Damping Asymmetry Trimming Based on the Resistance Heat Dissipation for Coriolis Vibratory Gyroscope in Whole-Angle Mode
Abstract
1. Introduction
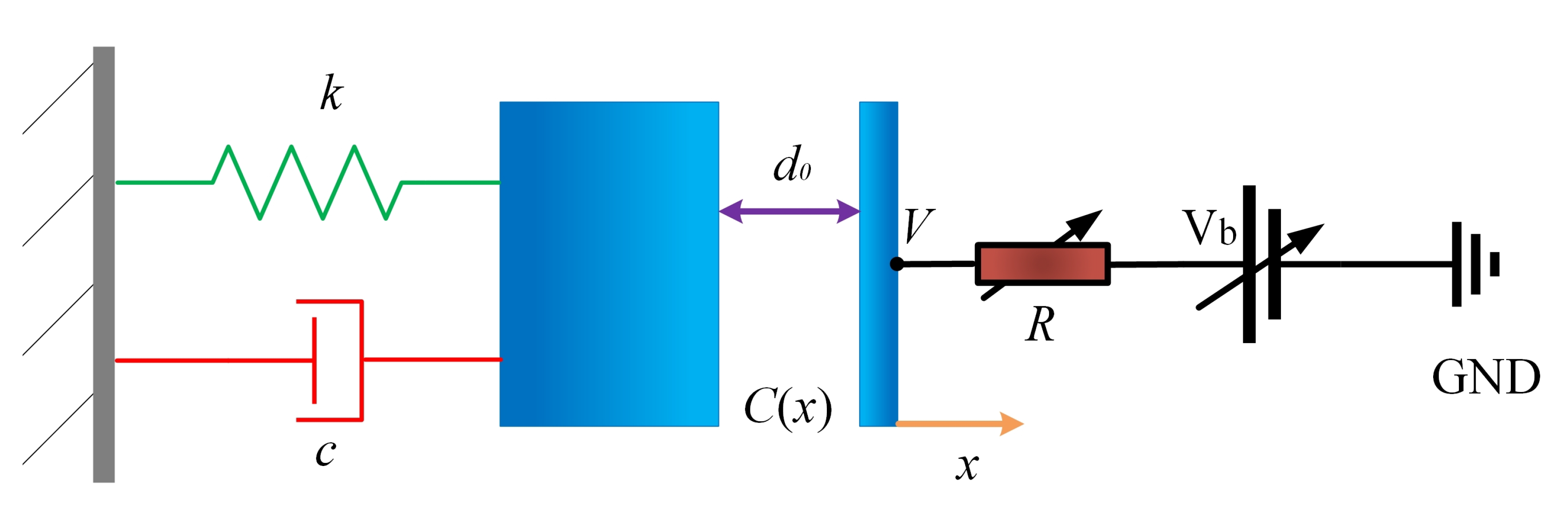
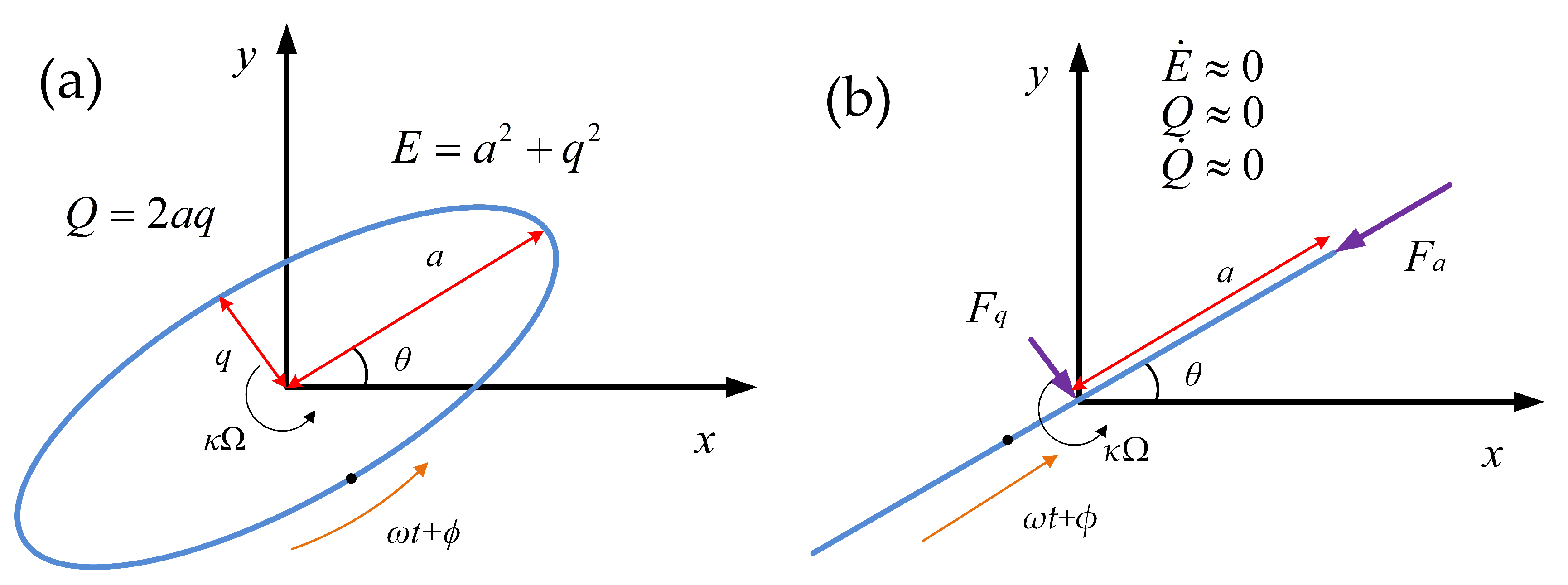
2. The Basic Theory of Damping Tuning
3. Practical Damping Tuning Method for CVG
3.1. The Concept of Damping Tuning in CVG
3.2. Approach for Damping Asymmetry Observation
4. Experimental Results
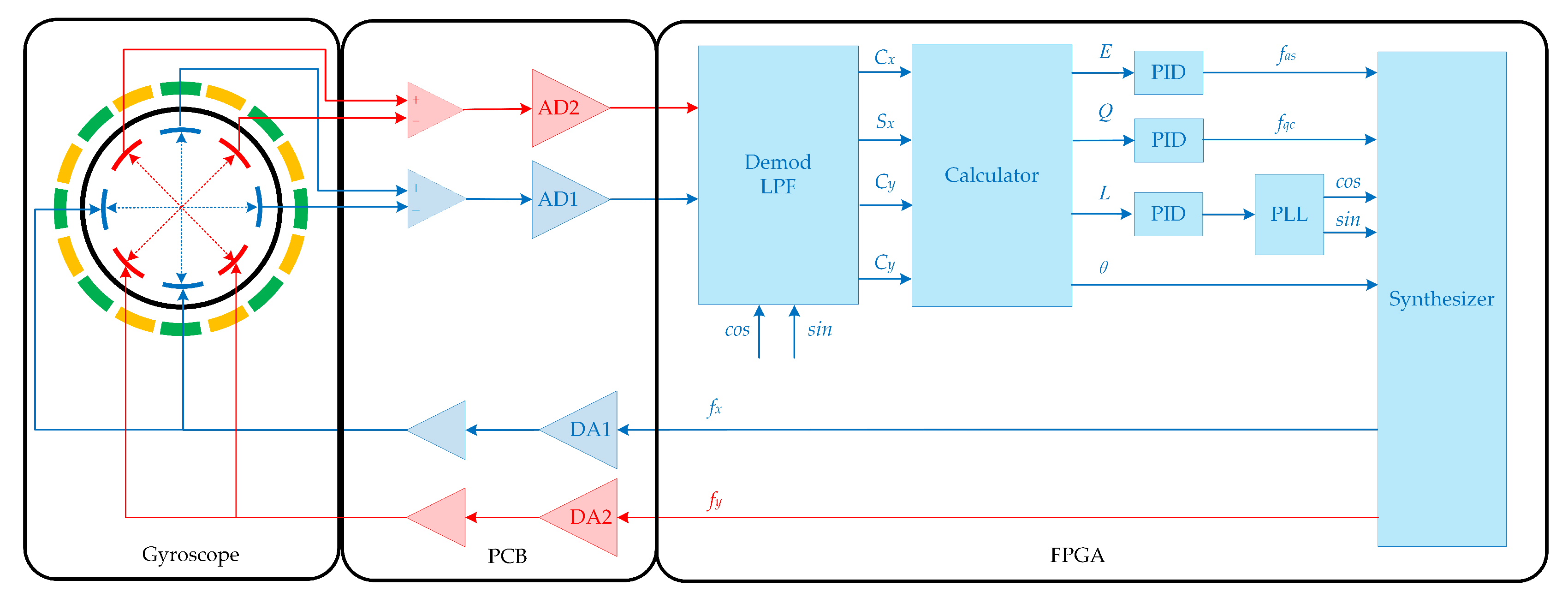
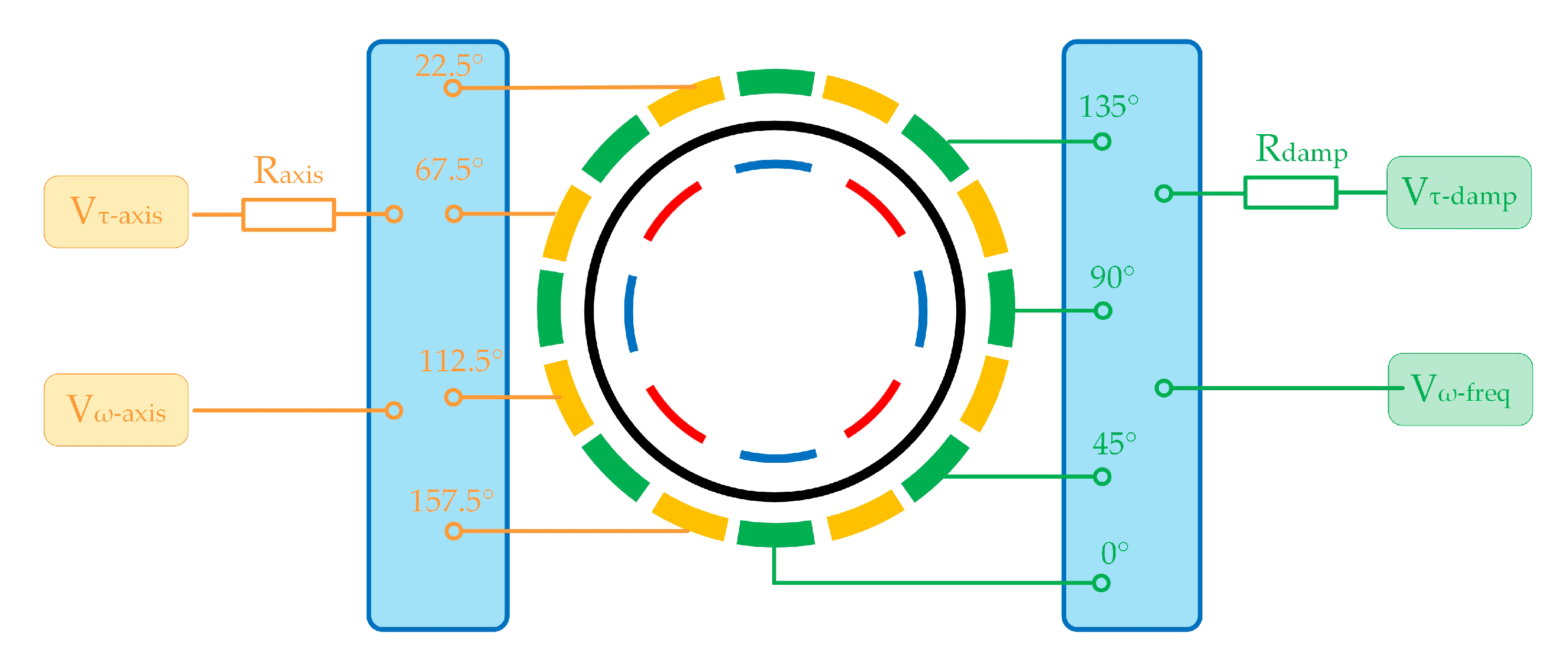
4.1. Device and Testing Platform
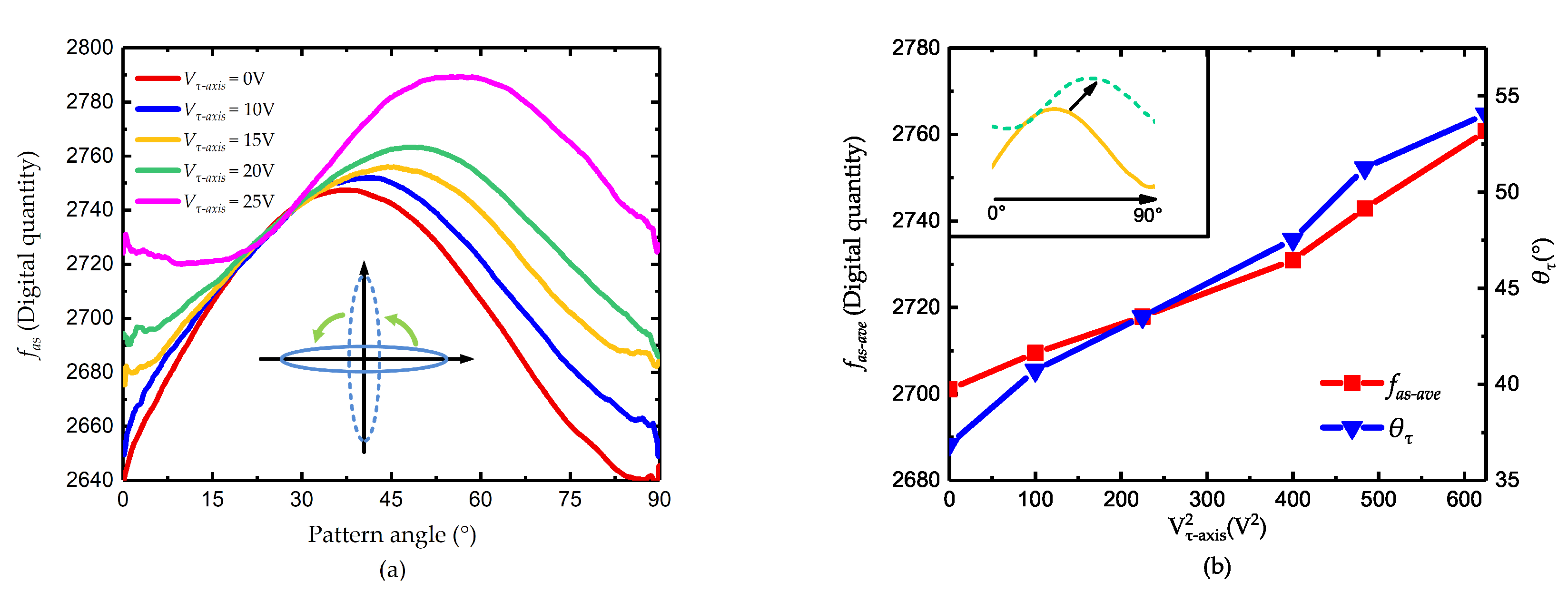
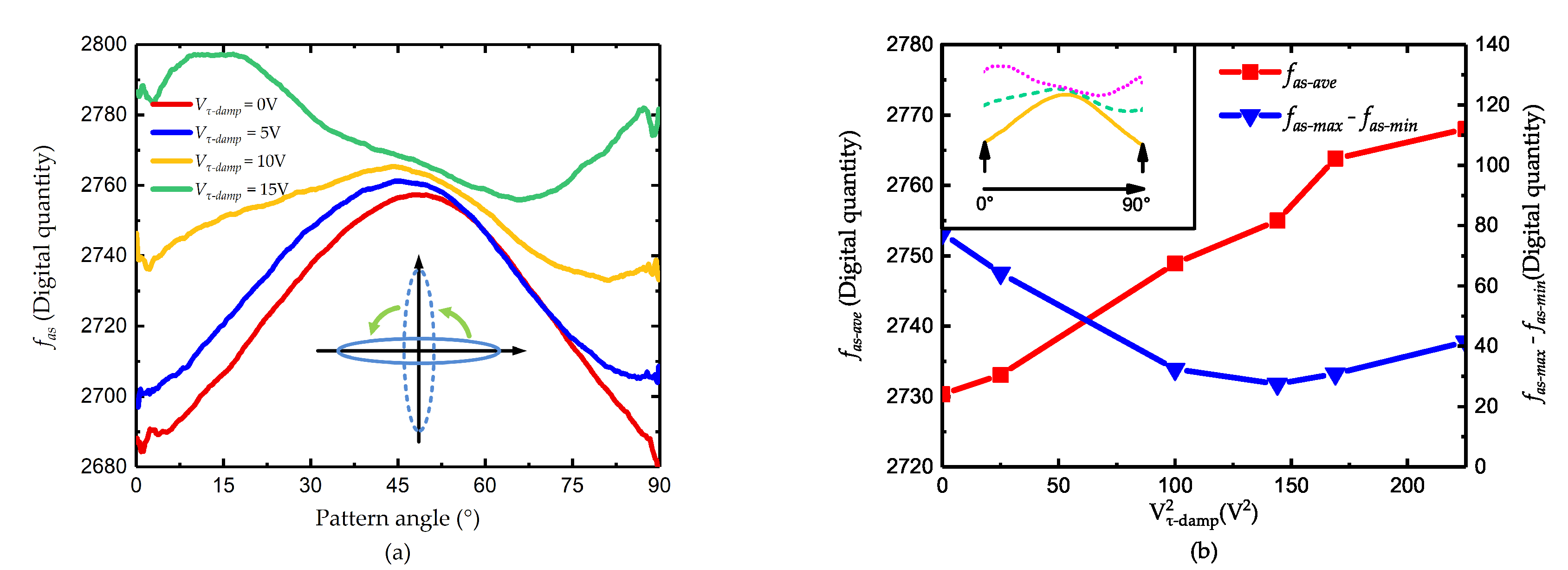
4.2. Damping Axis Tuning and Mismatch Tuning
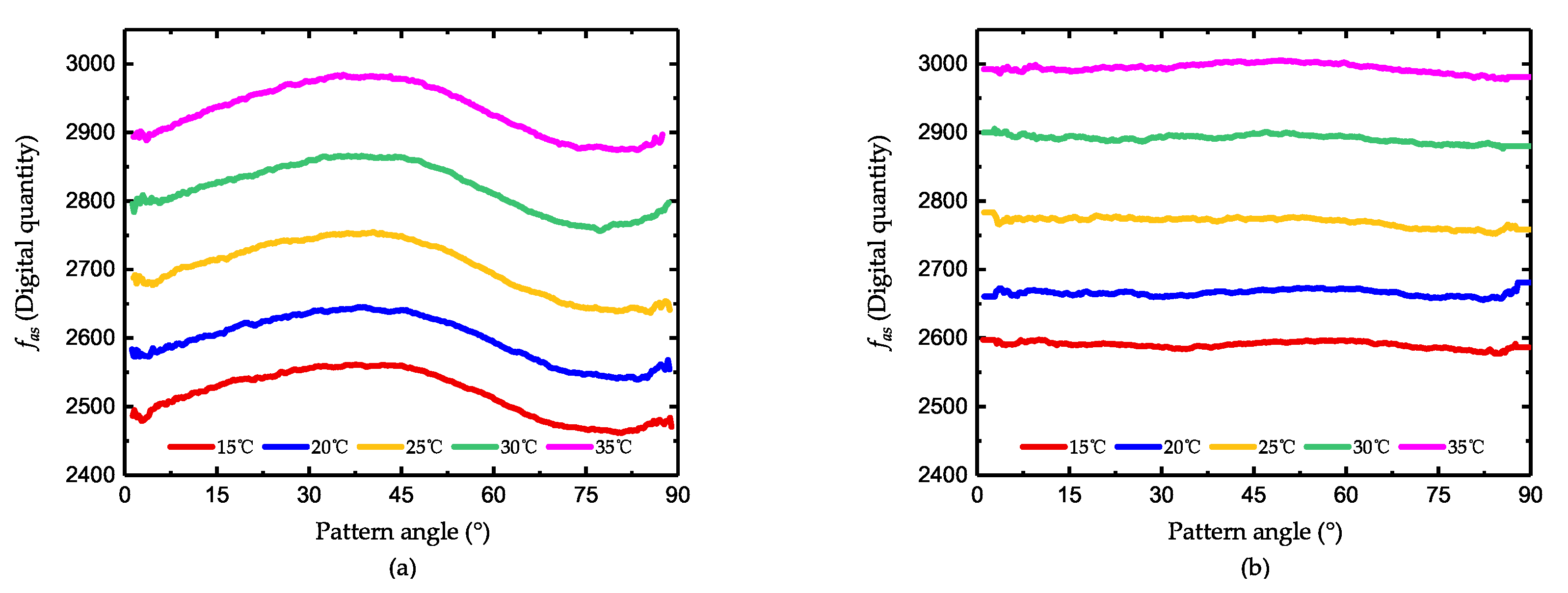
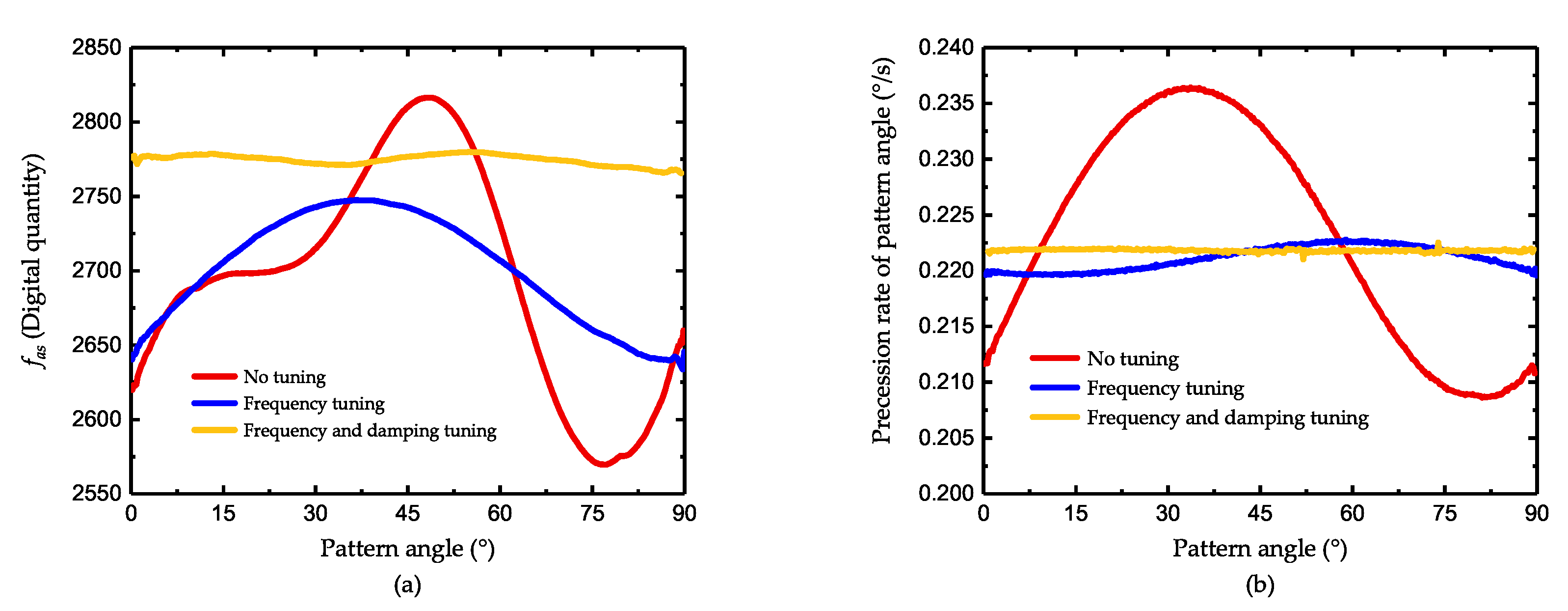
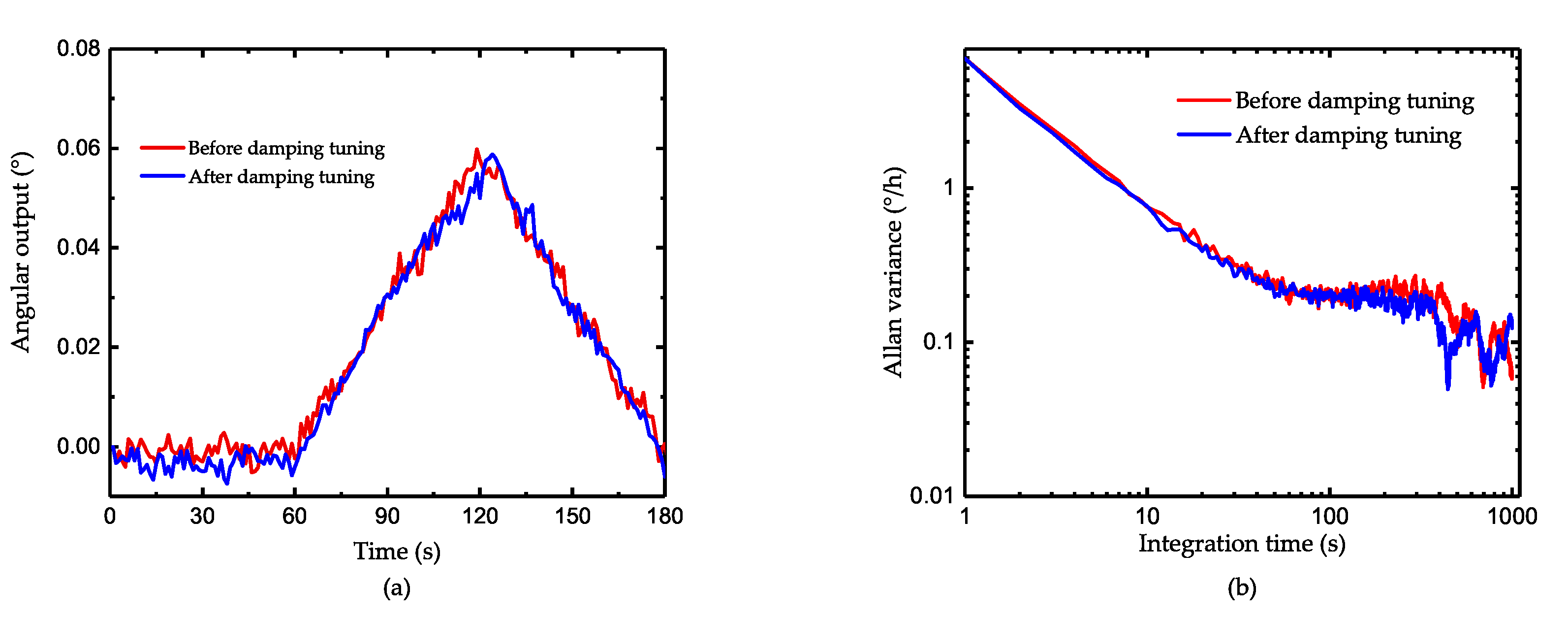
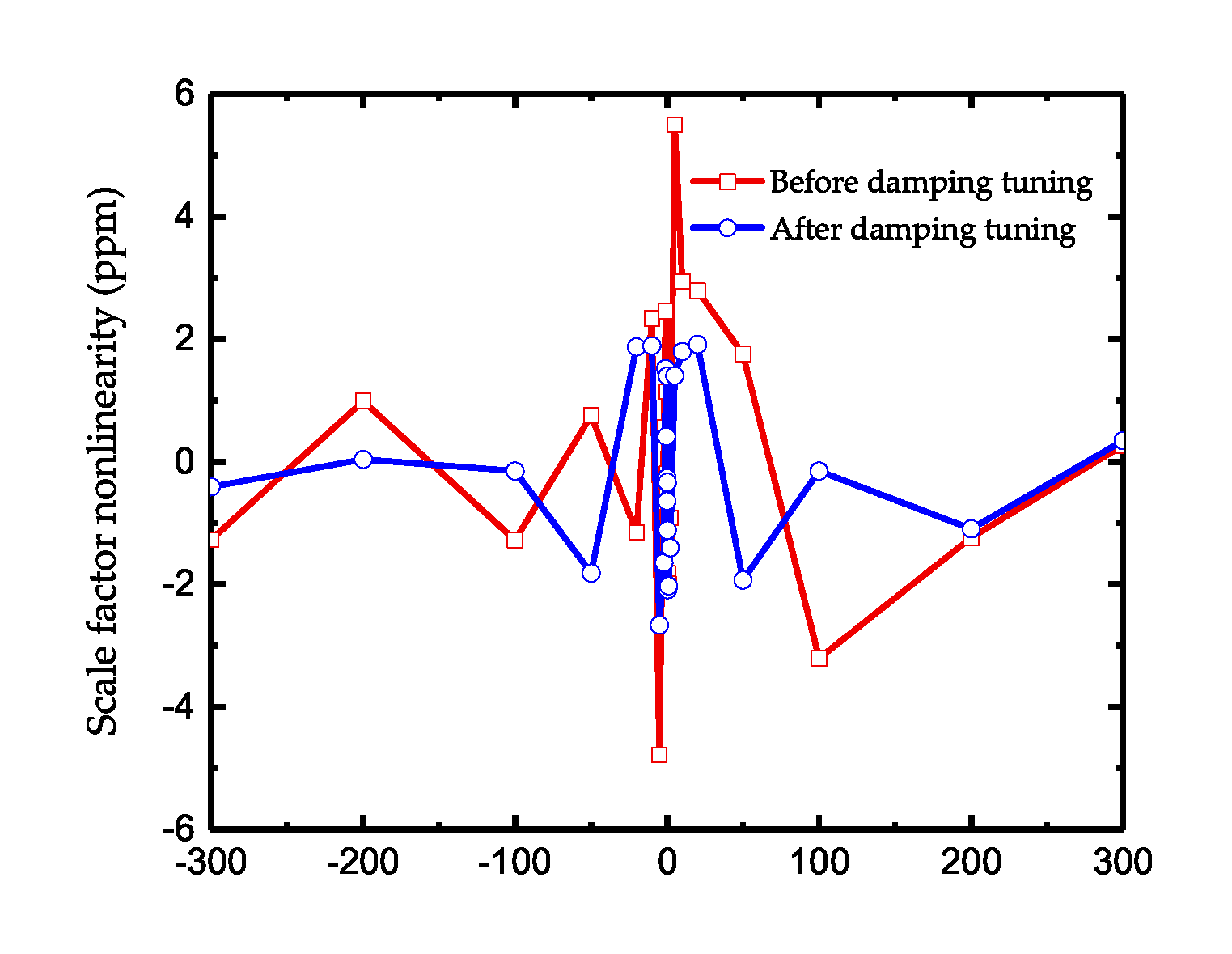
4.3. The Improvement after Damping Asymmetry Trimming
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruan, Z.; Ding, X.; Qin, Z.; Jia, J.; Li, H. Automatic Mode-Matching Method for MEMS Disk Resonator Gyroscopes Based on Virtual Coriolis Force. Micromachines 2020, 11, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, F.; Din, H.; Lee, B. Single Drive Multi-Axis Gyroscope with High Dynamic Range, High Linearity and Wide Bandwidth. Micromachines 2019, 10, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, J.; Li, J.; Xu, L. The Effect of Displacement Constraints on the Failure of MEMS Tuning Fork Gyroscopes under Shock Impact. Micromachines 2019, 10, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armenise, M.N.; Ciminelli, C.; Dell’Olio, F.; Passaro, V.M. Advances in Gyroscope Technologies; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Burdess, J.; Harris, A.; Cruickshank, J.; Wood, D.; Cooper, G. A review of vibratory gyroscopes. Eng. Sci. Educ. J. 1994, 3, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Leland, R.P. The adaptive control system of a MEMS gyroscope with time-varying rotation rate. In Proceedings of the 2005, American Control Conference, Portland, OR, USA, 8–10 June 2005; pp. 3592–3597. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, L.; Zheng, Q.; Gao, Z. On Control System Design for the Conventional Mode of Operation of Vibrational Gyroscopes. IEEE Sens. J. 2008, 8, 1871–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challoner, A.D.; Howard, H.G.; Liu, J.Y. Boeing disc resonator gyroscope. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium-PLANS 2014, Monterey, CA, USA, 5–8 May 2014; pp. 504–514. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, J.Y.; Woo, J.K.; He, G.; Yang, D.; Boyd, C.; Singh, S.; Darvishian, A.; Shiari, B.; Najafi, K. 1.5-million Q-factor vacuum-packaged birdbath resonator gyroscope (BRG). In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 32nd International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Seoul, Korea, 27–31 January 2019; pp. 210–213. [Google Scholar]
- Izmailov, E.; Kolesnik, M.; Osipov, A.; Akimov, A. Hemispherical resonator gyro technology. Problems and possible ways of their solutions. In Proceedings of the 6th Saint Petersburg International Conference on Integrated Navigation Systems, St. Petersburg, Russia, 24–26 May 1999; pp. 24–26. [Google Scholar]
- Leland, R.P. Adaptive Control of a MEMS Gyroscope Using Lyapunov Methods. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2006, 14, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, J.; Cho, J.; Najafi, K. MEMS rate and rate-integrating gyroscope control with commercial software defined radio hardware. In Proceedings of the 2011 16th International Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems Conference, Beijing, China, 5–9 June 2011; pp. 2394–2397. [Google Scholar]
- Jeanroy, A.; Grosset, G.; Goudon, J.C.; Delhaye, F. HRG by Sagem from laboratory to mass production. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Inertial Sensors and Systems, Laguna Beach, CA, USA, 22–25 February 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Jeanroy, A.; Bouvet, A.; Remillieux, G. HRG and marine applications. Gyroscopy Navig. 2014, 5, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Gallacher, B.J. Precision mode tuning towards a low angle drift MEMS rate integrating gyroscope. Mechatronics 2017, 56, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, J.; Bang, H. Imperfection Parameter Observer and Drift Compensation Controller Design of Hemispherical Resonator Gyros. Int. J. Aeronaut. Space Sci. 2013, 14, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, S.; Sung, W.T.; Kim, C.; Yun, S.; Lee, Y.J. On the Mode-Matched Control of MEMS Vibratory Gyroscope via Phase-Domain Analysis and Design. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 2009, 14, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhou, B.; Song, M.; Lin, Z.; Jin, S.; Zhang, R. Structural Parameter Identification of the Center Support Quadruple Mass Gyro (CSQMG). IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 3765–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.R.; Boynton, C.; Cabuz, E.; Chang, S.; Christ, K.; Moore, S.; Reinke, J.; Winegar, K. Toroidal resonators with small frequency mismatch for rate integrating gyroscopes. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Symposium on Inertial Sensors and Systems (ISISS), Laguna Beach, CA, USA, 25–26 February 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Prabhakar, S.; Vengallatore, S. Theory of thermoelastic damping in micromechanical resonators with two-dimensional heat conduction. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2008, 17, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Zaman, M.F.; Sharma, A.; Ayazi, F. Energy loss mechanisms in a bulk-micromachined tuning fork gyroscope. In Proceedings of the SENSORS, 2006 IEEE, Daegu, Korea, 22–25 October 2006; pp. 1333–1336. [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg, M.; Candler, R.; Chandorkar, S.; Varsanik, J.; Kenny, T.; Duwel, A. Energy loss in MEMS resonators and the impact on inertial and RF devices. In Proceedings of the TRANSDUCERS 2009-2009 International Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems Conference, Denver, CO, USA, 21–25 June 2009; pp. 688–695. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, J.; Zhou, J. Robust adaptive control of MEMS triaxial gyroscope using fuzzy compensator. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. Part B (Cybern.) 2012, 42, 1599–1607. [Google Scholar]
- Leland, R. Adaptive mode tuning for vibrational gyroscopes. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2003, 11, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Horowitz, R.; Tan, C.W. Dynamics and control of a MEMS angle measuring gyroscope. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2008, 144, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, J.A.; Cho, J.; Najafi, K. Novel mismatch compensation methods for rate-integrating gyroscopes. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium, Myrtle Beach, SC, USA, 23–26 April 2012; pp. 252–258. [Google Scholar]
- Prikhodko, I.P.; Gregory, J.A.; Bugrov, D.I.; Judy, M.W. Overcoming limitations of rate integrating gyroscopes by virtual rotation. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Inertial Sensors and Systems, Laguna Beach, CA, USA, 22–25 February 2016; pp. 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Taheri-Tehrani, P.; Challoner, A.D.; Horsley, D.A. Micromechanical rate integrating gyroscope with angle-dependent bias compensation using a self-precession method. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 3533–3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, T.; Tanaka, S. Virtually rotated MEMS whole angle gyroscope using independently controlled CW/CCW oscillations. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Inertial Sensors and Systems (INERTIAL), Moltrasio, Italy, 26–29 March 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Gallacher, B. Control and damping imperfection compensation for a rate integrating MEMS gyroscope. In Proceedings of the 2015 DGON Inertial Sensors and Systems Symposium (ISS), Karlsruhe, Germany, 22–23 September 2015; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Gallacher, B. Extended Kalman filtering based parameter estimation and drift compensation for a MEMS rate integrating gyroscope. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2016, 250, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gando, R.; Maeda, S.; Masunishi, K.; Tomizawa, Y.; Ogawa, E.; Hatakeyama, Y.; Itakura, T.; Ikehashi, T. A MEMS rate integrating gyroscope based on catch-and-release mechanism for low-noise continuous angle measurement. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Belfast, UK, 21–25 January 2018; pp. 944–947. [Google Scholar]
- Gando, R.; Ono, D.; Kaji, S.; Ota, H.; Itakura, T.; Tomizawa, Y. A Compact Microcontroller-based MEMS Rate Integrating Gyroscope Module with Automatic Asymmetry Calibration. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 33rd International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 January 2020; pp. 1296–1299. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuo, M.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wu, X.; Xiao, D. Damping Tuning in the Disk Resonator Gyroscope Based on the Resistance Heat Dissipation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE SENSORS, Montreal, QC, Canada, 27–30 October 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Rabenimanana, T.; Walter, V.; Kacem, N.; Le Moal, P.; Bourbon, G.; Lardiès, J. Functionalization of electrostatic nonlinearities to overcome mode aliasing limitations in the sensitivity of mass microsensors based on energy localization. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2020, 117, 033502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacem, N.; Hentz, S.; Baguet, S.; Dufour, R. Forced large amplitude periodic vibrations of non-linear Mathieu resonators for microgyroscope applications. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 2011, 46, 1347–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitsev, S.; Shtempluck, O.; Buks, E.; Gottlieb, O. Nonlinear damping in a micromechanical oscillator. Nonlinear Dyn. 2012, 67, 859–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imboden, M.; Williams, O.; Mohanty, P. Nonlinear dissipation in diamond nanoelectromechanical resonators. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 103502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, D.D. Vibratory gyro analysis by the method of averaging. In Proceedings of the 2nd St. Petersburg Conference on Gyroscopic Technology and Navigation, St. Petersburg, Russia, 24–25 May 1995; pp. 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F. Control and Self-Calibration of Microscale Rate Integrating Gyroscopes (MRIGs). Ph.D. Thesis, UC Berkeley, Berkeley, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, K.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Xiao, D.; Wu, X. Damping Asymmetry Trimming Based on the Resistance Heat Dissipation for Coriolis Vibratory Gyroscope in Whole-Angle Mode. Micromachines 2020, 11, 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11100945
Guo K, Wu Y, Zhang Y, Sun J, Xiao D, Wu X. Damping Asymmetry Trimming Based on the Resistance Heat Dissipation for Coriolis Vibratory Gyroscope in Whole-Angle Mode. Micromachines. 2020; 11(10):945. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11100945
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Kechen, Yulie Wu, Yongmeng Zhang, Jiangkun Sun, Dingbang Xiao, and Xuezhong Wu. 2020. "Damping Asymmetry Trimming Based on the Resistance Heat Dissipation for Coriolis Vibratory Gyroscope in Whole-Angle Mode" Micromachines 11, no. 10: 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11100945
APA StyleGuo, K., Wu, Y., Zhang, Y., Sun, J., Xiao, D., & Wu, X. (2020). Damping Asymmetry Trimming Based on the Resistance Heat Dissipation for Coriolis Vibratory Gyroscope in Whole-Angle Mode. Micromachines, 11(10), 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11100945



