The Road to Unconventional Detections: Paper-Based Microfluidic Chips
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overview of Paper-Based Microfluidic Chips
2.1. Characteristics of Paper-Based Microfluidic Chips
2.2. Materials of Paper-Based Microfluidic Chips
3. Preparation Method of Paper-Based Microfluidic Chip
3.1. Two-Dimensional Paper Chip Preparation
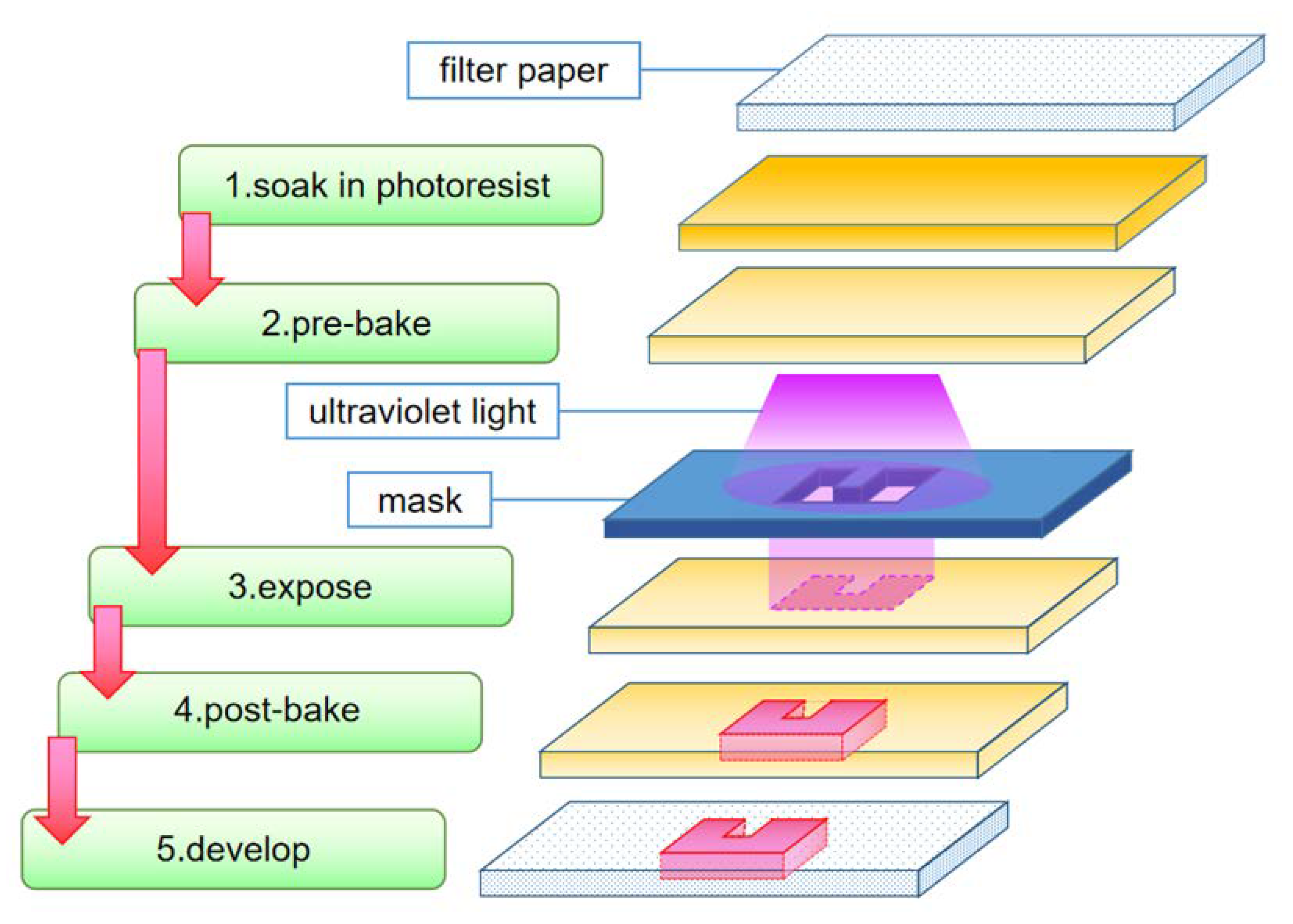
3.1.1. Photolithography
3.1.2. Plasma Treatment Technology
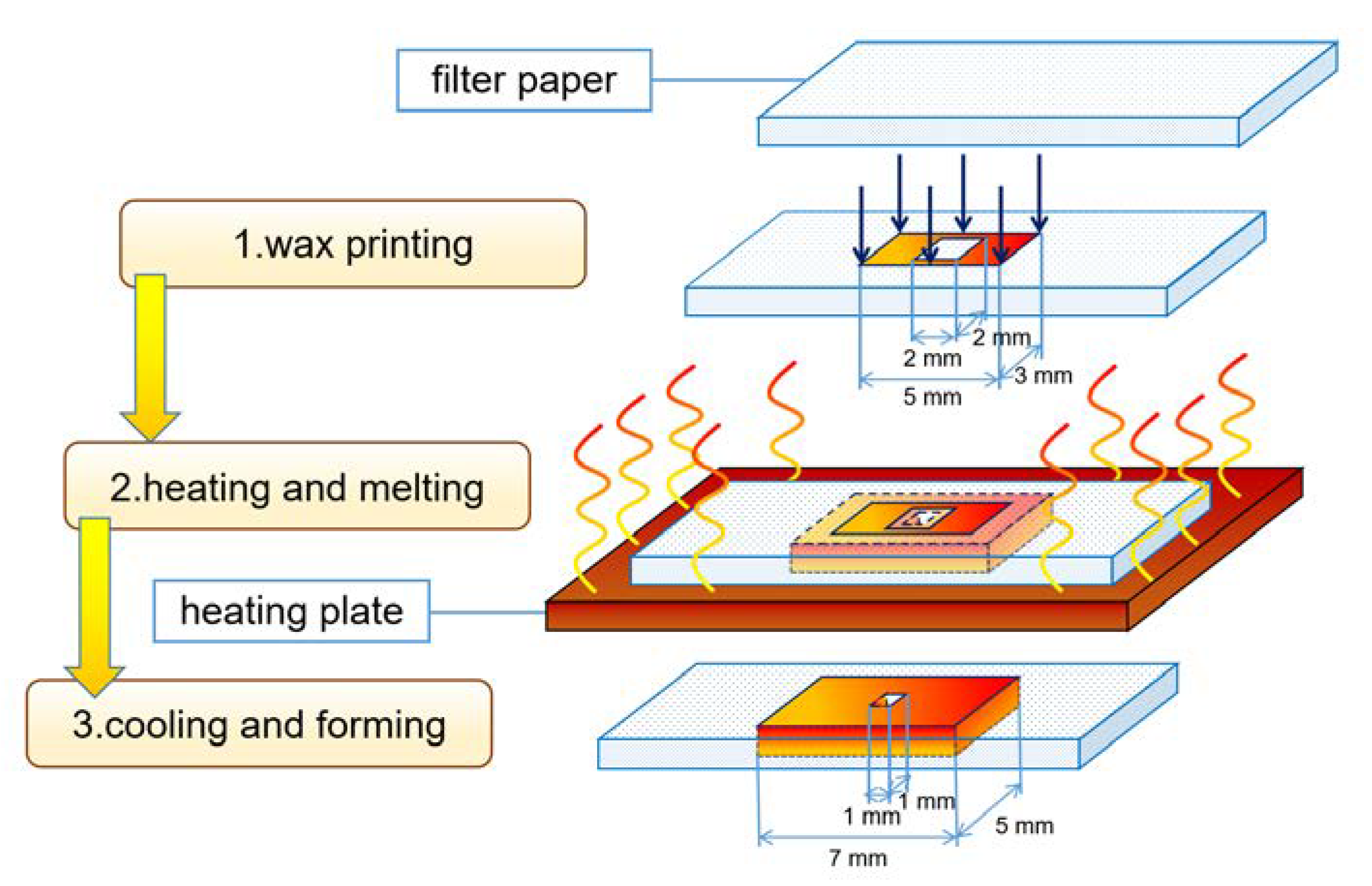
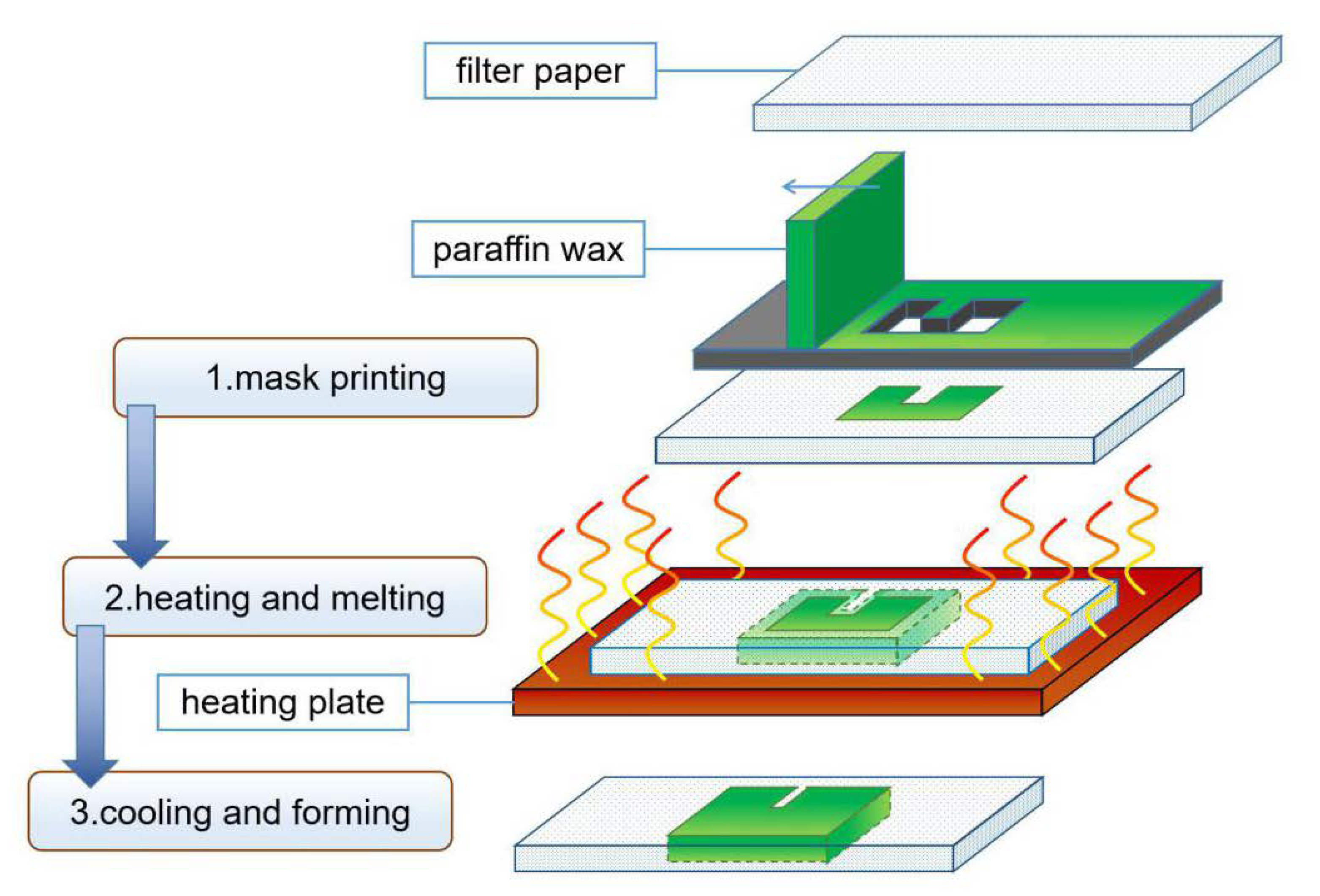
3.1.3. Wax Printing
3.1.4. Inkjet Method
3.1.5. Screen Printing
3.1.6. Laser Processing Technology
3.2. Three-Dimensional Paper Chips Preparation
3.2.1. Origami Method
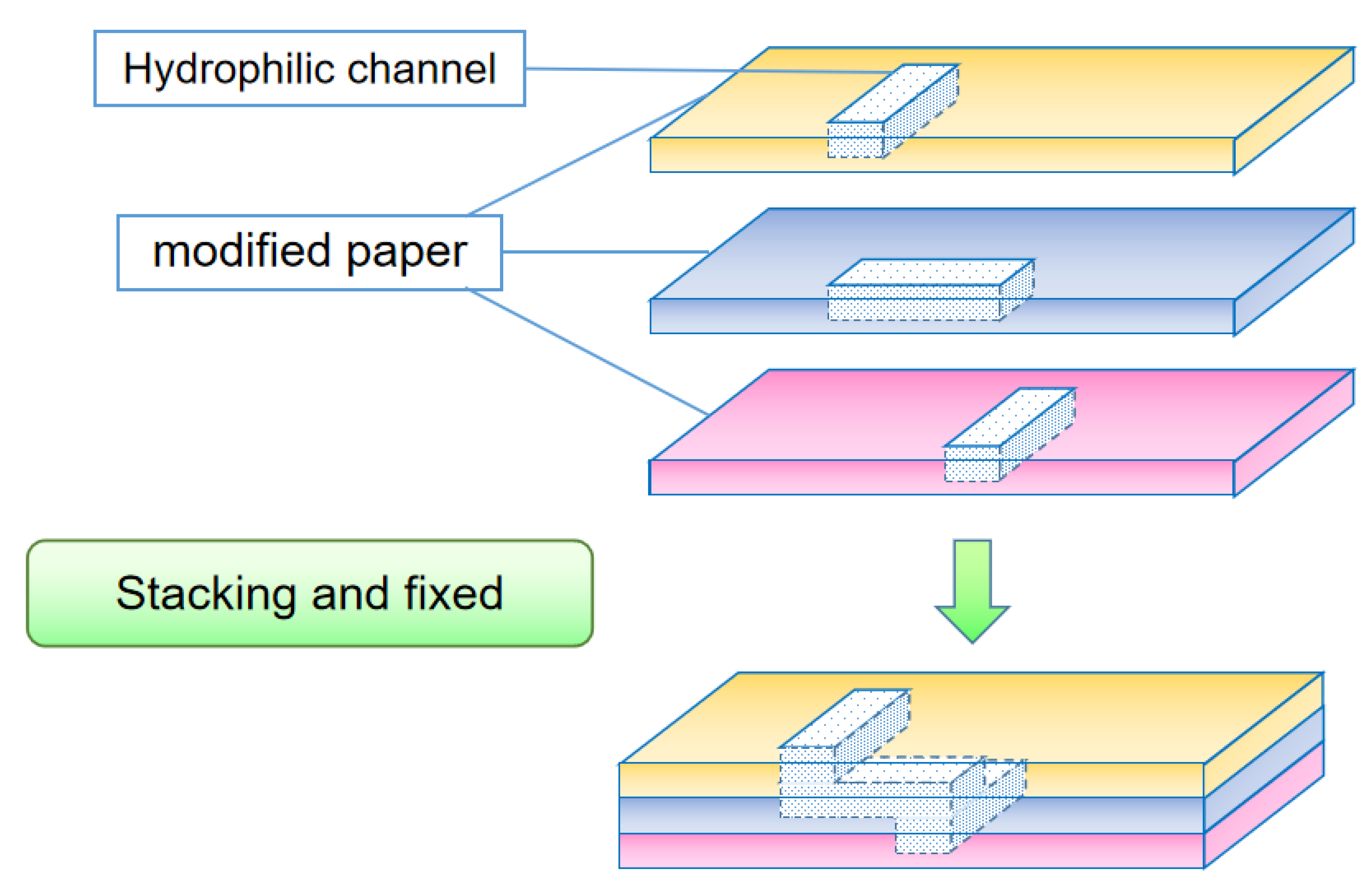
3.2.2. Lamination Method
3.2.3. Other Methods
4. Analysis Method of Paper-Based Microfluidic Chip
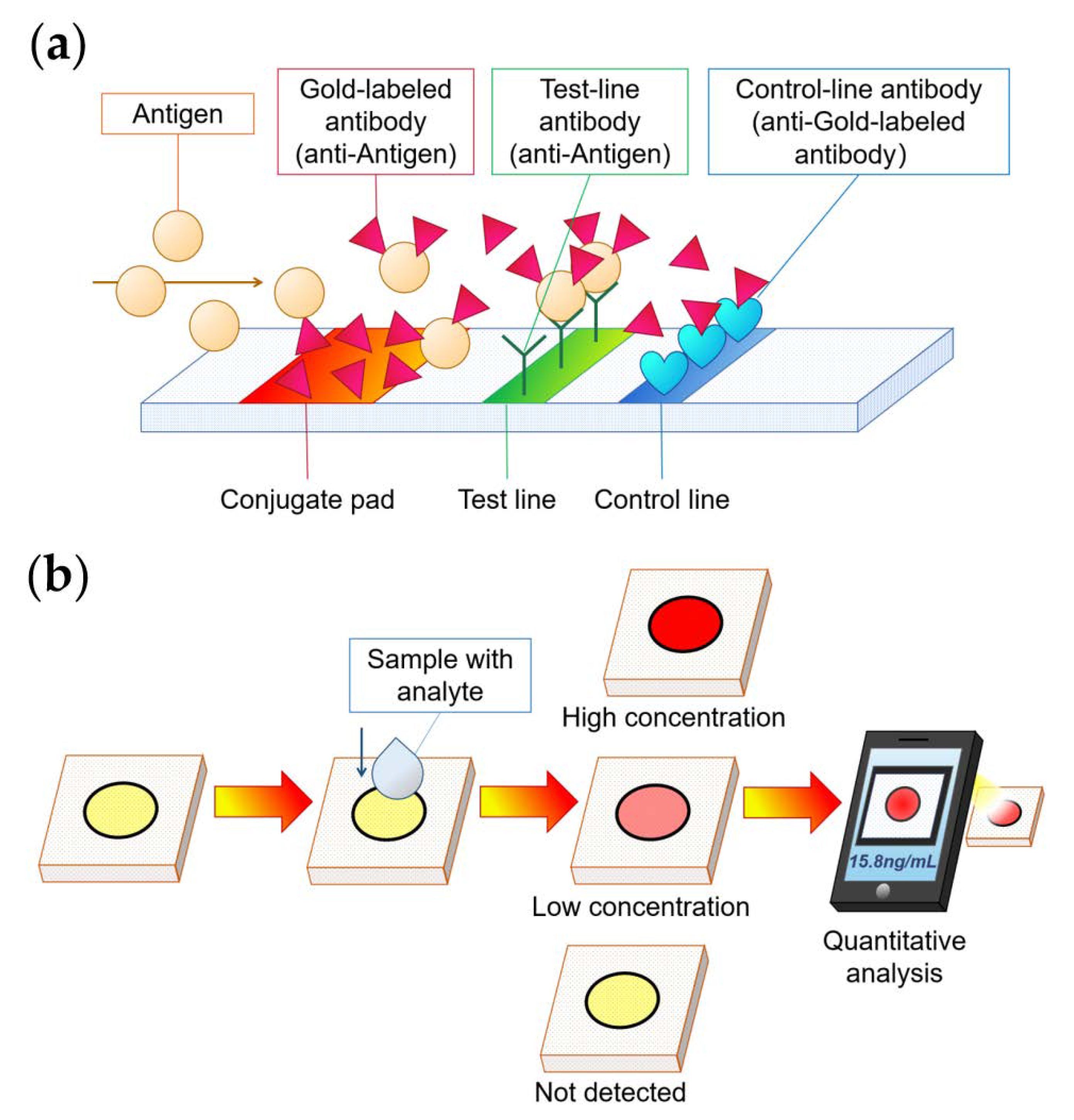
4.1. Colorimetric Method
4.2. Electrochemical Method
4.3. Fluorescence Method
4.4. Combining with Electronic Equipment
5. Application of Paper-Based Microfluidic Chip
5.1. Biochemical Marker Detection
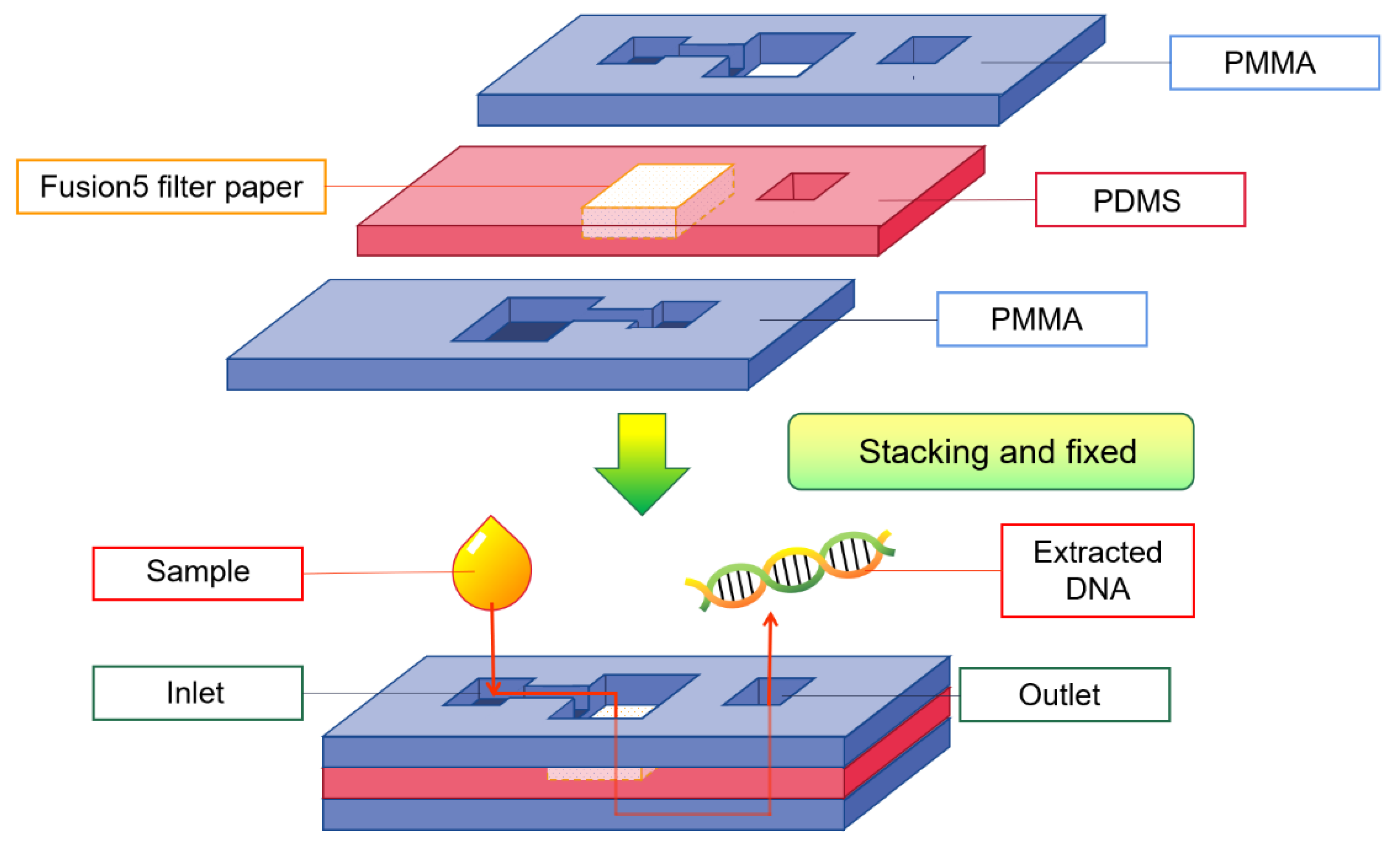
5.2. Nucleic Acid Preparation
5.2.1. DNA Extraction
5.2.2. Nucleic Acid Amplification
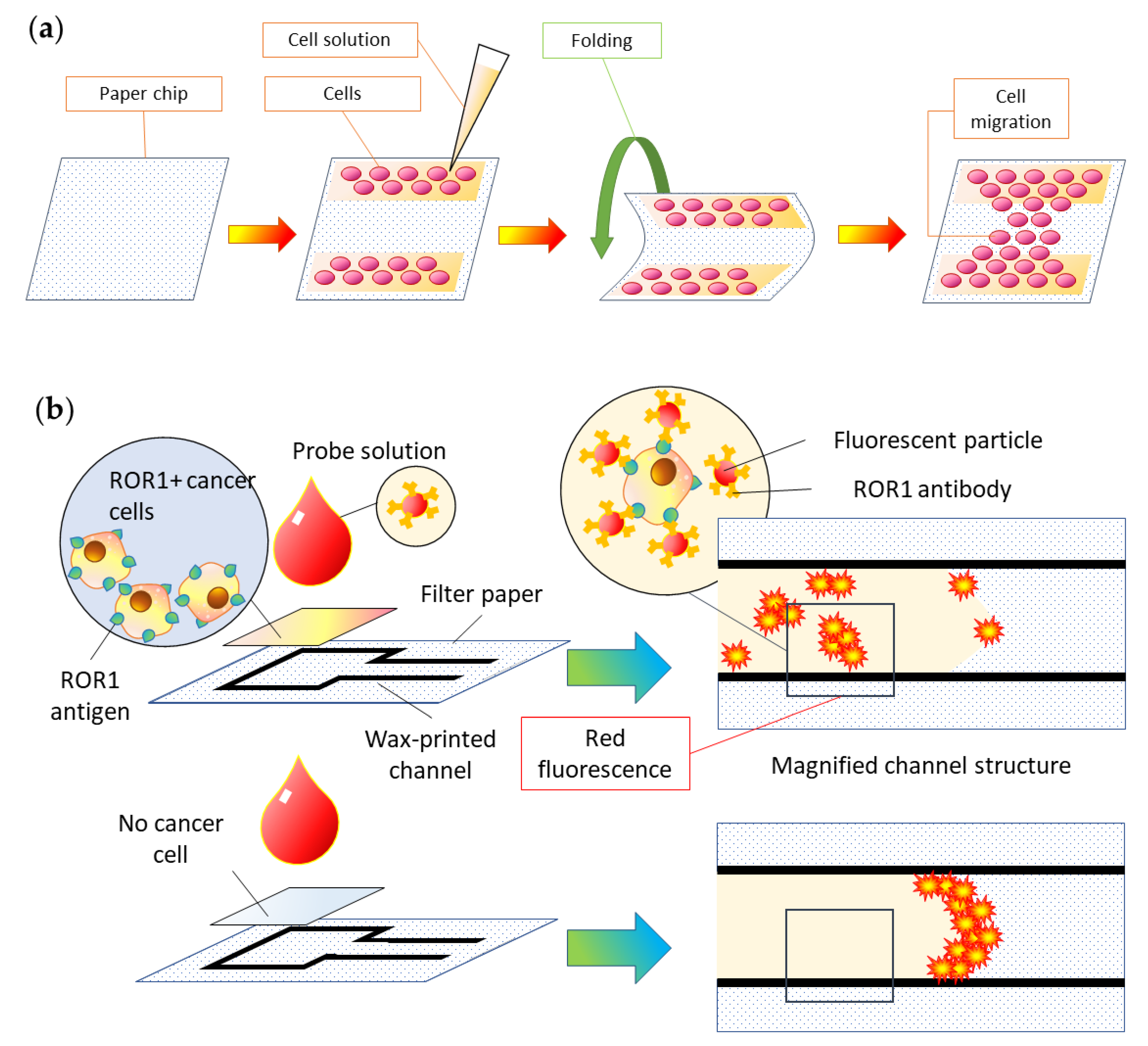
5.3. Cell Analysis
5.4. Other Applications
6. Summary and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manz, A.; Graber, N.; Widmer, H.M. Miniaturized total chemical-analysis systems—A novel concept for chemical sensing. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 1990, 1, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitesides, G.M. The origins and the future of microfluidics. Nature 2006, 442, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Kong, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, Y. Roll-to-roll wax transfer for rapid and batch fabrication of paper-based microfluidics. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2019, 24, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimchuk, E.; Nilghaz, A.; Sun, S.; Lu, X. Determination of norfloxacin residues in foods by exploiting the coffee-ring effect and paper-based microfluidics device coupling with smartphone-based detection. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewjua, K.; Nakthong, P.; Chailapakul, O.; Siangproh, W. Flow-based System: A Highly Efficient Tool Speeds Up Data Production and Improves Analytical Performance. Anal. Sci. 2021, 37, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.-Y. Lab-on-a-Chip Biosensors. In Introduction to Biosensors: From Electric Circuits to Immunosensors; Yoon, J.-Y., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 257–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisowski, P.; Zarzycki, P.K. Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Devices (μPADs) and Micro Total Analysis Systems (μTAS): Development, Applications and Future Trends. Chromatographia 2013, 76, 1201–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.W.; Phillips, S.T.; Butte, M.J.; Whitesides, G.M. Patterned Paper as a Platform for Inexpensive, Low-Volume, Portable Bioassays. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1318–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.I.G.S.; Jayawardane, B.M.; Kolev, S.D.; McKelvie, I.D. Developments of microfluidic paper-based analytical devices (μPADs) for water analysis: A review. Talanta 2018, 177, 176–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, M.; Sanjay, S.T.; Benhabib, M.; Xu, F.; Li, X. Low-cost bioanalysis on paper-based and its hybrid microfluidic platforms. Talanta 2015, 145, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabbott, S.; Fernandes, S.C.; Schechinger, M.; Cote, G.L.; Faulds, K.; Mace, C.R.; Graham, D. Detection of cardiovascular disease associated miR-29a using paper-based microfluidics and surface enhanced Raman scattering. Analyst 2020, 145, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Liang, D.; Zheng, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Mari, G.M.; Jiang, H. A simple and rapid immunochromatography test based on readily available filter paper modified with chitosan to screen for 13 sulfonamides in milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-H.; Wu, J.-J.; Lee, G.-B. Screening of highly-specific aptamers and their applications in paper-based microfluidic chips for rapid diagnosis of multiple bacteria. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 284, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D.; Lin, Q.; Li, H.; Huang, Z.; Kuang, Y.; Chen, H.; Kong, J. Rapid detection of malachite green residues in fish using a surface-enhanced Raman scattering-active glass fiber paper prepared by in situ reduction method. Talanta 2019, 200, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, E.; Gabriel, E.F.M.; Coltro, W.K.T.; Garcia, C.D. Rational selection of substrates to improve color intensity and uniformity on microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. Analyst 2014, 139, 2127–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noviana, E.; Ozer, T.; Carrell, C.S.; Link, J.S.; McMahon, C.; Jang, I.; Henry, C.S. Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Devices: From Design to Applications. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 11835–11885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, J.C.; Mace, C.R. Scalable Methods for Device Patterning as an Outstanding Challenge in Translating Paper-Based Microfluidics from the Academic Benchtop to the Point-of-Care. J. Anal. Test. 2019, 3, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, K.; Purohit, B.; Kumar, A.; Srivastava, A.; Chandra, P. Next-Generation Immunosensing Technologies Based on Nano-Bio-Engineered Paper Matrices. In Immunodiagnostic Technologies from Laboratory to Point-of-Care Testing; Suman, P., Chandra, P., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-M.; Chen, C.-Y.; Liao, W.-S. Enclosed paper-based analytical devices: Concept, variety, and outlook. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1144, 158–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busa, L.S.A.; Maeki, M.; Ishida, A.; Tani, H.; Tokeshi, M. Simple and sensitive colorimetric assay system for horseradish peroxidase using microfluidic paper-based devices. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 236, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tian, J.; Garnier, G.; Shen, W. Fabrication of paper-based microfluidic sensors by printing. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 76, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, L.; Philipp, J.; Mattern, K.; Dietzel, A.; Klages, C.-P. Controlling wettability in paper by atmospheric-pressure microplasma processes to be used in µPAD fabrication. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2016, 20, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cui, J.; Yan, Z.; Jin, M.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, G.; Shui, L. Paper-based electrowetting devices fabricated with cellulose paper and paraffin wax. Results Phys. 2021, 31, 105042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, G.V.; Marques, A.C.; Fortunato, E.; Sales, M.G.F. Wax-printed paper-based device for direct electrochemical detection of 3-nitrotyrosine. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 284, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Shi, W.; Jiang, L.; Qin, J.; Lin, B. Rapid prototyping of paper-based microfluidics with wax for low-cost, portable bioassay. Electrophoresis 2009, 30, 1497–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, P.; Song, L.; Li, Y.; Pang, H.; Liu, W. Hybrid ternary rice paper/polypyrrole ink/pen ink nanocomposites as components of flexible supercapacitors. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 13219–13229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Filonanko, Y.; Truong, Y.; Parker, I.H.; Brack, N.; Pigram, P.; Liesegang, J. Contact angle measurement and surface energetics of sized and unsized paper. Colloids Surfaces. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2000, 173, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahbar, M.; Nesterenko, P.N.; Paull, B.; Macka, M. High-throughput deposition of chemical reagents via pen-plotting technique for microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1047, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitanurak, J.; Fukana, N.; Wongpakdee, T.; Thepchuay, Y.; Ratanawimarnwong, N.; Amornsakchai, T.; Nacapricha, D. T-shirt ink for one-step screen-printing of hydrophobic barriers for 2D- and 3D-microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. Talanta 2019, 205, 120113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhang, C. A novel screen-printed microfluidic paper-based electrochemical device for detection of glucose and uric acid in urine. Biomed. Microdevices 2016, 18, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dungchai, W.; Chailapakul, O.; Henry, C.S. A low-cost, simple, and rapid fabrication method for paper-based microfluidics using wax screen-printing. Analyst 2010, 136, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, M.A.; Blondeel, E.J.M.; Kaddoura, M.; MacDonald, B.D. Creating compact and microscale features in paper-based devices by laser cutting. Analyst 2016, 141, 6449–6454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Savitha, R.; Renganathan, T.; Pushpavanam, S. Fabrication of laser printed microfluidic paper-based analytical devices (LP-µPADs) for point-of-care applications. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, H.; Tashkhourian, J.; Hemmateenejad, B. A 3D origami paper-based analytical device combined with PVC membrane for colorimetric assay of heavy metal ions: Application to determination of Cu(II) in water samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1126, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Zhang, H.; Yu, X.; Wang, W. A microfluidic paper-based laser-induced fluorescence sensor based on duplex-specific nuclease amplification for selective and sensitive detection of miRNAs in cancer cells. Talanta 2020, 216, 120996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, W.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Nie, J.; Li, J. Enhanced 3D paper-based devices with a personal glucose meter for highly sensitive and portable biosensing of silver ion. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 137, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Park, J.-K. Pressed region integrated 3D paper-based microfluidic device that enables vertical flow multistep assays for the detection of C-reactive protein based on programmed reagent loading. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 246, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, G.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, X.; Zhang, R.; Qin, X.; Sun, H.; Yang, X.; Rong, J. A versatile microfluidic paper chip platform based on MIPs for rapid ratiometric sensing of dual fluorescence signals. Microchem. J. 2020, 157, 105050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.-G.; Lee, S.-H.; Choi, C.-H.; Kim, J.; Lee, C.-S. Toward instrument-free digital measurements: A three-dimensional microfluidic device fabricated in a single sheet of paper by double-sided printing and lamination. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 1188–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Song, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhao, H.; Cui, Y.; Gu, F.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, G. A three-dimensional pinwheel-shaped paper-based microfluidic analytical device for fluorescence detection of multiple heavy metals in coastal waters by rational device design. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 3299–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.W.; Wang, Z.P.; Huang, G.X.D. Investigation of wax and paper materials for the fabrication of paper-based microfluidic devices. Microsyst. Technol. 2012, 18, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiahao, L.; Xin, W.; Yanke, S.; Huachuan, H.; Dan, J.; Liang, X.; Shouyu, W.; Fei, L. Handheld Inkjet Printing Paper Chip Based Smart Tetracycline Detector. Micromachines 2019, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidon, N.N.; Hong, Y.; Salentijn, G.I.J.; Verpoorte, E. Water-based alkyl ketene dimer ink for user-friendly patterning in paper microfluidics. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1000, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Han, G.-C.; Xiao, H.; Chen, Z.; Fang, C. A novel 3D paper-based microfluidic electrochemical glucose biosensor based on rGO-TEPA/PB sensitive film. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1096, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yukird, J.; Soum, V.; Kwon, O.-S.; Shin, K.; Chailapakul, O.; Rodthongkum, N. 3D paper-based microfluidic device: A novel dual-detection platform of bisphenol A. Analyst 2020, 145, 1491–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, N.; Chen, C.; Wang, P.; Sun, J.; Mao, H. Structure optimization method of microfluidic paper chip based on image grey-level statistics for chromogenic reaction. Chem. Eng. Process. 2019, 143, 107627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yang, J.; Xu, H.; Cao, B.; Qin, Q.; Liao, X.; Wo, Y.; Jin, Q.; Cui, D. Smartphone-imaged multilayered paper-based analytical device for colorimetric analysis of carcinoembryonic antigen. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 2517–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruecha, N.; Yamada, K.; Suzuki, K.; Citterio, D. (Bio)Chemical Sensors Based on Paper. In Materials for Chemical Sensing; Cesar Paixão, T.R.L., Reddy, S.M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 29–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Wang, K.; Xu, H.; Zheng, C.; Cao, B.; Qin, Q.; Jin, Q.; Cui, D. Strategies for the detection of target analytes using microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 2429–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.-M.; Wang, Y.-N. Detection methods and applications of microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 107, 196–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.E.; Shah, K.G.; Yager, P. Sensitive Protein Detection and Quantification in Paper-Based Microfluidics for the Point of Care. Methods Enzymol. 2017, 589, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Li, J.; He, J.; Zhao, W.; Wang, F.; Song, X.; Xu, K.; Wang, J.; Zhao, C. Paper chip-based colorimetric assay for detection of Salmonella typhimurium by combining aptamer-modified FeO@Ag nanoprobes and urease activity inhibition. Mikrochim. Acta 2020, 187, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabria, D.; Caliceti, C.; Zangheri, M.; Mirasoli, M.; Simoni, P.; Roda, A. Smartphone–based enzymatic biosensor for oral fluid L-lactate detection in one minute using confined multilayer paper reflectometry. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 94, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemmeli, D.; Marcoccio, E.; Moscone, D.; Dridi, C.; Arduini, F. Highly sensitive paper-based electrochemical sensor for reagent free detection of bisphenol A. Talanta 2020, 216, 120924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, N.; Zhou, X.; Yu, D.; Jiao, S.; Han, X.; Zhang, S.; Yin, H.; Mao, H. Pesticide residues identification by impedance time-sequence spectrum of enzyme inhibition on multilayer paper-based microfluidic chip. J. Food Process Eng. 2020, 43, e13544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ding, S.-N.; Chen, F.-F.; Zhang, Q. Electrochemical paper-based analytical device for flow injection analysis based on locally enhanced evaporation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 371, 132517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, J.L.; Hogan, C.F.; Tian, J.; Shen, W. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence detection in paper-based microfluidic sensors.(Author abstract)(Report). Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulep, T.-H.; Zenhausern, R.; Gonzales, A.; Knoff, D.S.; Lengerke Diaz, P.A.; Castro, J.E.; Yoon, J.-Y. Smartphone based on-chip fluorescence imaging and capillary flow velocity measurement for detecting ROR1+ cancer cells from buffy coat blood samples on dual-layer paper microfluidic chip. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 153, 112042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yehia, A.M.; Farag, M.A.; Tantawy, M.A. A novel trimodal system on a paper-based microfluidic device for on-site detection of the date rape drug “ketamine”. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1104, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Y. Transforming the blood glucose meter into a general healthcare meter for in vitro diagnostics in mobile health. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivas, K.; Patel, S.; Sinha, D.; Thakur, S.S.; Patle, T.K.; Kant, T.; Dewangan, K.; Satnami, M.L.; Nirmalkar, J.; Kumar, S. Colorimetric and smartphone-integrated paper device for on-site determination of arsenic (III) using sucrose modified gold nanoparticles as a nanoprobe. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, S.; Kukreti, S.; Kaushik, M. Designing a two-stage colorimetric sensing strategy based on citrate reduced gold nanoparticles: Sequential detection of Sanguinarine (anticancer drug) and visual sensing of DNA. Spectrochim. Acta. Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 246, 119039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Dou, L.; Bu, T.; Huang, Q.; Wang, R.; Yang, Q.; Huang, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, D. Highly sensitive furazolidone monitoring in milk by a signal amplified lateral flow assay based on magnetite nanoparticles labeled dual-probe. Food Chem. 2018, 261, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Lu, F.; Lyu, C.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Tian, P.; Xue, L.; Xu, T.; Wang, D. Broad-range and effective detection of human noroviruses by colloidal gold immunochromatographic assay based on the shell domain of the major capsid protein. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Wu, X.; Ren, W.; Zou, Y.; Xia, X.; Sun, H. A colloidal gold test strip assay for the detection of African swine fever virus based on two monoclonal antibodies against P30.(Report). Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lizeng, G.; Jie, Z.; Leng, N.; Jinbin, Z.; Yu, Z.; Ning, G.; Taihong, W.; Jing, F.; Dongling, Y.; Sarah, P.; et al. Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Duan, D.; Gao, L.; Zhou, M.; Fan, K.; Tang, Y.; Xi, J. Standardized assays for determining the catalytic activity and kinetics of peroxidase-like nanozymes. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S.; Brennan, J. [Beta]-Galactosidase-Based Colorimetric Paper Sensor for Determination of Heavy Metals. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-C.; Wang, Y.-N.; Fu, L.-M.; Chen, K.-L. Microfluidic paper-based chip platform for benzoic acid detection in food. Food Chem. 2018, 249, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Singh, G.; Mahajan, D.K.; Kaur, N.; Singh, N. A low-cost device for rapid ‘color to concentration’ quantification of cyanide in real samples using paper-based sensing chip. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 322, 128622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Gao, G.; Zhai, K.; Xu, L.; Zhang, D. A visual Hg2+ detection strategy based on distance as readout by G-quadruplex DNAzyme on microfluidic paper. Food Chem. 2020, 331, 127208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.D.; Nguyen, P.T.; Le, T.N.; Kim, M.I. DNA-copper hybrid nanoflowers as efficient laccase mimics for colorimetric detection of phenolic compounds in paper microfluidic devices. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 182, 113187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eduardo da Silva Ferreira, M.; Canhete de Moraes, N.; Souza Ferreira, V.; Amorim Bezerra da Silva, R.; Marques Petroni, J.; Gabriel Lucca, B. A novel 3D-printed batch injection analysis (BIA) cell coupled to paper-based electrochemical devices: A cheap and reliable analytical system for fast on-site analysis. Microchem. J. 2022, 179, 107663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nantaphol, S.; Kava, A.A.; Channon, R.B.; Kondo, T.; Siangproh, W.; Chailapakul, O.; Henry, C.S. Janus electrochemistry: Simultaneous electrochemical detection at multiple working conditions in a paper-based analytical device. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1056, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Díez-Pérez, I.; Paolucci, F. Editorial overview: Organic and molecular electrochemistry section (2022) electrosynthesis, electrocatalysis, electroanalysis, and molecular device. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2022, 101156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Cui, K.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Xu, M.; Ge, S.; Wang, Y.; Yu, J. Ultrasensitive lab-on-paper device via Cu/Co double-doped CeO2 nanospheres as signal amplifiers for electrochemical/visual sensing of miRNA-155. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 321, 128499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Xu, Y.; Qi, J.; Zheng, X.; Liu, S.; Lin, D.; Zhang, L.; Liu, P.; Li, B.; Chen, L. A self-powered rotating paper-based analytical device for sensing of thrombin. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 351, 130917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, E.; Domini, C.E.; Whitehead, D.C.; Garcia, C.D. From glow-sticks to sensors: Single-electrode electrochemical detection for paper-based devices. Sens. Diagn. 2022, 1, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Chakraborty, S. Analytics with blood on hybrid paper-rotating disc device. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2022, 4, 100122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.-M.; Liu, C.-C.; Yang, C.-E.; Wang, Y.-N.; Ko, C.-H. A PET/paper chip platform for high resolution sulphur dioxide detection in foods. Food Chem. 2019, 286, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukumar, R.; Kapoor, A.; Balasubramanian, S.; Vaishampayan, V.; Gabhane, M. Detection of adulteration in sunflower oil using paper-based microfluidic lab-on-a-chip devices. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 34, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, M.C.; Oliveira, K.A.; de Fátima, Â.; Coltro, W.K.T.; Santos, J.C.C. Paper-based analytical device with colorimetric detection for urease activity determination in soils and evaluation of potential inhibitors. Talanta 2021, 230, 122301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.Z.; Lu, Y.; Yu, L. Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Devices for Point-of-Care Diagnosis. In Next Generation Point-of-Care Biomedical Sensors Technologies for Cancer Diagnosis; Chandra, P., Tan, Y.N., Singh, S.P., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 365–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, K.T.L.; Chae, W.R.; Lee, N.Y. Recent advances in the fabrication strategies of paper-based microfluidic devices for rapid detection of bacteria and viruses. Microchem. J. 2022, 180, 107548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suntornsuk, W.; Suntornsuk, L. Recent applications of paper-based point-of-care devices for biomarker detection. Electrophoresis 2020, 41, 287–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, T.; Jin, Y.; Geng, C.; Aziz, A.u.R.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, S.; Ren, H.; Liu, B. Microfluidic Paper-based Analytical Devices in Clinical Applications. Chromatographia 2020, 83, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, I.; Ko, H.; You, G.; Lee, H.; Paek, S.; Chae, H.; Lee, J.; Choi, S.; Kwon, O.-S.; Shin, K.; et al. Application of paper EWOD (electrowetting-on-dielectrics) chip: Protein tryptic digestion and its detection using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. BioChip J. 2017, 11, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batule, B.S.; Seok, Y.; Kim, M.-G. An innovative paper-based device for DNA extraction from processed meat products. Food Chem. 2020, 321, 126708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batule, B.S.; Seok, Y.; Kim, M.-G. Paper-Based Molecular Diagnostics. In Paper-Based Medical Diagnostic Devices: As a Part of Bioanalysis-Advanced Materials, Methods, and Devices; Lee, J.H., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 155–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Wang, G.; Li, F. Shaping up field-deployable nucleic acid testing using microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 4401–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Geng, Y.; Cao, F.; Sun, D.; Xu, S.; Chang, J.; Xu, W.; Chen, Q. A Smartphone-assisted Paper-based Analytical Device for Fluorescence Assay of Hg2+. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2019, 35, 972–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonkaew, S.; Chaiyo, S.; Jampasa, S.; Rengpipat, S.; Siangproh, W.; Chailapakul, O. An origami paper-based electrochemical immunoassay for the C-reactive protein using a screen-printed carbon electrode modified with graphene and gold nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noviana, E.; Jain, S.; Hofstetter, J.; Geiss, B.J.; Dandy, D.S.; Henry, C.S. Paper-based nuclease protection assay with on-chip sample pretreatment for point-of-need nucleic acid detection.(Paper in Forefront). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Miao, C.; Li, R.; Ji, Y. Fluorescent paper-based sensor based on carbon dots for detection of folic acid. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.K.; Oh, J.; Lee, J.; Cho, Y.G.; Park, J.S.; Choi, J.S.; Kim, D.S.; Kwon, J. Paper-based multiplex analytical device for simultaneous detection of Clostridioides difficile toxins and glutamate dehydrogenase. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 176, 112894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, A.; Toley, B.J. Barrier-Free Microfluidic Paper Analytical Devices for Multiplex Colorimetric Detection of Analytes. Anal. Chem 2021, 93, 8954–8961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, G.; He, J.; Chen, X.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, F.; Xia, Q.; Yu, L.; Lu, Z. A wearable, cotton thread/paper-based microfluidic device coupled with smartphone for sweat glucose sensing. Cellulose 2019, 26, 4553–4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.; Freitas, S.; Duarte, L.; Souza, J.; Paixão, T.; Coltro, W. Salivary diagnostics on paper microfluidic devices and their use as wearable sensors for glucose monitoring. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 4919–4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, W.; Zhuang, B.; Zhang, P.; Han, J.; Li, C.-X.; Liu, P. A filter paper-based microdevice for low-cost, rapid, and automated DNA extraction and amplification from diverse sample types. Lab A Chip 2014, 14, 3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Yang, H.; Choi, J.R.; Gong, Y.; Hu, J.; Wen, T.; Li, X.; Xu, B.; Mei, Q.; Xu, F. Paper-based device with on-chip reagent storage for rapid extraction of DNA from biological samples. (Report). Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil-Joshi, A.; Rangaswamy, B.E.; Apte-Deshpande, A. Paper-based PCR method development, validation and application for microbial detection. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2021, 19, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Chen, C.; Liu, Y.; Du, W.; Feng, X.; Liu, B.-F. Fully integrated nucleic acid pretreatment, amplification, and detection on a paper chip for identifying EGFR mutations in lung cancer cells. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 283, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.; Batule, B.S.; Seok, Y.; Kim, M.-G. Single-Step Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assay Based on a Paper Chip for Simultaneous Detection of Multiple Foodborne Pathogens. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 10211–10216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiju, T.M.; Tripura, C.; Saha, P.; Mansingh, A.; Challa, V.; Bhatnagar, I.; Nagesh, N.; Asthana, A. Ready-to-use vertical flow paper device for instrument-free room temperature reverse transcription. New Biotechnol. 2022, 68, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaarj, K.; Madias, M.; Akarapipad, P.; Cho, S.; Yoon, J.-Y. Paper-based in vitro tissue chip for delivering programmed mechanical stimuli of local compression and shear flow. J. Biol. Eng. 2020, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samae, M.; Ritmetee, P.; Chirasatitsin, S.; Kojić, S.; Kojić, T.; Jevremov, J.; Stojanović, G.; Al Salami, H. Precise Manufacturing and Performance Validation of Paper-Based Passive Microfluidic Micromixers. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2020, 21, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.; Xue, P.; Wu, Y.; Bao, J.; Chuah, Y.; Kang, Y. A concentration gradient generator on a paper-based microfluidic chip coupled with cell culture microarray for high-throughput drug screening. Biomed. Microdevices 2016, 18, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, S.Y.; Lee, H.; Kim, S.J. Paper-based ion concentration polarization device for selective preconcentration of muc1 and lamp-2 genes. Micro Nano Syst. Lett. 2017, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Bhattacharya, S. Paper Microfluidic Based Device for Blood/Plasma Separation. In Paper Microfluidics: Theory and Applications; Bhattacharya, S., Kumar, S., Agarwal, A.K., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.-C.; Zhou, T.; Niu, L.-L.; Xie, Z.-S.; Fang, F.; Yang, F.-Q.; Wu, Z.-Y. Simultaneous pre-concentration and separation on simple paper-based analytical device for protein analysis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 1689–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atabakhsh, S.; Jafarabadi Ashtiani, S. Programmable paper-based microfluidics device with prefabricated patterns for prototyping of µPADs. Microfluid. Nanofluid 2019, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Dong, H.; Zheng, J. An Ultra-Fast and Large-Scale Fabrication Method for Paper-Based Microfluidic Chips; Advances in Mechanical Design, Singapore, 2018; Tan, J., Gao, F., Xiang, C., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 1561–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Guo, X.; Liu, W.; Zhang, L. Paper-based fluorometric immunodevice with quantum-dot labeled antibodies for simultaneous detection of carcinoembryonic antigen and prostate specific antigen. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, J.; Liu, J.; Sun, S.; Xiong, Y.; Ma, Y.; Yan, S.; Yang, Y.; Yin, H.; Cai, X. Label-free microfluidic paper-based electrochemical aptasensor for ultrasensitive and simultaneous multiplexed detection of cancer biomarkers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 136, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.; Lv, Q.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Q. Quantum-dot-functionalized paper-based device for simultaneous visual detection of Cu(II), Mn(II), and Hg(II). Talanta Open 2022, 5, 100099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chutvirasakul, B.; Nuchtavorn, N.; Macka, M.; Suntornsuk, L. Distance-based paper device using polydiacetylene liposome as a chromogenic substance for rapid and in-field analysis of quaternary ammonium compounds.(Research Paper). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Zheng, Q.; Jin, L.; Zhou, S.; Chen, H.; Liu, X.; Lu, C. Rapid measurement of total polyphenol content in tea by kinetic matching approach on microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. Food Chem. 2021, 342, 128368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xu, G.; Wu, W.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Zhou, S.; You, F. A novel combination of quick response code and microfluidic paper-based analytical devices for rapid and quantitative detection. Biomed. Microdevices 2018, 20, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Wu, C.; Luan, C.; Gao, P.; Wang, H.; Chi, J.; Kong, T. Distance-based quantification of miRNA-21 by the coffee-ring effect using paper devices. Mikrochim. Acta 2020, 187, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.-x.; Zuo, P.; Ye, B.-C. A Novel Wick-Like Paper-Based Microfluidic Device for 3D Cell Culture and Anti-Cancer Drugs Screening. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 16, 2000126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Kim, S.J. Spontaneous diffusiophoretic separation in paper-based microfluidic device. Micro Nano Syst. Lett. 2020, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.-Y.; Wang, Y.-H.; Niu, B.-S.; Yang, Y.; Fang, F.; Song, Y.-Y. Simultaneous enrichment and separation based on ion concentration polarization effect on a paper based analytical device. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1208, 339844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Material | Characteristics | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Filter paper | Suitable water absorption, easy to obtain, low cost, poor strength | Suitable for all kinds of paper chips, the most widely used paper-based materials |
| Nitrocellulose paper | It can bind and fix protein, and high cost | Detection based on Western blot reaction, colloidal gold test paper reaction zone |
| Glass fiber paper | Stable properties, not easy to break, high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance | Detection based on chemical reactions |
| Methods | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Photolithography | The earliest method for making paper chips, precise channel structure [20] | The process is complicated The resulting paper chips are not suitable for bending [8] |
| Plasma treatment technology | More suitable for mass production and have low cost [21] | Depends on templates, reducing flexibility [22] |
| Wax printing | Simple processing, environmentally friendly materials [23,24] | Rely on wax spray printers, heating-induced horizontal diffusion reduces structure accuracy [25] |
| Inkjet method | Simple processing can be drawn with ink pen, no heating diffusion, more precise structure [26,27] | Hydrophobic inks can be toxic, ink pens are inaccurate for hand drawing, still rely on inkjet printers [28] |
| Screen printing | Ideal for mass production, simple process, and low cost [29,30] | Rely on templates, greatly reducing flexibility during research [31] |
| Laser processing technology | Very precise structures can be prepared [32] | Rely on expensive laser equipment and difficult to popularize [33] |
| 3D origami method | 3D structure has more functions, direct registration of each layer [34,35] | Means of fixing are required between layers, only single material can be used [36] |
| 3D lamination method | 3D structure has more functions, can use a variety of materials [37] | Fixed means are required between layers, registration methods are required [38] |
| Other 3D methods | Highly innovative and has huge development potential [39] | Special uses, difficult to promote [40] |
| Methods | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Colorimetric method | Intuitive results, easy to read with the naked eye, low cost [51,52] | Unable to achieve accurate quantitative detection [53] |
| Electrochemical method | Quantitatively accurate, fast reading [54,55] | Rely on electrochemical workstation, increase cost and reduce flexibility [56] |
| Fluorescence method | Low detection limit, very sensitive [57,58] | Relying on fluorescence detection equipment, easily affected by the signal of paper fluorescent agent [59] |
| United electronics | Combining the aforementioned methods enables non-professionals to obtain accurate results [60,61] | Need to install a mobile APP or even larger devices, reducing flexibility [4] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, Y.; Aziz, A.u.R.; Wu, B.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, N.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Z. The Road to Unconventional Detections: Paper-Based Microfluidic Chips. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1835. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13111835
Jin Y, Aziz AuR, Wu B, Lv Y, Zhang H, Li N, Liu B, Zhang Z. The Road to Unconventional Detections: Paper-Based Microfluidic Chips. Micromachines. 2022; 13(11):1835. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13111835
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Yuhang, Aziz ur Rehman Aziz, Bin Wu, Ying Lv, Hangyu Zhang, Na Li, Bo Liu, and Zhengyao Zhang. 2022. "The Road to Unconventional Detections: Paper-Based Microfluidic Chips" Micromachines 13, no. 11: 1835. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13111835
APA StyleJin, Y., Aziz, A. u. R., Wu, B., Lv, Y., Zhang, H., Li, N., Liu, B., & Zhang, Z. (2022). The Road to Unconventional Detections: Paper-Based Microfluidic Chips. Micromachines, 13(11), 1835. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13111835








