Micro Direct Methanol Fuel Cell Based on Reduced Graphene Oxide Composite Electrode
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Preparation of Catalyst Layer Slurry
2.3. Preparation of Electrode
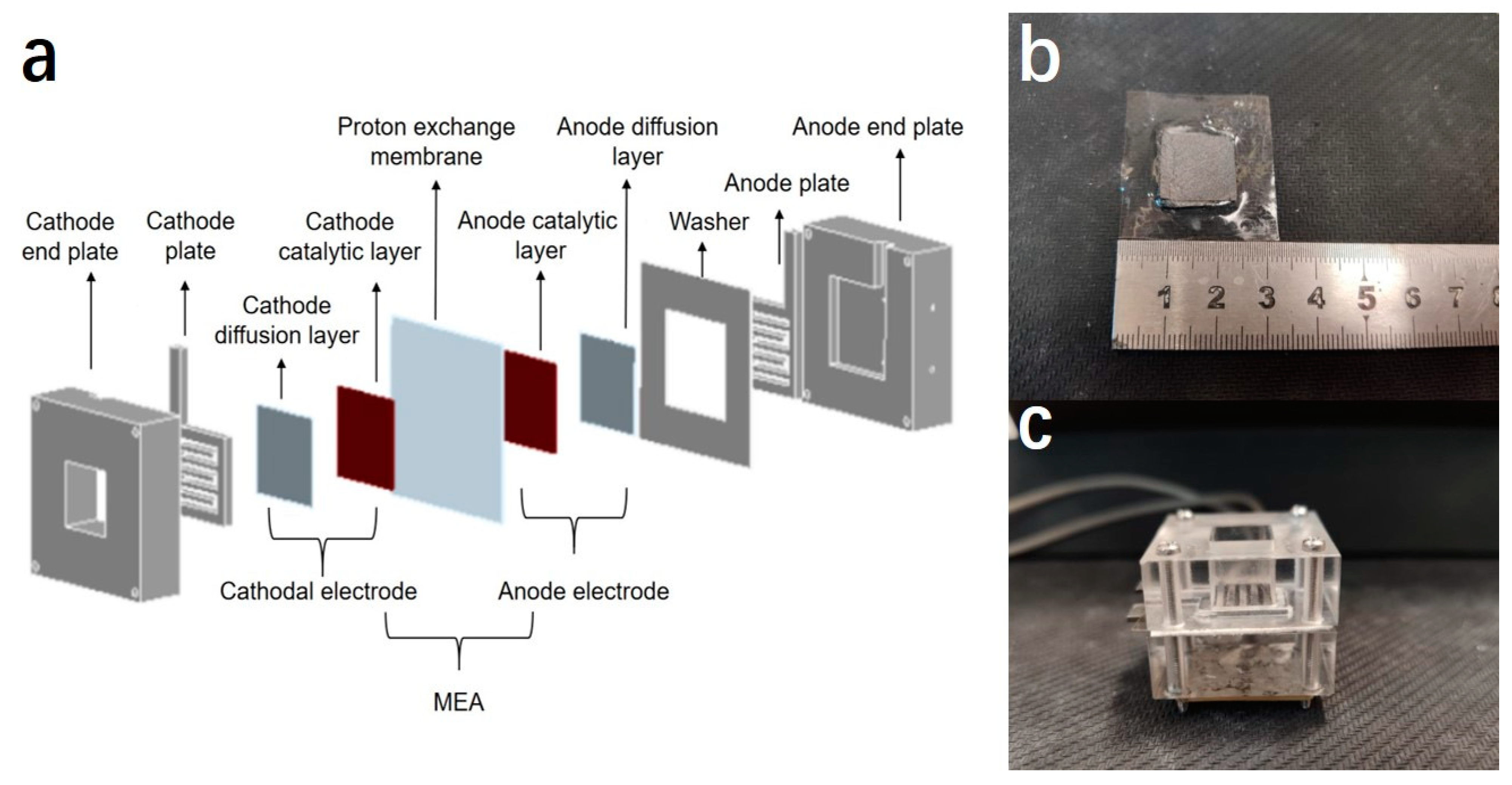
2.4. Preparation of Membrane Electrode Assembly (MEA)
2.5. Assembling, Activation and Performance Testing of Single Cells
3. Results and Discussion
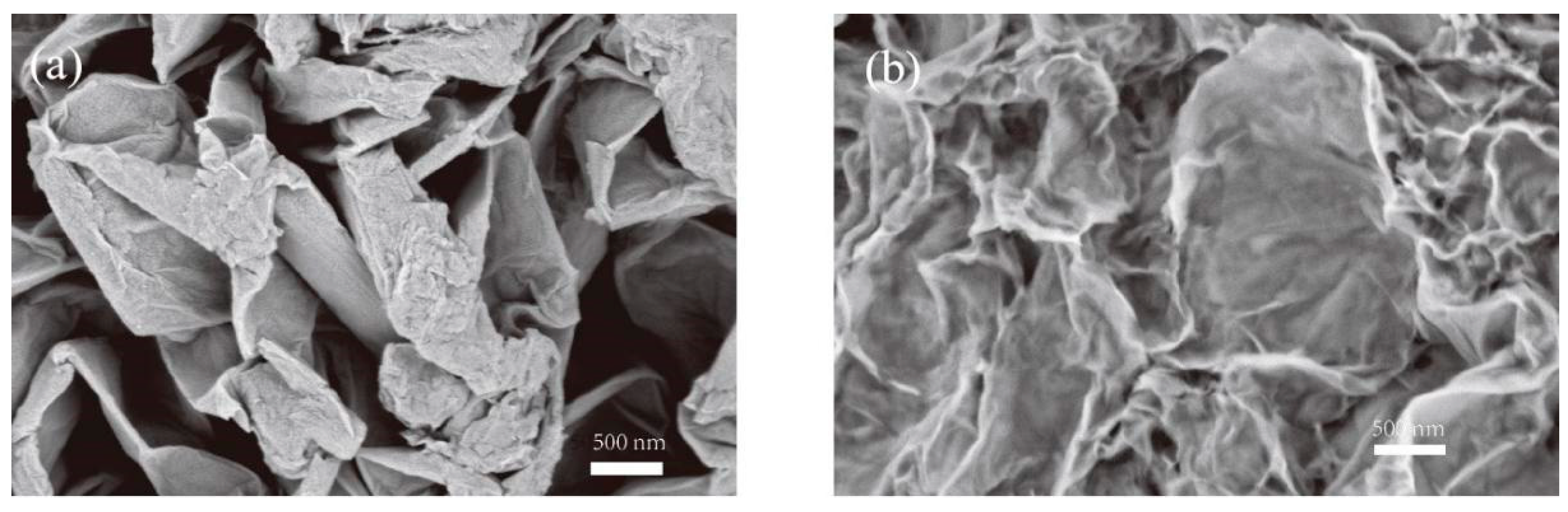
3.1. Structural Characterizations of Graphene Oxide (GO) and Reduced Graphene Oxide (rGO)
3.2. Influence of High-Temperature Polyol Preparation Process on the Performance of Micro Direct Methanol Fuel cEll (μDMFC)
3.2.1. The Effect of Reducing pH on the Performance of μDMFC
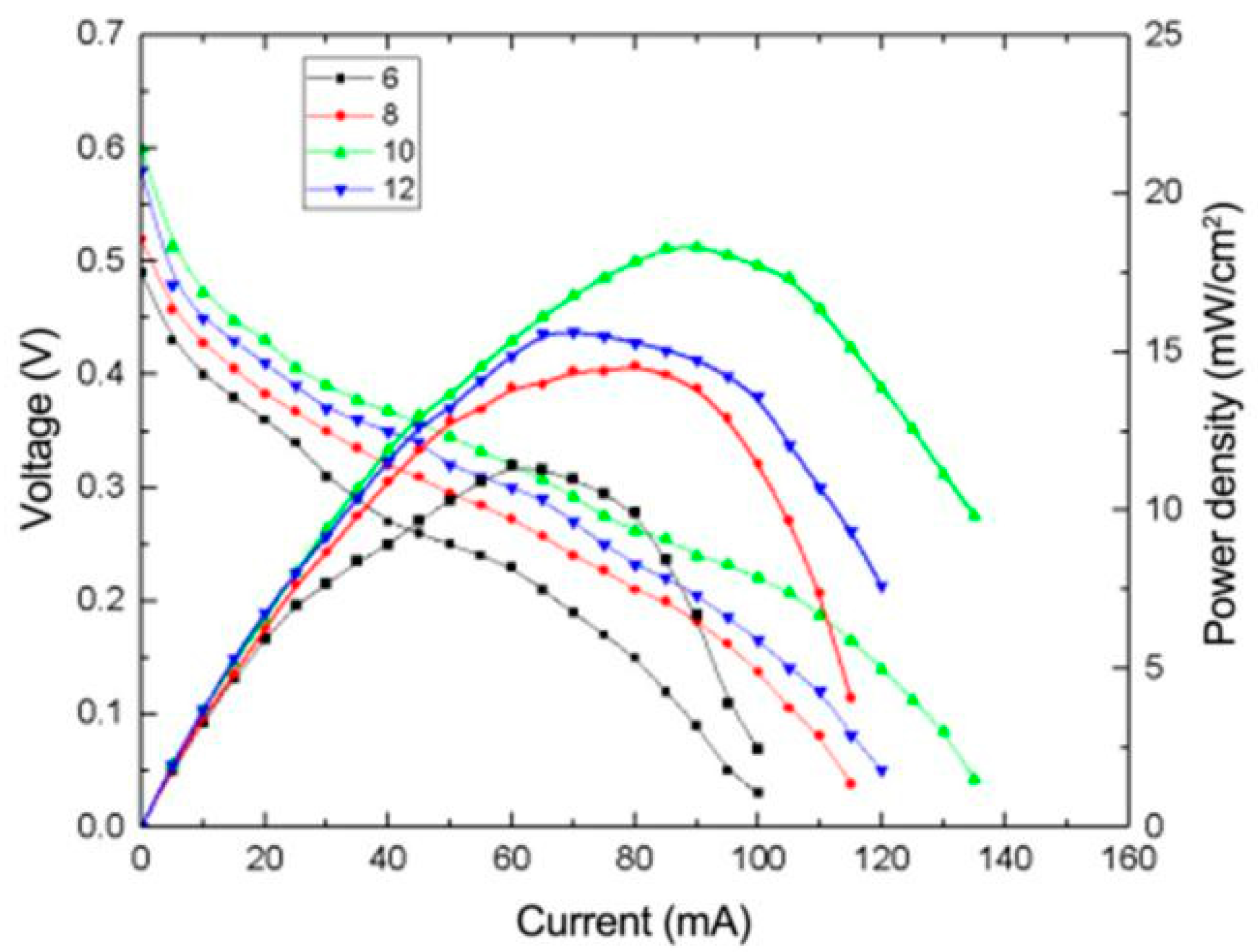
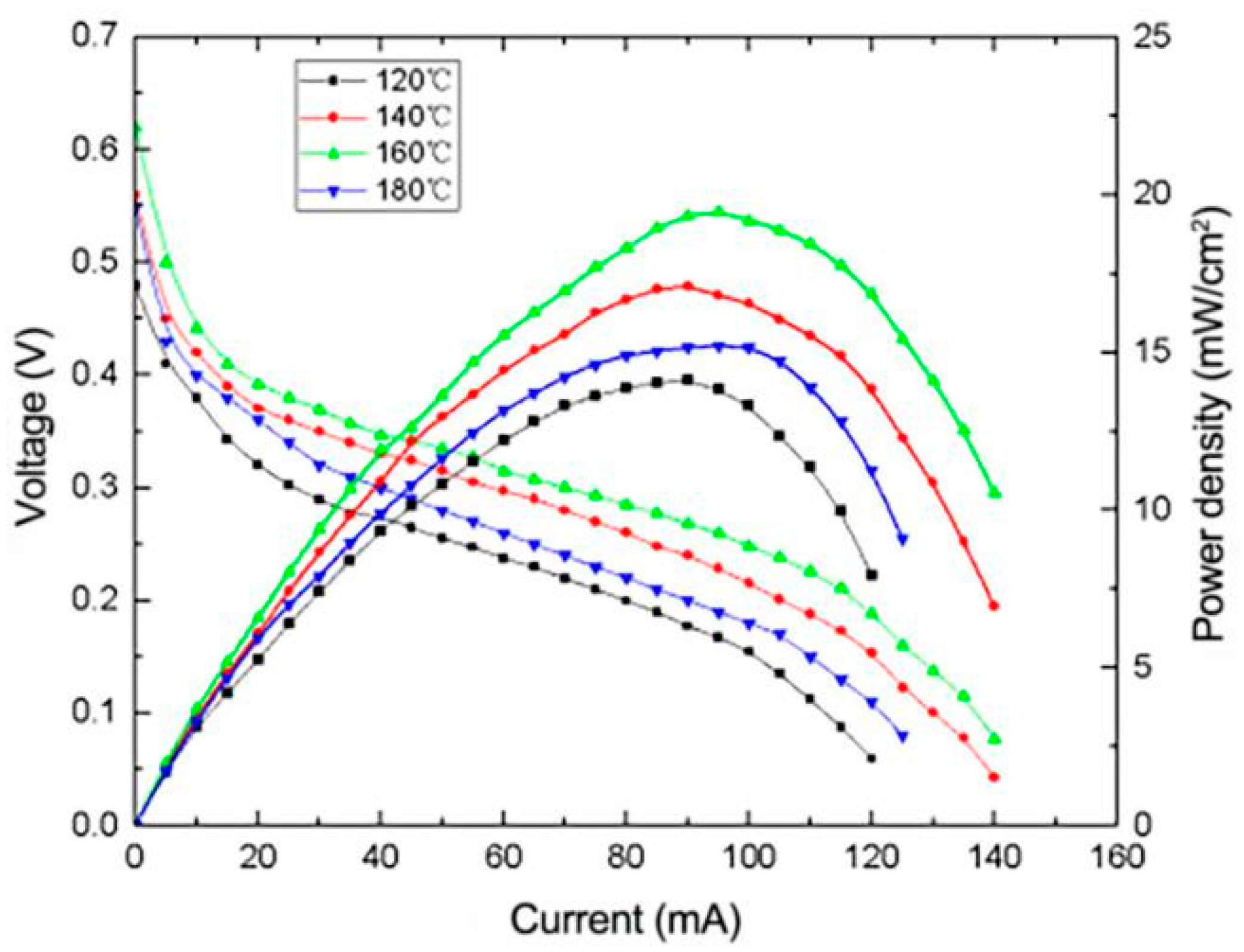
3.2.2. Effect of Heating Temperature on the Performance of μDMFC
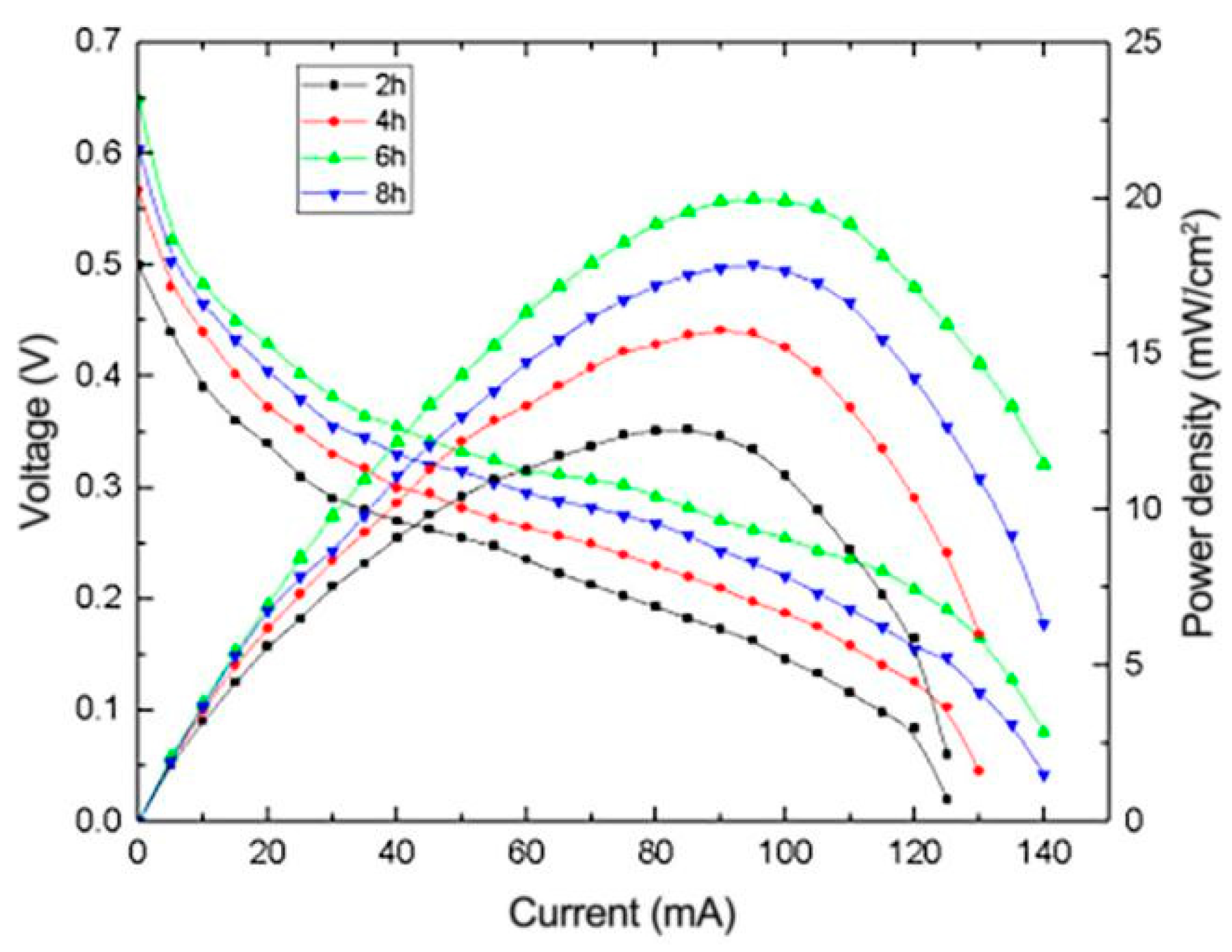
3.2.3. The Effect of Heating Time on the Performance of μDMFC
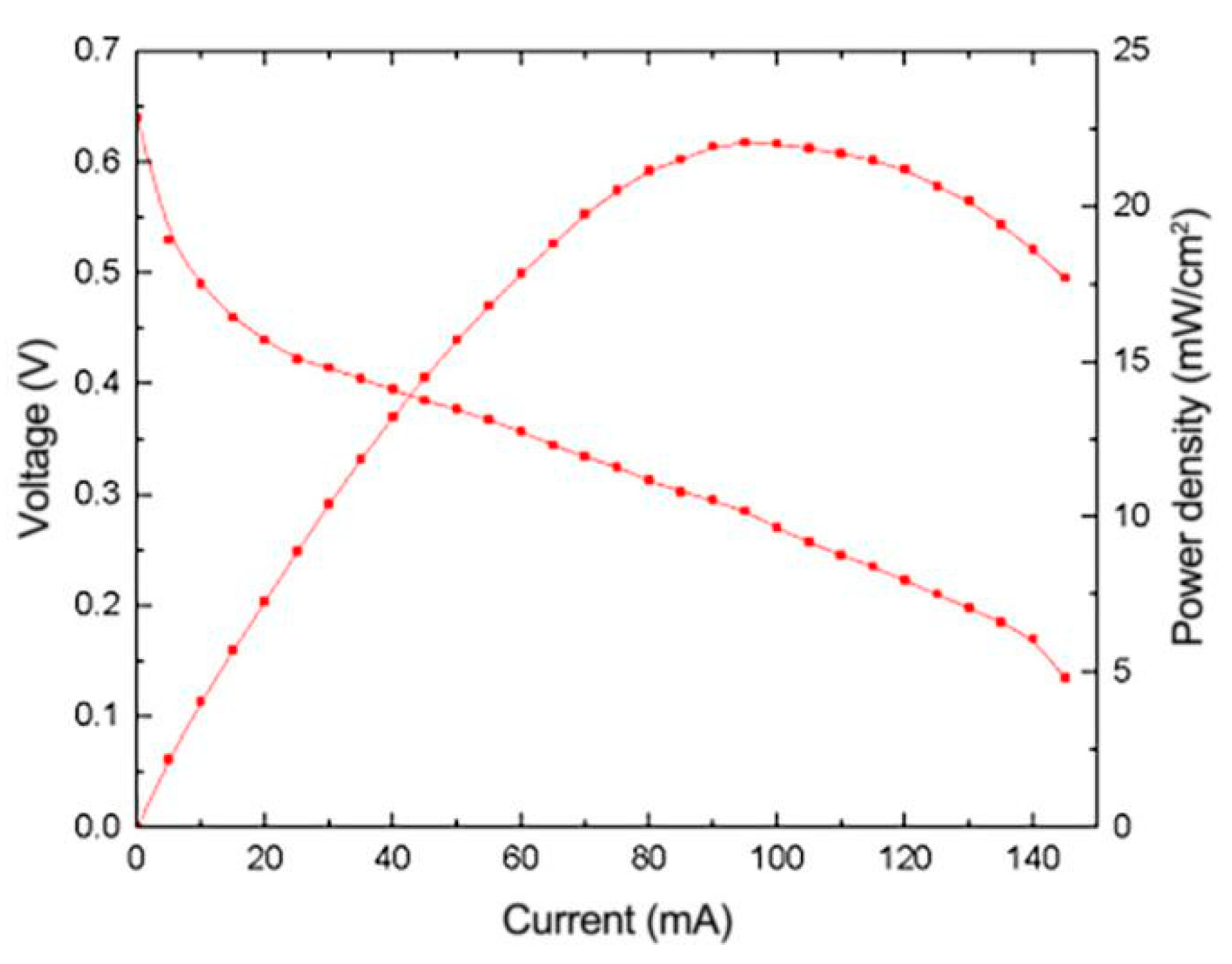
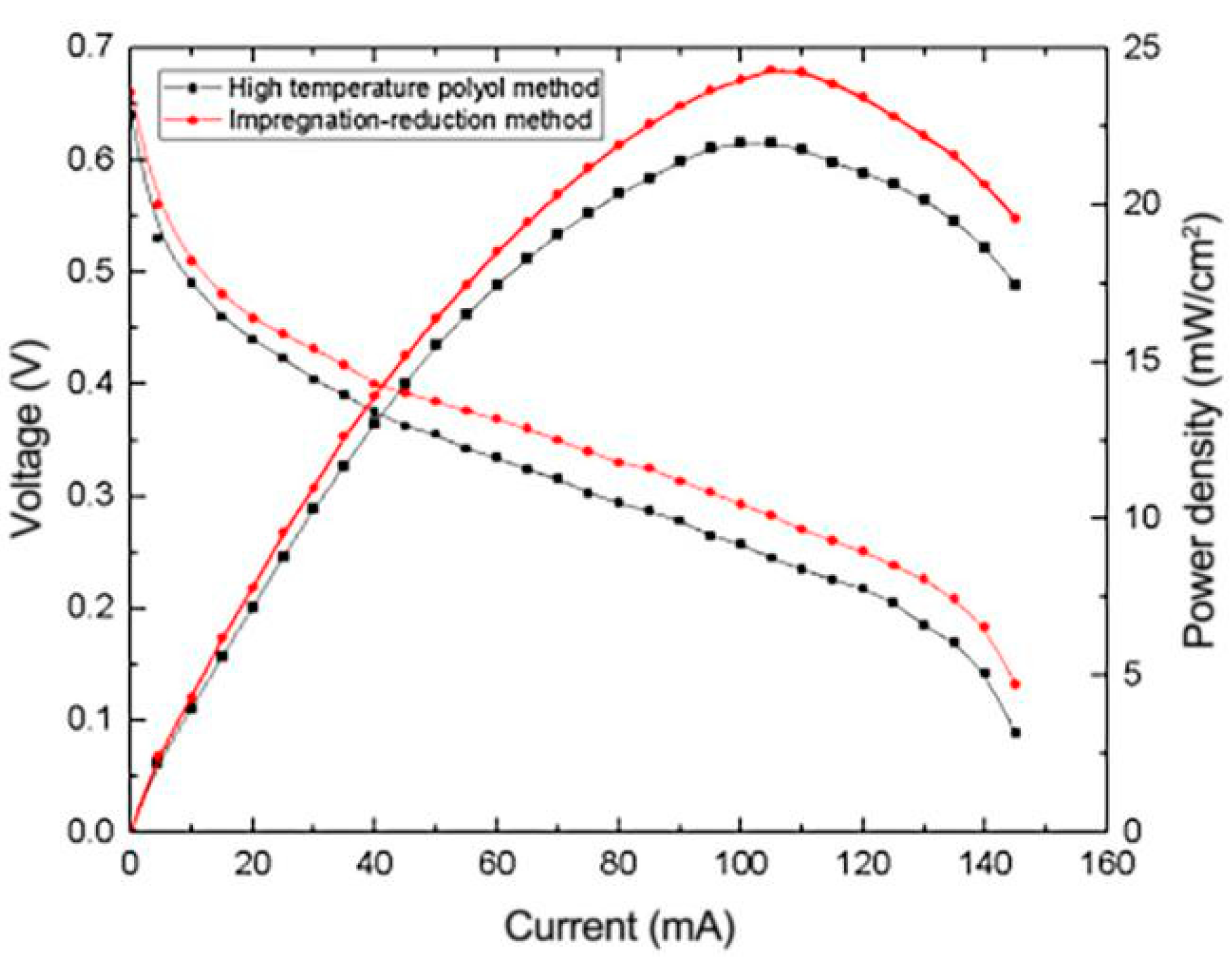
3.3. Effect of Impregnation Reduction Method on the Performance of μDMFC
3.4. Effect of Composition of Catalytic Layer on the Performance of μDMFC
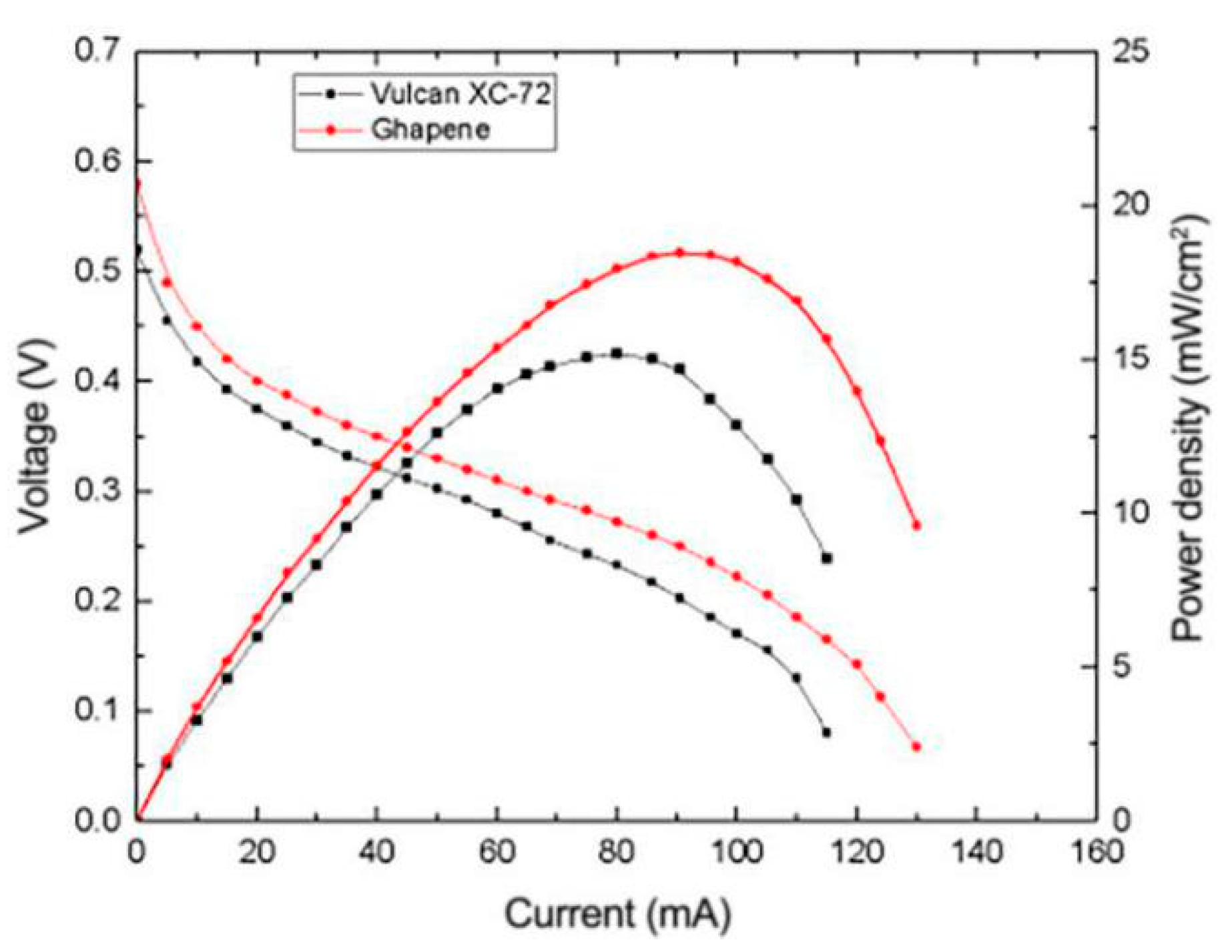
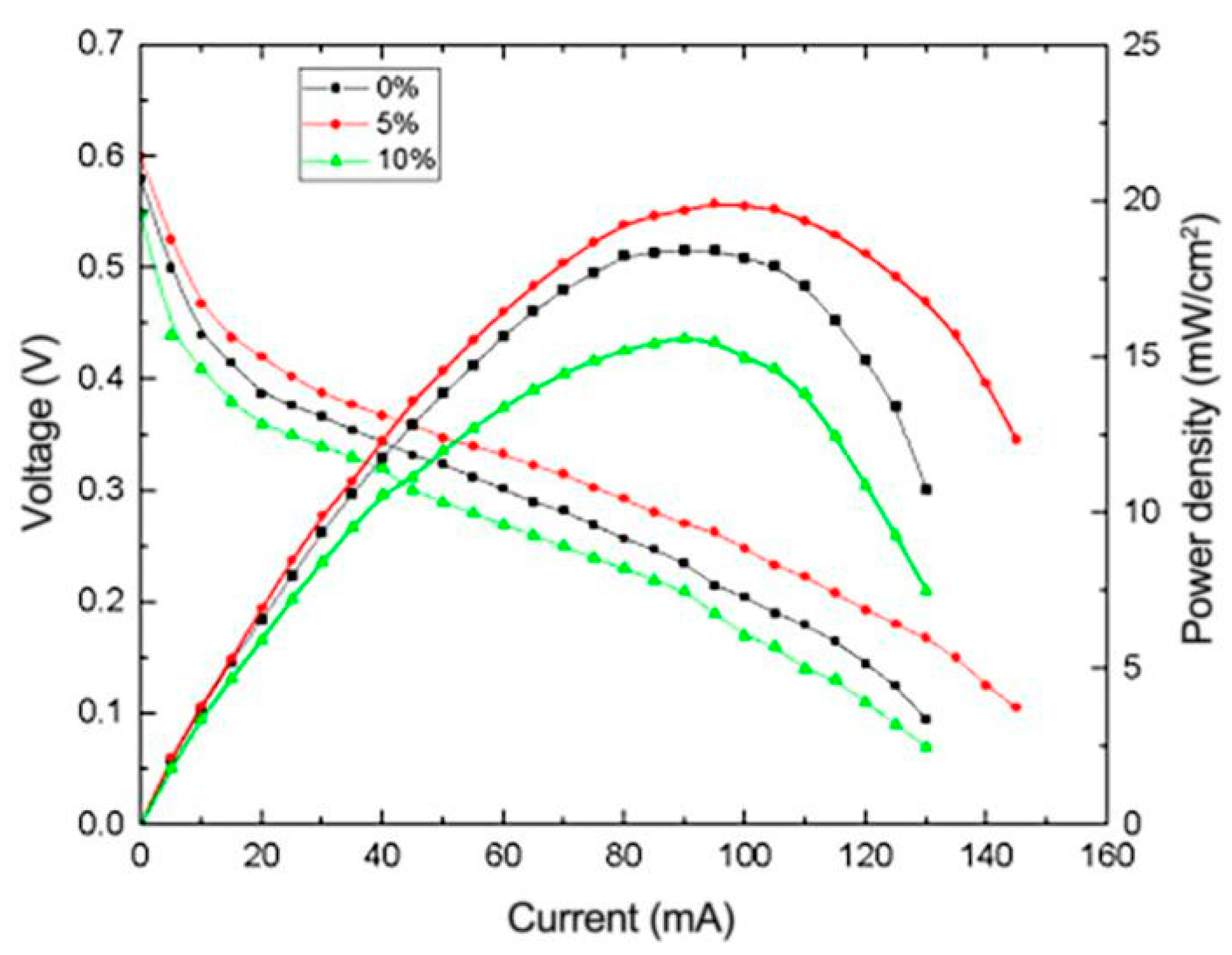
3.4.1. Effects of Different Catalyst Carriers on the Performance of μDMFC
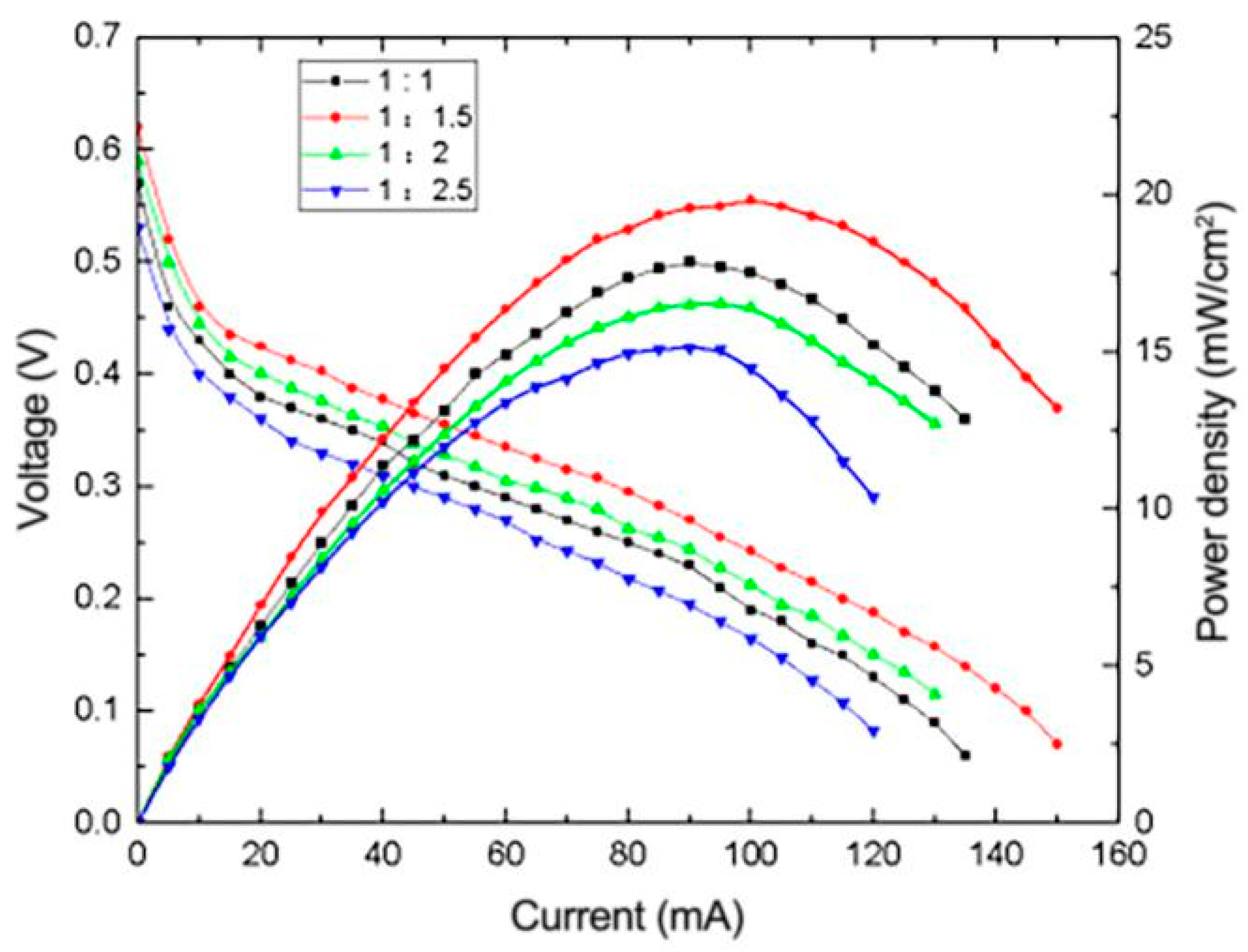
3.4.2. Effect of Pt-Ru Molar Ratio on the Performance of μDMFC
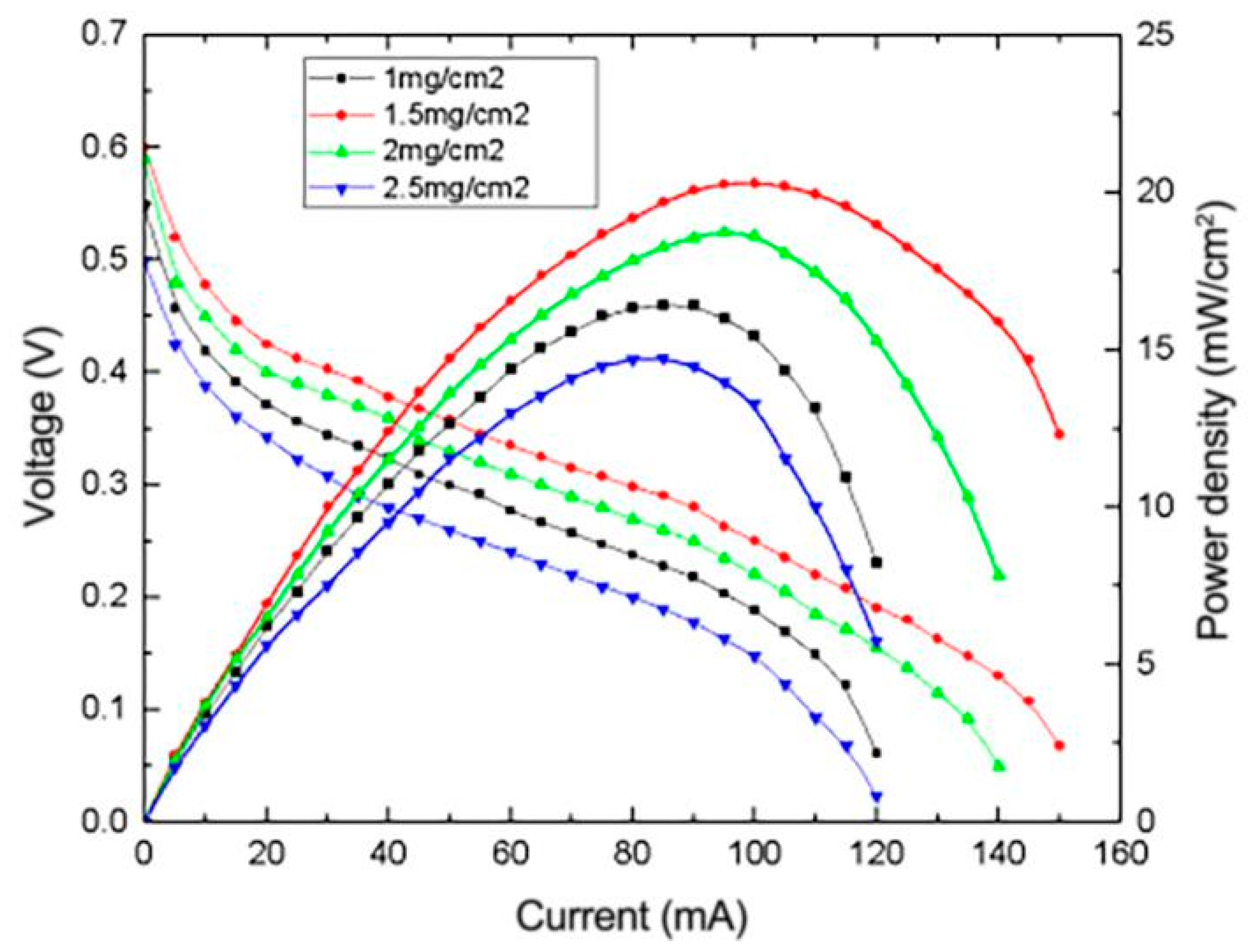
3.4.3. Effect of Pt Content on the Performance of μDMFC
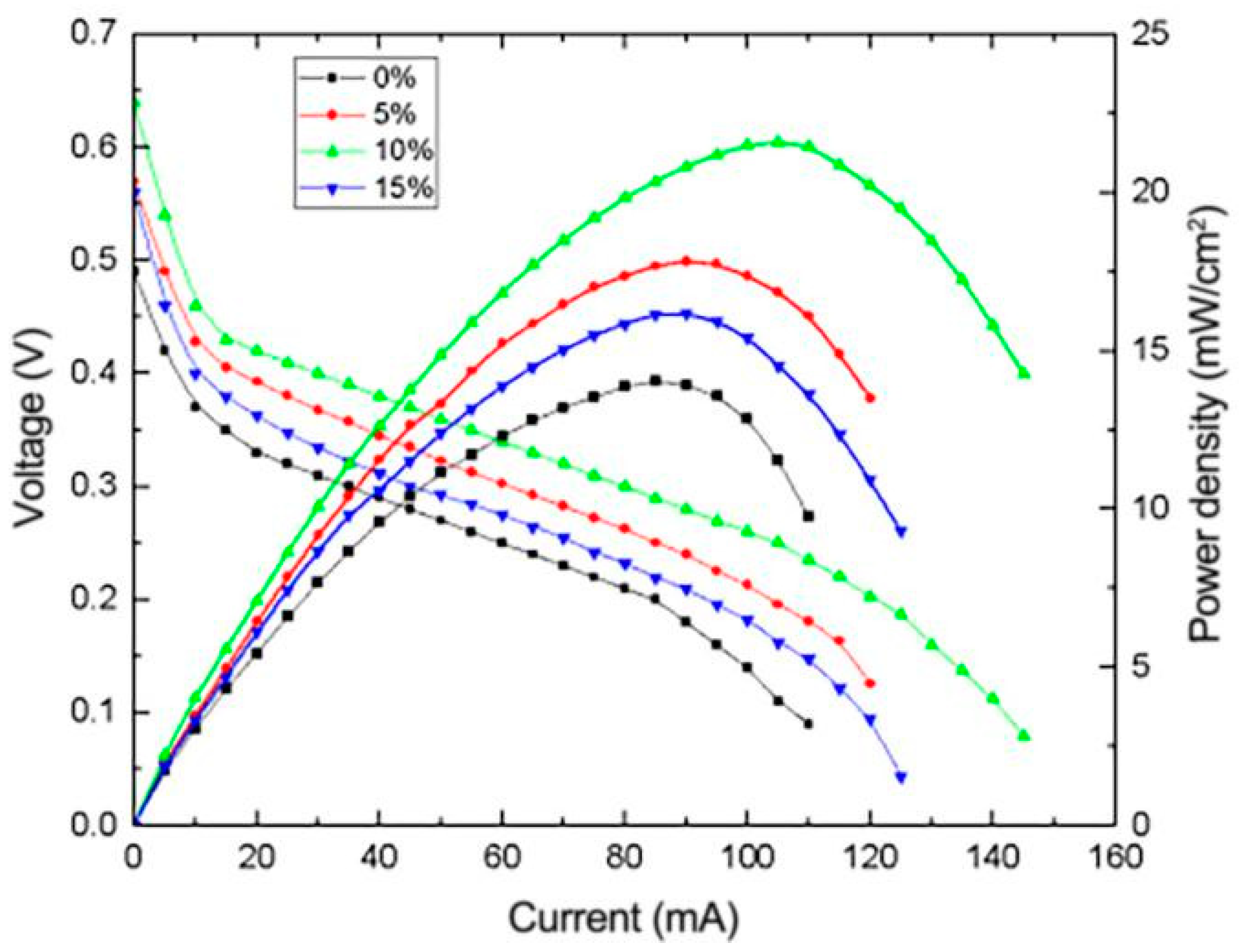
3.4.4. Effect of Nafion Content on the Performance of μDMFC
3.5. Effect of Micro-Porous Layer Composition on Performance of μDMFC
3.5.1. Effect of Different Carbon Loading Amounts on the Performance of μDMFC
3.5.2. Effect of Different PTFE Content Amounts on the Performance of μDMFC
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gong, L.Y.; Yang, Z.Y.; Li, K.; Xing, W.; Liu, C.P.; Ge, J.J. Recent development of methanol electrooxidation atalysts for direct methanol fuel cell. J. Energy Chem. 2018, 27, 1618–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.Y.; Chuai, W.H.; Guo, Z.M.; Tu, Z.Y.; Kong, F.B. The Self-Adaptive Fuel Supply Mechanism in Micro DMFC Based on the Microvalve. Micromachines 2019, 10, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.W.; Yin, L.; Yang, W.L.; Cheng, Y.H.; Wen, F.; Liu, C.R.; Dong, L.X.; Wang, M.H.; Ma, S.P.; Feng, X. Evaluation of structural aspects and operation environments on the performance of passive micro direct methanol fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 2594–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.W.; Yuan, Z.X.; Wen, F.; Cheng, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.F.; Wang, G.F. A bipolar passive DMFC stack for portable applications. Energy 2018, 144, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.W.; He, M.Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.F.; Liu, X.W.; Wang, G.F. A “4-cell” modular passive DMFC (direct methanol fuel cell) stack for portable applications. Energy 2015, 82, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, S.S.; Chen, W.C. Performance Tests and Pressure Drop Measurements in the Anode Flow field of a μDMFC. Fuel Cells 2010, 10, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.S.; Zhu, H.; Guo, Y. Experimental Test and Performance Optimization of Single Cell in Direct methanol fuel cell. J. Beijing Jiaotong Univ. 2010, 34, 90–94. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, L.Y.; Wang, X.H.; Jiang, Y.Q.; Zhang, Q.; Qiu, X.P.; Zhou, Y.A.; Liu, L.T. A micro-direct methanol fuel cell stack with optimized design and microfabrication. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2008, 143, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.M.; Wang, H.J.; Peng, F.; Liang, J.H.; Yu, H.; Yang, J. MnO2/CNT supported Pt and Pt-Ru nanocatalysts for direct methanol fuel cells. Langmuir 2009, 25, 7711–7717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainoodin, A.M.; Kamarudin, S.K.; Daud, W.R.W. Electrode in direct methanol fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2010, 35, 4606–4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, V.B.; Rangel, C.M.; Pinto, A.M.F.R. Water management in direct methanol fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2009, 34, 8246–8256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muliani, M.; Sharifah, N.T.; Lim, K.L. Recent progress of anode catalysts and their support materials for methanol electrooxidation. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2019, 44, 14744–14769. [Google Scholar]
- Sakthivel, M.; Schlange, A.; Kunz, U.; Turek, T. Microwave assisted synthesis of surfactant stabilized platinum/carbon nanotube electrocatalysts for direct methanol fuel cell applications. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 7083–7089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.W.; Fang, S.; Zhang, Y.F. Structure Design and Implementation of the Passive μ-DMFC. Micromachines 2015, 6, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Zhu, Y.M.; Shen, C.W.; Zhou, Y.A.; Wu, X.M.; Liu, L.T. A novel assembly method using multi-layer bonding technique for micro direct methanol fuel cells and their stack. Sens. Actuators A 2012, 188, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, K.Y.; Yuan, Z.Y. Design and experimental analysis of a dual-cavity high-concentration adaptive passive micro direct methanol fuel cell. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ozden, A.; Ercelik, M.; Ouellette, D.; Colpan, C.O.; Ganjehsarabi, H.; Hamdullahpur, F. Designing, modeling and performance investigation of bio-inspired flow field based DMFCs. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 21546–21558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.F.; He, Q.; Liu, C.; Yuan, T.; Zhang, S.; Hui, Y. Nafion-microporous organic polymer networks composite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 476, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adilbish, G.; Yu, Y.T. Effect of the Nafion content in the MPL on the catalytic activity of the Pt/C-Nafion electrode prepared by pulsed electrophoresis deposition. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.P.; Chang, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.X.; Liu, Z.; Li, J. Electro-osmotic drag coefficient and proton conductivity in Nafion® membrane for PEMFC. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2010, 35, 3120–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, X.; Cao, L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, B.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Z. Enhanced proton conductivity of Nafion composite membrane by incorporating phosphoric acid-loaded covalent organic framework. J. Power Sources 2016, 332, 265–273. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, J.C.; Lin, C.K. Effect of PTFE content in gas diffusion layer based on Nafion/PTFE membrane for low humidity proton exchange membrane fuel cell. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2011, 42, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.Q.; Wang, C.Y. Development of micro direct methanol fuel cells for high power applications. J. Power Sources 2005, 144, 141–145. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Hu, S.; Yin, L.; Yang, W.; Yu, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, G.; Wang, L. Micro Direct Methanol Fuel Cell Based on Reduced Graphene Oxide Composite Electrode. Micromachines 2021, 12, 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12010072
Liu C, Hu S, Yin L, Yang W, Yu J, Xu Y, Li L, Wang G, Wang L. Micro Direct Methanol Fuel Cell Based on Reduced Graphene Oxide Composite Electrode. Micromachines. 2021; 12(1):72. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12010072
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Chaoran, Sanshan Hu, Lu Yin, Wenli Yang, Juan Yu, Yumin Xu, Lili Li, Gaofeng Wang, and Luwen Wang. 2021. "Micro Direct Methanol Fuel Cell Based on Reduced Graphene Oxide Composite Electrode" Micromachines 12, no. 1: 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12010072
APA StyleLiu, C., Hu, S., Yin, L., Yang, W., Yu, J., Xu, Y., Li, L., Wang, G., & Wang, L. (2021). Micro Direct Methanol Fuel Cell Based on Reduced Graphene Oxide Composite Electrode. Micromachines, 12(1), 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12010072




