A Novel Non-Isolated High-Gain Non-Inverting Interleaved DC–DC Converter
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- The proposed converter topology is operated utilizing two distinct duty cycle ratios to achieve higher voltage gain.
- (2)
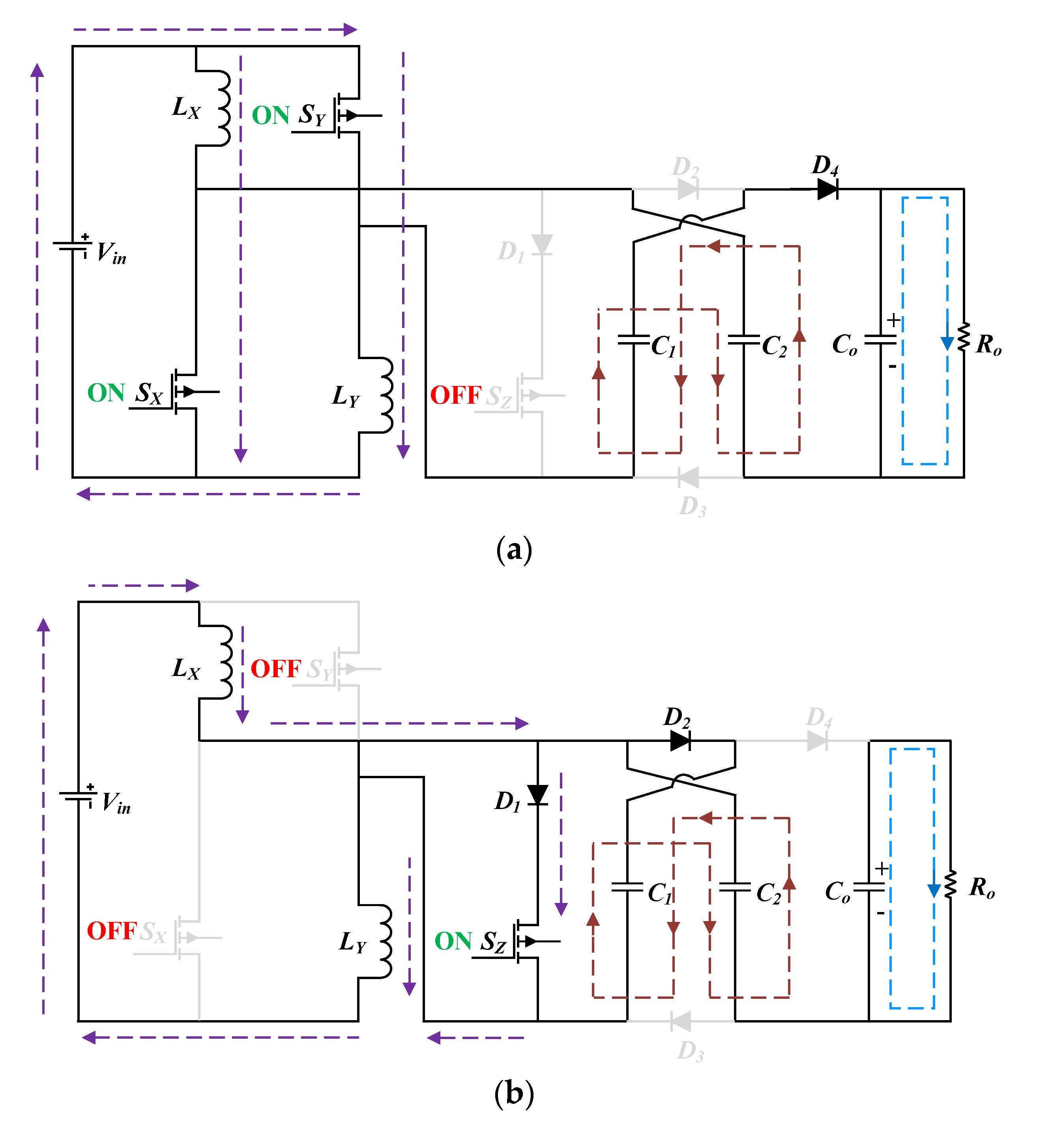
- The energy stored in the inductor is delivered to the voltage multiplier and supplied to the load.
- (3)
- (4)
- Voltage stress is significantly lower across the diodes and the switches as compared to the voltage output percentage.
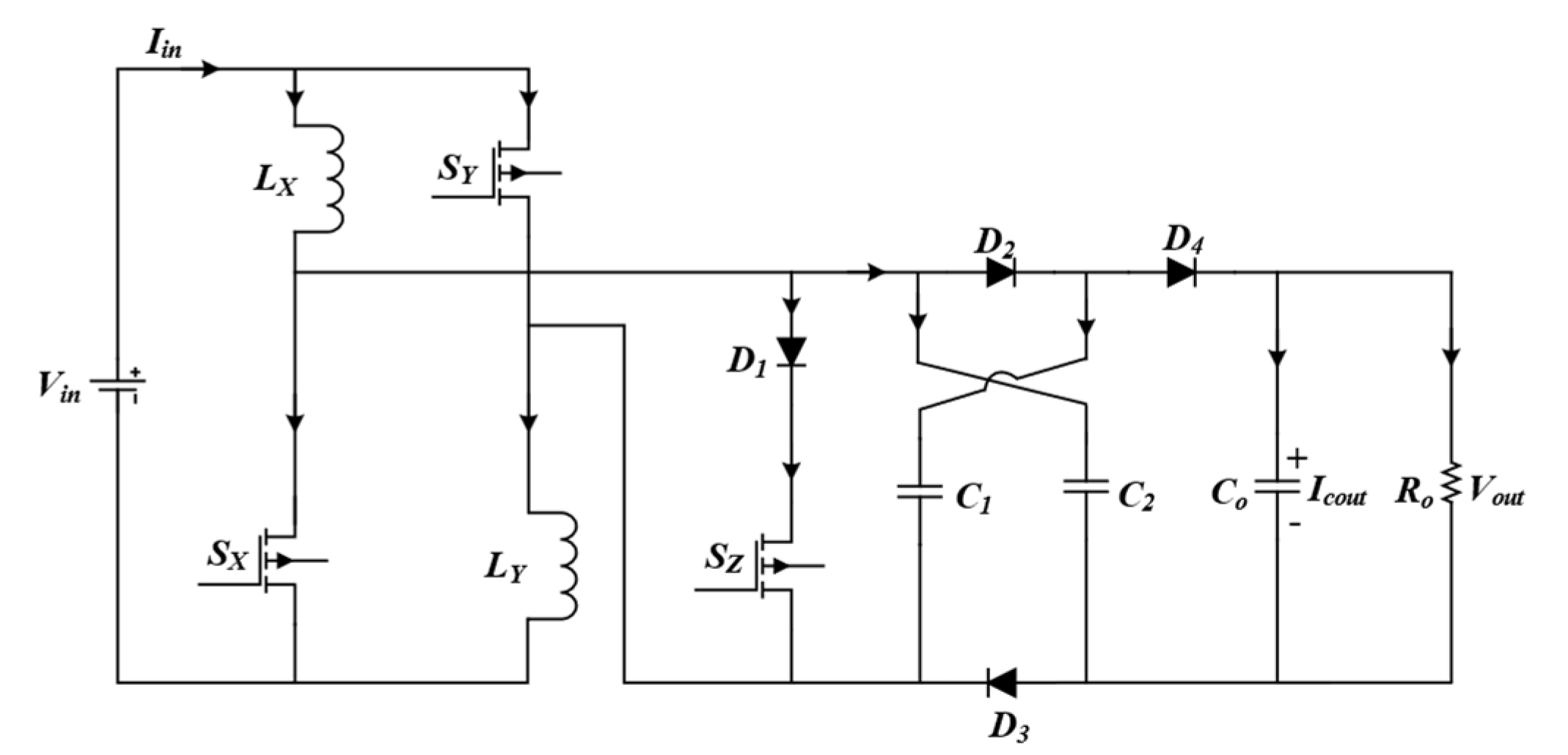
2. Circuit Configuration
3. Proposed Converter’s Steady-State Analysis
3.1. Working in Continuous Conduction Mode
3.2. Switching Stress
3.3. Diode Voltage Stress
3.4. Component Selection
3.4.1. For Inductor
3.4.2. For Capacitor
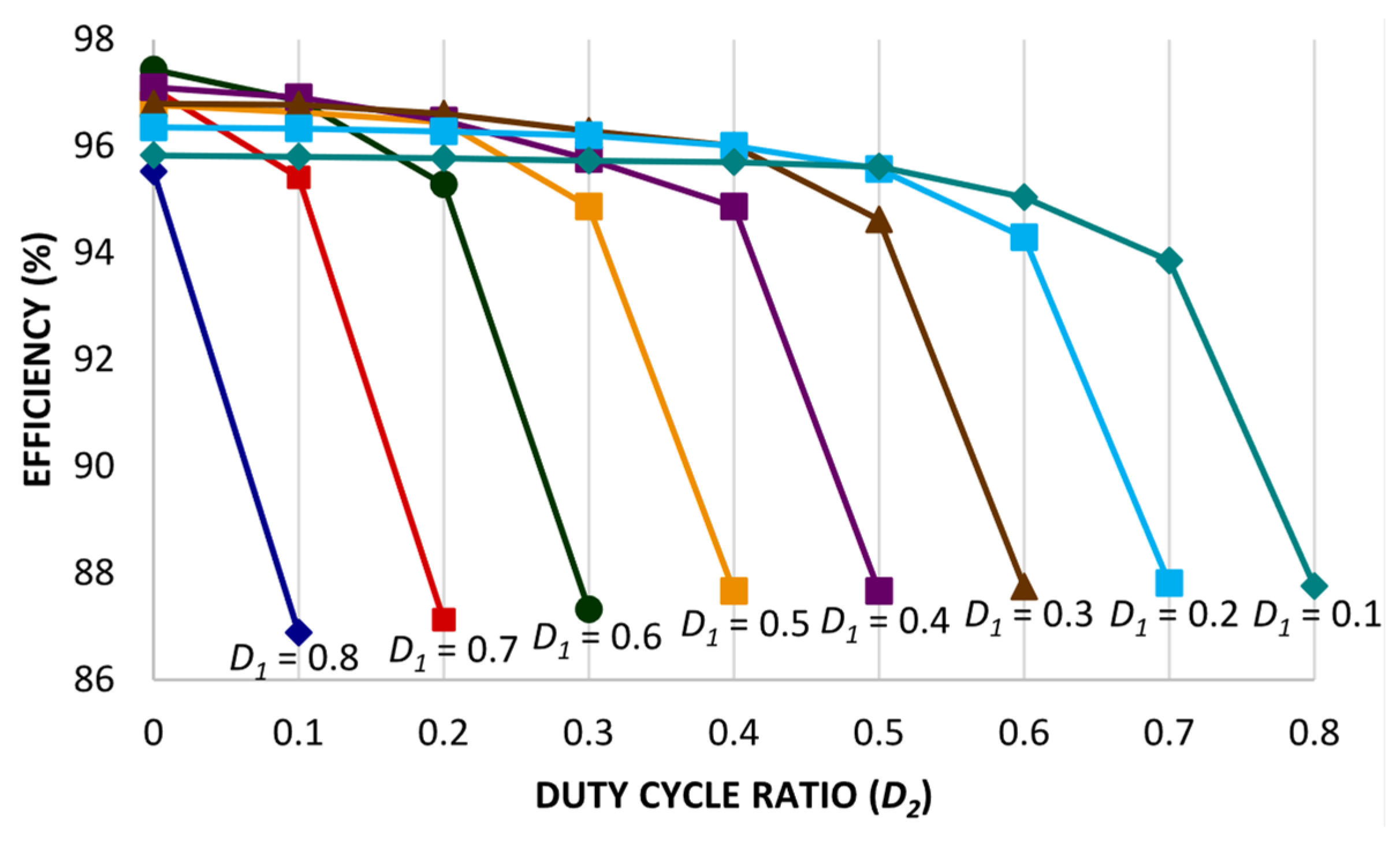
4. Efficiency Evaluation
5. Comparative Performance Analysis
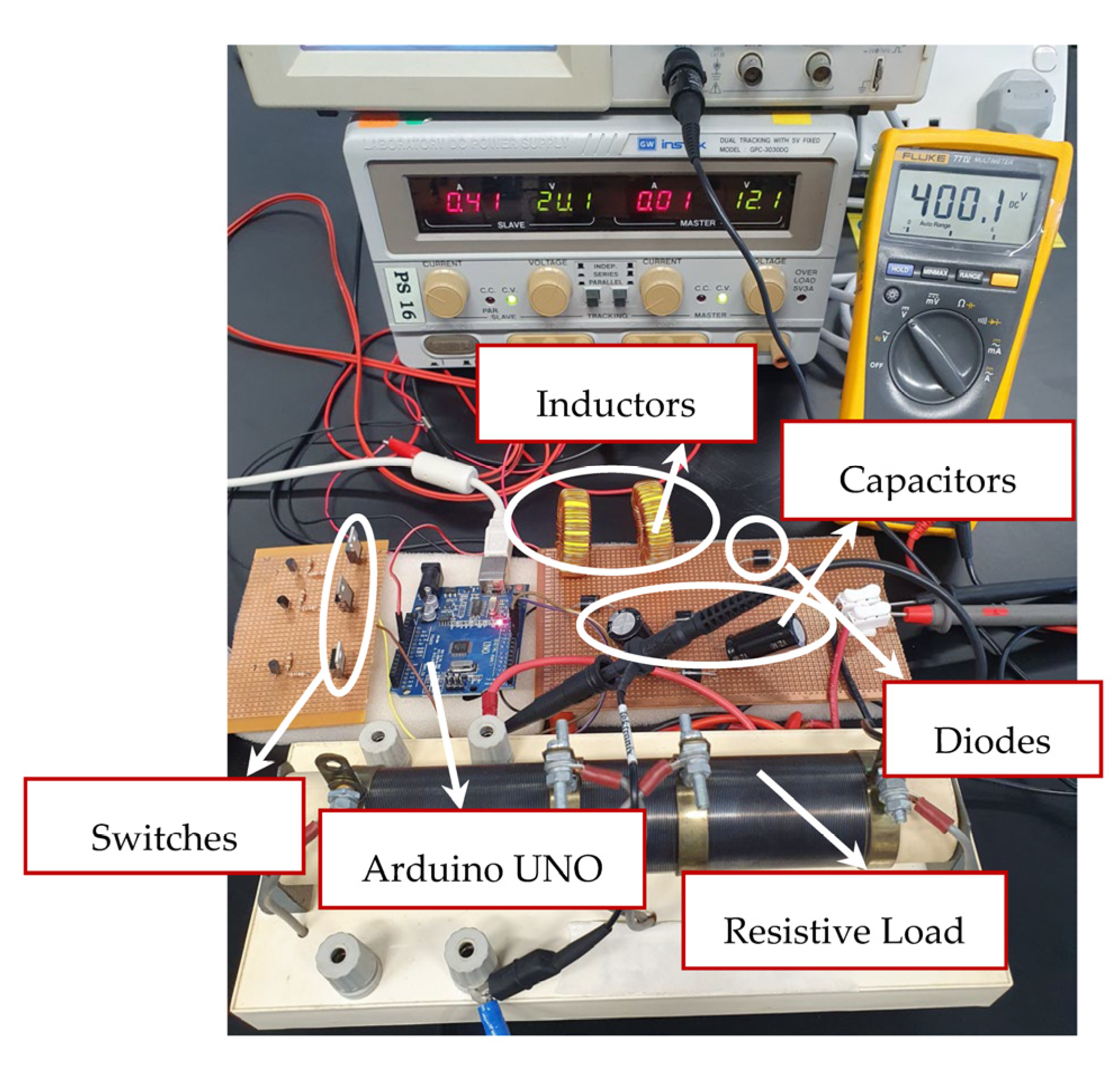
6. Experimental Results
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Vin | Input voltage | rD2 | Parasitic resistance of diode D2 |
| Vout | Output voltage | rD3 | Parasitic resistance of diode D3 |
| Iin | Input current | rD4 | Parasitic resistance of diode D4 |
| Icout | Output capacitor current | VLX | Inductor voltage LX |
| LX | Inductor LX | VLY | Inductor voltage LY |
| LY | Inductor LY | ILX | Inductor current LX |
| C1 | Capacitor C1 | ILY | Inductor current LY |
| C2 | Capacitor C2 | VGSX | Switching voltage for switch SX |
| Co | Output Capacitor Co | VGSY | Switching voltage for switch SY |
| SX | Switch SX | VGSZ | Switching voltage for switch SZ |
| SY | Switch SY | VDSX | Voltage stress at switch SX |
| SZ | Switch SZ | VDSY | Voltage stress at switch SY |
| D1 | Diode 1 | VDSZ | Voltage stress at switch SZ |
| D2 | Diode 2 | VD1 | Voltage stress at diode D1 |
| D3 | Diode 3 | VD2 | Voltage stress at diode D2 |
| D4 | Diode 4 | VD3 | Voltage stress at diode D3 |
| Ro | Load resistance | VD4 | Voltage stress at diode D4 |
| fsw | Switching frequency | IC1 | Capacitor current C1 |
| rLX | Parasitic resistance of inductor LX | IC2 | Capacitor current C2 |
| rLY | Parasitic resistance of inductor LY | Pin | Input power |
| rSX | Parasitic resistance of switch SX | Pout | Output power |
| rSY | Parasitic resistance of switch SY | Psw | Switching power losses |
| rSZ | Parasitic resistance of switch SZ | Prc | Capacitor power losses |
| rD1 | Parasitic resistance of diode D1 | η | Efficiency |
References
- Taghvaee, M.H.; Radzi, M.A.M.; Moosavain, S.M.; Hizam, H.; Marhaban, M.H. A Current and Future Study on Non-Isolated DC-DC Converters for Photovoltaic Applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 17, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A. Advancements in Power Electronics and Drives in Interface with Growing Renewable Energy Resources. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 1816–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipu, M.S.H.; Ansari, S.; Miah, M.S.; Hasan, K.; Meraj, S.T.; Faisal, M.; Jamal, T.; Ali, S.H.M.; Hussain, A.; Muttaqi, K.M.; et al. A Review of Controllers and Optimizations Based Scheduling Operation for Battery Energy Storage System towards Decarbonization in Microgrid: Challenges and Future Directions. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 360, 132188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahi, R.; Mishra, S.K.; Srivastava, S.C.; Srivastava, A.K.; Schulz, N.N. Grid Integration of Small-Scale Photovoltaic Systems in Secondary Distribution Network—A Review. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 3178–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmani, K.; Haddad, A.; Lemenand, T.; Castanier, B.; Ramadan, M. An Investigation on Maximum Power Extraction Algorithms from PV Systems with Corresponding DC-DC Converters. Energy 2021, 224, 120092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foray, E.; Martin, C.; Allard, B.; Bevilacqua, P. Design of a High-to-Low Voltage, Low-Power, Isolated DC/DC Converter for EV Applications. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2022, 10, 6929–6937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, F.; Yahaya, N.Z.; Meraj, S.T.; Kannan, R.; Singh, B.S.M.; Ibrahim, O. Multi-Input Multi-Output DC-DC Converter Network for Hybrid Renewable Energy Applications. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Innovation and Intelligence for Informatics, Computing and Technologies (3ICT), Sakheer, Bahrain, 20–21 December 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, A.; Amir, A.; Che, H.S.; Elkhateb, A.; Rahim, N.A. Comparative Analysis of High Voltage Gain DC-DC Converter Topologies for Photovoltaic Systems. Renew. Energy 2019, 136, 1147–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorji, S.A.; Sahebi, H.G.; Ektesabi, M.; Rad, A.B. Topologies and Control Schemes of Bidirectional DC–DC Power Converters: An Overview. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 117997–118019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroti, P.K.; Al-Ammari, R.; Bhaskar, M.S.; Meraj, M.; Iqbal, A.; Padmanaban, S.; Rahman, S. New Tri-Switching State Non-Isolated High Gain DC-DC Boost Converter for Microgrid Application. IET Power Electron. 2019, 12, 2741–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhurayyis, I.; Elkhateb, A.; Morrow, J. Isolated and Nonisolated DC-to-DC Converters for Medium-Voltage DC Networks: A Review. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2021, 9, 7486–7500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummara, V.G.R.; Zeb, K.; Muthusamy, A.; Krishna, T.N.V.; Kumar, S.V.S.V.P.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, M.S.; Cho, H.G.; Kim, H.J. A Comprehensive Review of DC–DC Converter Topologies and Modulation Strategies with Recent Advances in Solar Photovoltaic Systems. Electronics 2020, 9, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Haneda, R.; Akagi, H. Design and Performance of the 850-V 100-KW 16-KHz Bidirectional Isolated DC–DC Converter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 10013–10025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanthi, T.; Prabha, S.U.; Sundaramoorthy, K. Non-Isolated n-Stage High Step-up DC-DC Converter for Low Voltage DC Source Integration. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 1625–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopi, R.R.; Sreejith, S. Converter Topologies in Photovoltaic Applications—A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 94, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, B.; Jasni, J.; Radzi, M.A.M.; Azis, N.; Zhang, Q. Model Control and Digital Implementation of the Three Phase Interleaved Parallel Bidirectional Buck–Boost Converter for New Energy Electric Vehicles. Energies 2022, 15, 7178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.A.; Alajmi, B.N.; Abdelsalam, I.; Marei, M.I. Soft Switching Multiphase Interleaved Boost Converter with High Voltage Gain for EV Applications. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 27698–27716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alajmi, B.N.; Marei, M.I.; Abdelsalam, I.; Ahmed, N.A. Multiphase Interleaved Converter Based on Cascaded Non-Inverting Buck-Boost Converter. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 42497–42506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smadi, A.A.; Khoucha, F.; Amirat, Y.; Benrabah, A.; Benbouzid, M. Active Disturbance Rejection Control of an Interleaved High Gain DC-DC Boost Converter for Fuel Cell Applications. Energies 2023, 16, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sferlazza, A.; Albea-Sanchez, C.; Garcia, G. A Hybrid Control Strategy for Quadratic Boost Converters with Inductor Currents Estimation. Control Eng. Pract. 2020, 103, 104602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chincholkar, S.H.; Jiang, W.; Chan, C.Y. A Normalized Output Error-Based Sliding-Mode Controller for the DC-DC Cascade Boost Converter. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2020, 67, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Do, H.L. High Step-Up Coupled-Inductor Cascade Boost DC-DC Converter with Lossless Passive Snubber. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 7753–7761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, M.S.; Alammari, R.; Meraj, M.; Padmanaban, S.; Iqbal, A. A New Triple-Switch-Triple-Mode High Step-Up Converter with Wide Range of Duty Cycle for DC Microgrid Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 7425–7441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheri, H.M.; Babaei, E.; Sabahi, M.; Hosseini, S.H. High Step-Up DC-DC Converter with Minimum Output Voltage Ripple. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 3568–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, M.S.; Almakhles, D.J.; Padmanaban, S.; Blaabjerg, F.; Subramaniam, U.; Ionel, D.M. Analysis and Investigation of Hybrid DC-DC Non-Isolated and Non-Inverting Nx Interleaved Multilevel Boost Converter (Nx-IMBC) for High Voltage Step-Up Applications: Hardware Implementation. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 87309–87328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, V.F.; Cordeiro, A.; Foito, D.; Silva, J.F. High Step-Up DC–DC Converter for Fuel Cell Vehicles Based on Merged Quadratic Boost–Ćuk. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 7521–7530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipu, M.S.H.; Miah, M.S.; Ansari, S.; Meraj, S.T.; Hasan, K.; Elavarasan, R.M.; Al Mamun, A.; Zainuri, M.A.A.M.; Hussain, A. Power Electronics Converter Technology Integrated Energy Storage Management in Electric Vehicles: Emerging Trends, Analytical Assessment and Future Research Opportunities. Electronics 2022, 11, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marimuthu, M.; Vijayalakshmi, S.; Shenbagalakshmi, R. A Novel Non-Isolated Single Switch Multilevel Cascaded DC–DC Boost Converter for Multilevel Inverter Application. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2020, 15, 2157–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, F.; Zaihar, N.; Tanzim, S.; Singh, B.; Kannan, R. Review on Non-Isolated DC-DC Converters and Their Control Techniques for Renewable Energy Applications Review on Non-Isolated DC-DC Converters and Their Control Techniques for Renewable Energy Applications. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 12, 3747–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.S.; Liang, T.J. Analysis and Implementation of a Novel Bidirectional DC-DC Converter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, M.; Hemamalini, S. Nonisolated High Gain DC-DC Converter for DC Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 65, 1205–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, M.S.; Meraj, M.; Iqbal, A.; Padmanaban, S.; Maroti, P.K.; Alammari, R. High Gain Transformer-Less Double-Duty-Triple-Mode DC/DC Converter for DC Microgrid. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 36353–36370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadaf, S.; Al-Emadi, N.; Maroti, P.K.; Iqbal, A. A New High Gain Active Switched Network-Based Boost Converter for DC Microgrid Application. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 68253–68265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.S.; Liang, T.J.; Chen, J.F. Transformerless DC-DC Converters with High Step-up Voltage Gain. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 3144–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.H. Devices, Circuits, and Applications. In Power Electronics Handbook; Academic: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 245–259. [Google Scholar]








| Converter Topologies | Voltage Gain | Voltage Gain (%) | Switching Stress | Diode Stress | Switches | Inductors | Diodes | Capacitors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional Boost Converter [8] | 10 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Converter in ref. [22] | 12 | 1 | 4 | 6 | 4 | |||
| Converter in ref. [23] | 11.11 | ) | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | ||
| Converter in ref. [30] | 3 | - | 3 | 2 | 0 | 1 | ||
| Converter in ref. [31] | 10 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |||
| Converter in ref. [32] | 10.52 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | |||
| Converter in ref. [33] | 13.33 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | |||
| Converter in ref. [34] | 8.3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Proposed Converter | 20 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 3 |
| Parameters | Ratings (Units) |
|---|---|
| Rated Power | 160 W |
| Source Voltage | 20 V |
| Output Voltage | 400 V |
| Duty Cycle Ratio (D1) | 50% |
| Duty Cycle Ratio (D2) | 35% |
| Switching Frequency (fsw) | 50 kHz |
| Inductors (LX, LY) | 360 μH |
| Capacitor (C1, C2, Co) | 100 μF |
| Switches (SX, SY, SZ) | 600 V MOSFET FCP20N60 |
| Diodes (D1, D2, D3, D4) | 10A10 Power Diodes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mumtaz, F.; Yahaya, N.Z.; Meraj, S.T.; Singh, N.S.S.; Abro, G.E.M. A Novel Non-Isolated High-Gain Non-Inverting Interleaved DC–DC Converter. Micromachines 2023, 14, 585. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14030585
Mumtaz F, Yahaya NZ, Meraj ST, Singh NSS, Abro GEM. A Novel Non-Isolated High-Gain Non-Inverting Interleaved DC–DC Converter. Micromachines. 2023; 14(3):585. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14030585
Chicago/Turabian StyleMumtaz, Farhan, Nor Zaihar Yahaya, Sheikh Tanzim Meraj, Narinderjit Singh Sawaran Singh, and Ghulam E Mustafa Abro. 2023. "A Novel Non-Isolated High-Gain Non-Inverting Interleaved DC–DC Converter" Micromachines 14, no. 3: 585. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14030585
APA StyleMumtaz, F., Yahaya, N. Z., Meraj, S. T., Singh, N. S. S., & Abro, G. E. M. (2023). A Novel Non-Isolated High-Gain Non-Inverting Interleaved DC–DC Converter. Micromachines, 14(3), 585. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14030585






