Effects of the Electric Double Layer Characteristic and Electroosmotic Regulation on the Tribological Performance of Water-Based Cutting Fluids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
2.1. Preparation of Water-Based Cutting Fluids
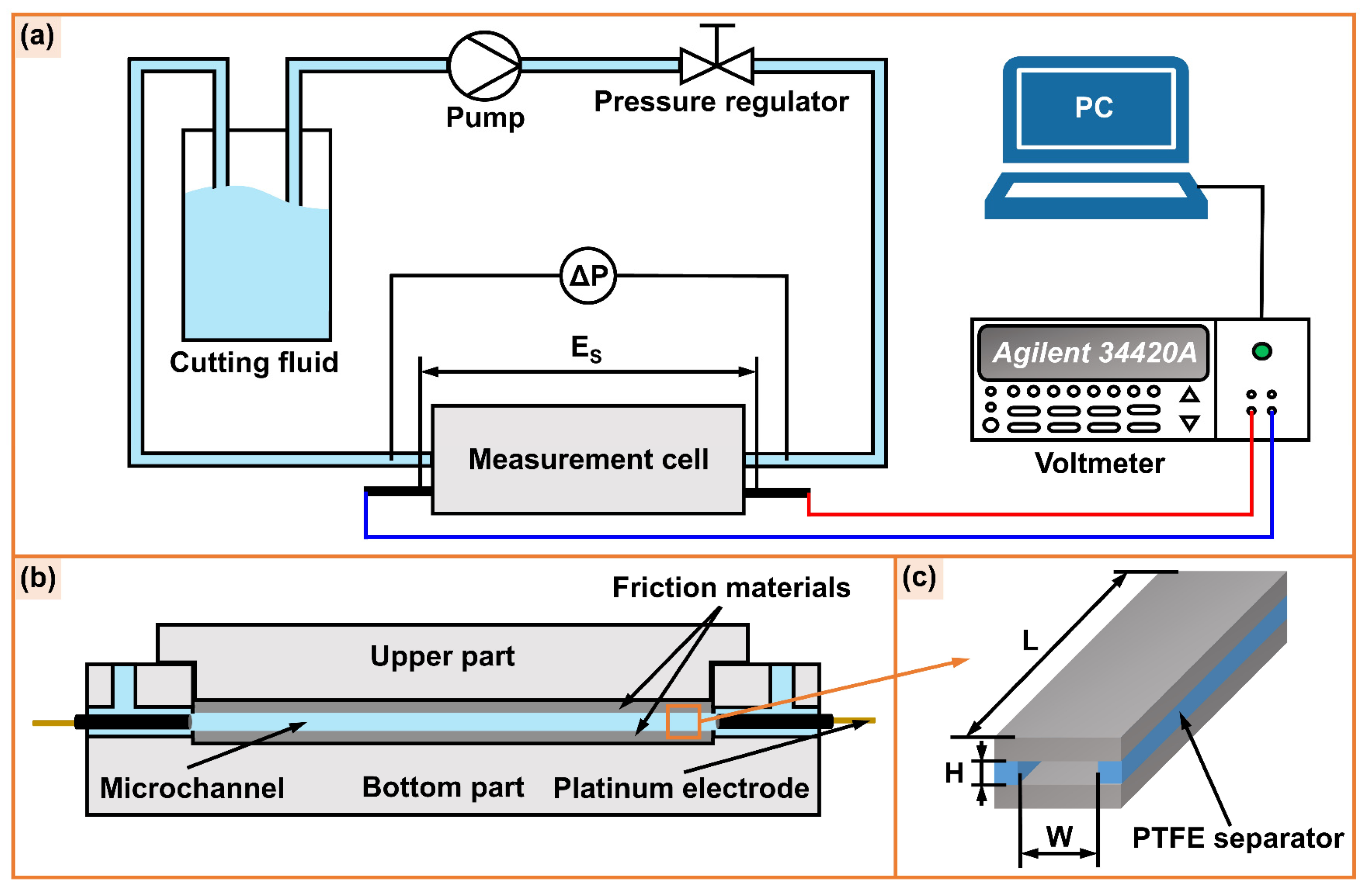
2.2. Capillary Electroosmotic Experiment
2.3. Streaming Potential Testing and Zeta-Potential Calculation
2.4. Tribological Tests
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Electroosmotic Performance Levels of Single-Component Additive Aqueous Solutions
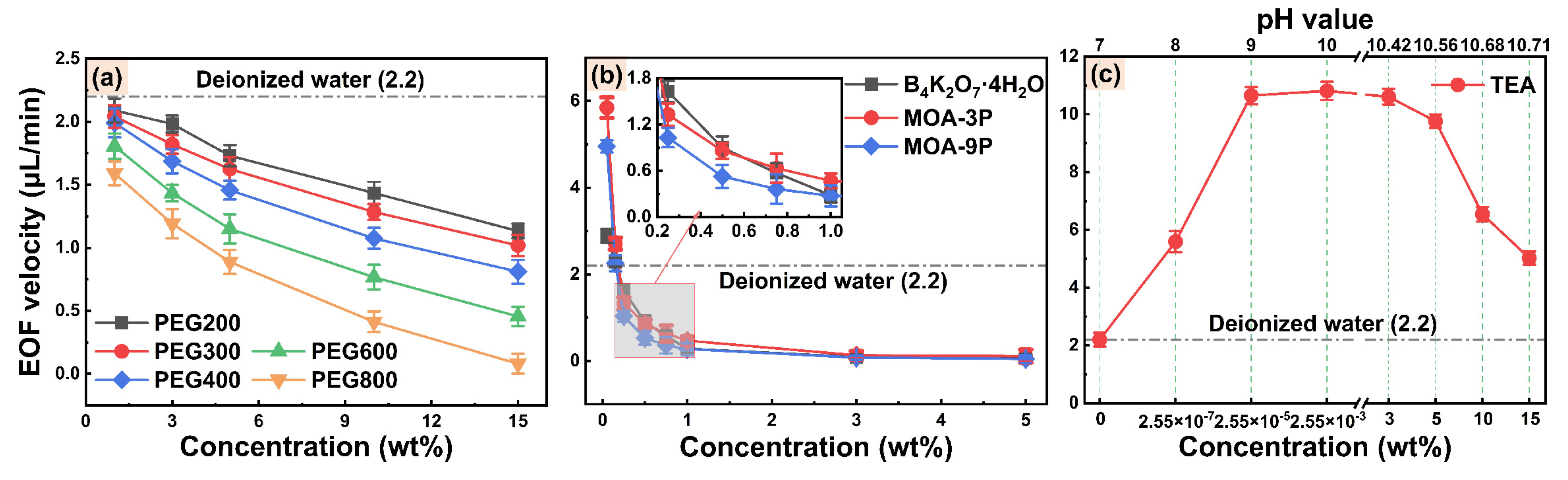
3.1.1. EOF Velocity
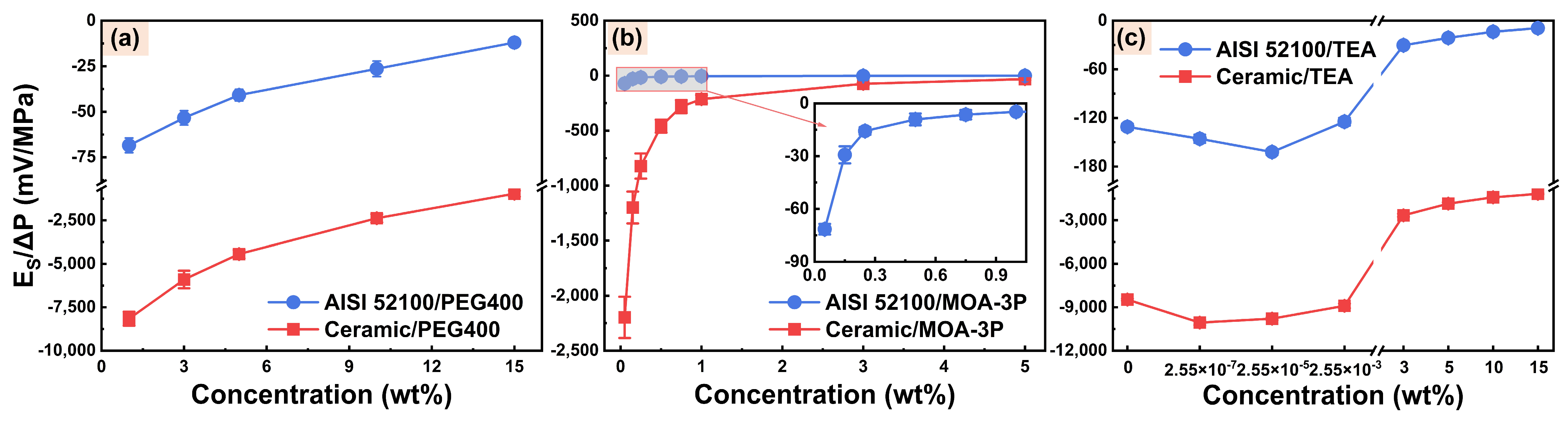
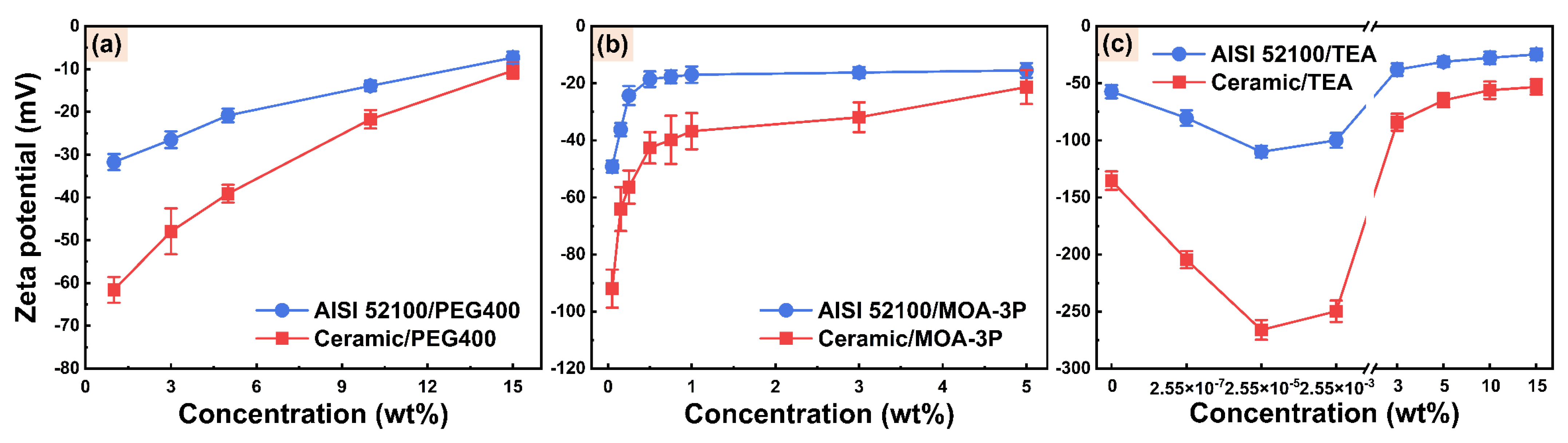
3.1.2. Streaming Potential and Zeta Potential
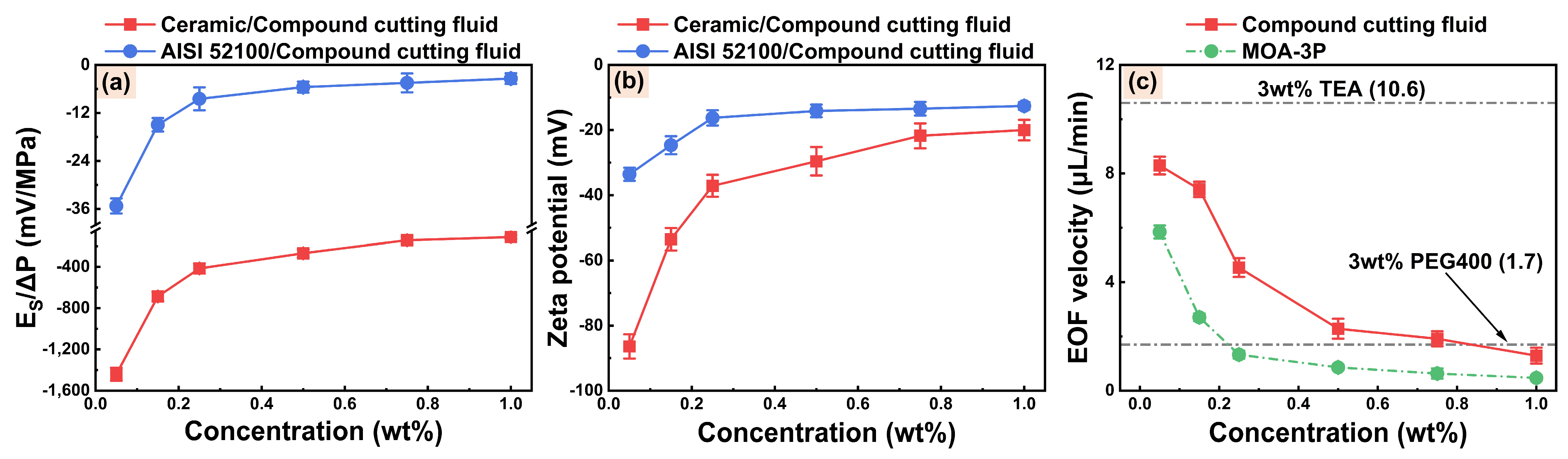
3.2. Electroosmotic Characteristics of Compound Cutting Fluids
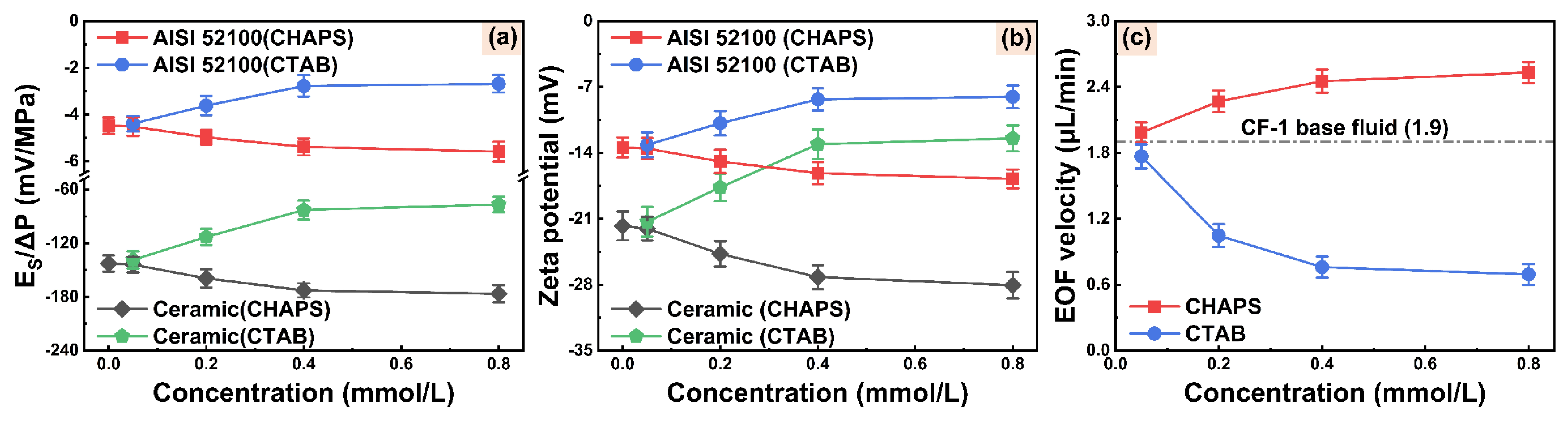
3.3. Electroosmotic Regulation Characteristics of WCF Cutting Fluids
3.4. Tribological Performance Characteristics of WCF Cutting Fluids
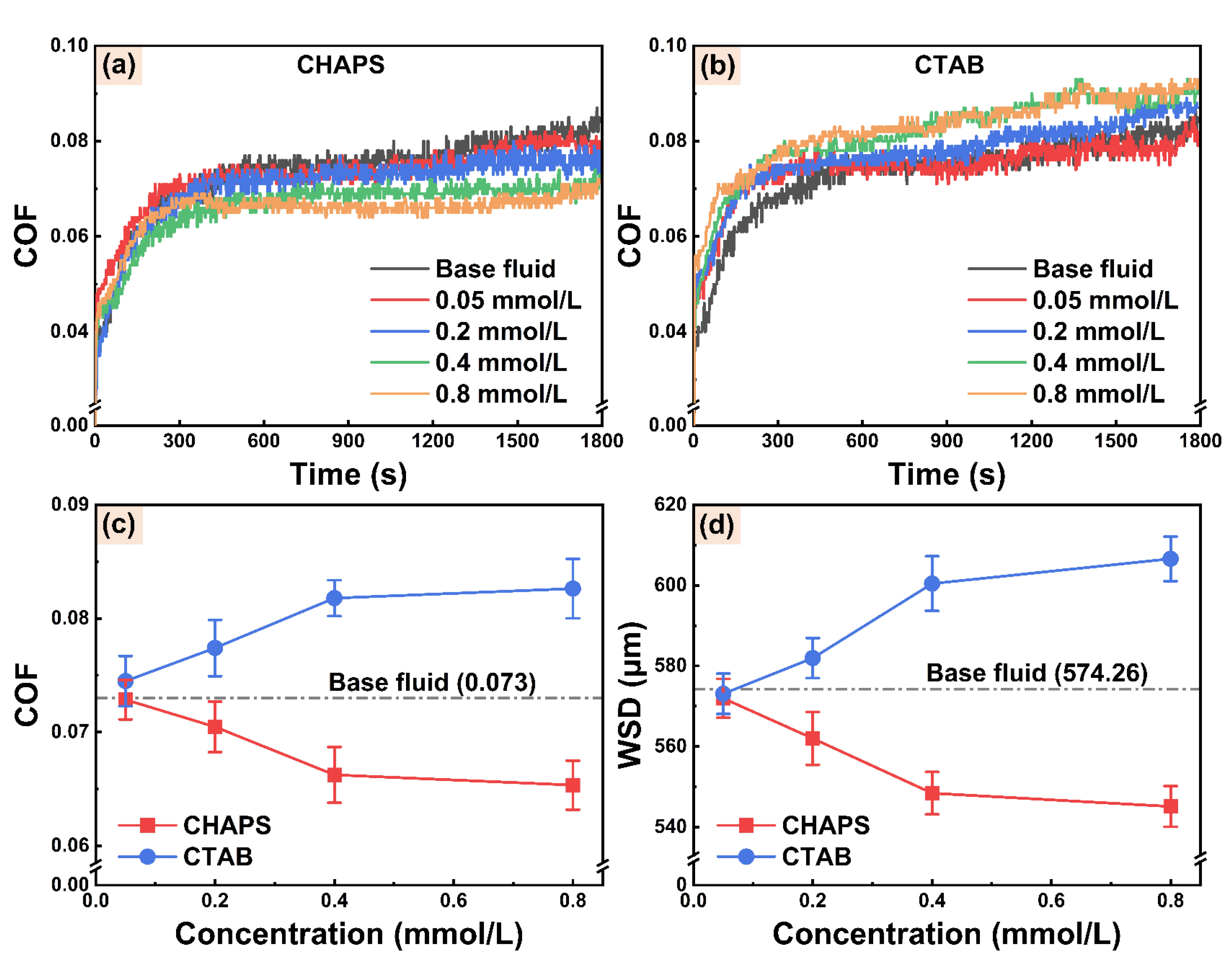
3.4.1. Effects of Electroosmotic Regulators on the Tribological Performance of WCF Cutting Fluid
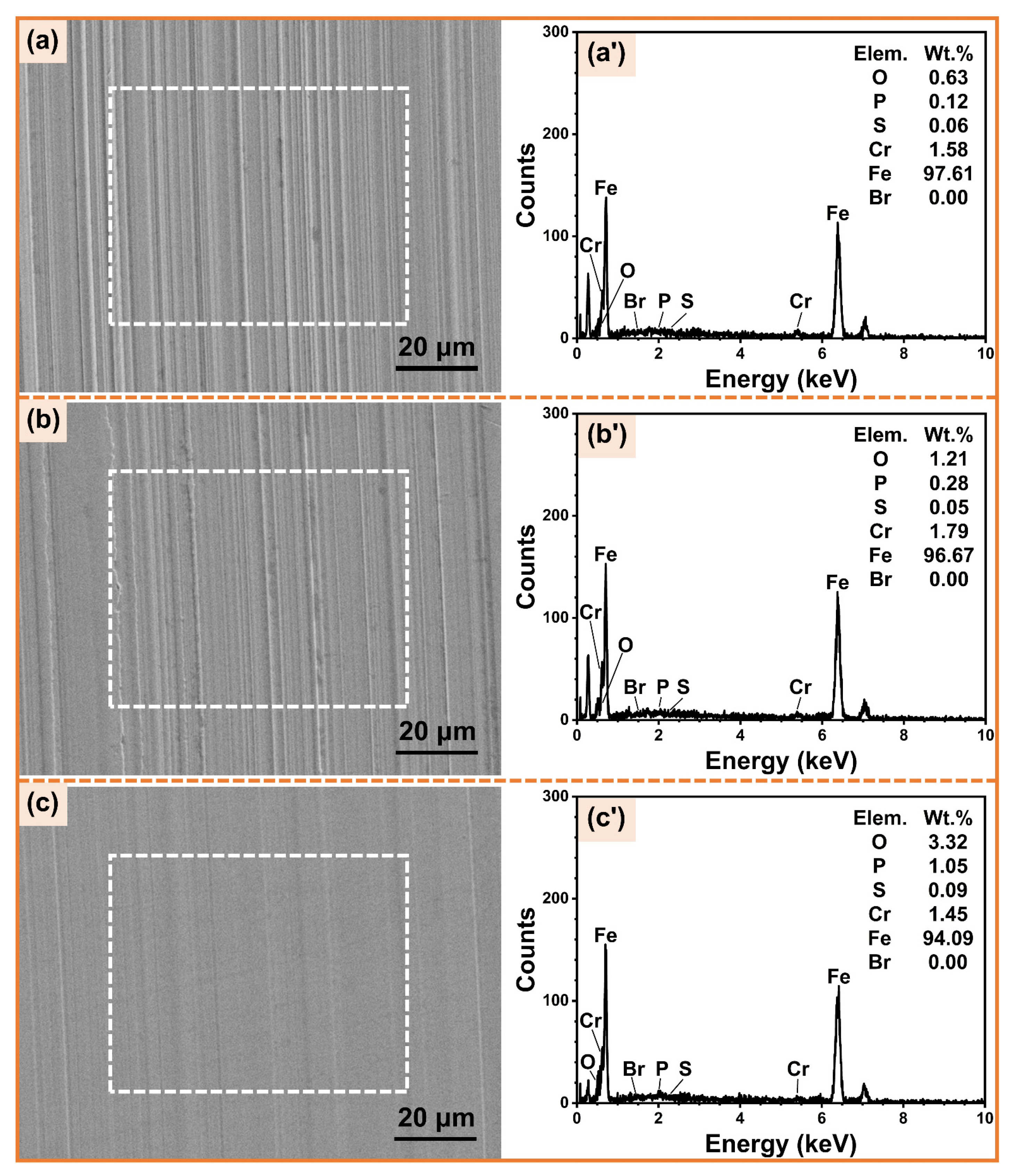
3.4.2. Worn Surfaces Analysis
3.5. Electroosmotic Regulation Mechanism
4. Conclusions
- (1)
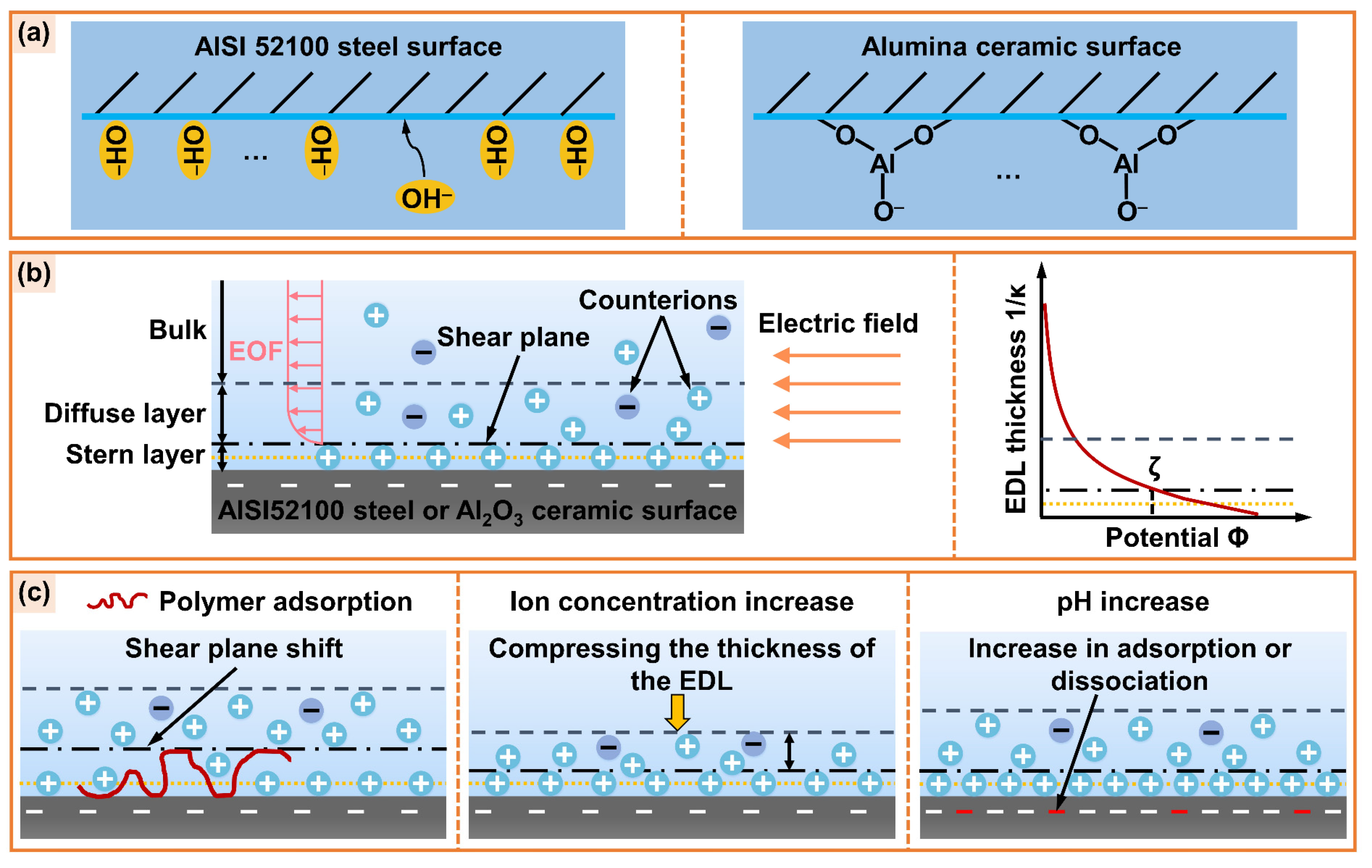
- MOA-3P and TEA are used as EP additive and pH buffer, respectively, for water-based cutting fluid. Their excessive ion concentration will lead to a compression of EDL at the friction material/solution interface, causing the absolute value of the zeta potential and EOF to decrease.
- (2)
- PEG400 is used as a lubricity additive for water-based cutting fluid. Its chain segments are adsorbed to the surface of friction material to produce steric hindrance, which makes the shear plane move away from the solid surface, and the absolute value of zeta potential and EOF decrease.
- (3)
- The specific adsorption of OH− ions on the AISI 52100 steel surface and the dissociation of Al-OH groups on the alumina ceramic surface can be promoted to some extent by an increase in pH value in a water-based cutting-fluid system, which increases the absolute value of zeta potential and EOF.
- (4)
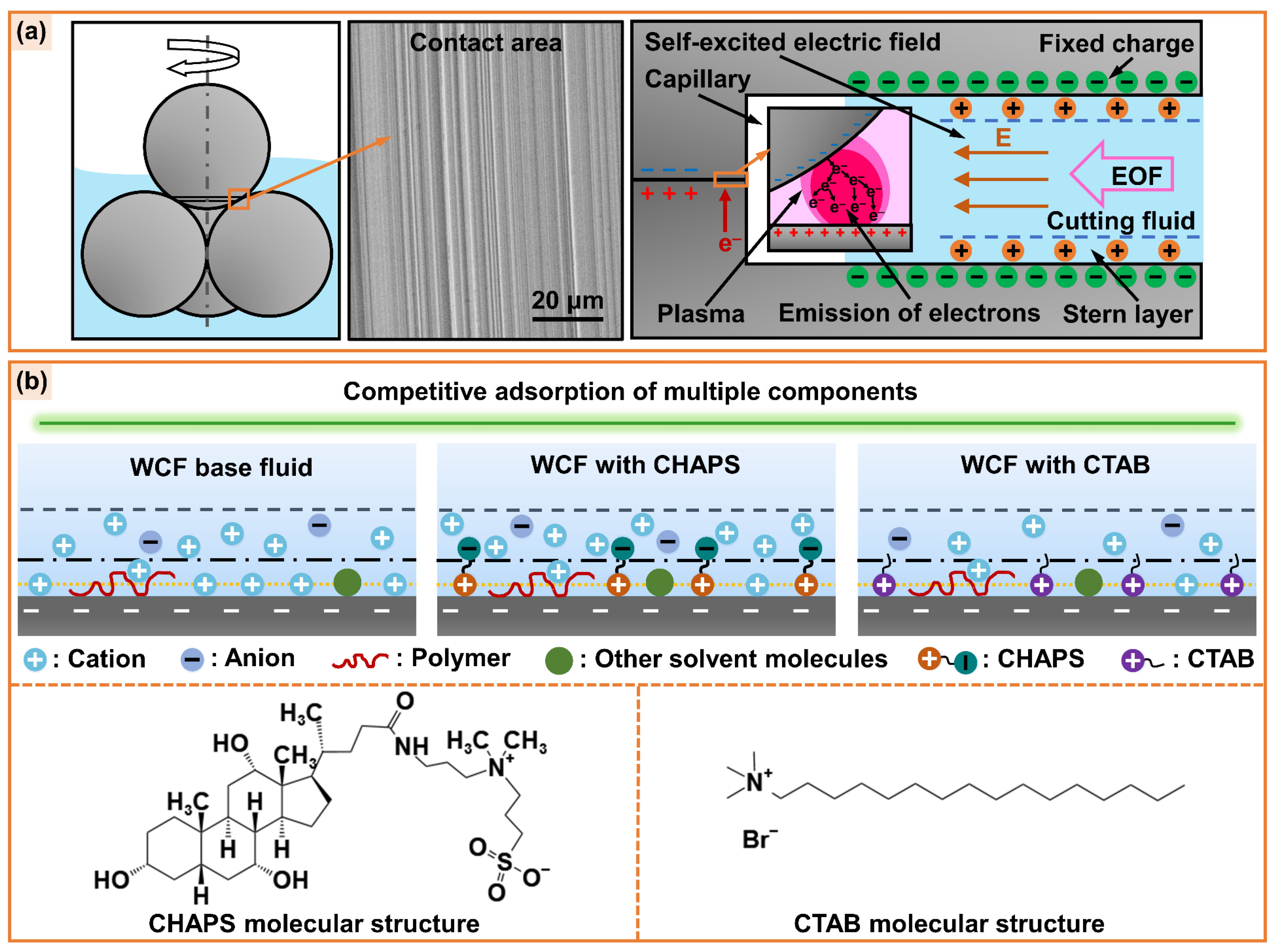
- The electroosmotic performance of water-based cutting fluid can be further adjusted by adding electroosmotic regulators. The electroosmotic promoter CHAPS increases the absolute value of zeta potential by electrostatic adsorption, which promotes the penetration ability of cutting fluid in the capillary zone of the friction interface, improving the tribological performance of cutting fluid at the steel–steel interface. The electroosmotic suppressant CTAB reduces the absolute value of the zeta potential and suppresses EOF, exhibiting poor tribological performance.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yan, P.; Rong, Y.; Wang, G. The Effect of Cutting Fluids Applied in Metal Cutting Process. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2016, 230, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, D.; Jin, T.; Qi, Y. A Novel Bionic Micro-Textured Tool with the Function of Directional Cutting-Fluid Transport for Cutting Titanium Alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2023, 311, 117816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Deng, J.; Xing, Y.; Li, S.; Gao, H. Effect of Microscale Texture on Cutting Performance of WC/Co-Based TiAlN Coated Tools under Different Lubrication Conditions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 326, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, A.E.; Micaroni, R. Influence of the Direction and Flow Rate of the Cutting Fluid on Tool Life in Turning Process of AISI 1045 Steel. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2007, 47, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.H.; Sugihara, T.; Enomoto, T. Interrupted Cutting of Inconel 718 with AlTiSiN Coated Cemented Carbide Tool under High Pressure Coolant Supply. Precis. Eng. J. Int. Soc. Precis. Eng. Nanotechnol. 2022, 78, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godlevski, V.A.; Volkov, A.V.; Latyshev, V.N.; Maurin, L.N. The Kinetics of Lubricant Penetration Action during Machining. Lubr. Sci. 1997, 9, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godlevskiy, V.A. Technological Lubricating Means: Evolution of Materials and Ideas. Front. Mech. Eng. 2016, 11, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godlevski, V.A.; Volkov, A.V.; Latyshev, V.N.; Maurin, L.N. A Description of the Lubricating Action of the Tribo-Active Components of Cutting Fluids. Lubr. Sci. 1998, 11, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.J.; Pei, H.J.; Wang, G.C.; Shen, C.G. A Theoretical Investigation on the Capillary Model of Lubricant Penetration. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 383–390, 3871–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, K.; Nevshupa, R.A. Plasma Generation in a Gap around a Sliding Contact. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2002, 35, L53–L56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, K. Triboemission of Charged Particles from Various Solids under Boundary Lubrication Conditions. Wear 1994, 178, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, K. Triboplasma Generation and Triboluminescence in the Inside and the Front Outside of the Sliding Contact. Tribol. Lett. 2016, 63, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, K.; Yagasaki, F. The Flow of Triboplasma. Tribol. Lett. 2019, 67, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Luan, Z.; Zhang, R.; Xia, Y.; Yao, W.; Liu, J.; Ma, Y.; Hu, X.; Xu, X. Effect of Electroosmosis on Lubricant Penetration at the Tool–Chip Interface. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2022, 307, 117653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, Z.; Liu, W.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, R.; Feng, B.; Hu, X.; Huang, S.; Xu, X. Effects of an Electrical Double Layer and Tribo-Induced Electric Field on the Penetration and Lubrication of Water-Based Lubricants. Lubricants 2022, 10, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Luan, Z.; Zhang, T.; Liu, J.; Feng, B.; Lv, T.; Hu, X. Effects of Electroosmotic Additives on Capillary Penetration of Lubricants at Steel/Steel and Steel/Ceramic Friction Interfaces. Tribol. Int. 2020, 151, 106441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falahati, H.; Wong, L.; Davarpanah, L.; Garg, A.; Schmitz, P.; Barz, D.P.J. The Zeta Potential of PMMA in Contact with Electrolytes of Various Conditions: Theoretical and Experimental Investigation. Electrophoresis 2014, 35, 870–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, R.; Freudenberg, U.; Schweiß, R.; Küttner, D.; Werner, C. Hydroxide and Hydronium Ion Adsorption—A Survey. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 15, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xing, W.; Xu, N.; Wong, F.-S. Effects of Inorganic Electrolytes on Zeta Potentials of Ceramic Microfiltration Membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 42, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.A.; Goel, A.; Abbas, Z. Effect of Electrolyte Concentration on the Stern Layer Thickness at a Charged Interface. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 3790–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childress, A.E.; Elimelech, M. Effect of Solution Chemistry on the Surface Charge of Polymeric Reverse Osmosis and Nanofiltration Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1996, 119, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maršálek, R. The Influence of Surfactants on the Zeta Potential of Coals. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2008, 31, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sęk, A.; Perczyk, P.; Wydro, P.; Gruszecki, W.I.; Szcześ, A. Effect of Trace Amounts of Ionic Surfactants on the Zeta Potential of DPPC Liposomes. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2021, 235, 105059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Na, J.; Lim, S. Control of Adhesion and Desorption Behavior of Silica Particles on InGaAs Surfaces by Addition of Hexadecyltrimethylammonium Bromide in Ammonium Hydroxide–Hydrogen Peroxide Mixture Solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 590, 152949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khademi, M.; Wang, W.; Reitinger, W.; Barz, D.P.J. Zeta Potential of Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) (PMMA) in Contact with Aqueous Electrolyte–Surfactant Solutions. Langmuir 2017, 33, 10473–10482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucy, C.A.; Underhill, R.S. Characterization of the Cationic Surfactant Induced Reversal of Electroosmotic Flow in Capillary Electrophoresis. Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Luan, Z.; Zhang, T.; Liu, J.; Hu, X.; Guan, J.; Xu, X. Capillary Electroosmosis Properties of Water Lubricants with Different Electroosmotic Additives under a Steel-on-Steel Sliding Interface. Friction 2022, 10, 1019–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.; Cen, Y.; Yang, H.; Honda, T.; Nakanishi, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, B.; Zeng, X. The Enhanced Lubrication of Water-Based Cutting Fluid by Functionalized GO. Tribol. Lett. 2020, 68, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Zhou, Z.; Nie, X.; Chen, Y.; Cao, H.; Liu, B.; Zhang, N.; Said, Z.; et al. Biological Stability of Water-Based Cutting Fluids: Progress and Application. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2022, 35, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.Z.; Guo, P.; Hong, D.M.; Hui, J.D.; Hui, Z.M.; Geng, F. The Effect of Preparation and Characterisation of Polyurea Grease. Mater. Res. Innov. 2015, 19, 588–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.; Zheng, Y.; Ba, M.; Wang, Y.; Kong, J.; Liu, J.; Wu, Q. Long Time Super-Hydrophobic Fouling Release Coating with the Incorporation of Lubricant. Prog. Org. Coat. 2021, 152, 106136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhu, G.; Dai, J.; Zhu, Y.; Lin, N. Cellulose Nanocrystals as Sustainable Additives in Water-Based Cutting Fluids. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 298, 120139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinksmeier, E.; Meyer, D.; Huesmann-Cordes, A.G.; Herrmann, C. Metalworking Fluids—Mechanisms and Performance. CIRP Ann. 2015, 64, 605–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.H.; Zhao, Y.C.; Björling, M.; Wang, Y.; Luo, J.B.; Prakash, B. EHL Properties of Polyalkylene Glycols and Their Aqueous Solutions. Tribol. Lett. 2012, 45, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Wang, Y.; Dai, E.; Xiang, H. Study on the properties of self-emulsifying ester in synthetic cutting fluid. Lubr. Eng. 2021, 46, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, M.; Zhang, Q.; Mei, H.; Zhang, J.; Zuo, X.; Geng, F. Preparation and Characterization of Polymer Microcapsules Containing Ammonium Persulfate with Controlled Burst Release. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 105332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, G.; Zhao, C.; Huang, B.; Li, S.; Wang, L. Tribological properties of aqueous solutions with polyether and borate. J. Mech. Eng. 2016, 52, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goindi, G.S.; Jayal, A.D.; Sarkar, P. Application of Ionic Liquids in Interrupted Minimum Quantity Lubrication Machining of Plain Medium Carbon Steel: Effects of Ionic Liquid Properties and Cutting Conditions. J. Manuf. Process. 2018, 32, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedicto, E.; Rubio, E.M.; Aubouy, L.; Sáenz-Nuño, M.A. Formulation of Sustainable Water-Based Cutting Fluids with Polyol Esters for Machining Titanium Alloys. Metals 2021, 11, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, T.; Yin, S. Synthesis of nonylphenol polyoxyethylene ether phosphate ester phosphate and its application in metal cutting fluids. Adv. Fine Petrochem. 2011, 12, 30–32. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, C. Preparation of synthetic cutting fluids and the synergistic effect of extreme pressure agent and anti-rust agent. Lubr. Eng. 2018, 43, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Luo, J. Friction and Wear Performance of Titanium Alloy against Tungsten Carbide Lubricated with Phosphate Ester. Tribol. Int. 2016, 95, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Sun, M.; Xu, X. Effect of organic alcohol amines in metalworking fluids on product performance. Lubr. Eng. 2019, 44, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, L.; Dong, L.; Li, H.; Yu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lv, G.; Ma, H. pH-Responsive Smart Wettability Surface with Dual Bactericidal and Releasing Properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 46065–46075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Zhang, A.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, G.; Zhang, S.; Feng, Z.; Feng, J.; Yang, J. Designing a Lysosome Targeting Nanomedicine for pH-Triggered Enhanced Phototheranostics. Mater. Chem. Front. 2021, 5, 2694–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byers, J.P. Metalworking Fluids, 2nd ed.; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2011; ISBN 978-7-122-11076-3. [Google Scholar]
- Burts, K.S.; Plisko, T.V.; Bildyukevich, A.V.; Rodrigues, G.; Sjölin, M.; Lipnizki, F.; Ulbricht, M. Development of Polysulfone Ultrafiltration Membranes with Enhanced Antifouling Performance for the Valorisation of Side Streams in the Pulp and Paper Industry. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 632, 127742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymczyk, A.; Fatin-Rouge, N.; Fievet, P. Tangential Streaming Potential as a Tool in Modeling of Ion Transport through Nanoporous Membranes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 309, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaroshchuk, A.; Ribitsch, V. Role of Channel Wall Conductance in the Determination of ζ-Potential from Electrokinetic Measurements. Langmuir 2002, 18, 2036–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fievet, P. Determining the ζ-Potential of Plane Membranes from Tangential Streaming Potential Measurements: Effect of the Membrane Body Conductance. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 226, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, C. Capillary Electrophoresis Technology and Its Application; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2000; ISBN 978-7-5025-2959-8. [Google Scholar]
- Michna, A. Macroion Adsorption—Electrokinetic and Optical Methods. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 250, 95–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razunguzwa, T.T.; Timperman, A.T. Fabrication and Characterization of a Fritless Microfabricated Electroosmotic Pump with Reduced pH Dependence. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 1336–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’Pandou, A.; Siffert, B. Polyethyleneglycol Adsorption at the TiO2-H2O Interface: Distortion of Ionic Structure and Shear Plane Position. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1987, 24, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barany, S. Polymer Adsorption and Electrokinetic Potential of Dispersed Particles in Weak and Strong Electric Fields. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 222, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Feng, A.; Liu, Z.; Li, D. Zeta Potentials of PDMS Surfaces Modified with Poly(Ethylene Glycol) by Physisorption. Electrophoresis 2020, 41, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siffert, B.; Jada, A.; Letsango, J.E. Location of the Shear Plane in the Electric Double Layer in an Organic Medium. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1994, 163, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seebergh, J.E.; Berg, J.C. Evidence of a Hairy Layer at the Surface of Polystyrene Latex Particles. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1995, 100, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D. (Ed.) EDL Potential. In Encyclopedia of Microfluidics and Nanofluidics; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2008; pp. 444–453. ISBN 978-0-387-48998-8. [Google Scholar]
- Szymczyk, A.; Fievet, P.; Mullet, M.; Reggiani, J.C.; Pagetti, J. Comparison of Two Electrokinetic Methods—Electroosmosis and Streaming Potential—To Determine the Zeta-Potential of Plane Ceramic Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1998, 143, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z. Metal Cutting Fluid: Selection, Preparation and Use; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2007; ISBN 978-7-122-00962-3. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Spikes, H. On the Mechanism of ZDDP Antiwear Film Formation. Tribol. Lett. 2016, 63, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamann, C.H.; Hamnelt, A.; Wolf, I.T. Electrochemistry, 2nd ed.; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2010; ISBN 978-7-122-07045-6. [Google Scholar]
- Yopps, J.A.; Fuerstenau, D.W. The Zero Point of Charge of Alpha-Alumina. J. Colloid Sci. 1964, 19, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Qiao, D.; Guo, Y.; Feng, D.; Shi, L. Influence of Competitive Adsorption on Lubricating Property of Phosphonate Ionic Liquid Additives in PEG. Tribol. Lett. 2016, 64, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Types of Additives | Reagents | Chemical Formulas | Manufacturers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lubricity additive | Polyethylene glycol (PEG200, PEG300, PEG400, PEG600 and PEG800) | HO(CH2CH2O)nH | Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China |
| EP additive | Potassium tetraborate (B4K2O7·4H2O) | H8B4K2O11 | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China |
| Fatty alcohol ether phosphate (MOA-3P and MOA-9P) | RO(CH2CH2O)nPO(OH)2 and [RO(CH2CH2O)n]2PO(OH) | Jiangsu Haian Petrochemical Plant, Nantong, China | |
| pH buffer | Triethanolamine (TEA) | C6H15NO3 | Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China |
| Electroosmotic promoter | 3-[(3-cholamidopropyl)-dimethylammonio]-1-propanesulfonate (CHAPS) | C32H58N2SO7 | Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China |
| Electroosmotic suppressant | Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) | C19H42BrN | Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China |
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Material | AISI 52100 steel ball (diameter 12.7 mm, hardness 59–61 HRC) |
| Load | 147 N |
| Rotational speed | 1200 rpm |
| Time | 30 min |
| Types of cutting fluids | WCF base fluid |
| WCF base fluid + x mmol/L CHAPS (x = 0.05, 0.2, 0.4, 0.8) | |
| WCF base fluid + x mmol/L CTAB (x = 0.05, 0.2, 0.4, 0.8) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, R.; Liu, W.; Luan, Z.; Xia, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X.; Duraihem, F.Z.; Xu, X. Effects of the Electric Double Layer Characteristic and Electroosmotic Regulation on the Tribological Performance of Water-Based Cutting Fluids. Micromachines 2023, 14, 2029. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14112029
Zhang R, Liu W, Luan Z, Xia Y, Wang Y, Hu X, Duraihem FZ, Xu X. Effects of the Electric Double Layer Characteristic and Electroosmotic Regulation on the Tribological Performance of Water-Based Cutting Fluids. Micromachines. 2023; 14(11):2029. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14112029
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ruochong, Wenshuai Liu, Zhiqiang Luan, Yu Xia, Ying Wang, Xiaodong Hu, Faisal Z. Duraihem, and Xuefeng Xu. 2023. "Effects of the Electric Double Layer Characteristic and Electroosmotic Regulation on the Tribological Performance of Water-Based Cutting Fluids" Micromachines 14, no. 11: 2029. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14112029
APA StyleZhang, R., Liu, W., Luan, Z., Xia, Y., Wang, Y., Hu, X., Duraihem, F. Z., & Xu, X. (2023). Effects of the Electric Double Layer Characteristic and Electroosmotic Regulation on the Tribological Performance of Water-Based Cutting Fluids. Micromachines, 14(11), 2029. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14112029





