Biosensors for Seafood Safety Control—A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
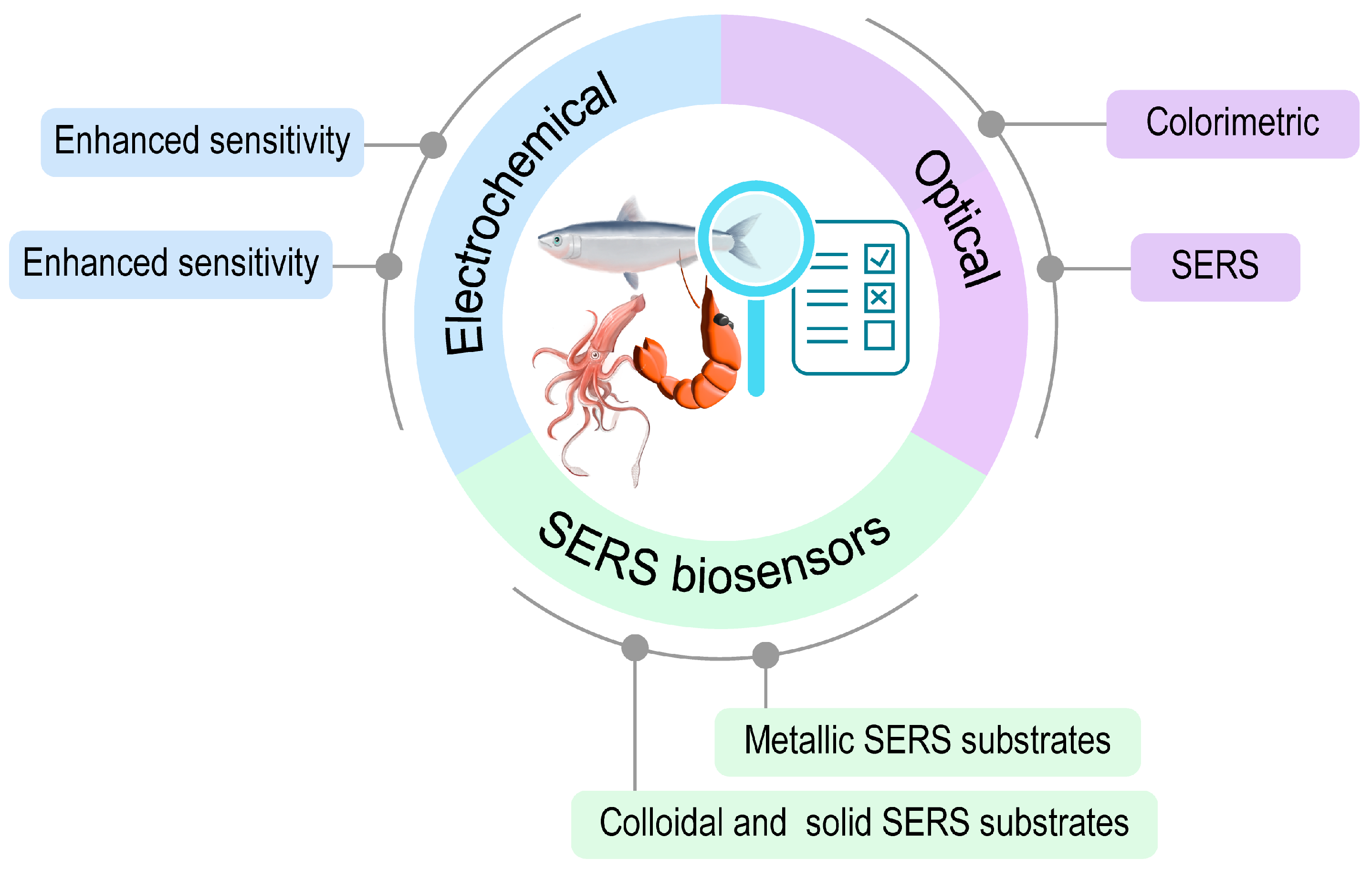
2. Common Types of Biosensors for Seafood Monitoring
2.1. Electrochemical Biosensors
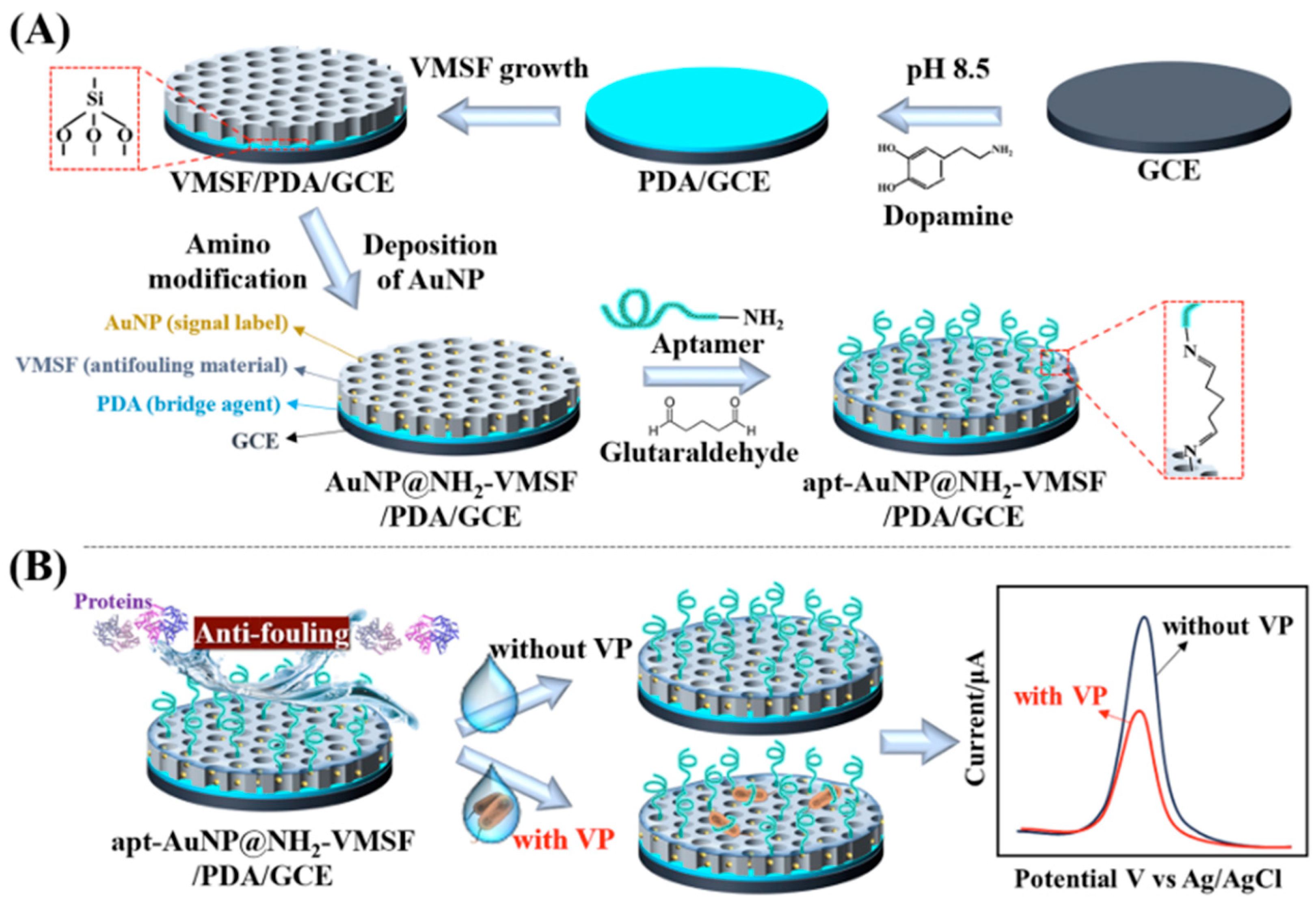
Electrochemical Biosensors with Enhanced Specificity and Sensitivity
2.2. Optical Biosensors
2.2.1. Colorimetric Biosensors
Gold Nanoparticles
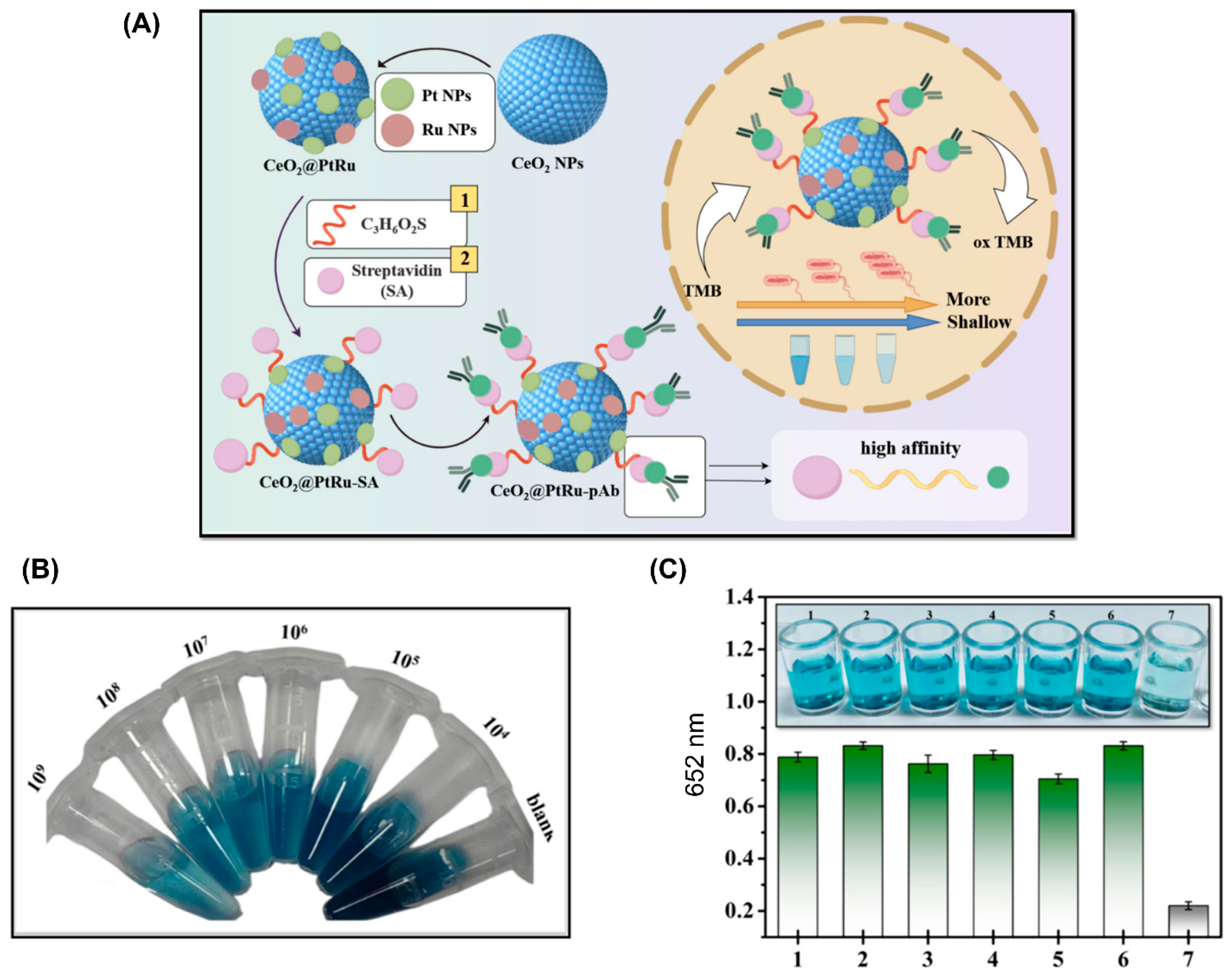
Nanozymes
2.2.2. SERS Biosensors
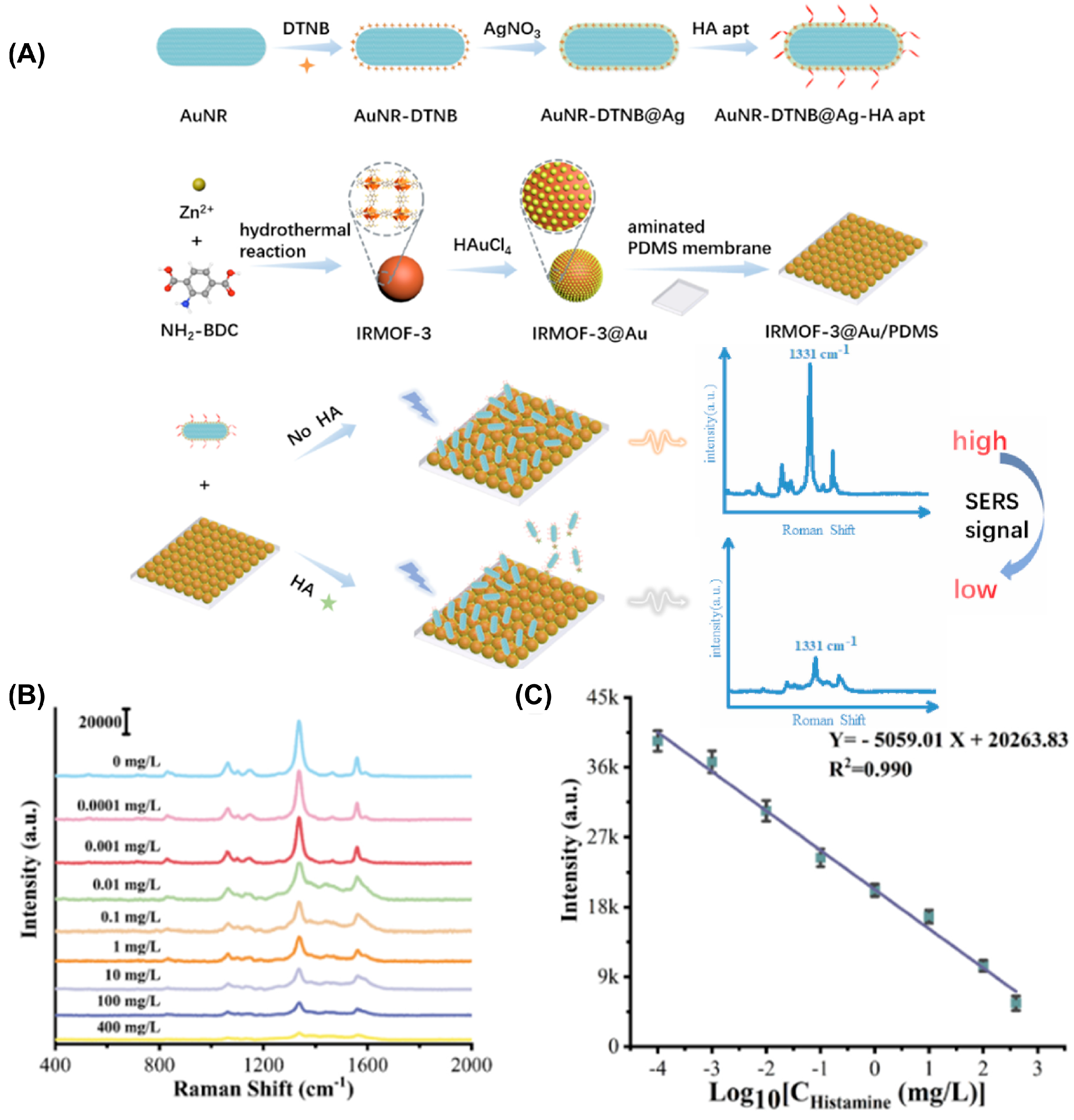
Metallic SERS Substrates
Colloidal and Solid SERS Substrates
| Biosensors and Materials | Application | LOD | Target | Type of Sample |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrochemical biosensor, carbon black modified SPEs [29] | Detect marine toxin | 0.18 ng/mL | Okadaic acid | Mussel extract |
| Electrochemical biosensor, 2D carbon nitride-aptamer-based electrode [82] | Detect marine toxin | 0.08 pg/mL | Okadaic acid | Shellfish samples |
| Electrochemical biosensor, K3Fe(CN)6 regulated Ag NPs@Apt [83] | Detect marine toxin | 1 nM | Saxitoxin (STX) | Clams, Mantis shrimps |
| Electrochemical biosensor, MIP sensor [39] | Detect marine toxin | 1.14 μg/mL | Tetrodotoxin | Mussel samples |
| Electrochemical biosensor, MoS2-PLL-Apt electrode [27] | Detect foodborne pathogen | 5.74 CFU/mL | Vibrio parahaemolyticus | Shrimp food samples |
| Electrochemical biosensor, apt-AuNP@NH2-VMSF/PDA/GCE [28] | Detect foodborne pathogen | 103 CFU/mL | Vibrio parahaemolyticus | Marine shrimp |
| Electrochemical biosensor, HIROF/SPE electrode [84] | Detect foodborne pathogen | 103 CFU/mL | Vibrio parahaemolyticus | Fish samples |
| Electrochemical biosensor, COOH-MWCNTs-Fe3O4-GO nanohybrids [85] | Detect antimicrobial | 0.003 ng/mL | Sulfadimidine | Crayfish |
| Electrochemical biosensor, PDA@ZnMoO4/MXene composite [17] | Detect foodborne pathogen | 12 CFU/mL | Listeria monocytogenes | Smoked seafood |
| Electrochemical biosensor, magnetic-MIP [33] | Monitor seafood freshness | 1.6 × 10−6 mg/L | Scombrotoxin (histamine) | Fish samples |
| Colorimetric biosensor, CDs@FMs probe [62] | Detect residues of antifungal agent | 56.7 pM | Malachite green | Fish samples |
| Colorimetric biosensor, BTSIXO [86] | Detect Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals (EDC) | 0.02 ppm | Bisphenol A | Fish samples |
| Colorimetric biosensor, magnetic bead IgG-HRP [87] | Detect neurotoxin | 1 μg/kg (oyster and razor clam samples) 3.3 μg/kg (mussel samples) | Tetrodotoxin (TTX) | Pacific oysters Razor clams Mussels |
| Colorimetric biosensor, QD@MOF*Ab probes [63] | Detect neurotoxin | 0.4 ng/mL | Tetrodotoxin (TTX) | Fishes Clams |
| Colorimetric biosensor, Au@Pt NPs/horseradish peroxidase [53] | Detect marine toxin | 0.6 µg/kg (mussel tissues) | Okadaic acid | Oysters Mussels Clams |
| Colorimetric biosensor, Fe3O4@MOF@AuNPs [64] | Detect marine toxin | 0.015 ng/mL | Okadaic acid | Shellfish samples |
| Colorimetric biosensor, CeO2@PtRu nanozyme [52] | Detect foodborne pathogen | 193 CFU/mL | Vibrio vulnificus | Clams, Shrimps |
| Colorimetric biosensor, E. amoenum extract [88] | Monitor seafood freshness | Respond to pH by changing color from red to yellow over the pH range of 2–12 | pH value | Shrimp samples |
| Colorimetric biosensor, self-assembled polydiacetylene [89] | Monitor seafood freshness | 70 ppm | Histamine | Spanish mackerel, Tuna, Mackerel |
| Colorimetric biosensor, Au0-NPsALz [90] | Monitor seafood freshness | 59.32 μmol/L | Histamine | White shrimp, giant tiger prawn, cuttlefish, and splendid squid |
| Colorimetric biosensor, CF/CNF10/SSA [91] | Monitor seafood freshness | Respond to pH by changing color from red to yellow over the pH range of 1–12 | Ammonia and pH | Shrimp |
| SERS biosensor, heterogeneous nano pineapples [92] | Detect residues of antifungal agent | 7.8 × 10−11 M | Malachite green | Clams |
| SERS biosensor, Ag TNP@SiO2 [76] | Detect residues of antifungal agent | 0.49 pM | Malachite green | Spiked water |
| SERS biosensor, HAuCl4/K4Fe(CN)6 reaction mediated silver nanosol [80] | Detect residues of antifungal agent | 0.032 μM | Malachite green | Tilapia, shrimps |
| SERS biosensor, aptamer-recognized SERS tag [93] | Detect toxin | 0.1 ng/L | Microcystin-LR (MC-LR) | Fish organs |
| SERS biosensor, GO-Au [94] | Detect marine toxin | 5.47 nM | Stonehouse clam toxin | Clam muscle tissue |
| SERS biosensor, Fe3O4@MOF-GNS-MBA-Apt [95] | Detect foodborne pathogen | 7 CFU/mL | Vibrio parahaemolyticus | Shrimps |
| SERS biosensor, β-CD-AgNPs [96] | Monitor seafood freshness | 7.2 nM | Histamine | Fishes |
3. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Javeed, A.; Jian, C.; Zeng, Q.; Han, B. Precautions for Seafood Consumers: An Updated Review of Toxicity, Bioaccumulation, and Rapid Detection Methods of Marine Biotoxins. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 274, 116201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafra, L.L.; De Souza, D.A.; Menezes, M.; Schramm, M.A.; Hoff, R. Marine Biotoxins: Latest Advances and Challenges toward Seafood Safety, Using Brazil as a Case Study. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2023, 53, 101078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauge, T.; Mougin, J.; Ells, T.; Midelet, G. Sources and Contamination Routes of Seafood with Human Pathogenic Vibrio Spp.: A Farm-to-Fork Approach. Comp. Rev. Food Sci. Food Safe 2024, 23, e13283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Parisi, A.; Conversano, M.C.; Iannacci, A.; D’Emilio, F.; Mercurio, V.; Normanno, G. Food-Borne Bacteria Associated with Seafoods: A Brief Review. JFQHC 2020, 7, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, X.; Gao, H. Marine Toxins in Seafood: Recent Updates on Sample Pretreatment and Determination Techniques. Food Chem. 2024, 438, 137995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varnakavi, N.; Lee, N. A Review on Biosensors and Recent Development of Nanostructured Materials-Enabled Biosensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uniyal, A.; Srivastava, G.; Pal, A.; Taya, S.; Muduli, A. Recent Advances in Optical Biosensors for Sensing Applications: A Review. Plasmonics 2023, 18, 735–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Pandey, V.K.; Srivastava, S.; Singh, R. A Systematic Review on Recent Trends and Perspectives of Biosensors in Food Industries. J. Food Saf. 2023, 43, e13071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riu, J.; Giussani, B. Electrochemical Biosensors for the Detection of Pathogenic Bacteria in Food. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 126, 115863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalonga, A.; Sánchez, A.; Mayol, B.; Reviejo, J.; Villalonga, R. Electrochemical Biosensors for Food Bioprocess Monitoring. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2022, 43, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Lu, X.; Wang, W.; Hubbe, M.A.; Liu, Y.; Mu, J.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Rojas, O.J. Recent Developments in Colorimetric and Optical Indicators Stimulated by Volatile Base Nitrogen to Monitor Seafood Freshness. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2021, 28, 100634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zuo, J.; Yang, C.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Ping, J.; Li, P. Current Trends in Biosensors for Biotoxins (Mycotoxins, Marine Toxins, and Bacterial Food Toxins):Principles, Application, and Perspective. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 165, 117144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinzaru, S.C.; Müller, C.; Ujević, I.; Venter, M.M.; Chis, V.; Glamuzina, B. Lipophilic Marine Biotoxins SERS Sensing in Solutions and in Mussel Tissue. Talanta 2018, 187, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juneja, S.; Zhang, B.; Nujhat, N.; Wang, A.X. Quantitative Sensing of Domoic Acid from Shellfish Using Biological Photonic Crystal Enhanced SERS Substrates. Molecules 2022, 27, 8364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rippa, M.; Sagnelli, D.; Vestri, A.; Marchesano, V.; Munari, B.; Carnicelli, D.; Varrone, E.; Brigotti, M.; Tozzoli, R.; Montalbano, M.; et al. Plasmonic Metasurfaces for Specific SERS Detection of Shiga Toxins. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 4969–4979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, B.; Dong, Y.; Qian, J.; Wang, M.; Yang, Y.; Nikitina, M.A.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, X. Hydrogel Coating Flexible pH Sensor System for Fish Spoilage Monitoring. Mater. Today Chem. 2022, 26, 101183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskaran, N.; Sakthivel, R.; Karthik, C.S.; Lin, Y.-C.; Liu, X.; Wen, H.-W.; Yang, W.; Chung, R.-J. Polydopamine-Modified 3D Flower-like ZnMoO4 Integrated MXene-Based Label-Free Electrochemical Immunosensor for the Food-Borne Pathogen Listeria Monocytogenes Detection in Milk and Seafood. Talanta 2025, 282, 127008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yibar, A.; Ajmi, N.; Duman, M. First Report and Genomic Characterization of Escherichia Coli O111:H12 Serotype from Raw Mussels in Türkiye. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalita, N.; Gogoi, S.; Minteer, S.D.; Goswami, P. Advances in Bioelectrode Design for Developing Electrochemical Biosensors. ACS Meas. Sci. Au 2023, 3, 404–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thulasiprevinnah, S.; Bashir, S.; Ramesh, K.; Ramesh, S. Recent Advances in Electrochemical Biosensors for the Determination of Biomolecules on Modified and Unmodified Electrodes. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2024, 21, 1739–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseine, M.; Naghib, S.M.; Khodadadi, A. Label-Free Electrochemical Biosensor Based on Green-Synthesized Reduced Graphene Oxide/Fe3O4/Nafion/Polyaniline for Ultrasensitive Detection of SKBR3 Cell Line of HER2 Breast Cancer Biomarker. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siciliano, G.; Alsadig, A.; Chiriacò, M.S.; Turco, A.; Foscarini, A.; Ferrara, F.; Gigli, G.; Primiceri, E. Beyond Traditional Biosensors: Recent Advances in Gold Nanoparticles Modified Electrodes for Biosensing Applications. Talanta 2024, 268, 125280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, N.; Mitra, R.; Pramanick, B. C-MEMS-Derived Glassy Carbon Electrochemical Biosensors for Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2023, 9, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanbhag, M.M.; Manasa, G.; Mascarenhas, R.J.; Mondal, K.; Shetti, N.P. Fundamentals of Bio-Electrochemical Sensing. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2023, 16, 100516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, W.; Ma, B.; Ju, H. Device Integration of Electrochemical Biosensors. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 2023, 1, 346–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Guo, W.; Lv, C.; Liu, X.; Yang, M.; Guo, M.; Fu, Q. Electrochemical Biosensors Represent Promising Detection Tools in Medical Field. Adv. Sens. Energy Mater. 2023, 2, 100081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Sun, Z.; Guo, Q.; Weng, X. Microfluidic Thread-Based Electrochemical Aptasensor for Rapid Detection of Vibrio Parahaemolyticus. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 182, 113191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Gong, L.; Liang, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, K.; Yang, T.; Zeng, H. Polydopamine-Enhanced Vertically-Ordered Mesoporous Silica Film Anti-Fouling Electrochemical Aptasensor for Indicator-Free Vibrio Parahaemolyticus Discrimination Using Stable Inherent Au Signal. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2024, 407, 135485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelis, J.L.D.; Migliorelli, D.; Mühlebach, L.; Generelli, S.; Stewart, L.; Elliott, C.T.; Campbell, K. Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Detection of the Marine Toxins Okadaic Acid and Domoic Acid with Carbon Black Modified Screen Printed Electrodes. Talanta 2021, 228, 122215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Thakur, D.; Kumar, D. Novel Enzymatic Biosensor Utilizing a MoS2/MoO3 Nanohybrid for the Electrochemical Detection of Xanthine in Fish Meat. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 31962–31971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayerdurai, V.; Cieplak, M.; Kutner, W. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Electrochemical Sensors for Food Contaminants Determination. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 158, 116830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, M.A.; Rahmawati, F.; Jamal, J.A.; Ibrahim, S.; Said, M.M.; Ahmad, M.S. Inspecting Histamine Isolated from Fish through a Highly Selective Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor Approach. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 13352–13361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.H.A.; Sappia, L.; Moura, S.L.; Ali, F.H.M.; Moselhy, W.A.; Sotomayor, M.D.P.T.; Pividori, M.I. Biomimetic Magnetic Sensor for Electrochemical Determination of Scombrotoxin in Fish. Talanta 2019, 194, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Guo, Y.; He, P.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y. Enhanced Sensitivity and Selectivity of an Electrochemical Sensor for Real-Time Propofol Monitoring in Anesthesia. Alex. Eng. J. 2024, 87, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curulli, A. Functional Nanomaterials Enhancing Electrochemical Biosensors as Smart Tools for Detecting Infectious Viral Diseases. Molecules 2023, 28, 3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Liang, Z. Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Sensor for Rapid Detection of Vibrio Parahaemolyticus in Shrimp. Food Meas. 2024, 18, 6921–6927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Yang, Q.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, W.; Zhang, W. An Ultrasensitive and Specific Ratiometric Electrochemical Biosensor Based on SRCA-CRISPR/Cas12a System for Detection of Salmonella in Food. Food Control. 2023, 146, 109528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Kroon, R.; Zeglio, E.; Herland, A. P-Type Accumulation Mode Organic Electrochemical Transistor Biosensor for Xanthine Detection in Fish. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2025, 269, 116928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, P.; Rebelo, P.; Pacheco, J.G.; Geraldo, D.; Bento, F.; Leão-Martins, J.M.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Nouws, H.P.A. Electrochemical Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Sensor for Simple and Fast Analysis of Tetrodotoxin in Seafood. Talanta 2025, 282, 127002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, S.; Lv, Q.; Wang, C.; Liang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Li, G. Colorimetric Biosensor for Visual Determination of Golgi Protein 73 Based on Reduced Graphene Oxide-Carboxymethyl Chitosan-Hemin/Platinum@palladium Nanozyme with Peroxidase-like Activity. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.-Q.; Ge, L. Colorimetric Sensors: Methods and Applications. Sensors 2023, 23, 9887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, H. Chromogenic Mechanisms of Colorimetric Sensors Based on Gold Nanoparticles. Biosensors 2023, 13, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Cai, S.; Luo, J.; Liu, X.; Ou, L.; Zhang, Q.; Liedberg, B.; Wang, Y. Colorimetric Biosensing Assays Based on Gold Nanoparticles Functionalized/Combined with Non-Antibody Recognition Elements. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 173, 117654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unabia, R.B.; Reazo, R.L.D.; Rivera, R.B.P.; Lapening, M.A.; Omping, J.L.; Lumod, R.M.; Ruda, A.G.; Sayson, N.L.B.; Dumancas, G.; Malaluan, R.M.; et al. Dopamine-Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles for Colorimetric Detection of Histamine. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 17238–17246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Lao, Y.; Sasaki, Y.; Lyu, X.; Gao, P.; Wu, S.; Minami, T.; Liu, Y. Freshness Monitoring of Raw Fish by Detecting Biogenic Amines Using a Gold Nanoparticle-Based Colorimetric Sensor Array. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 6803–6810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Wu, Y.; Shen, Q. A Simple and Selective Colorimetric Aptasensor for Detection of Toxins Microcystin-LR in Fish Tissue Using a Truncated Aptamer. Food Anal. Methods 2022, 15, 2202–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadsri, V.; Trakulsujaritchok, T.; Tangwattanachuleeporn, M.; Hoven, V.P.; Na Nongkhai, P. Simple Colorimetric Assay for Vibrio Parahaemolyticus Detection Using Aptamer-Functionalized Nanoparticles. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 21437–21442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Xu, X.; Song, Y.; Huang, J.; Xu, H. Research Progress of Nanozymes in Colorimetric Biosensing: Classification, Activity and Application. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 487, 150612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zhang, B.; Tu, H.; Pan, C.; Chai, Y.; Chen, W. Advances in Colorimetric Biosensors of Exosomes: Novel Approaches Based on Natural Enzymes and Nanozymes. Nanoscale 2024, 16, 1005–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Wang, L.; Li, M.; Wang, M.; Liu, G.; Ping, J. Nanozyme-Based Biosensor for Organophosphorus Pesticide Monitoring: Functional Design, Biosensing Strategy, and Detection Application. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 165, 117152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, D.; Zhang, X.; Luo, X.; Lin, W.; Li, Z.; Huang, J. Silver Nanoparticles Deposited Carbon Microspheres Nanozyme with Enhanced Peroxidase-like Catalysis for Colorimetric Detection of Hg2+ in Seafood. Microchim. Acta 2023, 190, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Xie, J.; Yu, L.; Shu, B.; Liu, X.; Chen, S.; Li, Q.; Qi, S.; Zhao, S. Sensitive Colorimetric Detection of Vibrio Vulnificus Based on Target-Induced Shielding against the Peroxidase-Mimicking Activity of CeO2@PtRu Nanozyme. Food Chem. 2024, 454, 139757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, M.; He, Y.; Lin, X. Sensitive Detection of the Okadaic Acid Marine Toxin in Shellfish by Au@Pt NPs/Horseradish Peroxidase Dual Catalysis Immunoassay. Anal. Methods 2022, 14, 1261–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Liao, T.; Sang, Y.; Mao, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Sun, D.; Jiang, W. Sensitive Detection of Vibrio Parahaemolyticus via a Dual-Recognition Colorimetric Biosensor Comprising Cefe-PEG-MNPs and Apt-Fe@PDA. Food Control. 2025, 168, 110955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Cao, L.; Sui, J.; Wang, L.; Lin, H.; Wang, K. Bimetallic Fe/Ni Metal Organic Framework-Based Hypoxanthine Biosensor for Early Monitoring of Freshness Changes of Aquatic Products. Food Chem. 2024, 447, 138902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, J.; Ju, P.; Bi, F.; Wen, S.; Xiang, Z.; Chen, J.; Qiu, M. A Smartphone-Assisted Ultrasensitive Colorimetric Aptasensor Based on DNA-Encoded Porous MXene Nanozyme for Visual Detection of Okadaic Acid. Food Chem. 2025, 464, 141776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, F.; Xu, G.; Zhou, S.; Chen, S.; He, D. Principles and Applications of Green Fluorescent Protein-Based Biosensors: A Mini-Review. Analyst 2023, 148, 2882–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, N.; Hong, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shafi, S.; Pan, J.; Zhao, R.; Yang, Y.; Hou, W. Application of Fluorescent Nano-Biosensor for the Detection of Cancer Bio-Macromolecular Markers. Polym. Test. 2022, 115, 107746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reja, S.I.; Minoshima, M.; Hori, Y.; Kikuchi, K. Recent Advancements of Fluorescent Biosensors Using Semisynthetic Probes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 247, 115862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, H.; Fan, C.; Chen, M.; Zhang, X.; Yan, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Gong, Z.; Shi, L.; Li, X.; et al. Recent Advances of Fluorescent Biosensors Based on Cyclic Signal Amplification Technology in Biomedical Detection. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, A.M.; Yasin, G.; Zourob, M.; Lu, J. Fluorescent Biosensors for the Detection of Viruses Using Graphene and Two-Dimensional Carbon Nanomaterials. Biosensors 2022, 12, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Mao, Q.; Cui, Y.; Gong, S.; Xiao, L.; Gong, X.; Guan, T.; Yang, Z. Carbon Dots-Based Fluorescence Microspheres for Ultrasensitive Detection of Malachite Green in Fish Samples. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 134, 106497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Huo, Y.; Yin, S.; Chen, C.; Shi, T.; Mi, W.; Hu, Z.; Gao, Z. A Smartphone-Based Fluorescent Biosensor with Metal-Organic Framework Biocomposites and Cotton Swabs for the Rapid Determination of Tetrodotoxin in Seafood. Anal. Chim. Acta 2024, 1311, 342738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, Q.; Huang, G.; Huang, S.; Lin, C.; Lin, X.; Xie, Z. Oriented-Aptamer Encoded Magnetic Nanosensor with Laser-Induced Fluorescence for Ultrasensitive Test of Okadaic Acid. Talanta 2024, 266, 124984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Long, F.; Chen, W.; Chen, J.; Chu, P.K.; Wang, H. Fundamentals and Applications of Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy–Based Biosensors. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 13, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Dang, H.; Moon, J.-I.; Kim, K.; Joung, Y.; Park, S.; Yu, Q.; Chen, J.; Lu, M.; Chen, L.; et al. SERS-Based Microdevices for Use as in Vitro Diagnostic Biosensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 5394–5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, N.; Saxena, K.; Rawal, R.; Yadav, L.; Jain, U. Advances in Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy-Based Sensors for Detection of Various Biomarkers. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2023, 184, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usman, F.; Ghazali, K.H.; Fen, Y.W.; Meriaudeau, F.; Jose, R. Biosensing through Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy: A Review on the Role of Plasmonic Nanoparticle-Polymer Composites. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 195, 112250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumalasari, M.R.; Alfanaar, R.; Andreani, A.S. Gold Nanoparticles (AuNPs): A Versatile Material for Biosensor Application. Talanta Open 2024, 9, 100327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, N.; Ning, X.; Gao, F. Comparative Analysis of the Application Efficiency of Gold Nanoparticles-Based SERS in Four Foodborne Pathogenic Microbes. Discov. Appl. Sci. 2024, 6, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Wu, J.; Hassan, M.M.; Jiao, T.; Xu, Y.; Ding, Z.; Li, H.; Chen, Q. Generalized Ratiometric Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Biosensor for Okadaic Acid in Food Based on Au-Triggered Signal Amplification. Anal. Chim. Acta 2024, 1310, 342705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Li, Y.; Pi, F. Sensitive and Reproducible Gold Nanostar@metal–Organic Framework-Based SERS Membranes for the Online Monitoring of the Freshness of Shrimps. Analyst 2023, 148, 2081–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Xu, S.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, C.; Ma, X. Sensitive SERS Aptasensor for Histamine Detection Based on Au/Ag Nanorods and IRMOF-3@Au Based Flexible PDMS Membrane. Anal. Chim. Acta 2024, 1288, 342147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.Y.F.; Rusin, C.J.; McDermott, M.T. Gold Nanostars as a Colloidal Substrate for In-Solution SERS Measurements Using a Handheld Raman Spectrometer. Analyst 2020, 145, 1396–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Liang, Y.; Jialading, A.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J. Application of SERS Quantitative Analysis Method in Food Safety Detection. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2021, 40, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.-Y.; Zhu, J.; Weng, G.-J.; Li, J.-J.; Zhao, J.-W. Fabrication of SERS Composite Substrates Using Ag Nanotriangles-Modified SiO2 Photonic Crystal and the Application of Malachite Green Detection. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2024, 318, 124472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Li, H.; Yin, M.; Yang, D.; Xiao, F.; Kumar Tammina, S.; Yang, Y. Fluorescence-SERS Dual-Mode for Sensing Histamine on Specific Binding Histamine-Derivative and Gold Nanoparticles. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 273, 121047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Terry, L.R.; Guo, H. A Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Based Smart Petri Dish for Sensitive and Rapid Detection of Bacterial Contamination in Shrimp. Food Chem. Adv. 2023, 2, 100222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Wu, J.; Hassan, M.M.; Zhu, A.; Jiao, T.; Xu, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, Q. Ratiometric SERS Biosensor for Detection of Tetrodotoxin Based on Three-Way Junction Catalytic Hairpin Assembly. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2025, 426, 137088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zeng, W.; Liu, C.; Popp, J.; Cialla-May, D. HAuCl4/K4Fe(CN)6 Reaction Mediated Silver Nanosol as SERS Substrate for Robust Detection of Malachite Green Residue in Seafood. Microchem. J. 2024, 199, 110139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adade, S.Y.-S.S.; Lin, H.; Johnson, N.A.N.; Qianqian, S.; Nunekpeku, X.; Ahmad, W.; Kwadzokpui, B.A.; Ekumah, J.-N.; Chen, Q. Rapid Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Benzo(b)Fluoranthene (BbF) in Shrimp Using SERS-Based Sensor Coupled with Chemometric Models. Food Chem. 2024, 454, 139836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, P.; Liu, S.; Wang, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, W.; Qu, Z.; Du, L.; et al. A 2D Carbon Nitride-Based Electrochemical Aptasensor with Reverse Amplification for Highly Sensitive Detection of Okadaic Acid in Shellfish. Anal. Methods 2024, 16, 1538–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, W.; Tang, X.; Wu, T.; Han, B.; Wu, L. Development of a Highly Sensitive Aptamer-Based Electrochemical Sensor for Detecting Saxitoxin Based on K3Fe(CN)6 Regulated Silver Nanoparticles. Anal. Chim. Acta 2024, 1287, 342134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Gao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ma, C.; Shi, C. A pH Ultra-Sensitive Hydrated Iridium Oxyhydroxide Films Electrochemical Sensor for Label-Free Detection of Vibrio Parahaemolyticus. Anal. Biochem. 2024, 693, 115597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wen, Y.; Hu, W.; Lu, X.; Chen, L.; Zhao, L.; Zeng, Q.; Tang, H.; Hong, Y.; Tang, K. A Signal-Amplified Electrochemical Immunosensor for the Detection of Sulfadimidine in Crayfish Using COOH-MWCNTs-Fe3O4-GO Nanohybrids Modified Working Electrode. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 134, 106501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, E.; Manna, A.; Lakshmi Servarayan, K.; Sivasamy Vasantha, V. Colorimetric Detection and Bio-Magnification of Bisphenol A in Fish Organs and Water Sources Using 3′,6′-Bis(Diethylamino)-2- ((3,4,5trimethyl Benzylidene) Amino) Spiro [Isoindoline -1,9′-Xanthen ]-3-One (BTSIXO)-Fe3+ Ion Conjugate. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campàs, M.; Reverté, J.; Rambla-Alegre, M.; Campbell, K.; Gerssen, A.; Diogène, J. A Fast Magnetic Bead-Based Colorimetric Immunoassay for the Detection of Tetrodotoxins in Shellfish. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 140, 111315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadalinejhad, S.; Almasi, H.; Moradi, M. Immobilization of Echium Amoenum Anthocyanins into Bacterial Cellulose Film: A Novel Colorimetric pH Indicator for Freshness/Spoilage Monitoring of Shrimp. Food Control. 2020, 113, 107169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ren, S.; Peng, Y.; Lv, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, Z.; Gao, Z. A Colorimetric Strip for Rapid Detection and Real-Time Monitoring of Histamine in Fish Based on Self-Assembled Polydiacetylene Vesicles. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 1611–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phoungsiri, A.; Lerdpiriyaskulkij, N.; Mathaweesansurn, A.; Detsri, E. Ultrasonic-Driven Chemical Reduction Synthesis of Alizarin Complexone-Modified Gold Nanoparticles for Dual-Signal Colorimetric and Fluorometric Sensing of Histamine in Seafood Products. Talanta 2024, 280, 126703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, X.; Xia, Y.; Xue, Y.; Cheng, J.; Yang, F.; Cui, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, R.; Li, X. Sugarcane-Derived Bio-Amine-Responsive Colorimetric Films for Real-Time Visual Monitoring of the Seafood Freshness. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 199, 116784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Weng, G.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, J. Reliable Detection of Malachite Green by Self-Assembled SERS Substrates Based on Gold–Silicon Heterogeneous Nano Pineapple Structures. Food Chem. 2024, 451, 139454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, W.; Lin, B.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Chen, L.; Zeng, Y.; Li, L.; Qian, Z.; Guo, L. Toxicity Evaluation of MC-LR in Different Fish Organs Based on Aptamer-Recognized SERS Tag Coupled with Magnetic Separation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 380, 133319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Xu, P.; Ren, J.; Shi, J.; Huang, R.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Y.; You, R. Monolayer Graphene Oxide-Au Loaded Compound (GO-Au) as a Flexible, Stable and Sensitive SERS Active Substrate for Detection of Stonehouse Clam Toxin (STX). J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 133, 106484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lin, X.; Wu, J.; Ying, D.; Duan, N.; Wang, Z.; Wu, S. Multifunctional Magnetic Composite Nanomaterial for Colorimetric-SERS Dual-Mode Detection and Photothermal Sterilization of Vibrio Parahaemolyticus. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 477, 147113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, L.; Li, L.; Wei, S.; Tian, Y.; Hou, X.; Wu, L. Sensitive Detection of Histamine Utilizing the SERS Platform Combined with an Azo Coupling Reaction and a Composite Hydrophobic Layer. Talanta 2024, 278, 126531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trinh, T.N.D.; Nguyen, H.A.; Thi, N.P.A.; Nam, N.N.; Tran, N.K.S.; Trinh, K.T.L. Biosensors for Seafood Safety Control—A Review. Micromachines 2024, 15, 1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15121509
Trinh TND, Nguyen HA, Thi NPA, Nam NN, Tran NKS, Trinh KTL. Biosensors for Seafood Safety Control—A Review. Micromachines. 2024; 15(12):1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15121509
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrinh, Thi Ngoc Diep, Hanh An Nguyen, Nguyen Pham Anh Thi, Nguyen Nhat Nam, Nguyen Khoi Song Tran, and Kieu The Loan Trinh. 2024. "Biosensors for Seafood Safety Control—A Review" Micromachines 15, no. 12: 1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15121509
APA StyleTrinh, T. N. D., Nguyen, H. A., Thi, N. P. A., Nam, N. N., Tran, N. K. S., & Trinh, K. T. L. (2024). Biosensors for Seafood Safety Control—A Review. Micromachines, 15(12), 1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15121509








