Amperometric Monitoring of Dissolution of pH-Responsive EUDRAGIT® Polymer Film Coatings
Abstract
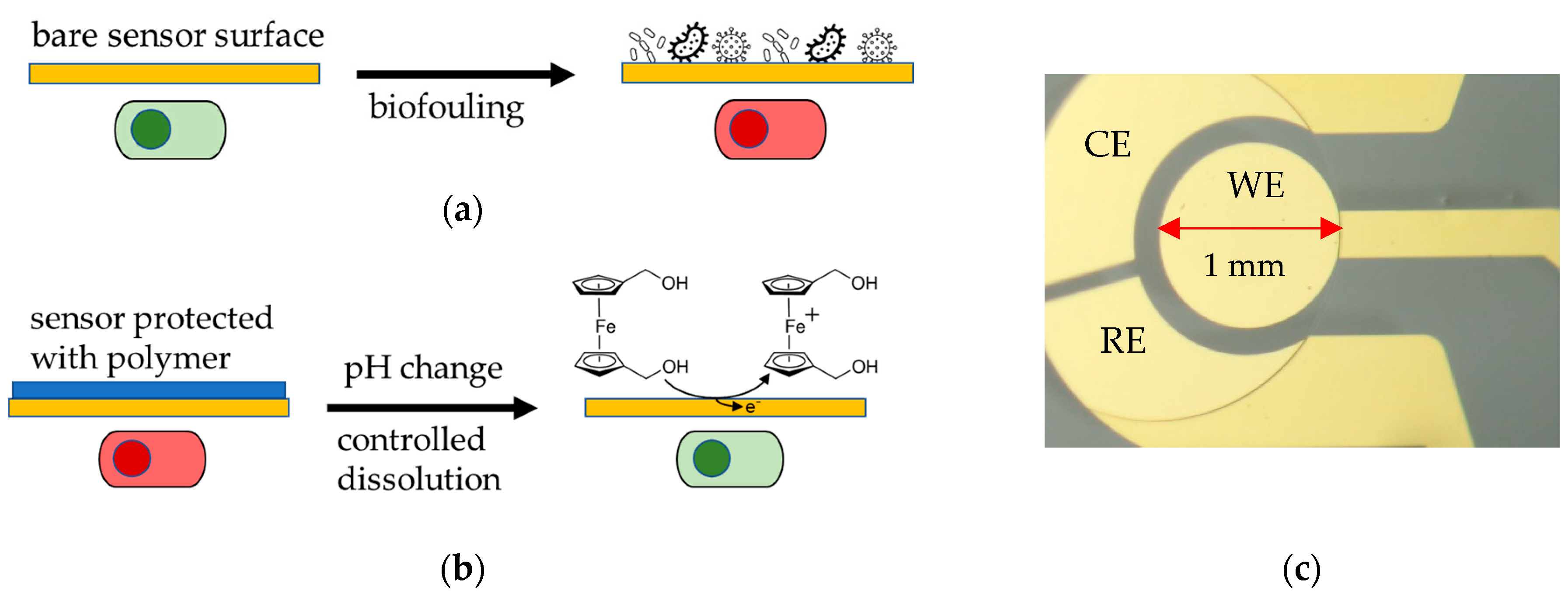
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
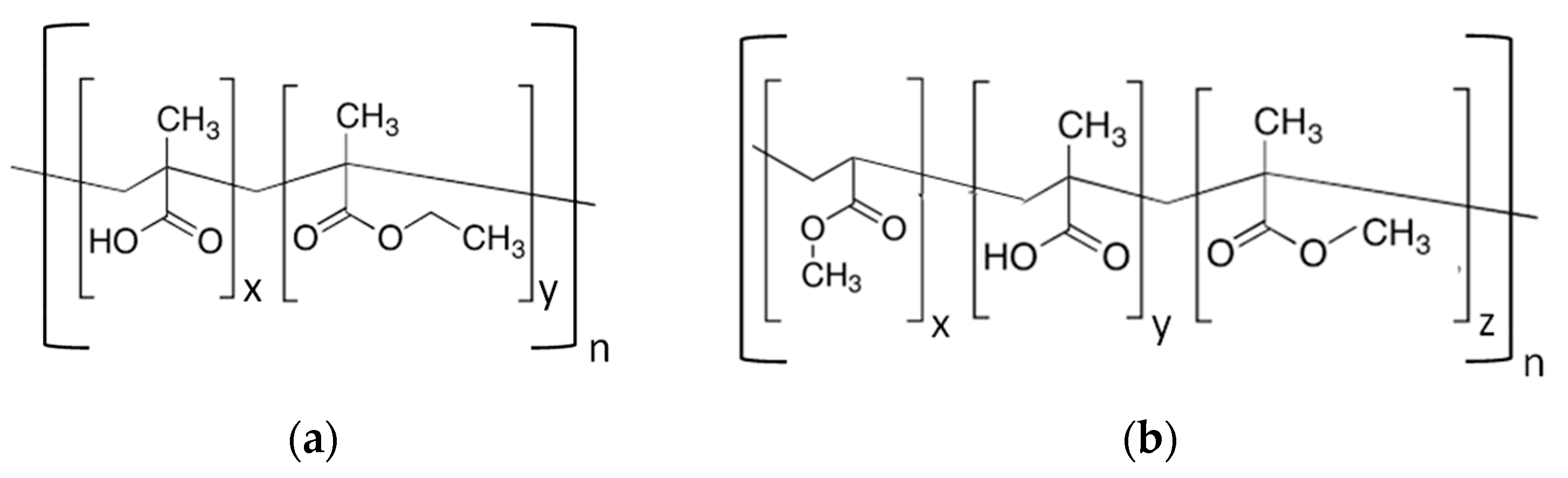
2.1. Materials
2.2. Membrane Preparation
2.3. Methods
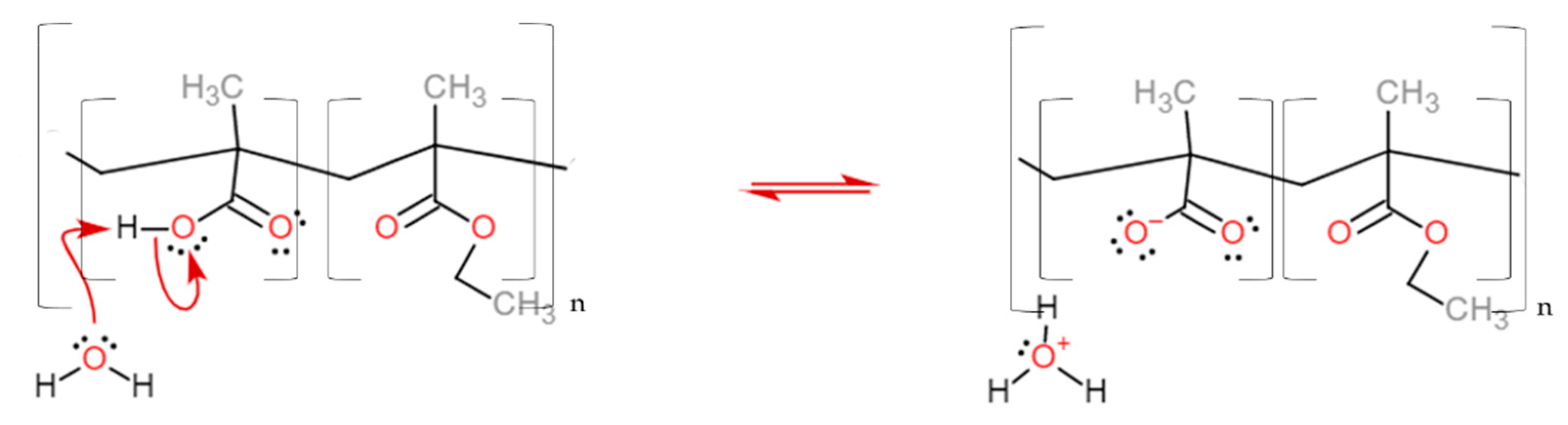
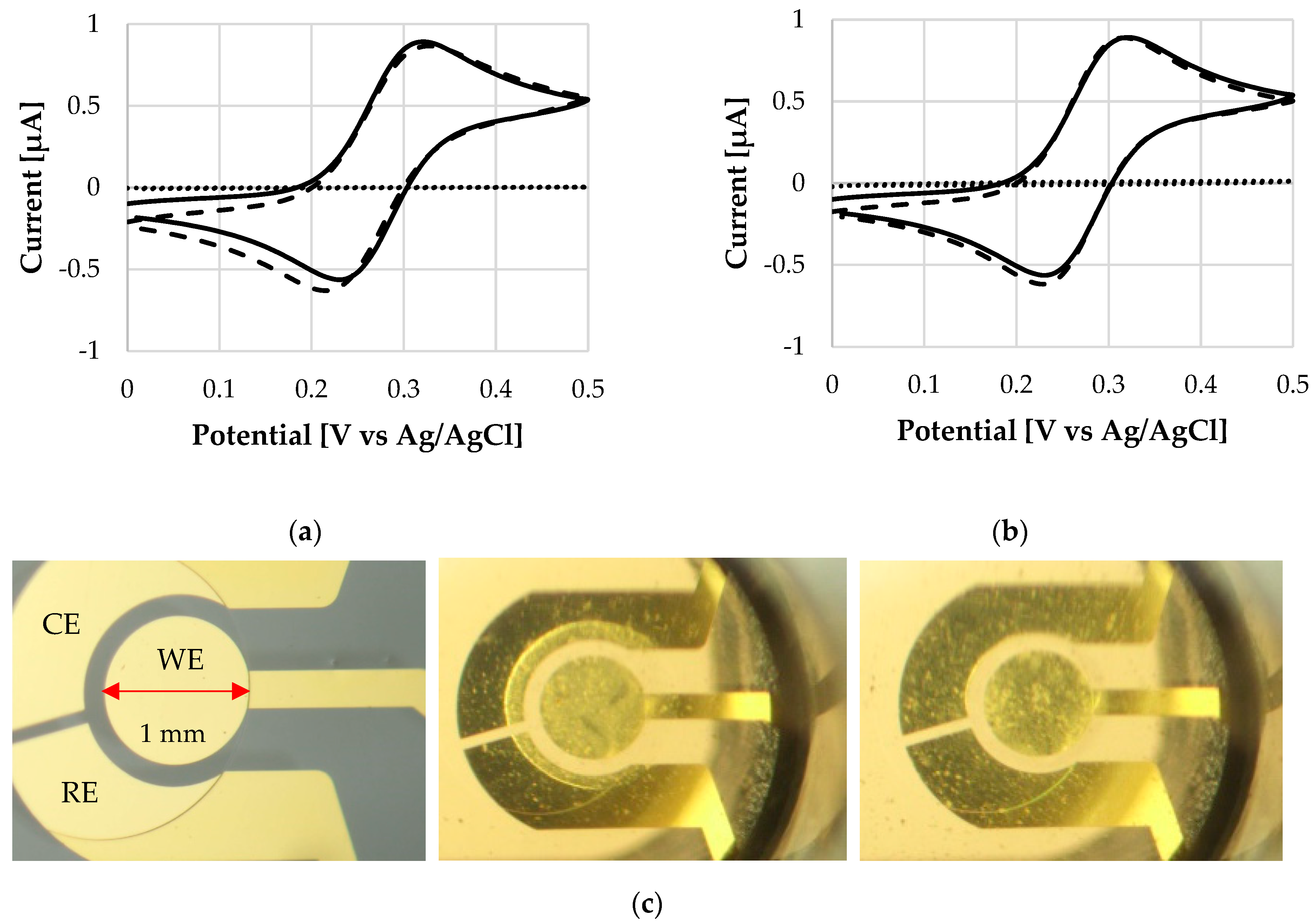
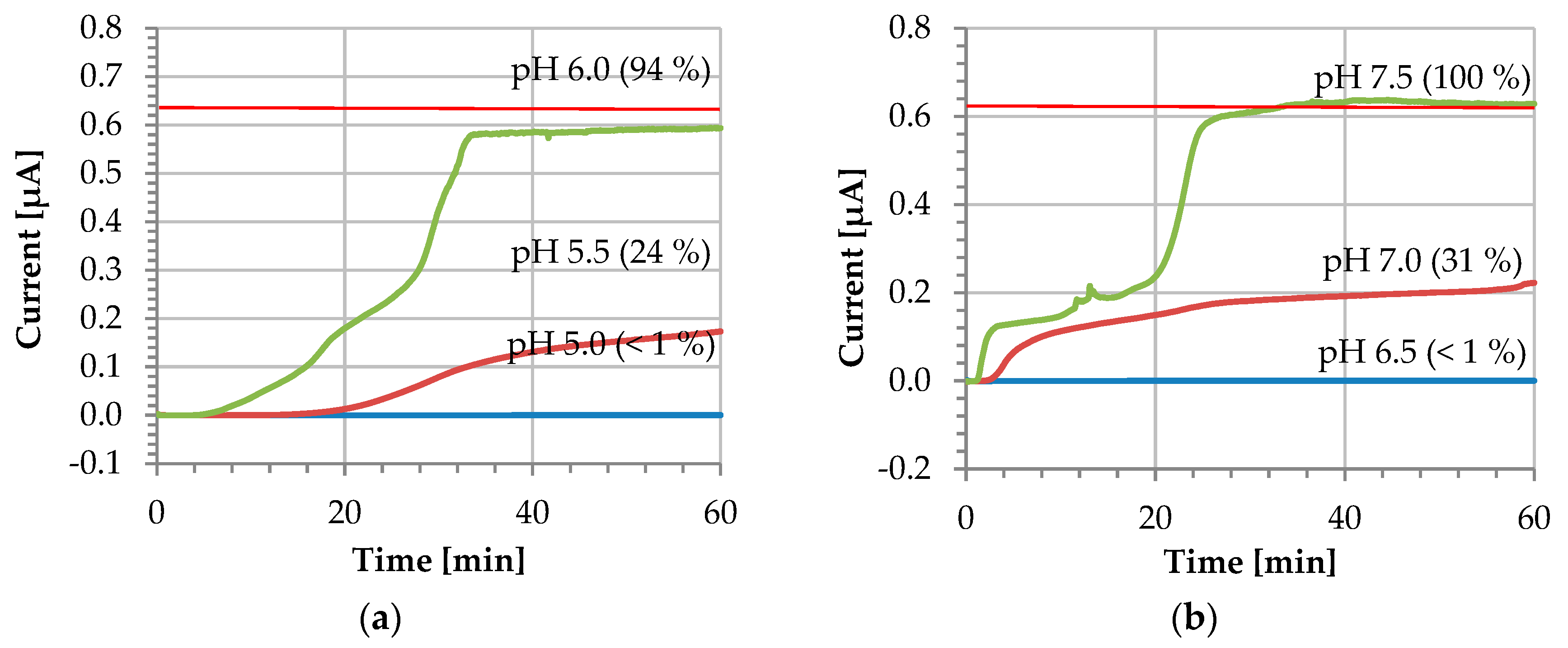
3. Results and Discussion
Dissolution Profile Characterisation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meyer, A.M.; Klein, C.; Fünfrocken, E.; Kautenburger, R.; Beck, H.P. Real-Time Monitoring of Water Quality to Identify Pollution Pathways in Small and Middle Scale Rivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 2323–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckingham, B.; Caswell, K.; Wilson, D.M. Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2007, 14, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Ha, N.; Ou, J.Z.; Berean, K.J. Ingestible Sensors. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 468–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, P.H.; Li, B.R. Antifouling Strategies in Advanced Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors. Analyst 2020, 145, 1110–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Jin, G.; Wang, G.; Liu, T.; Liu, X.; Wang, B.; Cao, H. Current Sampling Methods for Gut Microbiota: A Call for More Precise Devices. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Berean, K.J.; Ha, N.; Chrimes, A.F.; Xu, K.; Grando, D.; Ou, J.Z.; Pillai, N.; Campbell, J.L.; Brkljača, R.; et al. A Human Pilot Trial of Ingestible Electronic Capsules Capable of Sensing Different Gases in the Gut. Nat. Electron. 2018, 1, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bik, E.M.; Eckburg, P.B.; Gill, S.R.; Nelson, K.E.; Purdom, E.A.; Francois, F.; Perez-Perez, G.; Blaser, M.J.; Relman, D.A. Molecular Analysis of the Bacterial Microbiota in the Human Stomach. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Ward, S.A. Future Is Ready for Swallowable Sensors. HepatoBiliary Surg. Nutr. 2019, 8, 267–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakral, S.; Thakral, N.K.; Majumdar, D.K. Eudragit®: A Technology Evaluation. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kshirsagar, S.J.; Bhalekar, M.R.; Umap, R.R. In Vitro in Vivo Comparison of Two PH Sensitive Eudragit Polymers for Colon Specific Drug Delivery. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2009, 1, 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- Patra, C.N.; Priya, R.; Swain, S.; Kumar Jena, G.; Panigrahi, K.C.; Ghose, D. Pharmaceutical Significance of Eudragit: A Review. Future J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 3, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghimipour, E.; Rezaei, M.; Kouchak, M.; Fatahiasl, J.; Angali, K.A.; Ramezani, Z.; Amini, M.; Dorkoosh, F.A.; Handali, S. Effects of Coating Layer and Release Medium on Release Profile from Coated Capsules with Eudragit FS 30D: An in Vitro and in Vivo Study. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Valdepenas Montiel, V.; Sempionatto, J.R.; Esteban-Fernández De Ávila, B.; Whitworth, A.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarrón, J.M.; Wang, J. Delayed Sensor Activation Based on Transient Coatings: Biofouling Protection in Complex Biofluids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 14050–14053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evonik Health Care. Available online: https://healthcare.evonik.com/en/products/pharmaceutical-excipients/EUDRAGIT (accessed on 1 April 2021).
- Liu, F.; Merchant, H.A.; Kulkarni, R.P.; Alkademi, M.; Basit, A.W. Evolution of a Physiological PH 6.8 Bicarbonate Buffer System: Application to the Dissolution Testing of Enteric Coated Products. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 78, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fadda, H.M.; Basit, A.W. Dissolution of PH Responsive Formulations in Media Resembling Intestinal Fluids: Bicarbonate versus Phosphate Buffers. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2005, 15, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Sánchez, C.; McNeil, C.J.; Rawson, K. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Studies of Polymer Degradation: Application to Biosensor Development. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2005, 24, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajkossy, T.; Jurczakowski, R. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy in Interfacial Studies. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2017, 1, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications; Department of Chemistry, University of Texas at Austin: Austin, TX, USA, 2000; p. 833. [Google Scholar]
- Analysis, Q.C. Quantitative Chemical Analysis. Methods Geochem. Geophys. 1971, 5, 89–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Function | Ingredient | [%] |
| Polymer | EUDRAGIT® FS 30 D | 60.6 |
| Anti-tacking | PlasACRYL™ T20 | 9.1 |
| Diluent | Water | 30.3 |
| Function | Ingredient | [%] |
| Polymer | EUDRAGIT® L 30 D-55 | 57.0 |
| Anti-tacking | PlasACRYL™ HTP20 | 14.6 |
| Diluent | Water | 28.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mestres, J.; Leonardi, F.; Mathwig, K. Amperometric Monitoring of Dissolution of pH-Responsive EUDRAGIT® Polymer Film Coatings. Micromachines 2022, 13, 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13030362
Mestres J, Leonardi F, Mathwig K. Amperometric Monitoring of Dissolution of pH-Responsive EUDRAGIT® Polymer Film Coatings. Micromachines. 2022; 13(3):362. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13030362
Chicago/Turabian StyleMestres, Júlia, Francesca Leonardi, and Klaus Mathwig. 2022. "Amperometric Monitoring of Dissolution of pH-Responsive EUDRAGIT® Polymer Film Coatings" Micromachines 13, no. 3: 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13030362
APA StyleMestres, J., Leonardi, F., & Mathwig, K. (2022). Amperometric Monitoring of Dissolution of pH-Responsive EUDRAGIT® Polymer Film Coatings. Micromachines, 13(3), 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13030362







