Precision Cutting of the Molds of an Optical Functional Texture Film with a Triangular Pyramid Texture
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Technical Requirements for the Light-Trapping Texture of the Triangular Pyramid
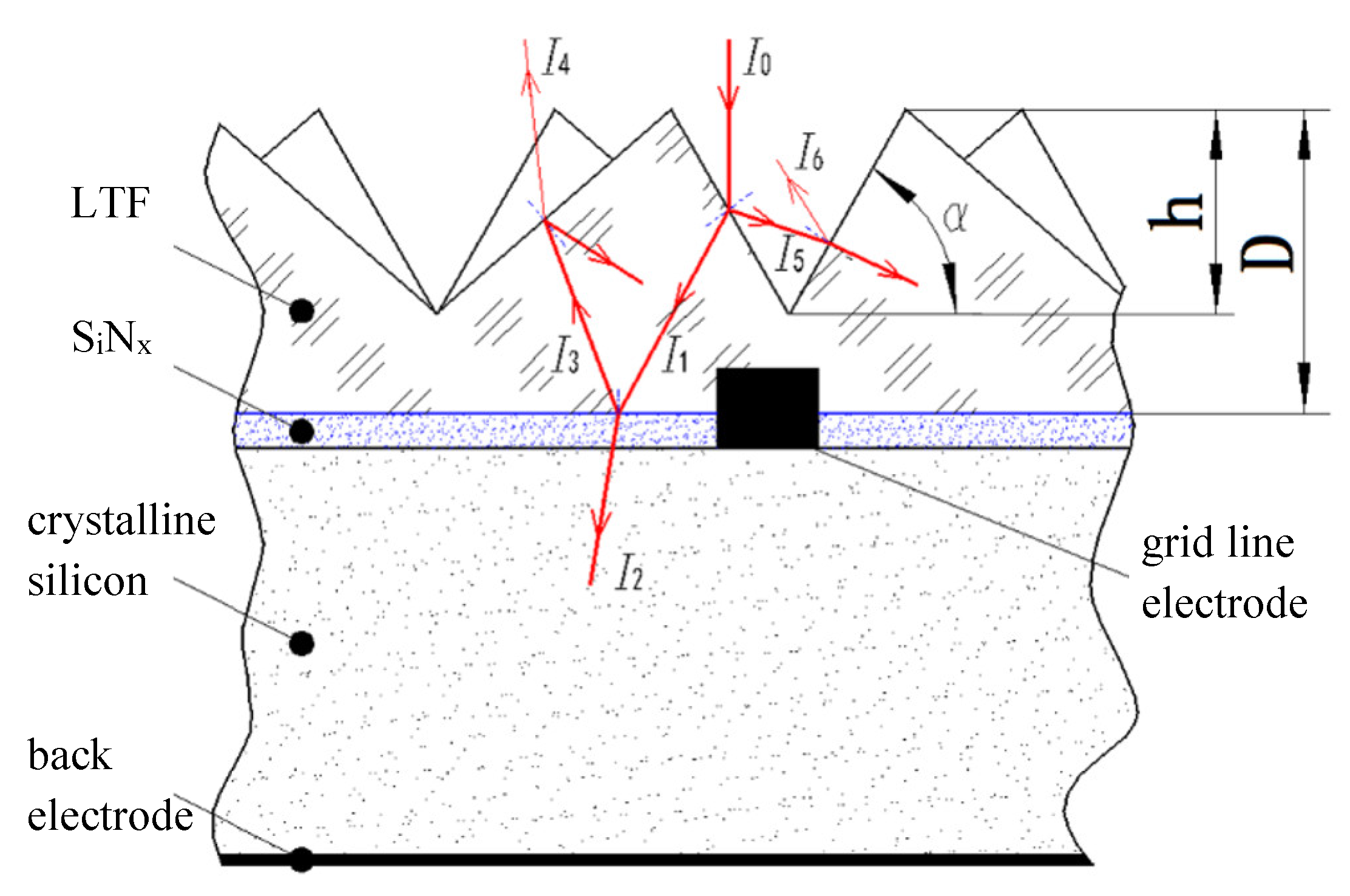
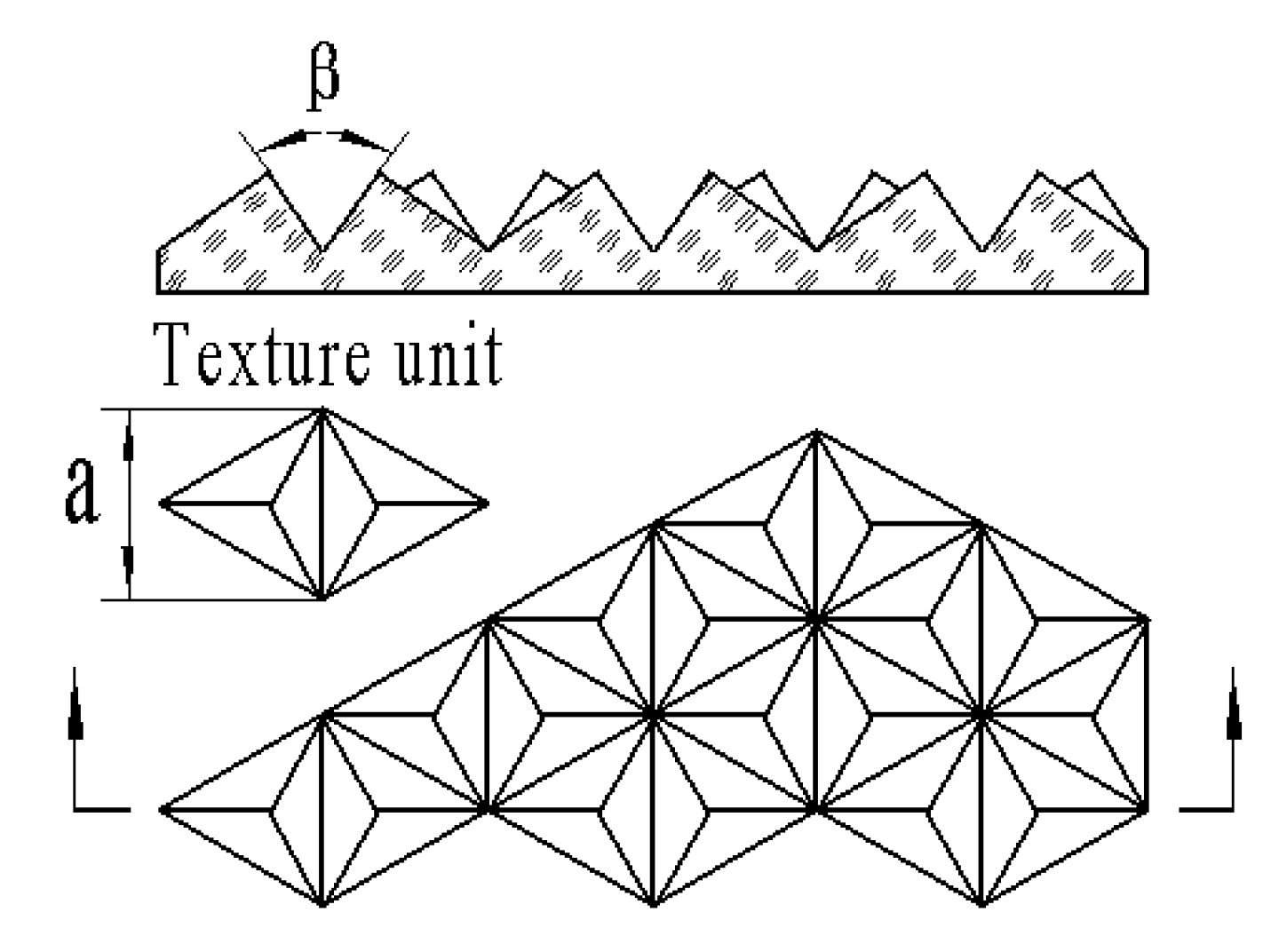
2.1. Optical Functional Textured Film for Light-Trapping
2.2. Light-Trapping Film Mold
2.2.1. Precision of the Size and Surface
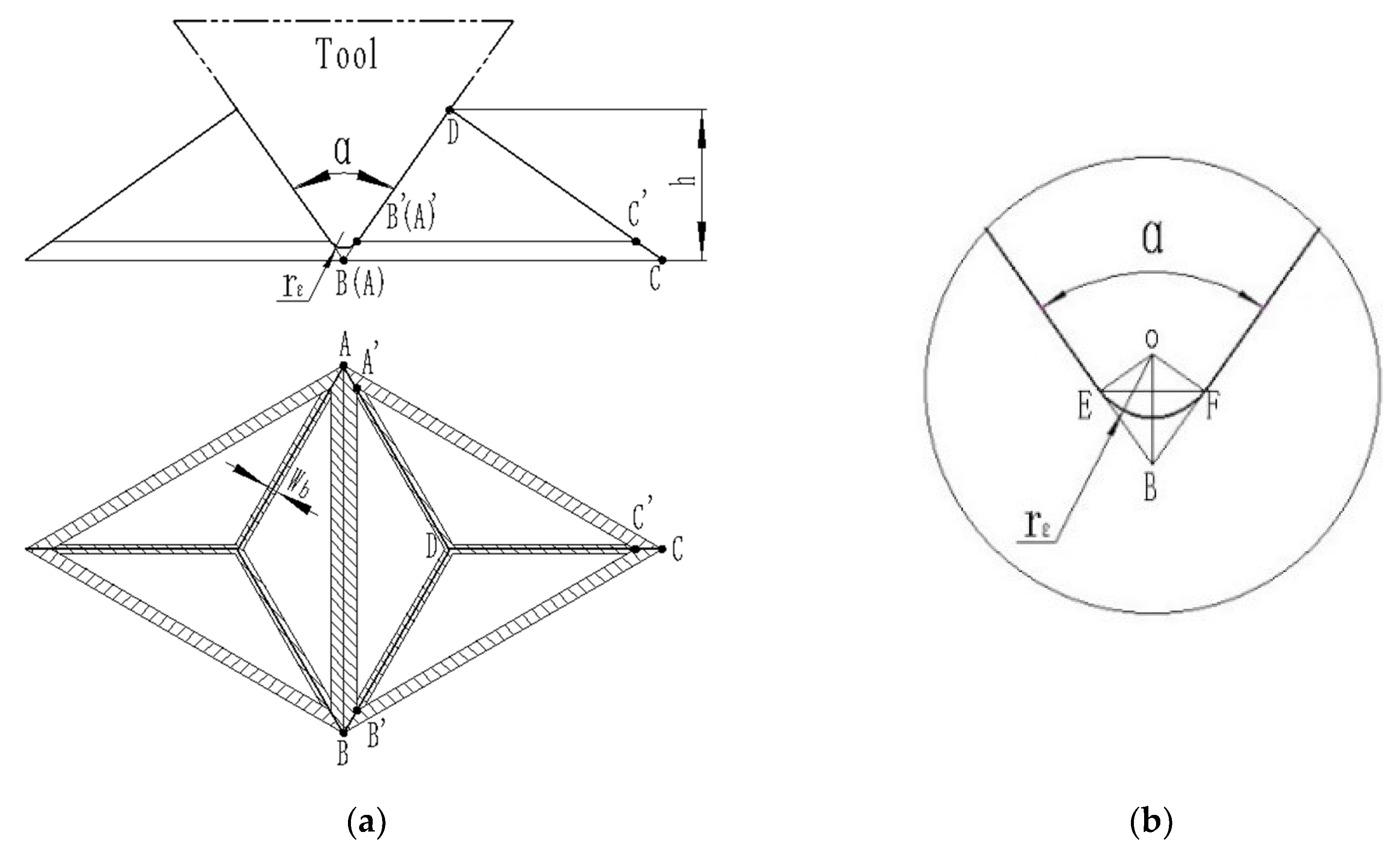
2.2.2. Shape Precision
3. Cutting Experiment of the Mold
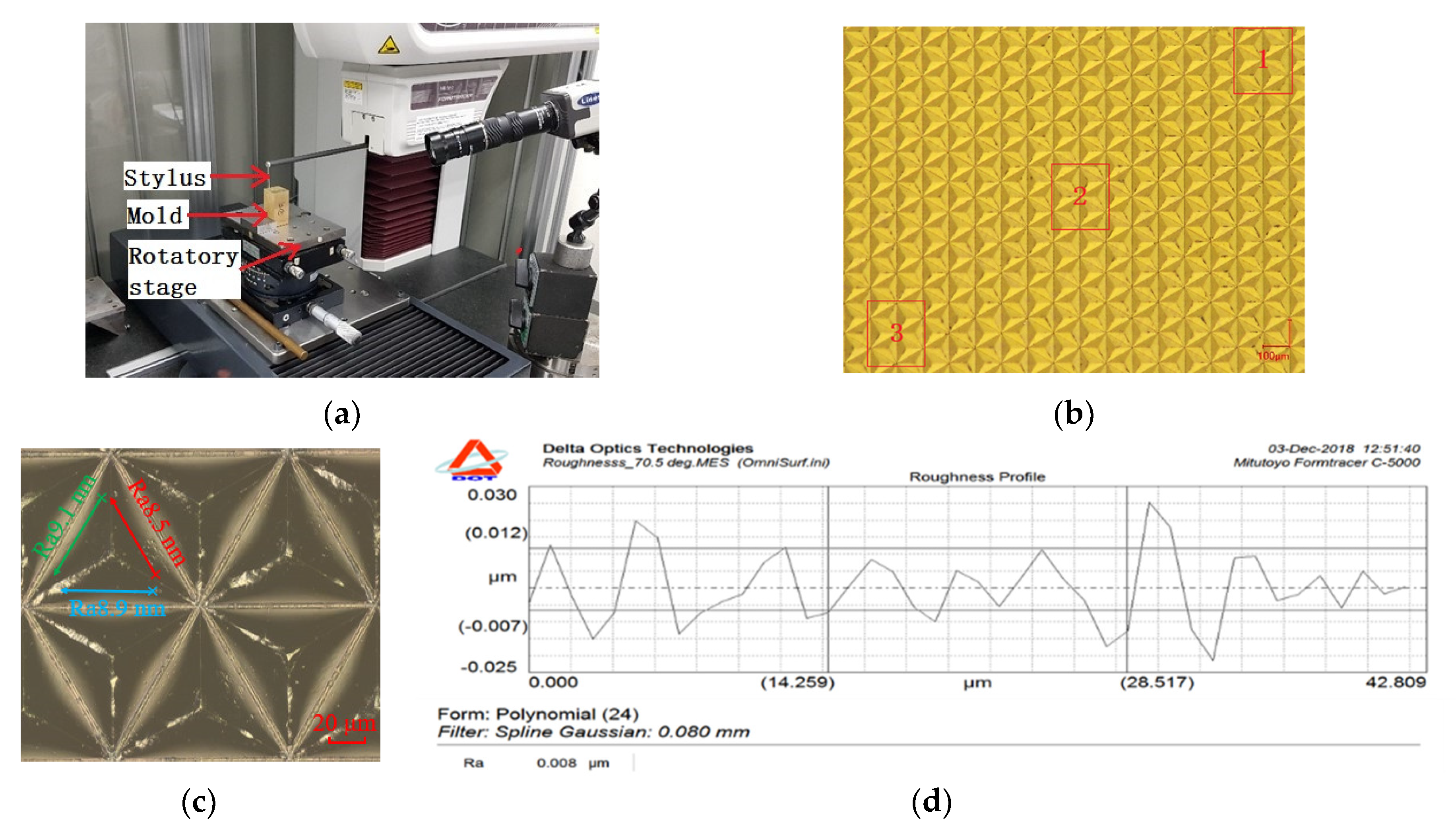
3.1. Equipment and Cutting Tools
3.2. Selection of the Cutting Parameters
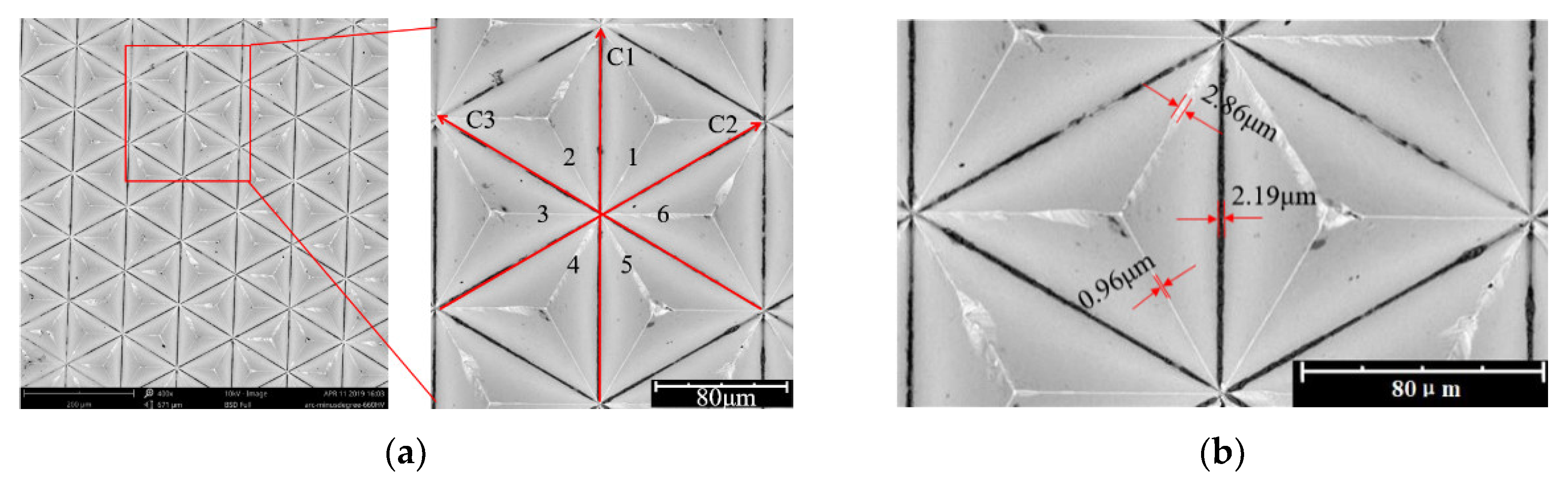
3.3. Quality Inspection of the Mold
3.3.1. Surface Roughness
3.3.2. Dimensional Accuracy
3.3.3. The Evaluation of the Area Ratio of the Retro-Reflection
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hsu, Q.C.; Chen, Y.L. Fabrication of 3D random microlens array composite optical film with self-assembly. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 76, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, C.; Wang, G.; Cai, W.; Zhang, H. Plasma-etching enhanced titanium oxynitride active phase with high oxygen content for ambient electrosynthesis of ammonia. Electrochem. Commun. 2019, 100, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Lai, Y.; Chi, L. Advanced colloidal lithography: From patterning to applications. Nano Today 2018, 22, 36–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, P.; Deng, Y.; Shu, Y.; Peng, L. Experimental studies on a novel roll-to-roll powder hot embossing for large-area fabrication of micropyramid arrays on polymers. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2018, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velten, T.; Schuck, H.; Haberer, W.; Bauerfeld, F. Investigations on reel-to-reel hot embossing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2010, 47, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, M.; Otto, M.; Hadam, B.; Vratzov, B.; Spangenberg, B.; Kurz, H. Fabrication of nanostructures using a UV-based imprint technique. Microelectron. Eng. 2000, 53, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-Y.; Ke, K.-C.; Yang, S.-Y. Fabrication of large-area V-groove microstructures using gasbag-pressuring edge-irradiating UV imprinting. Microsyst. Technol. 2018, 25, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Ashraf, A.; Xin, H.; Tong, X.; Sutter, P.; Eisaman, M.D.; Black, C.T. Sub-50-nm self-assembled nanotextures for enhanced broadband antireflection in silicon solar cells. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 5963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, Z.; Hirte, J.; Chen, W.; Spatz, J.P. Inverse Moth Eye Nanostructures with Enhanced Antireflection and Contamination Resistance. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 5012–5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirino, G.A.; Granado, R.M.; Mohammed-Brahim, T.; Jasinevicius, R.G. Assessment of replication fidelity of optical microstructures by hot embossing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 88, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, R.; Liu, K.; Kumar, A.S.; Shan, X. Rotating-tool diamond turning of Fresnel lenses on a roller mold for manufacturing of functional optical film. Precis. Eng. 2018, 51, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Lin, S.; Jiang, W.; Pan, N. Hot embossing holographic images in BOPP shrink films through large-area roll-to-roll nanoimprint lithography. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 311, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Li, Y.; Kong, Q.; Tan, Q.; Li, C. Uniform concentrating design and mold machining of Fresnel lens for photovoltaic systems. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.J.; To, S.; Wang, S.J.; Zhu, Z.W. A review of surface roughness generation in ultra-precision machining. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2015, 91, 76–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinksmeier, E.; Gläbe, R.; Flucke, C. Manufacturing of molds for replication of micro cube corner retroreflectors. Prod. Eng. 2008, 2, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.E.; Jeon, E.; Je, T.J.; Kang, M.C. Machining Characteristics of Micro Structure using Single-Crystal Diamond Tool on Cu-plated Mold. J. Korean Powder Metall. Inst. 2015, 22, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lan, P.; Lu, Y.; Li, J.; Xu, H.; Zhang, J.; Lee, Y.; Rhee, J.Y.; Choy, K.L.; Song, W. Multifunctional antireflection coatings based on novel hollow silica–silica nanocomposites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 1415–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.S.; Lee, H.; Kim, D.; Lee, H. Fabrication of anti-reflection structure on protective layer of solar cells by hot-embossing method. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2009, 93, 1214–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amalathas, A.P.; Alkaisi, M.M. Efficient light trapping nanopyramid structures for solar cells patterned using UV nanoimprint lithography. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2017, 57, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dottermusch, S.; Schmager, R.; Klampaftis, E.; Paetel, S.; Kiowski, O.; Ding, R.; Richards, B.S.; Paetzold, U.W. Micro-cone textures for improved light in-coupling and retroreflection-inspired light trapping at the front surface of solar modules. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2019, 27, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Yang, X.; Huang, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Fang, F. Research of photoelectric characteristics of crystallline silicon composite cell with smooth surface and light trpping film. Acta Energ. Sol. Sin. 2017, 12, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, N.S.; Qian, W.H.; Hu, X.Y.; Zhu, Z.W. Preparation of a Microprism Ni-Ceo2Nanocomposite Mold by Electroforming. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2014, 29, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, N.S.; Koh, Y.H.; Fu, Y.Q. Microlens array produced using hot embossing process. Microelectron. Eng. 2002, 60, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qiao, Z.; Qu, D.; Wu, Y.; Xue, J.; Li, D.; Wang, B. Experimental Investigation on Form Error for Slow Tool Servo Diamond Turning of Micro Lens Arrays on the Roller Mold. Materials (Basel) 2018, 11, 1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, C.F.; Lee, W.B. Characterisation of nanosurface generation in single-point diamond turning. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2001, 41, 851–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Xiao, X.; Liang, X. Analytical modeling of residual stress in orthogonal cutting considering tool edge radius effect. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 103, 2965–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, L.; He, N.; Hao, X.; Yao, C.; Zhong, L. Investigation on the ploughing force in microcutting considering the cutting edge radius. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 86, 2441–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchant, M.E. Mechanics of the Metal Cutting Process. I. Orthogonal Cutting and a Type 2 Chip. J. Appl. Phys. 1945, 16, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.Z.; Liu, Y.C. On minimum exit-burr in micro cutting. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2004, 14, 984–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Bayesteh, A.; Ko, J.; Dong, Z.; Jun, M.B. Numerical simulation of chip ploughing volume in micro ball-end mill machining. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2017, 18, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Rake Angle (°) | Clearance Angle (°) | Included Angle (°) | Tool Nose Aadius (µm) | Cutting-Edge Radius (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 15 | 70.5 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Material | Young’s Modulus (GPa) | Poisson’s Ratio | Density (g/cm3) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Specific Heat (J/(kg·K)) | Hardness (HB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single diamond | 960 | 0.2 | 3.5 | 2000 | 507.9 | 8000 |
| Brass | 105 | 0.324 | 8.4 | 104.7 | 374 | 69.3 |
| Sampling Area | Triangular Pyramid Edge Length | Triangular Pyramid Height | Roughness (nm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Value (µm) | Deviation | Mean Value (µm) | Deviation | ||
| 1 | 113.41 | −1.38% | 51.41 | 2.82% | 9.5 |
| 2 | 114.51 | −0.42% | 49.62 | −0.76% | 8.9 |
| 3 | 113.41 | −1.38% | 50.74 | 1.48% | 9.3 |
| Mean value | 113.78 | 1.06% | 50.59 | 1.18% | 9.2 |
| Sampling Area | Arc Width of the Valley Bottom EF | Edge Burr Width at the Cut-in | Edge Burr Width at the Cut-out |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Value (µm) | Mean Value (µm) | Mean Value (µm) | |
| 1 | 2.75 | 0.96 | 2.13 |
| 2 | 2.64 | 0.97 | 2.08 |
| 3 | 2.74 | 0.97 | 2.11 |
| Mean value | 2.71 | 0.97 | 2.11 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Xu, Z.; Pi, J.; Zhou, F. Precision Cutting of the Molds of an Optical Functional Texture Film with a Triangular Pyramid Texture. Micromachines 2020, 11, 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11030248
Li H, Xu Z, Pi J, Zhou F. Precision Cutting of the Molds of an Optical Functional Texture Film with a Triangular Pyramid Texture. Micromachines. 2020; 11(3):248. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11030248
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Huang, Zhilong Xu, Jun Pi, and Fei Zhou. 2020. "Precision Cutting of the Molds of an Optical Functional Texture Film with a Triangular Pyramid Texture" Micromachines 11, no. 3: 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11030248
APA StyleLi, H., Xu, Z., Pi, J., & Zhou, F. (2020). Precision Cutting of the Molds of an Optical Functional Texture Film with a Triangular Pyramid Texture. Micromachines, 11(3), 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11030248




