A Review of Emerging Technologies in Ultra-Smooth Surface Processing for Optical Components
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Ultra-Smooth Surface Processing Technology
3. Atomic-Level Removal of Materials under Chemical Reaction
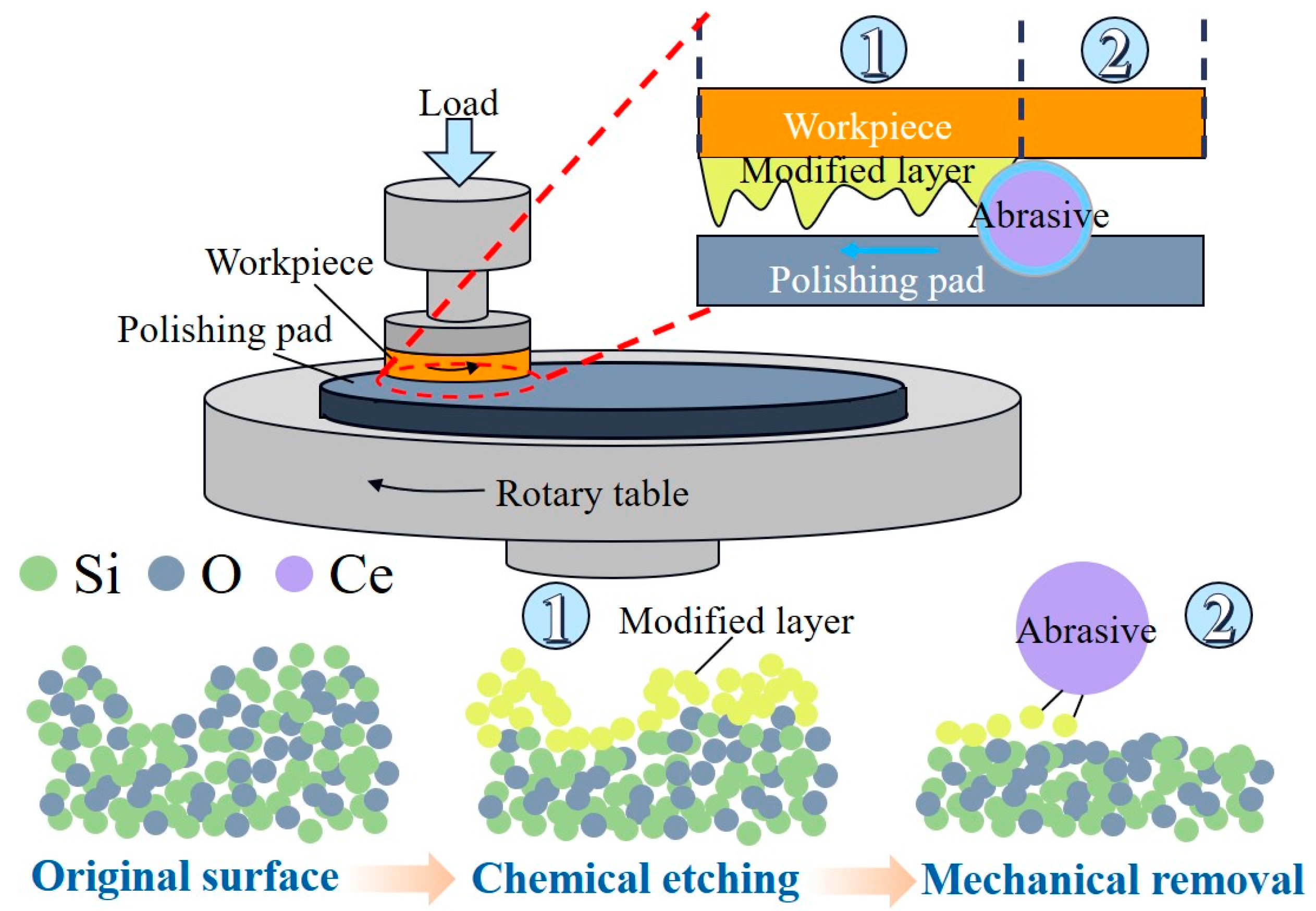
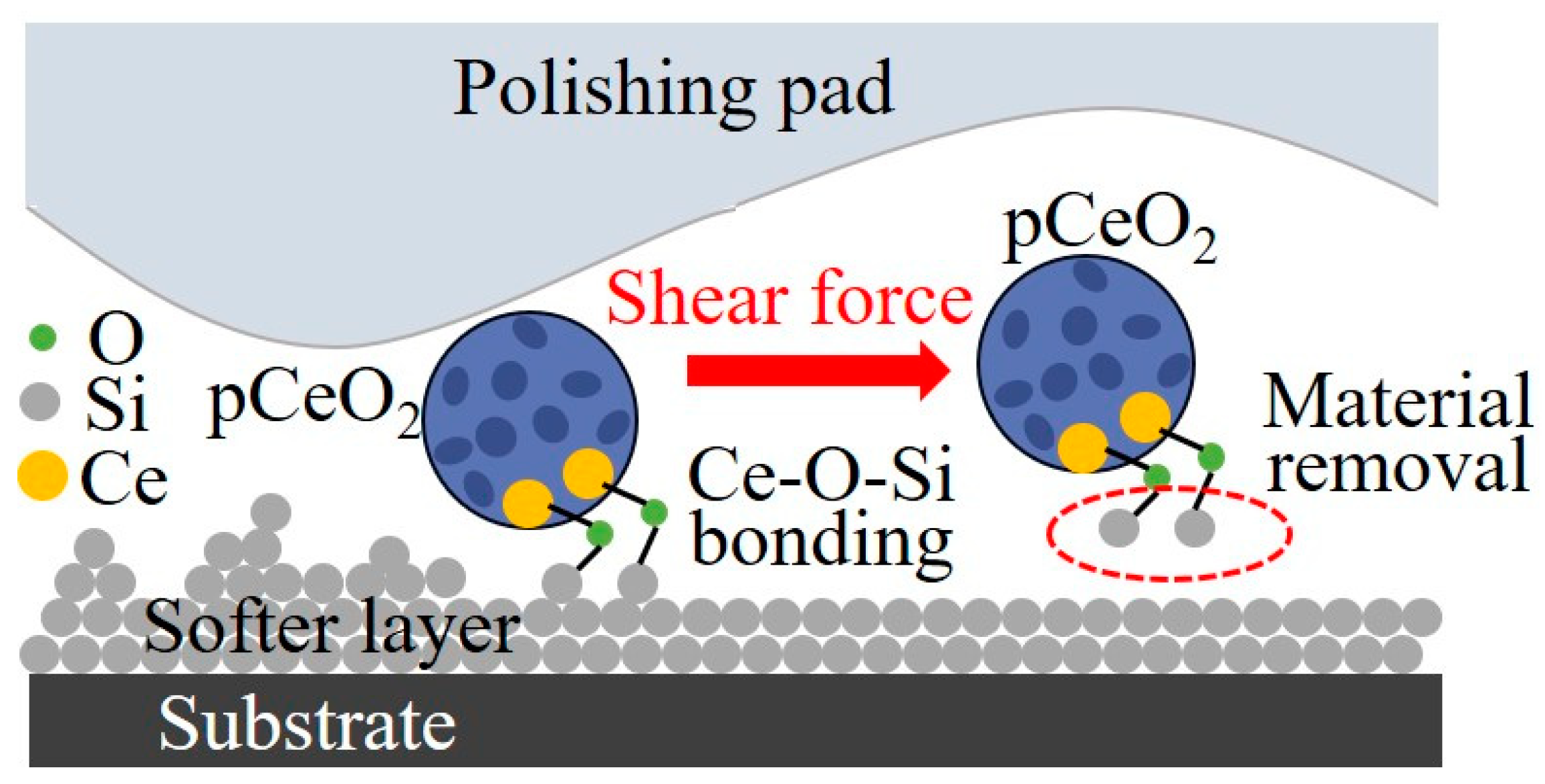
3.1. Chemical Mechanical Polishing
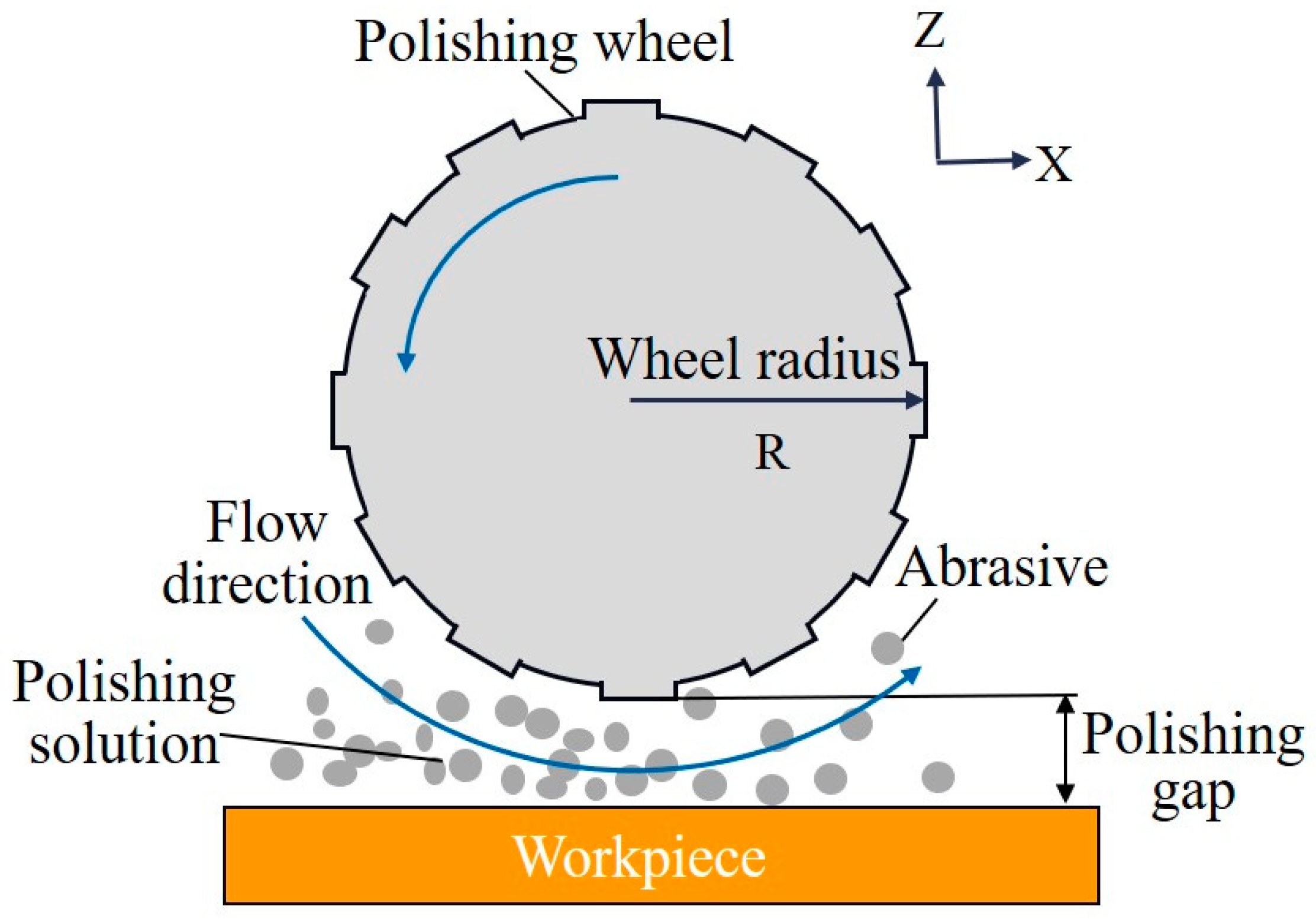
3.2. Elastic Emission Machining
4. Atomic-Level Removal of Materials under Energy Beam Effect
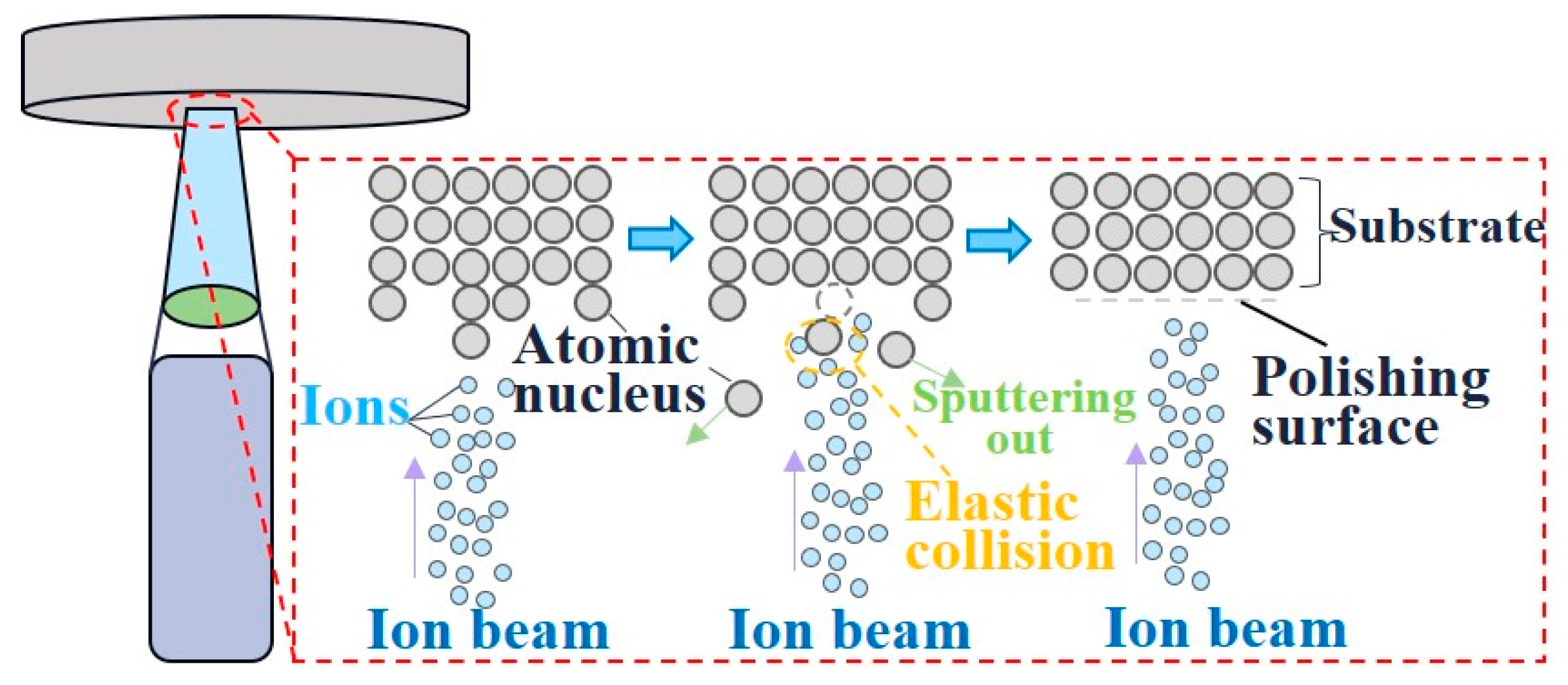
4.1. Ion Beam Finishing
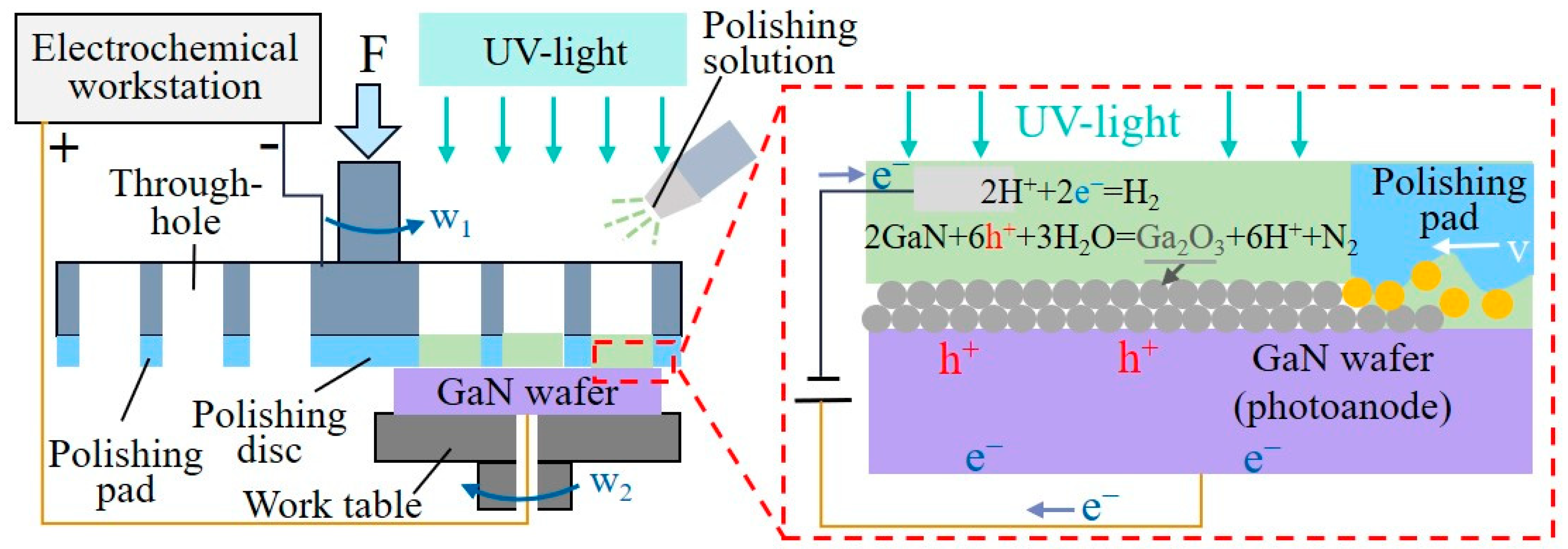
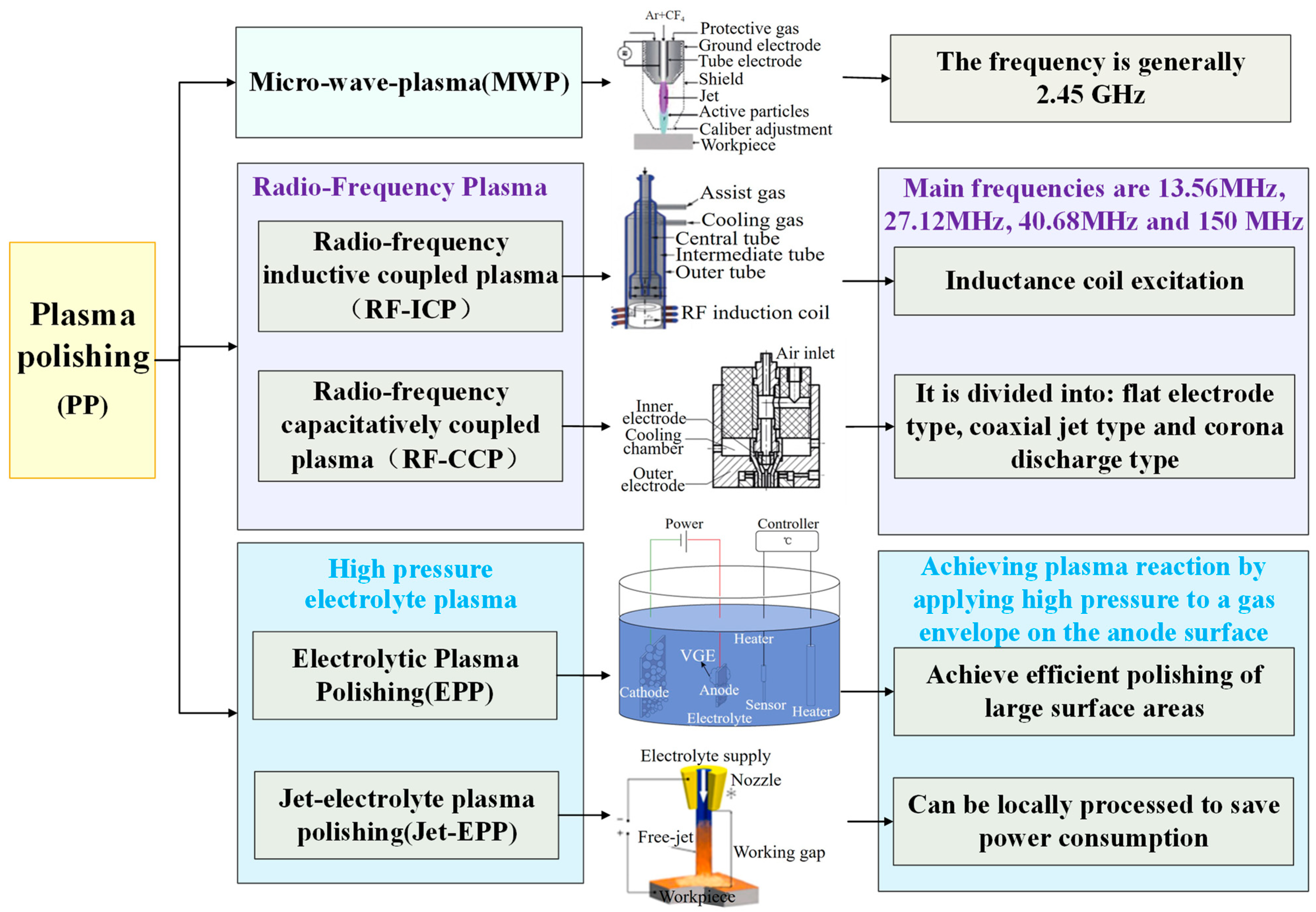
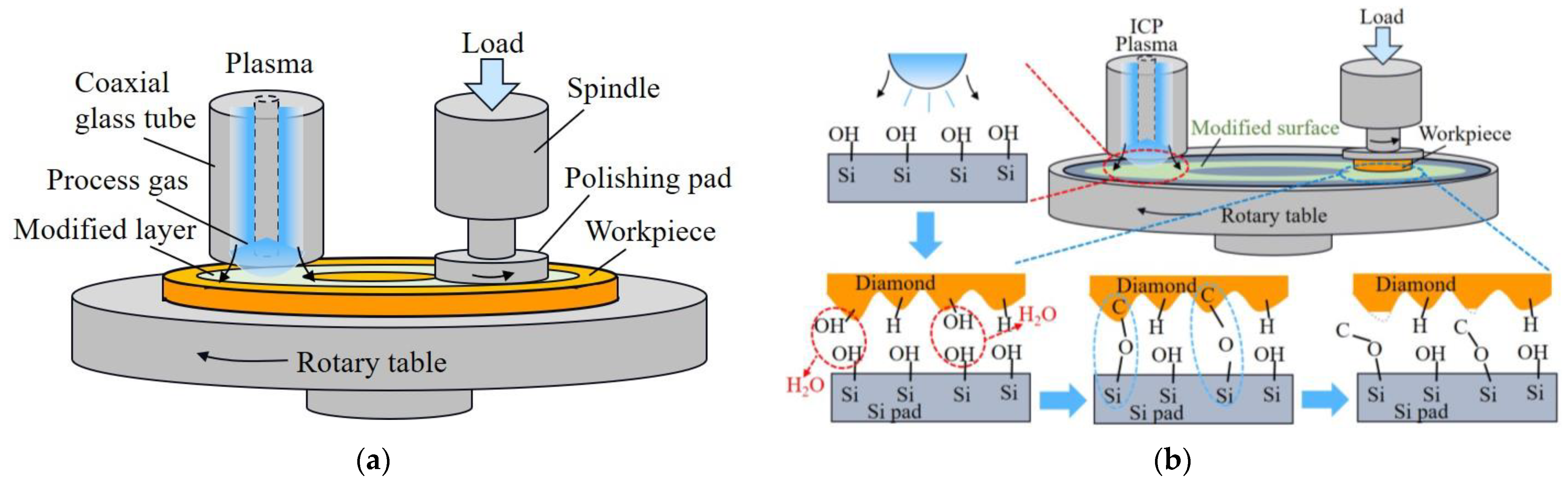
4.2. Plasma Polishing
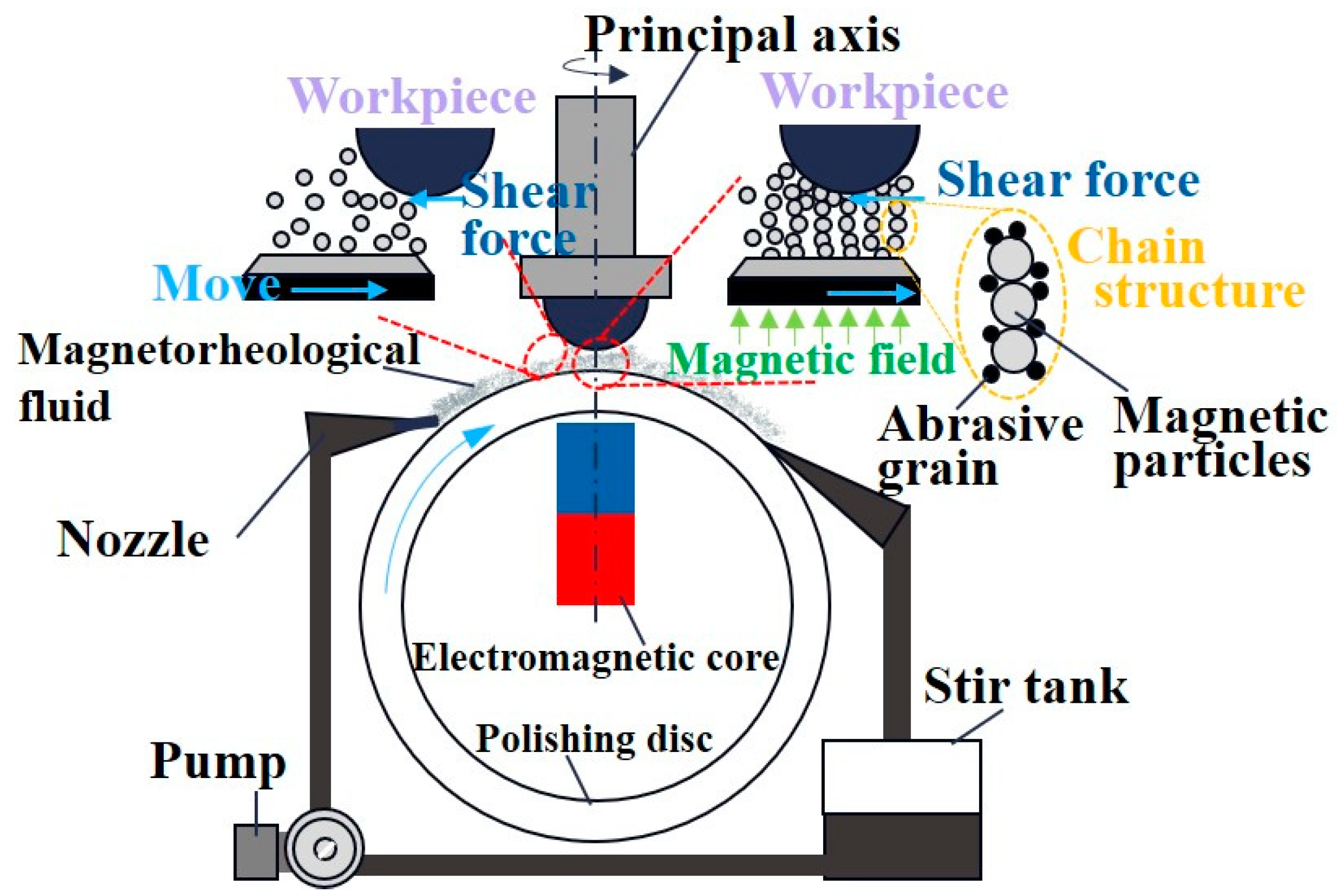
5. Application of Flexible Contact Wear Processing Technology
6. Comparison of Technical Properties of Ultra-Smooth Surface Processing
7. Summary and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, L.; Quan, H.; Hu, S.; Liu, J.; Hou, X. Review of absolute measurement of wavefront aberration in lithography objective. Opto-Electron. Eng. 2023, 50, 220001–220024. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Hou, X.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. A highly powerful calibration method for robotic smoothing system calibration via using adaptive residual extended Kalman filter. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2024, 86, 102660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Liu, H.; Yan, F.; Zhang, S.; Wan, Y.; Wu, F. Overview of advanced manufacturing technology of large-aperture aspheric mirror. Opto-Electron. Eng. 2020, 47, 200203–200223. [Google Scholar]
- Weiser, M. Ion beam figuring for lithography optics. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2009, 267, 1390–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verlaan, A.L.; Hogenhuis, H.; Pijnenburg, J.; Lemmen, M.; Lucarelli, S.; Scheulen, D.; Ende, D. LISA telescope assembly optical stability characterization for ESA. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Space Optics—ICSO, Ajaccio, France, 9–12 October 2012; CNES: Paris, France, 2012; pp. 168–174. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, R.; Luo, Z. Laser ranging and data communication for space gravitational wave detection. Chin. Opt. 2019, 12, 486–492. [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsov, A.; Molchanov, A.; Chirkin, M.; Izmailov, E. Precise laser gyroscope for autonomous inertial navigation. Quantum Electron. 2015, 45, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Henriet, R.; Coillet, A.; Jacquot, M.; Furfaro, L.; Cibiel, G.; Larger, L.; Chembo, Y. Dependence of quality factor on surface roughness in crystalline whispering-gallery mode resonators. Opt. Lett. 2018, 43, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, J.; Hawley-Fedder, R.; Stolz, C.; Menapace, J.; Borden, M.; Whitman, P.; Yu, J.; Runkel, M.; Riley, M.; Feit, M. NIF optical materials and fabrication technologies: An overview. Opt. Eng. Lawrence Livermore Natl. Lab. II Natl. Ignition Facil. 2004, 5341, 84–101. [Google Scholar]
- Dan, J.; Wang, C.; He, S.; Yu, H.; Wan, X. Research on Bidirectional-driven Effects of Large Science Project and Advanced Manufacture: Taking High Power Solid Laser Device as an Example. J. Eng. Stud. 2018, 10, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Hou, X.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. Review on mid-spatial frequency error suppression in optical components manufacturing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 126, 4827–4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Miao, W.; Luo, M.; Zhao, Y.; Bao, H. Influence of structure of vitrified bond diamond grinding wheel on its performance. Jingangshi Yu Moliao Moju Gongcheng Diam. Abras. Eng. 2020, 40, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Q.; Shan, K.; Li, Z. Investigation of grain wear in diamond abrasive belt grinding tita-nium alloy blade for aeroengine. Diam. Abras. Eng. 2020, 40, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Xie, R.; Chen, X. Analysis and optimization on cross section profile of fused silica grinding wheel. Diam. Abras. Eng. 2018, 38, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Hou, X.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. A novel method for improving optical component smoothing quality in robotic smoothing systems by compensating path errors. Opt. Express 2023, 31, 30359–30378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; He, J.; Huang, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, C.; Wang, J. Ultra-precision grinding and polishing processing technology research and equipment development. Opto-Electron. Eng. 2023, 50, 220097–220116. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y. Large optical glass ultra-smooth surface processing technology. Optoelectron. Technol. 2003, 3, 46. [Google Scholar]
- Takeshi, S.; Takumi, I.; Kazuaki, O.; Mutsumi, T.; Takashi, F. Ultraviolet-assisted polishing of 2 inch SiC substrate. JSAT 2014, 58, 235–240. [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich, W.; Beiersdörfer, S.; Mann, H.-J. Trends in optical design of projection lenses for UV and EUV lithography. In Proceedings of the Soft X-ray and EUV Imaging Systems, San Diego, CA, USA, 30 July–4 August 2000; SPIE: St Bellingham, WA, USA, 2000; pp. 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- Bakshi, V. EUV Lithography, 2nd ed.; SPIE: Bellingham, DC, USA, 2018; pp. 273–279. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.; Cao, J.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, C. The development and application of ultra-smooth surfaces. Physics 2000, 29, 610–614. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Li, Y.; Deng, H. Plasma-induced atom migration manufacturing of fused silica. Precis. Eng. 2022, 76, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, L.M. Chemical processes in glass polishing. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1990, 120, 152–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Chen, L.; Qian, L.; Song, D.; Cai, Y. Investigation of humidity-dependent nanotribology behaviors of Si (1 0 0)/SiO2 pair moving from stick to slip. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 265, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuki, F.; Saguchi, A.; Takahashi, W.; Watanabe, J. The atomic-scale removal mechanism during Si tip scratching on Si and SiO2 surfaces in aqueous KOH with an atomic force microscope. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 41, 4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuki, F. Single asperity tribochemical wear of silicon by atomic force microscopy. J. Mater. Res. 2009, 24, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.-L.; Chen, G.; Xu, L.; Kang, C.; Luo, G.; Luo, H.; Zhou, Y.; Dargusch, M.S.; Pan, G. Achieving ultralow surface roughness and high material removal rate in fused silica via a novel acid SiO2 slurry and its chemical-mechanical polishing mechanism. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 500, 144041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Z.; Huang, N.; Castelli, M.; Fang, F. Polishing Approaches at Atomic and Close-to-Atomic Scale. Micromachines 2023, 14, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, F.; Liu, L.; Liu, D.; Shi, C.; Cui, X.; Wang, J.; Wen, W. Atomic-scale surface of fused silica induced by chemical mechanical polishing with controlled size spherical ceria abrasives. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 85, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zantye, P.B.; Kumar, A.; Sikder, A. Chemical mechanical planarization for microelectronics applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2004, 45, 89–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.-Y.; Yang, W.-Z. Combined ultrasonic vibration and chemical mechanical polishing of copper substrates. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2012, 53, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Xu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zou, C.; Wang, R.; Pan, G. An in situ study of chemical-mechanical polishing behaviours on sapphire (0001) via simulating the chemical product-removal process by AFM-tapping mode in both liquid and air environments. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 19692–19700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Pan, G.; Zhou, Y.; Gu, Z.; Gong, H.; Zou, C. Characterization of colloidal silica abrasives with different sizes and their chemical–mechanical polishing performance on 4H-SiC (0 0 0 1). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 307, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.-Y.; Kim, G.; Sun, H.; Hwang, U.; Kim, J.; Kwak, D.; Park, I.-K.; Kim, T.; Suhr, J.; Nam, J.-D. A nanoclustered ceria abrasives with low crystallinity and high Ce3+/Ce4+ ratio for scratch reduction and high oxide removal rates in the chemical mechanical planarization. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 12318–12328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janoš, P.; Ederer, J.; Pilařová, V.; Henych, J.; Tolasz, J.; Milde, D.; Opletal, T. Chemical mechanical glass polishing with cerium oxide: Effect of selected physico-chemical characteristics on polishing efficiency. Wear 2016, 362, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Wang, S.; Pan, J.; Wang, T.; Chen, Y. Development of Zr-and Gd-doped porous ceria (pCeO2) abrasives for achieving high-quality and high-efficiency oxide chemical mechanical polishing. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 14039–14049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Xu, N.; Hu, J.; Luo, Y.; Lin, Y.; Pu, Y. Doping strategy on properties and chemical mechanical polishing performance of CeO2 Abrasives: A DFT assisted experimental study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 623, 156997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Ma, J.; Liu, Q.; Luo, Y.; Pu, Y. Preparation of CeO2 abrasives by reducing atmosphere-assisted molten salt method for enhancing their chemical mechanical polishing performance on SiO2 substrates. J. Rare Earths 2023, 41, 1627–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, Y.; Teng, F.; Li, G.; Wang, F.; Jin, Y. Fused silica with sub-angstrom roughness and minimal surface defects polished by ultrafine nano-CeO2. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2023, 106, 1766–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Jiang, X.; Mao, Y.; Long, X.; Luo, H. Ultra-smooth surface with 0.4 Å roughness on fused silica. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 7245–7251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Liu, S. 2D nanomaterials as lubricant additive: A review. Mater. Des. 2017, 135, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, C.; Ren, Z.; Feng, J.; Zhou, H.; Liu, Z.; Meng, F.; Zhao, S. Novel green chemical mechanical polishing of fused silica through designing synergistic CeO2/h-BN abrasives with lubricity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 637, 157978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Luo, H.; Chen, G.; Luo, G.; Pan, G. Study on pitch performance deterioration in chemical mechanical polishing of fused silica. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2021, 10, 084005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Zhai, W.; Zhai, Q.; Xia, Y.; Wang, C.; Peng, K. Electro-chemical mechanical polishing of 4H-SiC for scratch-free surfaces with less oxide layer at high efficiency. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2019, 8, P677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, X.; Aoki, K.; Yamamura, K. Slurryless electrochemical mechanical polishing of 4-inch 4H–SiC (0001) and (000–1) surfaces. Precis. Eng. 2023, 83, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, T.; Pan, G.; Lu, X. Effects of catalyst concentration and ultraviolet intensity on chemical mechanical polishing of GaN. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 378, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, L.; Pan, G. Chemical mechanical polishing of 4H-SiC wafer with UV-LED light, Nanotechnol. Precis. Eng. 2017, 15, 342–346. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.; Zhang, B.; Wang, W.; Li, H.; Li, Y. Effect of photocatalytic oxidation on corrosion electrochemistry and chemical mechanical polishing of GaN. Electroplat. Finish. 2021, 40, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, B.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, R.; Zeng, N. Improved chemical mechanical polishing performance in 4H-SiC substrate by combining novel mixed abrasive slurry and photocatalytic effect. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 575, 151676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Song, S.; Gao, X.; Deng, W. Investigation on material removal mechanisms in photocatalysis-assisted chemical mechanical polishing of 4H–SiC wafers. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2021, 22, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, A.; Rahaeifard, M.; Mojahedi, M. Analytical and numerical investigations of the ultrasonic microprobe considering size effects. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2020, 27, 2043–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Lu, X.; Pan, G.; Lei, Y.; Luo, J. Ultrasonic flexural vibration assisted chemical mechanical polishing for sapphire substrate. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 3936–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Lu, X.; Pan, G.; Lei, Y.; Luo, J. Effects of the ultrasonic flexural vibration on the interaction between the abrasive particles; pad and sapphire substrate during chemical mechanical polishing (CMP). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 2905–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Cheng, Y.; Zhong, M. Effects of process parameters on chemical-mechanical interactions during sapphire polishing. Microelectron. Eng. 2019, 216, 111029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.; Yuan, R.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Xu, W. Effects of abrasive particles and pads’ characteristics on ultrasonic assisted chemical mechanical polishing for sapphire. China Surf. Eng. 2018, 31, 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, H.; Zhong, M.; Xu, W. Effects of different dispersants on chemical reaction and material removal in ultrasonic assisted chemical mechanical polishing of sapphire. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2022, 11, 033007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Dornfeld, D.A. Material removal mechanism in chemical mechanical polishing: Theory and modeling. IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 2001, 14, 112–133. [Google Scholar]
- Zarepour, H.; Yeo, S. Single abrasive particle impingements as a benchmark to determine material removal modes in micro ultrasonic machining. Wear 2012, 288, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Zhong, M.; Xu, W. Novel model of material removal rate on ultrasonic-assisted chemical mechanical polishing for sapphire. Friction 2023, 11, 2073–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachowiak, G.; Batchelor, A.W. Engineering Tribology; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Li, Q.; Zhu, B.; Yan, J. Removal Mechanism and Processes in Atomized Slurry Applied CMP. Lubr. Eng. 2014, 39, 56–60. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z.; Ou, L.; Kang, R.; Hu, H.; Zhang, B.; Guo, D.; Shi, K. Photoelectrochemical mechanical polishing method for n-type gallium nitride. CIRP Ann. 2019, 68, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhong, X. Research progress of elastic emission machining in optical manufacturing. Chin. Opt. 2021, 14, 1089–1103. [Google Scholar]
- Inagaki, K.; Yamauchi, K.; Mimura, H.; Sugiyama, K.; Hirose, K.; Mori, Y. First-principles evaluations of machinability dependency on powder material in elastic emission machining. Mater. Trans. 2001, 42, 2290–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Yamauchi, K.; Endo, K. Mechanism of atomic removal in elastic emission machining. Precis. Eng. 1988, 10, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Yamauchi, K.; Endo, K.; Ide, T.; Toyota, H.; Nishizawa, K.; Hasegawa, M. Evaluation of elastic emission machined surfaces by scanning tunneling microscopy. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A Vac. Surf. Film. 1990, 8, 621–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.-T.; Kao, Y.-C. An experimental study on machining rate distribution of hydrodynamic polishing process. Wear 1999, 224, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Chiovelli, S.; Minev, P.; Luo, J.; Nandakumar, K. A comprehensive phenomenological model for erosion of materials in jet flow. Powder Technol. 2008, 187, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J. Super-smooth surface fabrication technique and experimental research. Appl. Opt. 2012, 51, 6612–6617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, F.; Yamaguchi, H.; Krajnik, P.; Wegener, K.; Chaudhari, R.; Hoffmeister, H.-W.; Kuster, F. Abrasive fine-finishing technology. CIRP Ann. 2016, 65, 597–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong-hui, W.; Zhong-yu, P.; Tai-hua, Z. A hydrodynamic suspension polishing method for ultrasmooth and low-damage surface. Precis. Eng. 2016, 46, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Lin, B.; Cao, Z.; Jiang, X. Modeling and experimenting of disc hydrodynamic polishing process for ultra-smooth surfaces. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 72, 80–92. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, Y.; Yamauchi, K.; Endo, K. Elastic emission machining. Precis. Eng. 1987, 9, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Guan, C.; Li, S. Ultrasmooth surface polishing based on the hydrodynamic effect. Appl. Opt. 2013, 52, 6411–6416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaoka, M.; Nomura, K.; Yamauchi, K.; Mori, Y. Efficiency-enhanced elastic emission machining on the basis of processing mechanism. In Proceedings of the 12th Euspen International Conference, Stockholm, Sweden, 4–7 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q. Study on the Technology of Elastic Emission Machining with Dual-Rotor Based on Hydrodynamic Lubrication. Master’s Thesis, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, O., IV. On the theory of lubrication and its application to Mr. Beauchamp tower’s experiments, including an experimental determination of the viscosity of olive oil. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1886, 177, 157–234. [Google Scholar]
- Runnels, S. Tribology analysis of chemical-mechanical polishing. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1998, 141, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runnels, S.R. Feature-scale fluid-based erosion modeling for chemical-mechanical polishing. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1994, 141, 1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, T.; Takei, Y.; Mimura, H. Machining property in smoothing of steeply curved surfaces by elastic emission machining. Procedia CIRP 2014, 13, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshinori, T.; Hidekazu, M. Effect of focusing flow on stationary spot machining properties in elastic emission machining. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 237–242. [Google Scholar]
- Kubota, A.; Mimura, H.; Inagaki, K.; Mori, Y.; Yamauchi, K. Effect of particle morphology on removal rate and surface topography in elastic emission machining. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2006, 153, G874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, A.; Shinbayashi, Y.; Mimura, H.; Sano, Y.; Inagaki, K.; Mori, Y.; Yamauchi, K. Investigation of the surface removal process of silicon carbide in elastic emission machining. J. Electron. Mater. 2007, 36, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Wang, J. Simulation of mechanism and experimental study in micro fluid jet Polishing. Opto-Electron. Eng. 2012, 39, 139–144. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J. Ultraprecision optical fabrication on fused silica. In Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on Advanced Optical Manufacturing and Testing Technologies: Advanced Optical Manufacturing Technologies, Xiamen, China, 26–29 April 2012; pp. 458–463. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Lin, B.; Jiang, X.; Li, Y. Flow field analysis of the thin fluid film in disc hydrodynamic polishing. Procedia CIRP 2018, 77, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Yu, J.; Hong, T.; He, J. Influence of shapes of grooved polishing tool on hydrodynamic suspension polishing. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2012, 28, 87–91. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Xue, K.; Wen, D.; Xu, Y.; Ying, F. Study on Hydrodynamic Pressure Characteristics of Linear Hydrodynamic Pressure Polishing. China Mech. Eng. 2020, 31, 907. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, K. Study on the Dynamic Pressure Characteristics of Linear Hydrodynamic Pressure Polishing. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang University of Technology, Hangzhou, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Wen, D.; Kong, F.; Gan, Z.; Cheng, Z. Research on Characteristics of Flow Field during Linear Hydrodynamic Polishing Process. China Mech. Eng. 2023, 34, 1306–1314. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.; Zhou, L.; Xie, X.; Jiao, C.; Li, S. Deterministic Figuring in Optical Machining by Ion Beam. Acta Opt. Sin. 2008, 28, 1131–1135. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.T.; Fan, X.W.; Xu, L.; Ma, Z.; Wang, Y.J.; Wu, X.G. High-precision resin layer polishing of carbon fiber mirror based on optimized ion beam figuring process. Optik 2020, 206, 163575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinel, A.; Bashkin, S.; Loomis, D. Controlled figuring of optical surfaces by energetic ionic beams. Appl. Opt. 1965, 4, 1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, H.R.; Reader, P.D.; Isaacson, G.C. Ion sources for ion machining applications. AIAA J. 1977, 15, 843–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, S.; Fukabori, T.; Pahlovy, S.; Miyamoto, I. Low energy ion beam smoothening of artificially synthesized single crystal diamond chips with initial surface roughness of 0.08–0.4 nm rms. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2012, 24, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. Study on lon Beam Polishing Technology of Fused Quartz Plane Element. Master’s Thesis, Xi’an Technological University, Xi’an, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, W.; Nie, X.; Liu, Z.; Nie, X.; Wan, W. Researches on formation mechanism of ultra-smooth surface during ion beam sputtering of fused silica. Optik 2019, 179, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Xiang, X.; Tian, C.; Hou, C.; Liao, W.; Deng, H.; Jiang, X.; Wang, H.; Yuan, X.; Jiang, X. Anisotropic ion beam etching of fused silica to mitigate subsurface damage. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2020, 34, 2050060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, T.; Shi, Z.; Li, Q.; Li, W.; Ye, X.; Sun, L.; Yang, L.; Zheng, W. Combination of scanning ion beam etching and dynamic chemical etching for improving laser damage resistance of fused silica optics. Opt. Mater. 2022, 134, 113076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, P.; Xin, Q.; Wu, X.; Wu, Y.; Fan, B.; Chen, Q. Research status of key technologies in plasma optics fabrication. J. Appl. Opt. 2022, 43, 359–374. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, R. The Research Progress in Plasma Spectral Light Source Technology for Atomic Emission Spectroscopy. Chin. J. Inorg. Anal. Chem. 2019, 9, 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Fan, B.; Xin, Q.; Gao, G.; Jiao, P.; Shao, J.; Luo, Q.; Liang, Z. The Tailored Material Removal Distribution on Polyimide Membrane Can Be Obtained by Introducing Additional Electrodes. Polymers 2023, 15, 2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, H.; Sun, H.; JI, G.; Yang, D.; Li, S. Evolution of Chemical Speciation and Interfacial Reaction of Elements on the Surface of Stainless Steel during Electrolytic Plasma Polishing. Surf. Technol. 2022, 51, 346–353+389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Fang, F.; Deng, H. A generic approach of polishing metals via isotropic electrochemical etching. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2020, 150, 103517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Deng, H. Plasma-based isotropic etching polishing of synthetic quartz. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 60, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Endo, K.; Yamamura, K. Damage-free finishing of CVD-SiC by a combination of dry plasma etching and plasma-assisted polishing. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2017, 115, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, R.; Liang, Y.; Deng, H. An efficient approach for atomic-scale polishing of single-crystal silicon via plasma-based atom-selective etching. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2020, 159, 103649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, H. Highly efficient and atomic scale polishing of GaN via plasma-based atom-selective etching. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 620, 156786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamura, K.; Takiguchi, T.; Ueda, M.; Deng, H.; Hattori, A.; Zettsu, N. Plasma assisted polishing of single crystal SiC for obtaining atomically flat strain-free surface. CIRP Ann. 2011, 60, 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Kazuya, Y.; Deng, H. Plasma-assisted polishing for atomic surface fabrication of single crystal SiC. Acta Phys. Sin. 2021, 70, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Sugimoto, K.; Yoshitaka, N.; Yamada, H.; Sun, R.; Kawai, K.; Arima, K.; Yamamura, K. Effects of polishing pressure and sliding speed on the material removal mechanism of single crystal diamond in plasma-assisted polishing. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2022, 124, 108899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, A.; Nagae, S.; Touge, M. Improvement of material removal rate of single-crystal diamond by polishing using H2O2 solution. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2016, 70, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, A.; Motoyama, S.; Touge, M. Development of an ultra-finishing technique for single-crystal diamond substrate utilizing an iron tool in H2O2 solution. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2016, 64, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Ajmal, K.M.; Liu, W.; Yamamura, K.; Deng, H. Atomic-scale and damage-free polishing of single crystal diamond enhanced by atmospheric pressure inductively coupled plasma. Carbon 2021, 182, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eker, J.; Malmborg, J. Design and implementation of a hybrid control strategy. IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 1999, 19, 12–21. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, Q.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, M.; Wang, C. Surface roughness tuning at sub-nanometer level by considering the normal stress field in magnetorheological finishing. Micromachines 2021, 12, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Kumar, A.; Alok, A.; Das, M. Magnetorheological method applied to optics polishing: A review. Proc. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 804, 012012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, M.; Mishra, V.; Sharma, R.; Iqbal, F.; Ali, S.W.; Kumar, S.; Khan, G.S. Development of magnetic nanoparticle based nanoabrasives for magnetorheological finishing process and all their variants. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 6254–6261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Yan, Q.; Lu, J.; Xu, X.; Chen, S. Cluster magnetorheological effect plane polishing technology. J. Mech. Eng. 2014, 50, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Yan, Q. Material removal mechanism of cluster magnetorheological effect in plane polishing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 81, 2017–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yin, S.; Ohmori, H.; Li, M.; Chen, F.; Huang, S. A novel high efficiency magnetorheological polishing process excited by Halbach array magnetic field. Precis. Eng. 2022, 74, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Lu, J.; Yan, Q. Technological experiment of cluster magnetorheological finishing of InP wafer with dynamic magnetic fields. Lubr. Eng. 2021, 46, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Shi, F.; Song, C.; Tie, G.; Wang, B.; Qiao, S.; Sun, G.; Guo, S. Design of arrayed magnetorheological equipment applied in optics manufacture. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 158, 108892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, W.; Huang, W.; Zhang, J. Precise localization of rotary symmetrical aspheric workpiece in magnetorheological polishing. Opt. Precis. Eng. 2020, 28, 610–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; YU, B.; Tan, H.; Yuan, H.; Gu, Y. Magnetorheological Finishing Process of CoCrMo Alloy. Surf. Technol. 2022, 51, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Yan, H.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, S. High precision edge extrapolation technique in continuous phase plate magnetorheological polishing. Infrared Laser Eng. 2019, 48, 442001–0442007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Li, S.; Guan, C.; Li, Y.; Hu, X. Ultra-precision optical surface fabricated by hydrodynamic effect polishing combined with magnetorheological finishing. Optik 2018, 156, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Cai, Z.; Pan, J. Process and mechanism of magnetorheological variable gap dynamic pressure planarization finishing. J. Mech. Eng. 2023, 59, 231–241. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, Q.; Zhai, W.; Gao, B.; Shi, Y.; Cheng, X. Effect of core-diameters and shell-thicknesses of Fe3O4/SiO2 composite abrasives on the performance of ultrasound-assisted magnetorheological polishing for sapphire. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 625, 126871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H. Study on the Material Removal Characteristics of Magnetorheological-Hydrodynamic Compound Polishing Technique. Master’s Thesis, Guangdong University of Technology, Guanzhou, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, B.; Yan, Q.; Chai, J.; Song, W.; Pan, J. An ultra-smooth planarization method for controlling fluid behavior in cluster magnetorheological finishing based on computational fluid dynamics. Precis. Eng. 2022, 74, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Li, Y.; Yan, Q.; Chai, J.; Song, W.; Lan, X. Cluster magnetorheological global dynamic pressure planarization processing of single crystal sapphire. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 128, 1213–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Yan, Q.; Pan, J.; Lu, J.; Fu, Y. Simulation and experimental research on magnetorheological finishing under dynamic pressure with a gap-varying. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 82, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Fu, Y.; He, J.; Xu, L.; Yan, Q. Magnetorheological chemical compound polishing of single crystal SiC substrate. Diam. Abras. Eng. 2022, 42, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhuo, Z.; Wang, H.; Zheng, Q.; Yan, Q. Experimental study of single-crystal GaN wafer electro-Fenton magnetorheological complex friction wear. Tribol. Int. 2023, 180, 108260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




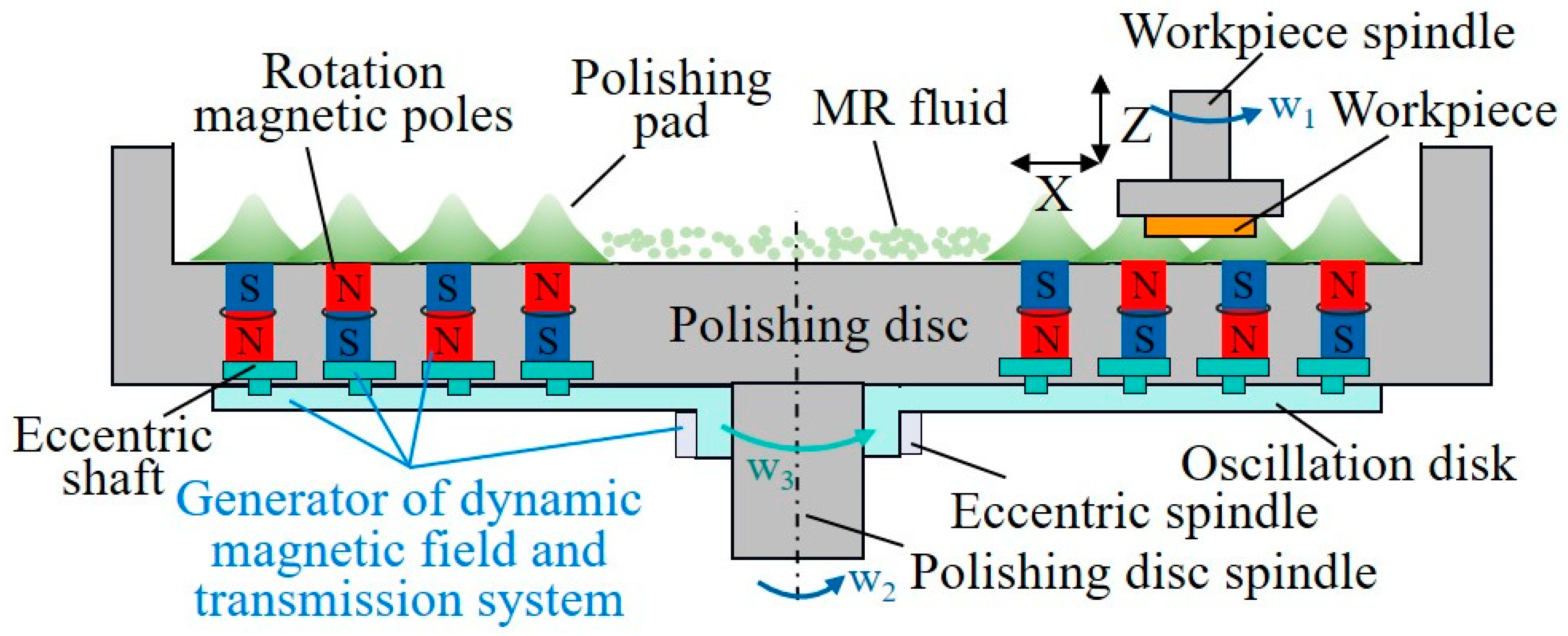
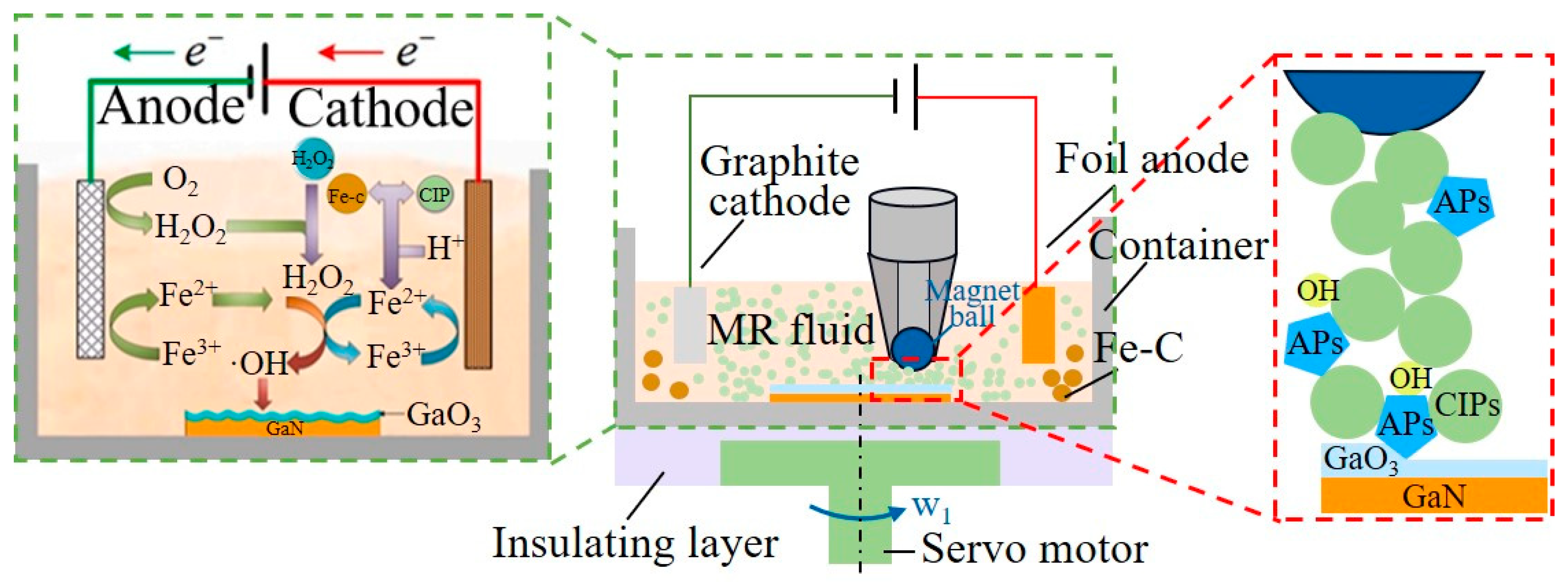
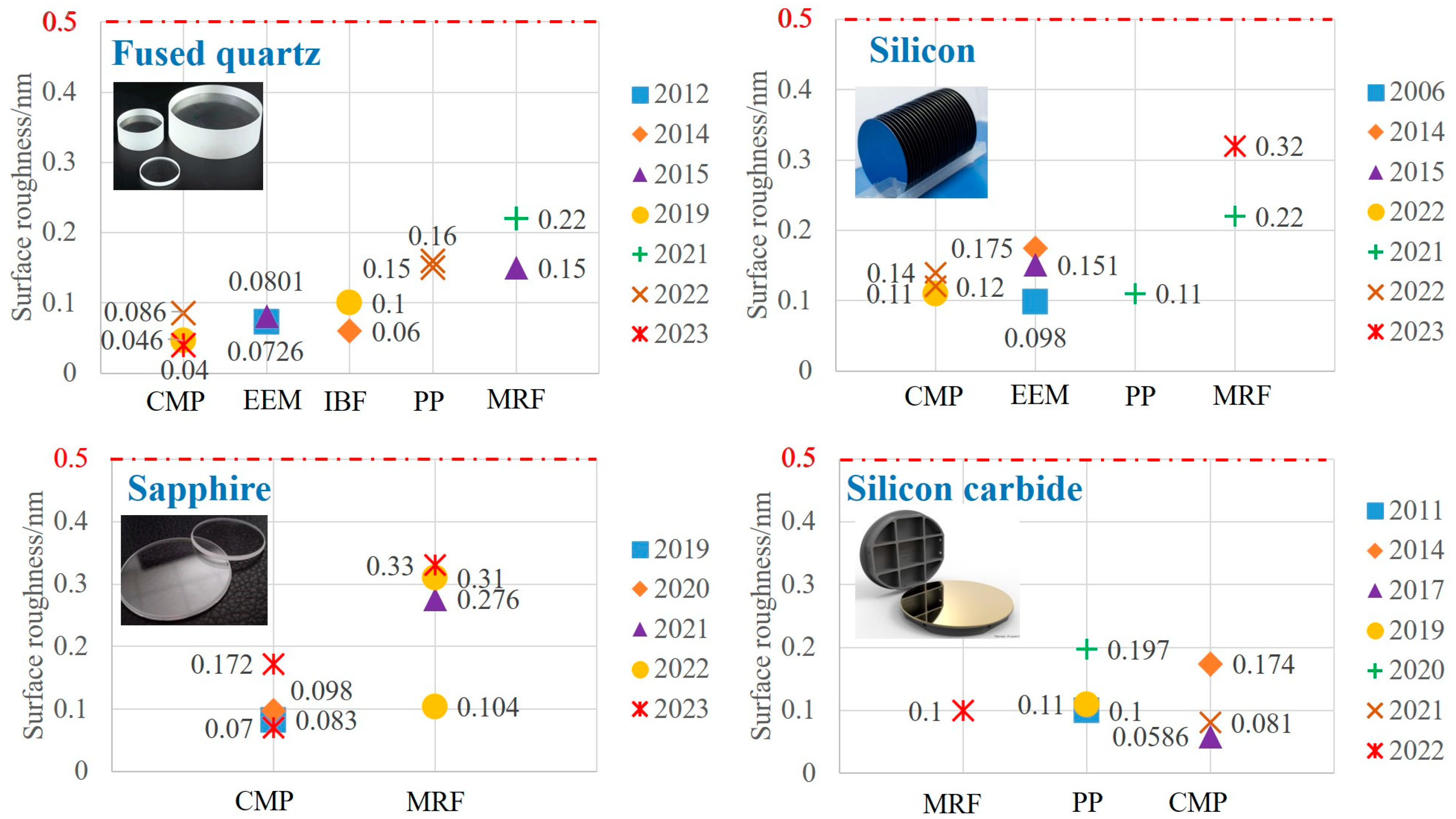
| Name | Component | New Mohs | Chemical Activity | Processing Difficulty |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fused silica | SiO2 | 7 | Relatively stable under common chemical substances and resistant to acid and alkali | It is easy to crack during machining and integrity of crystal structure needs to be considered |
| Silicon | Si | 7 | Oxidation reaction occurs under the action of high temperature and oxygen | Cracks occur during machining, and there is often an oxide layer on the surface |
| Silicon carbide | SiC | 13 | Oxidation reaction occurs under the action of high temperature and oxygen | Material removal is difficult to achieve due to high hardness |
| Sapphire | Al2O3 | 12 | Possible hydrolysis when encountering strong alkalis | High hardness prone to cracking during processing |
| Processing Method | Machining Accuracy | Processing Efficiency | Characteristics | Application Advantages | Limitations | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical mechanical polishing | Sub-nanometer/Sub-angstrom | √√√ | Chemical reaction modified and softened. | Numerous materials that can be processed and achieve ultra-low surface roughness. | The removal efficiency is low and the stability is insufficient, mainly used for machining flat and low-curvature workpieces. | Optical components; integrated circuits. |
| Elastic emission machining | Sub-nanometer/Sub-angstrom | √ | Hydrodynamic pressure produces shear stress. | High machining accuracy, atomic-level elimination, and no subsurface damage. | High precision requirements for equipment movement and low polishing efficiency. | Hubble Space Telescope; James Webb Space Telescope. |
| Magnetorheological finishing | Sub-nanometer | √√√ | Magnetic fields regulate the viscosity of magnetorheological fluids. | High machining precision and numerous materials that can be processed. | Magnetorheological fluids have high costs, insufficient stability, and small scratches on the machining surface. | Hemispherical resonator of gyroscope; large astronomical telescopes. |
| Ion beam finishing | Sub-nanometer/Sub-angstrom | √√ | Elastic collision, energy transfer, physical sputtering. | High machining precision, suitable for complex surface shapes, stable removal function, and no pollution. | The equipment is expensive, and the vacuum environment limits the processing size. | DUV; EUV; laser systems. |
| Plasma polishing | Nanometer/Sub-nanometer | √√√√ | Active particles promote chemical reaction removal on the surfaces of materials. | Suitable for large-scale and complex surface polishing and no pollution. | The processing area can easily produce material oxidation and sputtering deposition. | Lightweight space optical systems. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Xin, Q.; Fan, B.; Chen, Q.; Deng, Y. A Review of Emerging Technologies in Ultra-Smooth Surface Processing for Optical Components. Micromachines 2024, 15, 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15020178
Li W, Xin Q, Fan B, Chen Q, Deng Y. A Review of Emerging Technologies in Ultra-Smooth Surface Processing for Optical Components. Micromachines. 2024; 15(2):178. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15020178
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Wei, Qiang Xin, Bin Fan, Qiang Chen, and Yonghong Deng. 2024. "A Review of Emerging Technologies in Ultra-Smooth Surface Processing for Optical Components" Micromachines 15, no. 2: 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15020178
APA StyleLi, W., Xin, Q., Fan, B., Chen, Q., & Deng, Y. (2024). A Review of Emerging Technologies in Ultra-Smooth Surface Processing for Optical Components. Micromachines, 15(2), 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15020178