Virulence Genes of S. aureus from Dairy Cow Mastitis and Contagiousness Risk
Abstract
:1. Introduction
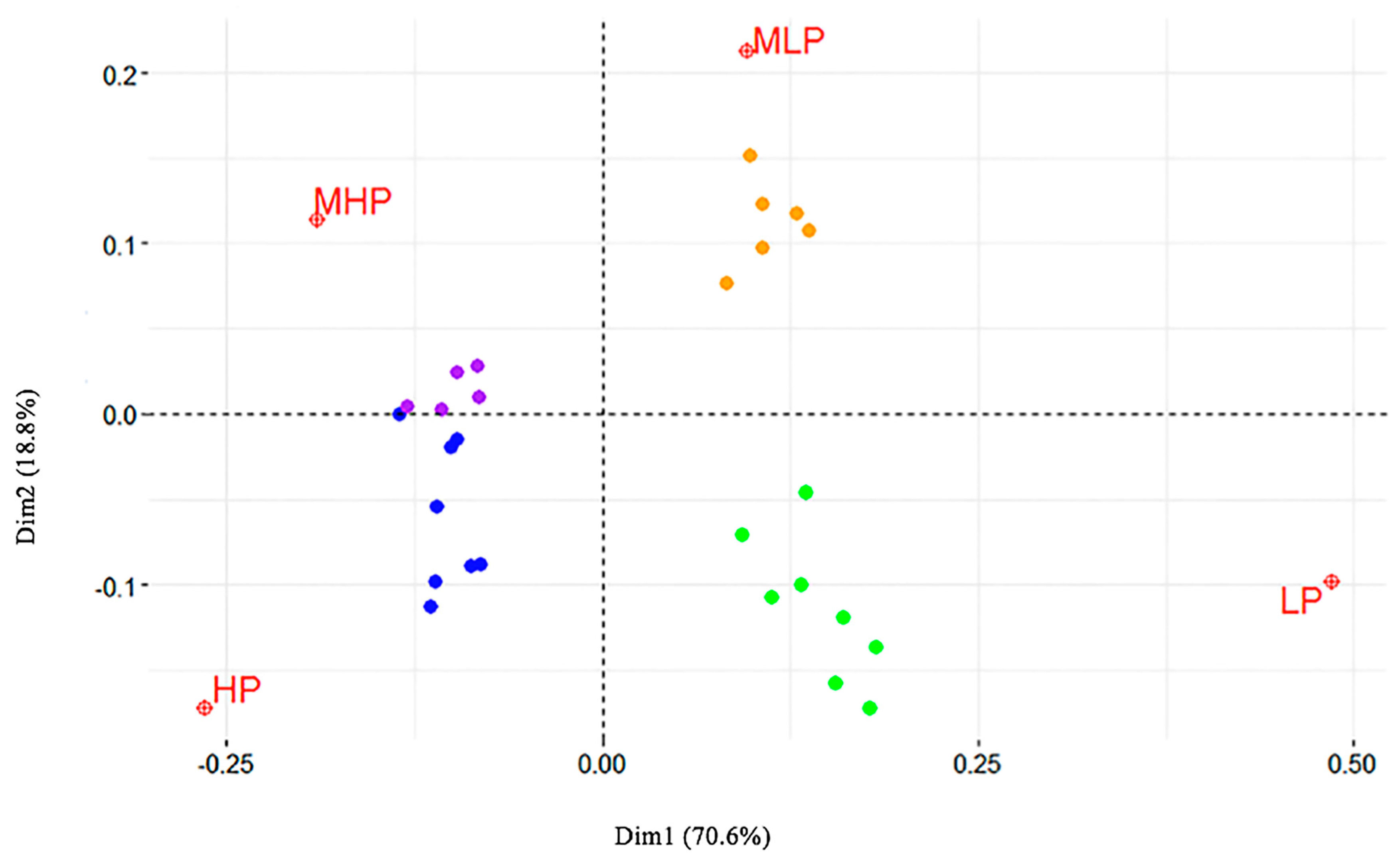
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
Herds, Sampling and Microarray Analysis
5. Statistical Analysis
5.1. Binary Logistic Regression (BLR) and Risk Factors Calculation
5.2. Data Editing and Correspondence Analysis (CA)
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Halasa, T.; Nielen, M.; Huirne, R.B.M.; Hogeveen, H. Stochastic bio-economic model of bovine intramammary infection. Livest. Sci. 2009, 124, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, J.A.; Holden, M.T. Staphylococcus aureus: Superbug, super genome? Trends Microbiol. 2004, 12, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.; Okuma, K.; Ma, X.X.; Yuzawa, H.; Hiramatsu, K. Insights on antibiotic resistance of Staphylococcus aureus from its whole genome: Genomic island SCC. Drug Resist. Updates 2003, 6, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifrian, E.; Guidry, A.J.; O’Brien, C.N.; Marquardt, W.W. Effect of antibodies to staphylococcal α and β toxins and Staphylococcus aureus on the cytotoxicity for and adherence of the organism to bovine mammary epithelial cells. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1996, 57, 1308–1311. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fluit, A.C. Livestock-associated Staphylococcus aureus. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 18, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, H.D.; Huda, A.; Eriksen, N.H.R.; Jensen, N.E. Differences between Danish bovine and human Staphylococcus aureus isolates in possession of superantigens. Vet. Microbiol. 2000, 76, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zecconi, A.; Cesaris, L.; Liandris, E.; Daprà, V.; Piccinini, R. Role of several Staphylococcus aureus virulence factors on the inflammatory response in bovine mammary gland. Microb. Pathog. 2006, 40, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez, C.; Pinal, L.; Franco, J.; Carrillo, J.M.; Ramírez, J. Identification of Staphylococcus aureus strains negative for enterotoxins A; B and C isolated from bovine mastitis in México. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2007, 117, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrio, M.B.; Rainard, P.; Prevost, G. LukM/LukF′-PV is the most active Staphylococcus aureus leukotoxin on bovine neutrophils. Microbes Infect. 2006, 8, 2068–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, T.; Tochimaru, N.; Nakasuji, S.; Hata, E.; Kobayashi, H.; Eguchi, M.; Kaneko, J.; Kamio, Y.; Kaidoh, T.; Takeuchi, S. Leukotoxin family genes in Staphylococcus aureus isolated from domestic animals and prevalence of lukM-lukF-PV genes by bacteriophages in bovine isolates. Vet. Microbiol. 2005, 110, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlotter, K.; Ehricht, R.; Hotzel, H.; Monecke, S.; Pfeffer, M.; Donat, K. Leukocidin genes lukF-P83 and lukM are associated with Staphylococcus aureus clonal complexes 151, 479 and 133 isolated from bovine udder infections in Thuringia, Germany. Vet. Res. 2012, 43, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, S.R.; Foster, S.J. Surface adhesins of Staphylococcus aureus. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 2006, 51, 187–224. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Speziale, P.; Pietrocola, G.; Foster, T.J.; Geoghegan, J.A. Protein-based biofilm matrices in Staphylococci. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2014, 4, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroda, M.; Ito, R.; Tanaka, Y.; Yao, M.; Matoba, K.; Saito, S.; Tanaka, I.; Ohta, T. Staphylococcus aureus surface protein SasG contributes to intercellular autoaggregation of Staphylococcus aureus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 377, 1102–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabat, A.; Melles, D.C.; Martirosian, G.; Grundmann, H.; van Belkum, A.; Hryniewicz, W. Distribution of the serine-aspartate repeat protein-encoding sdr genes among nasal carriage and invasive Sthapylococcus aureus strains. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 1135–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, K.; Huesca, M.; Vaz, D.; McGavin, M.J. Variance in fibronectin binding and fnb locus polymorphisms in Staphylococcus aureus: identification of antigenic variation in a fibronectin binding protein adhesin of the epidemic CMRSA-1 strain of methicillin-resistant S. aureus. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 3791–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendixen, M. Compositional perceptual mapping using chi-squared tree analysis and Correspondence Analysis. J. Mark. Manag. 1995, 11, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healey, J.F. The Essentials of Statistics: A Tool for Social Research, 2nd ed.; Wadsworth Publishing: Belmont, CA, USA, 2009; p. 287. [Google Scholar]
- Greenacre, M.J. Correspondence Analysis in Practice, 2nd ed.; Chapman & Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Monecke, S.; Kuhnert, P.; Hotzel, H.; Slickers, P.; Ehricht, R. Microarray based study on virulence-associated genes and resistance determinants of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from cattle. Vet. Microbiol. 2007, 125, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccinini, R.; Borromeo, V.; Zecconi, A. Relationship between S. aureus gene pattern and dairy herd mastitis prevalence. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 145, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snel, G.G.M.; Monecke, S.; Ehricht, R.; Piccinini, R. Molecular characteristics of bap-positive Staphylococcus aureus strains from dairy cow mastitis. J. Dairy Res. 2015, 82, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artursson, K.; Söderlund, R.; Liu, L.; Monecke, S.; Schelin, J. Genotyping of Staphylococcus aureus in bovine mastitis and correlation to phenotypic characteristics. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 193, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luini, M.; Cremonesi, P.; Magro, G.; Bianchini, V.; Minozzi, G.; Castiglioni, B.; Piccinini, R. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is associated with low within-herd prevalence of intra-mammary infections in dairy cows: Genotyping of isolates. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 178, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakwinska, O.; Giddey, M.; Moreillon, M.; Morisset, D.; Waldvogel, A.; Moreillon, P. Staphylococcus aureus host range and human-bovine host shift. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 5908–5915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, R.C.; Fabres-Klein, M.H.; Brito, M.; Fietto, L.G.; Ribon, A.D.B. Staphylococcus aureus of bovine origin: Genetic diversity; prevalence and the expression of adhesin-encoding genes. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 160, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luedicke, C.; Slickers, P.; Ehricht, R.; Monecke, S. Molecular fingerprinting of Staphylococcus aureus from bone and joint infections. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010, 29, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resch, G.; François, P.; Morisset, D.; Stojanov, M.; Bonetti, E.J.; Schrenzel, J.; Sakwinska, O.; Moreillon, P. Human-to-Bovine Jump of Staphylococcus aureus CC8 is associated with the loss of a β-hemolysin converting prophage and the acquisition of a new staphylococcal cassette chromosome. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kot, B.; Szweda, P.; Frankowska-Maciejewska, A.; Piechota, M.; Wolska, K. Virulence gene profiles in Staphylococcus aureus isolated from cows with subclinical mastitis in eastern Poland. J. Dairy Res. 2016, 83, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, H.; Lu, H.; Zhao, X. Sequence diversities of serine-aspartate repeat genes among Staphylococcus aureus isolates from different hosts presumably by horizontal gene transfer. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolar, S.L.; Ibarra, A.; Rivera, F.E.; Mootz, J.M.; Davenport, J.E.; Stevens, S.M.; Alexander, R.; Horswill, A.R.; Shaw, L.S. Extracellular proteases are key mediators of Staphylococcus aureus virulence via the global modulation of virulence-determinant stability. MicrobiologyOpen 2013, 2, 18–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, G.; Monecke, S.; Ehricht, R.; Söderquist, B. Prevalence of clonal complexes and virulence genes among commensal and invasive Staphylococcus aureus isolates in Sweden. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scali, F.; Camussone, C.; Calvinho, L.F.; Cipolla, M.; Zecconi, A. Which are important targets in developm nt of S. naureus mastitis vaccine? Res. Vet. Sci. 2015, 100, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, J.S.; Gonzales, R.N.; Harmon, R.J.; Nickerson, S.C.; Oliver, S.P.; Pankey, J.W.; Smith, K.L. Laboratory Handbook on Bovine Mastitis, revised ed.; National Mastitis Council Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1999; p. 222. [Google Scholar]
- Pilla, R.; Snel, G.G.M.; Malvisi, M.; Piccinini, R. Duplex real-time PCR assay for rapid identification of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from dairy cow milk. J. Dairy Res. 2013, 80, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdi, H.; Béra, M. Correspondence analysis. In Encyclopedia of Social Networks and Mining; Alhajj, R., Rokne, J., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 275–284. [Google Scholar]
- Nenadic, O.; Greenacre, M. Correspondence analysis in R, with two- and three-dimensional graphics: The ca package. J. Stat. Softw. 2007, 20, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Lê, S.; Josse, J.; Husson, F. FactoMineR: An R package for multivariate analysis. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, D.; Zeileis, A.; Hornik, K. The Strucplot framework: Visualizing multi-way contingency tables with vcd. J. Stat. Softw. 2006, 17, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, G. CAinterprTools: An R package to help interpreting Correspondence Analysis’ results. SoftwareX 2015, 1–2, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2008; Available online: http://www.R-project.org (accessed on 20 June 2017).

| Prevalence Class | Cubicle Houses (No.) | Stanchion Barns (No.) | Lactating Cows, Average (min.–max.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LP | 20 | - | 96.2 (15–245) |
| MLP | 15 | 1 | 67.6 (40–130) |
| MHP | 10 | 1 | 52.0 (15–120) |
| HP | 13 | - | 70.6 (15–195) |
| CC | Number of Strains | Overall Distribution of CCs (%) | Distribution of CCs in the Groups of Prevalence (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LP | MLP | MHP | HP | |||
| CC1 | 7 | 4.14 | 4.55 | 2.22 | 0 | 8.51 |
| CC5 | 4 | 2.37 | 0 | 0 | 12.12 | 0 |
| CC8 | 70 | 41.42 | 11.36 | 46.67 | 42.42 | 63.83 |
| CC20 | 4 | 2.37 | 6.82 | 0 | 3.03 | 0 |
| CC97 | 21 | 12.43 | 9.09 | 22.22 | 6.06 | 10.64 |
| CC101 | 1 | 0.59 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.13 |
| CC133 | 3 | 1.77 | 6.82 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| CC398 | 24 | 14.20 | 36.36 | 8.89 | 0 | 8.51 |
| CC479 | 5 | 2.96 | 6.82 | 4.44 | 0 | 0 |
| CC522 | 2 | 1.18 | 0 | 4.44 | 0 | 0 |
| CC705 | 12 | 7.10 | 9.09 | 11.11 | 9.09 | 0 |
| ST126 | 14 | 8.28 | 4.55 | 0 | 27.27 | 6.38 |
| ST72 | 1 | 0.59 | 2.27 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| agr IV, undef. CC | 1 | 0.59 | 2.27 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Genes | Relative Risk to the LP Class | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sign. | MLP | MHP | HP | ||
| sea | 0.034 | 1.61 | 3.41 | 5.53 | enterotoxin A |
| sed | 0.001 | 1.91 | 4.84 | 7.97 | enterotoxin D |
| ser | 0.001 | 1.64 | 4.92 | 8.05 | enterotoxin R |
| sej | 0.001 | 1.64 | 4.92 | 8.05 | enterotoxin J |
| lukD | 0.001 | 5.53 | 16.12 | 6.76 | leukocidin D component |
| lukE | 0.010 | 3.50 | >25.00 | 6.76 | leukocidin E component |
| hlb probe 3 | 0.007 | 4.66 | 4.126 | 6.09 | haemolysin beta |
| sak | 0.020 | 1.50 | 3.69 | 5.78 | staphylokinase |
| scn | 0.020 | 1.50 | 3.69 | 5.78 | staphylococcal complement inhibitor |
| splA | 0.036 | 3.65 | >25.00 | 5.71 | serin–protease A |
| splB | 0.050 | 3.56 | >25.00 | 4.90 | serin–protease B |
| splE | 0.000 | 5.04 | 7.25 | 10.47 | serin–protease E |
| aur ★ | 0.050 | 3.56 | >25.00 | 4.90 | aureolysin |
| fib | 0.050 | 3.56 | >25.00 | 4.90 | fibrinogen-binding protein |
| ebpS probe 612 | 0.004 | 5.48 | >25.00 | 6.75 | cell surface elastin-binding protein |
| clfB ▲ | 0.000 | 8.60 | 11.74 | 17.40 | clumping factor B |
| fnbA ✦ | 0.000 | 2.94 | 7.11 | 7.21 | fibronectin-binding protein A |
| fnbB ✦ | 0.000 | 16.99 | 13.93 | 31.81 | fibronectin-binding protein B |
| sasG ▲ | 0.000 | 5.82 | 3.69 | 6.19 | S. aureus surface protein G |
| sasG * | 0.000 | 5.26 | 2.23 | 6.54 | |
| sdrC ✦ | 0.002 | 3.97 | 2.29 | 5.68 | Serine–aspartate repeat protein C |
| sdrC * | 0.000 | 3.28 | 12.75 | 15.22 | |
| sdrD ※ | 0.002 | 4.27 | 3.25 | 7.52 | Serine–aspartate repeat protein D |
| vwb ※ | 0.000 | 4.55 | 3.38 | 12.78 | van Willebrand factor-binding protein |
| Gene | Prevalence Class | |
|---|---|---|
| ebpS ♦ | LP | cell surface elastin-binding protein |
| tetM | LP | tetracycline resistance |
| aur Y | LP | aureolysin |
| fib Y | LP | fibrinogen-binding protein |
| vga † | LP | ATP-binding protein, streptogramin A resistance |
| cna | LP | collagen-binding adhesin |
| dfrS1 | LP | dihydrofolate reductase type 1 |
| clfB ◈ | LP | clumping factor B |
| capJ1 | LP | O antigen polymerase |
| fexA | LP | chloramphenicol/florfenicol exporter |
| fnbB ♦ | HP | fibronectin-binding protein B |
| sej | HP | enterotoxin J |
| ser | HP | enterotoxin R |
| sed | HP | enterotoxin D |
| vwb ※ | HP | van Willebrand factor-binding protein |
| sdrD ※ | HP | serine-aspartate repeat protein D |
| fnbA ♦ | HP | fibronectin-binding protein A |
| sak | HP | staphylokinase |
| scn | HP | staphylococcal complement inhibitor |
| sea | HP | enterotoxin A |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Magro, G.; Biffani, S.; Minozzi, G.; Ehricht, R.; Monecke, S.; Luini, M.; Piccinini, R. Virulence Genes of S. aureus from Dairy Cow Mastitis and Contagiousness Risk. Toxins 2017, 9, 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9060195
Magro G, Biffani S, Minozzi G, Ehricht R, Monecke S, Luini M, Piccinini R. Virulence Genes of S. aureus from Dairy Cow Mastitis and Contagiousness Risk. Toxins. 2017; 9(6):195. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9060195
Chicago/Turabian StyleMagro, Giada, Stefano Biffani, Giulietta Minozzi, Ralf Ehricht, Stefan Monecke, Mario Luini, and Renata Piccinini. 2017. "Virulence Genes of S. aureus from Dairy Cow Mastitis and Contagiousness Risk" Toxins 9, no. 6: 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9060195
APA StyleMagro, G., Biffani, S., Minozzi, G., Ehricht, R., Monecke, S., Luini, M., & Piccinini, R. (2017). Virulence Genes of S. aureus from Dairy Cow Mastitis and Contagiousness Risk. Toxins, 9(6), 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9060195







