Electrochemical Mill Grinding of (TiB+TiC)/Ti6Al4V Composites Using Abrasive Tool with Bottom Outlet Holes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
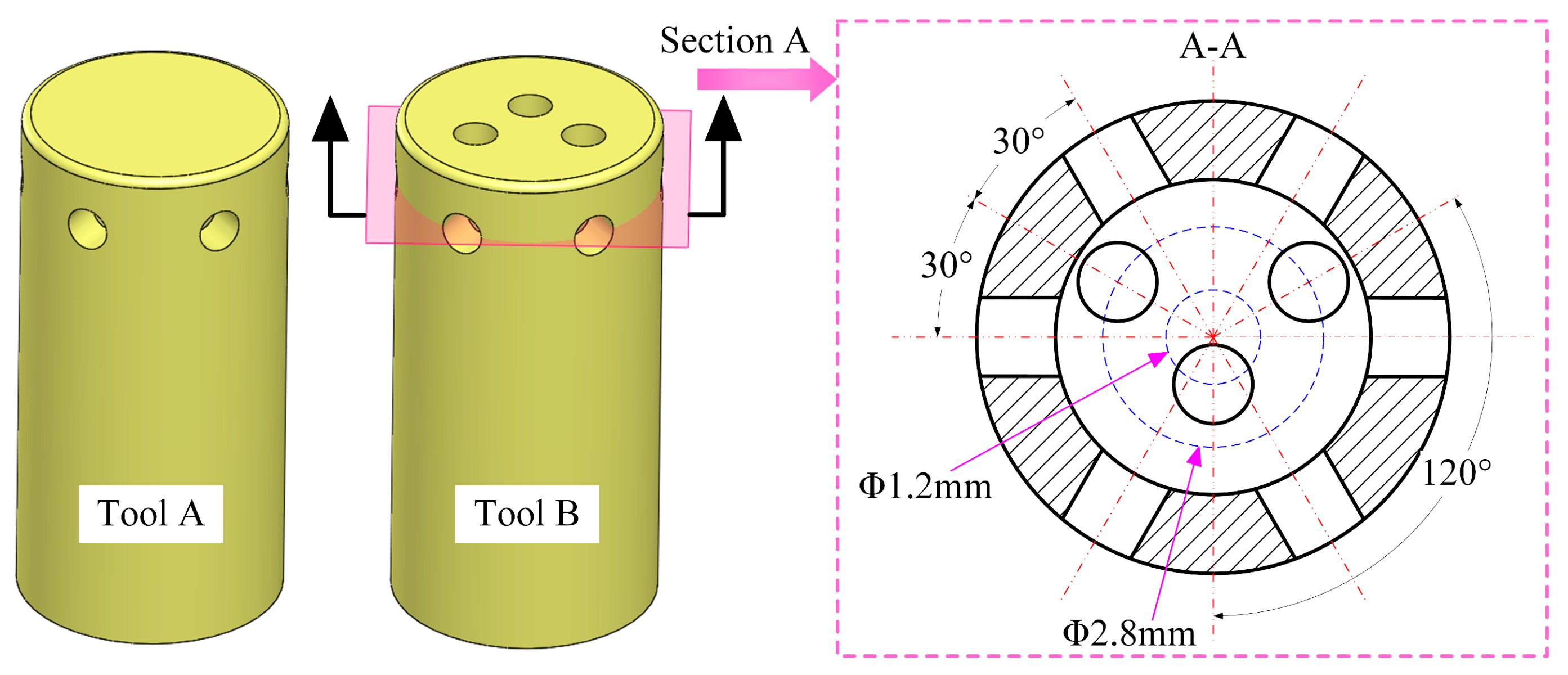
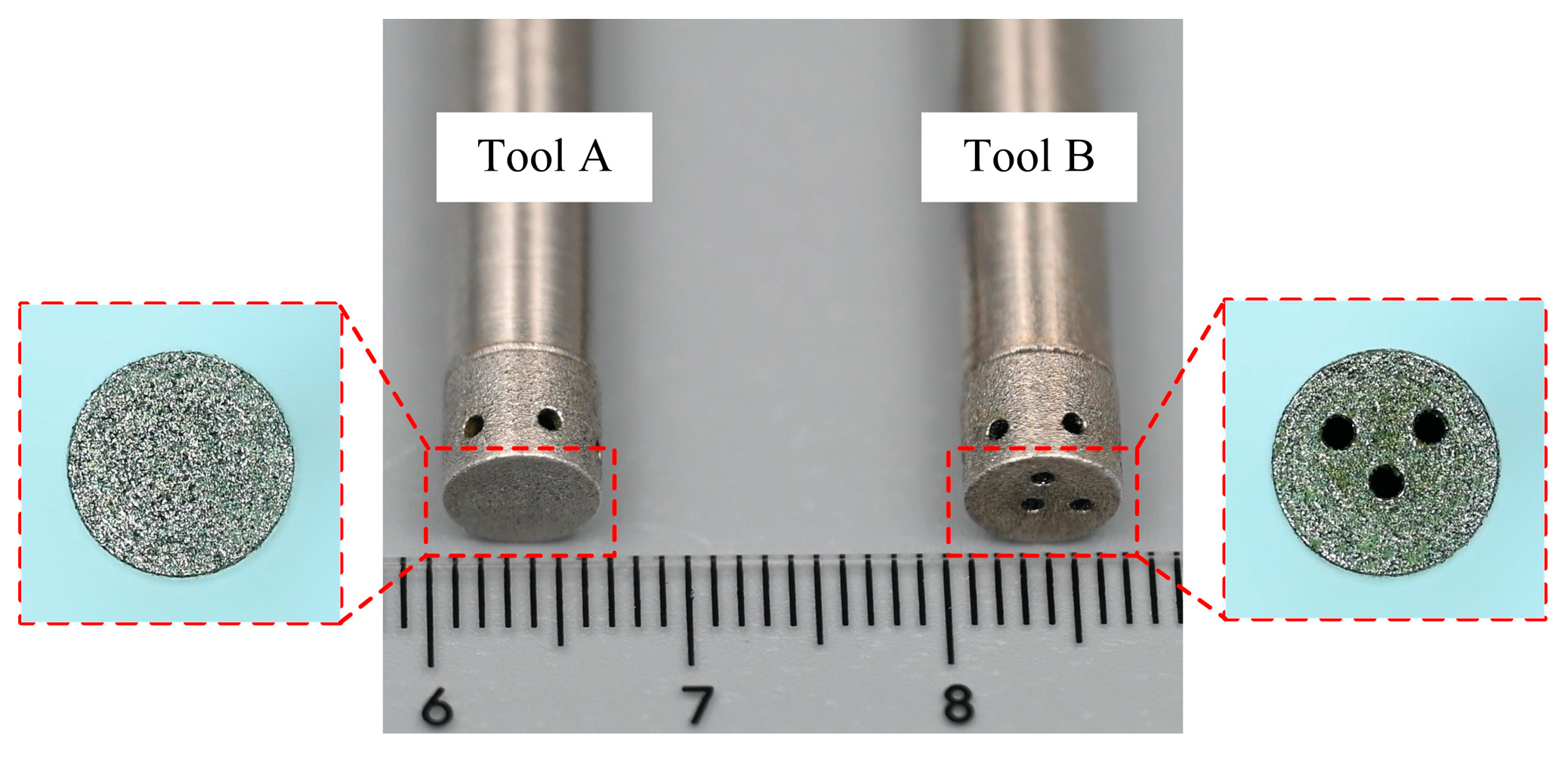
2.1. Design of the Tool with Bottom Outlet Holes
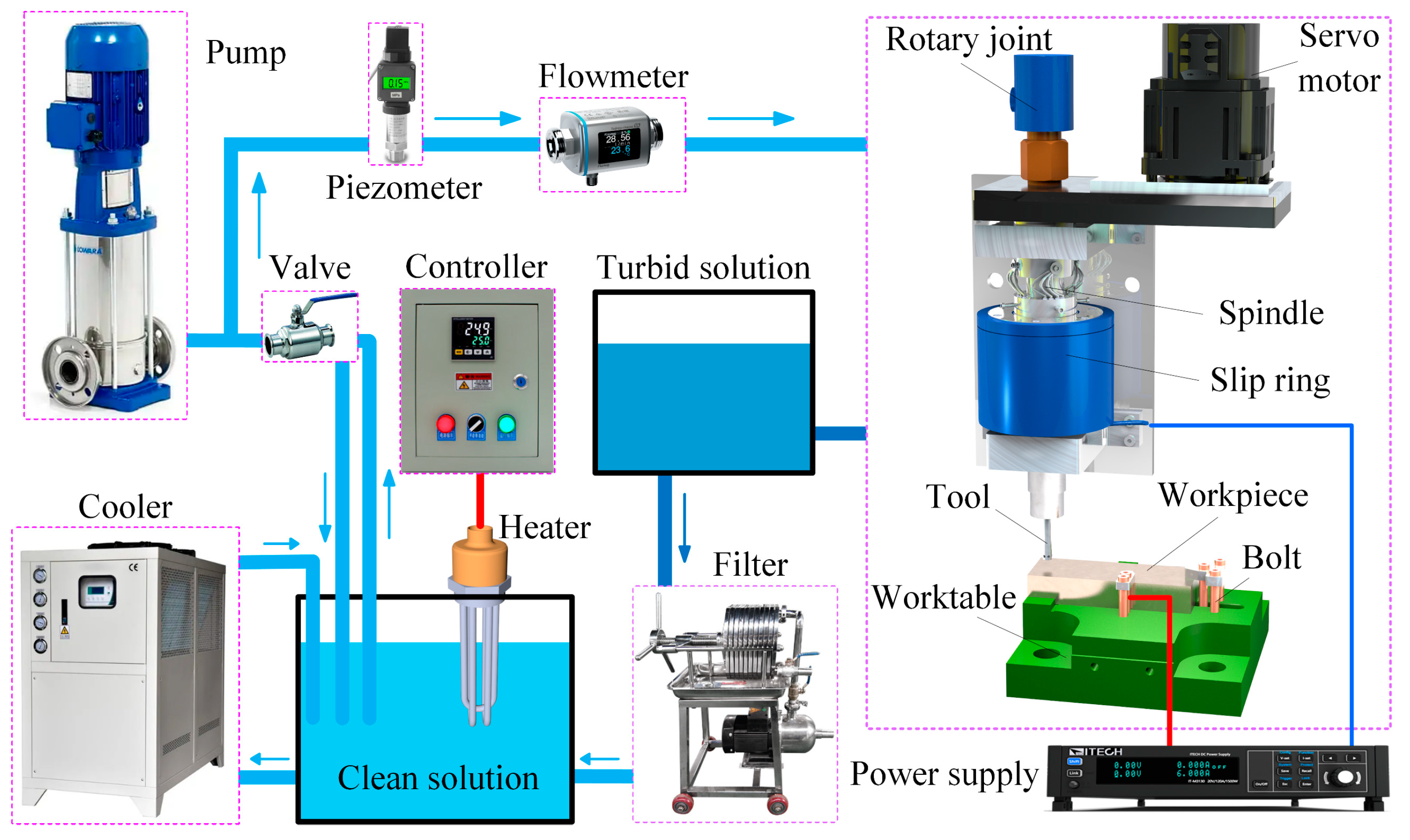
2.2. Experimental System and Arrangement
3. Results and Discussion
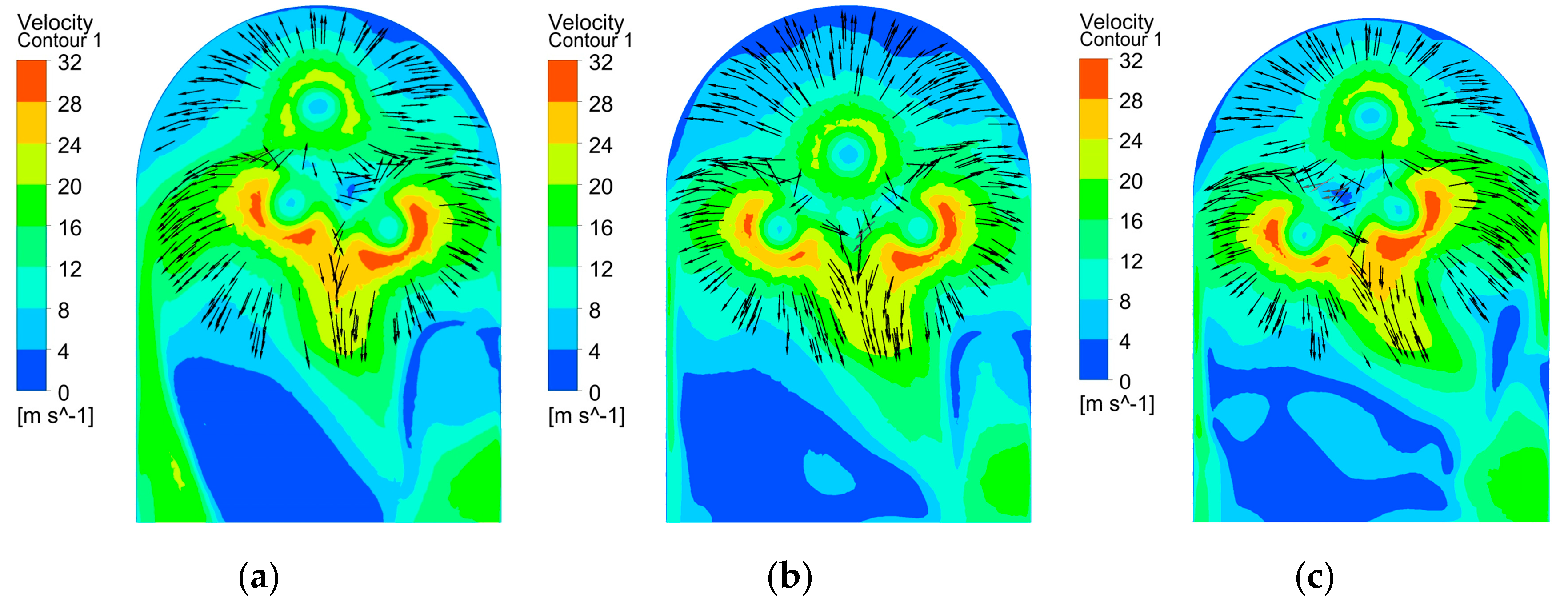
3.1. Flow Field Simulation Analysis
3.2. Machining with ECMG
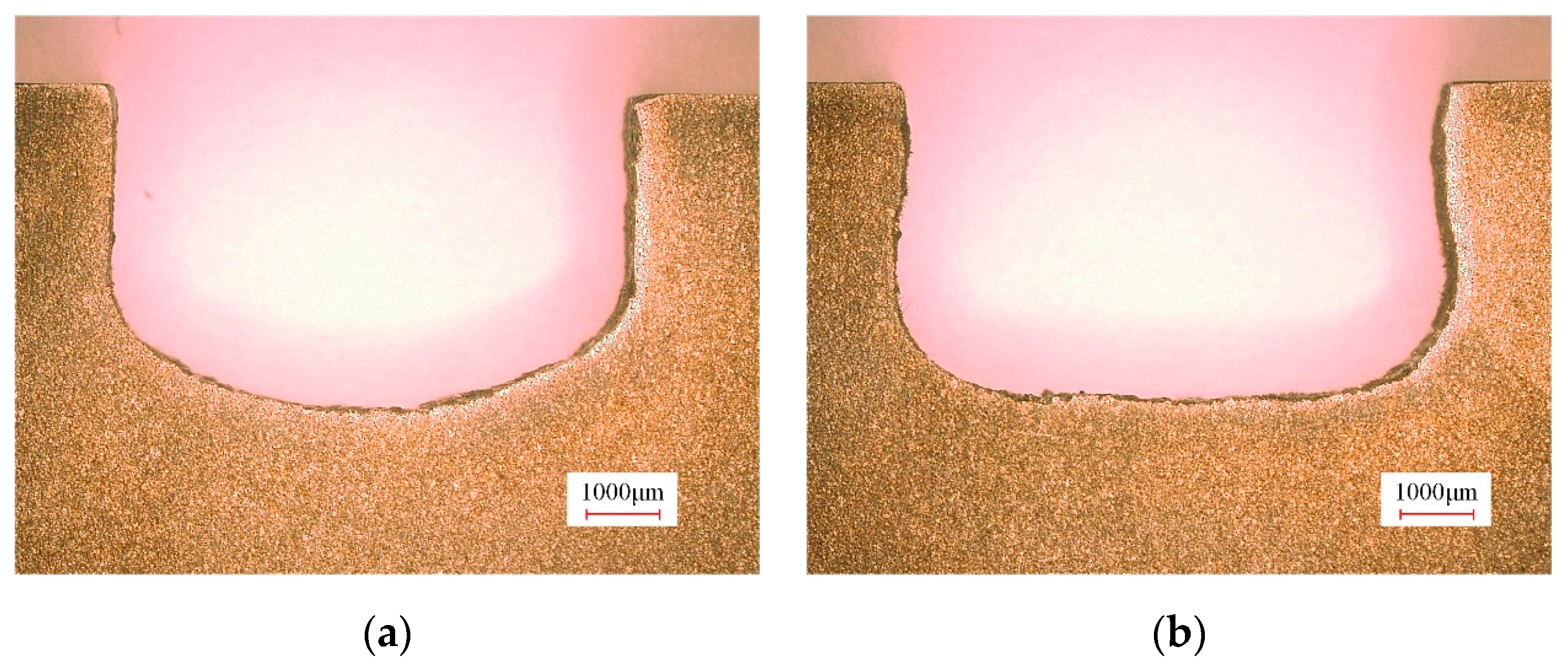
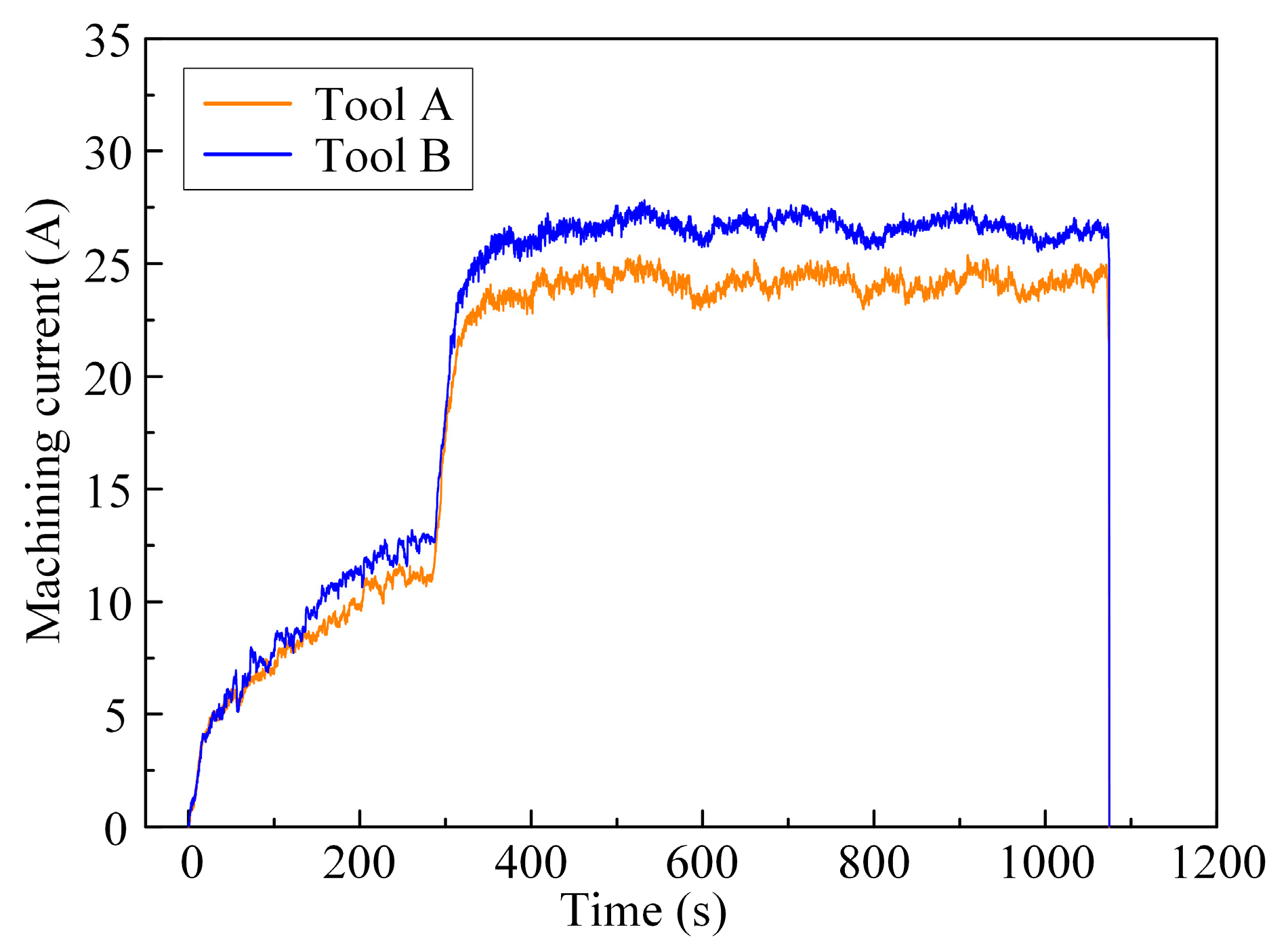
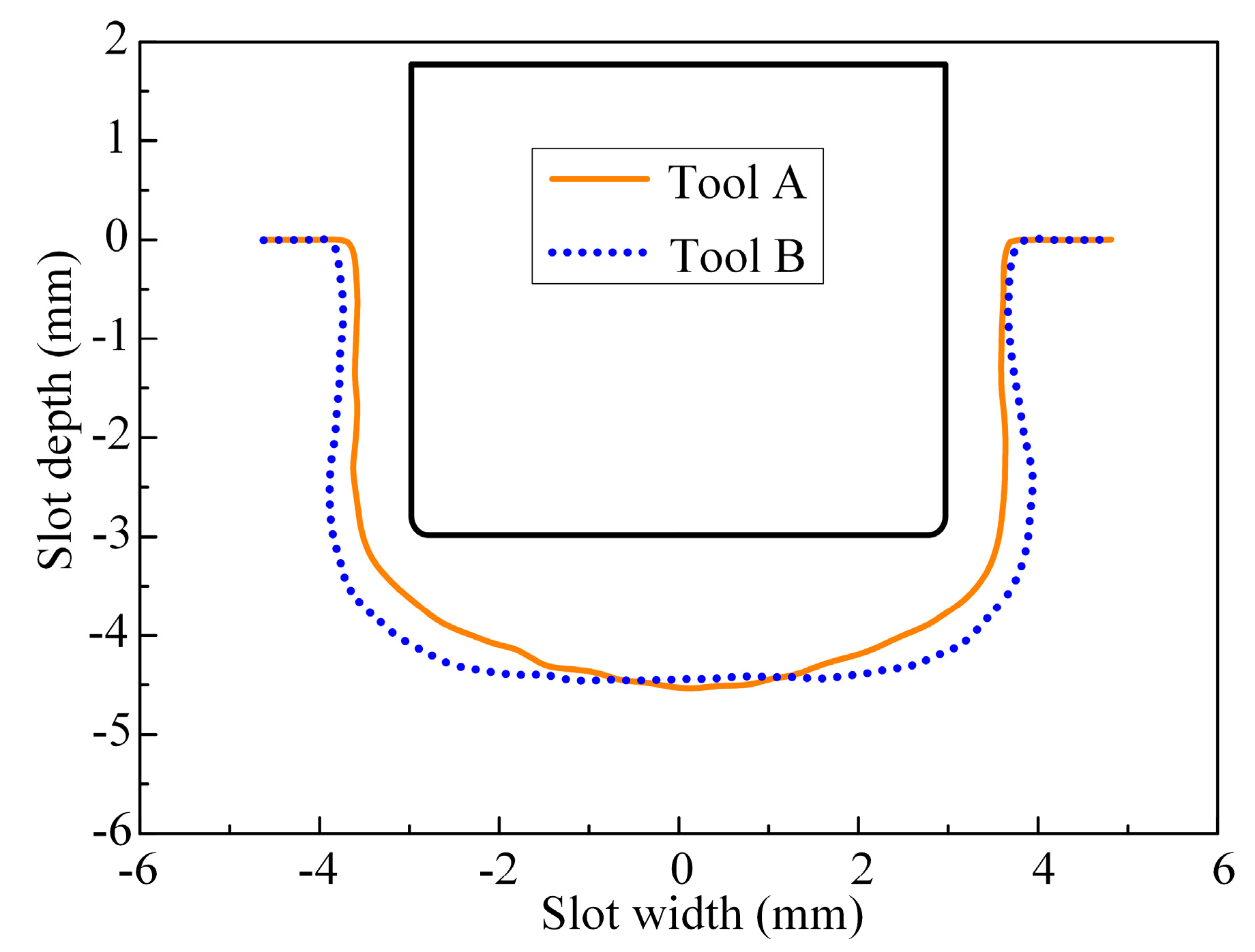
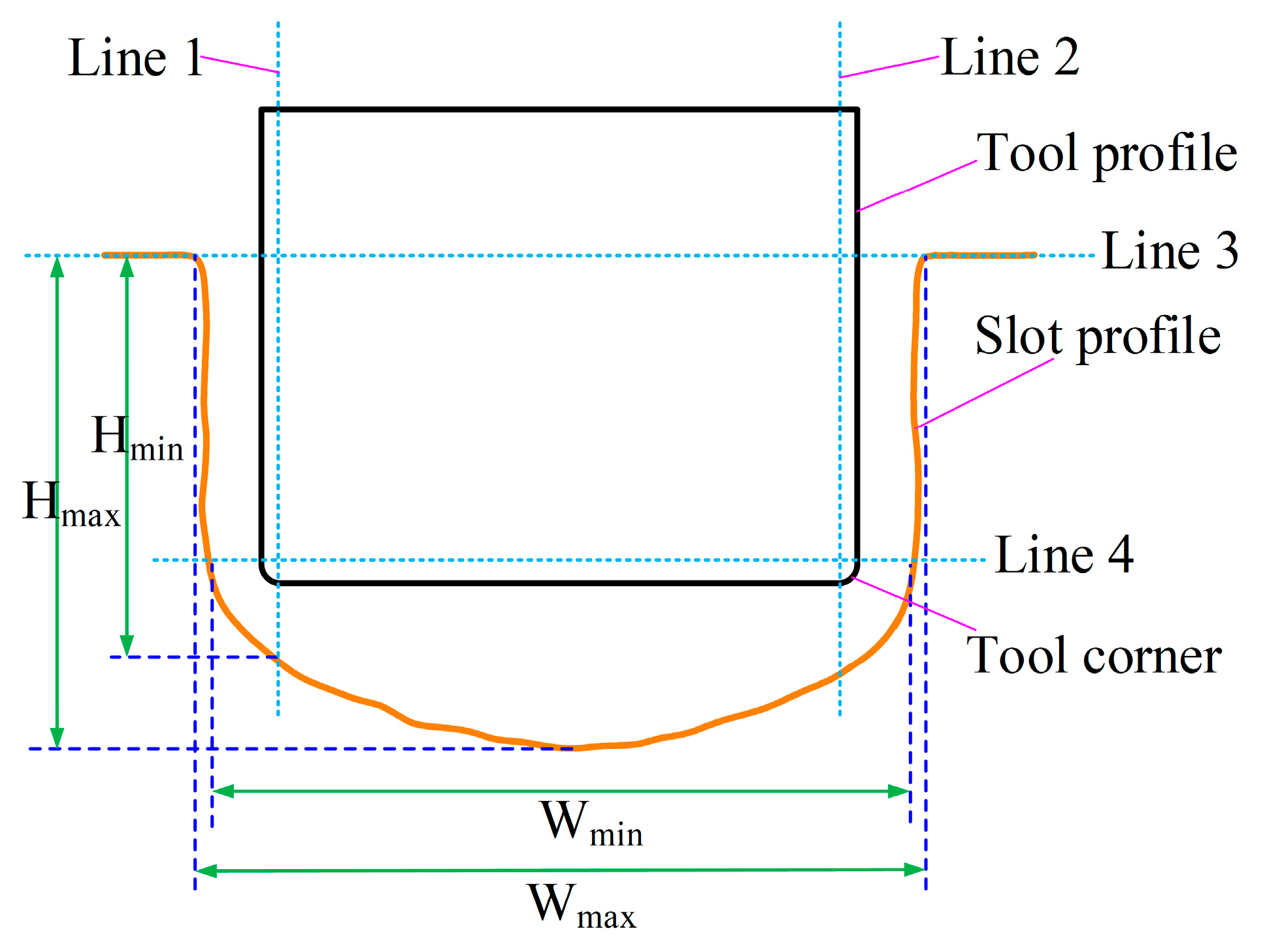
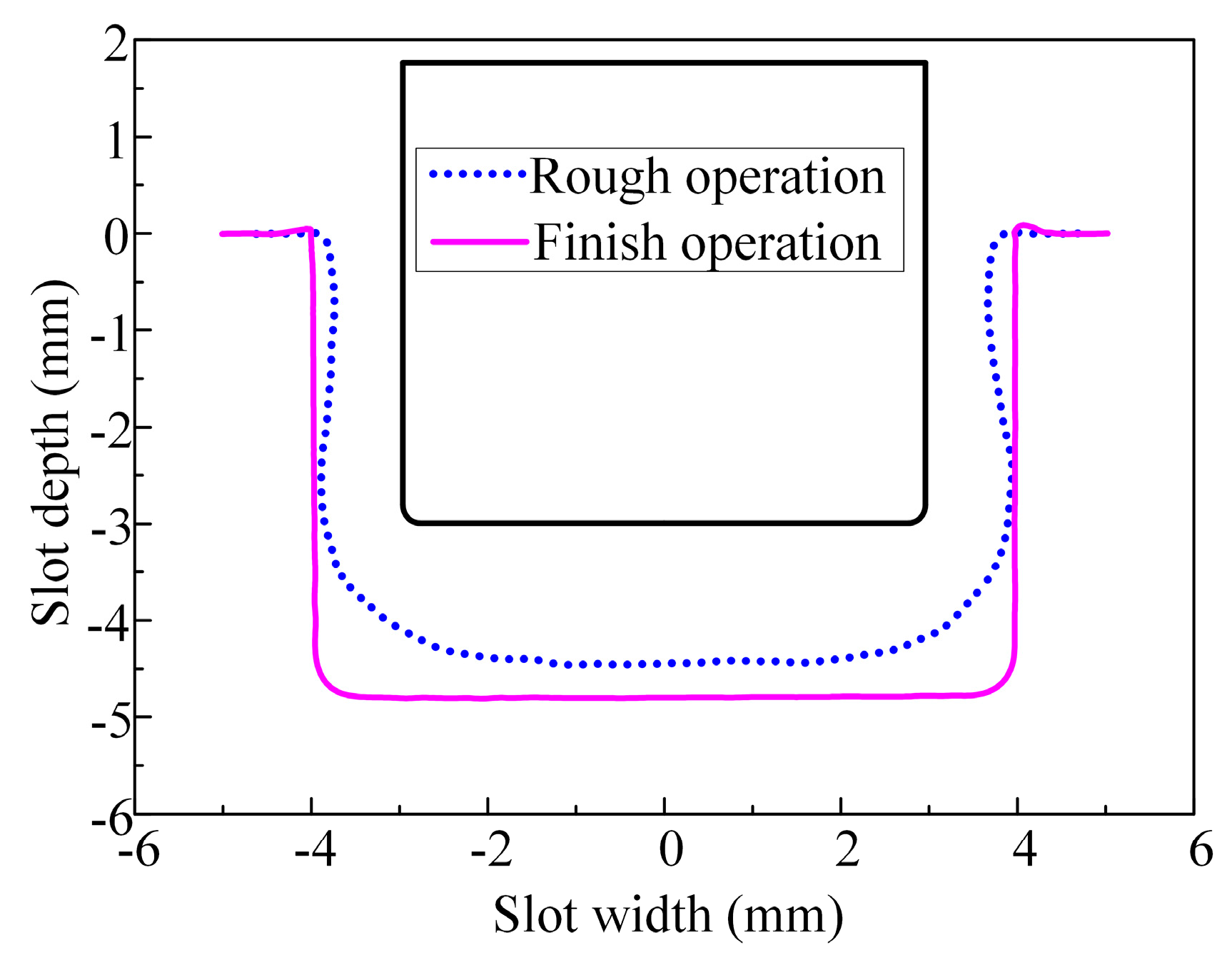
3.2.1. Rough Machining with ECMG
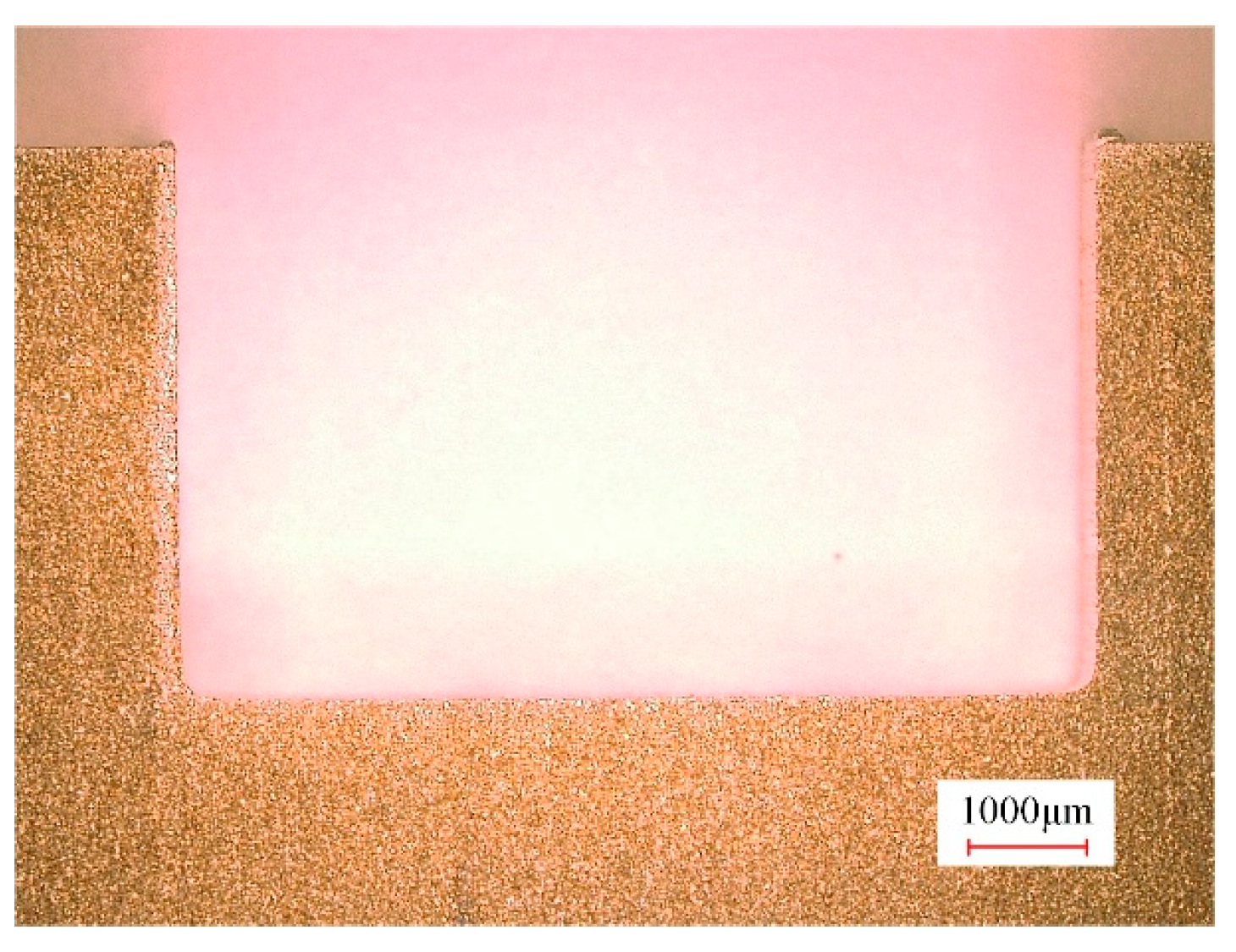
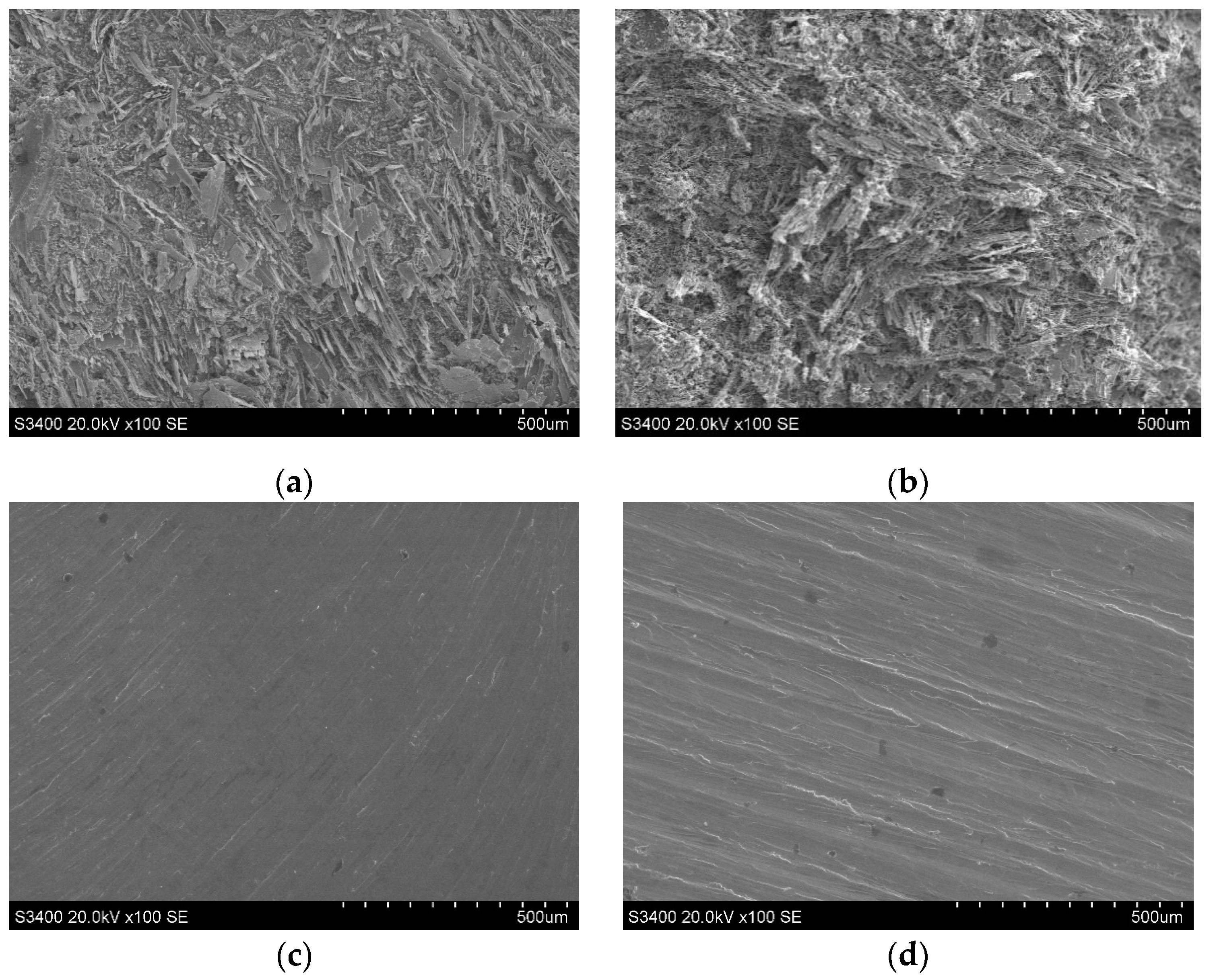
3.2.2. Finish Machining with ECMG
4. Conclusions
- The results of the dynamic flow field simulation indicate that, in comparison with the tool without bottom outlet holes, the electrolyte flow rates in both side regions of the bottom surface can be significantly increased with a reasonable layout for the bottom outlet holes, which can improve the uniformity of the flow field in the bottom surface.
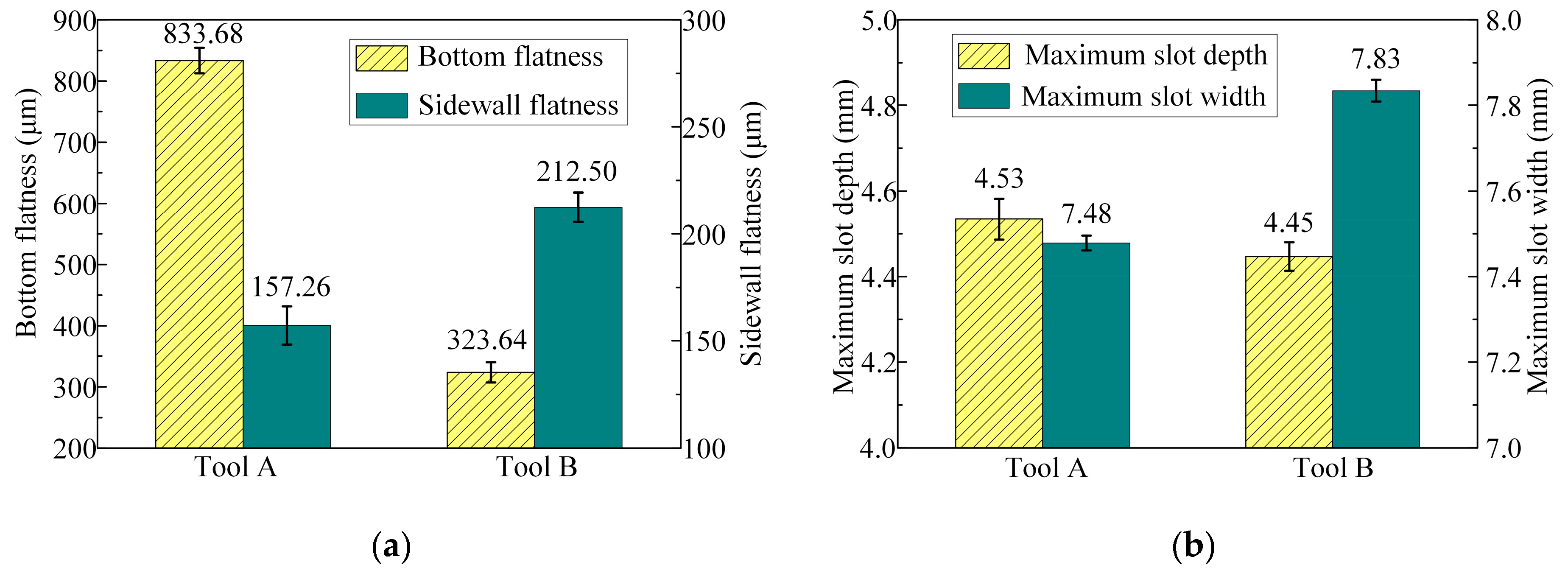
- The results of the rough machining experiment demonstrate that, compared with the tool without bottom outlet holes, a reasonable layout of bottom outlet holes significantly improves the flatness of the machined bottom surface. This optimization results in a 61.2% reduction in the bottom flatness of the slot, thereby reducing the machining allowance for finish machining.
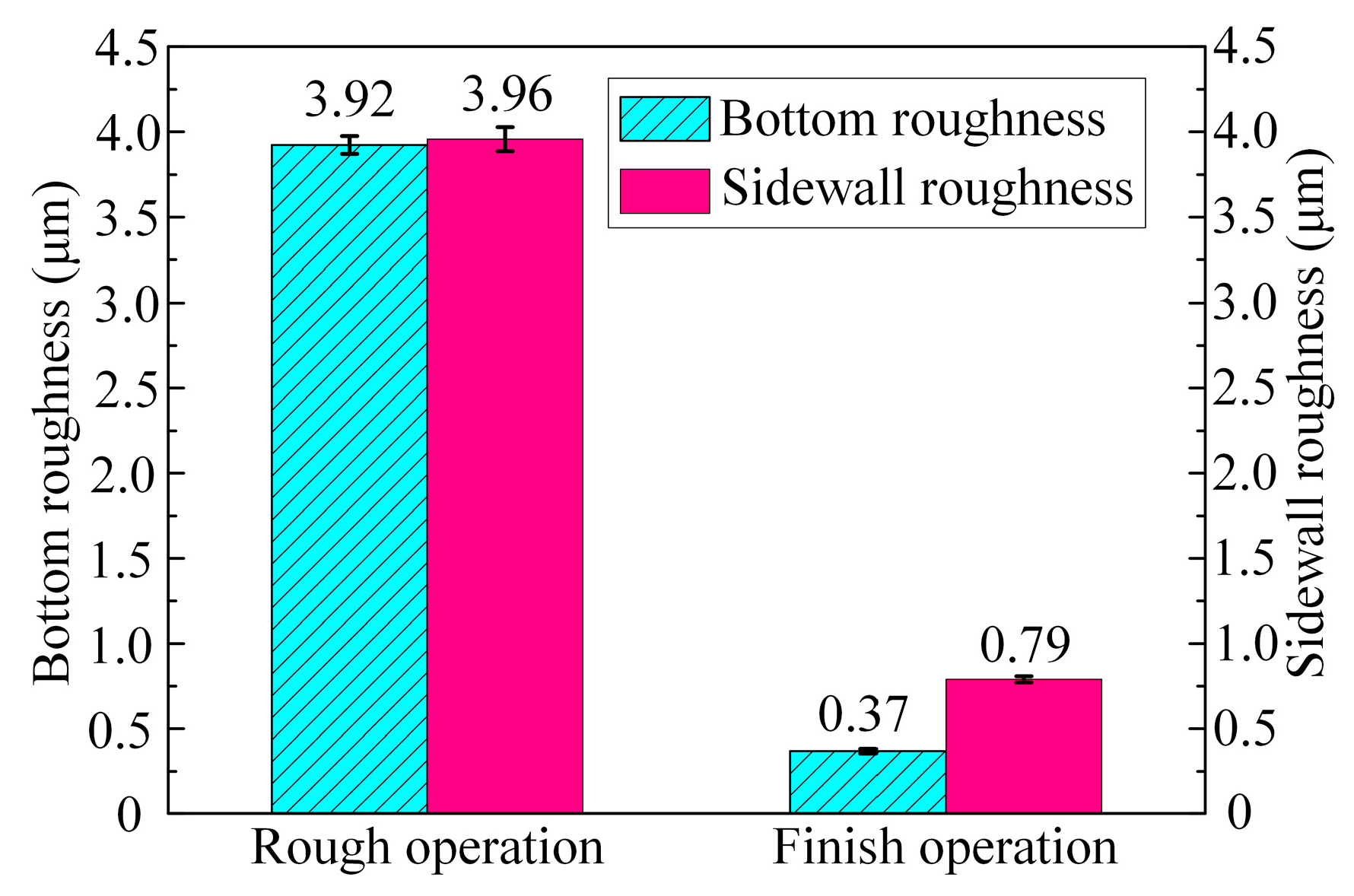
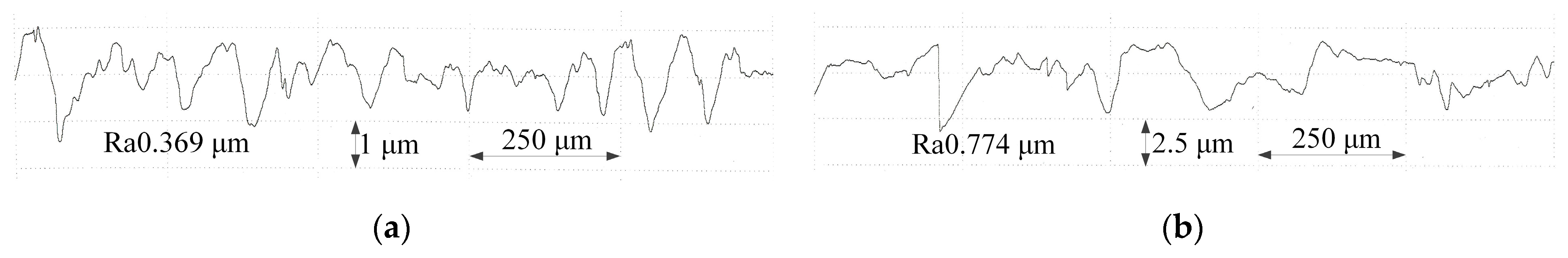
- In comparison with rough machining, both the surface flatness and quality of the slots significantly improved after the finish machining. The bottom flatness and sidewall flatness were reduced by 93.4% and 91.2%, respectively. Furthermore, the surface roughness of the bottom and sidewall surfaces was reduced by 90.6% and 80.1%, respectively.
- A slot was obtained in the (TiB+TiC)/Ti6Al4V composites via ECMG using the newly proposed tool, which has a width of 8 mm and a depth of 4.8 mm. The bottom flatness and sidewall flatness were 21.22 μm and 18.62 μm, respectively. In addition, the bottom and sidewall surface roughness were 0.37 μm and 0.79 μm, respectively.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hayat, M.D.; Singh, H.; He, Z.; Cao, P. Titanium Metal Matrix Composites: An Overview. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2019, 121, 418–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmah, P.; Gupta, K. A Review on the Machinability Enhancement of Metal Matrix Composites by Modern Machining Processes. Micromachines 2024, 15, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.; Huang, L.; Geng, L. Progress on Discontinuously Reinforced Titanium Matrix Composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 767, 1196–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, M.; Qin, J.; Zhang, D.; Lu, W. Effects of Degree of Deformation on the Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Texture of Hybrid-Reinforced Titanium Matrix Composites. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 2656–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamalizadeh, S.; Niknam, S.A.; Asgari, A.; Balazinski, M. Tool Wear Characterization in High-Speed Milling of Titanium Metal Matrix Composites. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 100, 2901–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ding, W.; Yu, T.; Yang, C. Materials Removal Mechanism in High-Speed Grinding of Particulate Reinforced Titanium Matrix Composites. Precis. Eng. 2018, 51, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hu, Y.; Gong, S.; Wang, Z. Experimental Study on the Comparison between Network Microstructure Titanium Matrix Composites and Ti6Al4V on EDM Milling. Materials 2024, 17, 2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, W.; Cao, H.; Shen, J.; Fan, S.; Duan, X. Agglomeration-Free Nanoscale TiC Reinforced Titanium Matrix Composites Achieved by in-Situ Laser Additive Manufacturing. Scr. Mater. 2020, 187, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fang, X.; Qu, N.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, J. Simultaneous Gas Electrical Discharge and Electrochemical Jet Micromachining of Titanium Alloy in High-Conductivity Salt Solution. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2023, 317, 118000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qu, N.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z. Boundary Fluid Constraints during Electrochemical Jet Machining of Large Size Emerging Titanium Alloy Aerospace Parts in Gas–Liquid Flows: Experimental and Numerical Simulation. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liu, Y.; Wang, K.; Lv, Z. Investigation on a Sustainable Composite Method of Glass Microstructures Fabrication—Electrochemical Discharge Milling and Grinding (ECDM-G). J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 387, 135788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Hu, X.; Li, H.; Yang, Y. Electrochemical Properties and Electrochemical Milling of (TiB+TiC)/TC4 Composites. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 063522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Hu, X.; Ma, X.; Lu, Y.; Li, H. Removal Mechanism and Electrochemical Milling of (TiB+TiC)/TC4 Composites. Materials 2022, 15, 7046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Li, H.; Yue, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, L.; Xu, G. Electrochemical Turning of (TiB+TiC)/TC4 Composites Using a Rectangular Cathode. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 013502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajurkar, K.P.; Sundaram, M.M.; Malshe, A.P. Review of Electrochemical and Electrodischarge Machining. Procedia CIRP 2013, 6, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, G.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Y. Precision Electrochemical Micro-Machining of Molybdenum in Neutral Salt Solution Based on Electrochemical Analysis. Micromachines 2024, 15, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Chen, X.; Saxena, K.K.; Liu, J.; Guo, Z. Jet Electrochemical Micromachining of Micro-Grooves with Conductive-Masked Porous Cathode. Micromachines 2020, 11, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.; Qu, N. Jet Electrochemical Milling of Ti-6Al-4 V Alloy with Ultra-High Current Density. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 129, 4091–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, N.; Zhang, Q.; Fang, X.; Ye, E.; Zhu, D. Experimental Investigation on Electrochemical Grinding of Inconel 718. Procedia CIRP 2015, 35, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Niu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, S.; Qu, N. Investigation of Material Removal in Inner-Jet Electrochemical Grinding of GH4169 Alloy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Qu, N.; Yue, X.; Li, H. Effect of Tool-Sidewall Outlet Hole Design on Machining Performance in Electrochemical Mill-Grinding of Inconel 718. J. Manuf. Process. 2019, 41, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Qu, N.; Niu, S.; Li, H. Improving the Machined Bottom Surface in Electrochemical Mill-Grinding by Adjusting the Electrolyte Flow Field. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2020, 276, 116413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Qu, N.; Yue, X.; Liu, G.; Li, H. Combined Rough and Finish Machining of Ti–6Al–4V Alloy by Electrochemical Mill-Grinding. Mach. Sci. Technol. 2020, 24, 621–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, H.; Hu, X.; Niu, S.; Xu, G. Simulation Analysis and Experimental Validation of Cathode Tool in Electrochemical Mill-Grinding of Ti6Al4V. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Qu, N.; Li, H. Investigation of Electrochemical Mill-Grinding Using Abrasive Tools with Bottom Insulation. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 97, 1371–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, N.; Fang, X.; Zhang, J.; Kong, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Yue, X.; Ma, Y.; Shen, Z.; Chen, J. Macro Electrochemical Milling and Its Hybrid Variants. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2023, 37, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhou, J.; Wu, S.; Kang, X.; Zhao, W. Study on Material Removal Mechanism of Photocatalytic-Assisted Electrochemical Milling-Grinding SiCp/Al. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 124, 817–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Fu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Niu, S.; Qu, N. Simulation and Experimental Investigation of Inner-Jet Electrochemical Grinding of GH4169 Alloy. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2018, 31, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Element | Ti | V | Fe | Al | H | O | N | C | TiB | TiC |
| Content (wt%) | 81.996 | 3.671 | 0.275 | 5.507 | 0.014 | 0.184 | 0.046 | 0.092 | 6.470 | 1.745 |
| Parameter | Rough Machining | Finish Machining |
|---|---|---|
| Applied voltage | 25 V | 2 V |
| Depth of cut | 3 mm | 25 μm |
| Electrolyte inlet pressure | 0.5 MPa | 0.2 MPa |
| Rotation speed | 1000 rpm | 1000 rpm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niu, S.; Huang, K.; Ming, P.; Qin, G.; Peng, Y. Electrochemical Mill Grinding of (TiB+TiC)/Ti6Al4V Composites Using Abrasive Tool with Bottom Outlet Holes. Micromachines 2024, 15, 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15121410
Niu S, Huang K, Ming P, Qin G, Peng Y. Electrochemical Mill Grinding of (TiB+TiC)/Ti6Al4V Composites Using Abrasive Tool with Bottom Outlet Holes. Micromachines. 2024; 15(12):1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15121410
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiu, Shen, Kaiqiang Huang, Pingmei Ming, Ge Qin, and Yansen Peng. 2024. "Electrochemical Mill Grinding of (TiB+TiC)/Ti6Al4V Composites Using Abrasive Tool with Bottom Outlet Holes" Micromachines 15, no. 12: 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15121410
APA StyleNiu, S., Huang, K., Ming, P., Qin, G., & Peng, Y. (2024). Electrochemical Mill Grinding of (TiB+TiC)/Ti6Al4V Composites Using Abrasive Tool with Bottom Outlet Holes. Micromachines, 15(12), 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15121410






