FPGA Implementation of AI-Based Inverter IGBT Open Circuit Fault Diagnosis of Induction Motor Drives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
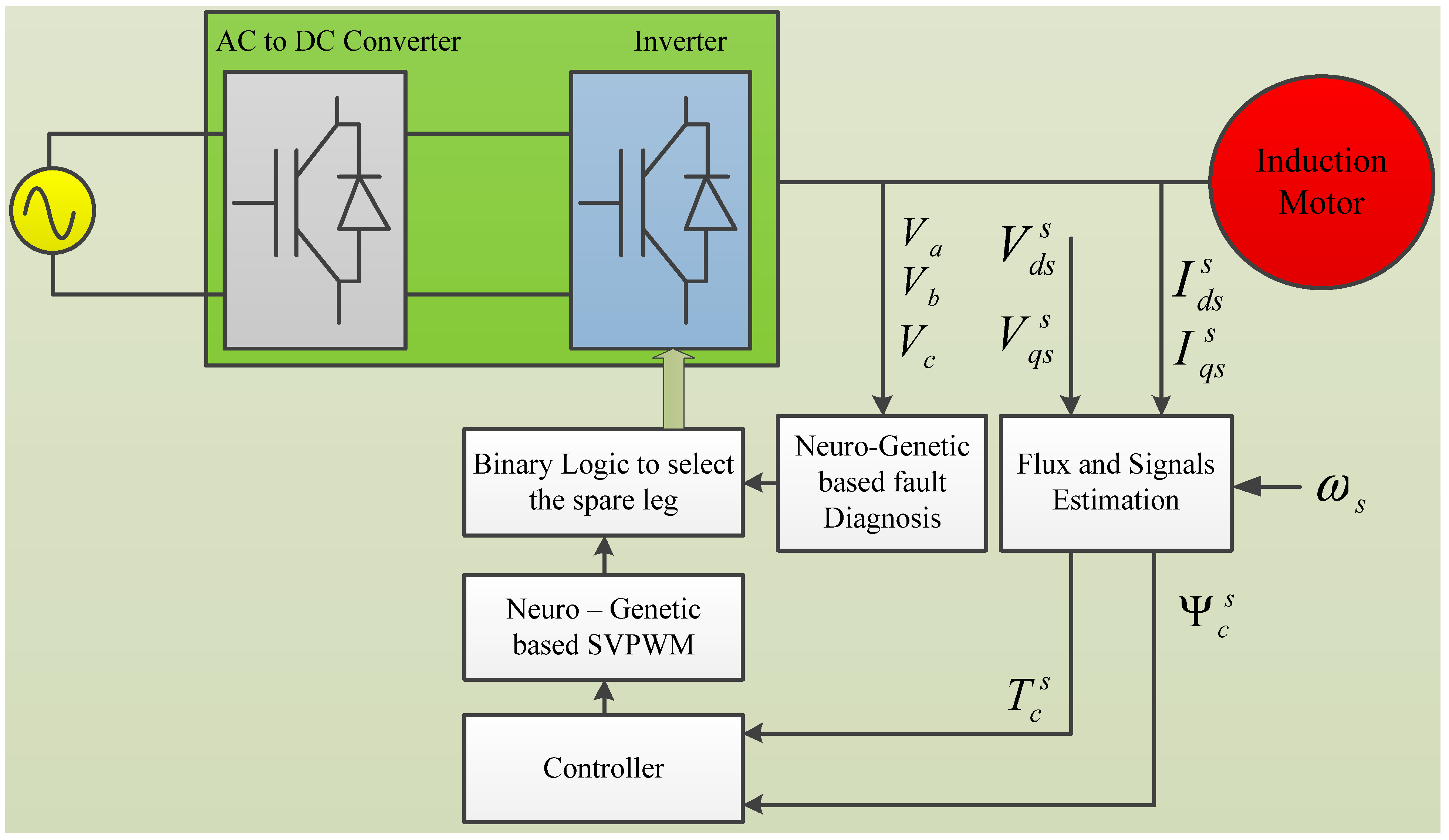
2. Proposed System Description
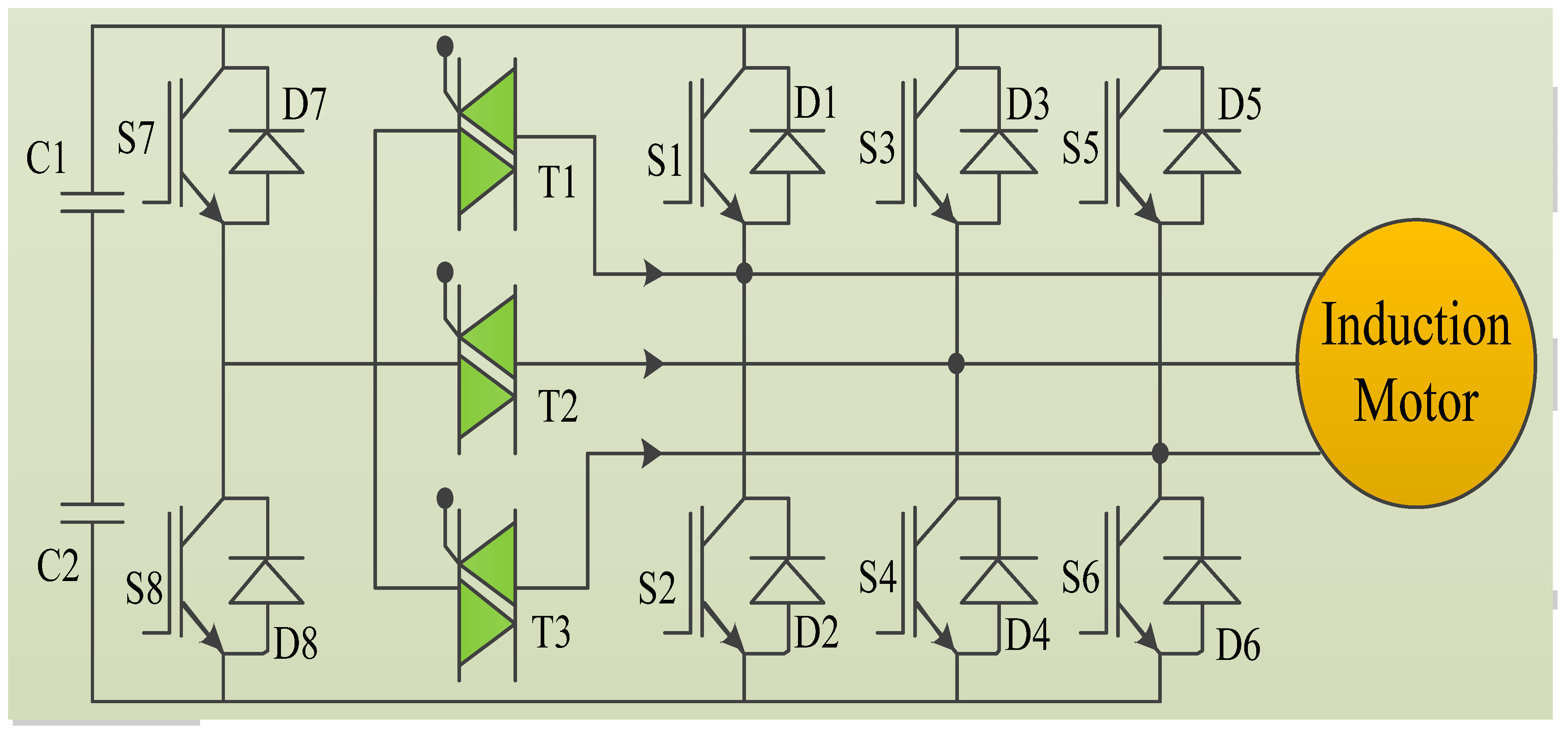
2.1. Reconfiguration of Inverter Topology
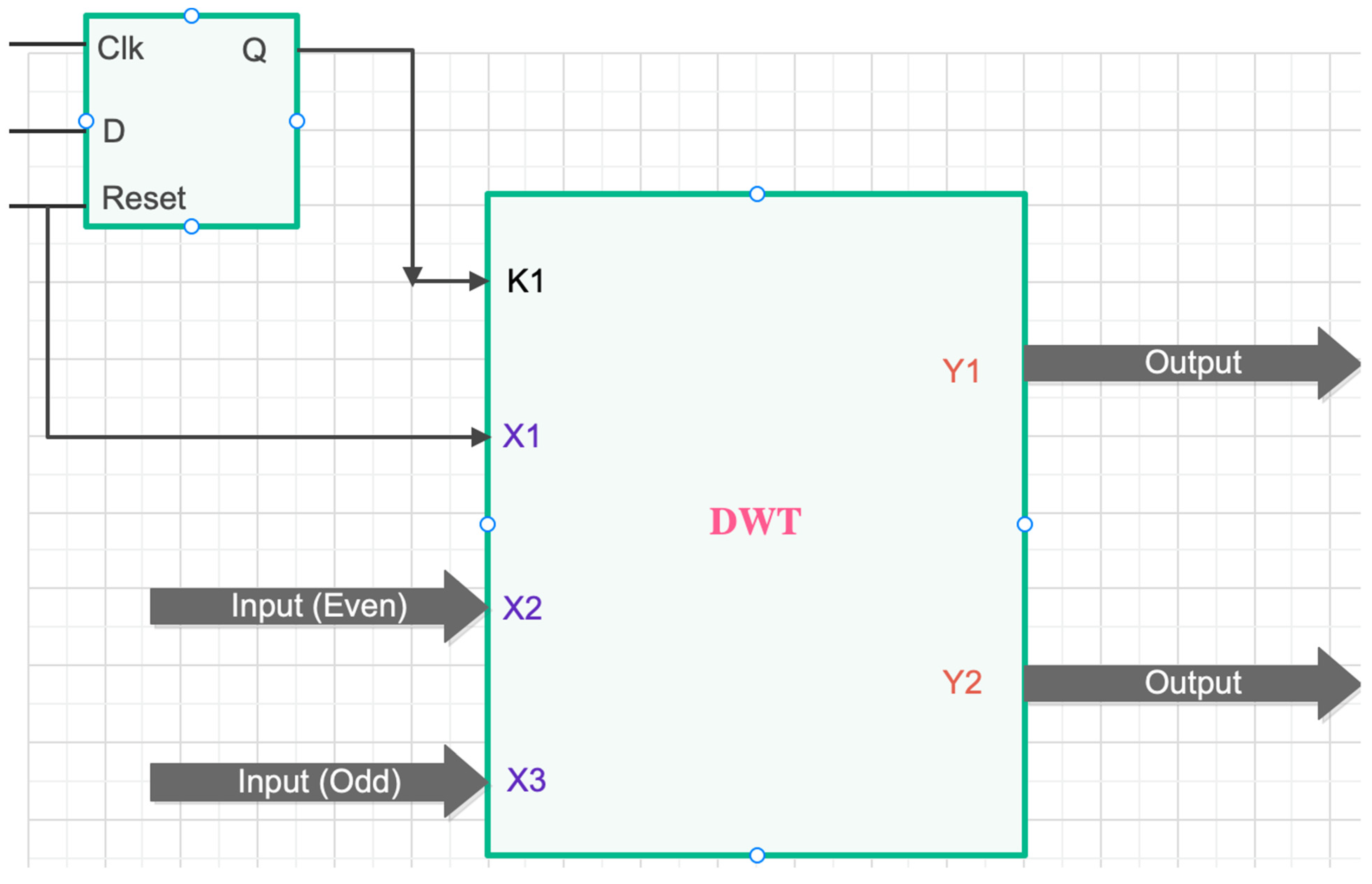
2.2. Fault Diagnosis Based on a FPGA
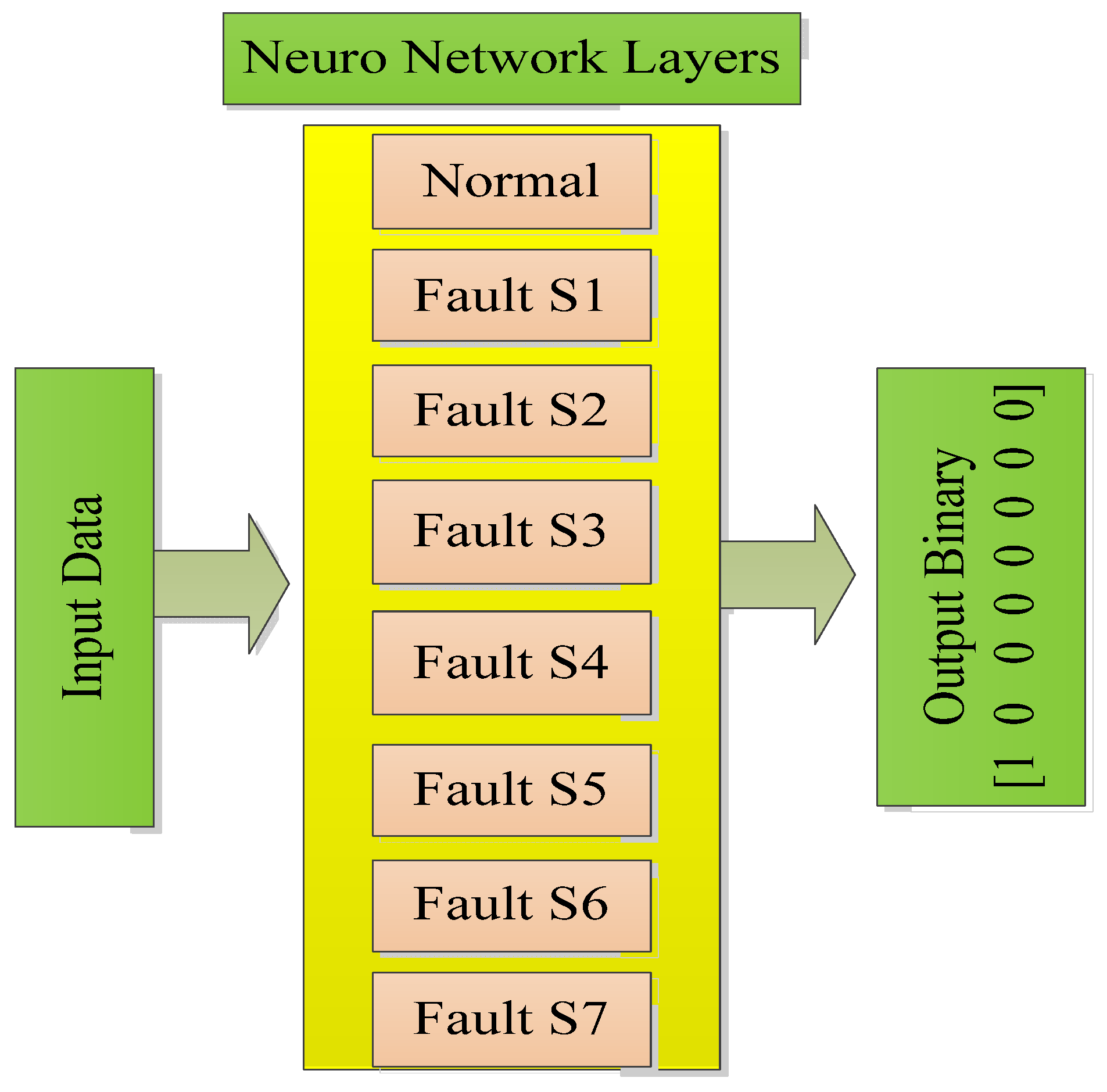
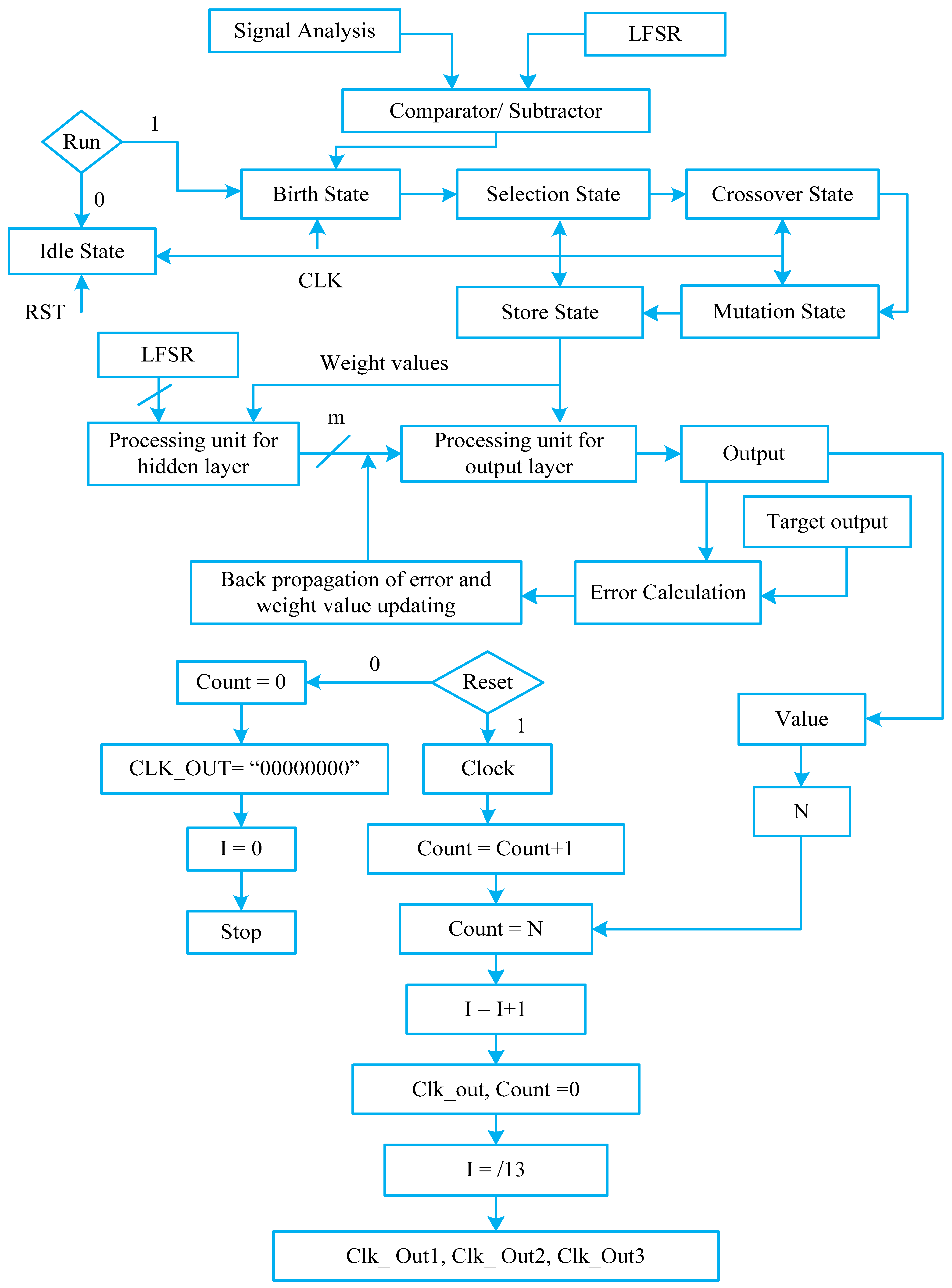
3. Neuro-Genetic Approach for Fault Classification
Neuro-Genetic Architecture Design
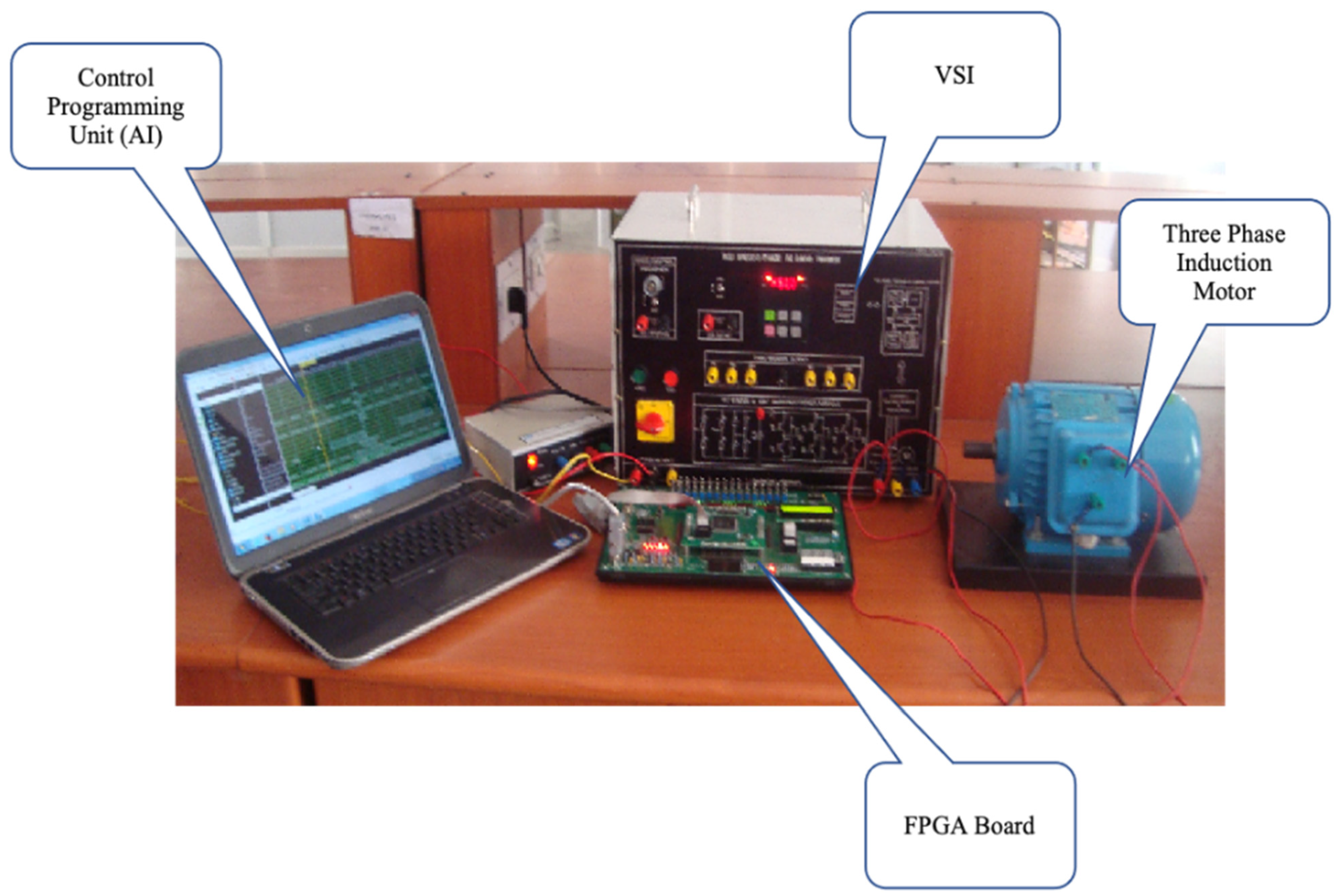
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gangsar, P.; Tiwari, R. Signal based condition monitoring techniques for fault detection and diagnosis of induction motors: A state-of-the-art review. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 144, 106908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoualdia, T.; Lakehal, A.; Chelli, Z.; Khoualdia, K.; Nessaib, K. Optimized multi-layer perceptron artificial neural network-based fault diagnosis of induction motor using vibration signals. Diagnostyka 2021, 22, 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Popa, L.M.; Jensen, B.B.; Ritchie, E.; Boldea, I. Condition monitoring of Wind Generators. In Proceedings of the 38th IAS Annual Meeting on Conference Record of the Industry Applications Conference, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 12–16 October 2003; Volume 3, pp. 1839–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Janabi, S.; Rawat, S.; Patel, A.; Al-Shourbaji, I. Design and evaluation of a hybrid system for detection and prediction of faults in electrical transformers. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2015, 67, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sica, F.C.; Guimarães, F.G.; de Oliveira Duarte, R.; Reis, A.J. A cognitive system for fault prognosis in power transformers. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2015, 127, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.N.; Hao, W. Development of a self- tuned neuro-fuzzy controller for induction motor drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2007, 43, 1108–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihet-Popa, L.; Bak-Jensen, B.; Ritchie, E.; Boldea, I. Current Signature Analysis to Diagnose Incipient Faults in Wind Generator Systems. In Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Advanced Electromechanical Motion Systems-Electromotion, ELECTROMOTION 2003, Marrakech, Morocco, 26–28 November 2003; Volume 2, pp. 647–652. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, B. Developments in intelligent condition monitoring and diagnostics in System Integrity and Maintenance. In Proceedings of the 2nd Asia-Pacific Conference (ACSIM2000), Nanjing, China, 1 January 2000; Queensland University of Technology: Brisbane, Australia, 2000; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Naber, N.; Getz, T.; Kim, Y.; Petrosky, J. Real-Time Fault Detection and Diagnostics Using FPGA-Based Architectures. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Field Programmable Logic and Applications, Milan, Italy, 31 August–2 September 2010; IEEE Computer Society. pp. 346–351. [Google Scholar]
- Mihet-Popa, L.; Pacas, J.M. Failure Detection in Converter Fed Induction Machines under Different Operation Conditions. In Proceedings of the International Electric Machines and Drives Conference (IEMDC), San Antonio, TX, USA, 15–18 May 2005; Volume 3, pp. 967–974. [Google Scholar]
- Verucchi, C.J.; Acosta, G.G. Fault Detection and Diagnosis Techniques in Induction Electrical Machines. Lat. Am. Trans. 2007, 5, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.; Elhattab, A.; Shu, X.; He, C. A second-order stochastic resonance method enhanced by fractional-order derivative for mechanical fault detection. Nonlinear Dyn. 2021, 106, 707–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihet-Popa, L.; Prostean, O.; Szeidert, I.; Filip, I.; Vasar, C. Fault Detection Methods for Frequency Converters Fed Induction Machines. In Proceedings of the 12th IEEE Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation-ETFA, Patras, Greece, 25–28 September 2007; pp. 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zidani, F.; Diallo, D.; Benbouzid, M.E.H.; Said, R.N.A. Fuzzy-based approach for the diagnosis of fault modes in a voltage-fed PWM inverter induction motor drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Jiang, B.; Wang, Y. Incipient winding fault detection and diagnosis for squirrel-cage induction motors equipped on CRH trains. ISA Trans. 2020, 99, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihet-Popa, L. Current Signature Analysis as Diagnosis Media for incipient fault detection. J. Adv. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2007, 7, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatikonda, S.; Agarwal, P. Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) based neural network implementation of Motion Control and fault diagnosis of induction motor drive. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology, Chengdu, China, 21–24 April 2008; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Toma, R.N.; Prosvirin, A.E.; Kim, J.M. Bearing fault diagnosis of induction motors using a genetic algorithm and machine learning classifiers. Sensors 2020, 20, 1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ali, M.Z.; Shabbir, M.N.S.K.; Zaman, S.M.K.; Liang, X. Single-and multi-fault diagnosis using machine learning for variable frequency drive-fed induction motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 2324–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Hati, A.S. Review on machine learning algorithm-based fault detection in induction motors. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2021, 28, 1929–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, S.M.K.; Liang, X. An effective induction motor fault diagnosis approach using graph-based semi-supervised learning. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 7471–7482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabul, A.; Ünsal, A. A diagnosis method of multiple faults of induction motors based on vibration signal analysis. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 13th International Symposium on Diagnostics for Electrical Machines, Power Electronics and Drives (SDEMPED), Dallas, TX, USA, 22–25 August 2021; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Bazan, G.H.; Goedtel, A.; Duque-Perez, O.; Morinigo-Sotelo, D. Multi-Fault Diagnosis in Three-Phase Induction Motors Using Data Optimization and Machine Learning Techniques. Electronics 2021, 10, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamudio-Ramirez, I.; Antonino-DAVIU, J.A.; Osornio, R.A.; Dunai, L. Tracking of high-order stray-flux harmonics under starting for the detection of winding asymmetries in wound-rotor induction motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 69, 8463–8471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, P.K.; Biao, J.S. Fault Diagnosis of Induction Motors Under Untrained Loads with a Feature Adaptation and Improved Broad Learning Framework. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2021, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauricio, A.; Smith, W.A.; Randall, R.B.; Antoni, J.; Gryllias, K. Improved Envelope Spectrum via Feature Optimization-gram (IESFOgram): A novel tool for rolling element bearing diagnostics under non-stationary operating conditions. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 144, 106891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, O.A.; Abed, N.Y.; Ganu, S. Modelling and Characterization of Induction Motor Internal Faults Using Finite Element and Discrete Wavelet Transforms. IEEE Trans. Magnet. 2006, 42, 3434–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlShorman, O.; Alkahatni, F.; Masadeh, M.; Irfan, M.; Glowacz, A.; Althobiani, F.; Kozik, J.; Glowacz, W. Sounds and acoustic emission-based early fault diagnosis of induction motor: A review study. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2021, 13, 1687814021996915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerda, J.C.; Martinez, C.D.; Comer, J.M.; Hoe, D.H.K. An efficient FPGA random number generator using LFSRs and cellular automata. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 55th International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), Boise, ID, USA, 5–8 August 2012; pp. 912–915. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhary, A.; Goyal, D.; Shimi, S.L.; Akula, A. Condition monitoring and fault diagnosis of induction motors: A review. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2019, 26, 1221–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Range |
|---|---|
| Speed | 1390 rpm |
| Volts | 415 V |
| Frequency | 50 Hz |
| Power | 0.75 kW |
| Pole | 4 |
| Parameter | Power (W) | Voltage | Range | Icc (A) | Iccq (A) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vccint | 0.031 | 1.20 | 1.14 to 1.25 | 0.000 | 0.026 |
| Vccaux | 0.045 | 2.5 | 0.000 | 0.018 | |
| Vcco25 | 0.005 | 2.5 | 0.000 | 0.002 |
| Logic Utilization | Used | Available | Range |
| Total number of slice registers | 188 | 9312 | 2% |
| Number used as flip flops | 105 | ||
| Number used as latches | 83 | 2.5 | |
| Number of 4 input LUTs | 270 | 9312 | 2% |
| Logic Distribution | Used | Available | Range |
| Number of occupied slices | 217 | 4656 | 4% |
| Number of slices containing only related logic | 217 | 217 | 100% |
| Number of slices containing unrelated logic | 0 | 217 | 0% |
| Total Number of 4 input LUTs | 303 | 9312 | 3% |
| Number used as logic | 270 | ||
| Number used as a route-through | 33 | ||
| Number of bonded IOBs | 81 | 159 | 51% |
| IOB latches | 11 | ||
| Number of BUFGMUXs | 3 | 24 | 12% |
| Number of M|ULT|I18X18SIOs | 4 | 20 | 20% |
| Clock Net | Resource | Locked | Fanout | Net Skew (ns) | Max Delays (ns) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X4/y0_not001 | BUFGMUX_X2Y10 | No | 12 | 0.011 | 0.142 |
| Clk1_BUFGP | BUFGMUX_X2Y11 | No | 75 | 0.076 | 0.196 |
| State_out1_1_OBUF | BUFGMUX_X1Y10 | No | 11 | 0.030 | 0.148 |
| x3/ov4 | Local | 16 | 0.045 | 1.249 | |
| x3/ov1 | Local | 6 | 0.211 | 1.988 | |
| x3/ov3 | Local | 5 | 0.460 | 1.124 | |
| x3/ov2 | Local | 6 | 0.224 | 2.235 |
| Parameters | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Minimum period | 10.857 ns |
| Maximum frequency | 92.108 MHz |
| Minimum input arrival time before clock | 20.18 ns |
| Maximum output required time after clock | 11.99 ns |
| Maximum combinational path delay | 8.610 ns |
| Total REAL time to Xst completion | 11.00 s |
| Total CPU time to Xst completion | 10.41 s |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rajeswaran, N.; Thangaraj, R.; Mihet-Popa, L.; Krishna Vajjala, K.V.; Özer, Ö. FPGA Implementation of AI-Based Inverter IGBT Open Circuit Fault Diagnosis of Induction Motor Drives. Micromachines 2022, 13, 663. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13050663
Rajeswaran N, Thangaraj R, Mihet-Popa L, Krishna Vajjala KV, Özer Ö. FPGA Implementation of AI-Based Inverter IGBT Open Circuit Fault Diagnosis of Induction Motor Drives. Micromachines. 2022; 13(5):663. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13050663
Chicago/Turabian StyleRajeswaran, Nagalingam, Rajesh Thangaraj, Lucian Mihet-Popa, Kesava Vamsi Krishna Vajjala, and Özen Özer. 2022. "FPGA Implementation of AI-Based Inverter IGBT Open Circuit Fault Diagnosis of Induction Motor Drives" Micromachines 13, no. 5: 663. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13050663
APA StyleRajeswaran, N., Thangaraj, R., Mihet-Popa, L., Krishna Vajjala, K. V., & Özer, Ö. (2022). FPGA Implementation of AI-Based Inverter IGBT Open Circuit Fault Diagnosis of Induction Motor Drives. Micromachines, 13(5), 663. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13050663







