The Cardiovascular and Neurotoxic Effects of the Venoms of Six Bony and Cartilaginous Fish Species
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of Crude Venoms on the Cardiovascular System
2.2. Effects of Crude Venoms on the Chick Biventer Cervicis Nerve-Muscle (CBCNM) Preparation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Crude Venom
4.1.1. Sample Collection and Storage
Chondrichthyes (Cartilaginous Fish)
Osteichthyes (Bony Fish)
4.1.2. Protein Extraction
4.2. Cardiovascular Assays
4.3. Neurotoxicity Assays
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Church, J.E.; Hodgson, W.C. The pharmacological activity of fish venoms. Toxicon 2002, 40, 1083–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.L.; Wheeler, W.C. Venom evolution widespread in fishes: A phylogenetic road map for the bioprospecting of piscine venoms. J. Hered. 2006, 97, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, L.; Stern, J.H.; Girard, M.G.; Davis, M.P. Evolution of venomous cartilaginous and ray-finned fishes. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2016, 56, 950–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, J. Diversity, phylogenetic distribution, and origins of venomous catfishes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2009, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, K.; Casewell, N.R.; Ali, S.A.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Vetter, I.; Dobson, J.S.; Cutmore, S.C.; Nouwens, A.; Lavergne, V.; Fry, B.G. A ray of venom: Combined proteomic and transcriptomic investigation of fish venom composition using barb tissue from the blue-spotted stingray (Neotrygon kuhlii). J. Proteom. 2014, 109, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, G.F. Venoms as a platform for human drugs: Translating toxins into therapeutics. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2011, 11, 1469–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helfman, G.S. The Diversity of Fishes: Biology, Evolution, and Ecology; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Casewell, N.R.; Wüster, W.; Vonk, F.J.; Harrison, R.A.; Fry, B.G. Complex cocktails: The evolutionary novelty of venoms. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2013, 28, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borondo, J.C.; Sanz, P.; Nogué, S.; Poncela, J.L.; Garrido, P.; Valverde, J.L. Fatal weeverfish sting. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2001, 20, 118–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Church, J.E.; Hodgson, W.C. Stonefish (Synanceia trachynis) antivenom: In vitro efficacy and clinical use. J. Toxicol. Toxin Rev. 2003, 22, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivan, G. Fish venom: pharmacological features and biological significance. Fish Fish 2009, 10, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J. A case of poisoning by the stonefish, Synanceja verrucosa. Copeia 1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, J.; Fenner, P.J.; Burnett, J.W.; Rifkin, J.F. Venomous and Poisonous Marine Animals: A Medical and Biological Handbook; UNSW Press: Kensington, NSW, Australia, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Andrew, M.E.; Cyril, F.R.; Santosh, P.; Kitmun, H.; Christine, A.O.; Kelly, L.W.; Michelle, A.D.; Wayne, C.H.; Jamie, S.; Peter, K.D.; Rodney, K.T.; James, C.W.; Sheena, M. Stonefish toxin defines an ancient branch of the perforin-like superfamily. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2015, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, J.E.; Hodgson, W.C. Dose-dependent cardiovascular and neuromuscular effects of stonefish (Synanceja trachynis) venom. Toxicon 2000, 38, 391–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadessy, F.J.; Chen, D.; Kini, R.M.; Chung, M.C.; Jeyaseelan, K.; Khoo, H.E.; Yuen, R. Stonustoxin is a novel lethal factor from stonefish (Synanceja horrida) venom. cDNA cloning and characterization. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 25575–25581. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khoo, H.; Yuen, R.; Poh, C.; Tan, C. Biological activities of Synanceja horrida (stonefish) venom. Natural Toxins 1992, 1, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoo, H.E. Bioactive proteins from stonefish venom. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2002, 29, 802–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, K.S.Y.; Gwee, M.E.; Yuen, R.; Gopalakrishnakone, P.; Khoo, H.E. Stonustoxin: A highly potent endothelium-dependent vasorelaxant in the rat. Toxicon 1993, 31, 1471–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poh, C.H.; Yuen, R.; Khoo, H.E.; Chung, M.; Gwee, M.; Gopalakrishnakone, P. Purification and partial characterization of stonustoxin (lethal factor) from Synanceja horrida venom. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Comp. Biochem. 1991, 99, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, G.S.; Junqueira-de-Azevedo, I.L.M.; Lopes-Ferreira, M.; Lorenzini, D.M.; Ho, P.L.; Moura-da-Silva, A.M. Transcriptome analysis of expressed sequence tags from the venom glands of the fish Thalassophryne nattereri. Biochimie 2006, 88, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, B.J.; Hodgson, W.C. Cardiovascular studies on venom from the soldierfish (Gymnapistes marmoratus). Toxicon 1998, 36, 973–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, P.R. Venom of the stonefish Synanceja verrucosa. Science 1959, 129, 2272–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, P.R.; Taylor, P.B. Venom of the lionfish Pterois volitans. Am. J. Physiol. 1959, 197, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Auddy, B.; Alam, M.I.; Gomes, A. Pharmacological actions of the venom of the Indian catfish (Plotosus canius Hamilton). Indian J. Med. Res. 1994, 99, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carlson, R.W.; Schaeffer, R.C.; Whigham, H.; Weil, M.H.; Russell, F.E. Some pharmacological properties of the venom of the scorpionfish Scorpaena guttata—II. Toxicon 1973, 11, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, J.E.; Hodgson, W.C. Adrenergic and cholinergic activity contributes to the cardiovascular effects of lionfish (Pterois volitans) venom. Toxicon 2002, 40, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, R.W.; Schaeffer, R.C.; La Grange, R.G.; Roberts, C.M.; Russell, F.E. Some pharmacological properties of the venom of the scorpionfish Scorpaena guttata—I. Toxicon 1971, 9, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.J. Pharmacology of South American freshwater stingray venom (Potamotrygon motoro). Trans. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1972, 34, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, B.J.; Hodgson, W.C.; Sutherland, S.K. Evidence for adrenergic and tachykinin activity in venom of the stonefish (Synanceja trachynis). Toxicon 1996, 34, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, P.R. Pharmacological and chemical studies of the venom of the stonefish (genus Synanceja) and other scorpion fishes. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1960, 90, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, C.M.; Isbister, G.K.; Hodgson, W.C. Classic toxin review: Alpha neurotoxins. Toxicon 2013, 66, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhuri, D.; Karmakar, S.; Dasgupta, S.C.; Nagchaudhuri, A.K.; Gomes, A. Pharmacological studies on the venomous spotted butterfish (Scatophagus argus Linn) sting extract on experimental animals. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2004, 42, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chaisakul, J.; Isbister, G.K.; O’Leary, M.A.; Parkington, H.C.; Smith, A.I.; Hodgson, W.C.; Kuruppu, S. Prothrombin activator-like toxin appears to mediate cardiovascular collapse following envenoming by Pseudonaja textilis. Toxicon 2015, 102, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusmili, M.R.; Yee, T.T.; Mustafa, M.R.; Hodgson, W.C.; Othman, I. Isolation and characterization of a presynaptic neurotoxin P-elapitoxin-Bf1a from Malaysian Bungarus fasciatus venom. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 91, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A.; Kuruppu, S.; Othman, I.; Goode, R.J.; Hodgson, W.C.; Isbister, G.K. Neurotoxicity in Sri Lankan Russell’s viper (Daboia russelii) envenoming is primarily due to U1-viperitoxin-Dr1a, a pre-synaptic neurotoxin. Neurotox. Res. 2017, 31, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
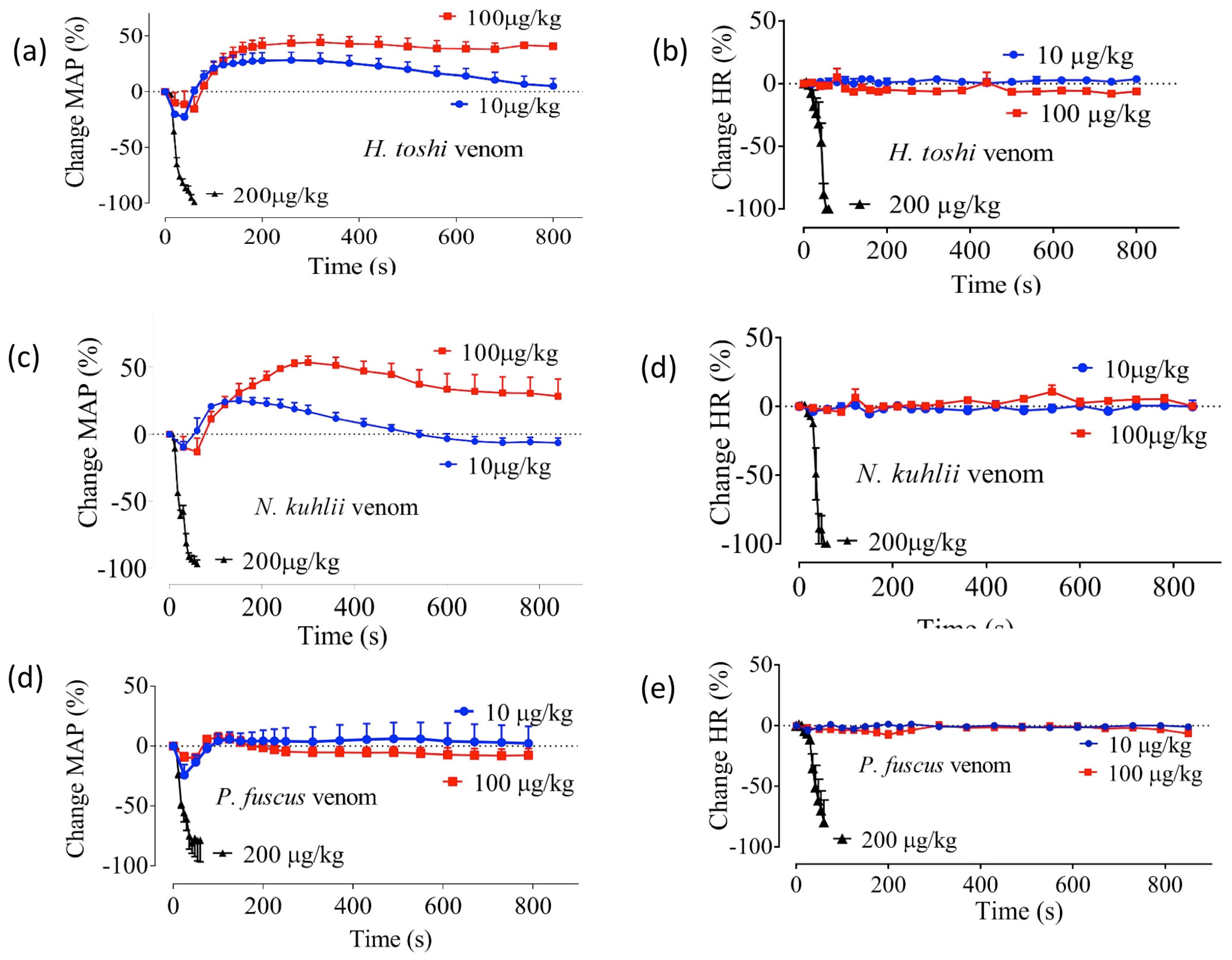
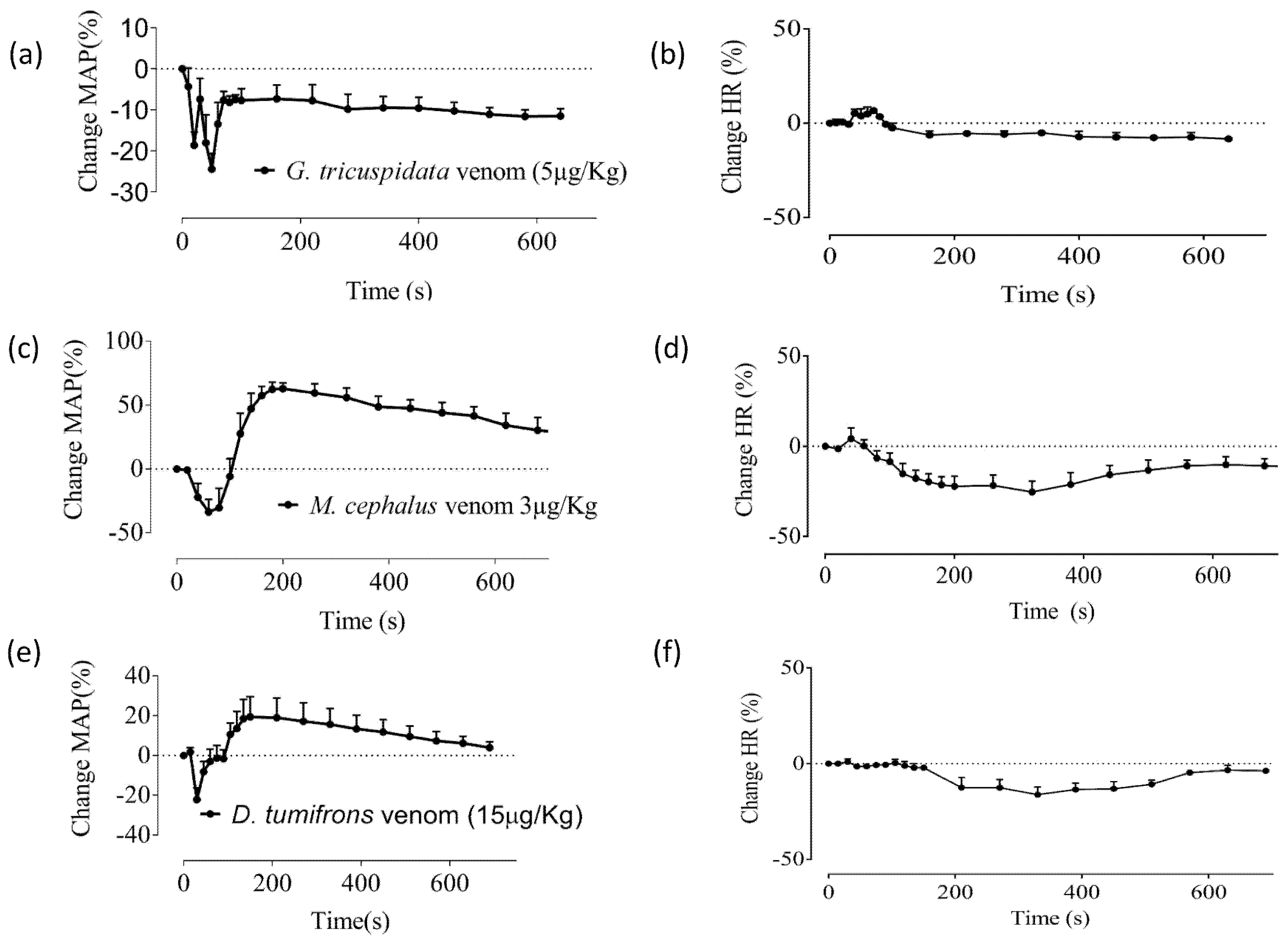
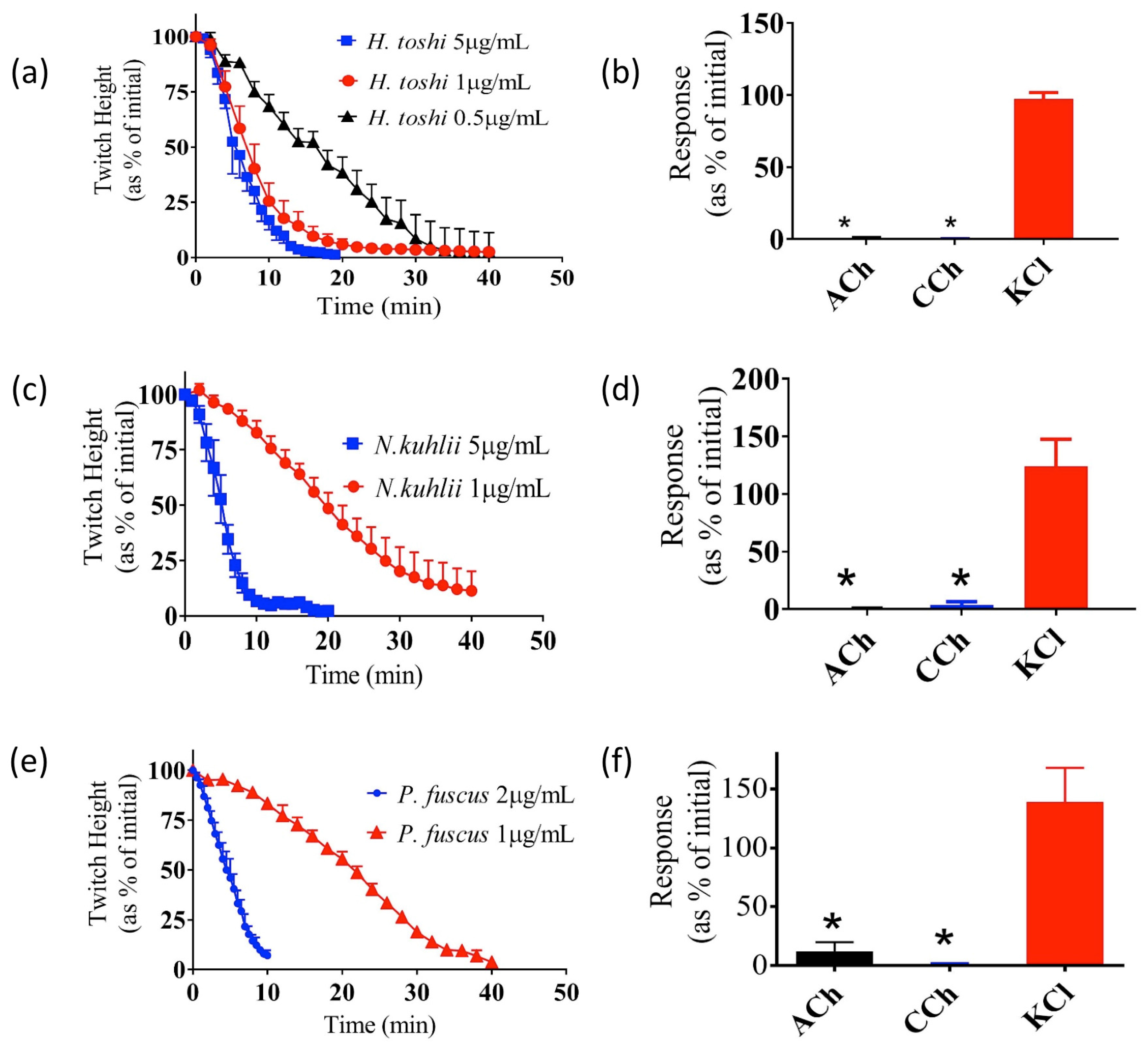
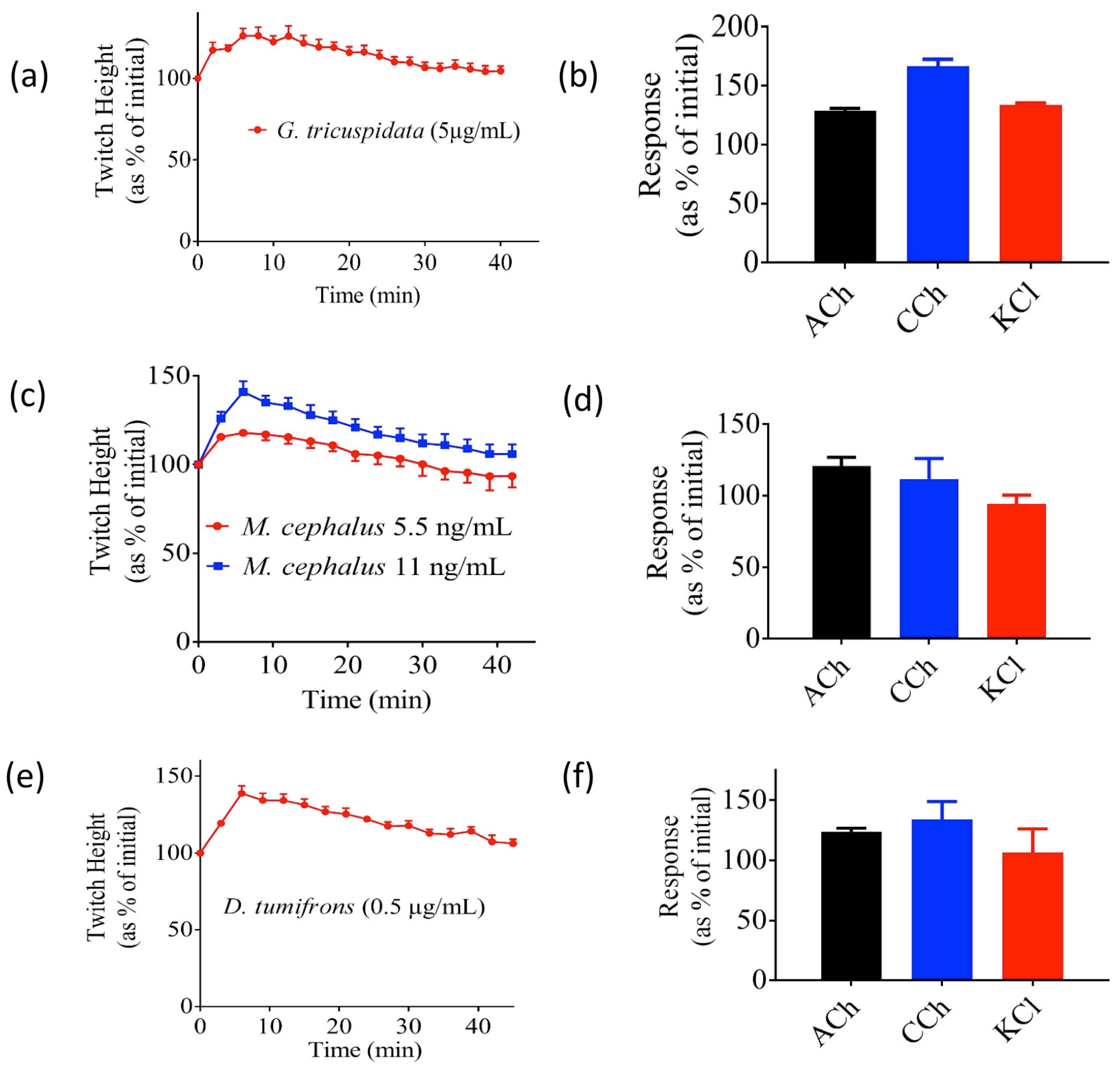
| Species | t50 (min) |
|---|---|
| N. kuhlii | 19 ± 0.3 |
| H. toshi | 7 ± 0.1 * |
| P. fuscus | 22 ± 0.2 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, H.; Baumann, K.; Casewell, N.R.; Ali, S.A.; Dobson, J.; Koludarov, I.; Debono, J.; Cutmore, S.C.; Rajapakse, N.W.; Jackson, T.N.W.; et al. The Cardiovascular and Neurotoxic Effects of the Venoms of Six Bony and Cartilaginous Fish Species. Toxins 2017, 9, 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9020067
Han H, Baumann K, Casewell NR, Ali SA, Dobson J, Koludarov I, Debono J, Cutmore SC, Rajapakse NW, Jackson TNW, et al. The Cardiovascular and Neurotoxic Effects of the Venoms of Six Bony and Cartilaginous Fish Species. Toxins. 2017; 9(2):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9020067
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Han, Kate Baumann, Nicholas R. Casewell, Syed A. Ali, James Dobson, Ivan Koludarov, Jordan Debono, Scott C. Cutmore, Niwanthi W. Rajapakse, Timothy N. W. Jackson, and et al. 2017. "The Cardiovascular and Neurotoxic Effects of the Venoms of Six Bony and Cartilaginous Fish Species" Toxins 9, no. 2: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9020067
APA StyleHan, H., Baumann, K., Casewell, N. R., Ali, S. A., Dobson, J., Koludarov, I., Debono, J., Cutmore, S. C., Rajapakse, N. W., Jackson, T. N. W., Jones, R., Hodgson, W. C., Fry, B. G., & Kuruppu, S. (2017). The Cardiovascular and Neurotoxic Effects of the Venoms of Six Bony and Cartilaginous Fish Species. Toxins, 9(2), 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9020067






