Abstract
Aflatoxins are highly carcinogenic, teratogenetic, and morbigenous secondary metabolites of Aspergillus flavus and A. parasiticus that can contaminate multiple staple foods, such as peanut, maize, and tree nuts. In this study, Zygosaccharomyces rouxii was screened out and identified from fermented soy paste—one kind of traditional Chinese food—to detoxify aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) by aerobic solid state fermentation in peanut meal. The optimal degradation condition was chosen from single factor experiment, and the most effective detoxification rate was about 97%. As for liquid fermentation, we tested the binding ability of Z. rouxii, and the highest binding rate reached was 74.3% (nonviable cells of Z. rouxii) in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Moreover, the biotransformation of AFB1 through fermentation of Z. rouxii in peanut meal was further verified by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry (LC/MS). According to TIC scan, after fermentation by Z. rouxii, the AFB1 in peanut meal was prominently degraded to the lowering peaks of AFB1. Additionally, m/s statistics demonstrated that AFB1 may be degraded to some new products whose structural properties may be different from AFB1, or the degradation products may be dissolved in the aqueous phase rather than the organic phase. As far as we know, this is the first report indicating that the safe strain of Z. rouxii has the ability to detoxify AFB1.
1. Introduction
Aflatoxins—highly morbigenous secondary metabolites mostly generated by Aspergillus flavus and A. parasiticus—contaminate multiple staple foods, such as peanut, maize, and tree nuts, and cause a great loss to the economy and public health [1,2]. More than 20 types of aflatoxins have been found, and the most known and important ones are aflatoxin B1 (AFB1), aflatoxin B2 (AFB2), aflatoxin G1 (AFG1) and aflatoxin G2 (AFG2) [3]. AFB1 is the most poisonous one, and is associated with liver cancer, dysfunction of the immune system, and protein deficiency syndromes of humans and animals [4]. The key carcinogenic site of AFB1 is the double bond of terminal furan rings, and the main carcinogenic mechanism is to inhibit the synthesis of RNA [5]. So, it is imperative to reduce the concentration of aflatoxins in foods.
A series of strategies have been recommended for the management of aflatoxins in foods. Physical, chemical, and biological methods should comply with the following principles: (1) aflatoxins should be transformed to innocuous products; (2) foods or feeds should retain their nutritional value, and the material properties should not be changed enormously; and (3) it should be highly efficient [6]. So far, many physical and chemical methods had been used to eliminate aflatoxins, including treatment with gamma rays, ultraviolet (UV) light, heat, calcium hydroxide, hydrogen peroxide, chlorine gas, and so on [7,8,9,10,11]. However, most physical and chemical methods have limitations, such as losses of nutritional value and high cost [8,9,10]. Therefore, biological controls provide an eligible, attractive, and safe method to remove aflatoxins in foods [12,13].
Traditional Chinese fermented foods have existed for thousands of years and have been consumed by generations of Chinese people, and were conventionally fermented by natural microorganisms. Many studies have proven the safety of traditional Chinese fermented foods [14,15]. Traditional Chinese fermented foods are reservoirs of microorganisms, such as bacteria, yeasts, and moulds [16], but the microbial distribution and functions need to be further studied. For example, some new strains isolated from traditional Chinese fermented pork had an excellent capacity for nitrite-reduction, and one strain isolated from fermented dairy food could inhibit vascular tension and hypertension [17,18]. For this reason, the idea of screening out strains for the removal of fungal toxins from traditional Chinese fermented foods was extremely feasible [19,20].
Earlier, we combined heat treatment and anaerobic solid state fermentation of Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. Bulgaricus to detoxify aflatoxins in peanut meal [21]. Saccharomyces cerevisiae is the most well-known species of yeast, and has been studied to evaluate their ability to remove aflatoxins from liquid media [22]. The ability of Bacillus megaterium to significantly inhibit the growth of A. flavus and the biosynthesis of AFB1 was previously identified in our lab [23]. We hypothesized that these two strains may also remove aflatoxins in solid state fermentation. In this study, we successfully screened out one detoxification strain (Z. rouxii), and designed a single factor experiment to optimize the degradation conditions. The identification of degradation products of AFB1 by Z. rouxii was also performed by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry (LC/MS).
2. Results
2.1. Screening Strains for the Detoxification of AFB1
Four yeasts and moulds were isolated from traditional Chinese foods, and the effect of different strains on the detoxification of AFB1 is presented in Table 1. AFB1 residual rates were significantly different in different strains (p < 0.01). The AFB1 residual rate of untreated sample was 100%, and the concentration of residual AFB1 was 115 μg/kg. After aerobic solid state fermentation, the residual rate of Strain B, Strain C, Strain D, S. cerevisiae, and B. megaterium groups had no conspicuous decrease. However, the AFB1 residual rate of Strain A and S. thermophilus groups was 16.18% and 17.63%, respectively, significantly lower than that of other groups (p < 0.01). Therefore, Strain A was selected for further identification and study.

Table 1.
Effect of different strains on aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) detoxification in peanut meal by solid state fermentation.
2.2. Identification of Strain A
Firstly, the culture of Strain A was checked for purity and was given preliminary identification on the basis of their cell and colony morphologies and biochemical profiles. The cell of Strain A was round, and the diameter was 5 μm. The colony morphologies were milky white, smooth, moist, and shiny.
Secondly, the 26S rDNA gene of Strain A was amplified and sequenced. The resulting sequence (582 bp) showed that it had 100% similarity with 26S rRNA (JQ689016) of Z. rouxii strain NRRL Y-229. This result confirmed that Strain A was a strain of Z. rouxii.
2.3. Effect of the Heat Temperature and Heat Time on AFB1 Detoxification
The effect of heating temperature on AFB1 decontamination is shown in Figure 1a. Ten grams of peanut meal was heated to 40, 60, 80, 100, or 110 °C for 10 min, and was then fermented by 10 mL cells liquid of Z. rouxii (approx. 1.0 × 109 CFU/mL). The residual rates of AFB1 were 61.08%, 62.46%, and 49.63% after the peanut meal was heated at 80 °C, 100 °C, and 110 °C for 10 min. Increasing the heating temperature decreased the AFB1 content in peanut meal. After fermentation, the remaining AFB1 was decreased. The residual rates were 32.73%, 20.85%, 16.18%, 5.13%, and 5.10%, respectively after aerobic solid state fermentation by Z. rouxii. Above 100 °C, the reduction in AFB1 did not increase, so 100 °C was chosen as the optimal temperature in the experiment.
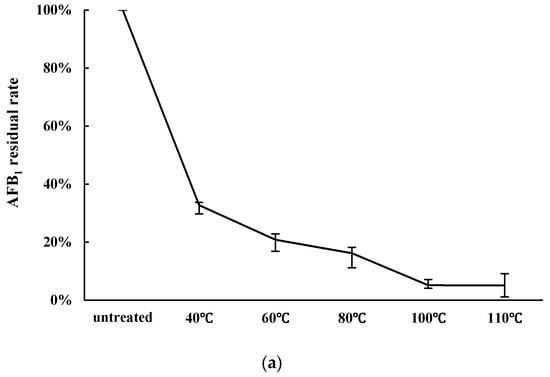
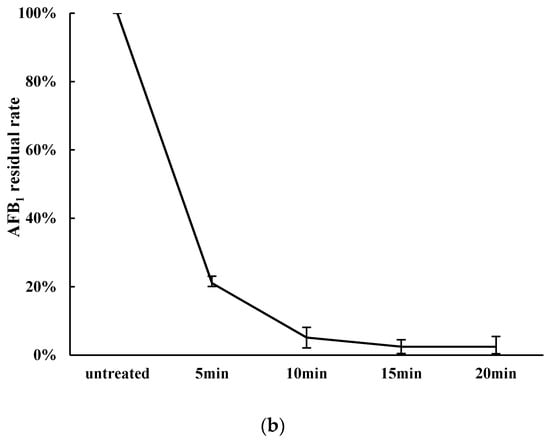
Figure 1.
The effect of heat temperature and heating time on AFB1 detoxification by Zygosaccharomyces rouxii. (a) Influence of heating temperature on AFB1 detoxification. Peanut meal was fermented by 10 mL cell liquid after being heated for 10 min at pH 10; (b) Effect of heat time on AFB1 detoxification. Peanut meal was fermented by cell liquid after being heated at 100 °C at pH 10.
As shown in Figure 1b, heating time can also influence the detoxification of AFB1. Ten grams of peanut meal was heated at 100 °C for 5, 10, 15, or 20 min, and was then fermented by 10 mL cells liquid of Z. rouxii (approx. 1.0 × 109 CFU/mL). The residual rates were 21.06%, 5.13%, 2.48%, and 2.44%, respectively, after aerobic solid state fermentation by Z. rouxii in peanut meal. When the heating time was 15 min, the residual rate of AFB1 reduced by 2.48%. As presented in Figure 1, with increasing heat temperature and heat time, the overall trend of detoxification rate was significantly increased. Thus, 100 °C and 15 min were chosen as the optimal condition in the experiment.
2.4. Removal of AFB1 in Liquid Fermentation
The results showed that binding was the main effect of the removal of AFB1 in liquid fermentation (Figure 2). The amount of AFB1 bound by Z. rouxii and S. thermophilus was more than 50%. Specifically, the binding rates were 74.3% (nonviable cells of Z. rouxii), 51.4% (viable cells of Z. rouxii), 68.7% (nonviable cells of S. thermophilus), and 58.5% (viable cells of S. thermophilus), respectively. The binding effect was different between nonviable and viable cells. However, the supernatant of Z. rouxii and S. thermophilus could not lower the AFB1 concentration in the liquid, and this indicated that the cells of Z. rouxii and S. thermophilus could only remove aflatoxins by binding instead of degrading in liquid fermentation.
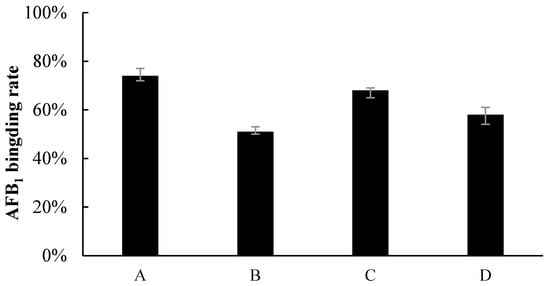
Figure 2.
Percentage of AFB1 binding by (A) nonviable Z. rouxii, (B) viable Z. rouxii, (C) nonviable S. thermophilus, and (D) viable S. thermophilus.
2.5. Verification of Detoxification of AFB1 by LC/MS
The LC/MS profile of AFB1 degradation can be distinctly observed from the positive ESI TIC scan of AFB1 (Figure 3). The AFB1 standard substance group (a) indicated that the retention time of AFB1 was about 33.6 min. Compared with the untreated group (b), the AFB1 peaks in the S. thermophilus fermentation group (c) and Z. rouxii fermentation group (d) were obviously lowered, meaning that the AFB1 was effectively detoxified by solid state fermentation, which is consistent with HPLC results.
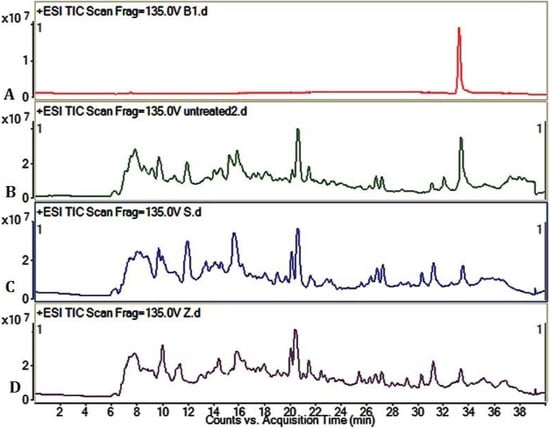
Figure 3.
Liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry (LC/MS) profile of AFB1 degradation. (A) +ESI TIC scan of AFB1 standard substance; (B) +ESI TIC scan of untreated group; (C) +ESI TIC scan of S. thermophilus fermentation group. Peanut meal was fermented by S. thermophilus for 3 days at 37 °C; (D) +ESI TIC scan of Z. rouxii fermentation group. Peanut meal was fermented by Z. rouxii for 3 days in 28 °C. AFB1 of all groups was adequately dissolved and extracted by methanol.
LC/MS spectrums of AFB1 showed the m/z 335, m/z 313 of AFB1 (Figure 4). As a comparison, the LC/MS results of the untreated group (b), S. thermophilus (c) group, and Z. rouxii (d) group revealed that AFB1 was detoxified and biotransformed to new substances whose structural properties were different from AFB1. This also demonstrated the complex compounds in peanut meal.
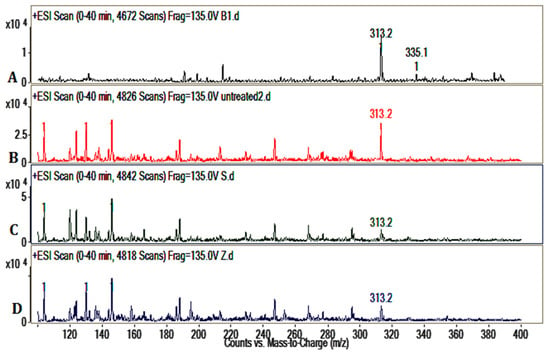
Figure 4.
Detection of AFB1 by electron-spray mass spectrometry. (A) AFB1 LC/MS spectrum; (B) LC/MS spectrum of untreated group; (C) LC/MS spectrum of S. thermophilus group; (D) LC/MS spectrum of Z. rouxii group.
3. Discussion
In this study, there was no obvious reduction of AFB1 by cell-free liquid of Z. rouxii and S. thermophilus. We also tested the binding effects of Z. rouxii and S. thermophilus (Figure 2); the results showed that the two strains indeed had the ability to bind aflatoxins, as previous reported [24]. In peanut meal, however, AFB1 interacted tightly with three major protein fractions of peanut in a certain way [25], so AFB1 could not be scrambled by the cells of Z. rouxii or S. thermophilus. In other words, the removal modes of AFB1 in liquid fermentation and solid state fermentation are different. Although alkalinity–heat treatment could remove a certain amount of AFB1, when we combined alkalinity–heat and solid state fermentation of Z. rouxii or S. thermophilus, AFB1 could be almost completely removed. In Coomes’ report, in the process of alkalinity–heat treatment, humidity, alkalinity, and high temperature could hydrolyze the lactone ring of AFB1 to form o-coumaric acid, the characteristic bond became more active, and AFB1 became more easily degraded [25]. Studies reported that AFB1-degrading enzymes play an essential part in feed fermentation [26]; lactic acid bacteria and yeast metabolism could play important roles. Most of AFB1 was transformed into a new fluorescing compound corresponding to aflatoxin B2a in acidogenous yoghurt [27]. Coincidentally, AFB1 was reduced during the fermentation of alcoholic beverages, and the degradation compound was also AFB2a [28], which may be influenced by yeast fermentation. Therefore, we can further speculate that it is possible that the solid state fermentation of Z. rouxii and S. thermophilus have the possibility to biotransform AFB1 into harmless products. In the current study, we utilized LC/MS to analyze the feasible primary structure of degradation products. ESI TIC scan (Figure 3) and MS spectra (Figure 4) showed that the AFB1 peak of the untreated group was significantly higher than that of fermentation groups, but the figures did not reflect the presence of any new peaks. The TIC and LC/MS spectrums confirmed that AFB1 was degraded by Z. rouxii or S. thermophilus, which was also found by HPLC (Figure 1). AFB1 is most likely degraded to some new products whose structural properties were different from AFB1 [28,29]. Previous studies demonstrated that the unknown by-products dissolved in the aqueous phase rather than in the organic phase [1]; this may be the reason why we could not detect any degradation products in our study.
4. Conclusions
This study successfully screened out one strain of Z. rouxii that had the ability detoxify AFB1 with aerobic solid state fermentation in peanut meal. Through a single factor experiment of heating time and heating temperature, the optimal management condition of peanut meal was heating for 15 min at 100 °C, and the AFB1 residual rate was 2.48% after solid state fermentation by Z. rouxii. However, in liquid fermentation, cell-free liquid had no influence on AFB1 removal, and cells of Z. rouxii and S. thermophilus could indeed bind AFB1—especially nonviable cells of Z. rouxii. This means that AFB1 is removed by Z. rouxii through physical binding or biological degradation in liquid fermentation or in solid state fermentation, respectively. In addition, no degradation product was discovered from the LC/MS results. AFB1 may be degraded to some new products whose structural properties were different from AFB1, or they dissolved in the aqueous phase rather than in the organic phase.
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Detoxification of Aflatoxins by Solid State Fermentation
5.1.1. Screening Strains for Detoxification of AFB1
Traditional Chinese foods (fermented soy paste and yoghourt) are safe strain sources. A 1 g sample was put into a sterile tube, and 9 mL of sterile saline was added. After being fully shaken on a spiral device for 10 min, the liquid supernatant was diluted to 10−5, 10−6, 10−7, or 10−8 diluent, and then 20 μL diluent was spread onto the Yeast Extract Peptone Dextrose Medium (YEPD: 1% yeast extract, 2% peptone, 2% glucose, 2% agar). Finally, all samples were cultivated in an incubator at 30°C for 3 days. The colonies were singled out and inoculated to the YEPD agar. S. cerevisiae was purchased from Angel Company (Yicang, Hubei Province, China). S. thermophilus and B. megaterium were preserved in the School of Food Science and Engineering, Ocean University of China [19,28].
To test the AFB1 detoxification effect, S. cerevisiae, S. thermophilus, B. megaterium, and four strains from Chinese food (Table 1) were examined by solid state fermentation. Firstly, 10 g of peanut meal (Luhua Company, Laiyang, Shandong, China) and 10 mL deionized water (peanut meal:deionized water = 1:1, w:v) were placed in a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask and the pH was adjusted to 10 with NaOH solution, then heated for 10 min at 80 °C. Secondly, the pH of the peanut meal was adjusted to 7 with HCl solution, and 10 mL precultured cells solution (approx. 109 CFU/mL) was added in Erlenmeyer flask. Lastly, the peanut meal was fermented at 30 °C for 3 days. This experiment was repeated three times.
5.1.2. Identification of Strain A
The isolated strains were identified by morphological, physiological, and chemotaxonomic features of the organism, and were confirmed by 26S rRNA basal phylogenetic analysis. Total genomic DNA as a template for PCR amplification was extracted by a Fungal Genomic DNA Isolation Kit (Sangon Biotech, Shanghai, China). The primers used for amplifying targeted conserved regions of the 26S rDNA gene were 5′-GCATATCAATAAGCGGAGGAAAAG-3′, 5′-GGTCCGTGTTTCAAGACGG-3′. EX-Taq DAN polymerase was purchased from Omega Bio-tek Company (Norcross, GA, USA). PCR was performed in an Applied Biosystems 2720 Thermal Cycler. The amplified PCR products were sent to Sangon Biotech for sequencing. The resulting sequence were submitted to NCBI [30] to compare with the published 26S rDNA sequences available in Genbank.
5.1.3. Effect of the Heating Temperature and Heating Time on AFB1 Detoxification
Ten grams of peanut meal was heated at 40 °C, 60 °C, 80 °C, 100 °C, or 110 °C for 10 min, then inoculated with 10 mL precultured cells suspension (approx. 109 CFU/mL) and fermented for two days. Next, the effect of heating time was investigated. Ten grams of peanut meal was heated at 100 °C for 5 min, 10 min, 15 min, or 20 min. Later, 10 mL precultured cells suspension (approx. 109 CFU/mL) was inoculated in peanut meal. The residual content of AFB1 was determined by HPLC.
5.2. Removal of Aflatoxins by Cell and Cell-Free Liquid
To examine the ability to bind AFB1, 10 mL of precultured Z. rouxii or S. thermophilus suspension (approx. 109 CFU/mL) was divided into two groups; the first group was viable cells, while the second group was boiled at 115 °C for 20 min (dead cells). Cells were centrifugated to pie at 5000 × g for 5 min. Cells was resuspended in 20 mL phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), and then 4 μL AFB1 (1 mg/mL) was added and cultured at 30 °C for 24 h and 48 h. As control, 4 μL AFB1 (1 mg/mL) was also added to the 20 mL PBS (without cells) and cultured at the same conditions. The bound percentage was calculated adhering to the formula: 100 × (1 − (amount of AFB1 in the supernatant/amount of AFB1 in the PBS control)).
In addition, to verify whether the fermentation supernatant had an influence on the removal of AFB1, 20 mL cell-free liquid was also cultivated with 4 μL AFB1 (1 mg/mL) for 24 h and 48 h at 30 °C. For comparison, YPD and MRS control groups were treated in the same way. The AFB1 concentrations of all samples were analyzed by HPLC.
5.3. Extraction of Residual AFB1 and HPLC Analysis
The fermented peanut meal (3 g) and NaCl (0.6 g) were weighed into a centrifuge tube. After adding 10 mL methanol/water (60:40, v/v) and homogeneous mixing for 10 min, the samples were centrifuged at 5000 × g for 20 min at room temperature. Five milliliters of supernatant was diluted with 5 mL ultrapure water. Next, 5 mL of the diluted sample was extracted in immunoaffinity columns (Huaan Magnech BioTech Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) and then eluted with 1 mL of methanol at a flow rate of about 1 drop per second. Then, the eluent was used to pre-column derivatization before they were quantified by HPLC analysis. The eluent was evaporated under a gentle stream of nitrogen at 45 °C up to dryness condition, and then it was derivatized with 200 μL n-hexane and 100 μL trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) for 15 min. After being evaporated to dryness again, the eluent was redissolved in 200 μL water–acetonitrile (85:15, v/v).
AFB1 standard substances were purchased from Sigma Chemical (St. Louis, MO, USA). AFB1 was analyzed according to retention time in the HPLC system. The samples were separated by HPLC equipped with a ZORBAX Eclipse XDB-C18 column (4.6 × 150 mm, 5 µm, Agilent, Palo Alto, CA, USA) and a 470 fluorescent detector (G1321A, Agilent, USA) (λexc 360 nm; λem 440 nm) using a mobile phase solvent of 10% acetonitrile, 40% methanol, and 50% water. The flow rate was 0.8 mL·min−1 and the injection volume was 20 μL.
5.4. Verification of Detoxification of AFB1 by LC/MS
To verify that the AFB1 was detoxified by Z. rouxii and S. thermophilus, 8 μL AFB1 (1 mg/mL) was added to 200 g peanut meal, and then fermented for at 30 °C for 3 days by Z. rouxii and S. thermophilus after alkalinity–heat treatment. Next, 300 mL methanol was added and shaken adequately for 3 h to extract aflatoxins. Peanut meal was filtered out with gauze. The methanol was dried to dryness and was then redissolved by 2 mL methanol. Finally, 1 mL sample solutions were waited for detection. The degradation products of AFB1 were determined by Agilent 6410 Triple Quad LC/MS coupled to a Agilent 1200 series HPLC (Agilent, Palo Alto, CA, USA) system. LC separation was implemented with a ZORBAX Eclipse XDB-C18 column (4.6 × 150 mm, 5 µm, Agilent, USA). The gradient elution method of LC/MS was applied as follows: (1) firstly, the column was eluted with acetonitrile-0.1% formic acid (5:95, v/v); (2) then the column was eluted for 20 min until the concentration of acetonitrile reached 40%; (3) the gradient elution was switched to acetonitrile-0.1% formic acid (60:40, v/v) in 5 min, and it was developed at 100% acetonitrile in 5 min and kept for 5 min; (4) the eluted ratio turned to acetonitrile-0.1% formic acid (5:95, v/v) again in 2 min, and kept for 3 min. Mass spectra were acquired within the range of m/z 100–500 in a positive ESI Scan analysis (Qualitative Analysis Mass Hunter software, Agilent, Palo Alto, CA, USA). The run time was 40 min with the flow rate of 0.2 mL/min.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the research grant from Qingdao Municipal Science and Technology Project (16-6-2-39-nsh) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (31471657).
Author Contributions
G.Z., Q.K. and Y.L. conceived and designed the experiments; G.Z. and Y.C. performed the experiments; G.Z., Y.C., and Y.M. analyzed the data; G.Z. and Q.K. wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Salati, S.; D’Imporzano, G.; Panseri, S.; Pasquale, E.; Adani, F. Degradation of aflatoxin B1 during anaerobic digestion and its effect on process stability. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 94, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F. Global impacts of aflatoxin in maize: Trade and human health. World Mycotoxin. J. 2015, 8, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Zhang, F.; Liu, S.; Yu, C.; Guan, D.; Pan, C. Removal of aflatoxin B1 in edible plant oils by oscillating treatment with alkalinity electrolysed water. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 3118–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teniola, O.D.; Addo, P.A.; Brost, I.M.; Färber, P.; Jany, K.D.; Alberts, J.F.; van Zyl, W.H.; Steyn, P.S.; Holzapfel, W.H. Degradation of aflatoxin B(1) by cell–free extracts of Rhodococcus erythropolis and Mycobacterium fluoranthenivorans sp. nov. DSM44556T. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2005, 105, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denissenko, M.F.; Cahil, J.; Koudriakova, T.B.; Gerber, N.; Pfeifer, G.P. Quantitation and mapping of aflatoxin B1-induced DNA damage in genomic DNA using aflatoxin B1–8,9-epoxide and microsomal activation systems. Mutat. Res.-Fundam. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 1999, 425, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chulze, S.N. Strategies to reduce mycotoxin levels in maize during storage: A review. Food Addit. Contam. 2010, 27, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, J.; He, B.; Zhang, L.; Li, P.; Zhang, Q.; Ding, X.; Zhang, W. A structure identification and toxicity assessment of the degradation products of aflatoxin B1 in peanut oil under UV irradiation. Toxins 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Stefano, V.; Pitonzo, R.; Bartolotta, A.; D’Oca, M.C.; Fuochi, P. Effects of gamma-irradiation on the alfa-tocopherol and fatty acids content of raw unpeeled almond kernels (Prunus dulcis). LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 59, 572–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stefano, V.; Pitonzo, R.; Cicero, N.; D’Oca, M.C. Mycotoxin contamination of animal feeding stuff: Detoxification by gamma-irradiation and reduction of aflatoxins and ochratoxin A concentrations. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2014, 7, 2034–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rustom, I.Y.S. Aflatoxin in food and feed: Occurrence, legislation and inactivation by physical methods. Food Chem. 1997, 59, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velazhahan, R.; Vijayanandraj, S.; Vijayasamundeeswari, A.; Paranidharan, V.; Samiyappan, R.; Iwamoto, T.; Friebe, B.; Muthukrishnan, S. Detoxification of aflatoxins by seed extracts of the medicinal plant, Trachyspermum ammi (L.) Sprague ex Turrill–Structural analysis and biological toxicity of degradation product of aflatoxin G1. Food Control 2010, 21, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Zhao, L.; Ma, Q.; Li, X.; Shi, H.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, J.; Ji, C. Effects of Bacillus subtilis ANSB060 on growth performance, meat quality and aflatoxin residues in broilers fed moldy peanut meal naturally contaminated with aflatoxins. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 59, 748–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberts, J.F.; Engelbrecht, Y.; Steyn, P.S.; Holzapfel, W.H.; van Zyl, W.H. Biological degradation of aflatoxin B1 by Rhodococcus erythropolis cultures. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 109, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, G.; Shen, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chi, Y. Microbial safety and sensory quality of instant low-salt Chinese paocai. Food Control 2016, 59, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Han, Y.; Zhou, Z. Lactic acid bacteria in traditional fermented Chinese foods. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, E.B. Commercial bacterial starter cultures for fermented foods of the future. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2002, 78, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, J.; Zhou, T.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Chen, W.; Xiong, Y.L. Two efficient nitrite-reducing Lactobacillus strains isolated from traditional fermented pork (Nanx Wudl) as competitive starter cultures for Chinese fermented dry sausage. Meat Sci. 2016, 121, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, W.; Xue, J.; Yang, J.; Chen, X.; Shao, Y.; Kwok, L.; Bilige, M.; Mang, L.; Zhang, H. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory activity of Lactobacillus helveticus strains from traditional fermented dairy foods and antihypertensive effect of fermented milk of strain H9. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 6680–6692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Sun, X. Inhibition of non-toxigenic Aspergillus niger FS10 isolated from Chinese fermented soybean on growth and aflatoxin B1 production by Aspergillus flavus. Food Control 2013, 32, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Jin, H.; Lan, J.; Zhang, R.; Ren, H. Detoxification of zearalenone by three strains of lactobacillus plantarum from fermented food in vitro. Food Control 2015, 54, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Kong, Q.; Chi, C.; Shan, S.; Guan, B. Biotransformation of aflatoxin B1 and aflatoxin G1 in peanut meal by anaerobic solid fermentation of S. thermophilus and Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. Bulgaricus. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 211, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joannis-Cassan, C.; Tozlovanu, M.; Hadjeba-Medjdoub, K.; Ballet, N.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A. Binding of zearalenone, aflatoxin B1, and ochratoxin A by yeastbased products: A method for quantification of adsorption performance. J. Food Prot. 2015, 74, 1175–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Q.; Shan, S.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Yu, F. Biocontrol of Aspergillus flavus on peanut kernels by use of a strain of marine Bacillus megaterium. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 139, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peltonen, K.; El-Nezami, H.; Haskard, C.; Ahokas, J.; Salminen, S. Aflatoxin B1 binding by dairy strains of lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria. J. Dairy Sci. 2001, 84, 2152–21562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coomes, T.J.; Crowther, P.C.; Feuell, A.J.; Francis, B.J. Experimental detoxification of groundnut meals containing aflatoxin. Nature 1966, 209, 406–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzapfel, W.H. Appropriate starter culture technologies for small-scale fermentation in developing countries. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2002, 75, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megalla, S.E.; Hafez, A.H. Detoxification of aflatoxin B1 by acidogenous yoghurt. Mycopathologia 1982, 77, 89–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, T.; Nagatomi, Y.; Uyama, A.; Mochizuki, N. Degradation of Aflatoxin B1 during the Fermentation of Alcoholic Beverages. Toxins 2013, 5, 1219–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangare, L.; Zhao, Y.; Foll, Y.M.E.; Chang, J.; Li, J.; Selvaraj, J.N.; Xing, F.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. Aflatoxin B1 Degradation by a Pseudomonas Strain. Toxins 2014, 6, 3028–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCBI. Available online: http://www.nvbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 20 August 2016).
© 2017 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).