Selective Membrane Redistribution and Depletion of Gαq-Protein by Pasteurella multocida Toxin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
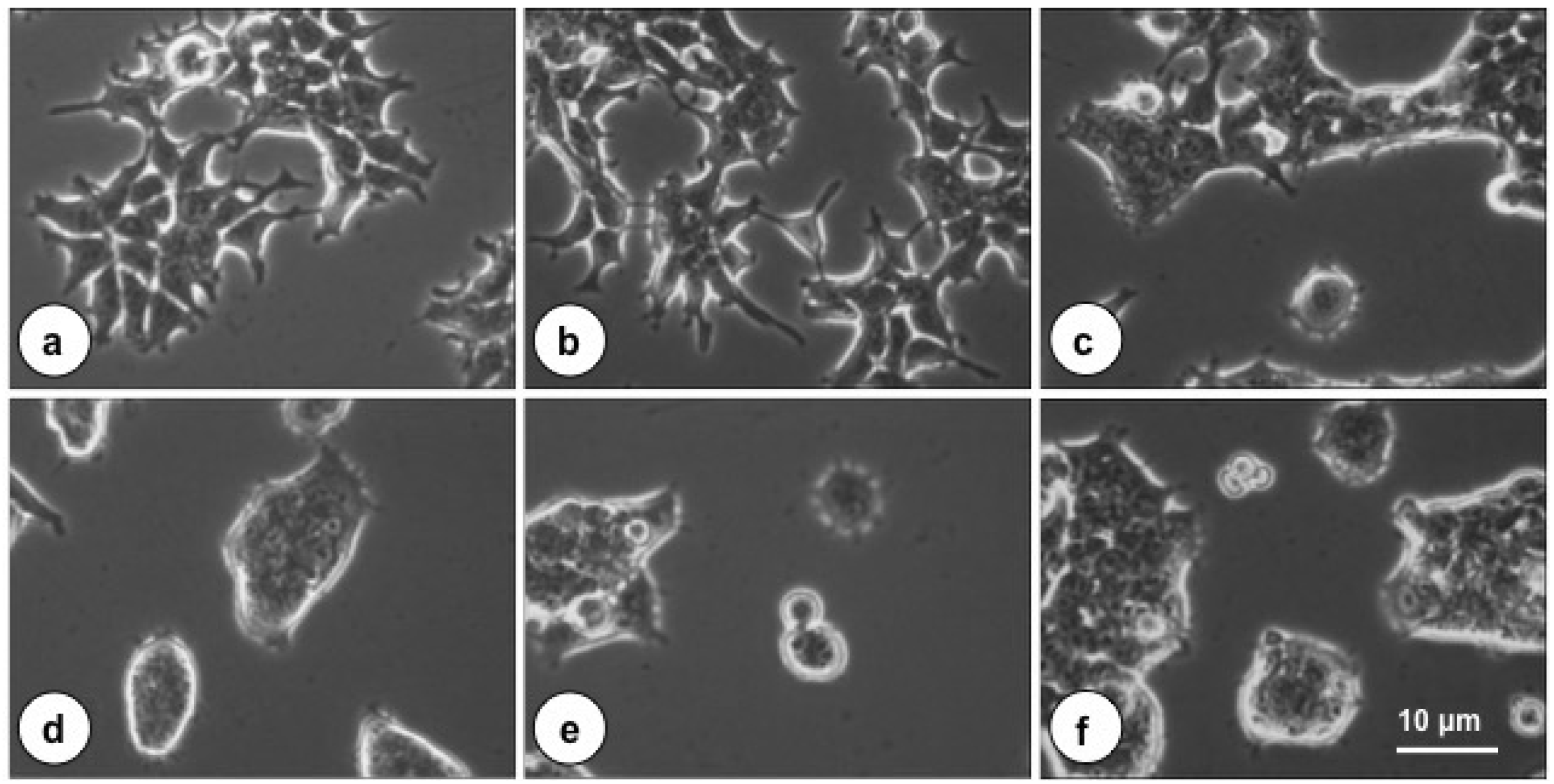
2.1. The Cytotoxic Effect of PMT on Cultured HEK-293T Cells
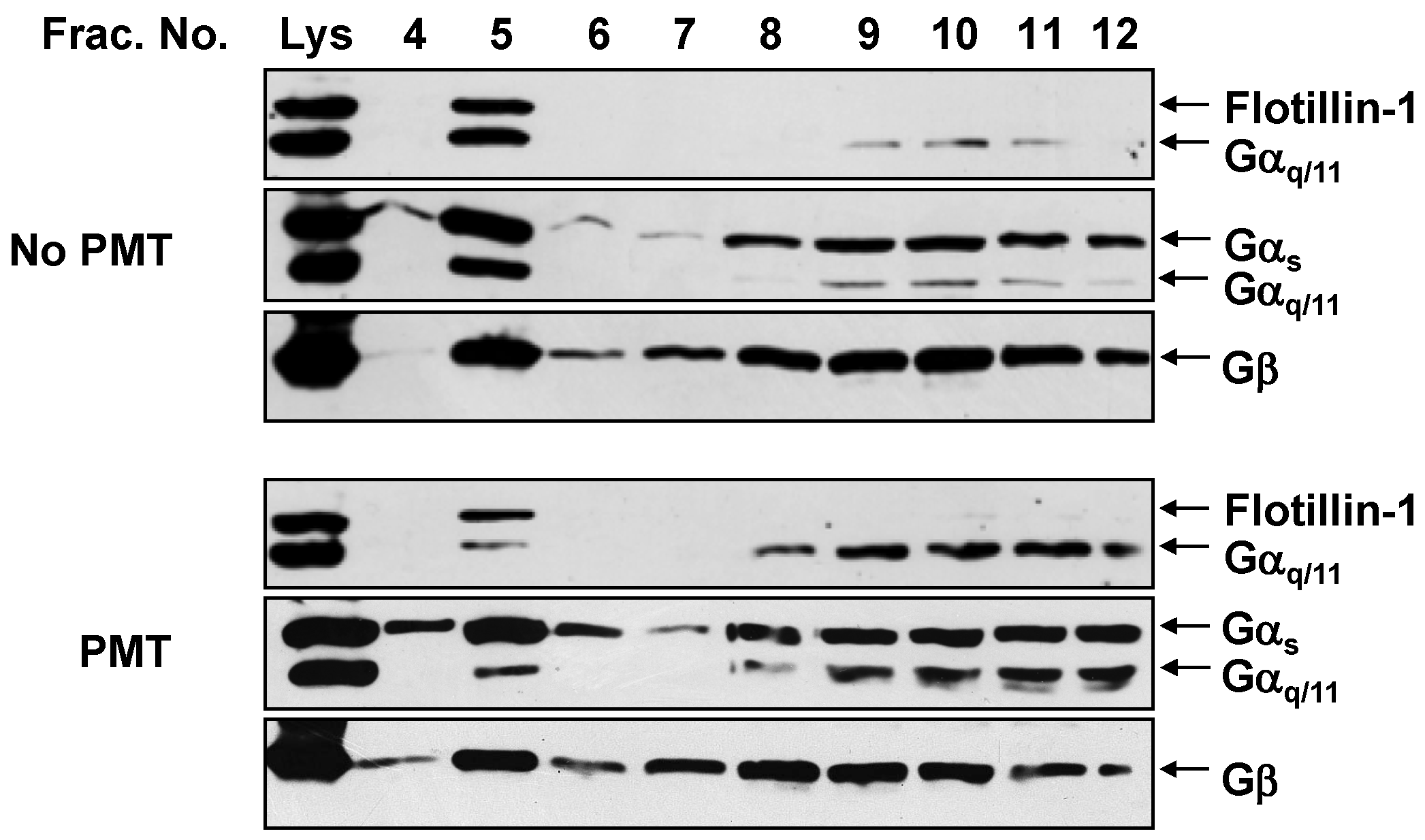
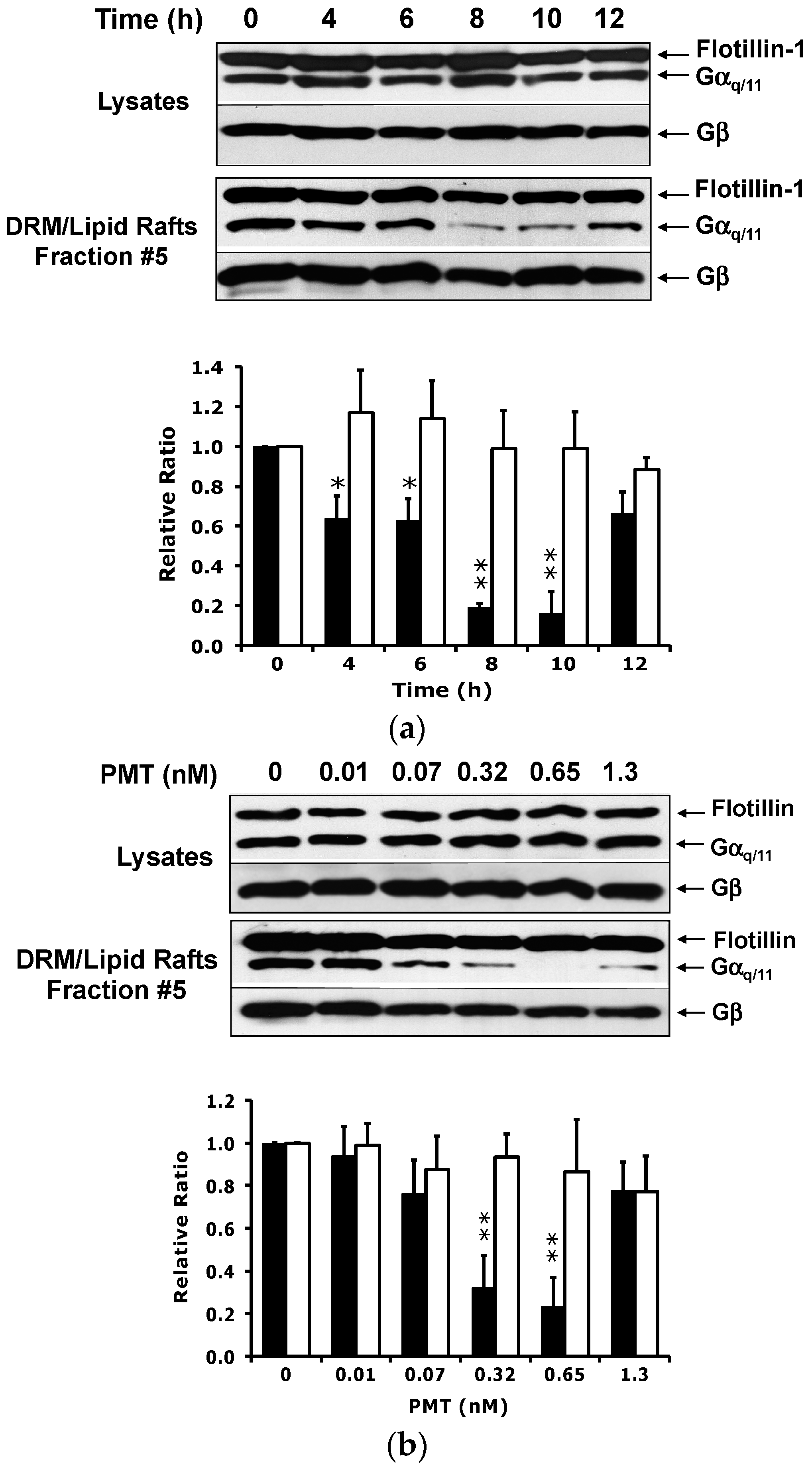
2.2. PMT Treatment Reduces Endogenous Gαq/11 Levels in Detergent Resistant Membranes (DRMs)
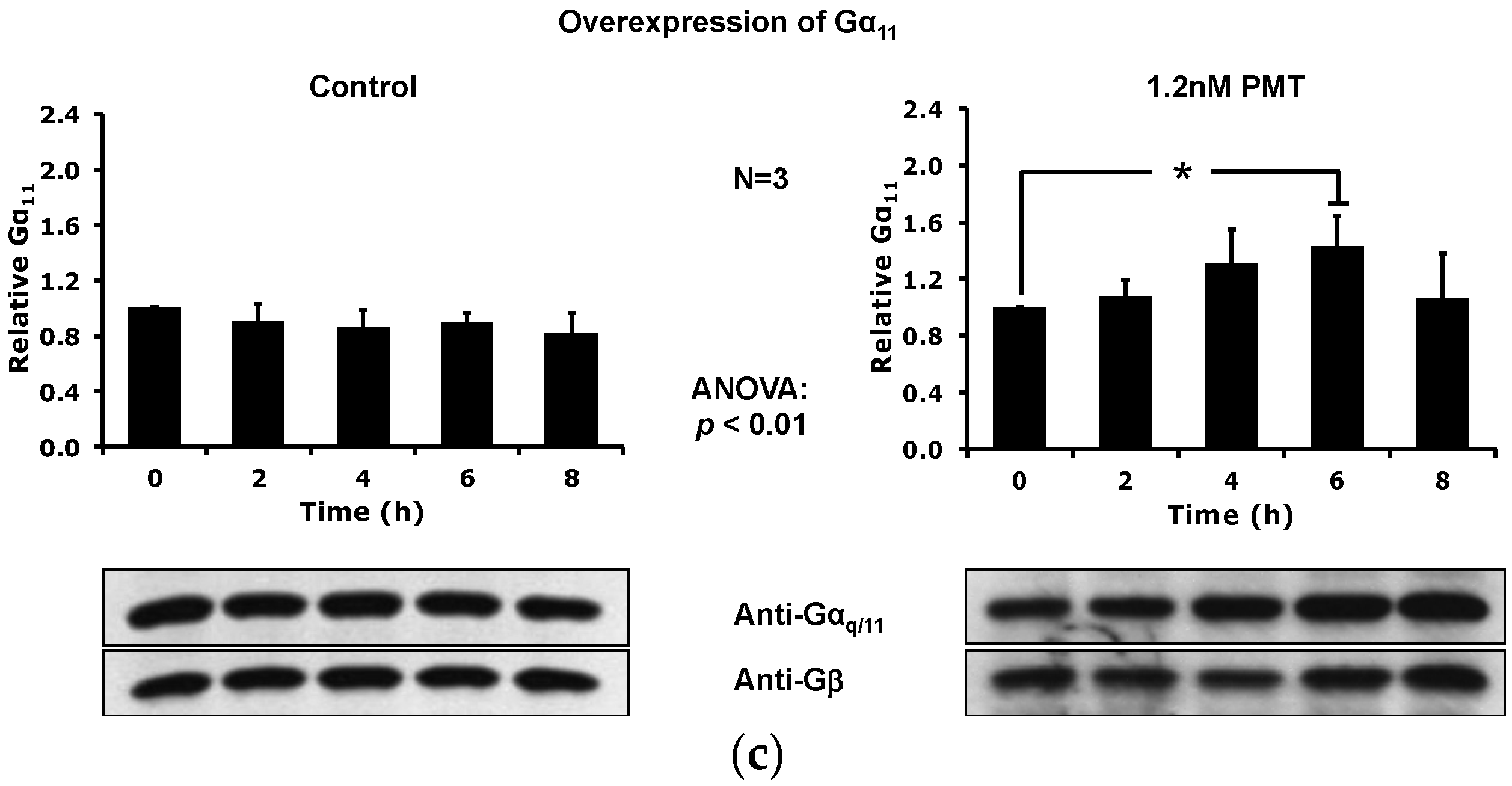
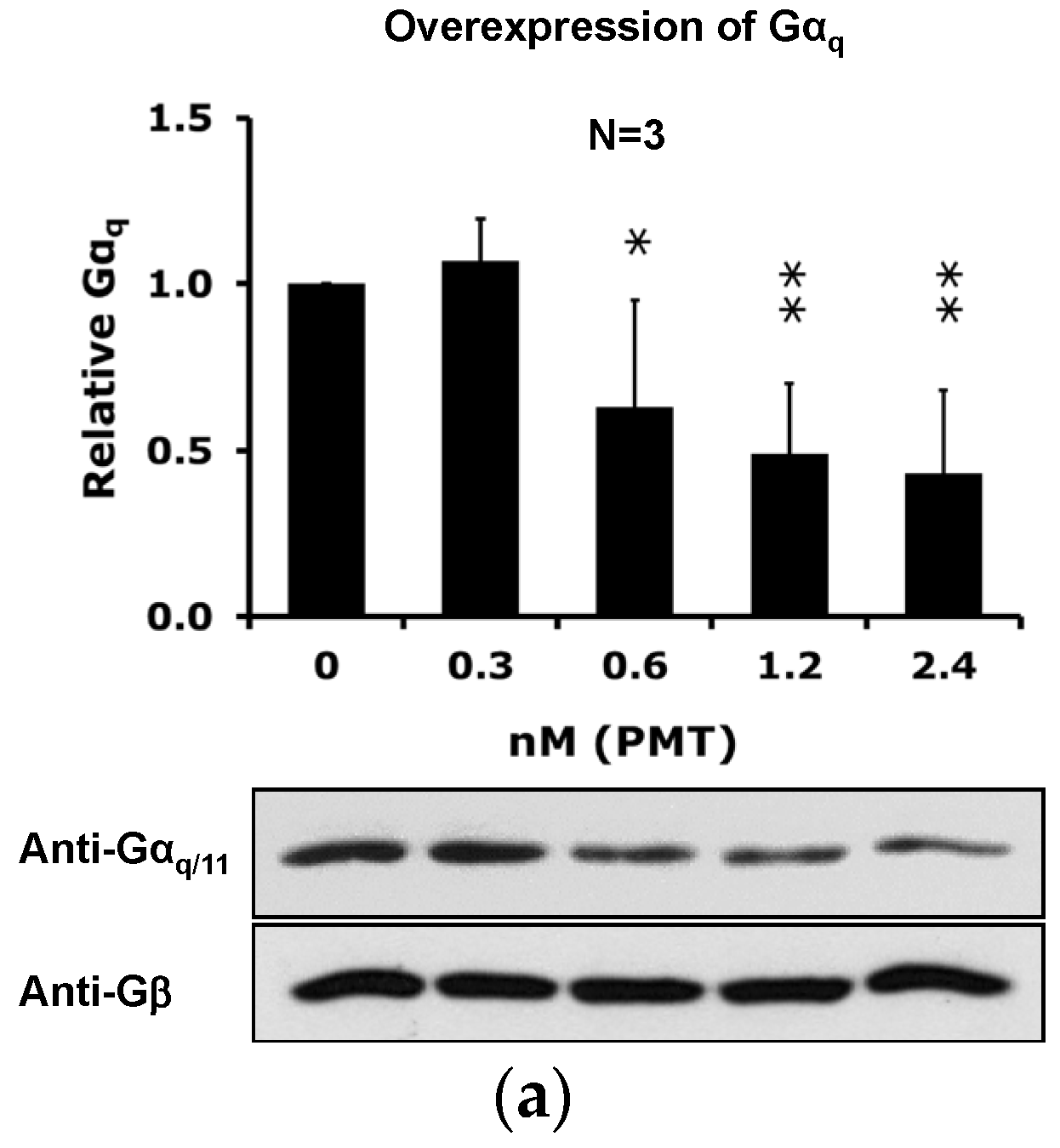
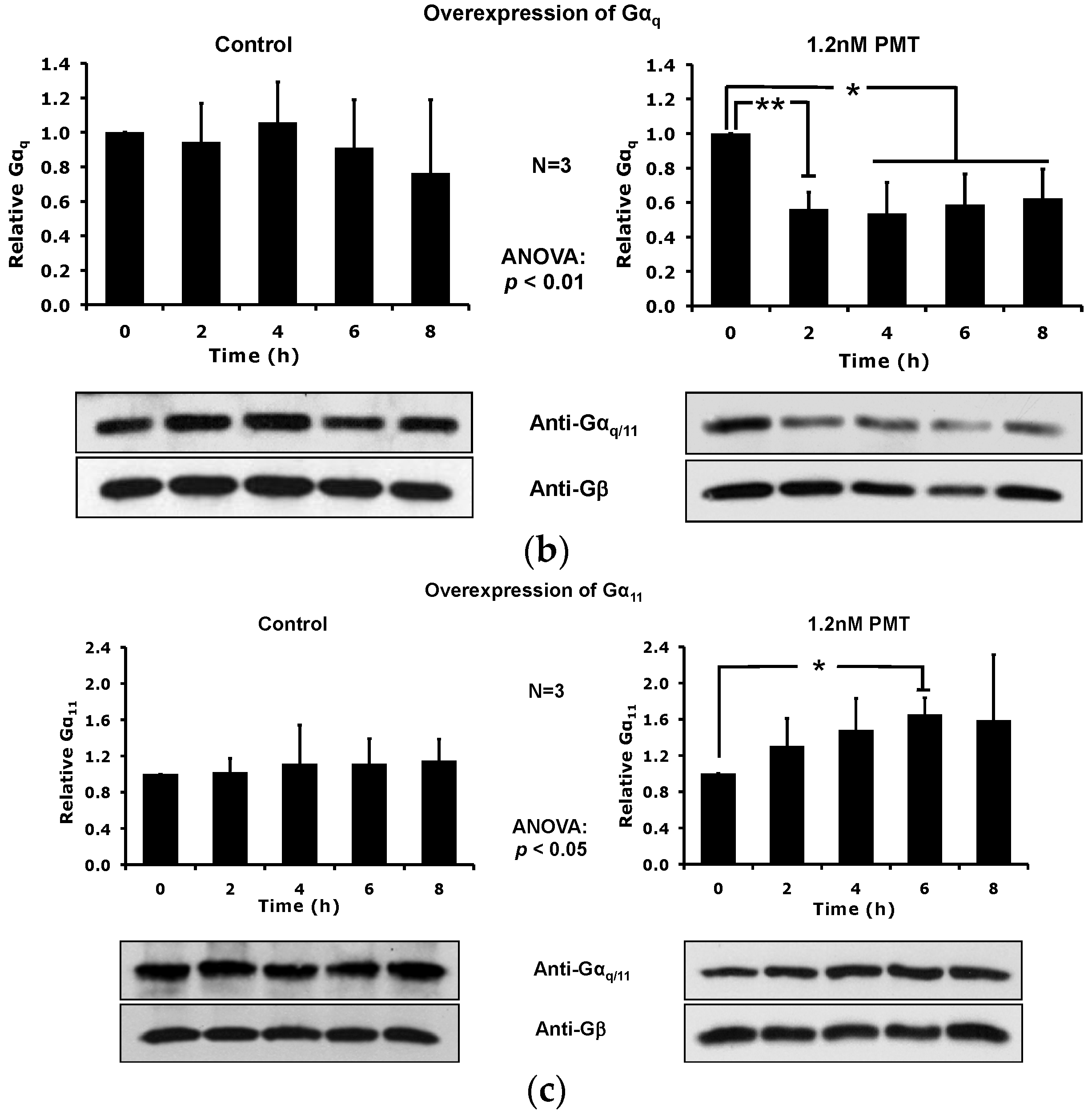
2.3. PMT Treatment Depletes Gαq, but Not Gα11, Protein Levels in DRMs and the Plasma Membrane
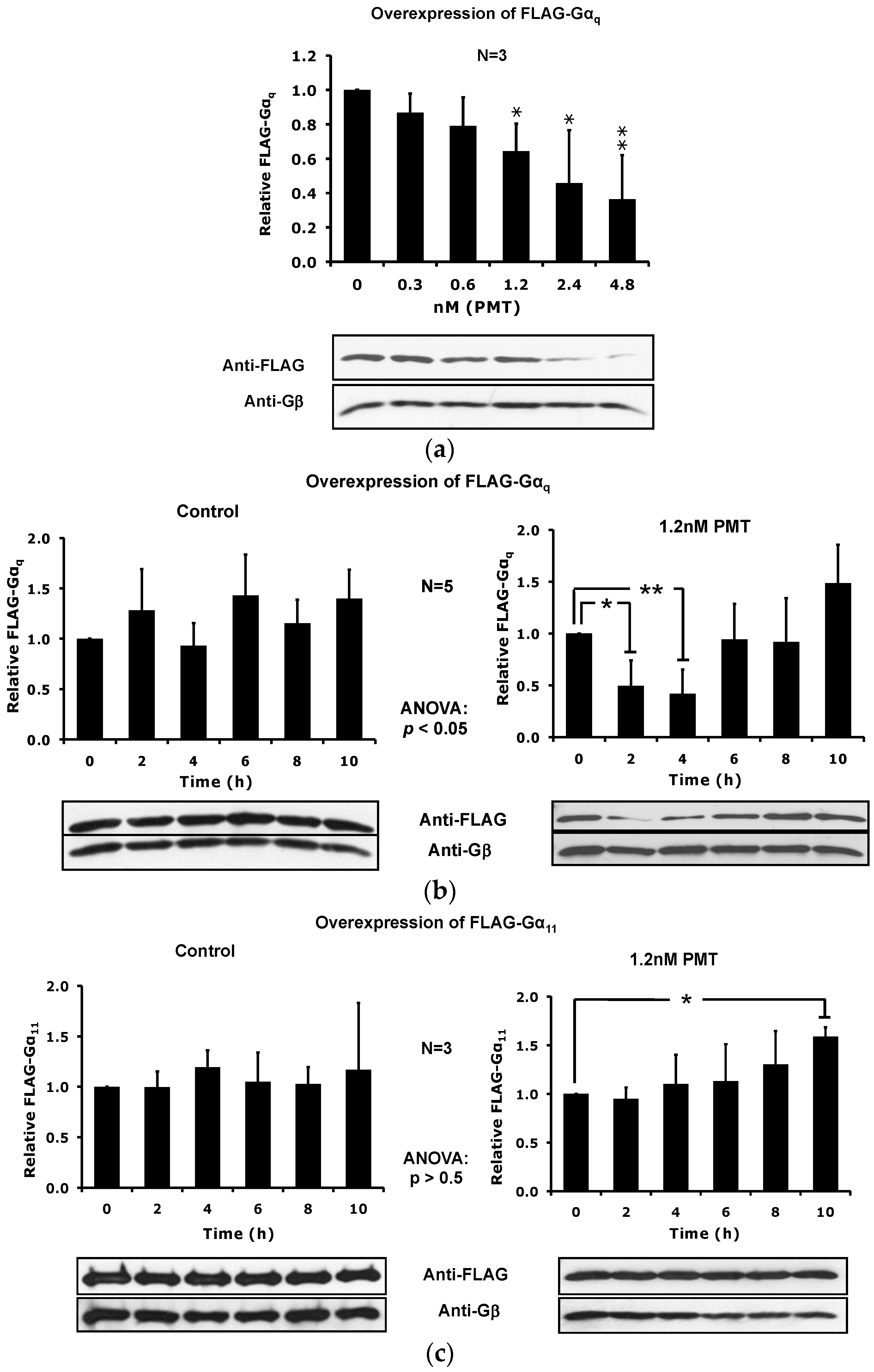
2.4. The Catalytic Activity of PMT Is Required for Membrane Depletion of Gαq
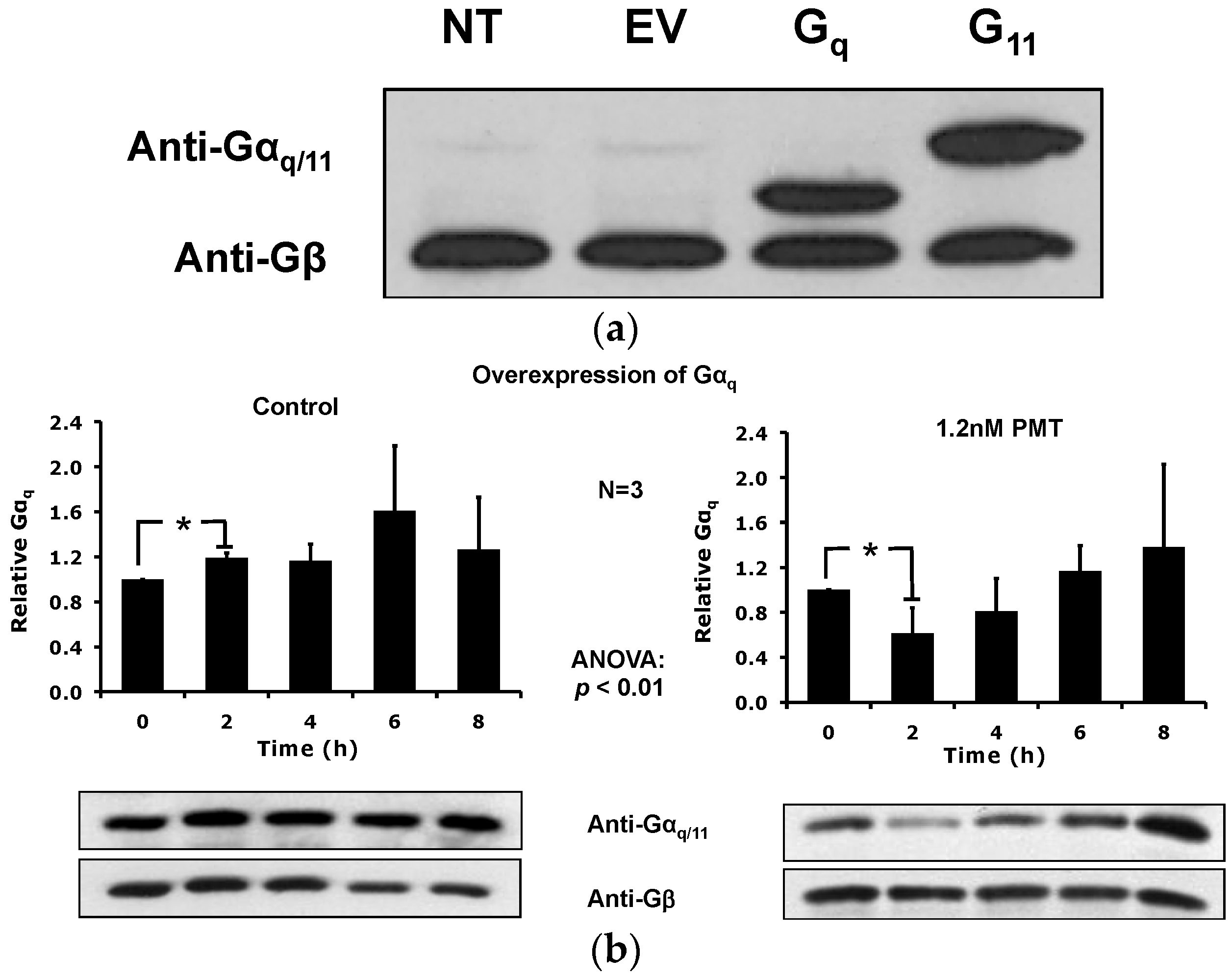
2.5. Overexpression of the Constitutively Active Forms of Gαq Alone nor in the Presence of PMT Is Sufficient to Induce Its Depletion from the Plasma Membrane
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Mammalian Expression Vectors Encoding Gα Proteins
| Gαq | F1: 5′-GCTTGGTACCACCATGACTCTGGAGTCCAT-3′ |
| Gαq | R1: 5′-GAGATATCCGCCGCCGCCAGACACCTTCCCACATCAAC-3′ |
| Gαq | F4: 5′-GAGATATCCCGATACAAAGACGATGACGACAAGGGCGGAGGCGGC-3′ |
| Gαq | F5: 5′-GACGACAAGGGCGGAGGCGGCTCTGCTTTTGAGAATCCATATGTAG-3′ |
| Gαq | R2: 5′-GACTCGAGTTAGACCAGATTGTACTC-3′ |
| Gα11 | F1: 5′-GCTTGGTACCACCATGACTCTGGAGTC-3′ |
| Gα11 | R1: 5′-GAGATATCCGCCGCCGCCGGACACCTTCTCCACGTCCAC-3′ |
| Gα11 | F3: 5′-GACGACAAGGGCGGAGGCGGCTCTACCTTCGAGCATCAGTACGTC-3′ |
| Gα11 | R2: 5′-CTAGACTCGAGTCAGACCAGGTTGTAC-3′ |
| Gαq | F1: 5′-CGATGTAGGCGGCGAAAGGTC-3′ |
| Gαq | R1: 5′-GACCTTTCGCCGCCTACATCG-3′ |
| Gαq | F2: 5′-TGTCGTAACAACTCCGCCCCA-3′ |
| Gαq | R2: 5′-ACACCTACTCAGACAATGCGATGCA-3′ |
| Gα11 | F1: 5′-GTGGGCGGCGAGCGGTCGG-3′ |
| Gα11 | R1: 5′-CCGACCGCTCGCCGCCCAC-3′ |
| Gα11 | F2: 5′-TGTCGTAACAACTCCGCCCCA-3′ |
| Gα11 | R2: 5′-ACACCTACTCAGACAATGCGATGCA-3′ |
4.3. Transient Transfection
4.4. Cellular Fractionation
4.5. Immunoblotting Analysis
4.6. OptiPrep or Sucrose Density Gradient Subcellular Fractionation
4.7. Data Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium |
| DRM | Detergent resistant membrane |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| EV | Empty vector |
| GPCR | G-protein coupled receptor |
| NT | No transfection and/or treatment |
| PLCβ1 | Phospholipase C β-1 |
| PMT | Pasteurella multocida toxin |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SDS-PAGE | Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
References
- Wilson, B.A.; Ho, M. Pasteurella multocida: From zoonosis to cellular microbiology. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 631–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brothers, M.C.; Ho, M.; Maharjan, R.; Clemons, N.C.; Bannai, Y.; Waites, M.A.; Faulkner, M.J.; Kuhlenschmidt, T.B.; Kuhlenschmidt, M.S.; Blanke, S.R.; et al. Membrane interaction of Pasteurella multocida toxin involves sphingomyelin. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 4633–4648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, S.; Jehle, D.; Schwan, C.; Orth, J.H.; Aktories, K. Pasteurella multocida toxin as a transporter of non-cell-permeating proteins. Infect Immun. 2013, 81, 2459–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Repella, T.L.; Ho, M.; Chong, T.P.; Bannai, Y.; Wilson, B.A. Arf6-dependent intracellular trafficking of Pasteurella multocida toxin and pH-dependent translocation from late endosomes. Toxins 2011, 3, 218–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozengurt, E.; Higgins, T.; Chanter, N.; Lax, A.J.; Staddon, J.M. Pasteurella multocida toxin: Potent mitogen for cultured fibroblasts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, B.A.; Bergmann, S.; Ho, M.; Orth, J.H.C. Pasteurella multocida toxin. In The Comprehensive Sourcebook of Bacterial Protein Toxins; Alouf, J.E., Ladant, D., Popoff, M.R., Eds.; Elsevier Science Publishers B.V.: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 463–498. [Google Scholar]
- Kamitani, S.; Ao, S.; Toshima, H.; Tachibana, T.; Hashimoto, M.; Kitadokoro, K.; Fukui-Miyazaki, A.; Abe, H.; Horiguchi, Y. Enzymatic actions of Pasteurella multocida toxin detected by monoclonal antibodies recognizing the deamidated alpha subunit of the heterotrimeric GTPase Gq. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 2702–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orth, J.H.; Fester, I.; Siegert, P.; Weise, M.; Lanner, U.; Kamitani, S.; Tachibana, T.; Wilson, B.A.; Schlosser, A.; Horiguchi, Y.; et al. Substrate specificity of Pasteurella multocida toxin for alpha subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 832–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, B.A.; Zhu, X.; Ho, M.; Lu, L. Pasteurella multocida toxin activates the inositol triphosphate signaling pathway in Xenopus oocytes via G(q)alpha-coupled phospholipase C-beta1. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 1268–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zywietz, A.; Gohla, A.; Schmelz, M.; Schultz, G.; Offermanns, S. Pleiotropic effects of Pasteurella multocida toxin are mediated by Gq-dependent and -independent mechanisms. involvement of Gq but not G11. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 3840–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orth, J.H.; Preuss, I.; Fester, I.; Schlosser, A.; Wilson, B.A.; Aktories, K. Pasteurella multocida toxin activation of heterotrimeric G proteins by deamidation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 7179–7184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staddon, J.M.; Barker, C.J.; Murphy, A.C.; Chanter, N.; Lax, A.J.; Michell, R.H.; Rozengurt, E. Pasteurella multocida toxin, a potent mitogen, increases inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and mobilizes Ca2+ in Swiss 3T3 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 4840–4847. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bannai, Y.; Aminova, L.R.; Faulkner, M.J.; Ho, M.; Wilson, B.A. Rho/ROCK-dependent inhibition of 3T3-L1 adipogenesis by G-protein-deamidating dermonecrotic toxins: Differential regulation of Notch1, Pref1/Dlk1, and beta-catenin signaling. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orth, J.H.; Lang, S.; Taniguchi, M.; Aktories, K. Pasteurella multocida toxin-induced activation of RhoA is mediated via two families of Gα proteins, Gαq and Gα12/13. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 36701–36707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagi, S.A.; Seasholtz, T.M.; Kobiashvili, M.; Wilson, B.A.; Toksoz, D.; Brown, J.H. Physical and functional interactions of Galphaq with Rho and its exchange factors. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 15445–15452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt, S.; Grosse, R.; Schultz, G.; Offermanns, S. Receptor-dependent RhoA activation in G12/G13-deficient cells: Genetic evidence for an involvement of Gq/G11. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 28743–28749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudet, L.I.; Chailler, P.; Dubreuil, J.D.; Martineau-Doize, B. Pasteurella multocida toxin stimulates mitogenesis and cytoskeleton reorganization in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. J. Cell. Physiol. 1996, 168, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacerda, H.M.; Lax, A.J.; Rozengurt, E. Pasteurella multocida toxin, a potent intracellularly acting mitogen, induces p125FAK and paxillin tyrosine phosphorylation, actin stress fiber formation, and focal contact assembly in Swiss 3T3 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Siegert, P.; Schmidt, G.; Papatheodorou, P.; Wieland, T.; Aktories, K.; Orth, J.H. Pasteurella multocida toxin prevents osteoblast differentiation by transactivation of the MAP-kinase cascade via the Gα(q/11)-p63RhoGEF-RhoA axis. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, W.; Pullinger, G.D.; Lax, A.J.; Rozengurt, E. Escherichia coli cytotoxic necrotizing factor and Pasteurella multocida toxin induce focal adhesion kinase autophosphorylation and Src association. Infect Immun. 2001, 69, 5931–5935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, B.A.; Aminova, L.R.; Ponferrada, V.G.; Ho, M. Differential modulation and subsequent blockade of mitogenic signaling and cell cycle progression by Pasteurella multocida toxin. Infect Immun. 2000, 68, 4531–4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babb, R.; Homer, K.; Robbins, J.B.; Lax, A.J. Modification of heterotrimeric G-Proteins in Swiss 3T3 cells stimulated with Pasteurella multocida toxin. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orth, J.H.; Fester, I.; Preuss, I.; Agnoletto, L.; Wilson, B.A.; Aktories, K. Activation of Galpha (i) and subsequent uncoupling of receptor-Galpha(i) signaling by Pasteurella multocida toxin. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 23288–23294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, B.A.; Ho, M. Cellular and molecular action of the mitogenic protein-deamidating toxin from Pasteurella multocida. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 4616–4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunemann, M.; Meyer, T.; Pott, L.; Hosey, M. Novel inhibition of Gbetagamma-activated potassium currents induced by M(2) muscarinic receptors via a pertussis toxin-insensitive pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 12537–12545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Q.; Talley, E.M.; Bayliss, D.A. Receptor-mediated inhibition of G protein-coupled inwardly rectifying potassium channels involves G(alpha)q family subunits, phospholipase C, and a readily diffusible messenger. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 16720–16730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, T.; Oles, M.; Pott, L. Ca2+ entry but not Ca2+ release is necessary for desensitization of ETA receptors in airway apithelial cells. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2000, 361, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, H.; Fukui, T.; Lassegue, B.; Shah, A.; Minieri, C.A.; Griendling, K.K. Prolonged exposure to agonist results in a reduction in the levels of the Gq/G11 alpha subunits in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 1996, 49, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lajat, S.; Harbon, S.; Tanfin, Z. Carbachol-induced desensitization of PLC-beta pathway in rat myometrium: Downregulation of Gqalpha/G11alpha. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 275, C636–C645. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.W.; Wise, A.; Cotecchia, S.; Milligan, G. A constitutively active mutant of the alpha 1B-adrenergic receptor can cause greater agonist-dependent down-regulation of the G-proteins G9 alpha and G11 alpha than the wild-type receptor. Biochem. J. 1996, 320, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Damjanoska, K.J.; Singh, R.K.; Carrasco, G.A.; Garcia, F.; Grippo, A.J.; Landry, M.; Sullivan, N.R.; Battaglia, G.; Muma, N.A. Agonist induced-phosphorylation of Galpha11 protein reduces coupling to 5-HT2A receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 323, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Zemaitaitis, B.; Muma, N.A. Phosphorylation of Galpha11 protein contributes to agonist-induced desensitization of 5-HT2A receptor signaling. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 71, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Westerlo, E.; Yang, J.; Logsdon, C.; Williams, J.A. Down-regulation of the G-proteins Gq alpha and G11 alpha by transfected human M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in Chinese hamster ovary cells is independent of receptor down-regulation. Biochem. J. 1995, 310, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise, A.; Lee, T.W.; MacEwan, D.J.; Milligan, G. Degradation of G11 alpha/Gq alpha is accelerated by agonist occupancy of alpha 1A/D, alpha 1B, and alpha 1C adrenergic receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 17196–17203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haraguchi, K.; Rodbell, M. Isoproterenol stimulates shift of G proteins from plasma membrane to pinocytotic vesicles in rat adipocytes: A possible means of signal dissemination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 1208–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullaney, I.; Dodd, M.W.; Buckley, N.; Milligan, G. Agonist activation of transfected human M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in CHO cells results in down-regulation of both the receptor and the alpha subunit of the G-protein Gq. Biochem. J. 1993, 289, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ransnas, L.A.; Svoboda, P.; Jasper, J.R.; Insel, P.A. Stimulation of beta-adrenergic receptors of S49 lymphoma cells redistributes the alpha subunit of the stimulatory G protein between cytosol and membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 7900–7903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugama, J.; Ohkubo, S.; Atsumi, M.; Nakahata, N. Mastoparan changes the cellular localization of Galphaq/11 and Gbeta through its binding to ganglioside in lipid rafts. Mol. Pharmacol. 2005, 68, 1466–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrom, R.S.; Insel, P.A. The evolving role of lipid rafts and caveolae in G protein-coupled receptor signaling: Implications for molecular pharmacology. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 143, 235–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aminova, L.R.; Luo, S.; Bannai, Y.; Ho, M.; Wilson, B.A. The C3 domain of Pasteurella multocida toxin is the minimal domain responsible for activation of Gq-dependent calcium and mitogenic signaling. Protein Sci. 2008, 17, 945–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orth, J.H.; Lang, S.; Preuss, I.; Milligan, G.; Aktories, K. Action of Pasteurella multocida toxin on Galpha(q) is persistent and independent of interaction with G-protein-coupled receptors. Cell. Signal. 2007, 19, 2174–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldwin, M.R.; Pullinger, G.D.; Lax, A.J. Pasteurella multocida toxin facilitates inositol phosphate formation by bombesin through tyrosine phosphorylation of G alpha q. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 32719–32725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macdonald, J.L.; Pike, L.J. A simplified method for the preparation of detergent-free lipid rafts. J. Lipid Res. 2005, 46, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langhorst, M.F.; Reuter, A.; Stuermer, C.A. Scaffolding microdomains and beyond: The function of reggie/flotillin proteins. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 2228–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, P.N.; Miles, A.J.; Sumner, I.G.; Thomas, L.H.; Lax, A.J. Activity of the mitogenic Pasteurella multocida toxin requires an essential C-terminal residue. Infect. Immun. 1998, 66, 5636–5642. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aminova, L.R.; Wilson, B.A. Calcineurin-independent inhibition of 3T3-L1 adipogenesis by Pasteurella multocida toxin: Suppression of Notch1, stabilization of beta-catenin and pre-adipocyte factor 1. Cell. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 2485–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oubrahim, H.; Wong, A.; Wilson, B.A.; Chock, P.B. Pasteurella multocida toxin (PMT) upregulates CTGF which leads to mTORC1 activation in Swiss 3T3 cells. Cell. Signal. 2013, 25, 1136–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oubrahim, H.; Wong, A.; Wilson, B.A.; Chock, P.B. Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) plays a role in Pasteurella multocida toxin (PMT)-induced protein synthesis and proliferation in Swiss 3T3 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 2805–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UMR cDNA Resource Center. Available online: http://www.cdna.org (accessed on 26 July 2016).
- Medina, R.; Grishina, G.; Meloni, E.G.; Muth, T.R.; Berlot, C.H. Localization of the effector-specifying regions of Gi2alpha and Gqalpha. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 24720–24727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Clemons, N.C.; Luo, S.; Ho, M.; Wilson, B.A. Selective Membrane Redistribution and Depletion of Gαq-Protein by Pasteurella multocida Toxin. Toxins 2016, 8, 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8080233
Clemons NC, Luo S, Ho M, Wilson BA. Selective Membrane Redistribution and Depletion of Gαq-Protein by Pasteurella multocida Toxin. Toxins. 2016; 8(8):233. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8080233
Chicago/Turabian StyleClemons, Nathan C., Shuhong Luo, Mengfei Ho, and Brenda A. Wilson. 2016. "Selective Membrane Redistribution and Depletion of Gαq-Protein by Pasteurella multocida Toxin" Toxins 8, no. 8: 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8080233





