Abstract
Botulinum neurotoxins (BoNTs), which have been exploited as cosmetics and muscle-disorder treatment medicines for decades, are well known for their extreme neurotoxicity to humans. They pose a potential bioterrorism threat because they cause botulism, a flaccid muscular paralysis-associated disease that requires immediate antitoxin treatment and intensive care over a long period of time. In addition to the existing seven established BoNT serotypes (BoNT/A–G), a new mosaic toxin type termed BoNT/HA (aka type FA or H) was reported recently. Sequence analyses indicate that the receptor-binding domain (HC) of BoNT/HA is ~84% identical to that of BoNT/A1. However, BoNT/HA responds differently to some potent BoNT/A-neutralizing antibodies (e.g., CR2) that target the HC. Therefore, it raises a serious concern as to whether BoNT/HA poses a new threat to our biosecurity. In this study, we report the first high-resolution crystal structure of BoNT/HA-HC at 1.8 Å. Sequence and structure analyses reveal that BoNT/HA and BoNT/A1 are different regarding their binding to cell-surface receptors including both polysialoganglioside (PSG) and synaptic vesicle glycoprotein 2 (SV2). Furthermore, the new structure also provides explanations for the ~540-fold decreased affinity of antibody CR2 towards BoNT/HA compared to BoNT/A1. Taken together, these new findings advance our understanding of the structure and function of this newly identified toxin at the molecular level, and pave the way for the future development of more effective countermeasures.
1. Introduction
Botulism is a rare but life-threatening disease caused by botulinum neurotoxins (BoNTs), one of the most poisonous natural substances known. BoNTs are categorized as a Tier 1 select agent by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and could be potentially misused for bioterrorism warfare [1,2]. Paradoxically, some BoNTs have been successfully used as prescription medicines to treat muscle disorders or as injectable facial rejuvenation agents. Naturally occurring botulism forms are mostly food-borne botulism and infant botulism [3,4], in which the toxins are absorbed in the intestine and colon, respectively, into the general circulation. BoNTs specifically target neuromuscular junctions (NMJ), where the toxins are internalized into neuronal cells, cleave the soluble N-ethylmaleimide sensitive factor attachment protein receptors (SNAREs) complex, inhibit the release of neurotransmitter acetylcholine, and eventually paralyze the affected muscles [5,6].
BoNTs are large proteins (~150 kDa), which are produced in bacteria in the form of progenitor toxin complexes (PTCs, 300–760 kDa) that are composed of BoNT and several non-toxic neurotoxin-associated proteins (NAPs) [7,8,9,10,11,12]. Structurally, BoNT consists of an N-terminal light chain (LC, ~50 kDa) that is a metalloprotease and a C-terminal heavy chain (HC, ~100 kDa). The latter could be further divided into two domains: the N-terminal portion (~50 kDa) is the translocation domain (HN) required for the LC to be released into the cytosol; the C-terminal part (HC) is the receptor-binding domain responsible for the highly specific binding and endocytosis of BoNT into motoneurons. Among the seven established serotypes of BoNT (BoNT/A-G) [13], more than 40 BoNT subtypes have been identified [14,15] (e.g., BoNT/A1–A8). In addition, two hybrid/mosaic types have been identified: BoNT/CD and BoNT/DC. BoNT/DC comprises a LC and a HN domain highly homologous to BoNT/D and a HC similar to BoNT/C, whereas BoNT/CD closely resembles BoNT/C in the LC and HN domains but shares a high sequence similarity with BoNT/D in the HC domain [14,16,17].
A new BoNT type, originally termed BoNT/H, was reported in 2014 [18,19]. This toxin was produced in the bivalent Clostridium botulinum strain IBCA10-7060, which also expresses BoNT/B2 [18,19,20]. This new toxin was later successfully separated from BoNT/B2 in native host strain by inactivating the bont/B2 gene [21]. This toxin was originally categorized as a new serotype because the strain supernatant failed to be neutralized by several existing antitoxins including a US Army-supplied equine heptavalent F(ab’)2 botulinum antitoxin A–G at a testing ratio as high as 595:1 (antitoxin:toxin) [18]. Subsequent studies showed that a licensed, commercially available antitoxin, BAT (Botulism Antitoxin Heptavalent (A, B, C, D, E, F, G)—Equine), was able to neutralize this newly identified toxin [20]. Furthermore, several polyclonal antibodies raised against BoNT/A1 were found to neutralize this toxin, but at a lower potency compared to BoNT/A1 [21]. A new potent monoclonal antibody directed against this new toxin was reported in 2016 [22].
Amino acid (AA) sequence alignments based on genome sequences of strain IBCA10-7060 [19,23] showed that the HC of this toxin is most similar to that of BoNT/A1 (~84% identity), while its LC and HN share ~81% and ~64% identity to that of BoNT/F5, respectively [20]. An alternative nomenclature of this toxin as BoNT/FA was then proposed [23]. Subsequently, it was confirmed that this new toxin cleaves VAMP-2 (also called synaptobrevin 2) between L54 and E55 [21,24], which is identical to the behavior of BoNT/F5, but different from all other BoNT/F subtypes that cut VAMP-2 between Q58 and K59 [25]. Interestingly, only one of the six anti-BoNT/F antibodies tested in a recent study showed binding to the new toxin, albeit weak (KD ~75 nM), suggesting that it is immunologically different from BoNT/F [22]. In contrast, monoclonal antibodies RAZ1 and CR2 (both target the HC of BoNT/A) precipitated the new toxin from the culture supernatant [24] and neutralized the new toxin in a mouse bioassay [22]. Based on these data, we suggested to name this new toxin as BoNT/HA [26].
Currently no consensus about the nomenclature of this new toxin has been reached [15]. The scientific debates on this topic are largely due to the lack of understanding of its structure and function at the molecular level. Most of the current studies on BoNT/HA have been based on genomic and amino acid sequence analysis. This approach has been proven erroneous in the case of a mosaic BoNT/DC, whose HC is very similar to BoNT/C based on sequence (~64% identity). However, the crystal structure of BoNT/DC clearly shows that its HC is more similar to BoNT/B (~22% identity) than BoNT/C, which has been confirmed by functional studies [17,27]. Therefore, a crystal structure of BoNT/HA is essential to compare it with the other known BoNTs at the molecular level.
In this paper, we focused our study on the HC that is a proven target for anti-BoNT antibody and vaccine development. In our previous study, we showed that the HC of BoNT/HA (HCHA) binds weakly to the protein moiety of its cell-surface receptor SV2C when compared to HCA1 in spite of high sequence similarity [26]. Furthermore, a highly potent anti-BoNT/A antibody CR2, which is currently in clinical trials, displayed a ~540-fold decreased affinity on BoNT/HA according to a recent neutralization study [22]. These findings thus raised questions on how BoNT/HA behaves differently than BoNT/A1 on neuronal receptor binding and responds differently to the known antitoxins. To gain a better understanding of the structure and function of BoNT/HA, we determined the crystal structure of HCHA at a high resolution.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Biochemical Characterization of HCHA
Sequence alignment showed that HCHA shares ~84% AA sequence identity to HCA1. While the HCN part is more variable between the two (~75%), the HCC portion is highly conserved (~93%). The HCC of BoNT/A bears important binding sites for two cell-surface receptors: polysialogangliosides (PSGs) and synaptic vesicle glycoprotein 2 (SV2, including three isoforms SV2A, SV2B, and SV2C), which are required for the extreme neurotoxicity of the toxin according to the dual-receptor binding model [28]. Given the high sequence similarity, it is not surprising that BoNT/HA also uses SV2 as its protein receptor [26]. We successfully expressed and purified HCHA (residues E860-L1288) and HCA1 (residues N872-L1296) using Escherichia coli. Interestingly, we noticed that HCHA has a significantly lower yield of expression than HCA1 and also has a very low solubility, ~1 mg/mL in a buffer that contains 150 mM NaCl at pH 7.5. In contrast, HCA1 could be concentrated to at least 15 mg/mL under the same condition. After large-scale crystallization screens, HCHA was successfully crystallized at 1 mg/mL, an unusually low protein concentration for protein crystallization in general.
Via sequence alignment we noticed that an arginine of HCA1 (R1156) was substituted by a methionine in HCHA (M1148). The solubility of HCHA was significantly increased when we introduced a single-point mutation (M1148R) to HCHA, which could be concentrated to over 8 mg/mL in the same buffer mentioned above. On the other hand, a reversed mutation on HCA1 (R1156M) severely decreased its solubility and also significantly hampered the expression yield of HCA1 in E. coli. In spite of low solubility in solution, HCHA is correctly folded as the protein-melting assay showed that the thermo-stability of HCHA is slightly better than HCA1 (59.9 °C for HCA1 and 62.7 °C for HCHA) [26].
2.2. The Crystal Structure of HCHA
We then determined the crystal structure of HCHA at 1.8 Å resolution (Table 1). The overall structure of HCHA and HCA1 are very similar with a root-mean-square (RMS) deviation of 0.526 Å over 341 Cα atoms (Pymol, www.pymol.org). Close inspection of the structures of HCHA and HCA1 (PDB 5JLV) revealed several unique structural features of HCHA [26]. First, the short α-helix (residues N872-T876) at the very N-terminus of HCA1 is unstructured in HCHA (Figure 1A,B). Second, the loop (residues M873-K877) that links the first and the second β-strand in HCHA is longer than that in HCA1 (residues S885-H887) because HCHA has two extra residues in this region (Figure 1B, blue box; Figure 1C). Interestingly, this loop is not conserved among BoNT/A subtypes. In BoNT/A8, this loop is longer than that in other subtypes because of a unique arginine insertion that makes BoNT/A8 the longest BoNT/A subtype [29]. The third notable difference is that a 3/10-helix (residues S955-S957) linking β8 and β9 in HCA1 is unstructured in HCHA due to the deletion of two residues in this region (Figure 1B, yellow box; Figure 1D).

Table 1.
Data collection and refinement statistics.
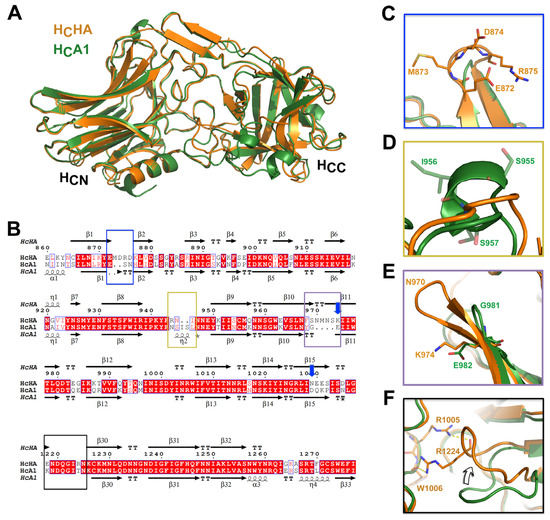
Figure 1.
Sequence alignment and structural comparison between HCHA and HCA1. (A) Superimposition of the structures of HCHA and HCA1. (B) Amino acid (AA) sequence alignment of HCHA and HCA1. Secondary structures of HCHA and HCA1 are placed on the top and the bottom, respectively. Blue arrows indicate the known pH-sensing residues on BoNT/A1 [11]. The four boxes highlight major AA sequence variations between HCHA and HCA1 that lead to structural changes. Close-up views of the structures in the corresponding areas are shown in (C) the blue box, (D) the yellow box, (E) the purple box, and (F) the black box. The AA sequence of HCA1 and HCHA are taken from GenBank: AAQ06331.1 (HCA1) and KGO15617.1 (HCHA). Sequence alignments were performed using Cluster Omega 1.2.2 and displayed with ESPript 3.0 [30,31].
We noticed that the β10 and β11 of HCHA are longer than those of HCA1 due to the insertion of four more residues (residues N970-S973) (Figure 1B, purple box; Figure 1E). Interestingly, this region of BoNT/A1 is involved in the release of BoNT/A1 from the PTC during oral intoxication. Earlier studies suggest that an auxiliary bacterial protein, non-toxic non-hemagglutinin (NTNHA), binds and protects BoNT/A1 in the gastrointestinal tract, and that BoNT/A1 is released from NTNHA upon absorption due to environmental pH change [7,11]. Notably, residue E982 located on β11 of HCA1 was reported as one of the pH sensing residues, which are deprotonated upon absorption and subsequently trigger the dissociation of BoNT/A1 from its NTNHA [11]. This residue is highly conserved in all BoNT/A subtypes. However, HCA1-E982 is replaced by a lysine in HCHA (K974). Interestingly, another pH sensing residue on HCA1, D1037, is also conserved in all BoNT/A subtypes, but differs from that of BoNT/HA (N1029) (Figure 1B, blue arrow) [11]. Nevertheless, BoNT/HA could be released from the M-PTC at neutral pH, as evidenced by the separation of BoNT/HA from NTNHA that is encoded in its operon at pH 7.6 [21]. Thus, BoNT/HA may employ a different set of pH sensing residues than BoNT/A to release it from the M-PTCs.
Another major structural difference between HCHA and HCA1 is found in the loop that links β29 and β30 (Figure 1B, black box; Figure 1F). In HCHA this loop (residues E1218-K1226) swings ~45 degrees towards the center of the HCC subdomain compared to that of HCA1. This is likely caused by residue HCHA-R1224 (equivalent to HCA1-T1232), which forms multiple hydrogen bonds with residues R1005 and W1006. The physiological relevance of this conformational difference on HCHA is currently unknown.
2.3. HCHA and HCA1 Bind Differently to Cell-Surface Receptors
According to a well-accepted dual-receptor binding model [28,32,33], BoNTs bind to neuronal cell surface through subsequent associations with two receptors: polysialogangliosides and a protein receptor. Sequence analysis and structural alignment show that the ganglioside-binding site (GBS) motif ‘E…H…SXWY…G’, which is highly conserved in BoNT/A, B, E (residue H is replaced by a K), F, and G (residue E is replaced by a Q) [34], is strictly conserved in HCHA (E1195, H1245, S1256, W1258, Y1259, and G1271) (Figure 2A, green stars). Interestingly, our sequence alignment shows that the HCC of BoNT/HA is most similar to BoNT/A8 (~95%). The alignment also suggests that a surface-exposed loop in the GBS neighborhood on BoNT/HA (residues I1263-A1266) is highly similar to BoNT/A8 (residues V1272-A1275), but differs from BoNT/A1 (residues I1271-S1274) (Figure 2A, blue arrows). This region of HCHA is likely flexible because the electron densities from residues R1261-R1268 were missing in our structure. Nevertheless, it is reasonable to speculate that the ganglioside-binding profile of BoNT/HA is more similar to BoNT/A8 than BoNT/A1. It is noteworthy that HCA8 has a weaker binding affinity to gangliosides on neuronal membranes compared to HCA1, which is possibly due to the negative influence of this altered loop [29]. Thus, we suspect that the reduced ganglioside-binding ability of BoNT/HA could partly contribute to its ~5-fold lower toxicity compared to BoNT/A1, as revealed by a mouse bioassay [21].
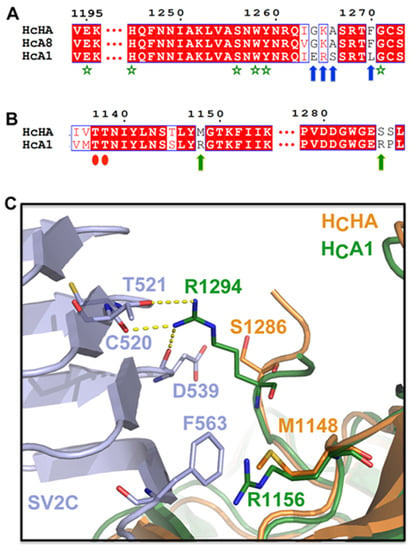
Figure 2.
Genetic changes between BoNT/HA and BoNT/A1 lead to different receptor-binding modes. (A) A sequence alignment suggests that the ganglioside-binding mode of BoNT/HA closely resembles that of BoNT/A8 and slightly differs from BoNT/A1. The conserved ganglioside-binding site (GBS) motif is indicated by green stars. Blue arrows highlight residues of HCHA that are identical to HCA8 but different from HCA1. The AA sequence of HCA1, HCA8, and HCHA are taken from GenBank: AAQ06331.1, AJA05787.1, and KGO15617.1. (B) A sequence alignment shows that two HCA1 residues, R1156 and R1294 (green arrows), whose side chains are engaged in SV2C binding, are not conserved in HCHA. Red ovals indicate two conserved residues that mediate backbone-backbone interactions between HCHA/HCA1 and SV2C. (C) Superimposition of the structures of HCHA (PDB 5V38) and the SV2C-HCA1 complex (PDB 5JLV) reveals the missing cation-π interaction and hydrogen bondings when HCHA binds to SV2C.
We have shown previously that BoNT/HA also uses SV2 as its cell-surface protein receptor [26]. The new structure of HCHA revealed that the subtle amino acid differences between BoNT/HA and BoNT/A actually lead to their substantially different protein-protein interactions with SV2. For example, an arginine on HCA1 (R1156) that contributes a crucial cation-π interaction with SV2C-F563 is replaced by a methionine (M1148) on HCHA (Figure 2B,C). Interestingly, this residue is not conserved amongst BoNT/A subtypes [26]. Apparently, the neighboring HCHA-R1134 cannot take over the cation-π interaction with SV2C-F563. Furthermore, while HCA1-R1294 forms three hydrogen bonds with C520, T521, and D539 of SV2C through its long, well-extended side-chain (Figure 2B,C), these hydrogen bondings are likely missing on HCHA because HCA1-R1294 is replaced by a serine (HCHA-S1286). These findings thus explain the observation that HCA1 was able to bind the non-glycosylated human SV2C-L4 (luminal domain 4), while HCHA showed a clearly decreased binding.
In spite of the weak protein-based interactions, HCHA binds strongly to the glycosylated SV2C (gSV2C), which clearly emphasizes the important role of SV2 glycan for BoNT/HA binding (Figure 3). Residues F953 and H1064 of HCA1 that form strong π-stacking interactions with the N559 glycan of gSV2C are conserved on HCHA (F943 and H1056). Disrupting the π-stacking interaction by introducing single point mutations on HCHA (e.g., F943R, F943G, and H1056R) showed strong reduction of binding to gSV2C based on a pull-down assay (Figure 3). Nevertheless, protein-protein interactions between HCHA and gSV2 are indispensable [26,35]. Disrupting two crucial backbone-backbone hydrogen bonds between HCHA and gSV2 (HCHA-T1137A/T1138A) led to dramatically decreased binding of HCHA to gSV2C (Figure 3).
Figure 3.
Protein-glycan interactions play an important role in BoNT/HA-SV2C recognition. The pulldown assay was performed to examine interactions between the glycosylated SV2C (gSV2C, bait) and HCA1 or HCHA variants (preys).
Interestingly, a recent study showed that BoNT/HA was ~4.3- and ~15-fold more active than BoNT/A1 when cleavage of VAMP-2 was examined using cultured primary rat spinal cord cells and human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSC)-derived neurons, respectively [21]. We suspect that the different potency of BoNT/HA revealed by cultured neuron-based assay and mouse bioassay could be partly caused by different tissue distribution of the three SV2 isoforms and potentially different N-linked glycosylation at N559. For example, SV2C is hardly present in cortical neurons [36,37,38], but dominant in motoneurons and spinal cord neurons, whereas SV2A is the dominant isoform in cortical neurons and the hiPSC-derived neurons [39]. Further research is needed to address these differences.
2.4. BoNT/HA and BoNT/A1 Respond Differently to Existing Antibodies
Antibody neutralization is currently the most effective way to counteract BoNTs. Due to the high degree of AA sequence identity between HCHA and HCA, it was expected that antibodies that target HCA are likely able to neutralize BoNT/HA and thus reduce this new threat to society. A recent study found that several antibodies could work in this regard, including RAZ1 and CR2, which are two of the three antibodies in the clinical-trial drug XOMA 3AB [40]. It was reported that RAZ1 (derived from 3D12) bound BoNT/HA tightly with a dissociation constant (KD) of ~4.96 pM, almost as good as BoNT/A1 (~2 pM) [22]. The binding epitope of 3D12 on BoNT/A1 has been mapped to residues N1127-R1131 [41,42]. This region is identical between BoNT/A1 and BoNT/HA (Figure 4A), thus explaining the high potency of RAZ1 on BoNT/HA.
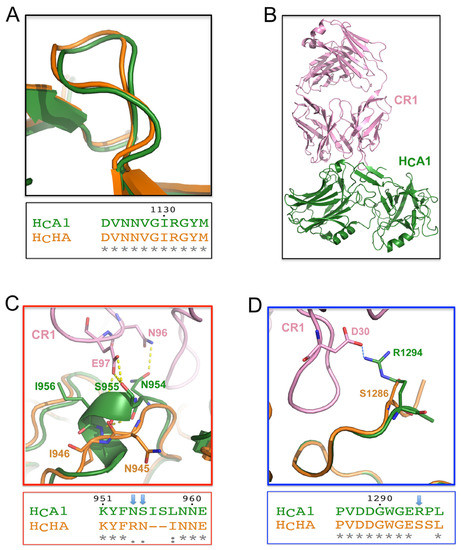
Figure 4.
Binding of BoNT/HA to two potent BoNT/A1-neutralizing antibodies. (A) The structure and sequence at the RAZ1 binding site are identical between HCHA and HCA1. (B) Overall structure of CR1 in complex with HCA1 (PDB 2NYY). Superimposition of the structures of HCHA and the CR1-BoNT/A1 complex shows that: (C) some hydrogen bonds at a 3/10 helix of HCA1 are missing on HCHA, and (D) a crucial salt bridge at the C-terminus of HCA1 is missing on HCHA.
Even though the overall structures of HCHA and HCA are highly similar, CR2 showed a surprisingly ~540-fold lower binding affinity to BoNT/HA (KD ~5.37 nM) than BoNT/A1 (KD ~10 pM) [22]. Since the structure of CR2 is not available, we used the crystal structure of a closely related antibody CR1 for analyses (Figure 4B), which differs from CR2 at only two residues (E6Q and V37I) that are far away from the BoNT/A1-binding interface [43]. CR1/CR2 efficiently neutralize BoNTA1 by occupying the SV2-binding site on the toxin [26]. We found that some crucial interactions between HCA1 and CR1/CR2 are missing on HCHA due to genetic changes. For example, while a 3/10-helix of HCA1 (residues S955-S957) and residue N954 form multiple hydrogen bonds with CR1/CR2 (through residues N96 and E97 of CR1), these polar contacts are missing on HCHA, which is very different from HCA in this region (Figure 4C). Furthermore, an important salt bridge between HCA1-R1294 and CR1-D30 is missing on HCHA due to the replacement of arginine by a serine on HCHA (HCHA-S1286) (Figure 4D). Taken together, these data suggest that BoNT/HA is able to escape from highly potent BoNT/A-neutralizing CR2 due to subtle genetic changes.
3. Conclusions
In summary, we have successfully expressed and purified the recombinant receptor-binding domain of the newly discovered botulinum neurotoxin type HA (HCHA). Dramatically different solubility in solution was observed between HCHA and HCA1, which was largely caused by variation of a single residue (HCA1-R1156 and HCHA-M1148). We then crystallized HCHA and determined its 3-dimensional structure at 1.8 Å resolution. Systematic sequence alignment and structural comparison between HCHA and HCA1 revealed many unique features of BoNT/HA. In brief, we found that BoNT/HA may use a different set of residues than BoNT/A to sense the environmental pH change in order to be released from the M-PTC during absorption in the gastrointestinal tract. Furthermore, BoNT/HA presumably displays different interactions with neuron-surface gangliosides. While the peptidic interactions of the protein receptor SV2C are weaker with BoNT/HA than BoNT/A1, the binding of BoNT/HA to the N559-glycan of SV2C compensates for this deficit. Importantly, the novel structure of HCHA also provides clear explanations to the high potency of RAZ1 and ~540-fold decreased potency of CR2 against BoNT/HA versus BoNT/A1. Taken together, the new structural insights into the neuron-binding mode of BoNT/HA and how it dampens binding of some existing BoNT/A neutralizing antibodies will facilitate further research exploring the function of BoNT/HA, and also help the development of more specific and potent antibodies against BoNT/HA as new research tools and potential therapeutic agents.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plasmid Construction
HCHA (residues E860-L1288 of BoNT/HA) was cloned into pGEX-4T-2 vector with an N-terminal glutathione S-transferase (GST) and a thrombin cleavage site. HCA1 (residues N872-L1296 of BoNT/A1) following a PreScission protease cleavage site was cloned into pQE30 vector with an N-terminal His6-tag. HCHA point mutations were generated with QuikChange site-directed mutagenesis (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The sequence corresponding to the core region of human SV2C-L4 (residues V473-T567) was cloned into pcDNA vector for mammalian expression. A human IL2 signal sequence (MYRMQLLSCIALSLALVTNS) and a His9-tag followed by a Factor Xa cleavage site were added to the N-terminus of SV2C.
4.2. Protein Expression and Purification
HCHA (wild-type and mutants) and HCA1 were expressed in E. coli strain BL21-Star (DE3) (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). Bacteria were cultured at 37 °C in LB (Luria-Bertani) medium containing appropriate selecting antibiotics. The temperature was set to 18 °C when OD600 reached 0.4. For induction, IPTG (isopropyl-b-d-thiogalactopyranoside) with a final concentration of 0.2 mM was added to the culture when OD600 reached 0.7. The expression was continued at 18 °C for 16 h after induction. The cells were harvested by centrifugation.
HCHA was purified using Glutathione Sepharose 4B affinity beads (GE Healthcare Life Sciences, Pittsburgh, PA, USA) in a buffer containing 50 mM Tris, pH 8.0; 400 mM NaCl. HCHA was released from the beads by on-column cleavage at 4 °C using thrombin. HCA1 was purified using Ni-NTA (Qiagen, Germantown, MD, USA) affinity resins in the same buffer supplemented with 40 mM imidazole and subsequently eluted with a high-imidazole buffer (50 mM Tris, pH 8.0; 400 mM NaCl; 300 mM imidazole). The proteins were then dialyzed at 4 °C against a buffer containing 20 mM HEPES, pH 7.5; 150 mM NaCl. The His6-tag of HCA1 was then excised by human rhinovirus 3C protease.
Tag-cleaved HCHA and HCA1 were further purified by MonoS ion-exchange chromatography (GE Healthcare Life Sciences, Pittsburgh, PA, USA) in a buffer containing 50 mM MES, pH 6.0 and eluted with a NaCl gradient. The peak fractions were then subjected to Superdex 200 size-exclusion chromatography (SEC, GE Healthcare Life Sciences, Pittsburgh, PA, USA) in a buffer containing 20 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, and 150 mM NaCl. Peak fractions were collected and concentrated for the downstream experiments.
Human SV2C-L4-core (gSV2C) was expressed and secreted from HEK 293 cells and purified directly from medium using Ni-NTA resins. The protein was eluted from the resins using high concentration of imidazole and dialyzed against a buffer containing 50 mM Tris, pH 8.0; 400 mM NaCl. gSV2C was then subjected to Superdex 200 SEC in a buffer containing 20 mM HEPES, pH 7.5; 150 mM NaCl.
4.3. Pull-Down Assay
The pull-down assay was performed using Ni-NTA resins in 1 mL buffer containing 50 mM Tris, pH 8.0; 400 mM NaCl; 10 mM imidazole and 0.1% Tween-20. gSV2C was used as the bait while HCA1-wildtype, HCHA-wildtype and mutants were preys. gSV2C was pre-incubated with Ni-NTA resins at 4 °C for 1 h. After the unbound protein was washed away, the resins were divided into small aliquots. Roughly, ~5 μg of gSV2C (~3 μM) was bound on the resins in each tube, and 30 μg of HC (~6 μM) was then added. The resins were washed twice after ~1.5 h incubation at 4 °C. The bound proteins and HC inputs were released from the resins using a SDS sample buffer containing 300 mM imidazole, and visualized by SDS-PAGE. All experiments were carried out in parallel for direct comparison.
4.4. Crystallization
Initial crystallization screens of HCHA were carried out using a Gryphon crystallization robot (Art Robbins Instrument, Sunnyvale, CA, USA) with high-throughput crystallization screening kits (Hampton Research, Aliso Viejo, CA, USA and Qiagen, Germantown, MD, USA). After extensive manual optimizations, single crystals were grown at 18 °C by the hanging-drop vapor-diffusion method using a 1:1 (v/v) ratio of protein and the reservoir (100 mM sodium acetate, pH 4.2, and 20% Polyethylene glycol (PEG) 3350). The crystals were cryoprotected in the original mother liquor supplemented with 20% (v/v) glycerol and flash-frozen in liquid nitrogen.
4.5. Data Collection and Structure Determination
Crystals were screened at SSRL and NE-CAT. The best diffraction data were collected at the NE-CAT beamline 24-ID, Advanced Photon Source (APS), Argonne, IL, USA. The data were processed with iMosflm [44]. The HCHA structure was determined with Phaser molecular replacement [45] using the structure of HCA1 (PDB code 5JLV) as the search model. The structural modeling and refinement were carried out iteratively using COOT [46] and Refmac from the CCP4 suite [47]. The refinement progress was monitored with the Rfreevalue with a 5% randomly selected test set [48]. The structure was validated by the MolProbity web server [49], and the refinement statistics are listed in Table 1. All structure figures were prepared with PyMOL (http://www.pymol.org/).
4.6. Accession Code
Coordinates and structure factors for HCHA have been deposited in the Protein Data Bank under accession code 5V38.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) grants R01AI091823, R01AI125704, and R21AI123920 to Rongsheng Jin and by the Swiss Federal Office for Civil Protection (BABS) grant #353005630 to Andreas Rummel. This work is based upon research conducted at the Northeastern Collaborative Access Team beamlines, which are funded by the National Institute of General Medical Sciences from the National Institutes of Health (P41 GM103403). The Pilatus 6M detector on 24-ID-C beam line is funded by a NIH-ORIP HEI grant (S10 RR029205). This research used resources of the Advanced Photon Source, a U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science User Facility operated for the DOE Office of Science by Argonne National Laboratory under Contract No. DE-AC02-06CH11357. Some experiments were conducted at the Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource, SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, which is supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science, Office of Basic Energy Sciences under Contract No. DE-AC02-76SF00515. The SSRL Structural Molecular Biology Program is supported by the DOE Office of Biological and Environmental Research, and by the National Institutes of Health, National Institute of General Medical Sciences (including P41GM103393).
Author Contributions
G.Y., K.-h.L., A.R. and R.J. conceived and designed the experiments; G.Y., K.-h.L., K.P. and J.W. performed the experiments; all authors analyzed the data; G.Y., A.R. and R.J. wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Arnon, S.S.; Schechter, R.; Inglesby, T.V.; Henderson, D.A.; Bartlett, J.G.; Ascher, M.S.; Eitzen, E.; Fine, A.D.; Hauer, J.; Layton, M.; et al. Botulinum toxin as a biological weapon: Medical and public health management. JAMA 2001, 285, 1059–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigalke, H.; Rummel, A. Medical aspects of toxin weapons. Toxicology 2005, 214, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aureli, P.; Fenicia, L.; Pasolini, B.; Gianfranceschi, M.; McCroskey, L.M.; Hatheway, C.L. Two cases of type E infant botulism caused by neurotoxigenic Clostridium butyricum in Italy. J. Infect. Dis. 1986, 154, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, E.A.; Montecucco, C. Botulism. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2008, 91, 333–368. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schiavo, G.; Benfenati, F.; Poulain, B.; Rossetto, O.; Polverino de Laureto, P.; DasGupta, B.R.; Montecucco, C. Tetanus and botulinum-B neurotoxins block neurotransmitter release by proteolytic cleavage of synaptobrevin. Nature 1992, 359, 832–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasi, J.; Chapman, E.R.; Link, E.; Binz, T.; Yamasaki, S.; De Camilli, P.; Sudhof, T.C.; Niemann, H.; Jahn, R. Botulinum neurotoxin a selectively cleaves the synaptic protein SNAP-25. Nature 1993, 365, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, S.; Jin, R. Assembly and function of the botulinum neurotoxin progenitor complex. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 364, 21–44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Lam, K.H.; Kruel, A.M.; Perry, K.; Rummel, A.; Jin, R. High-resolution crystal structure of HA33 of botulinum neurotoxin type B progenitor toxin complex. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 446, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Zhong, X.; Gu, S.; Kruel, A.M.; Dorner, M.B.; Perry, K.; Rummel, A.; Dong, M.; Jin, R. Molecular basis for disruption of E-cadherin adhesion by botulinum neurotoxin A complex. Science 2014, 344, 1405–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, M.D.; East, A.K. Phylogeny and taxonomy of the food-borne pathogen Clostridium botulinum and its neurotoxins. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1998, 84, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, S.; Rumpel, S.; Zhou, J.; Strotmeier, J.; Bigalke, H.; Perry, K.; Shoemaker, C.B.; Rummel, A.; Jin, R. Botulinum neurotoxin is shielded by NTNHA in an interlocked complex. Science 2012, 335, 977–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Gu, S.; Jin, L.; Le, T.T.; Cheng, L.W.; Strotmeier, J.; Kruel, A.M.; Yao, G.; Perry, K.; Rummel, A.; et al. Structure of a bimodular botulinum neurotoxin complex provides insights into its oral toxicity. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, K.K.; Smith, T.J. Genetic diversity within Clostridium botulinum serotypes, botulinum neurotoxin gene clusters and toxin subtypes. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 364, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rossetto, O.; Pirazzini, M.; Montecucco, C. Botulinum neurotoxins: Genetic, structural and mechanistic insights. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 535–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peck, M.W.; Smith, T.J.; Anniballi, F.; Austin, J.W.; Bano, L.; Bradshaw, M.; Cuervo, P.; Cheng, L.W.; Derman, Y.; Dorner, B.G.; et al. Historical perspectives and guidelines for botulinum neurotoxin subtype nomenclature. Toxins 2017, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriishi, K.; Koura, M.; Abe, N.; Fujii, N.; Fujinaga, Y.; Inoue, K.; Ogumad, K. Mosaic structures of neurotoxins produced from Clostridium botulinum types C and D organisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1307, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berntsson, R.P.; Peng, L.; Svensson, L.M.; Dong, M.; Stenmark, P. Crystal structures of botulinum neurotoxin DC in complex with its protein receptors synaptotagmin I and II. Structure 2013, 21, 1602–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barash, J.R.; Arnon, S.S. A novel strain of Clostridium botulinum that produces type B and type H botulinum toxins. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 209, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dover, N.; Barash, J.R.; Hill, K.K.; Xie, G.; Arnon, S.S. Molecular characterization of a novel botulinum neurotoxin type H gene. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 209, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maslanka, S.E.; Luquez, C.; Dykes, J.K.; Tepp, W.H.; Pier, C.L.; Pellett, S.; Raphael, B.H.; Kalb, S.R.; Barr, J.R.; Rao, A.; et al. A novel botulinum neurotoxin, previously reported as serotype H, has a hybrid-like structure with regions of similarity to the structures of serotypes A and F and is neutralized with serotype A antitoxin. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 213, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellett, S.; Tepp, W.H.; Bradshaw, M.; Kalb, S.R.; Dykes, J.K.; Lin, G.; Nawrocki, E.M.; Pier, C.L.; Barr, J.R.; Maslanka, S.E.; et al. Purification and characterization of botulinum neurotoxin FA from a genetically modified Clostridium botulinum strain. mSphere 2016, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Barash, J.R.; Lou, J.; Conrad, F.; Marks, J.D.; Arnon, S.S. Immunological characterization and neutralizing ability of monoclonal antibodies directed against botulinum neurotoxin type H. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 213, 1606–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Escalona, N.; Thirunavukkarasu, N.; Singh, A.; Toro, M.; Brown, E.W.; Zink, D.; Rummel, A.; Sharma, S.K. Draft genome sequence of bivalent Clostridium botulinum strain IBCA10–7060, encoding botulinum neurotoxin B and a new FA mosaic type. Genome Announc. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalb, S.R.; Baudys, J.; Webb, R.P.; Wright, P.; Smith, T.J.; Smith, L.A.; Fernandez, R.; Raphael, B.H.; Maslanka, S.E.; Pirkle, J.L.; et al. Discovery of a novel enzymatic cleavage site for botulinum neurotoxin F5. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasaki, S.; Baumeister, A.; Binz, T.; Blasi, J.; Link, E.; Cornille, F.; Roques, B.; Fykse, E.M.; Sudhof, T.C.; Jahn, R.; et al. Cleavage of members of the synaptobrevin/vamp family by types D and F botulinal neurotoxins and tetanus toxin. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 12764–12772. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yao, G.; Zhang, S.; Mahrhold, S.; Lam, K.H.; Stern, D.; Bagramyan, K.; Perry, K.; Kalkum, M.; Rummel, A.; Dong, M.; et al. N-linked glycosylation of SV2 is required for binding and uptake of botulinum neurotoxin A. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016, 23, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Berntsson, R.P.; Tepp, W.H.; Pitkin, R.M.; Johnson, E.A.; Stenmark, P.; Dong, M. Botulinum neurotoxin D-C uses synaptotagmin I and II as receptors, and human synaptotagmin II is not an effective receptor for type B, D-C and G toxins. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 3233–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montecucco, C. How do tetanus and botulinum toxins bind to neuronal membranes. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1986, 11, 314–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kull, S.; Schulz, K.M.; Weisemann, J.; Kirchner, S.; Schreiber, T.; Bollenbach, A.; Dabrowski, P.W.; Nitsche, A.; Kalb, S.R.; Dorner, M.B.; et al. Isolation and functional characterization of the novel Clostridium botulinum neurotoxin A8 subtype. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, X.; Gouet, P. Deciphering key features in protein structures with the new endscript server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W320–W324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievers, F.; Wilm, A.; Dineen, D.; Gibson, T.J.; Karplus, K.; Li, W.; Lopez, R.; McWilliam, H.; Remmert, M.; Soding, J.; et al. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using clustal omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rummel, A.; Eichner, T.; Weil, T.; Karnath, T.; Gutcaits, A.; Mahrhold, S.; Sandhoff, K.; Proia, R.L.; Acharya, K.R.; Bigalke, H.; et al. Identification of the protein receptor binding site of botulinum neurotoxins B and G proves the double-receptor concept. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strotmeier, J.; Mahrhold, S.; Krez, N.; Janzen, C.; Lou, J.; Marks, J.D.; Binz, T.; Rummel, A. Identification of the synaptic vesicle glycoprotein 2 receptor binding site in botulinum neurotoxin A. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rummel, A. Two feet on the membrane: Uptake of clostridial neurotoxins. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, R.M.; Frey, D.; Hilbert, M.; Kevenaar, J.T.; Wieser, M.M.; Stirnimann, C.U.; McMillan, D.; Ceska, T.; Lebon, F.; Jaussi, R.; et al. Structural basis for recognition of synaptic vesicle protein 2C by botulinum neurotoxin A. Nature 2014, 505, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janz, R.; Sudhof, T.C. SV2C is a synaptic vesicle protein with an unusually restricted localization: Anatomy of a synaptic vesicle protein family. Neuroscience 1999, 94, 1279–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardou, D.; Dassesse, D.; Cuvelier, L.; Deprez, T.; De Ryck, M.; Schiffmann, S.N. Distribution of SV2C mRNA and protein expression in the mouse brain with a particular emphasis on the basal ganglia system. Brain Res. 2011, 1367, 130–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crevecoeur, J.; Foerch, P.; Doupagne, M.; Thielen, C.; Vandenplas, C.; Moonen, G.; Deprez, M.; Rogister, B. Expression of SV2 isoforms during rodent brain development. BMC Neurosci. 2013, 14, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitemarsh, R.C.; Strathman, M.J.; Chase, L.G.; Stankewicz, C.; Tepp, W.H.; Johnson, E.A.; Pellett, S. Novel application of human neurons derived from induced pluripotent stem cells for highly sensitive botulinum neurotoxin detection. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 126, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, S.U.; Griffiss, J.M.; McKenzie, R.; Fuchs, E.J.; Jurao, R.A.; An, A.T.; Ahene, A.; Tomic, M.; Hendrix, C.W.; Zenilman, J.M. Safety and pharmacokinetics of XOMA 3AB, a novel mixture of three monoclonal antibodies against botulinum toxin A. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 5047–5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, R.; Forsyth, C.M.; LaPorte, S.L.; Geren, I.N.; Smith, L.A.; Marks, J.D. Fine and domain-level epitope mapping of botulinum neurotoxin type A neutralizing antibodies by yeast surface display. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 365, 196–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner, M.G.; Grate, J.W.; Tyler, A.; Ozanich, R.M.; Miller, K.D.; Lou, J.; Marks, J.D.; Bruckner-Lea, C.J. Quantum dot immunoassays in renewable surface column and 96-well plate formats for the fluorescence detection of botulinum neurotoxin using high-affinity antibodies. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 25, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Rodriguez, C.; Levy, R.; Arndt, J.W.; Forsyth, C.M.; Razai, A.; Lou, J.; Geren, I.; Stevens, R.C.; Marks, J.D. Molecular evolution of antibody cross-reactivity for two subtypes of type A botulinum neurotoxin. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battye, T.G.; Kontogiannis, L.; Johnson, O.; Powell, H.R.; Leslie, A.G. Imosflm: A new graphical interface for diffraction-image processing with mosflm. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2011, 67, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCoy, A.J.; Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W.; Adams, P.D.; Winn, M.D.; Storoni, L.C.; Read, R.J. Phaser crystallographic software. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2007, 40, 658–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emsley, P.; Cowtan, K. Coot: Model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2004, 60, 2126–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potterton, E.; Briggs, P.; Turkenburg, M.; Dodson, E. A graphical user interface to the CCP4 program suite. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2003, 59, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunger, A.T. Free R value: A novel statistical quantity for assessing the accuracy of crystal structures. Nature 1992, 355, 472–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, V.B.; Arendall, W.B., III; Headd, J.J.; Keedy, D.A.; Immormino, R.M.; Kapral, G.J.; Murray, L.W.; Richardson, J.S.; Richardson, D.C. Molprobity: All-atom structure validation for macromolecular crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).