Oil Conductivity, Electric-Field-Induced Interfacial Charge Effects, and Their Influence on the Electro-Optical Response of Electrowetting Display Devices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. EWD Device Fabrication
2.2. EWOD Sample (for Contact Angle Measurement) Fabrication
2.3. Oil Conductivity Measurement
2.4. Electrical and Optical Measurements
2.5. Optical Measurement Data Processing
2.6. Contact Angle Measurements
2.7. Oil–Water Surface Tension Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Driving Polarity and Oil Conductivity on Optical Response
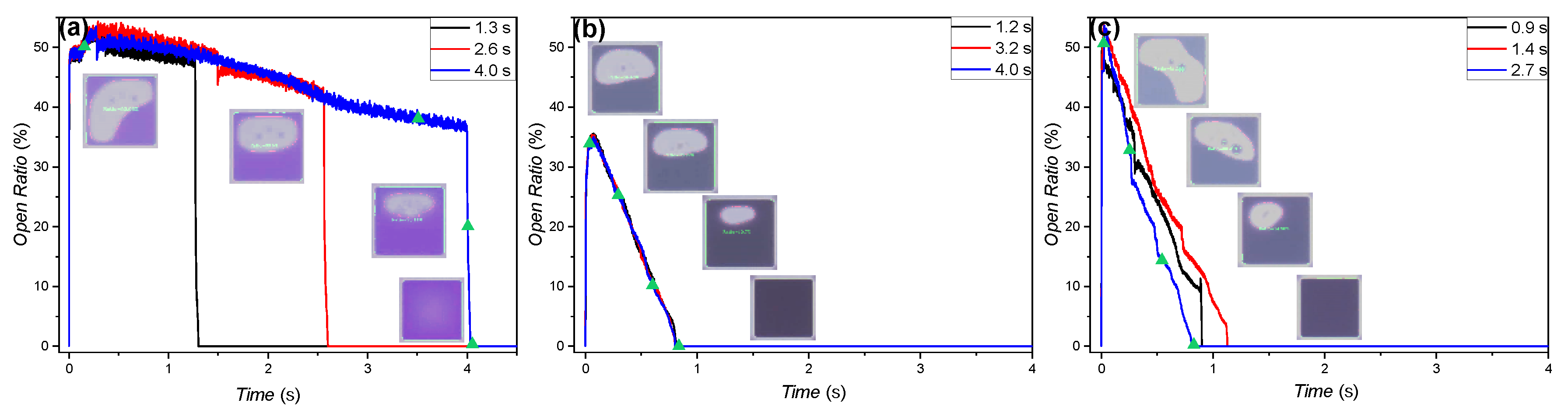
3.1.1. Oil Conductivity Effect on EWD Devices’ Behavior
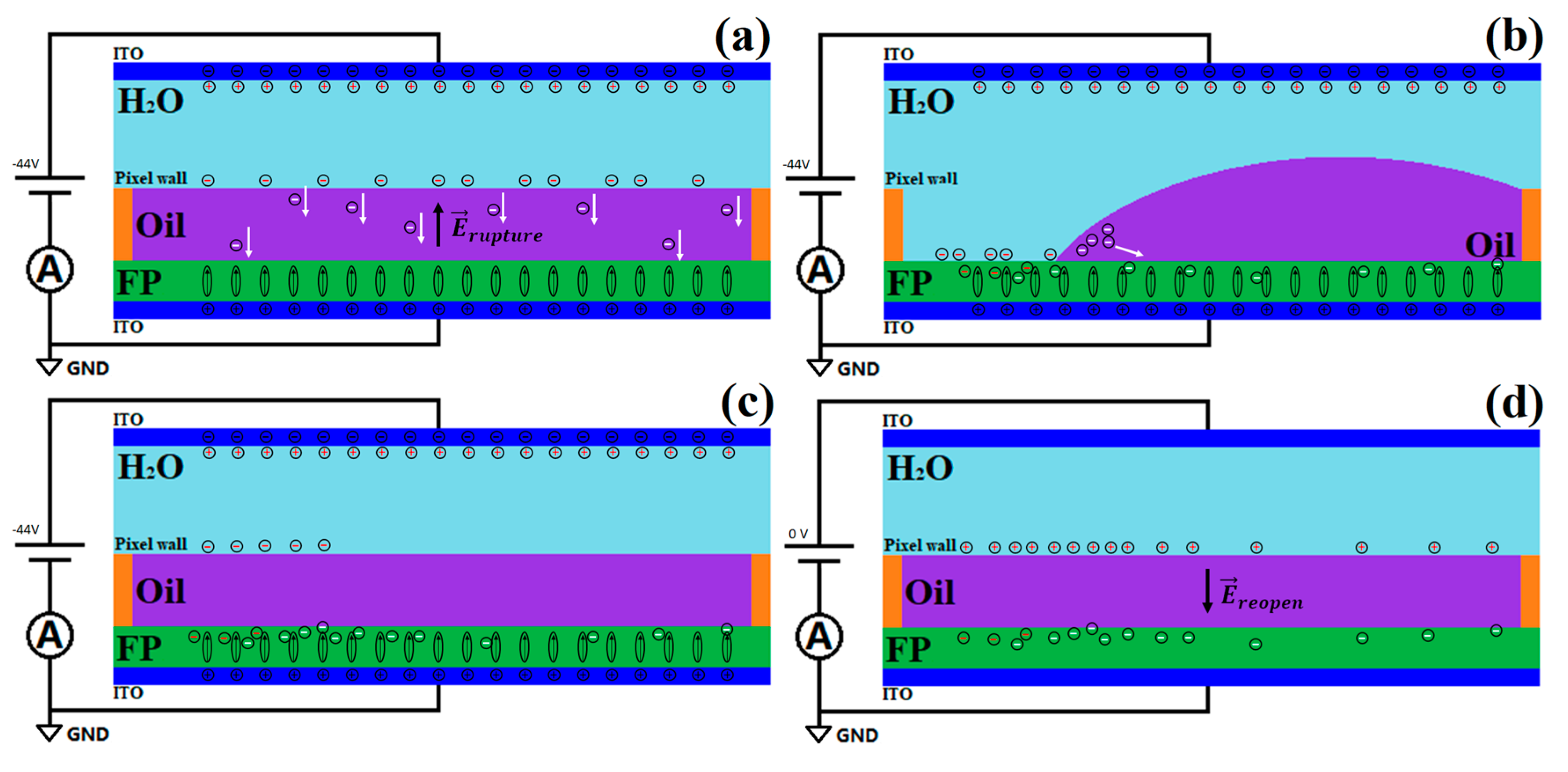
3.1.2. Charge Trapping Effect on EWD Devices’ Behavior
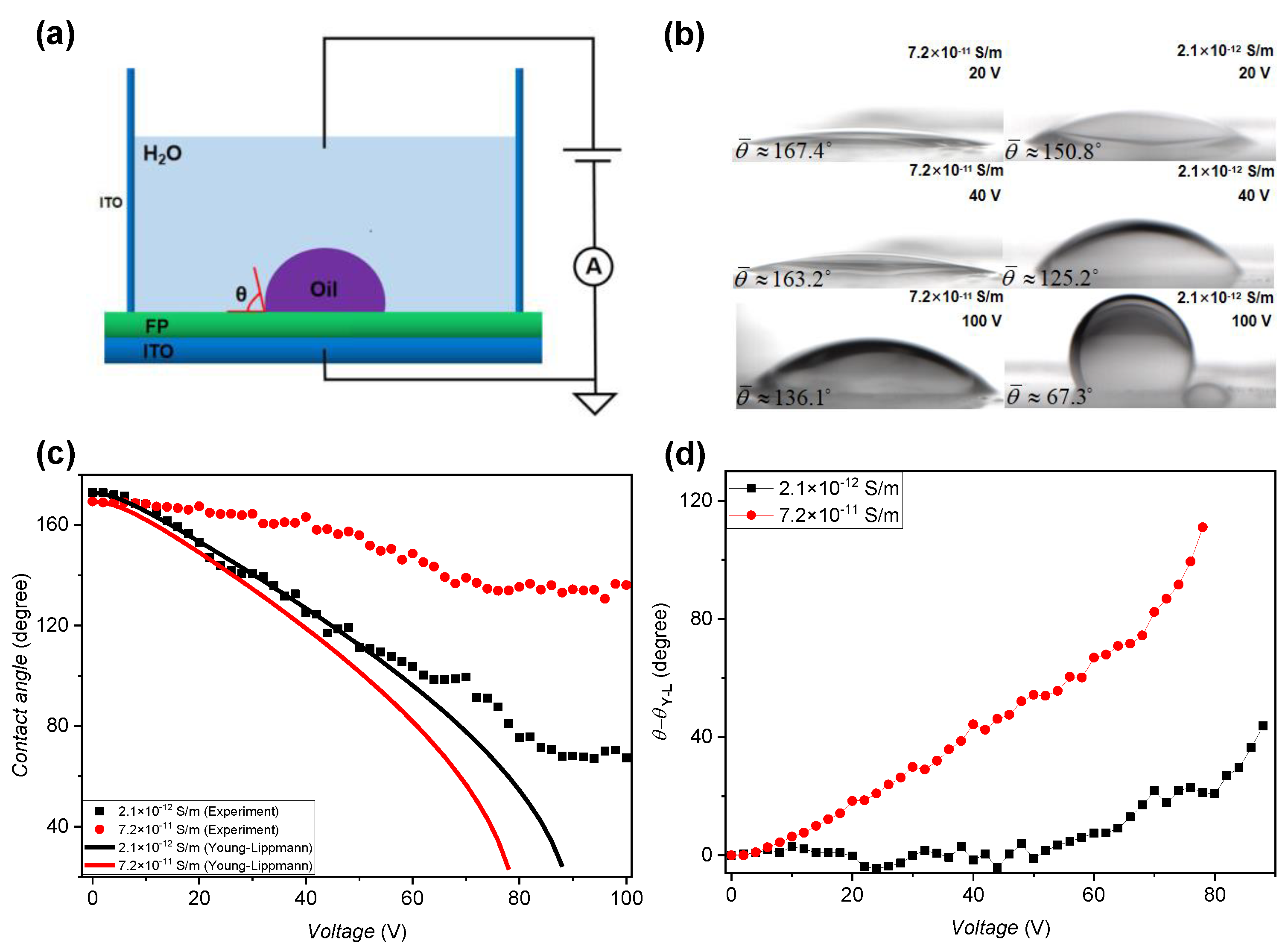
3.1.3. Effect of the Oil Conductivity on the Wettability of Conductive Liquid
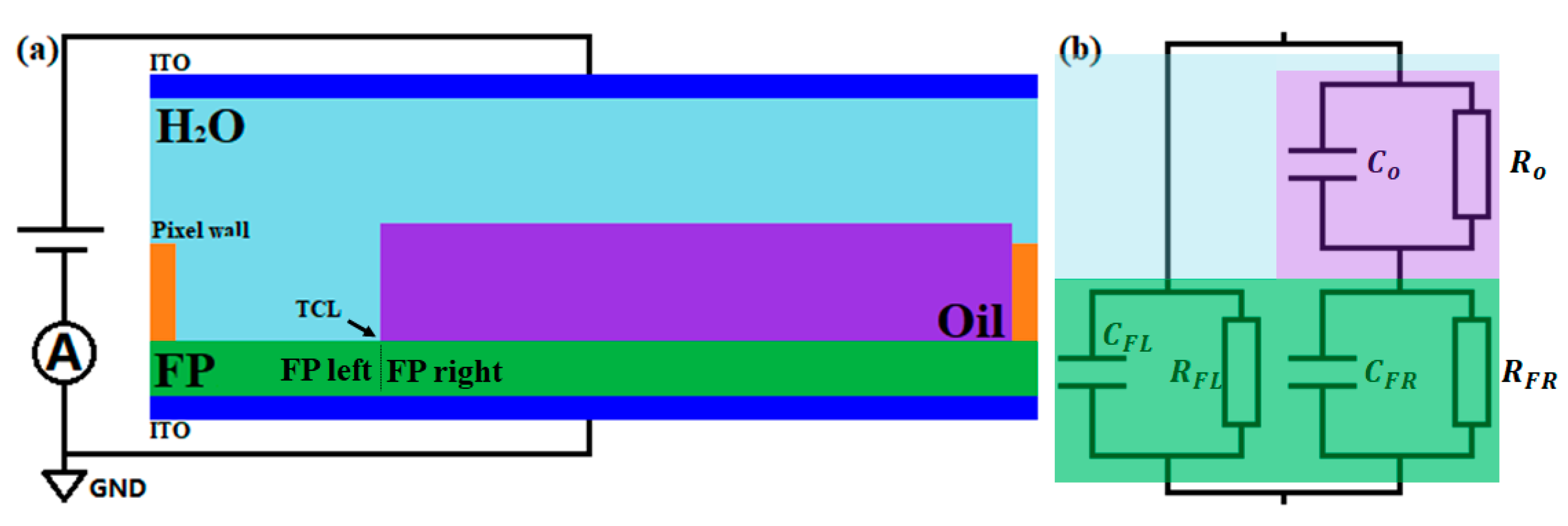
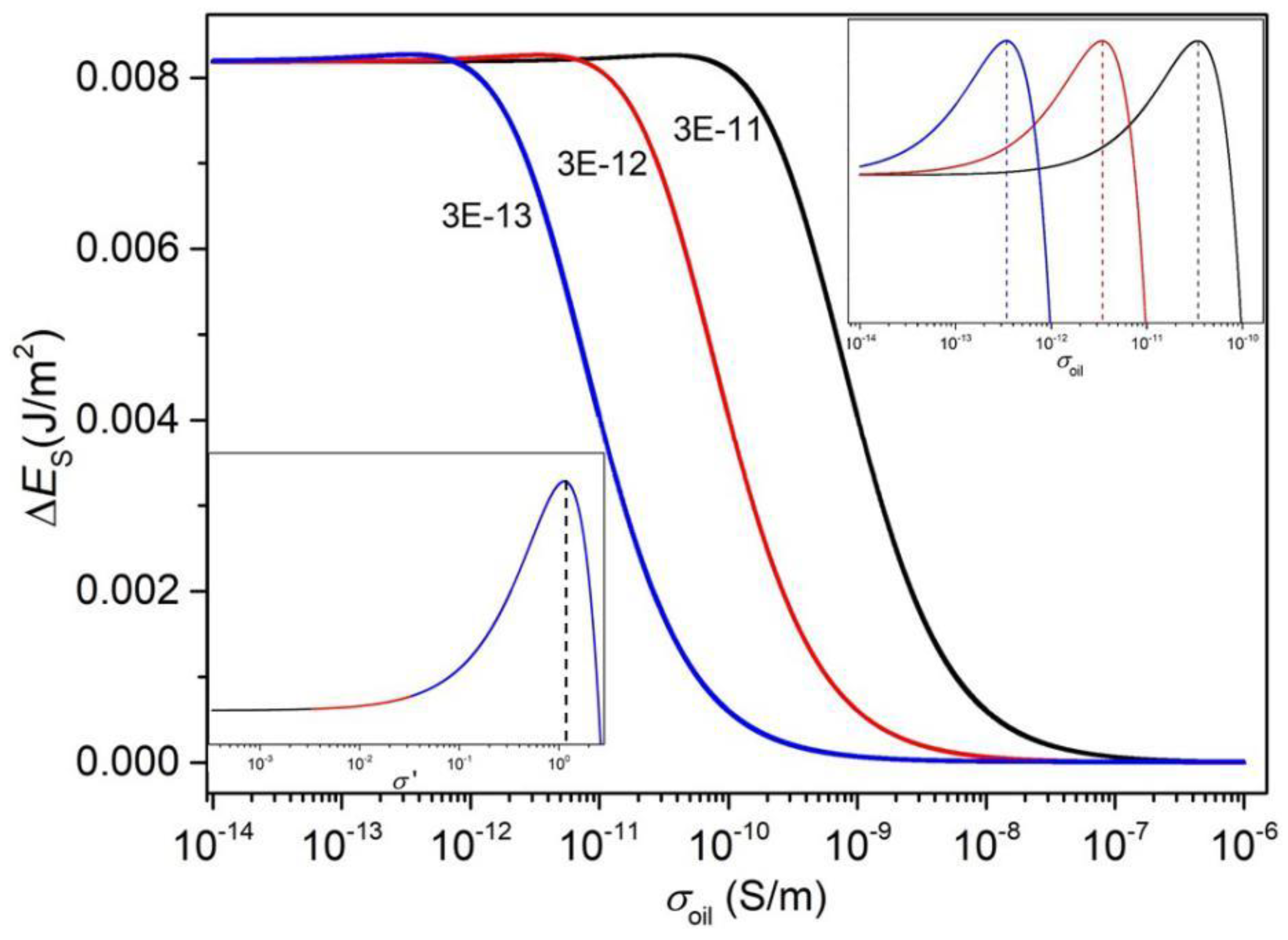
3.1.4. A Phenomenological Model
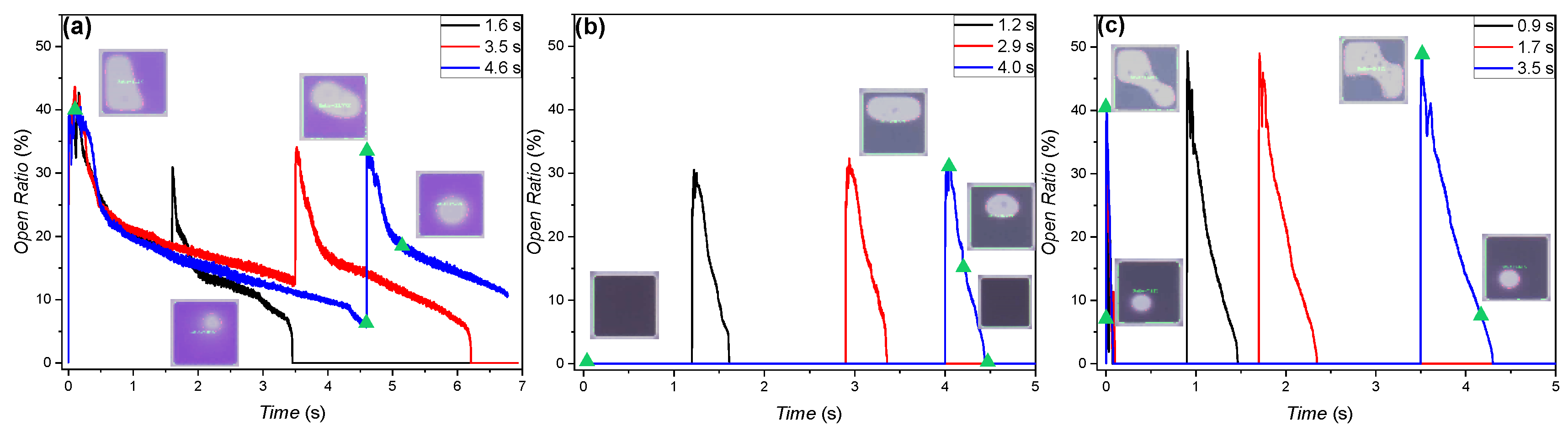
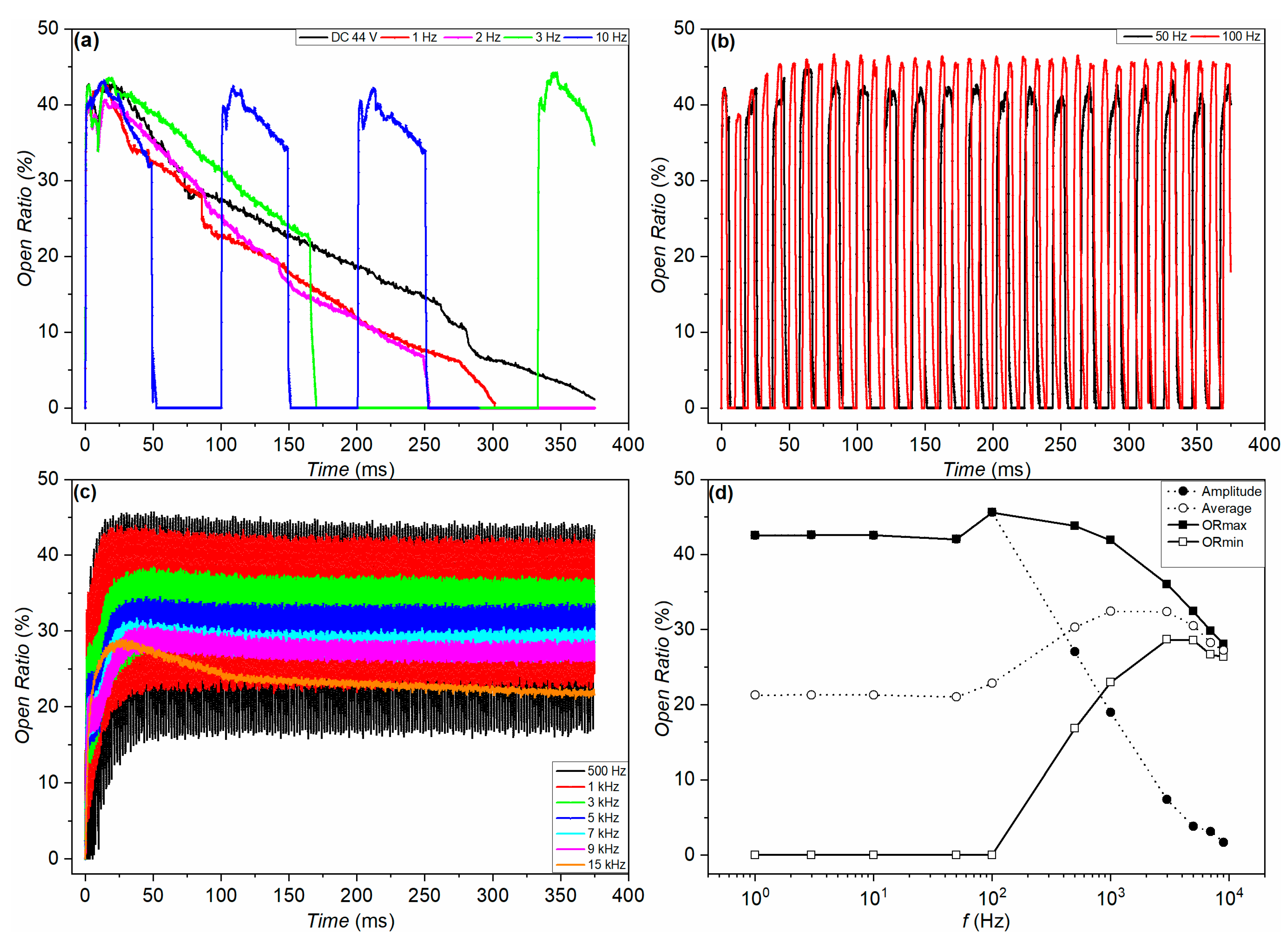
3.2. Driving Scheme Influence on the Interfacial Dynamics and Charge Trapping
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hayes, R.A.; Feenstra, B.J. Video-speed electronic paper based on electrowetting. Nature 2003, 425, 383–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shui, L.; Hayes, R.A.; Jin, M.L.; Zhang, X.; Bai, P.F.; Albert, V.D.B. Microfluidics for electronic paper-like displays. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 2374–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massard, R.; Mans, J.; Adityaputra, A. Colored oil for electrowetting displays. J. Inf. Disp. 2013, 14, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mibus, M.; Hu, X.Y.; Knospe, C.; Reed, M.L. Failure Modes during Low-Voltage Electrowetting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 15767–15777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klingner, A.; Buehrle, J.; Mugele, F. Capillary bridges in electric fields. Langmuir 2004, 20, 6770–6777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugele, F.; Baret, J.-C. Electrowetting: From basics to applications. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2005, 17, R705–R774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilaru, M.K.; Heikenfeld, J.; Lin, G.; Mark, J.E. Strong charge trapping and bistable electrowetting on nanocomposite fluoropolymer: Ba TiO3 dielectrics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 212906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalliot, S.; Kuiper, S.; Heikenfeld, J. Experimental validation of the invariance of electrowetting contact angle saturation. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2012, 26, 1909–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Steckl, A.J. Complementary electrowetting devices on plasma-treated fluoropolymer surfaces. Langmuir 2010, 26, 9474–9483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldo, A.; Massard, R.; Mans, J.; Derckx, E.; Aubert, J.; Mennen, J. 10.3: Ultra low-power Electrowetting-based Displays Using Dynamic Frame Rate Driving. In SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers; Blackwell Publishing Ltd: Oxford, UK, 2011; Volume 42, pp. 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sureshkumar, P.; Bhattacharyya, S.S. Display applications of electrowetting. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2012, 26, 1947–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banpurkar, A.G.; Sawane, Y.B.; Wadhai, S.M. Spontaneous electrification of fluoropolymer–water interfaces probed by electrowetting. Faraday Discuss. 2017, 199, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.M.; Tian, H.M.; Shao, J.Y.; Ding, Y.C.; Chen, X.L.; Wang, L.; Lu, B.H. Decreasing the Saturated Contact Angle in Electrowetting-on-Dielectrics by Controlling the Charge Trapping at Liquid–Solid Interfaces. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 2994–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.Y.; Deng, Y.; Tang, B.; Henzen, A. The Colored Oil Property Effect on Switching Behavior of Electro-Fluidic Display. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2020, 11, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homolka, D.; Vladimir, M.; Zdenek, S. The partition of amines between water and an organic solvent phase. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1984, 163, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girault, H.H. Charge Transfer across Liquid—Liquid Interfaces. In Modern Aspects of Electrochemistry; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1993; pp. 1–62. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, N.; Mineva, T.; Toscano, M.; Grand, A. Proton affinity and protonation sites of aniline. Energetic behavior and density functional reactivity indices. J. Phys. Chem. A 2000, 104, 4017–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Viraraghavan, T. Dye biosorption sites in Aspergillus niger. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 82, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praetorius, A.; Bailey, D.B.; Schwarzlose, T. Design of a fluorescent dye for indicator displacement from cucurbiturils: A macrocycle-responsive fluorescent switch operating through ap K a shift. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 4089–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerischer, H. Modern Aspects of Electrochemistry. Z. Phys. Chem. 1961, 29, 287–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.Y.; Deng, Y.; Xu, B.J.; Henzen, A.; Hayes, R.; Tang, B.; Zhou, G.F. Asymmetrical Electrowetting on Dielectrics Induced by Charge Transfer through an Oil/Water Interface. Langmuir 2018, 34, 11943–11951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beunis, F.; Strubbe, F.; Karvart, M. Inverse micelles as charge carriers in nonpolar liquids. In Proceedings of the 10th International Symposium on Electrokinetic Phenomena (ELKIN-2012), Tsukuba, Japan, 20–24 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, M. Electrokinetics of Nonpolar Dispersions for Electrophoretic Displays and Liquid Toner Printing. Ph.D. Thesis, Ghent University, Belgium, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, B.; Groenewold, J.; Zhou, M.; Hayes, R.A.; Zhou, G.F. Interfacial electrofluidics in confined systems. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leguijt, R.; Sluis, V.D. Method of Preparing a Compound. U.S. Patent 9,272,981 B1, 1 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Shiga, Y.; Takeda, U.; Ichinosawa, S.; Ishida, M. Ink Containing Heterocyclic Azo Dye, and Dye for Use in Said Ink. U.S. Patent 8,747,537 B2, 10 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Li, S.; Ye, D.C.; Jiang, H.W.; Tang, B.; Zhou, G.F. Synthesis and a Photo-Stability Study of Organic Dyes for Electro-Fluidic Display. Micromachines 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyrat, E.; Hayes, R.A. Amorphous fluoropolymers as insulators for reversible low-voltage electrowetting. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 90, 1383–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Tang, B.; Dong, B.Q.; Li, H.; Zhou, R.; Guo, Y.Y.; Dou, Y.Y.; Deng, Y.; Groenewold, J.; Henzen, A.; et al. Electrowetting on dielectric: Experimental and model study of oil conductivity on rupture voltage. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2018, 51, 195102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.; Audry, M.C.; Thibaut, R.M.; Kleimann, P.; Chassagneux, F. Charge injection in dielectric films during electrowetting actuation under direct current voltage. Thin Solid Films 2015, 590, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Dey, R.; Siretanu, I. Electrically Controlled Localized Charge Trapping at Amorphous Fluoropolymer–Electrolyte Interfaces. Small 2020, 16, 1905726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, Y.H.; Liang, C.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Lee, W.Y. Accurate-gray-level and quick-response driving methods for high-performance electrowetting displays. J. Soc. Inf. Disp. 2011, 19, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.J.; Zhang, W.N.; Liu, L.W.; Xie, S.T.; Zhou, G.F. Portable multi-gray scale video playing scheme for high-performance electrowetting displays. J. Soc. Inf. Disp. 2016, 24, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.; Hsieh, Y.-H.; Lee, H.-C. Humans perceive flicker artifacts at 500 Hz. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.S.; Ko, S.H.; Kang, K.H. A numerical investigation on AC electrowetting of a droplet. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2008, 5, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klarman, D.; Andelman, D.; Urbakh, M. A model of electrowetting, reversed electrowetting, and contact angle saturation. Langmuir 2011, 27, 6031–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jager, K.; Hezel, R. Optical stability of silicon nitride MIS inversion layer solar cells. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 1985, 32, 1824–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.-C.; Teng, C.W.; Coleman, D.J.; Nishimura, A. Interface trap-enhanced gate-induced leakage current in MOSFET. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 1989, 10, 216–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumin, D.J.; Maddux, J.R. Correlation of stress-induced leakage current in thin oxides with trap generation inside the oxides. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 1993, 40, 986–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecoffet, R.; Duzellier, S.; Guibert, L.; Inguimbert, C. Low LET cross-section measurements using high energy carbon beam [DRAMs/SRAMs]. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 1997, 44, 2230–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, D.P.; Tserepi, A.; Boudouvis, A.G.; Papathanasiou, A.G. Superior performance of multilayered fluoropolymer films in low voltage electrowetting. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 368, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilaru, M.; Cumby, B.; Heikenfeld, J. Electrowetting retroreflectors: Scalable and wide-spectrum modulation between corner cube and scattering reflection. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 041108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrab, S.; Watson, A.M.; Roath, C.; Gopinath, J.T.; Bright, V.M. Adaptive electrowetting lens-prism element. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 25838–25845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, C.; Tang, B.; Xu, B.; Groenewold, J.; Zhou, G. Oil Conductivity, Electric-Field-Induced Interfacial Charge Effects, and Their Influence on the Electro-Optical Response of Electrowetting Display Devices. Micromachines 2020, 11, 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11070702
Jiang C, Tang B, Xu B, Groenewold J, Zhou G. Oil Conductivity, Electric-Field-Induced Interfacial Charge Effects, and Their Influence on the Electro-Optical Response of Electrowetting Display Devices. Micromachines. 2020; 11(7):702. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11070702
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Chengdian, Biao Tang, Bojian Xu, Jan Groenewold, and Guofu Zhou. 2020. "Oil Conductivity, Electric-Field-Induced Interfacial Charge Effects, and Their Influence on the Electro-Optical Response of Electrowetting Display Devices" Micromachines 11, no. 7: 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11070702
APA StyleJiang, C., Tang, B., Xu, B., Groenewold, J., & Zhou, G. (2020). Oil Conductivity, Electric-Field-Induced Interfacial Charge Effects, and Their Influence on the Electro-Optical Response of Electrowetting Display Devices. Micromachines, 11(7), 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11070702




