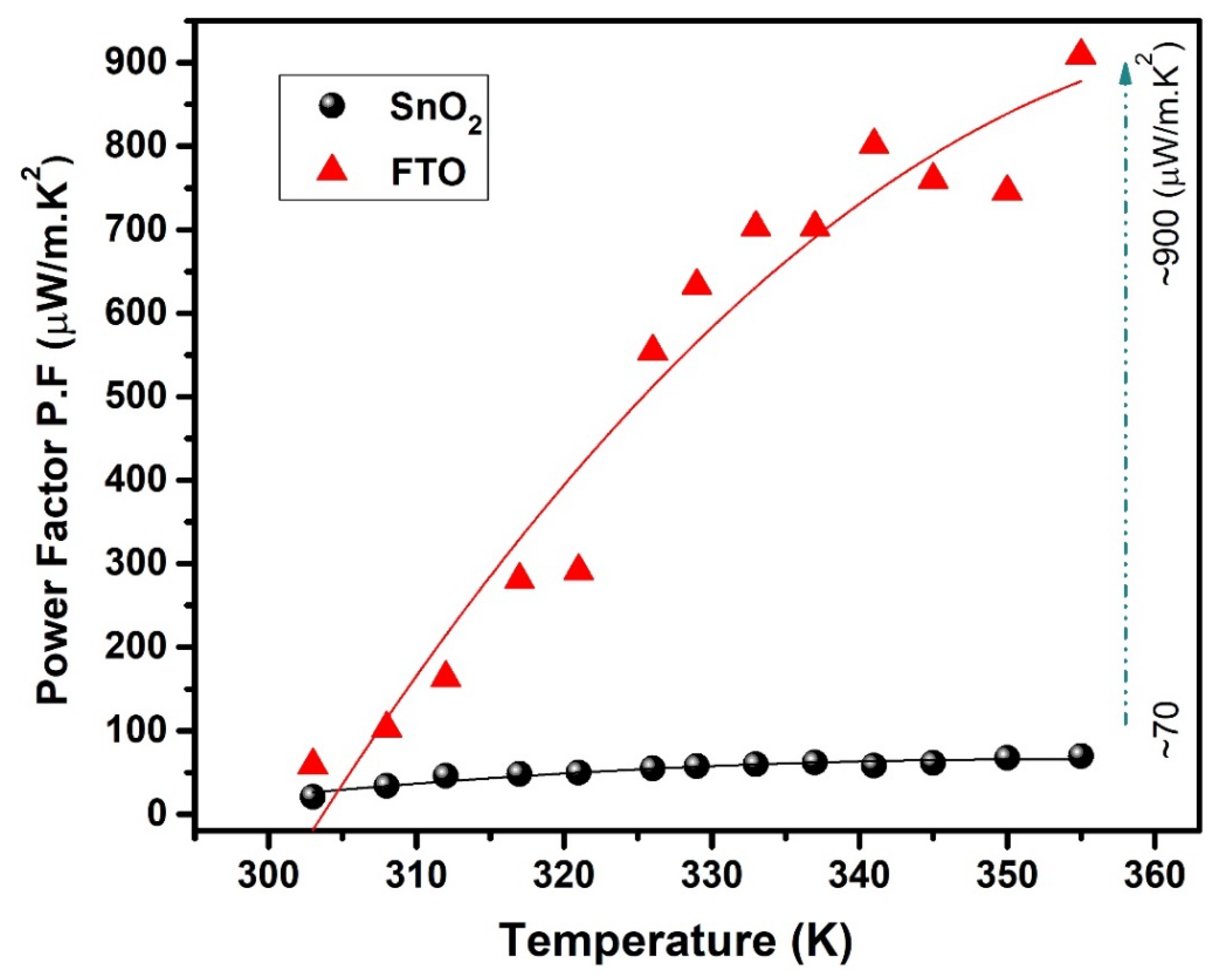
3.4. Thermoelectric Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zevenhoven, R.; Beyene, A. The relative contribution of waste heat from power plants to global warming. Energy 2011, 36, 3754–3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, A.; Pai, Y.H.; Wu, W.M.; Chang, C.L.; Liu, C.J. Low thermal conductivity and enhanced thermoelectric performance of nanostructured Al-doped ZnTe. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 1070–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.D.A.; Valanarasu, S.; Jeyadheepan, K.; Kim, H.S.; Vikraman, D. Evaluation of the physical, optical, and electrical properties of SnO2: F thin films prepared by nebulized spray pyrolysis for optoelectronics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 3648–3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.; Mathavan, T.; Jothirajan, M.A.; Somaily, H.H.; Zahran, H.Y.; Yahia, I.S. An effect of lanthanum doping on physical characteristics of FTO thin films coated by nebulizer spray pyrolysis technique. Opt. Mater. 2020, 99, 109518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consonni, V.; Rey, G.; Roussel, H.; Doisneau, B.; Blanquet, E.; Bellet, D. Preferential orientation of fluorine-doped SnO2 thin films: The effects of growth temperature. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Cheng, G.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J.; Jiang, Z. Optimization on thermoelectric characteristics of indium tin oxide/indium oxide thin film thermocouples based on screen printing technology. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2021, 92, 105001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, M.; Loureiro, J.; Nogueira, A.; Rodrigues, A.; Martins, R.; Ferreira, I. SnO2 thin film oxides produced by rf sputtering for transparent thermoelectric devices. Mater. Today Proc. 2015, 2, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordillo, G.; Paez, B.; Jacome, C.; Florez, J.M. Characterization of SnO2 thin ®lms through thermoelectric power measurements. Thin Solid Film. 1999, 342, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouaj, M.A.; Diaz, R.; Belayachi, A.; Rueda, F.; Abd-Lefdil, M. Comparative study of ITO and FTO thin films grown by spray pyrolysis. Mater. Res. Bull. 2009, 44, 1458–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paloly, A.R.; Bushiri, M.J. The effect of solvents on the growth and key properties of tin oxide thin films deposited via chemical spray pyrolysis. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 261, 124209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakuphanoglu, F. Electrical conductivity, Seebeck coefficient and optical properties of SnO2 film deposited on ITO by dip coating. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 470, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khelifi, C.; Attaf, A.; Yahia, A.; Dahnoun, M. Investigation of F doped SnO2 thin films properties deposited via ultrasonic spray technique for several applications. Surf. Interfaces 2019, 15, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, E.M.; Silva, J.P.B.; Veltruská, K.; Matolín, V.; Pires, A.L.; Pereira, A.M.; Goncalves, L.M. Highly sensitive thermoelectric touch sensor based on p-type SnOx thin film. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 435502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, N.; Chew, C.K.; Bhachu, D.S.; Waugh, M.R.; Carmalt, C.J.; Parkin, I.P. Influencing FTO thin film growth with thin seeding layers: A route to microstructural modification. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 9359–9368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukumar, A.; Rey, G.; Giusti, G.; Consonni, V.; Appert, E.; Roussel, H.; Bellet, D. Fluorine doped tin oxide (FTO) thin film as transparent conductive oxide (TCO) for photovoltaic applications. AIP Conf. Proc. 2013, 1512, 710–711. [Google Scholar]
- Thirumoorthi, M.; Prakash, J.T.J. Effect of F doping on physical properties of (211) oriented SnO2 thin films prepared by jet nebulizer spray pyrolysis technique. Superlattices Microstruct. 2016, 89, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.D.A.; Valanarasu, S.; Kathalingam, A.; Jeyadheepan, K. Nd3+ Doping effect on the optical and electrical properties of SnO2 thin films prepared by nebulizer spray pyrolysis for opto-electronic application. Mater. Res. Bull. 2018, 101, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nar, S.; Stolz, A.; Machon, D.; Bourhis, E.; Andreazza, P.; Boucherif, A.; Semmar, N. Effect of Nanographene Coating on the Seebeck Coefficient of Mesoporous Silicon. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vishwakarma, S.R.; Upadhyay, J.P.; Prasad, H.C. Physical properties of arsenic-doped tin oxide thin films. Thin Solid Films 1989, 176, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.A.; Masumdar, E.U.; Moholkar, A.V.; Neumann-Spallart, M.; Rajpure, K.Y.; Bhosale, C.H. Electrical, structural and optical properties of SnO2: F thin films: Effect of the substrate temperature. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 488, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthick, P.; Saravanakumar, K.; Sanjeeviraja, C.; Jeyadheepan, K. Realization of highly conducting and transparent SnO2 thin films by optimizing F/Sn molar ratio for electrochemical applications. Thin Solid Films 2020, 713, 138362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Giddings, A.D.; Verheijen, M.A.; Macco, B.; Prosa, T.J.; Larson, D.J.; Kessels, W.M. Dopant Distribution in Atomic Layer Deposited ZnO:Al Films Visualized by Transmission Electron Microscopy and Atom Probe Tomography. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, V.; Sakthivelu, A.; Kumar, K.D.A.; Valanarasu, S.; Kathalingam, A.; Ganesh, V.; Yahia, I.S. Rare earth Sm3+ co-doped AZO thin films for opto-electronic application prepared by spray pyrolysis. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 67306738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.L.; Zhang, H.; Lu, L.F.; Jiang, F.; Chao, Y.A.N.G. Preparation and properties of AZO thin films on different substrates. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2010, 20, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckeridge, J.; Catlow, C.R.A.; Farrow, M.R.; Logsdail, A.J.; Scanlon, D.O.; Keal, T.W.; Sherwood, P.; Woodley, S.M.; Sokol, A.A.; Walsh, A. Deep vs. shallow nature of oxygen vacancies and consequent n-type carrier concentrations in transparent conducting oxides. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2018, 2, 054604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.H.; Park, K.H.; Oh, J.S.; Kim, D.H.; Hong, C.K. Effect of TiO2 rutile nanorods on the photoelectrodes of dye-sensitized solar cells. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.D.A.; Meena, D.K.; Bose, R.S.; Meena, R.; Murahari, P.; Mele, P.; Ramesh, K. Optical and thermoelectric properties of Sb2Te3/ZnTe nanostructured composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 865, 158621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadavieslam, M.R.; Shahtahmasebi, N.; Rezaee-Roknabadi, M.; Bagheri-Mohagheghi, M.M. A study of the photoconductivity and thermoelectric properties of SnxSy optical semiconductor thin films deposited by the spray pyrolysis technique. Phys. Scr. 2011, 84, 035705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, P.S.; Kawar, R.K.; Seth, T.; Amalnerkar, D.P.; Chigare, P.S. Effect of substrate temperature on structural, electrical and optical properties of sprayed tin oxide (SnO2) thin films. Ceram. Int. 2003, 29, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Wang, J.S. Thermoelectric penta-silicene with a high room-temperature figure of merit. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 14298–14307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trejo-Zamudio, D.; Quiñones-Galván, J.G.; de Moure-Flores, F.J.; Gómez-Herrera, M.L.; Santos-Cruz, J. Structural and thermoelectric properties of SnO2:Bi thin films. In Proceedings of the 2022 19th International Conference on Electrical Engineering, Computing Science and Automatic Control (CCE), Mexico City, Mexico, 9–11 November 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Khademi, N.; Bagheri-Mohagheghi, M.M.; Shirpay, A. Bi-doped SnO2 transparent conducting thin films deposited by spray pyrolysis: Structural, electrical, optical, and photo-thermoelectric properties. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2022, 54, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibe, T.; Tomeda, A.; Komatsubara, Y.; Kitaura, R.; Uenuma, M.; Uraoka, Y.; Nakamura, Y. Carrier and phonon transport control by domain engineering for high-performance transparent thin film thermoelectric generator. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2021, 118, 151601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri-Mohagheghi, M.M.; Shahtahmasebi, N.; Alinejad, M.R.; Youssefi, A.; Shokooh-Saremi, M. Fe-doped SnO2 transparent semi-conducting thin films deposited by spray pyrolysis technique: Thermoelectric and p-type conductivity properties. Solid State Sci. 2009, 11, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri-Mohagheghi, M.M.; Shokooh-Saremi, M. The electrical, optical, structural and thermoelectrical characterization of n- and p-type cobalt-doped SnO2 transparent semiconducting films prepared by spray pyrolysis technique. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2010, 405, 4205–4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharrami, F.; Bagheri-Mohagheghi, M.M.; Azimi-Juybari, H. Study of structural, electrical, optical, thermoelectric and photoconductive properties of S and Al co-doped SnO2 semiconductor thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis. Thin Solid Films 2012, 520, 6503–6509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinzari, V.; Damaskin, I.; Trakhtenberg, L.; Cho, B.K.; Korotcenkov, G. Thermoelectrical properties of spray pyrolyzed indium oxide thin films doped by tin. Thin Solid Films 2014, 552, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, J.M.; Correia, F.C.; Kuzmin, A.; Jonane, I.; Kong, M.; Goñi, A.R.; Tavares, C.J. Influence of Nb-doping on the local structure and thermoelectric properties of transparent TiO2:Nb thin films. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 838, 155561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Electrical and TE Parameters | SnO2 | FTO | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 300 K | 360 K | 300 K | 360 K | |
| n (cm−3) | (2.92 ± 0.02) × 1019 | (2.52 ± 0.02) × 1019 | (1.63 ± 0.03) × 1020 | (1.56 ± 0.02) × 1020 |
| μ (cm2/V·s) | 2.41 ± 0.08 | 2.77 ± 0.04 | 8.40 ± 0.02 | 8.71 ± 0.02 |
| ρ (Ω·cm) | (8.96 ± 0.02) × 10−2 | (7.95 ± 0.03) × 10−2 | (4.64 ± 0.01) × 10−3 | (4.58 ± 0.01) × 10−3 |
| S (μV/K) | −135 ± 3 | −234 ± 3 | −52 ± 3 | −204 ± 3 |
| PF (μW/m·K2) | ~20 | ~70 | ~58 | ~900 |
| Materials | ρ (mΩ·m) | S (µV/K) | PF (mW/m·K2) | Working Temp. (K) | Method | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (i). SnO2 (ii). FTO | 0.889 0.046 | 135–234 52–204 | 0.02–0.07 0.058–0.90 | 300–360 300–360 | Nebulizer Spray Pyrolysis | Our results |
| SnO2 | 0.27 | 100–200 | 0.05–0.15 | 310–400 | Spray Pyrolysis | [35] |
| SnO2 | 0.61 | 255 | 0.1 | 300 | RF Sputtering | [7] |
| SnO2:Al (10%) | 0.32 | 250 | - | 300 | Spray Pyrolysis | [36] |
| In2O3:Sn (5%) | 0.04 | 120–200 | 1.5–4.7 | 300–723 | Spray Pyrolysis | [37] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deva Arun Kumar, K.; Valanarasu, S.; Capelle, A.; Nar, S.; Karim, W.; Stolz, A.; Aspe, B.; Semmar, N. Nanostructured Oxide (SnO2, FTO) Thin Films for Energy Harvesting: A Significant Increase in Thermoelectric Power at Low Temperature. Micromachines 2024, 15, 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15020188
Deva Arun Kumar K, Valanarasu S, Capelle A, Nar S, Karim W, Stolz A, Aspe B, Semmar N. Nanostructured Oxide (SnO2, FTO) Thin Films for Energy Harvesting: A Significant Increase in Thermoelectric Power at Low Temperature. Micromachines. 2024; 15(2):188. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15020188
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeva Arun Kumar, Karuppiah, S. Valanarasu, Alex Capelle, Sibel Nar, Wael Karim, Arnaud Stolz, Barthélemy Aspe, and Nadjib Semmar. 2024. "Nanostructured Oxide (SnO2, FTO) Thin Films for Energy Harvesting: A Significant Increase in Thermoelectric Power at Low Temperature" Micromachines 15, no. 2: 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15020188
APA StyleDeva Arun Kumar, K., Valanarasu, S., Capelle, A., Nar, S., Karim, W., Stolz, A., Aspe, B., & Semmar, N. (2024). Nanostructured Oxide (SnO2, FTO) Thin Films for Energy Harvesting: A Significant Increase in Thermoelectric Power at Low Temperature. Micromachines, 15(2), 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15020188







