A Hydrogel-Based Microfluidic Nerve Cuff for Neuromodulation of Peripheral Nerves
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
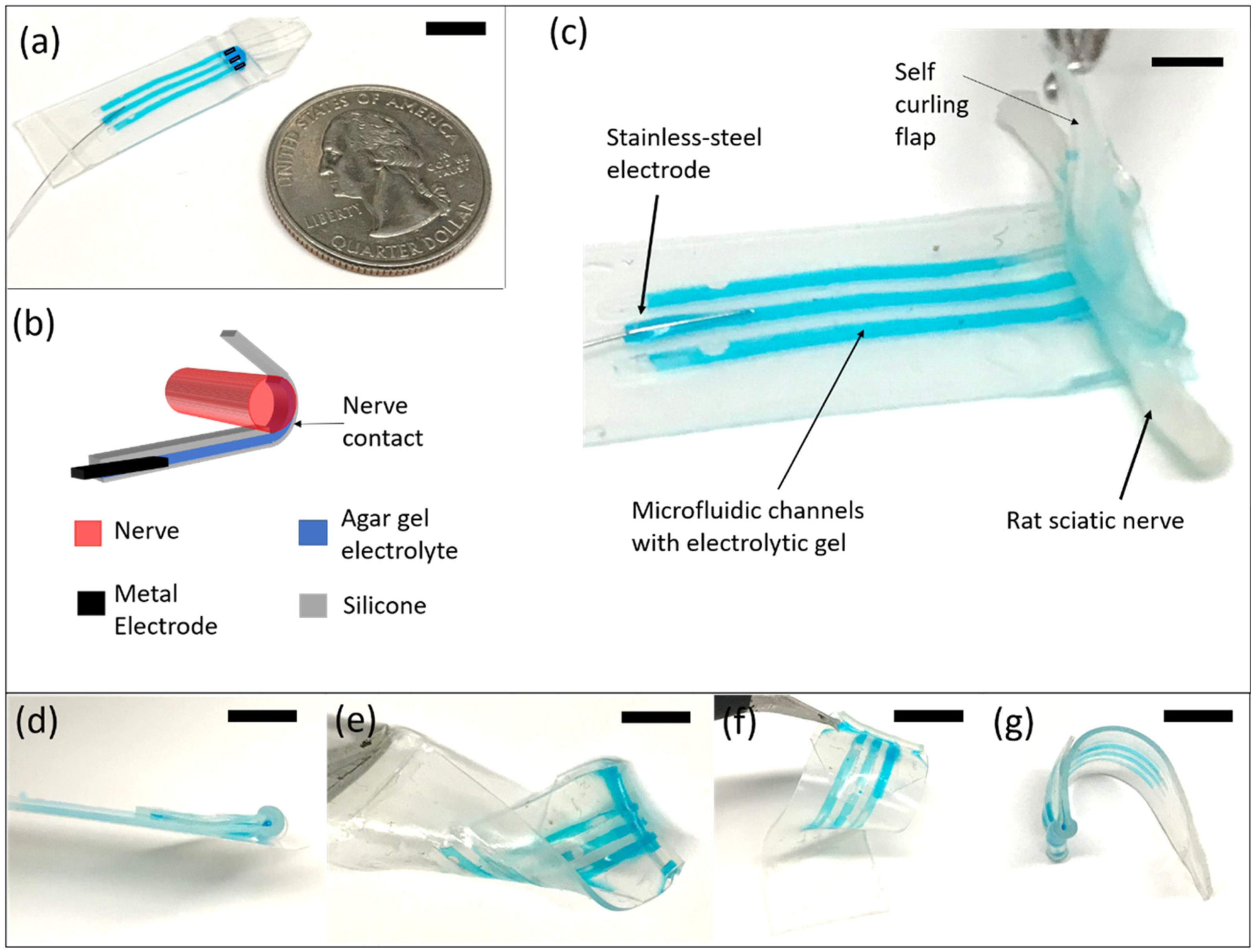
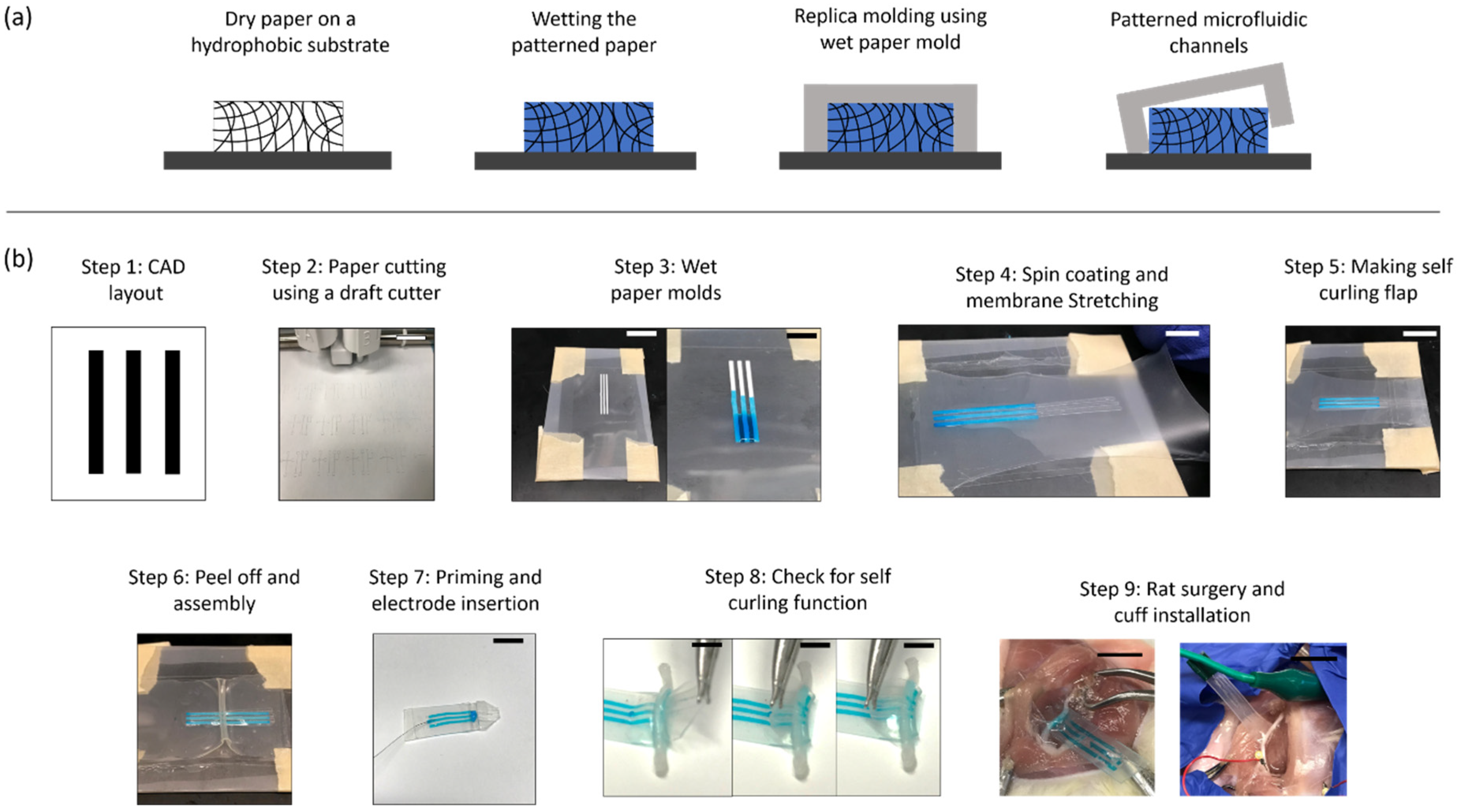
2.1. Microfluidic Nerve Cuff Fabrication Using Wet Paper Molds
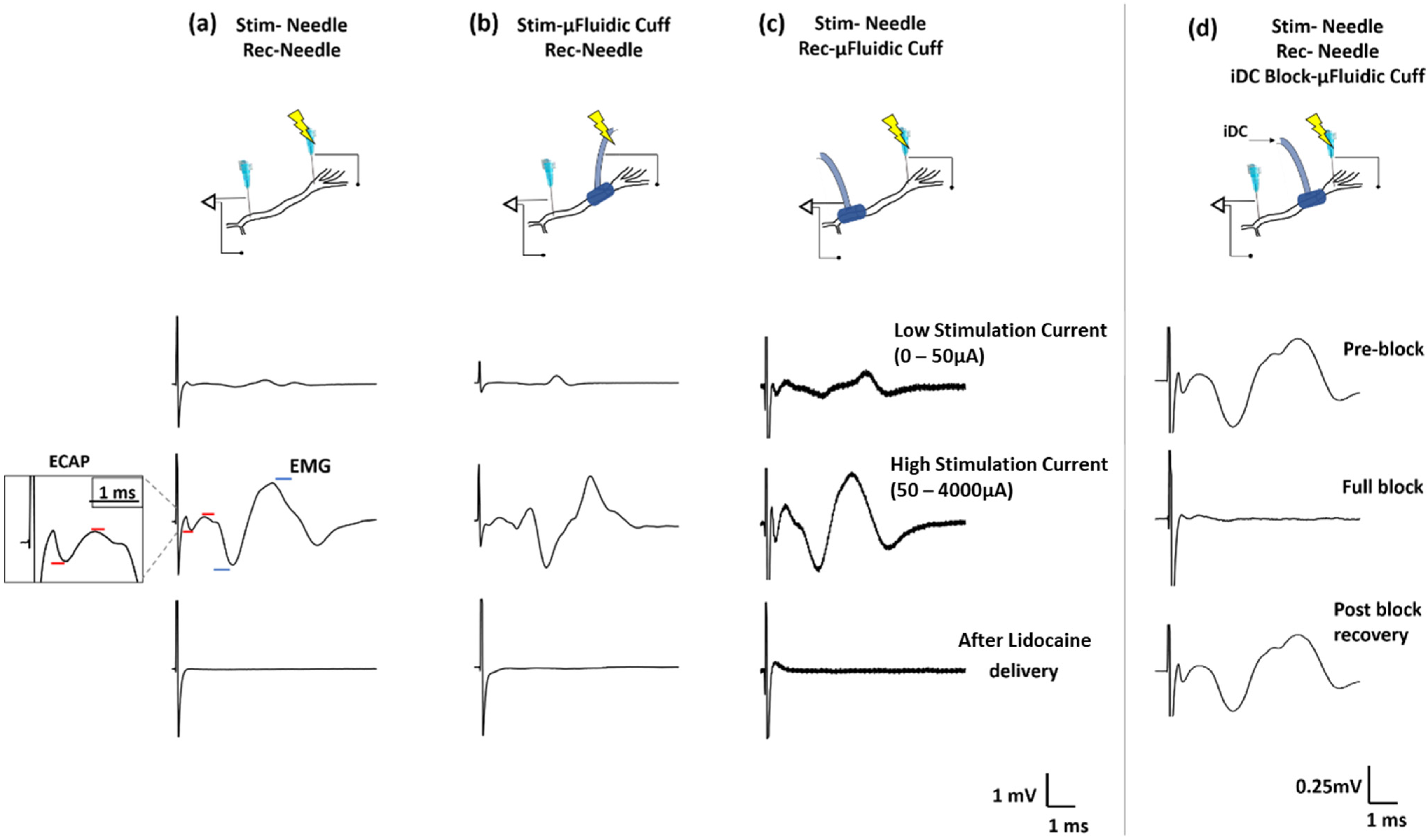
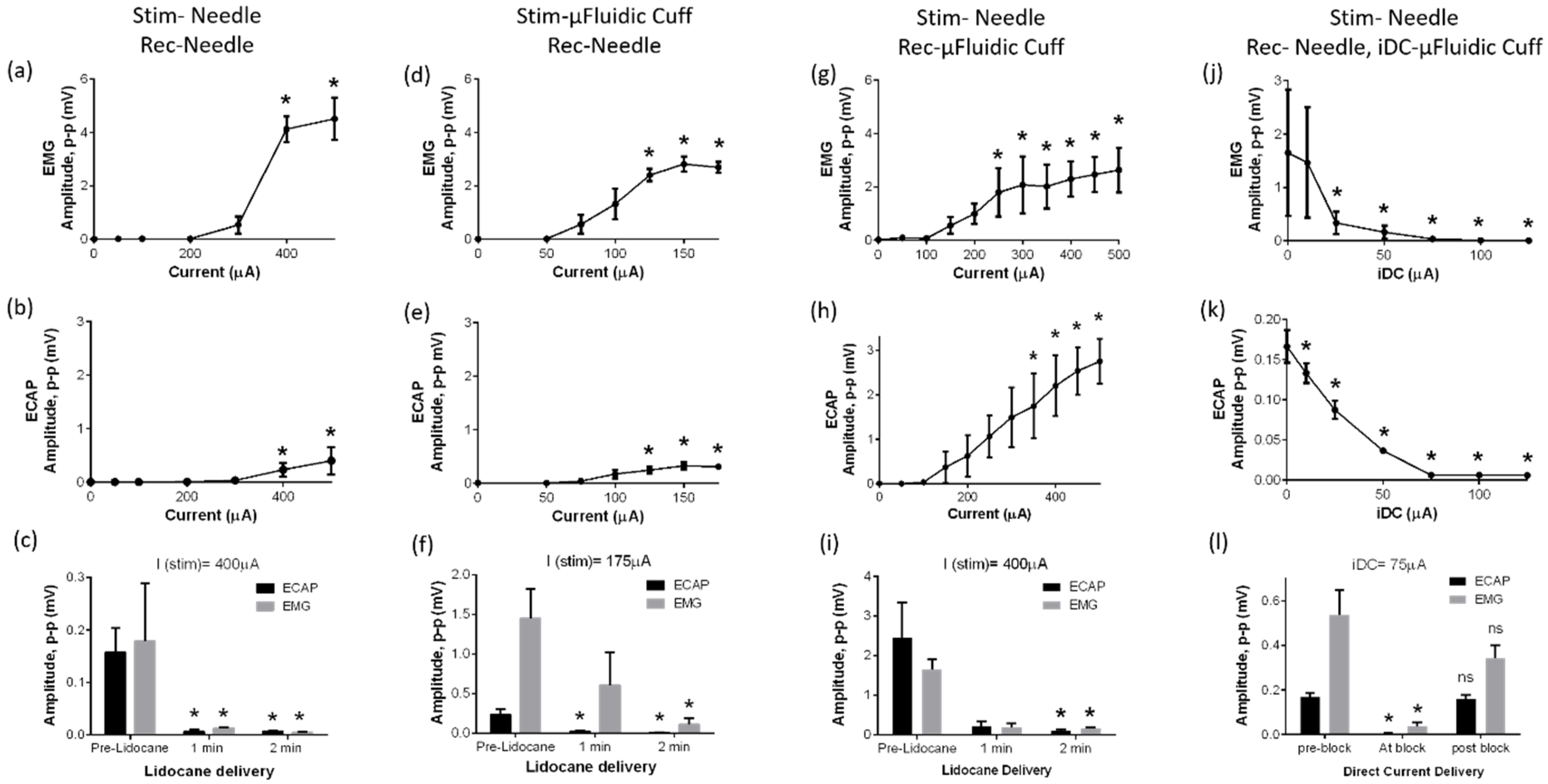
2.2. Neural Stimulation, Recording and Blocking Using Microfluidic Nerve Cuff
3. Experimental Methods
3.1. Microfluidic Nerve Cuff Fabrication Using Wet Paper Molds
3.2. Animals and Surgical Preparation
3.3. Nerve Stimulation and Recording
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cogan, S.F. Neural Stimulation and Recording Electrodes. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 10, 275–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.H. Soft implantable microelectrodes for future medicine: Prosthetics, neural signal recording and neuromodulation. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 959–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, R.; Abidian, M.R. Conducting Polymers for Neural Prosthetic and Neural Interface Applications. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 7620–7637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keefer, E.W.; Botterman, B.R.; Romero, M.I.; Rossi, A.F.; Gross, G.W. Carbon nanotube coating improves neuronal recordings. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, G.; Lieber, C.M. Novel electrode technologies for neural recordings. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 20, 330–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, J.A. Reversible blocking of nerve conduction by alternating-current excitation. Nature 1962, 195, 712–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, A.R. Electrical Stimulation Using Kilohertz-Frequency Alternating Current. Phys. Ther. 2009, 89, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhadra, N.; Kilgore, K.L. Direct current electrical conduction block of peripheral nerve. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2004, 12, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, C.; Roppolo, J.R.; de Groat, W.C. Analysis of nerve conduction block induced by direct current. J. Comput. Neurosci. 2009, 27, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitwam, J.G.; Kidd, C. The use of direct current to cause selective block of large fibres in peripheral nerves. Br. J. Anaesth. 1975, 47, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aplin, F.P.; Singh, D.; Santina, C.C.D.; Fridman, G.Y. Ionic Direct Current Modulation for Combined Inhibition/Excitation of the Vestibular System. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 66, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridman, G.Y.; Della Santina, C.C. Progress toward development of a multichannel vestibular prosthesis for treatment of bilateral vestibular deficiency. Anat. Rec. 2012, 295, 2010–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, F.; Anderson, M.; He, S.; Stephens, K.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Raja, S.N.; Aplin, F.; Guan, Y.; Fridman, G. Differential expression of voltage-gated sodium channels in afferent neurons renders selective neural block by ionic direct current. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaaq1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, P.; Yi, W.; Chen, C.; Hu, J.; Qi, J.; Zhang, B.; Cheng, M.M.C. Flexible 3D carbon nanotubes cuff electrodes as a peripheral nerve interface. Biomed. Microdevices 2018, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Kim, H.J.; Do, S.H.; Kang, J.Y.; Lee, S.H. Characterization of nerve-cuff electrode interface for biocompatible and chronic stimulating application. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 237, 924–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, D.J.; Durand, D.M. Functionally selective peripheral nerve stimulation with a flat interface nerve electrode. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2002, 10, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struijk, J.J.; Thomsen, M.; Larsen, J.O.; Sinkjær, T. Cuff electrodes for long-term recording of natural sensory information: Studying the relationship between nerve damage and electrophysiological parameters in long-term implants. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 1999, 18, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foldes, E.L.; Ackermann, D.M.; Bhadra, N.; Kilgore, K.L.; Bhadra, N. Design, fabrication and evaluation of a conforming circumpolar peripheral nerve cuff electrode for acute experimental use. J. Neurosci. Methods 2011, 196, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue, N.; Sun, T.; Tsang, W.M.; Delgado-Martinez, I.; Lee, S.H.; Sheshadri, S.; Xiang, Z.; Merugu, S.; Gu, Y.; Yen, S.C.; et al. Polymeric C-shaped cuff electrode for recording of peripheral nerve signal. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 210, 640–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naples, G.G.; Mortimer, J.T.; Scheiner, A.; Sweeney, J.D. A spiral Nerve Cuff Electrode for Peripheral Nerve S timulation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1988, 35, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merrill, D.R.; Bikson, M.; Jefferys, J.G.R. Electrical stimulation of excitable tissue: Design of efficacious and safe protocols. J. Neurosci. Methods 2005, 141, 171–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aregueta-Robles, U.A.; Woolley, A.J.; Poole-Warren, L.A.; Lovell, N.H.; Green, R.A. Organic electrode coatings for next-generation neural interfaces. Front. Neuroeng. 2014, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ackermann, D.M.; Bhadra, N.; Foldes, E.L.; Kilgore, K.L. Separated interface nerve electrode prevents direct current induced nerve damage. J. Neurosci. Methods 2011, 201, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vrabec, T.L.; Wainright, J.S.; Bhadra, N.; Shaw, L.; Kilgore, K.L.; Bhadra, N. A carbon slurry separated interface nerve electrode for electrical block of nerve conduction. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2019, 27, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridman, G.Y.; Della Santina, C.C. Safe Direct Current Stimulator 2: Concept and Design. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society EMBS, Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; Volume 2013, pp. 3126–3129. [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielsson, E.O.; Janson, P.; Tybrandt, K.; Simon, D.T.; Berggren, M. A Four-Diode Full-Wave Ionic Current Rectifier Based on Bipolar Membranes: Overcoming the Limit of Electrode Capacity. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5143–5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fridman, G.Y.; Della Santina, C.C. Safe Direct Current Stimulation to Expand Capabilities of Neural Prostheses. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2013, 21, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elyahoodayan, S.; Larson, C.; Cobo, A.M.; Meng, E.; Song, D. Acute in vivo testing of a polymer cuff electrode with integrated microfluidic channels for stimulation, recording, and drug delivery on rat sciatic nerve. J. Neurosci. Methods 2020, 336, 108634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proctor, C.M.; Uguz, I.; Slezia, A.; Curto, V.; Inal, S.; Williamson, A.; Malliaras, G.G. An Electrocorticography Device with an Integrated Microfluidic Ion Pump for Simultaneous Neural Recording and Electrophoretic Drug Delivery in Vivo. Adv. Biosyst. 2019, 3, 1800270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohlmeyer, E.A.; Jordon, L.R.; Kim, P.; Miller, L.E. A fully implanted drug delivery system for peripheral nerve blocks in behaving animals. J. Neurosci. Methods 2009, 182, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez, F.J.; Ceballos, D.; Schuttler, M.; Valero, A.; Valderrama, E.; Stieglitz, T.; Navarro, X. Polyimide cuff electrodes for peripheral nerve stimulation. J. Neurosci. Methods 2000, 98, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeb, G.E.; Peck, R.A. Cuff electrodes for chronic stimulation and recording of peripheral nerve activity. J. Neurosci. Methods 1996, 64, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Kim, G.H.; Baek, N.S.; Han, Y.H.; Kim, A.-Y.; Chung, M.-A.; Jung, S.-D. Fabrication of multi-electrode array platforms for neuronal interfacing with bi-layer lift-off resist sputter deposition. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2013, 23, 097001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo, A.M.; Larson, C.E.; Scholten, K.; Miranda, J.A.; Elyahoodayan, S.; Song, D.; Pikov, V.; Meng, E. Parylene-Based Cuff Electrode With Integrated Microfluidics for Peripheral Nerve Recording, Stimulation, and Drug Delivery. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2019, 28, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korivi, N.S.; Ajmera, P.K. Self-closing cuff electrode for functional neural stimulation and recording. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2011, 31, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakor, N.V.; Yen, S.-C.; Xiang, Z.; Xue, N.; Lee, C.; Lee, S.; Delgado-Martinez, I.; Sun, T.; Sheshadri, S. Selective stimulation and neural recording on peripheral nerves using flexible split ring electrodes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 242, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamei, K.I.; Mashimo, Y.; Koyama, Y.; Fockenberg, C.; Nakashima, M.; Nakajima, M.; Li, J.; Chen, Y. 3D printing of soft lithography mold for rapid production of polydimethylsiloxane-based microfluidic devices for cell stimulation with concentration gradients. Biomed. Microdevices 2015, 17, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, J.L.; Shariati, N.H.; Karantonis, D.M. Electrically evoked compound action potential recording in peripheral nerves. Bioelectron. Med. 2017, 1, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thakur, R.; Aplin, F.P.; Fridman, G.Y. A Hydrogel-Based Microfluidic Nerve Cuff for Neuromodulation of Peripheral Nerves. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1522. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12121522
Thakur R, Aplin FP, Fridman GY. A Hydrogel-Based Microfluidic Nerve Cuff for Neuromodulation of Peripheral Nerves. Micromachines. 2021; 12(12):1522. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12121522
Chicago/Turabian StyleThakur, Raviraj, Felix P. Aplin, and Gene Y. Fridman. 2021. "A Hydrogel-Based Microfluidic Nerve Cuff for Neuromodulation of Peripheral Nerves" Micromachines 12, no. 12: 1522. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12121522
APA StyleThakur, R., Aplin, F. P., & Fridman, G. Y. (2021). A Hydrogel-Based Microfluidic Nerve Cuff for Neuromodulation of Peripheral Nerves. Micromachines, 12(12), 1522. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12121522





