A Portable Sensor System with Ultramicro Electrode Chip for the Detection of Heavy-Metal Ions in Water
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Instruments and Reagents
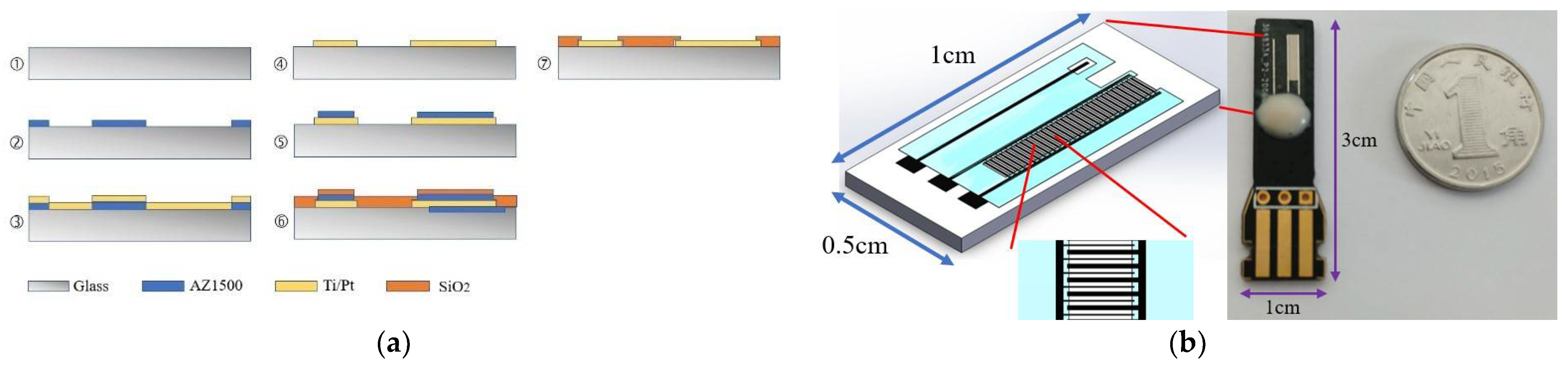
2.2. Ultramicro Interdigital Electrode Chip
2.3. System Hardware Design
2.4. System Software Design
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Gold Nanoparticle Modification
3.2. Optimization of Detection Parameters
3.3. Calibration Comparison Test of Ultramicro Electrode and Columnar Electrode
3.3.1. Calibration of the Ultramicro Electrode by SWV
3.3.2. Comparison of Performance with Columnar Electrode
3.4. Anti-Interference Test
3.5. Detection of Copper Ions in Real Water Sample
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akpor, O.B. Heavy Metal Pollutants in Wastewater Effluents: Sources, Effects and Remediation. Adv. Biosci. Bioeng. 2014, 2, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tekaya, N.; Saiapina, O.; Ben Ouada, H.; Lagarde, F.; Ben Ouada, H.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Ultra-sensitive conductometric detection of heavy metals based on inhibition of alkaline phosphatase activity from Arthrospira platensis. Bioelectrochemistry 2013, 90, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Racek, J.; Eiselt, J.; Opatrný, K. Metals, toxicity and oxidative stress. Curr. Med. Chem. 2002, 12, 1161–1208. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, F.F.H.; Abass, T.; Mahata, S.; Mahato, S.S.; Nandi, M.M.; Mondal, B.; Pirkarami, A.; Olya, M.E.; Nakata, K.; Fujishima, A. Heavy metal pollution and human biotoxic effects. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2012, 2, 112–118. [Google Scholar]
- Gumpu, M.B.; Sethuraman, S.; Krishnan, U.M.; Rayappan, J.B.B. A review on detection of heavy metal ions in water—An electrochemical approach. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 213, 515–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Wu, S.; Li, S. Progress on electrochemical sensors for the determination of heavy metal ions from contaminated water. J. Chin. Adv. Mater. Soc. 2018, 6, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X. Statistical analysis of major environmental emergencies in China from 2012 to 2017. GuangZhou Chem. Ind. 2018, 46, 146–148, 157. [Google Scholar]
- Ebab, C.; Sa, D.; Pt, D.; Jwa, B.; Pebc, E.; Aa, D.; Mdlab, C. Rapid and on-site simultaneous electrochemical detection of copper, lead and mercury in the Amazon river. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 307, 127620. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J. Research on New Electrochemical Sensors and Micro Measurement System for New Heavy metal Ion Detection. Ph.D. Thesis, North University of China, Taiyuan, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, S.K.; Singh, P.; Singh, J.; Sachan, S.; Srivastava, S.; Singh, S.K. Nanocarbon-based Electrochemical Detection of Heavy Metals. Electroanalysis 2016, 28, 2472–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Jia, M.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Li, P.; Chen, L. Sensitive, selective and simultaneous electrochemical detection of multiple heavy metals in environment and food using a lowcost Fe3O4 nanoparticles/fluorinated multi-walled carbon nanotubes sensor. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 175, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waheed, A.; Mansha, M.; Ullah, N. Nanomaterials-based electrochemical detection of heavy metals in water: Current status, challenges and future direction. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 105, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toghan, A.; Abd-Elsabour, M.; Abo-Bakr, A.M. A novel Electrochemical Sensor Based on EDTA-NQS/GC for Simultaneous Determination of Heavy Metals. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 322, 112603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications; Wiley Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Yao, Y.; Ying, Y.; Ping, J. Recent advances in nanomaterial-enabled screen-printed electrochemical sensors for heavy metal detection. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 115, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinero-Abad, B.; Izquierdo, D.; Perez, L.; Escudero, I.; Arcos-Martinez, M. Comparison of backing materials of screen printed electrochemical sensors for direct determination of the sub-nanomolar concentration of lead in seawater. Talanta 2018, 182, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanllorente-Méndez, S.; Domínguez-Renedo, O.M.; Arcos-Martínez, J. Determination of Arsenic(III) Using Platinum Nanoparticle-Modified Screen-Printed Carbon-Based Electrodes. Electroanalysis 2010, 21, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pungjunun, K.; Nantaphol, S.; Praphairaksit, N.; Siangproh, W.; Chaiyo, S.; Chailapakul, O. Enhanced sensitivity and separation for simultaneous determination of tin and lead using paper-based sensors combined with a portable potentiostat—ScienceDirect. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 318, 128241. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, J.; Gan, Y.; Liang, T.; Wan, H.; Ping, W. A miniaturized electrochemical system for high sensitive determination of chromium(VI) by screen-printed carbon electrode with gold nanoparticles modification. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 272, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Chang, F.; Han, X.; Ge, C.; Lin, S. Wireless water quality monitoring and spatial mapping with disposable whole-copper electrochemical sensors and a smartphone. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 306, 127557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkac, J.; Davis, J.J. An optimised electrode pre-treatment for SAM formation on polycrystalline gold. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2008, 621, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Index | Limit Value (mg/L) | Index | Limit Value (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Barium (Ba) | 0.7 | Lead (Pb) | 0.01 |
| Copper (Cu) | 2 | Manganese (Mn) | 0.5 |
| Hydrargyrum (Hg) | 0.001 | Zinc (Zn) | 3 |
| The Kind of Electrode | Effective Area of Electrode (mm2) | Sensitivity (μA·L·μg−1) | Sensitivity per Unit Area (μA·L·μg−1·mm−2) | Low Limit of Detection (μg/L) | Detection Range (μg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| columnar electrode | 7.065 | 0.0065 | 0.0009 | 29.76 | 0–400 |
| ultramicro electrode | 0.450 | 0.0138 | 0.0307 | 18.89 | 0–400 |
| Sample | Added (μg/L) | Detection Results of This Study * (μg/L) | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lake water | 150 | 138.53 ± 12.96 | 92.3% |
| 250 | 218.73 ± 4.90 | 87.5% | |
| 350 | 331.47 ± 12.68 | 94.7% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Li, Y.; Tong, J.; Bian, C. A Portable Sensor System with Ultramicro Electrode Chip for the Detection of Heavy-Metal Ions in Water. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12121468
Wang Y, Xu Y, Jiang J, Li Y, Tong J, Bian C. A Portable Sensor System with Ultramicro Electrode Chip for the Detection of Heavy-Metal Ions in Water. Micromachines. 2021; 12(12):1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12121468
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yuekun, Yuhao Xu, Jinhua Jiang, Yang Li, Jianhua Tong, and Chao Bian. 2021. "A Portable Sensor System with Ultramicro Electrode Chip for the Detection of Heavy-Metal Ions in Water" Micromachines 12, no. 12: 1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12121468
APA StyleWang, Y., Xu, Y., Jiang, J., Li, Y., Tong, J., & Bian, C. (2021). A Portable Sensor System with Ultramicro Electrode Chip for the Detection of Heavy-Metal Ions in Water. Micromachines, 12(12), 1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12121468






