A Biodegradable Bioactive Glass-Based Hydration Sensor for Biomedical Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Fabrication
2.2. Structural and Morphological Analysis
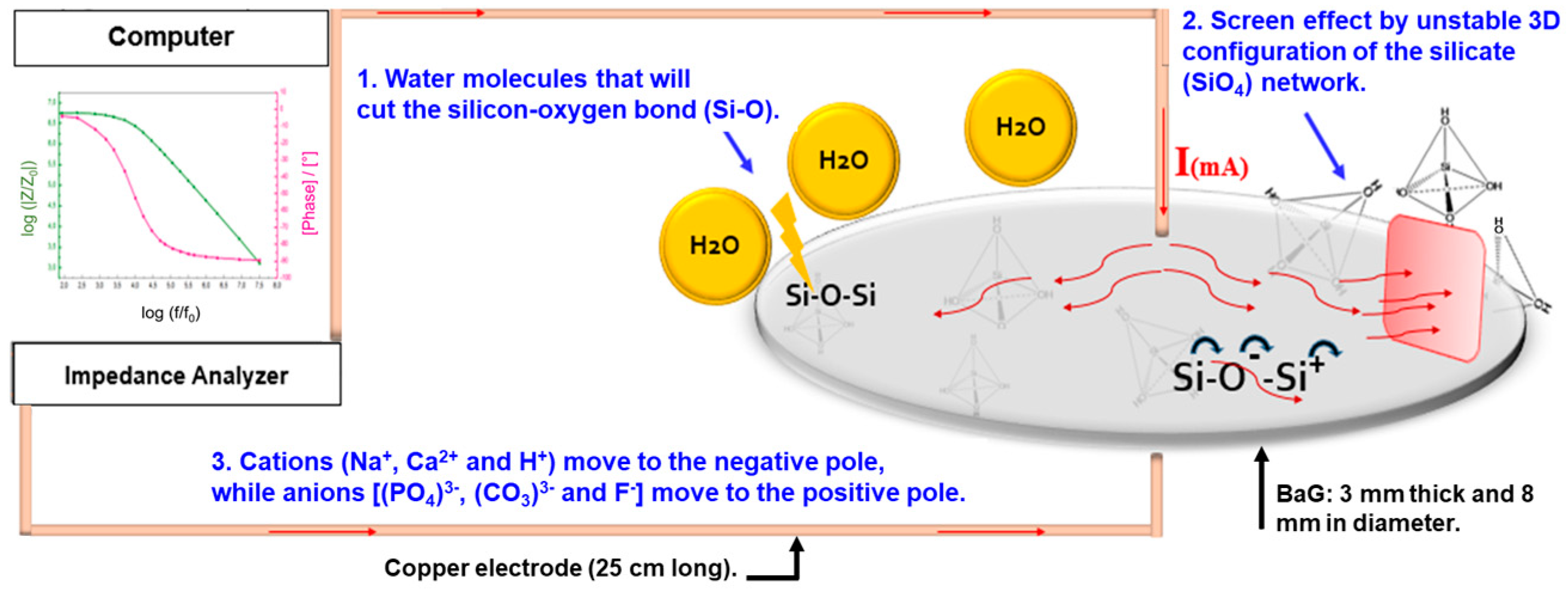
2.3. Electrical Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physical Characterization of Fluorine Bioactive Glass (BaG-F) Based Sensors
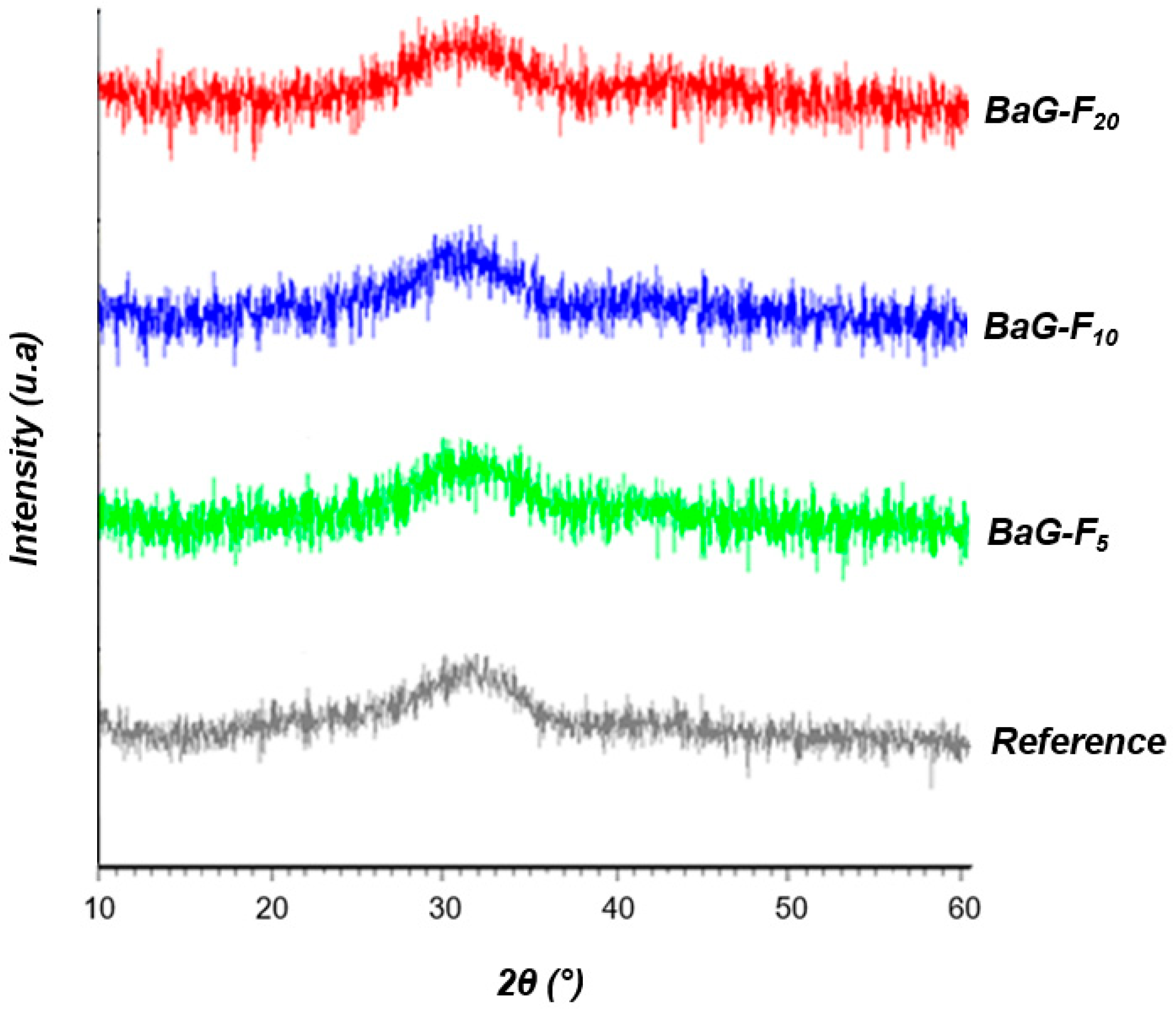
3.1.1. Structural Analysis
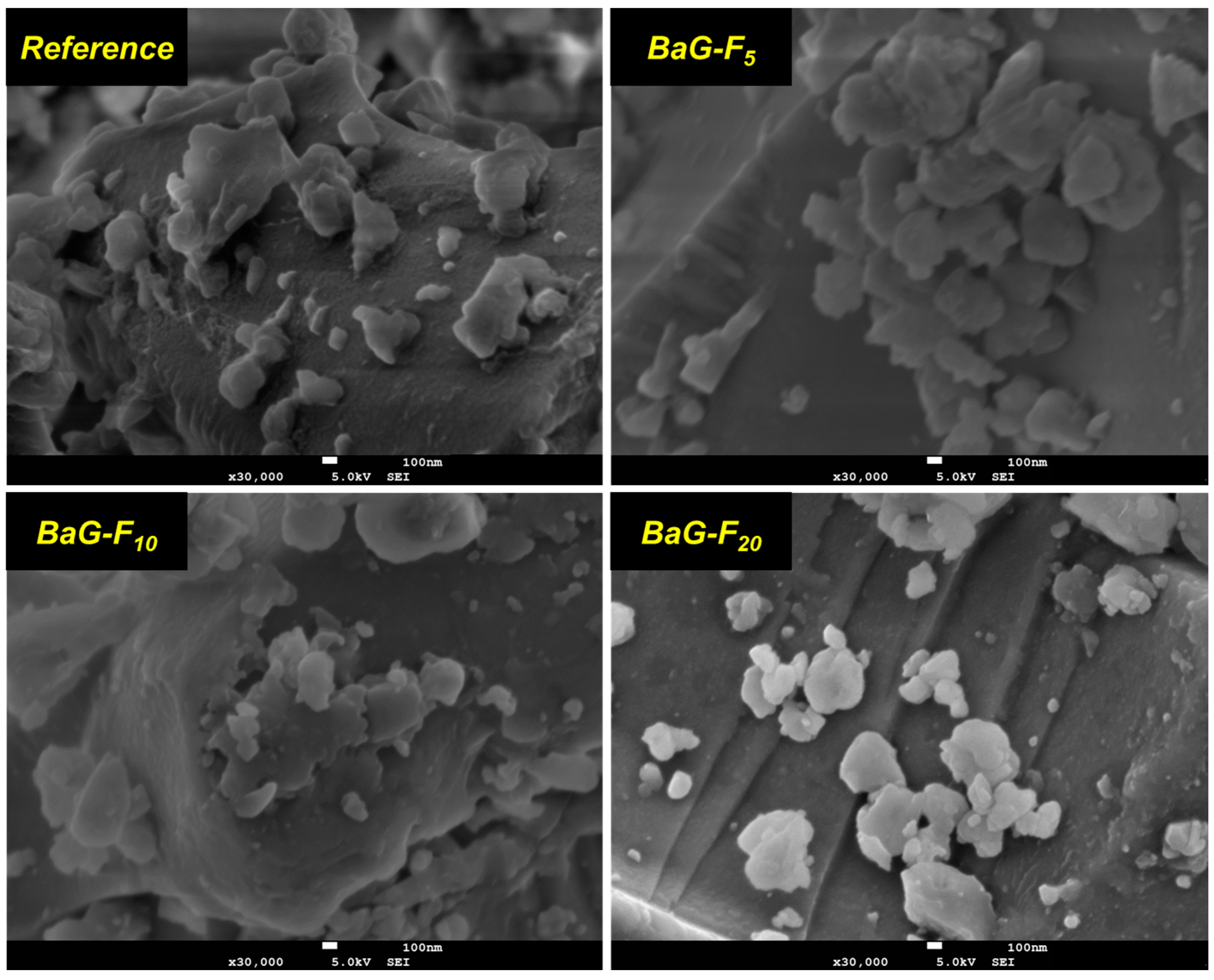
3.1.2. Morphological Analysis
3.1.3. Texture and Specific Surfaces Measurements
3.2. Electrical Behavior of Fluorine Bioactive Glass (BaG-F) Based Sensors
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hawryluk, G.W.J.; Citerio, G.; Hutchinson, P.; Kolias, A. Intracranial pressure: Current perspectives on physiology and monitoring. Intensive Care Med. 2022, 48, 1471–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlieger, G.D.; Meyfroidt, G. Kidney Dysfunction After Traumatic Brain Injury: Pathophysiology and General Management. J. Neurocrit. Care 2022, 891, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.; Ye, D.; Zhang, F.; Di, C. Implantable application of polymer-based biosensors. J. Polym. Sci. 2022, 60, 328–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandodkar, A.J.; Jeerapan, I.; Wang, J. Wearable Chemical Sensors: Present Challenges and Future Prospects. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 464–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, L.M.; MeiKhor, S. Current state and future prospects of sensors for evaluating polymer biodegradability and sensors made from biodegradable polymers: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1217, 339989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashammakhi, N.; Serlo, W. Reflections on complications to bioresorbable osteofixation devices. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2007, 18, 1242–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reich, K.M.; Viitanen, P.; Apu, E.H.; Tangl, S.; Ashammakhi, N. The Effect of Diclofenac Sodium-Loaded Poly (Lactide-co-Glycolide) Rods on Bone Formation and Inflammation: A Histological and Histomorphometric Study in the Femora of Rats. Micromachines 2020, 11, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellomäki, M.; Puumanen, K.; Ashammakhi, N.; Waris, T.; Paasimaa, S. Bioabsorbable laminated membranes for guided bone regeneration. Technol. Health Care 2002, 10, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashammakhi, N.; Hernandez, A.L.; Unluturk, B.D.; Quintero, S.A. Biodegradable Implantable Sensors: Materials Design, Fabrication, and Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2104149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, H.; Hyo, R.L.; Sehyun, P.; Jong, H.K. Recent Advances in Printing Technologies of Nanomaterials for Implantable Wireless Systems in Health Monitoring and Diagnosis. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2021, 10, 2100158. [Google Scholar]
- Henrotin, Y.; Kurz, B.; Aigner, T. Oxygen and reactive oxygen species in cartilage degradation: Friends or foes? Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2005, 13, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Koo, J.; Rogers, J.A. Inorganic materials for transient electronics in biomedical applications. MRS Bull. 2020, 45, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feiner, R.; Dvir, T. Tissue–electronics interfaces: From implantable devices to engineered tissues. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 3, 17076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirifar, L.; Shamloo, A.; Nasiri, R.; Ashammakhi, N. Brain-on-a-chip: Recent advances in design and techniques for microfluidic models of the brain in health and disease. Biomaterials 2022, 285, 121531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zberg, B.; Uggowitzer, P.J.; Löffler, J.F. MgZnCa glasses without clinically observable hydrogen evolution for biodegradable implants. Nature Mater. 2009, 8, 887–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, P.-C.; Tsai, P.-H.; Tsung, H.L.; Cheng, K.C. Degradation behavior and mechanical strength of Mg-Zn-Ca bulk metallic glass composites with Ti particles as biodegradable materials. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 699, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänzi, A.C.; Dalla Torre, F.H.; Sologubenko, A.S. Design strategy for microalloyed ultra-ductile magnesium alloys. Philos. Mag. Lett. 2009, 89, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Wei, Y.; Kuang, Y.; Qian, Y. Porous and conductive cellulose nanofiber/carbon nanotube foam as a humidity sensor with high sensitivity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 292, 119684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macanovic, A.; Marquette, C.; Polychronakos, C. Impedance-based detection of DNA sequences using a silicon transducer with PNA as the probe layer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, L.F.; Rodrigues, A.C.M. Electrical conductivity and relaxation frequency of lithium borosilicate glasses. Solid State Ion. 2004, 168, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfredi, S.; Saia, P.S.; Lebullenger, R. Electric conductivity and relaxation in fluoride, fluorophosphate and phosphate glasses: Analysis by impedance spectroscopy. Solid State Ion. 2002, 146, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdy, E.A.; Khattari, Z.Y.; Salem, W.M.; Ibrahim, S. Study the structural, physical, and optical properties of CaO–MgO–SiO2–CaF2 bioactive glasses with Na2O and P2O5 dopants. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 286, 126231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauer, D.S.; Karpukhina, N.; O’Donnell, M.D.; Law, R.V. Fluoride-containing bioactive glasses: Effect of glass design and structure on degradation, pH and apatite formation in simulated body fluid. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 3275–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furtos, G.; Cosma, V.; Prejmerean, C.; Moldovan, M. Fluoride release from dental resin composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2005, 25, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agathopoulos, S.; Tulyaganov, D.U.; Ventura, J.M.G.; Kannan, S. Formation of hydroxyapatite into glasses of the CaO–MgO–SiO2 system with B2O3, Na2O, CaF2 and P2O5 additives. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 1832–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ling, H.; Chen, Y.; Cui, Q. Hydrogel-enabled transfer-printing of conducting polymer films for soft organic bioelectronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1906016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hench, L.L.; Splinter, R.J.; Allen, W.C. Bonding mechanisms at the interface of ceramic prosthetic materials. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1971, 5, 117–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hench, L.L. Bioceramics: From Concept to Clinic. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1991, 74, 1487–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silicon. 2021. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Silicon&oldid=1057830496 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Özarslan, A.C.; Yücel, S. Evaluation of novel composition (SiO2–CaO–Na2O–P2O5, SrO–CuO) degradable amorphous silicate glasses properties and comprehensive characterization of the thermal features. Ceram. Int. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Shyu, J.J.; Lee, H.H. Sintering, Crystallization, and Properties of B2O3/P2O5-Doped Li2O·Al2O3·4SiO2 Glass-Ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1995, 78, 2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, F.J.; Alarcon, J. Mechanism of crystallization of pyroxene-based glass-ceramic glazes. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 2004, 34, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulyaganov, D.; Ribeiro, M.J.; Labrincha, J.A. Development of glass-ceramics by sintering and crystallization of fine powders of calcium-magnesium-aluminosilicate glass. Ceram. Int. 2002, 28, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauer, D.S.; Noaman, A.; Hill, R.G. Density–structure correlations in fluoride-containing bioactive glasses. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 130, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducheyne, P.; Qiu, Q. Bioactive ceramics: The effect of surface reactivity on bone formation and bone cell function. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 2287–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.R.; Sepulveda, P.; Hench, L.L. Dose-dependent behavior of bioactive glass dissolution. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 58, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conz, M.B.; Granjeiro, J.M.; Soares, G.A. Physicochemical characterization of six commercial hydroxyapatites for medical-dental applications as bone graft. J. Appl. Oral. Sci. 2005, 13, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramila, A.; Balas, F.; Vallet, R.M. Synthesis routes for bioactive sol-gel glasses: Alkoxides versus nitrates. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouquerol, F.; Luciani, L.; Llewellyn, P. Texture des matériaux pulvérulents ou poreux. Tech. De L’ingénieur: Anal. Et Caractérisation 2003, P2, 1050.1–1050.24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.H.; Yamamoto, T.; Sakai, Y. Development of microfluidic device for electrical/physical characterization of single cell. IEEE J. MEMS 2006, 15, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Hwang, S.W. Biodegradable materials for multilayer transient printed circuit boards. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 7371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.J. Structural Chemistry of Glasses, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; ISBN 9780080518039. [Google Scholar]
- Gerhardt, L.C.; Boccaccini, A.R. Bioactive Glass and Glass-Ceramic Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering. Materials 2010, 3, 3867–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharbi, A.; Feki, H.F. Novel alkali borosilicate glasses: Preparation, structural investigation and thermal study. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 32, 1456–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guirleo, G. Etude des Propriétés Electriques et Optiques D’hétérostructures Si/CaF2 Déposées sur des Substrats de Si; Id: tel-00002652; Université de la Méditerranée, Aix-Marseille II: Marseille, France, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Brain, T.F. The American Association of Neurological Surgeons. The Joint Section on Neurotrauma and critical Care. Recommendations for intracranial pressure monitoring technology. J. Neurotrauma 2007, 5, 45–54. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, J.; Yan, Y.; Bai, W.; Xue, Y.; Gamble, P.; Tian, L.; Kandela, I.; Haney, C.R.; Spees, W.; Lee, Y.; et al. Bioresorbable pressure sensors protected with thermally grown silicon dioxide for the monitoring of chronic diseases and healing processes. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Liu, Z.; Bai, W.; Liu, Y.; Yan, Y.; Xue, Y.; Kandela, I.; Pezhouh, M.; Macewan, M.R.; Huang, Y.; et al. Bioresorbable optical sensor systems for monitoring of intracranial pressure and temperature. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, 1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| BaG | SiO2 | CaO | Na2O | P2O5 | CaF2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference | 46 | 24 | 24 | 6 | 0 |
| BaG-F5 | 46 | 22 | 23 | 4 | 5 |
| BaG-F10 | 45 | 21 | 22 | 2 | 10 |
| BaG-F20 | 41 | 18 | 20 | 1 | 20 |
| Chemical Element | Valence Layer | Electronegativity (Pauling Scale) | Oxydation State | Electrical Conductivity (s·m−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14Si | 3s2 3p2 | 1.9 | +1, +2, +3, +4 | 2.52 × 10−4 |
| 9F | 2s2 2p5 | 3.98 | −1 | - |
| 8O | 3s2 3p4 | 3.44 | −2, −1 | - |
| 20Ca | 4s2 | 1 | +2 | 29.8 × 106 |
| 11Na | 3s1 | 0.93 | +1 | 21 × 106 |
| 15P | 3s2 3p3 | 2.19 | ±3, 5, 4 | 1.0 × 10−9 |
| Specific Surface (m2·g−1) | Pore Diameter (Å) | Specific Pore Volume 10−3 (cm3·g−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reference | 1.205 ± 0.03 | 52.11 ± 0.3 | 1.630 ± 0.04 |
| BaG-F5 | 1.004 ± 0.03 | 49.37 ± 0.3 | 1.185 ± 0.04 |
| BaG-F10 | 0.704 ± 0.03 | 46.2 ± 0.3 | 0.834 ± 0.04 |
| BaG-F20 | 0.098 ± 0.03 | 40.05 ± 0.3 | 0.073 ± 0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gharbi, A.; Kallel, A.Y.; Kanoun, O.; Cheikhrouhou-Koubaa, W.; Contag, C.H.; Antoniac, I.; Derbel, N.; Ashammakhi, N. A Biodegradable Bioactive Glass-Based Hydration Sensor for Biomedical Applications. Micromachines 2023, 14, 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14010226
Gharbi A, Kallel AY, Kanoun O, Cheikhrouhou-Koubaa W, Contag CH, Antoniac I, Derbel N, Ashammakhi N. A Biodegradable Bioactive Glass-Based Hydration Sensor for Biomedical Applications. Micromachines. 2023; 14(1):226. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14010226
Chicago/Turabian StyleGharbi, Amina, Ahmed Yahia Kallel, Olfa Kanoun, Wissem Cheikhrouhou-Koubaa, Christopher H. Contag, Iulian Antoniac, Nabil Derbel, and Nureddin Ashammakhi. 2023. "A Biodegradable Bioactive Glass-Based Hydration Sensor for Biomedical Applications" Micromachines 14, no. 1: 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14010226
APA StyleGharbi, A., Kallel, A. Y., Kanoun, O., Cheikhrouhou-Koubaa, W., Contag, C. H., Antoniac, I., Derbel, N., & Ashammakhi, N. (2023). A Biodegradable Bioactive Glass-Based Hydration Sensor for Biomedical Applications. Micromachines, 14(1), 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14010226











