Nanoresonator Enhancement of Majorana-Fermion-Induced Slow Light in Superconducting Iron Chains
Abstract
:1. Introduction
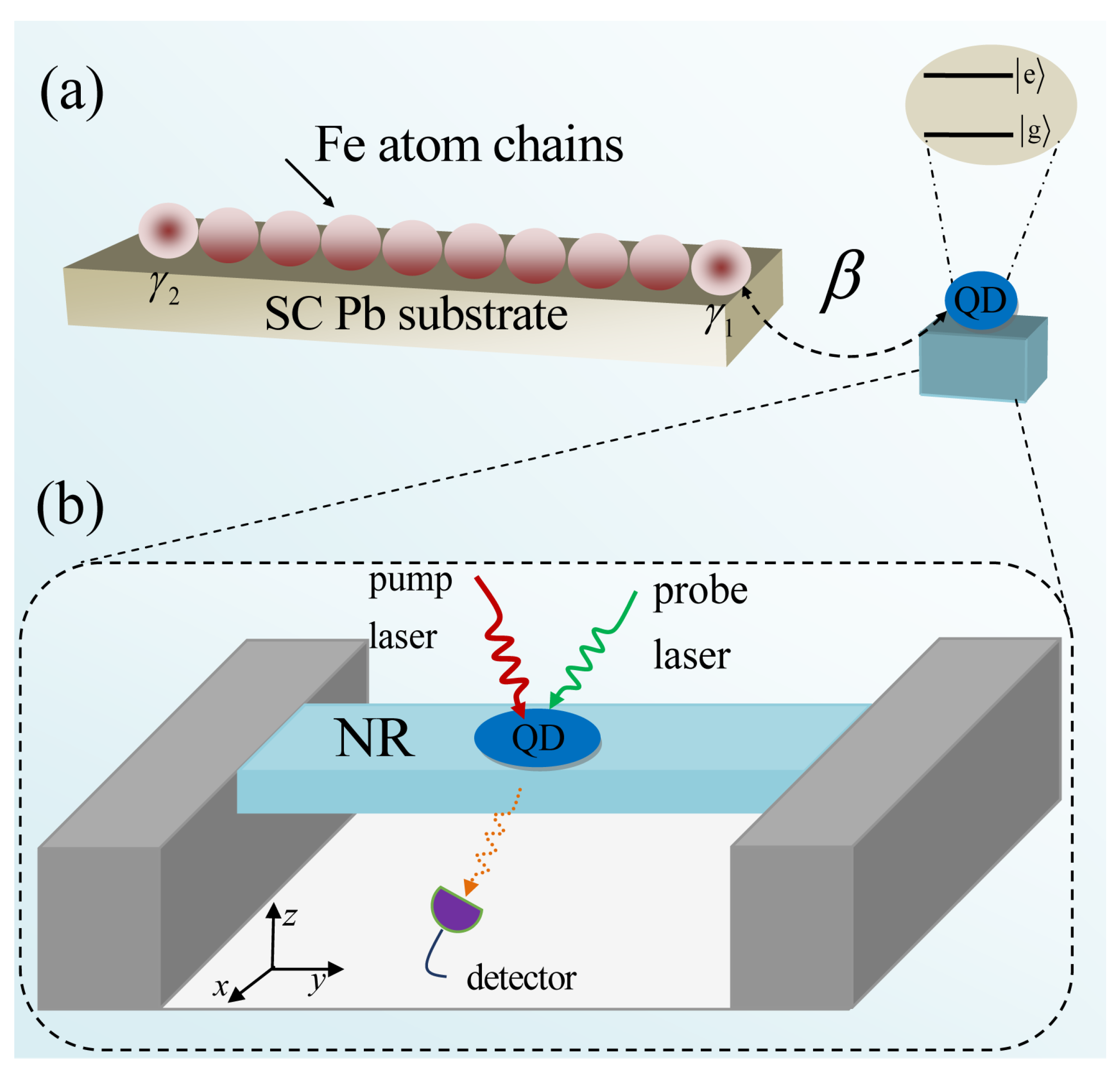
2. Model and Theory
2.1. The Hamiltonian of the System
2.2. Quantum Langevin Equations
2.3. Coherent Optical Spectrum
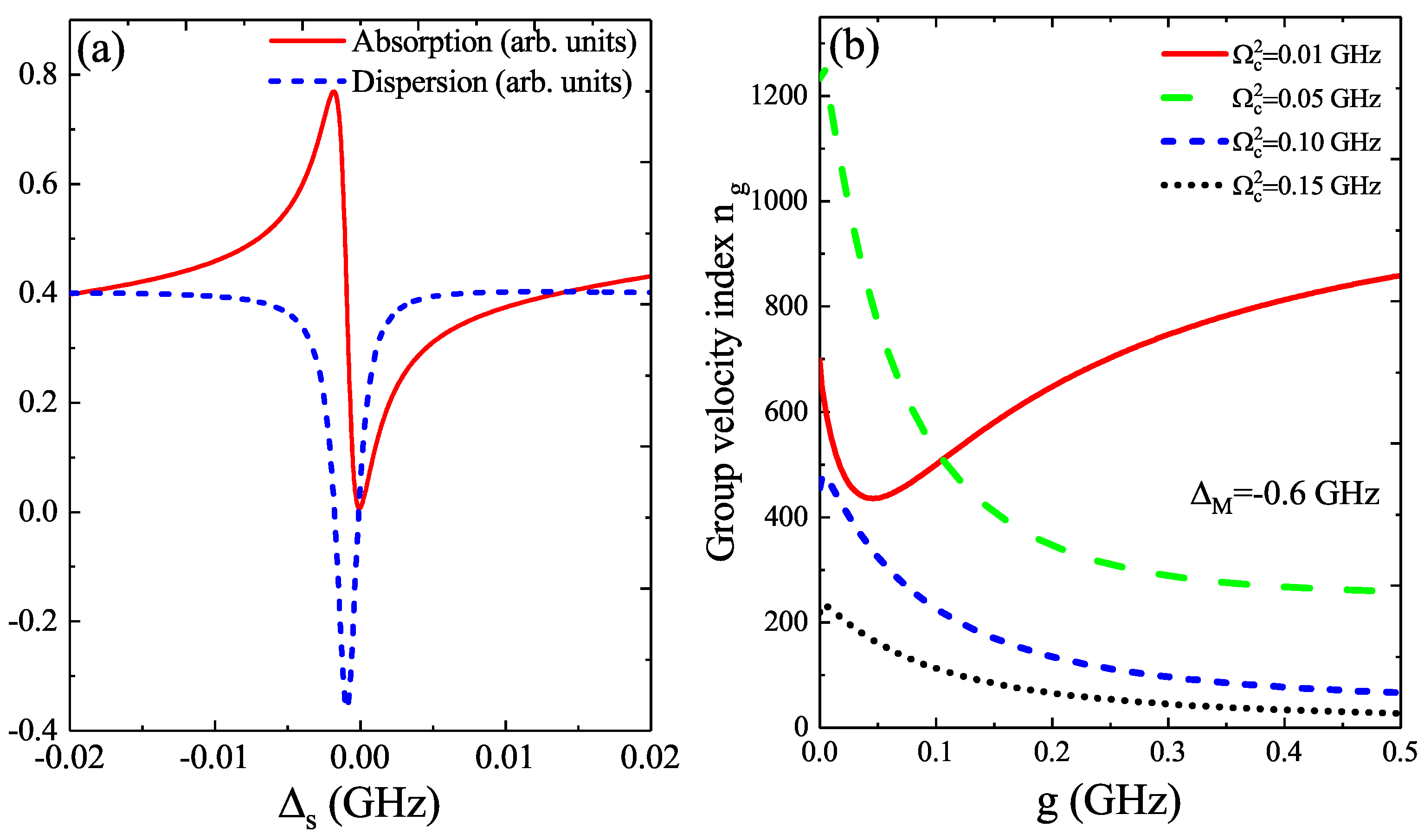
2.4. Group Velocity Index
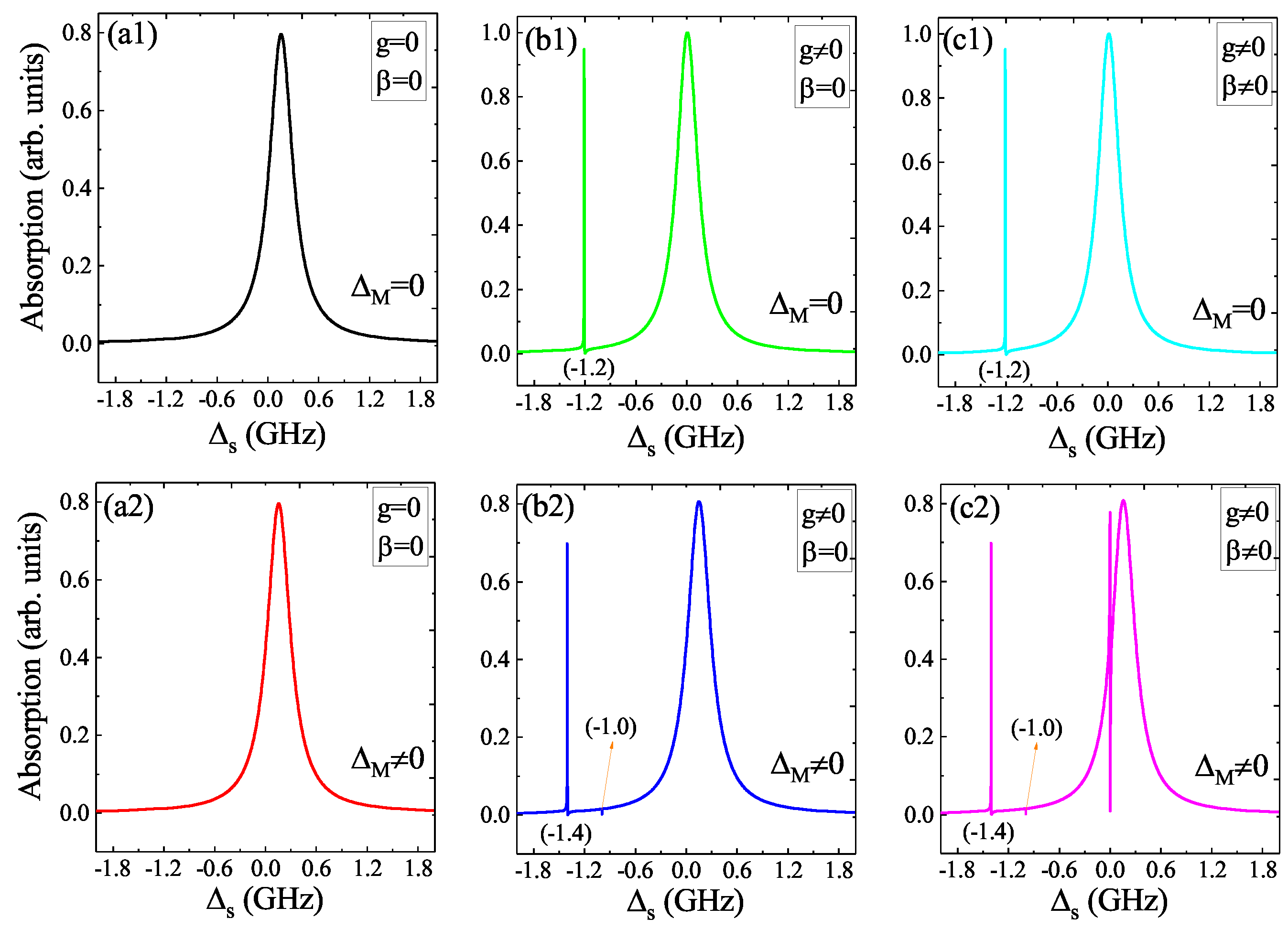
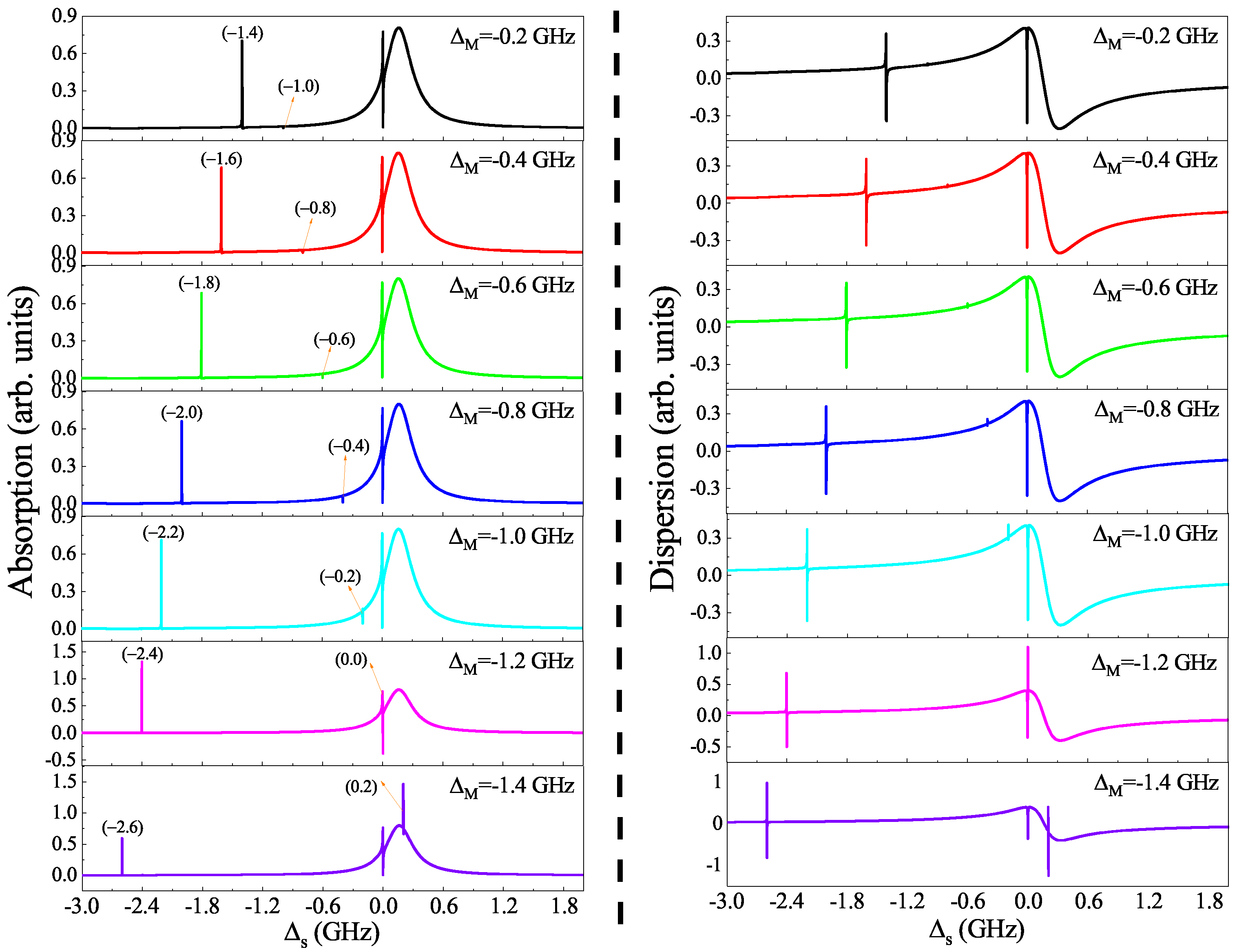
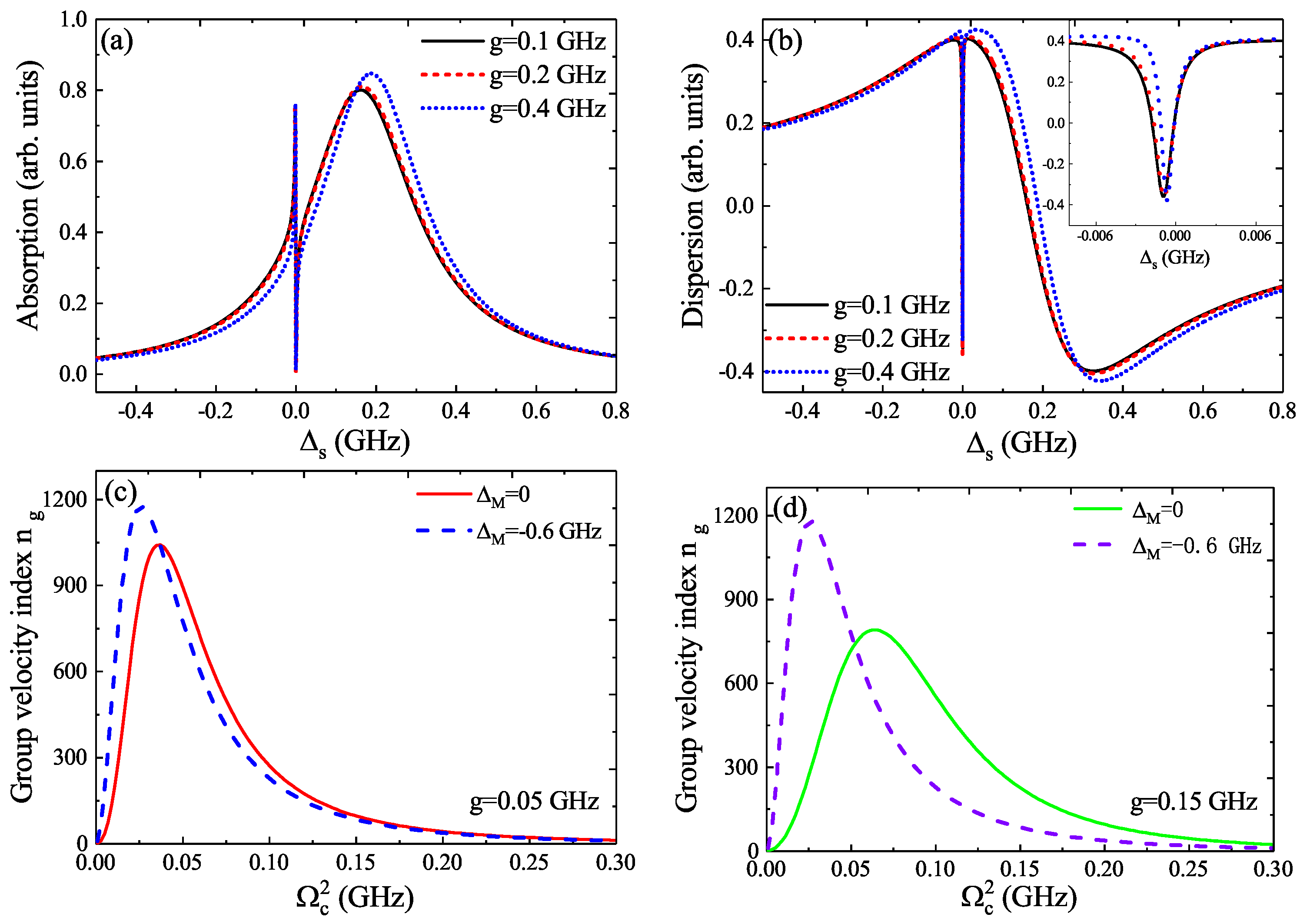
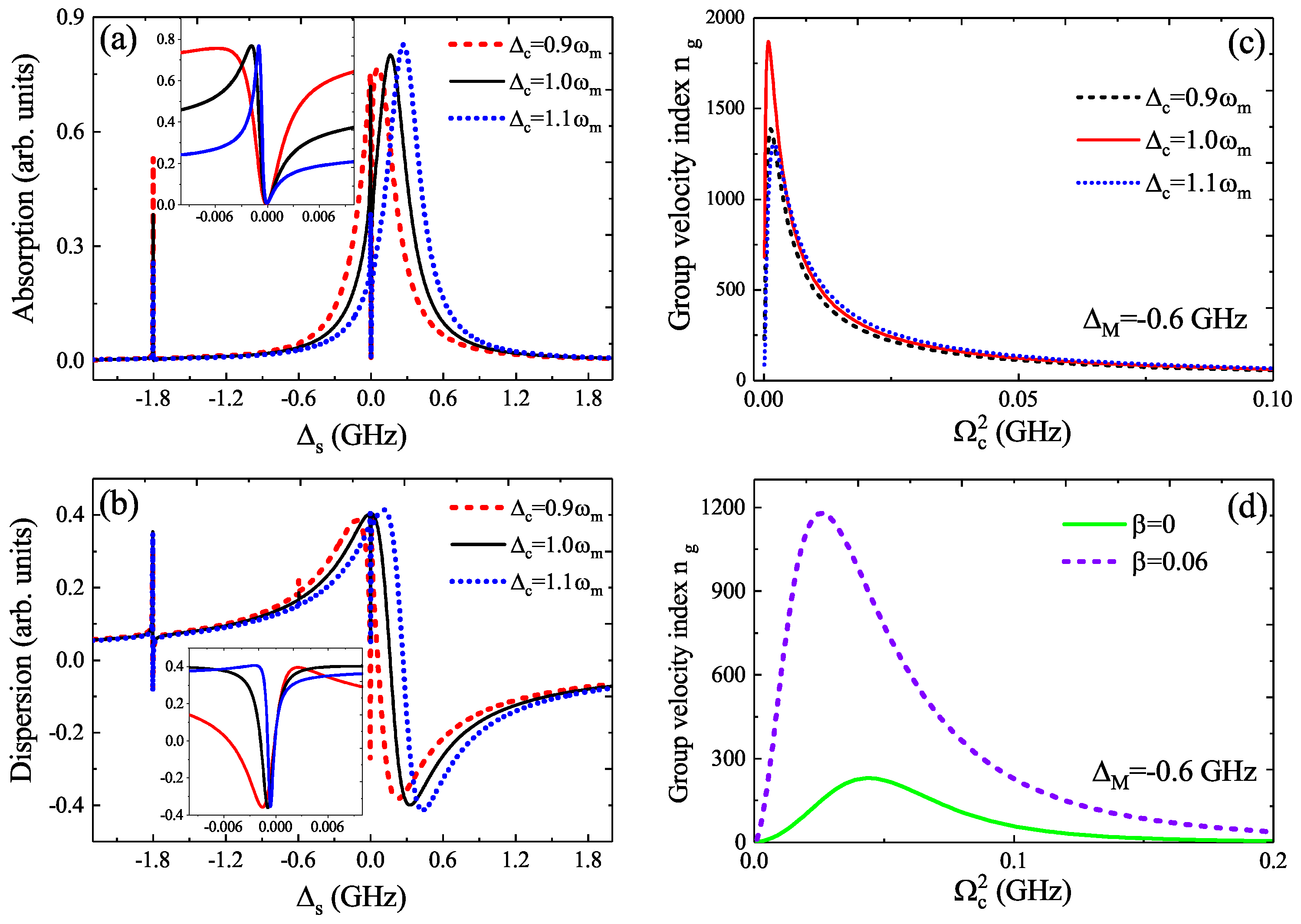
3. Numerical Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elliott, S.R.; Franz, M. Colloquium: Majorana fermions in nuclear, particle, and solid-state physics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2015, 87, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alicea, J. New directions in the pursuit of Majorana fermions in solid-state systems. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2012, 75, 076501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mourik, V.; Zuo, K.; Frolov, S.M.; Plissard, S.R.; Bakkers, E.P.; Kouwenhoven, L.P. Signatures of Majorana fermions in hybrid superconductor-semiconductor nanowire devices. Science 2012, 336, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, A.; Ronen, Y.; Most, Y.; Oreg, Y.; Heiblum, M.; Shtrikman, H. Zero-bias peaks and splitting in an Al–InAs nanowire topological superconductor as a signature of Majorana fermions. Nat. Phys. 2012, 8, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, M.T.; Yu, C.L.; Huang, G.Y.; Larsson, M.; Caroff, P.; Xu, H.Q. Anomalous zero-bias conductance peak in a Nb–InSb nanowire–Nb hybrid device. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 6414–6419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Yu, P.; Stenger, J.; Hocevar, M.; Car, D.; Plissard, S.R.; Bakkers, E.P.A.M.; Stanescu, T.D.; Frolov, S.M. Experimental phase diagram of zero-bias conductance peaks in superconductor/semiconductor nanowire devices. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1701476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nadj-Perge, S.; Drozdov, I.K.; Li, J.; Chen, H.; Jeon, S.; Seo, J.; MacDonald, A.H.; Bernevig, B.A.; Yazdani, A. Observation of Majorana fermions in ferromagnetic atomic chains on a superconductor. Science 2014, 346, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yin, J.X.; Wu, Z.; Wang, J.H.; Ye, Z.Y.; Gong, J.; Hou, X.Y.; Shan, L.; Li, A.; Liang, X.L.; Wu, X.X.; et al. Observation of a robust zero-energy bound state in iron-based superconductor Fe (Te, Se). Nat. Phys. 2015, 11, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, S.M.; Higginbotham, A.P.; Madsen, M.; Kuemmeth, F.; Jespersen, T.S.; Nygård, J.; Krogstrup, P.; Marcus, C.M. Exponential protection of zero modes in Majorana islands. Nature 2016, 531, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, H.H.; Zhang, K.W.; Hu, L.H.; Li, C.; Wang, G.Y.; Ma, H.Y.; Xu, Z.A.; Gao, C.L.; Guan, D.D.; Li, Y.Y.; et al. Majorana zero mode detected with spin selective Andreev reflection in the vortex of a topological superconductor. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 257003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, Q.L.; Pan, L.; Stern, A.L.; Burks, E.C.; Che, X.; Yin, G.; Wang, J.; Lian, B.; Zhou, Q.; Choi, E.S.; et al. Chiral Majorana fermion modes in a quantum anomalous Hall insulator–superconductor structure. Science 2017, 357, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rokhinson, L.P.; Liu, X.; Furdyna, J.K. The fractional ac Josephson effect in a semiconductor-superconductor nanowire as a signature of Majorana particles. Nat. Phys. 2012, 8, 795–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.; Xie, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Bernevig, B.A.; Yazdani, A. Distinguishing a Majorana zero mode using spin-resolved measurements. Science 2017, 358, 772–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urbaszek, B.; Marie, X.; Amand, T.; Krebs, O.; Voisin, P.; Maletinsky, P.; Högele, A.; Imamoglu, A. Nuclear spin physics in quantum dots: An optical investigation. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2013, 85, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.E.; Baranger, H.U. Detecting a Majorana-fermion zero mode using a quantum dot. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 84, 201308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flensberg, K. Non-Abelian operations on Majorana fermions via single-charge control. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 090503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leijnse, M.; Flensberg, K. Scheme to measure Majorana fermion lifetimes using a quantum dot. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 84, 140501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pientka, F.; Kells, G.; Romito, A.; Brouwer, P.W.; von Oppen, F. Enhanced zero-bias Majorana peak in the differential tunneling conductance of disordered multisubband quantum-wire/superconductor junctions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 227006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sau, J.D.; Sarma, S.D. Realizing a robust practical Majorana chain in a quantum-dot-superconductor linear array. Nat. Commu. 2012, 3, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deng, M.T.; Vaitiekėnas, S.; Hansen, E.B.; Danon, J.; Leijnse, M.; Flensberg, K.; Nygård, J.; Krogstrup, P.; Marcus, C.M. Majorana bound state in a coupled quantum-dot hybrid-nanowire system. Science 2016, 354, 1557–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.J.; Zhu, K.D. Nonlinear optomechanical detection for Majorana fermions via a hybrid nanomechanical system. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.J.; Fang, X.W.; Chen, C.Z.; Li, Y.; Tang, X.D. Robust signatures detection of Majorana fermions in superconducting iron chains. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.J.; Wu, H.W. Rabi splitting and opticalKerr nonlinearity of quantum dot mediated by Majorana fermions. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.J. Majorana fermions induced Fano resonance and fast-to-slow light in a hybrid semiconductor/superconductor ring device. Quantum Inf. Process. 2020, 19, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.X.; Wang, B.; Kong, C.; Xiong, H.; Wu, Y. Magnetic-field-dependent slow light in strontium atom-cavity system. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 112, 111109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.; Wang, B.; Liu, Z.X.; Xiong, H.; Wu, Y. Magnetically controllable slow light based on magnetostrictive forces. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 5544–5556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.X.; Xiong, H.; Wu, Y. Room-temperature slow light in a coupled cavity magnon-photon system. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 57047–57053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson-Rae, I.; Zoller, P.; Imamoglu, A. Laser cooling of a nanomechanical resonator mode to its quantum ground state. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 075507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.J. Multiple-Fano-resonance-induced fast and slow light in the hybrid nanomechanical-resonator system. Phys. Rev. A 2021, 104, 013708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridolfo, A.; Di Stefano, O.; Fina, N.; Saija, R.; Savasta, S. Quantum plasmonics with quantum dot-metal nanoparticle molecules: Influence of the Fano effect on photon statistics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 263601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Sun, B.; Berman, P.R.; Steel, D.G.; Bracker, A.S.; Gammon, D.; Sham, L.J. Coherent optical spectroscopy of a strongly driven quantum dot. Science 2007, 317, 929–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, R.W. Nonlinear Optics; Academic: San Diego, CA, USA, 1992; p. 225. [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner, C.W.; Zoller, P. Quantum Noise; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, G.S.; Huang, S. Electromagnetically induced transparency in mechanical effects of light. Phys. Rev. A 2010, 81, 041803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harris, S.E.; Field, J.E.; Kasapi, A. Dispersive properties of electromagnetically induced transparency. Phys. Rev. A 1992, 46, R29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennink, R.S.; Boyd, R.W.; Stroud, C.R.; Wong, V. Enhanced self-action effects by electromagnetically induced transparency in the two-level atom. Phys. Rev. A 2001, 63, 033804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boyd, R.W.; Gauthier, D.J. Controlling the velocity of light pulses. Science 2009, 326, 1074–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.J.; Zhu, K.D. Surface plasmon enhanced sensitive detection for possible signature of Majorana fermions via a hybrid semiconductor quantum Dot-Metal nanoparticle system. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, H. Nanoresonator Enhancement of Majorana-Fermion-Induced Slow Light in Superconducting Iron Chains. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12121435
Chen H. Nanoresonator Enhancement of Majorana-Fermion-Induced Slow Light in Superconducting Iron Chains. Micromachines. 2021; 12(12):1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12121435
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Huajun. 2021. "Nanoresonator Enhancement of Majorana-Fermion-Induced Slow Light in Superconducting Iron Chains" Micromachines 12, no. 12: 1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12121435
APA StyleChen, H. (2021). Nanoresonator Enhancement of Majorana-Fermion-Induced Slow Light in Superconducting Iron Chains. Micromachines, 12(12), 1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12121435





