Phase-Optimized Multi-Step Phase Acoustic Metasurfaces for Arbitrary Multifocal Beamforming
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
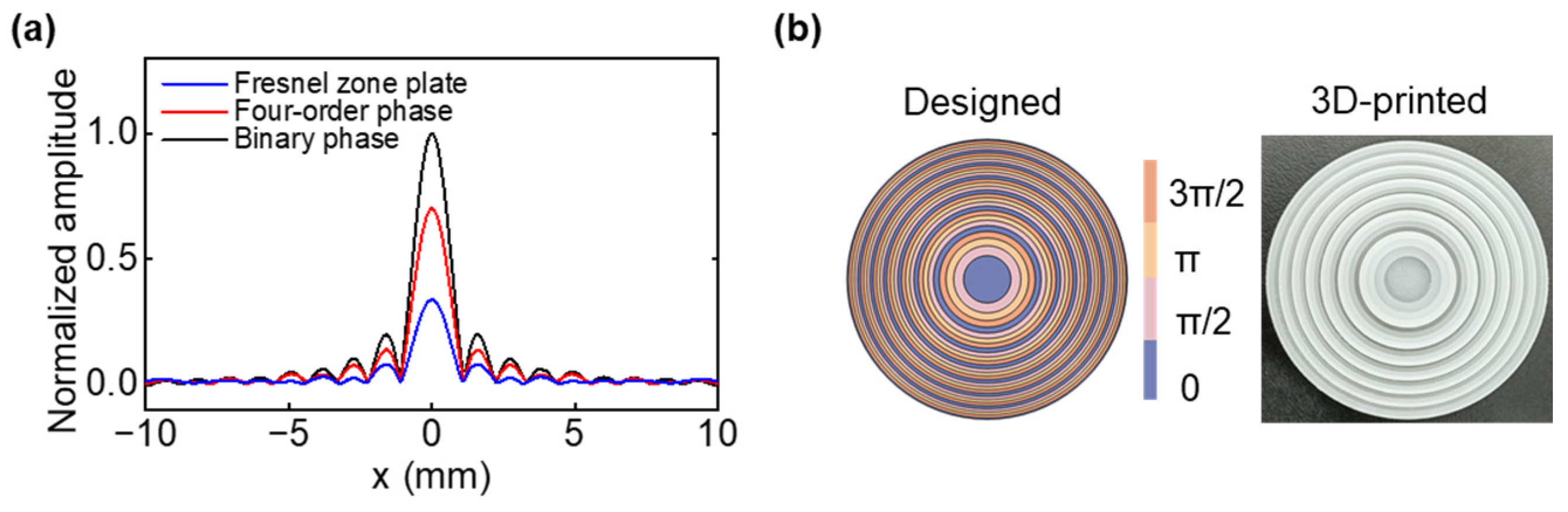
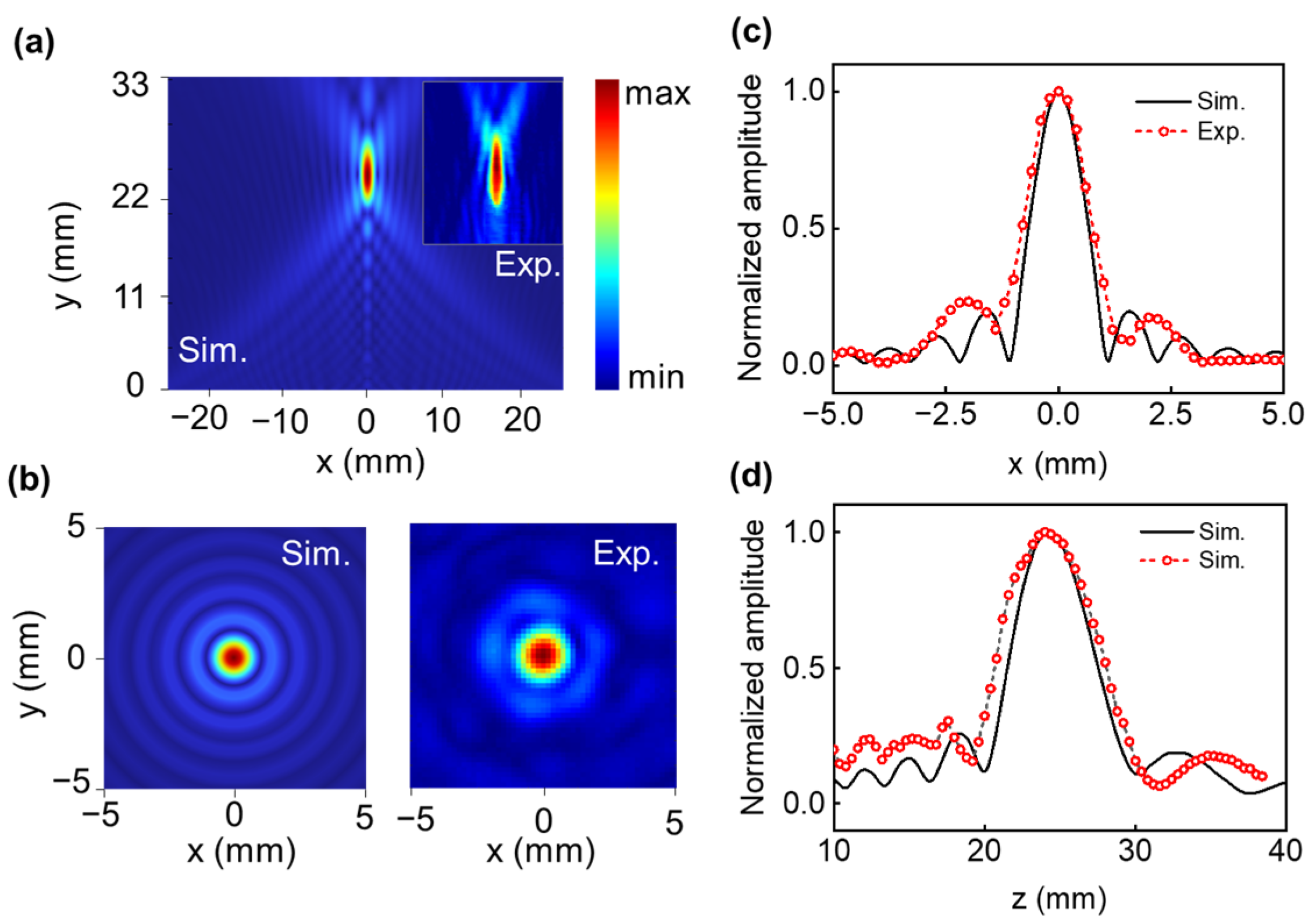
3.1. Four-Step Phase Fresnel for Single Beamforming
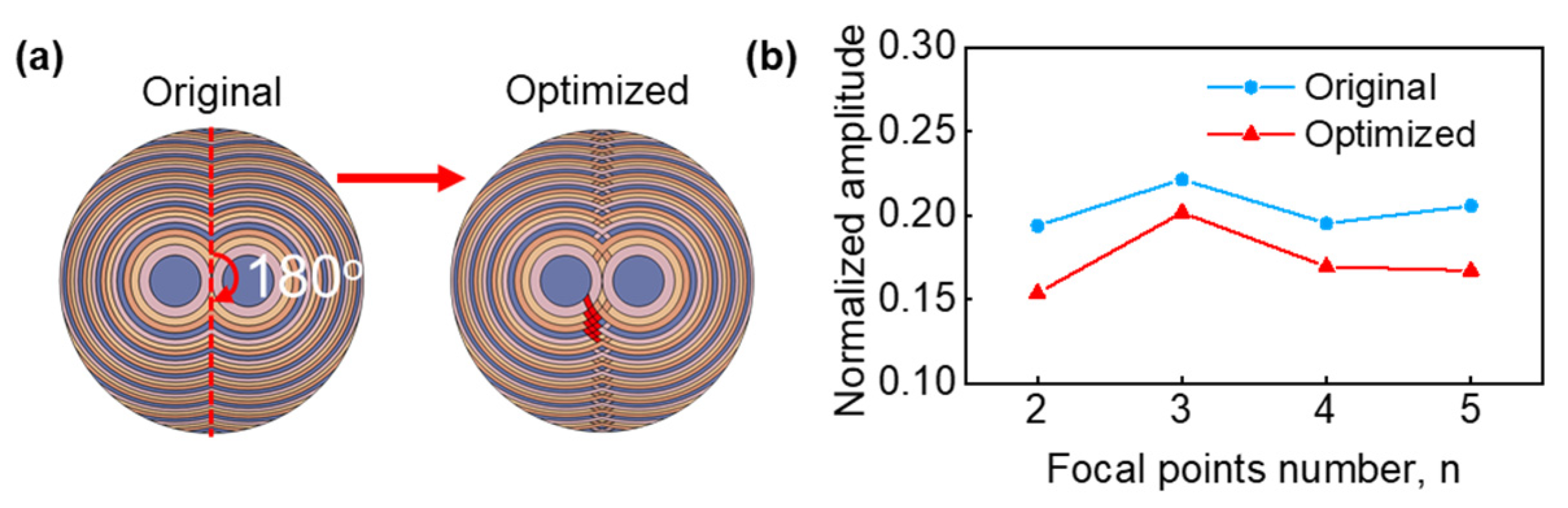
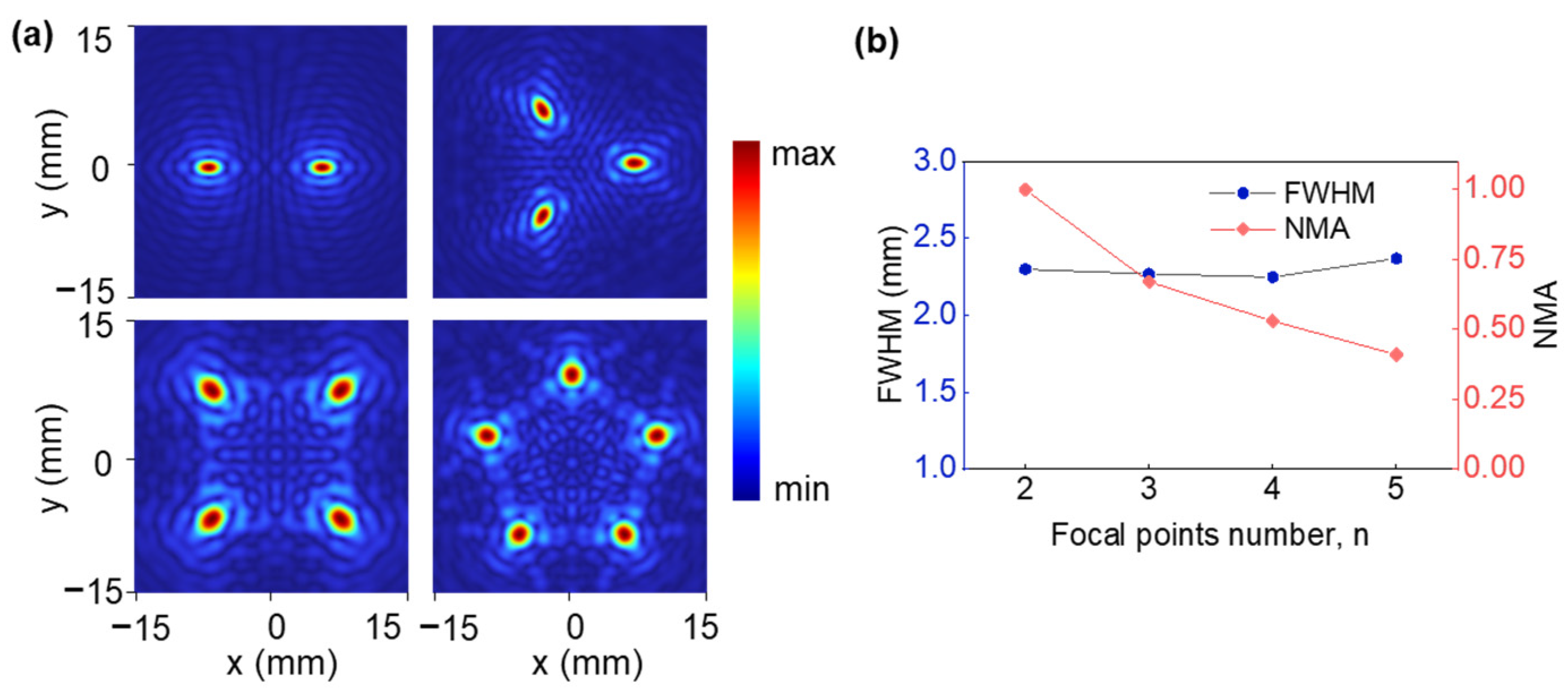
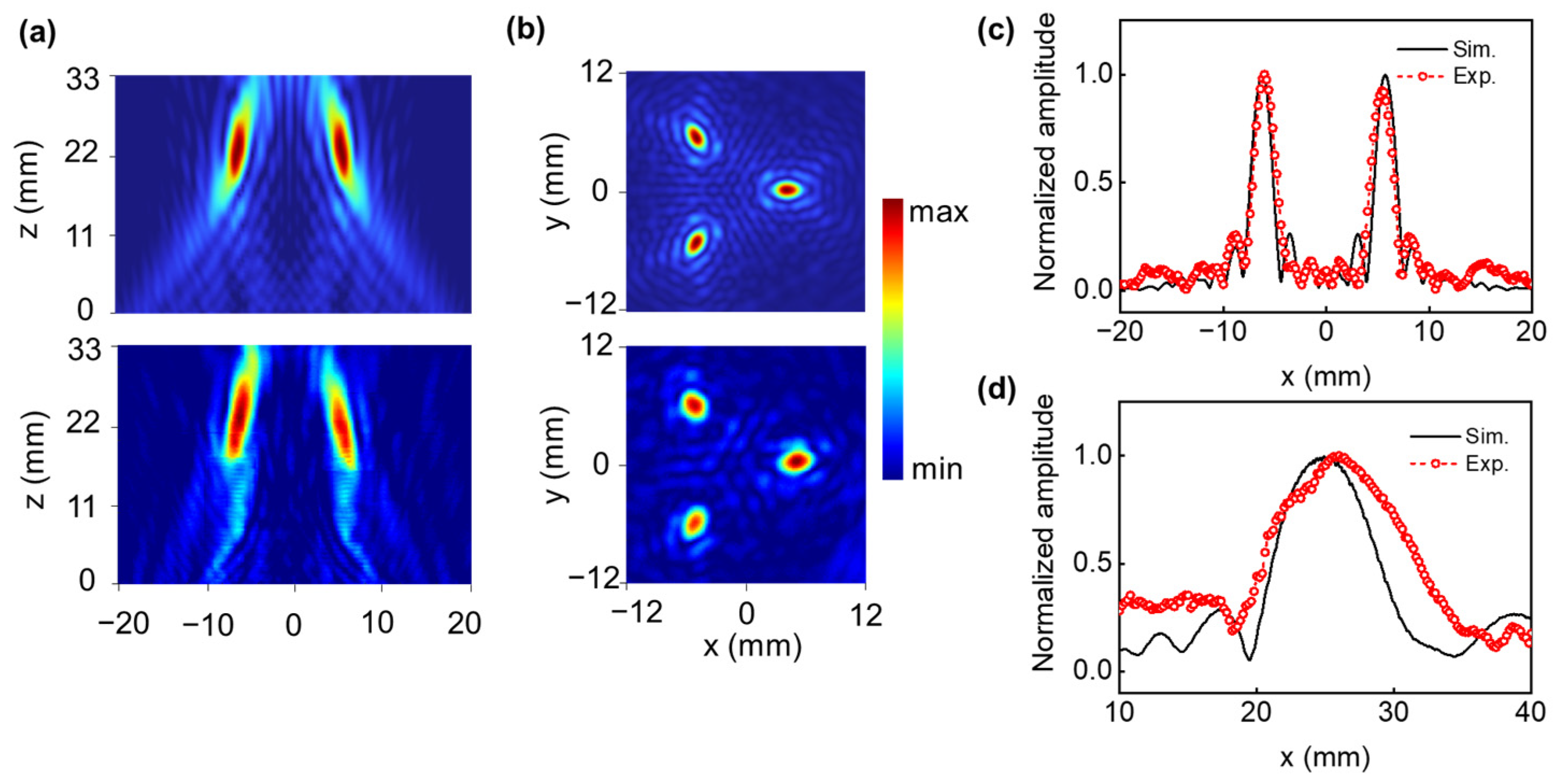
3.2. Arbitrary Multifocal Beamforming
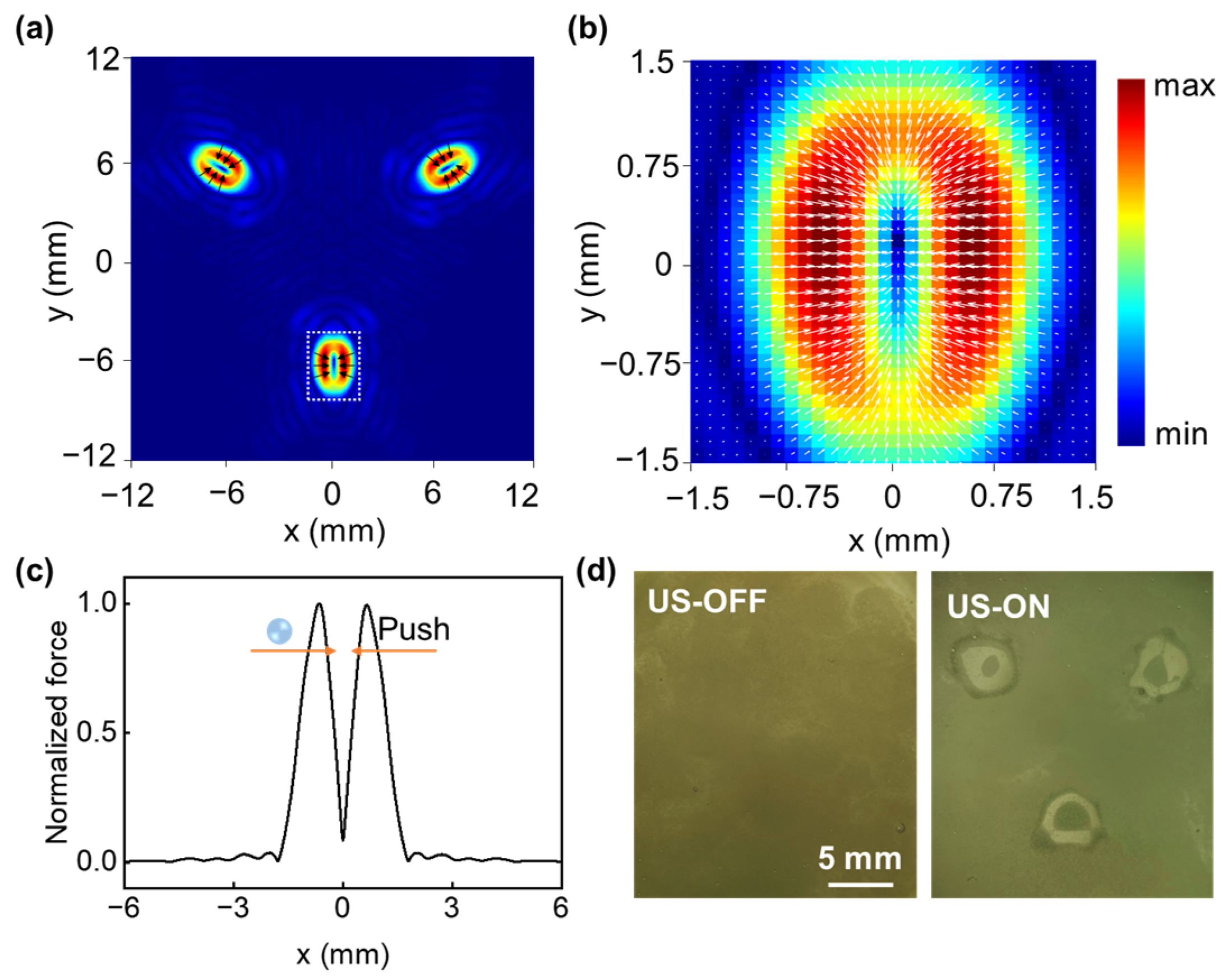
3.3. Contactless Particle Trapping Experiment
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wijlemans, J.W.; Bartels, L.W.; Deckers, R.; Ries, M.; Mali, W.P.T.M.; Moonen, C.T.W.; van den Bosch, M.A.A.J. Magnetic resonance-guided high-intensity focused ultrasound (MR-HIFU) ablation of liver tumours. Cancer Imaging 2012, 12, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, Y.H.; Kuo, S.J.; Tsai, H.D.; Chou, M.C.; Yeh, G.P. Clinical Application of High-intensity Focused Ultrasound in Cancer Therapy. J. Cancer 2016, 7, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, A.; Soteriou, D.; Xu, C.; Goswami, R.; Herbig, M.; Guck, J.; Girardo, S. Image-based cell sorting using focused travelling surface acoustic waves. Lab Chip 2023, 23, 372–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Tai, J.; Crivoi, A.; Li, J.; Cummer, S.; Fan, Z. Self-stabilizing three-dimensional particle manipulation via a single-transducer acoustic tweezer. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2023, 122, 094106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, W.; Fan, C.; Ho, Y.; Lin, C.; Yeh, C. Tornado-inspired acoustic vortex tweezer for trapping and manipulating microbubbles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2023188118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Li, P.; Ding, N.; Pu, S.; Guo, G.; Li, Y.; Ma, Q. Performance improvement of focused acoustic-vortex tweezers constructed by a hyperboloidal acoustic lens and a circular array. Appl. Acoust. 2022, 200, 109053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Xian, Q.; Hou, X.; Wong, K.; Zhu, T.; Chen, Z.; He, D.; Kala, S.; Murugappan, S.; Jing, J.; et al. The mechanosensitive ion channel Piezo1 contributes to ultrasound neuromodulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2300291120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurup, C.; Kamimura, H.A.S.; Konofagou, E.E. High-Resolution Focused Ultrasound Neuromodulation Induces Limb-Specific Motor Responses in Mice in Vivo. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2021, 47, 998–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, E.; Kim, H.; Sim, S.H.; Shin, S.; Shin, M. Principles and Applications of Ultrasonic-Based Nondestructive Methods for Self-Healing in Cementitious Materials. Materials 2017, 10, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, C.; He, J.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Jiang, X.; Ta, D. Nondestructive Evaluation of Special Defects Based on Ultrasound Metasurface. Front. Mater. 2021, 8, 802001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhao, J.; Fei, C.; Li, D.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Z.; Guo, R.; Lou, L.; Feng, W.; Yang, Y. Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm-Based Design Method for Ultrasonic Transducers. Micromachines 2020, 11, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, T.; Matsuok, T.; Yamazaki, M.; Qian, X.; Lu, G.; Safari, A.; Zhu, J.; Shung, K.K.; et al. Eco-friendly highly sensitive transducers based on a new KNN-NTK-FM lead-free piezoelectric ceramic for high-frequency biomedical ultrasonic imaging applications. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 66, 1580–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Li, J.; Niu, G.; Yuan, J.; Xue, K.; Xia, M.; Pan, W.; Yang, X.; Zhu, B.; Tang, J. Lead halide perovskite for efficient optoacoustic conversion and application toward high-resolution ultrasound imaging. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Shen, C.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Suo, D.; Popa, B.; Jing, Y.; Cummer, S.A. Acoustic holographic rendering with two-dimensional metamaterial-based passive phased array. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, B.; Cheng, H.; Tian, J.; Chen, S. Transmission-reflection-integrated multifunctional continuously tunable metasurfaces for decoupled modulation of acoustic waves. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2022, 17, 044027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xu, L.; Hao, Y.; Chen, H. Binary acoustic metasurfaces for dynamic focusing of transcranial ultrasound. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 984953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xu, L.; Jing, Y.; Chen, H. Airy-Beam-Enabled Binary Acoustic Metasurfaces for Underwater Ultrasound-Beam Manipulation. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2022, 18, 024070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Lam, K.H.; Zheng, H.; Qiu, W.; Shung, K.K. Piezoelectric single crystal ultrasonic transducers for biomedical applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2014, 66, 87–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Fei, C.; Chen, D.; Zhang, S.; Li, D.; Feng, W.; Yang, Y.; Chai, C. Design and fabrication of non-periodic 1–3 composite structure for ultrasonic transducer application. Compos. Struct. 2022, 285, 115249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ma, T.; Li, S.N.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, J.Q.; Liu, Y.F.; Zhuang, J.W.; Li, Y.C.; Du, X.M.; Niu, L.L.; et al. Self-navigated 3D acoustic tweezers in complex media based on time reversal. Research 2021, 2021, 9781394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzo, A.; Seah, S.A.; Drinkwater, B.W.; Sahoo, D.R.; Long, B.; Subramanian, S. Holographic acoustic elements for manipulation of levitated objects. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.G.; Kim, H.H.; Yoon, C.; Shung, K.K. A One-Sided Acoustic Trap for Cell Immobilization using 30-MHz Array Transducer. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2019, 67, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, P.; Xiao, B.; Wu, Y. Flat acoustic lens by acoustic grating with curled slits. Phys. Lett. A 2014, 378, 3389–3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assouar, B.; Liang, B.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Cheng, J.C.; Jing, Y. Acoustic metasurfaces. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2018, 3, 460–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wu, G.; Tao, M. Inverse design of broadband acoustic metasurfaces for reflective wavefront modulation through the topology optimization method. Appl. Acoust. 2023, 204, 109247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Fan, X.; Liang, B.; Cheng, J.; Jing, Y. Ultrathin Acoustic Metasurface-Based Schroeder Diffuser. Phys. Rev. X 2017, 7, 021034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Qiu, C.; Ke, M.; Lu, J.; Ye, Y.; Liu, Z. Anomalous refraction of airborne sound through ultrathin metasurfaces. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molerón, M.; Serra-Garcia, M.; Daraio, C. Acoustic Fresnel lenses with extraordinary transmission. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 114109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, W.; Chen, H.; Konneker, A.; Popa, B.; Cummer, S.A. Wavefront modulation and subwavelength diffractive acoustics with an acoustic metasurface. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Kim, E.S. Simple sacrificial-layer-free microfabrication processes for air-cavity Fresnel acoustic lenses (ACFALs) with improved focusing performance. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2022, 8, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Li, M.; Fu, C.; Ren, X.; Xu, Z.; Liu, X. Precise micro-particle and bubble manipulation by tunable ultrasonic bottle beams. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 75, 105602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, N.; Romero-García, V.; Picó, R.; Garcia-Raffi, L.M.; Staliunas, K. Nonlinear focusing of ultrasonic waves by an axisymmetric diffraction grating embedded in water. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 204103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Li, Y.; Ta, D.; Wang, W. Ultrasonic sharp autofocusing with acoustic metasurface. Phys. Rev. B 2020, 102, 064308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, T.A.; Pan, M.C.; Wu, T.H.; Le, T.L. Using SiO2 Hard Mask for Fabrication of Micro Fresnel Focusing Lens for Ultrasonic Ejectors. Key Eng. Mater. 2020, 863, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Shung, K.K. Effect of ultrasonic attenuation on the feasibility of acoustic tweezers. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2006, 32, 1575–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, J.; Wei, X.; Fei, C.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Lou, L.; Quan, Y.; Yang, Y. Phase-Optimized Multi-Step Phase Acoustic Metasurfaces for Arbitrary Multifocal Beamforming. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14061176
Zhao J, Wei X, Fei C, Li Y, Li Z, Lou L, Quan Y, Yang Y. Phase-Optimized Multi-Step Phase Acoustic Metasurfaces for Arbitrary Multifocal Beamforming. Micromachines. 2023; 14(6):1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14061176
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Jianxin, Xiongwei Wei, Chunlong Fei, Yi Li, Zhaoxi Li, Lifei Lou, Yi Quan, and Yintang Yang. 2023. "Phase-Optimized Multi-Step Phase Acoustic Metasurfaces for Arbitrary Multifocal Beamforming" Micromachines 14, no. 6: 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14061176
APA StyleZhao, J., Wei, X., Fei, C., Li, Y., Li, Z., Lou, L., Quan, Y., & Yang, Y. (2023). Phase-Optimized Multi-Step Phase Acoustic Metasurfaces for Arbitrary Multifocal Beamforming. Micromachines, 14(6), 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14061176







