The Acaricidal Activity of Venom from the Jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai against the Carmine Spider Mite Tetranychus cinnabarinus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Acaricidal Activity of NnFV against T. cinnabarinus
2.2. Repellent Activity of NnFV against T. cinnabarinus
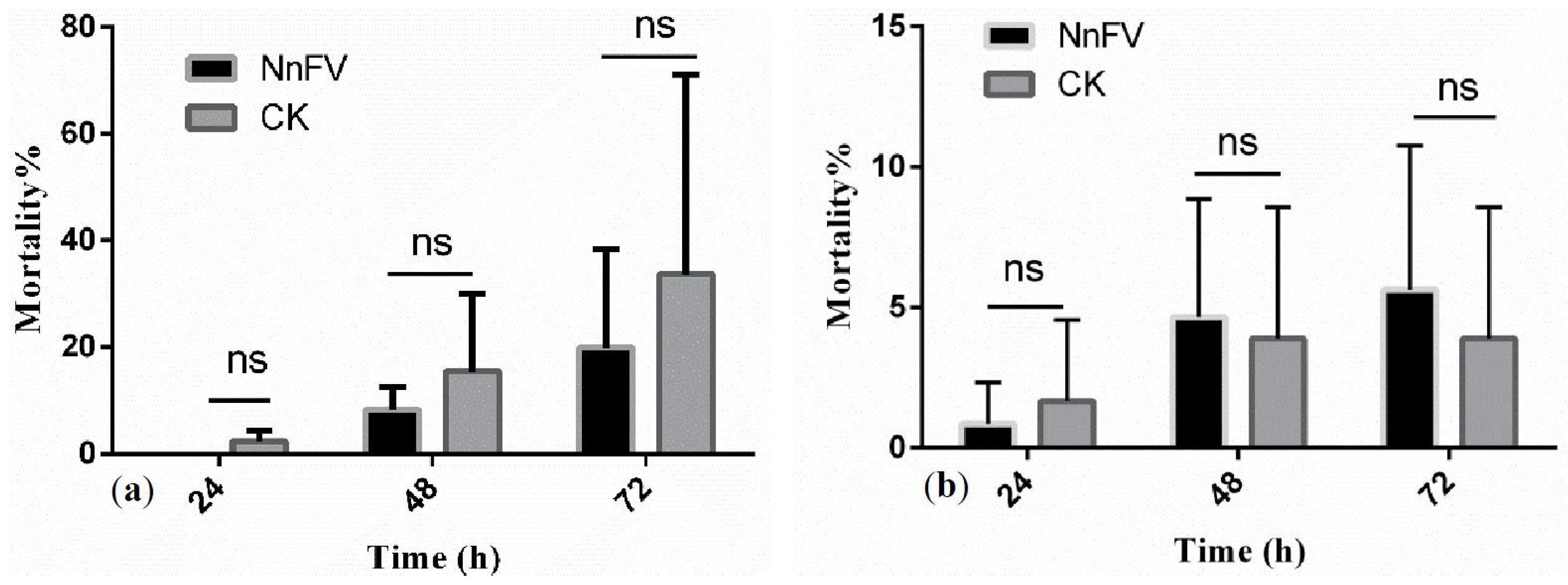
2.3. Systemic Toxicity of NnFV against T. cinnabarinus
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Biological Material
4.2. Venom Preparation
4.3. Acaricidal Activity Bioassays
4.4. Repellent Activity of NnFV against T. cinnabarinus
4.5. Systemic Toxicity of NnFV against T. cinnabarinus
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sertkaya, E.; Kaya, K.; Soylu, S. Acaricidal activities of the essential oils from several medicinal plants against the carmine spider mite (Tetranychus cinnabarinus Boisd.) (Acarina: Tetranychidae). Ind. Crop. Prod. 2010, 31, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Ding, W.; Zhao, Y.; Vanichpakorn, P. Acaricidal activity of Aloe vera L. leaf extracts against Tetranychus cinnabarinus (Boisduval) (Acarina: Tetranychidae). J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2011, 14, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Ding, W.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, J. Bioguided fractionation and isolation of esculentoside P from Phytolacca americana L. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2010, 44, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ding, W.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, J.; Fan, Y. Studies on acaricidal bioactivities of Artemisia annua L. extracts against Tetranychus cinnabarinus Bois. (Acari: Tetranychidae). Agric. Sci. China 2008, 7, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.S.; Lee, S.E.; Choi, W.S.; Jeong, C.Y.; Song, C.; Cho, K.Y. Insecticidal and acaricidal activity of pipernonaline and piperoctadecalidine derived from dried fruits of Piper longum L. Crop. Prot. 2002, 21, 249–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afify, A.E.M.M.; El-Beltagi, H.S.; Fayed, S.A.; Shalaby, E.A. Acaricidal activity of different extracts from Syzygium cumini L. Skeels (Pomposia) against Tetranychus urticae Koch. Asian. Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2011, 1, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouiaei, M.; Yanagihara, A.A.; Madio, B.; Nevalainen, T.J.; Alewood, P.F.; Fry, B.G. Ancient venom systems: a review on cnidaria toxins. Toxins 2015, 7, 2251–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Yu, H.; Liu, S.; Xing, R.; Guo, Z.; Li, P. Factors affecting the protease activity of venom from jellyfish Rhopilema esculentum Kishinouye. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 5370–5374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Li, C.; Li, R.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Li, P. Factors influencing hemolytic activity of venom from the jellyfish Rhopilema Esculentum. Kishinouye. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 1173–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Yu, H.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Qing, Y.; Li, K.; Li, B.; Meng, X.; Cui, J.; Li, P. Isolation and in vitro partial characterization of hemolytic proteins from the nematocyst venom of the jellyfish Stomolophus meleagris. Toxicol. In Vitr. 2013, 27, 1620–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Liu, X.; Dong, X.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Li, C.; Li, P. Insecticidal activity of proteinous venom from tentacles of jellyfish Rhopilema esculentum. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 4949–4952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Li, R.; Dong, X.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Li, P. Efficacy of venom from tentacle of jellyfish Stomolophus meleagris (Nemopilema nomurai) against the cotton bollworm Helicoverpa armigera. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Liu, X.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Guo, Z.; Li, C.; Li, P. In vitro determination of antioxidant activity of proteins from jellyfish Rhopilema esculentum. Food Chem. 2006, 95, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Yu, H.; Li, C.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Cai, S.; Li, P. Isolation and characterization of lethal proteins in nematocyst venom of the jellyfish Cyanea nozakii Kishinouye. Toxicon 2010, 55, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; He, Q.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Nie, F.; Li, Y.; Ye, X.; Zhang, L. Cyanea capillata tentacle-only extract as a potential alternative of nematocyst venom: Its cardiovascular toxicity and tolerance to isolation and purification procedures. Toxicon 2009, 53, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morabito, R.; Marino, A.; Dossena, S.; Paulmichl, M.; La Spada, G. Effects of Pelagia noctiluca crude venom on cell viability and volume regulation. J. Biol. Res. 2015, 88, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Hong, H.; Zhang, S. Fauna Sinica, Invertebrata (vol.27) Phylum Cnidaria: Class Hydrozoa Subclass Siphonophorae; Class Scyphomedusae, 1st ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002; pp. 225–226. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Zhang, F.; Li, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, M.; Tao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Sun, X. Breeding places, population dynamics, and distribution of the giant jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai (Scyphozoa: Rhizostomeae) in the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea. Hydrobiologia 2015, 754, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habbu, P.; Warad, V.; Shastri, R.; Madagundi, S.; Kulkarni, V.H. Antimicrobial metabolites from marine microorganisms. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2016, 14, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennaas, N.; Hammami, R.; Gomaa, A.; Bédard, F.; Biron, É.; Subirade, M.; Beaulieu, L.; Fliss, I. Collagencin, an antibacterial peptide from fish collagen: Activity, structure and interaction dynamics with membrane. Biochem. Bioph. Res. Co. 2016, 473, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visamsetti, A.; Ramachandran, S.S.; Kandasamy, D. Penicillium chrysogenum DSOA associated with marine sponge (Tedania anhelans) exhibit antimycobacterial activity. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 185, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dussault, D.; Vu, K.D.; Vansach, T.; Horgen, F.D.; Lacroix, M. Antimicrobial effects of marine algal extracts and cyanobacterial pure compounds against five foodborne pathogens. Food Chem. 2016, 199, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Yu, Y.; Bi, X. Acaricidal activity of extracts from mangrove plants. Agrochem 2007, 46, 568–570. [Google Scholar]
- Born, F.S.; Bianco, E.M.; da Camara, C.A.G. Acaricidal and repellent activity of terpenoids from seaweeds collected in Pernambuco, Brazil. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2012, 7, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sollod, B.L.; Wilson, D.; Zhaxybayeva, O.; Gogarten, J.P.; Drinkwater, R.; King, G.F. Were arachnids the first to use combinatorial peptide libraries? Peptides 2005, 26, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corzo, G.; Diego-Garcia, E.; Clement, H.; Peigneur, S.; Odell, G.; Tytyat, J.; Possani, L.D.; Alagon, A. An insecticidal peptide from the theraposid Brachypelma smithi spider venom reveals common molecular features among spider species from different genera. Peptides 2008, 29, 1901–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipkin, A.; Kozlov, S.; Nosyreva, E.; Blake, A.; Windass, J.D.; Grishin, E. Novel insecticidal toxins from the venom of the spider Segestria florentina. Toxicon 2002, 40, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rahman, M.A.; Quintero-Hernandez, V.; Possani, L.D. Venom proteomic and venomous glands transcriptomic analysis of the Egyptian scorpion Scorpio maurus palmatus (Arachnida: Scorpionidae). Toxicon 2013, 74, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J. Studies on Acaricidal Substance and Mechanism of Asarum. Ph.D. Thesis, Shengyang Agricultural University, Shenyang, China, December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mansour, F.; Azaizeh, H.B.; Saad, B.; Tadmor, Y.; Abo-Moch, F.; Said, O. The potential of middle eastern flora as a source of new safe bio-acaricides to control Tetranychus cinnabarinus, the Carmine Spider Mite. Phytoparasitica 2004, 32, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, F.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, D.; Dai, G. Biological activity of extracts from 8 species of plants against Tetranychus Cinnabarinus. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2011, 27, 286–291. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, A.; Yang, J. Conduction mode of pesticides in plant and pesticide-conduction biology. Chin. Plant Prot. 2012, 32, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zhao, F.; Liu, S.; Kong, W.; Shi, G. Acaricidal activity of extracts from Stellera chamaejasme root against to Tetranychus viennensis. J. Plant Resour. Environ. 2007, 16, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, W.; Cheng, J.; Bu, C.; Jin, Y.; Shi, G.; Wang, Y. Componential analysis and acaricidal activities of Stellera chamaejasme Extracts by Supercritical Fluid Extraction. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2012, 48, 181–185. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, W.; Bai, X.; Cheng, J.; Shi, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z. Isolation and identification of the principal acaricidal components from Stellera chamaejasme. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2011, 38, 947–954. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Yu, H.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Qing, Y.; Li, K.; Li, B.; Meng, X.; Cui, J.; Li, P. Application of nanoLC–MS/MS to the shotgun proteomic analysis of the nematocyst proteins from jellyfish Stomolophus meleagris. J. Chromatogr. B 2012, 899, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Li, R.; Chen, X.; Yue, Y.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Li, P. Effect of venom from the jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai on the silkworm Bombyx mori L. Toxins 2015, 7, 3876–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.A. Rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busvine, J.R. Recommended methods for measurement of pest resistance to pesticides (FAO plant production and protection papers); Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Roma, Italy, 1980; pp. 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, W.S. A method of computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. J. Econ. Entomol. 1925, 18, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | NnFV | Dicofol |
|---|---|---|
| Linear regression equation | Y = 7.21 + 1.44logx | Y = 4.58 + 3.22logx |
| LC50 (μg/mL) | 29.1 | 1350.9 |
| 95% Confidence interval for LC50 (μg/mL) | 22.0–38.5 | 1162.5–1569.8 |
| Toxicity index | 46.42 | 1 |
| χ2 | 9.8869 | 16.7776 |
| p | 0.6259 | 0.0523 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, H.; Yue, Y.; Dong, X.; Li, R.; Li, P. The Acaricidal Activity of Venom from the Jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai against the Carmine Spider Mite Tetranychus cinnabarinus. Toxins 2016, 8, 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8060179
Yu H, Yue Y, Dong X, Li R, Li P. The Acaricidal Activity of Venom from the Jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai against the Carmine Spider Mite Tetranychus cinnabarinus. Toxins. 2016; 8(6):179. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8060179
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Huahua, Yang Yue, Xiangli Dong, Rongfeng Li, and Pengcheng Li. 2016. "The Acaricidal Activity of Venom from the Jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai against the Carmine Spider Mite Tetranychus cinnabarinus" Toxins 8, no. 6: 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8060179
APA StyleYu, H., Yue, Y., Dong, X., Li, R., & Li, P. (2016). The Acaricidal Activity of Venom from the Jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai against the Carmine Spider Mite Tetranychus cinnabarinus. Toxins, 8(6), 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8060179