Temperature and Humidity PID Controller for a Bioprinter Atmospheric Enclosure System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Atmospheric Enclosure System Design
2.2. Mathematical Modelling
2.3. Experimental Evaluation
- SISO test to study inner temperature when heater (electric resistance) was switched on.
- SISO test to study inner humidity when humidifier (cold mist humidifier) was switched on.
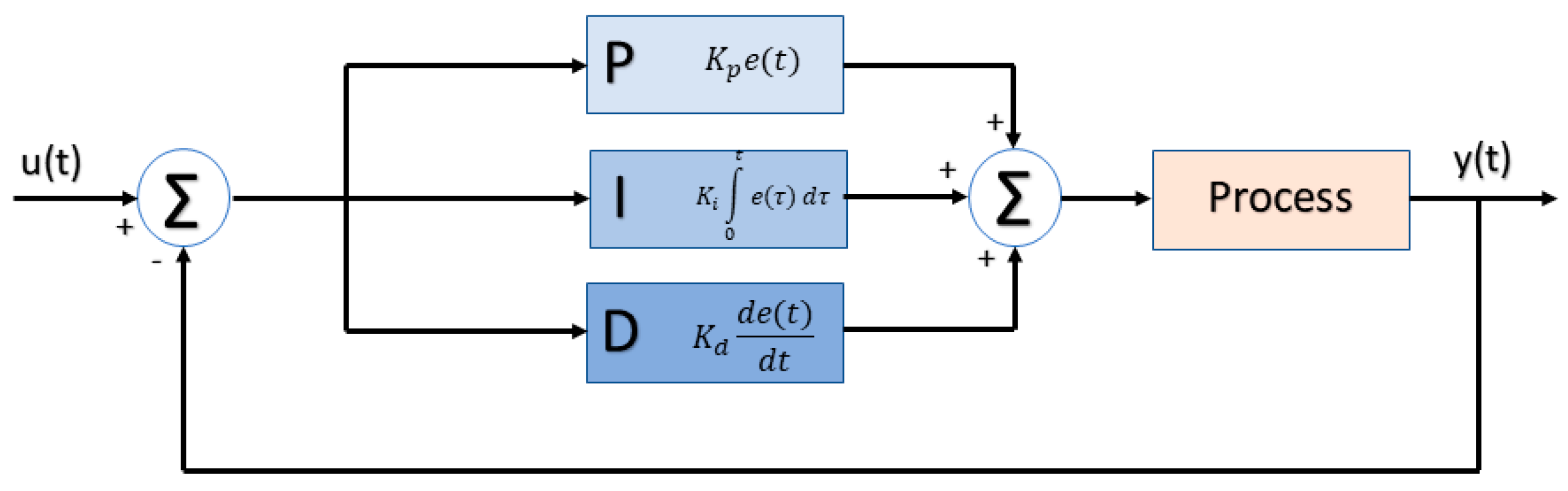
2.4. PID Controller
2.5. Procedure
3. Results
3.1. SISO Test to Study Inner Temperature When Heater (Electric Resistance) Was Switched on
3.2. SISO Test to Study Inner Humidity When Humidifier (Cold Mist Humidifier) Was Switched on
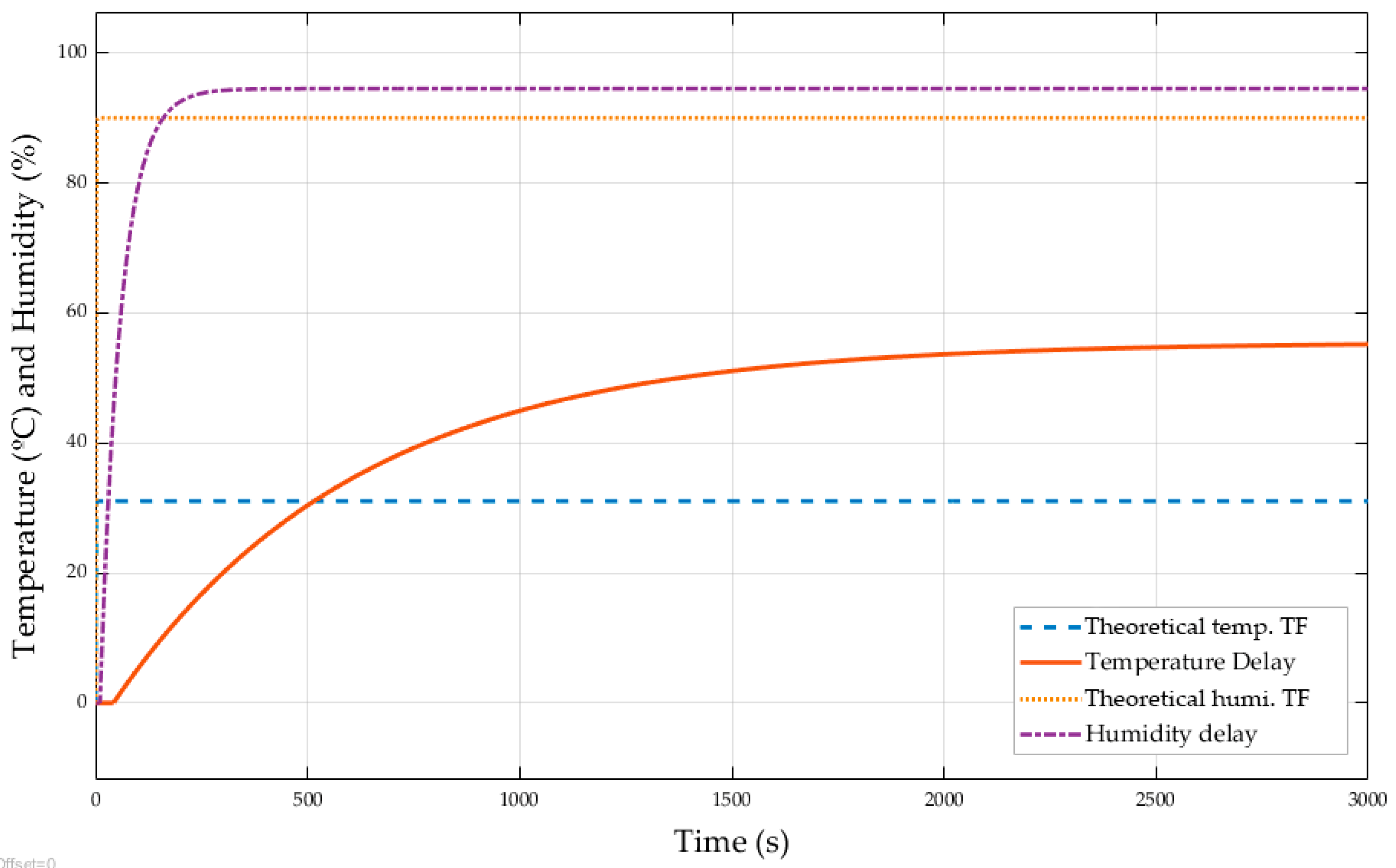
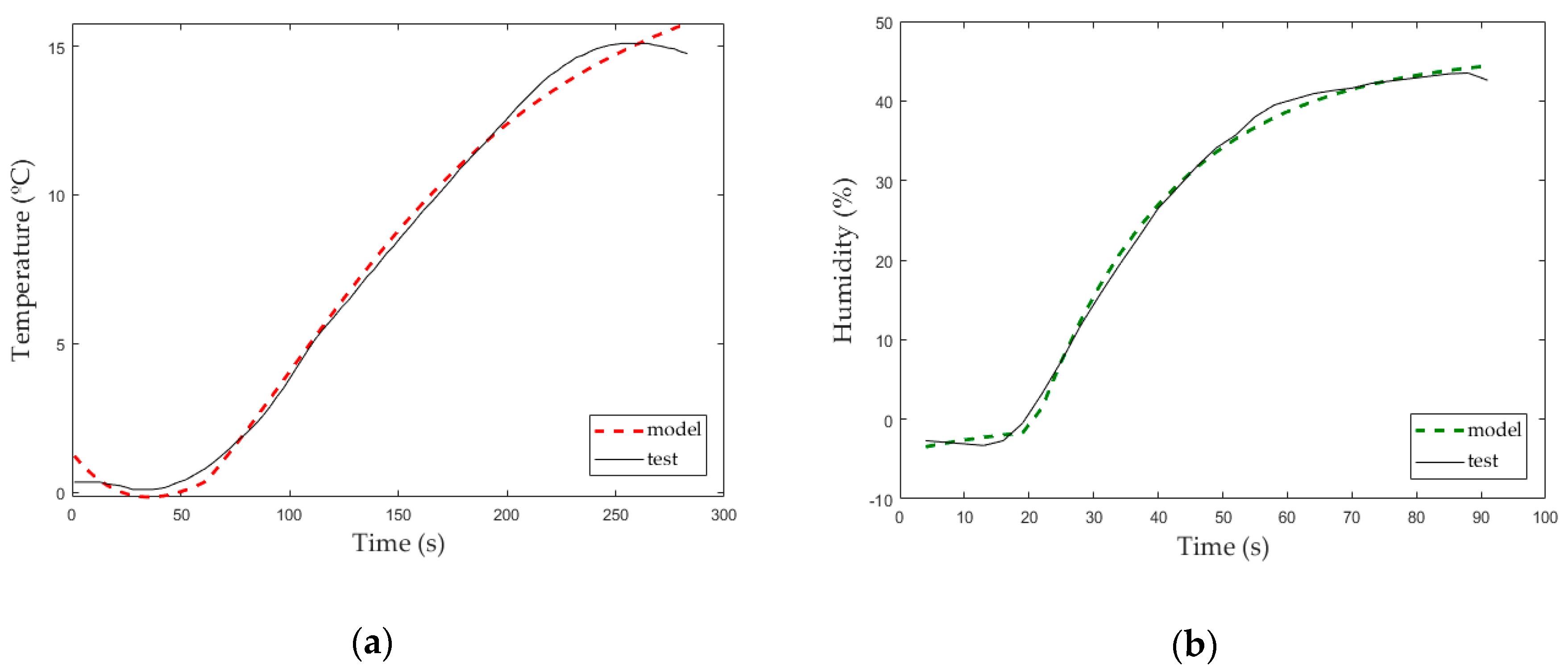
3.3. Comparative between Theoretical and Experimental Transfer Functions
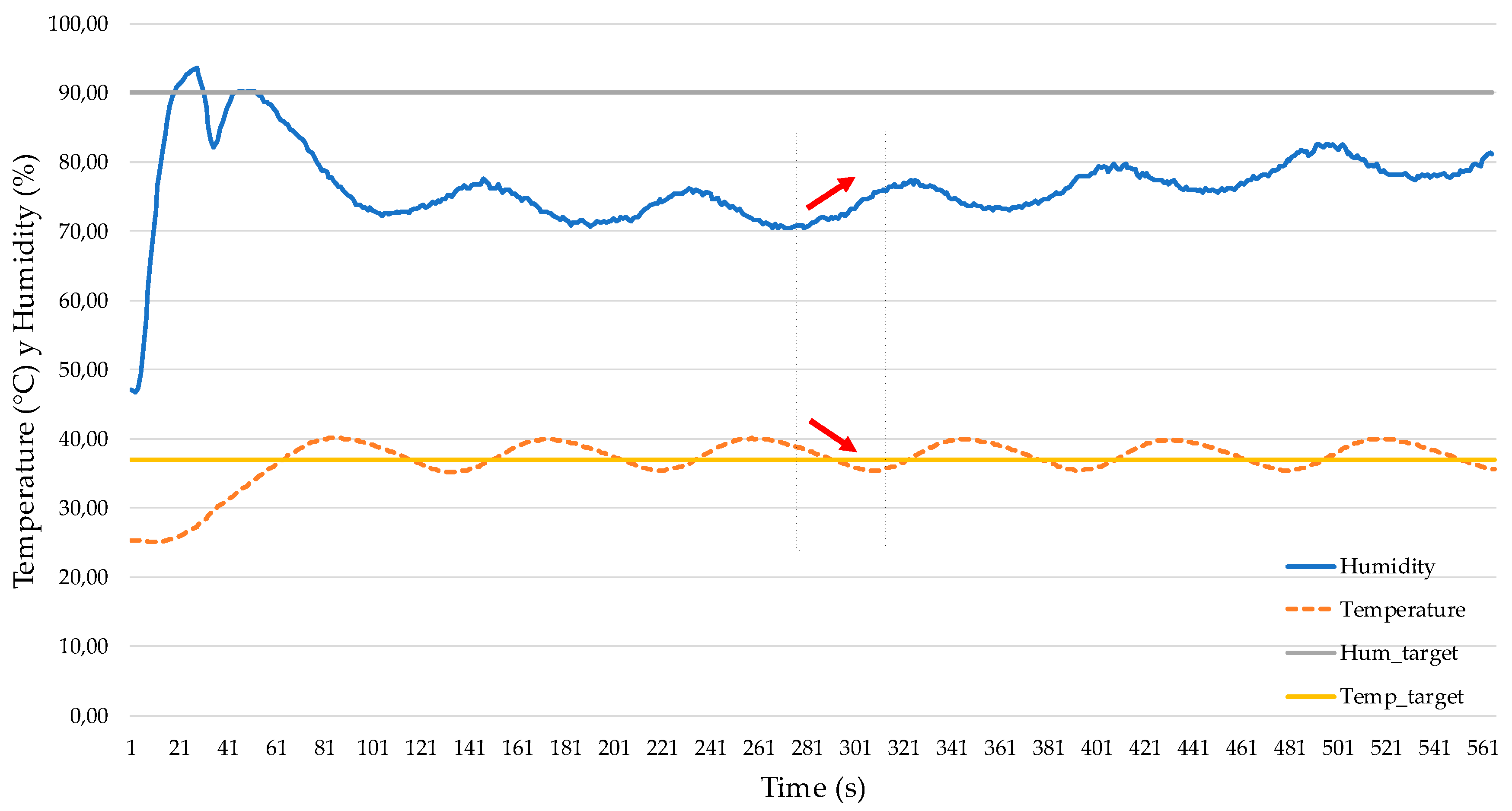
3.4. MIMO Test to Study Coupling of Inner Temperature and Humidity
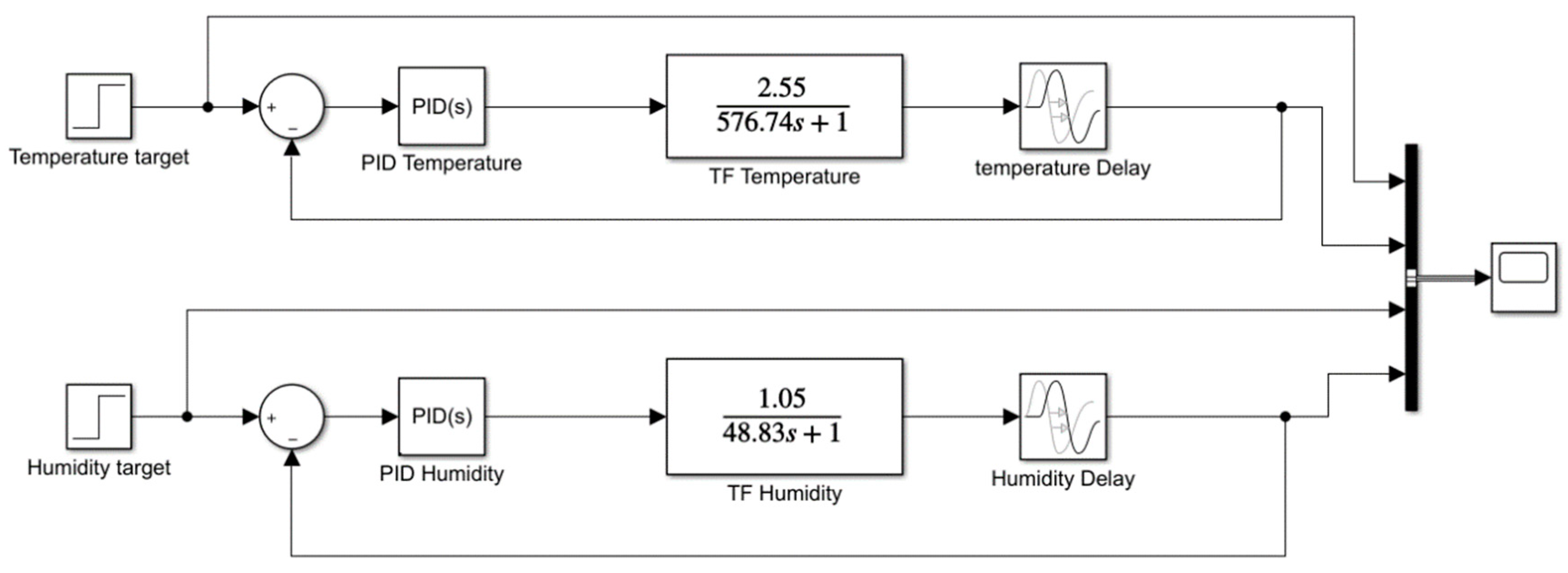
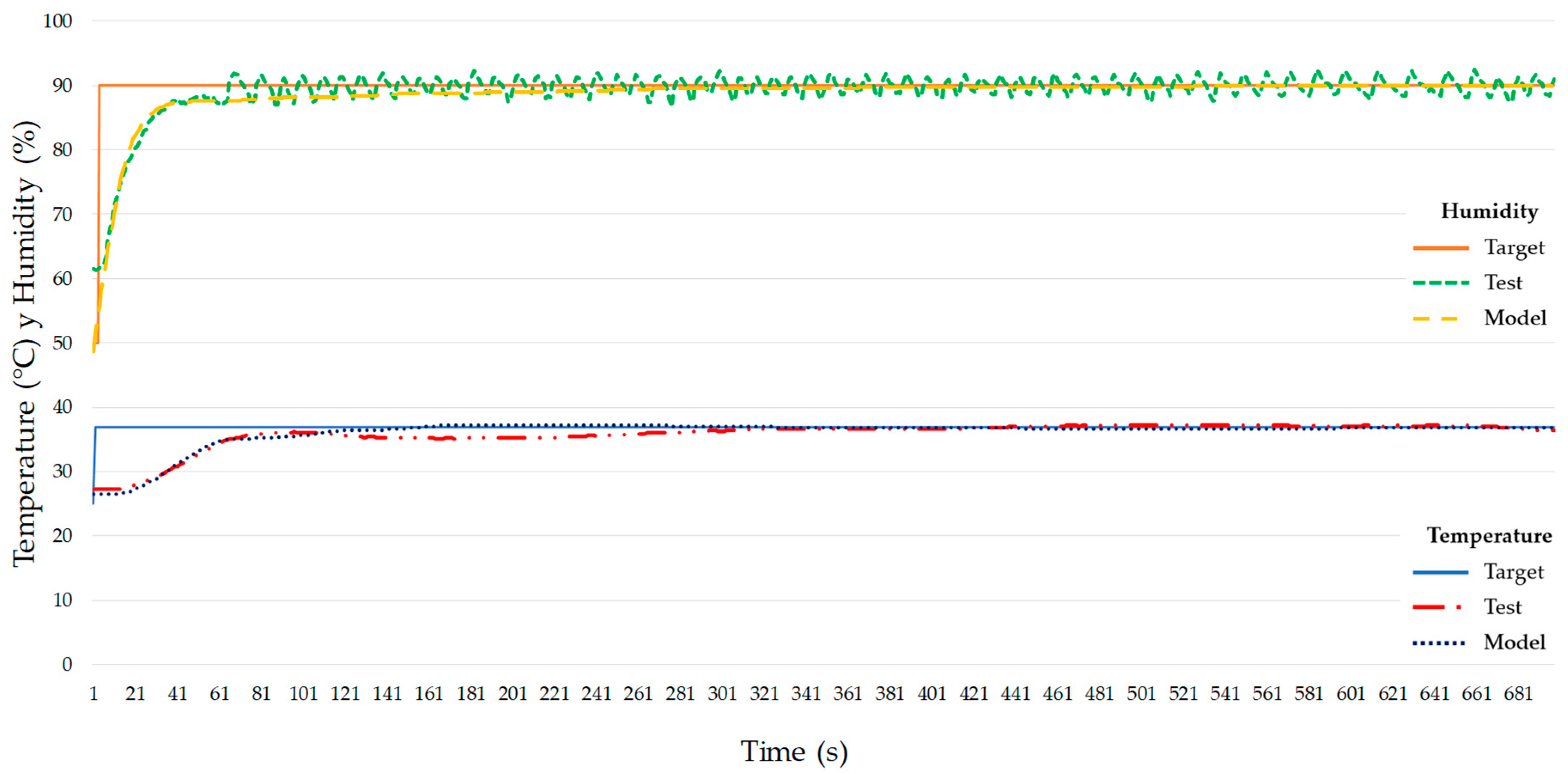
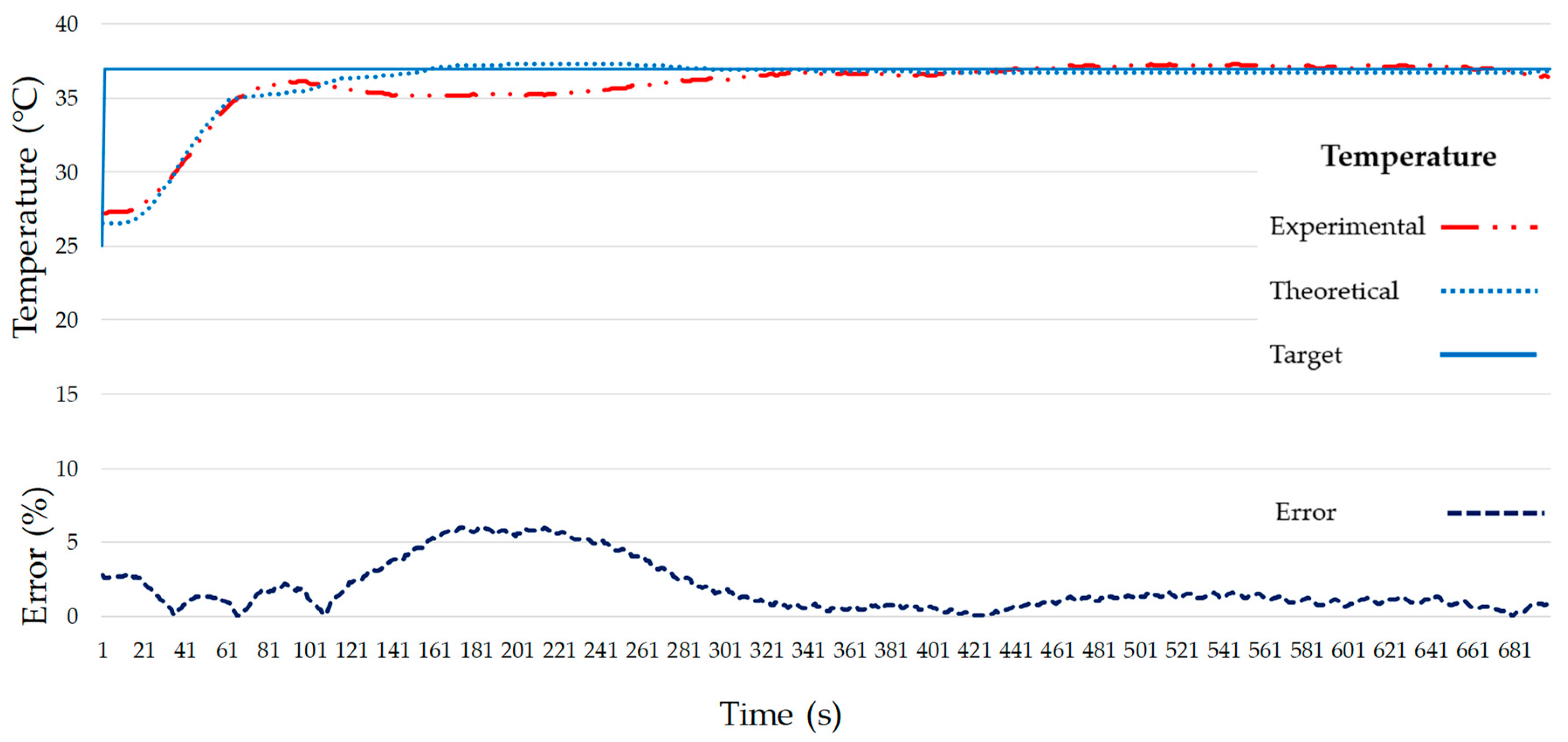
3.5. Obtaining PID Values and Modeling System in Matlab/Simulink™
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mao, A.S.; Mooney, D.J. Regenerative medicine: Current therapies and future directions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 14452–14459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eswaramoorthy, S.D.; Ramakrishna, S.; Rath, S.N. Recent advances in three-dimensional bioprinting of stem cells. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2019, 13, 908–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Munguia-Lopez, J.G.; Flores-Torres, S.; Kort-Mascort, J.; Kinsella, J.M. Extrusion bioprinting of soft materials: An emerging technique for biological model fabrication. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2019, 6, 011310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.W.; Lee, S.J.; Ko, I.K.; Kengla, C.; Yoo, J.J.; Atala, A. A 3D bioprinting system to produce human-scale tissue constructs with structural integrity. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boularaoui, S.; Al Hussein, G.; Khan, K.A.; Christoforou, N.; Stefanini, C. An overview of extrusion-based bioprinting with a focus on induced shear stress and its effect on cell viability. Bioprinting 2020, 20, e00093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Blanco, J.C.; Mancha-Sánchez, E.; Marcos, A.C.; Matamoros, M.; Díaz-Parralejo, A.; Pagador, J.B. Bioink Temperature Influence on Shear Stress, Pressure and Velocity Using Computational Simulation. Processes 2020, 8, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unagolla, J.M.; Jayasuriya, A.C. Hydrogel-based 3D bioprinting: A comprehensive review on cell-laden hydrogels, bioink formulations, and future perspectives. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 18, 100479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hölzl, K.; Lin, S.; Tytgat, L.; Van Vilerberghe, S.; Gu, L.; Ovsianikov, A. Bioink properties before, during and after 3D bioprinting. Biofabrication 2016, 8, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.M. 3D Bioprinting; Methods in Molecular Biology Series Editor; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2020; ISBN 978-1-0716-0519-6. [Google Scholar]
- CELLINK BIO X-CELLINK. Available online: https://www.cellink.com/product/cellink-bio-x/ (accessed on 30 October 2020).
- RegenHU Biofactory. Available online: https://www.regenhu.com/3d-bioprinters#biofactory (accessed on 30 October 2020).
- Poietis.—4D Bioprinting Next Generation. Available online: https://poietis.com/bioprinters/ (accessed on 3 November 2020).
- Crook, J.M. 3D Bioprinting Principles and Protocols; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, J.A.D.; Cordova, E.A.; Lévano, C.B.C. Design and Implementation of a Digital PID Temperature Controller for Neonatal Incubator ESVIN. J. Mech. Eng. Autom. 2015, 5, 167–172. [Google Scholar]
- Feki, E.; Zermani, M.A.; Mami, A. GPC Temperature Control of a Simulation Model Infant-Incubator and Practice with Arduino Board. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2017, 8, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, Z.S.A.; Hussain, F.S.A. Smart Incubator Based on PID Controller. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2017, 4, 2501–2509. [Google Scholar]
- Okpagu, P.E.; Nwosu, A.W. Development and Temperature Control of Smart Egg. Eur. J. Eng. Technol. 2016, 4, 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Riahi, J.; Vergura, S.; Mezghani, D.; Mami, A. Intelligent Control of the Microclimate of an Agricultural Greenhouse Powered by a Supporting PV System. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Ali, R.; Aridhi, E.; Abbes, M.; Mami, A. Fuzzy logic controller of temperature and humidity inside an agricultural greenhouse. In Proceedings of the 7th International Renewable Energy Congress (IREC), Hammamet, Tunisia, 22–24 March 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Daskalov, P.I.; Arvanitis, K.G.; Pasgianos, G.D.; Sigrimis, N.A. Non-linear adaptive temperature and humidity control in animal buildings. Biosyst. Eng. 2006, 93, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonomano, A.; Montanaro, U.; Palombo, A.; Santini, S. Temperature and humidity adaptive control in multi-enclosed thermal zones under unexpected external disturbances. Energy Build. 2017, 135, 263–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapen, P.T.; Mohamadou, Y.; Momo, F.; Jauspin, D.K.; Anero, G. An energy efficient neonatal incubator: Mathematical modeling and prototyping. Health Technol. (Berlin) 2019, 9, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, G.H.C.; Amorim, M.F.; Pacholok, C. A real-time predictive scheme for controlling hygrothermal conditions of neonate incubators. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2016, 38, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhu, Z. Research on Temperature and Humidity Decoupling Control of Constant Temperature and Humidity Test Chamber. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 711, 012104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albright, L.; Arvanitis, K.; Drysdale, A. Environmental control for plants on Earth and in space. IEEE Control. Syst. 2001, 21, 28–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jesus Rubio, J.; Salazar, M.; Lugo, R.; Pacheco, J.; Gomez, A.D. Modeling of the relative humidity and control of the temperature for a bird incubator. Adv. Intell. Soft Comput. 2009, 61 AISC, 369–377. [Google Scholar]
- Poudel, M.; Dunn, B. Greenhouse Carbon Dioxide Supplementation; HLA-6723; Oklahoma State University: Stillwater, OK, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yinping, M.; Lu, Z. Expert controller in multi-variable System of Temperature and Humidity. Int. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2017, 9, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz, Y.A. Low Cost Humidity/Temperature Calibration System. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2017, 4, 305–311. [Google Scholar]
- Ragazzini, G.; Mescola, A.; Corsi, L.; Alessandrini, A.; Ragazzini, G.; Mescola, A.; Corsi, L.; Alessandrini, A. Fabrication of a low-cost on-stage cell incubator with full automation. J. Biol. Educ. 2018, 9266, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astrom, K.J.; Hagglund, T. Control PID Avanzado, 1st ed.; PEARSON EDUCACIÓN, S.A.: Madrid, Spain, 2009; ISBN 978-84-8322-511-0. [Google Scholar]
- Morales, J.G. Diseño e Implementación de un Control de Temperatura y Humedad Para un Prototipo de Incubadora Artificial de Pollos. Repositorio de Pontificia Universidad JAVERIANA. 2017. Available online: http://vitela.javerianacali.edu.co/handle/11522/8610 (accessed on 17 June 2020).
- Widhiada, W.; Antara, I.N.G.; Budiarsa, I.N.; Karohika, I.M.G. The Robust PID Control System of Temperature Stability and Humidity on Infant Incubator Based on Arduino at Mega 2560. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 248, 012046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, J.; Barçante, G.M.; Cavalcante, M.U.; Da, O.; Torrico, B.C. PI multivariable control applied to temperature and humidity neonate incubators. In Proceedings of the 9th IEEE/IAS International Conference on Industry Applications—INDUSCON 2010, Sao Paulo, Brazil, 8–10 November 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jovic, T.H.; Kungwengwe, G.; Mills, A.C.; Whitaker, I.S. Plant-Derived Biomaterials: A Review of 3D Bioprinting and Biomedical Applications. Front. Mech. Eng. 2019, 5, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante, M.U.; Torrico, B.C.; Da Mota Almeida, O.; De Souza Braga, A.P.; Da Costa Filho, F.L.M. Filtered model-based predictive control applied to the temperature and humidity control of a neonatal incubator. In Proceedings of the 9th IEEE/IAS International Conference on Industry Applications—INDUSCON 2010, Sao Paulo, Brazil, 8–10 November 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
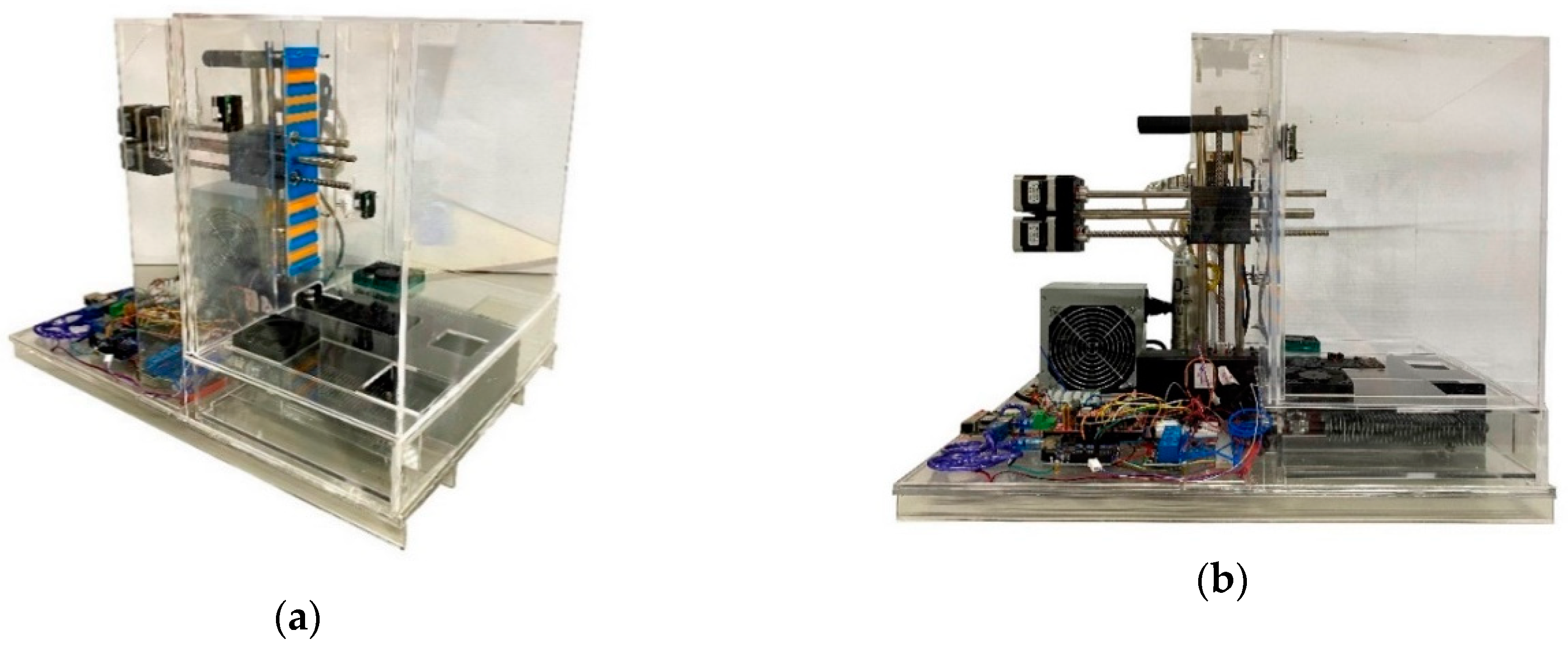

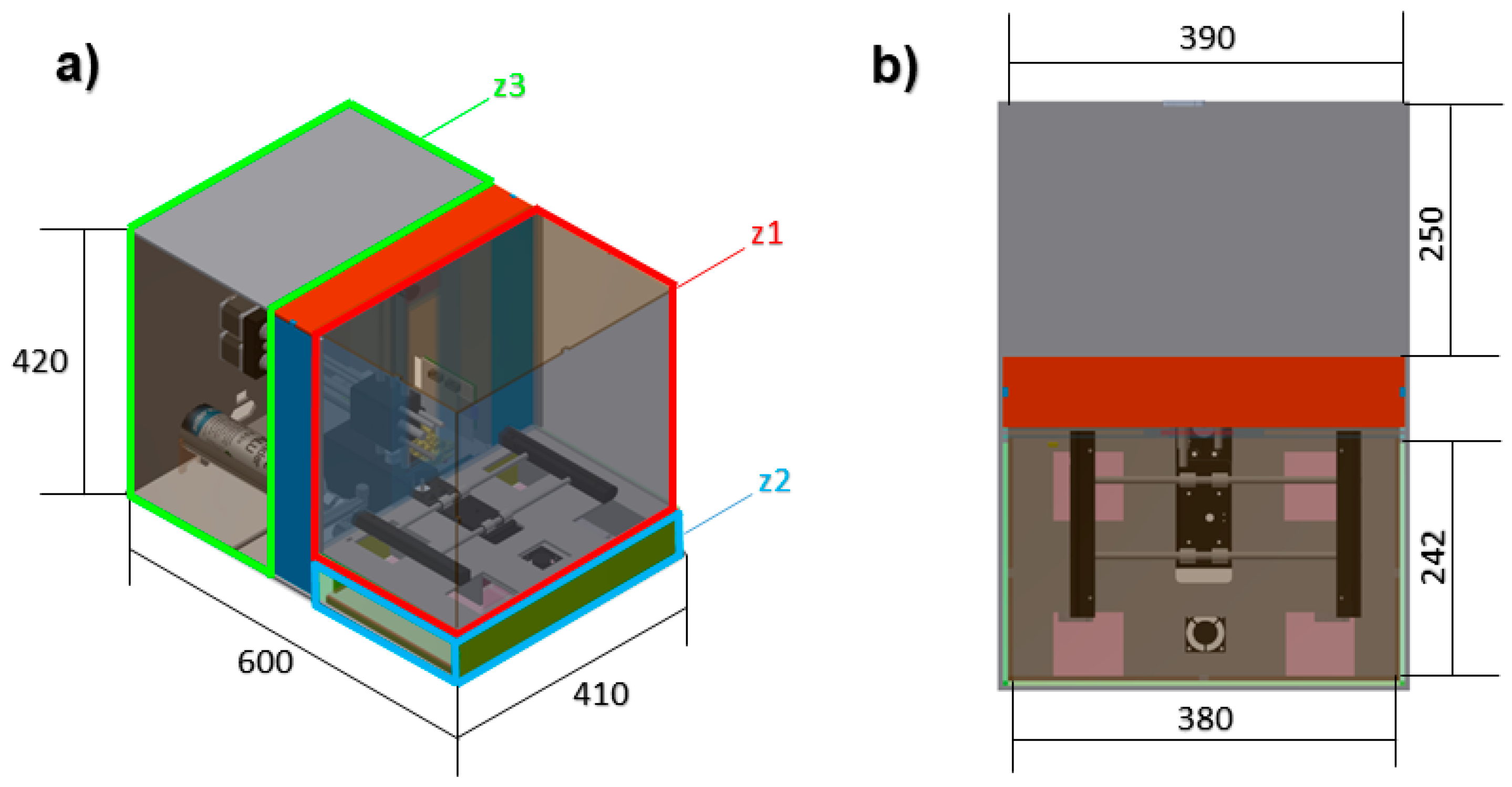
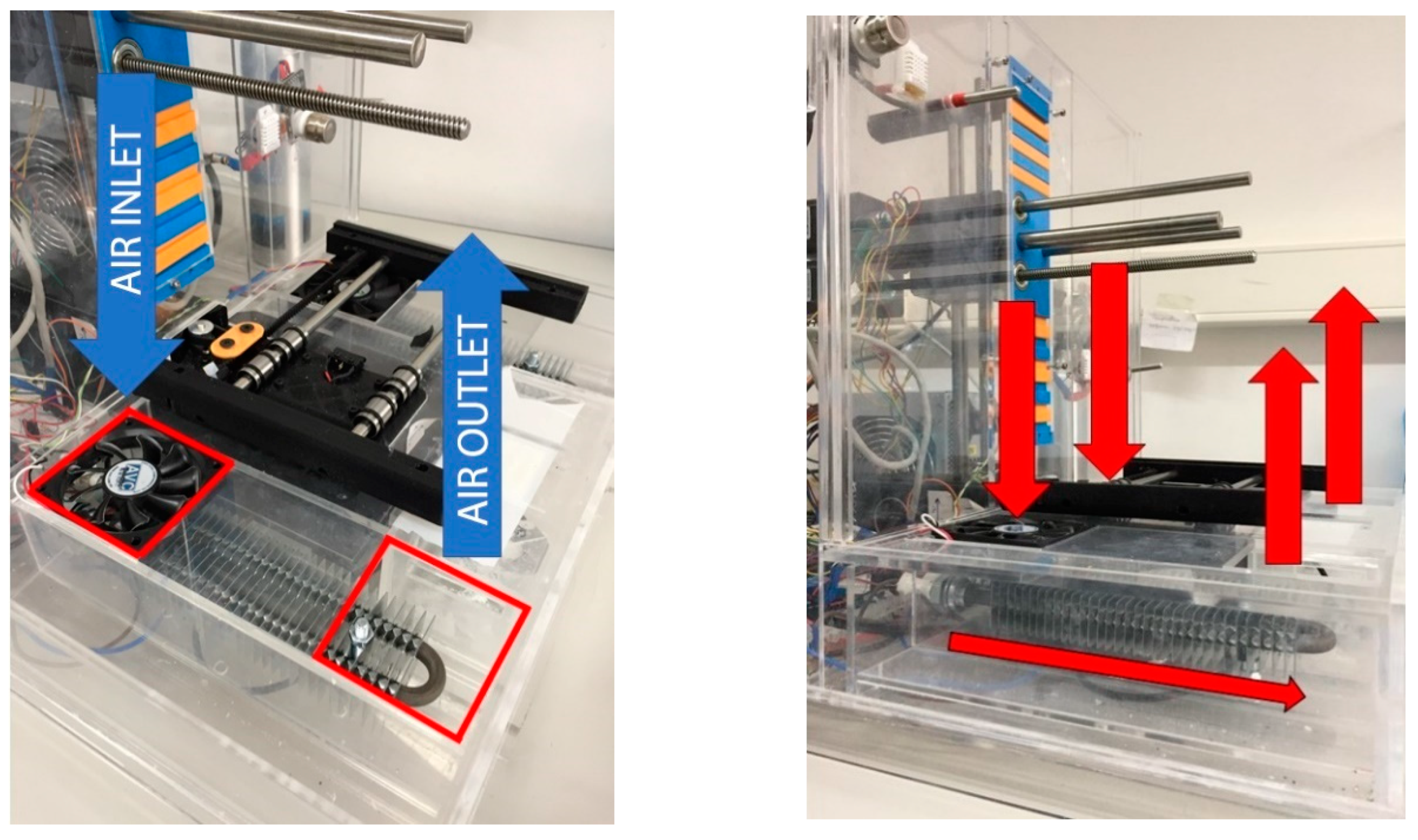



| Areas of the Atmospheric Enclosure | Size (mm) |
|---|---|
| Atmospheric enclosure full size | 600 × 410 × 420 |
| Bioprinting sub-chamber (z1) | 380 × 242 × 340 |
| Climatic conditions generation sub-chamber (z2) | 380 × 242 × 75 |
| Electronic and mechanical components sub-chamber (z3) | 390 × 250 × 410 |
| Sensors | Designation | Position |
|---|---|---|
| 2× Temperature sensor | PT 100 PRO | Top left and bottom right |
| 2× Humidity sensor | DHT22 | Top left and bottom right |
| 2× CO2 sensor | MG811 | Top left and bottom right |
| Variable | Input Value | Target Value |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 25 °C | 37 °C |
| Humidity | 50% | 90% |
| Value (s) | Temperature | Humidity |
|---|---|---|
| Delay time | 16.00 s | 6.00 s |
| Rise time | 40.00 s | 11.00 s |
| Peak time | 85.00 s | 26.00 s |
| Percent overshoot | 8.35% | 3.88% |
| Settling time | 155.00 s | 106.00 s |
| Value | Temperature (°C) | Humidity (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Proportional (Kp) | 150.00 | 25.00 |
| Integral (Ki) | 1.00 | 2.00 |
| Derivative (Kd) | 6000.00 | 100.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matamoros, M.; Gómez-Blanco, J.C.; Sánchez, Á.J.; Mancha, E.; Marcos, A.C.; Carrasco-Amador, J.P.; Pagador, J.B. Temperature and Humidity PID Controller for a Bioprinter Atmospheric Enclosure System. Micromachines 2020, 11, 999. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11110999
Matamoros M, Gómez-Blanco JC, Sánchez ÁJ, Mancha E, Marcos AC, Carrasco-Amador JP, Pagador JB. Temperature and Humidity PID Controller for a Bioprinter Atmospheric Enclosure System. Micromachines. 2020; 11(11):999. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11110999
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatamoros, Manuel, J. Carlos Gómez-Blanco, Álvaro J. Sánchez, Enrique Mancha, Alfonso C. Marcos, J. Pablo Carrasco-Amador, and J. Blas Pagador. 2020. "Temperature and Humidity PID Controller for a Bioprinter Atmospheric Enclosure System" Micromachines 11, no. 11: 999. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11110999
APA StyleMatamoros, M., Gómez-Blanco, J. C., Sánchez, Á. J., Mancha, E., Marcos, A. C., Carrasco-Amador, J. P., & Pagador, J. B. (2020). Temperature and Humidity PID Controller for a Bioprinter Atmospheric Enclosure System. Micromachines, 11(11), 999. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11110999







