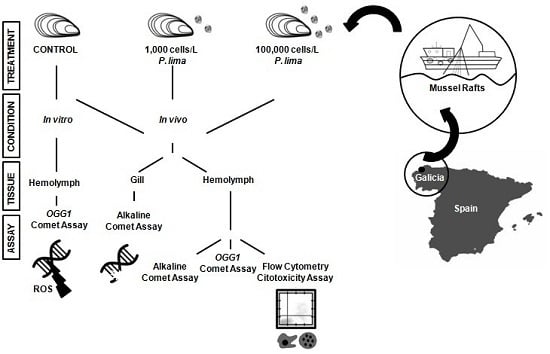
Early Genotoxic and Cytotoxic Effects of the Toxic Dinoflagellate Prorocentrum lima in the Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
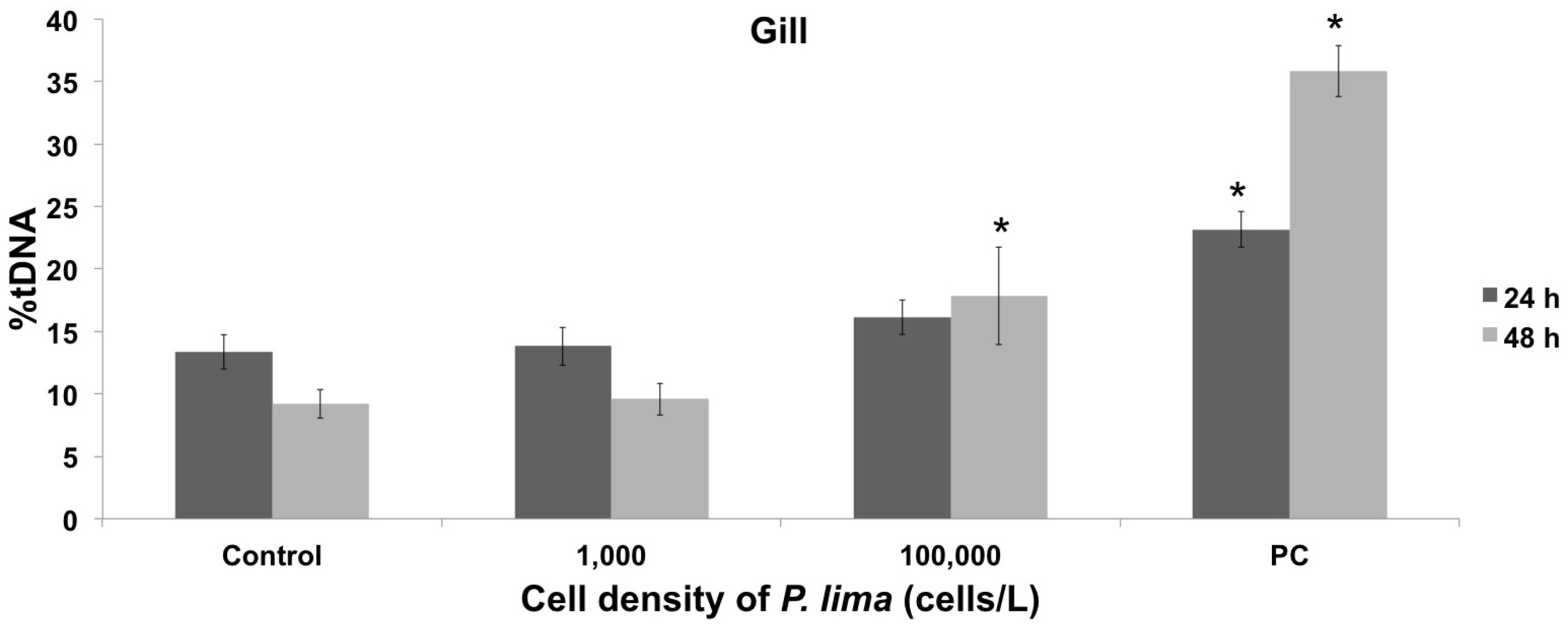
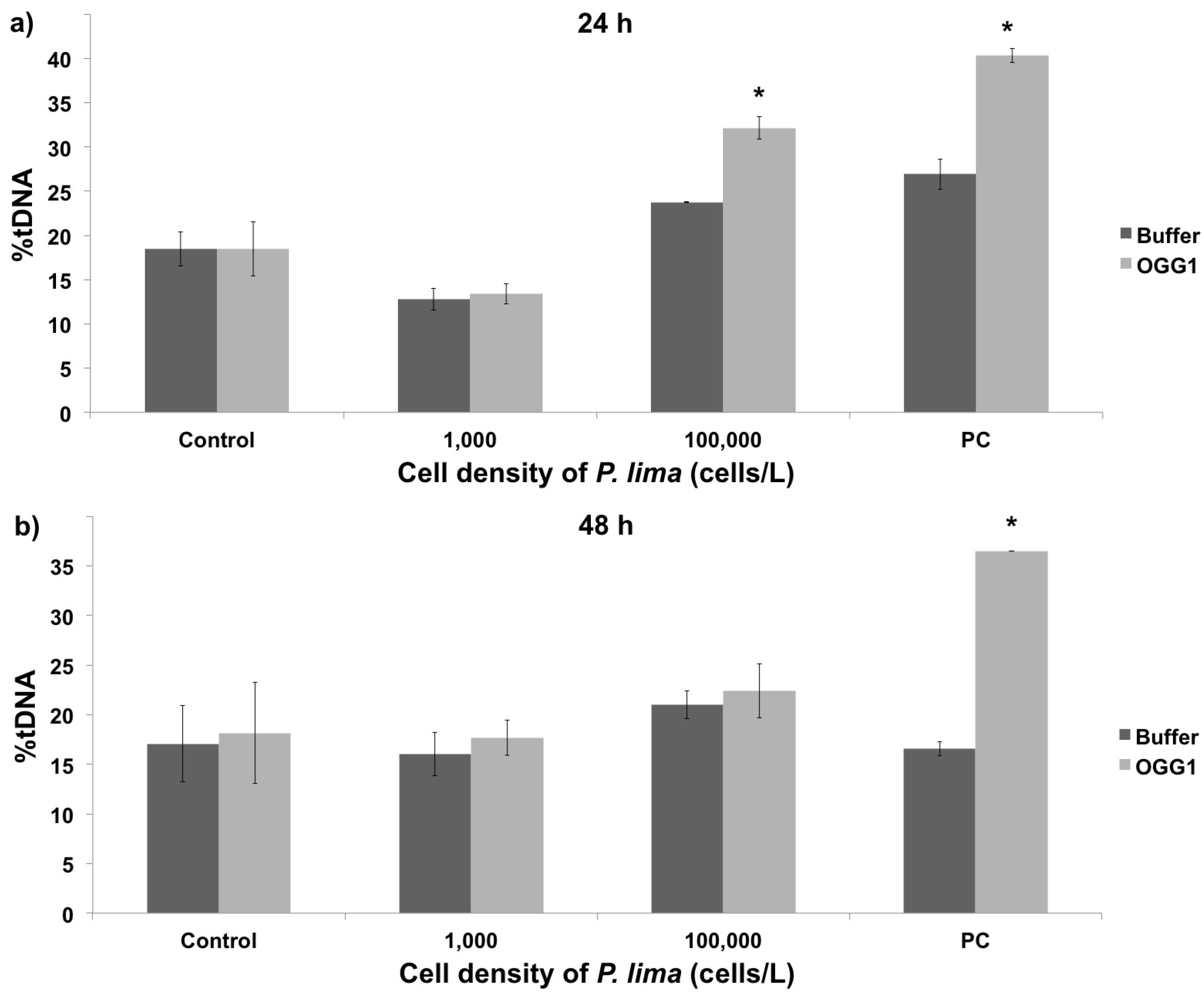
2.1. Toxin Accumulation and DNA Damage Resulting from In Vivo Exposure to P. lima
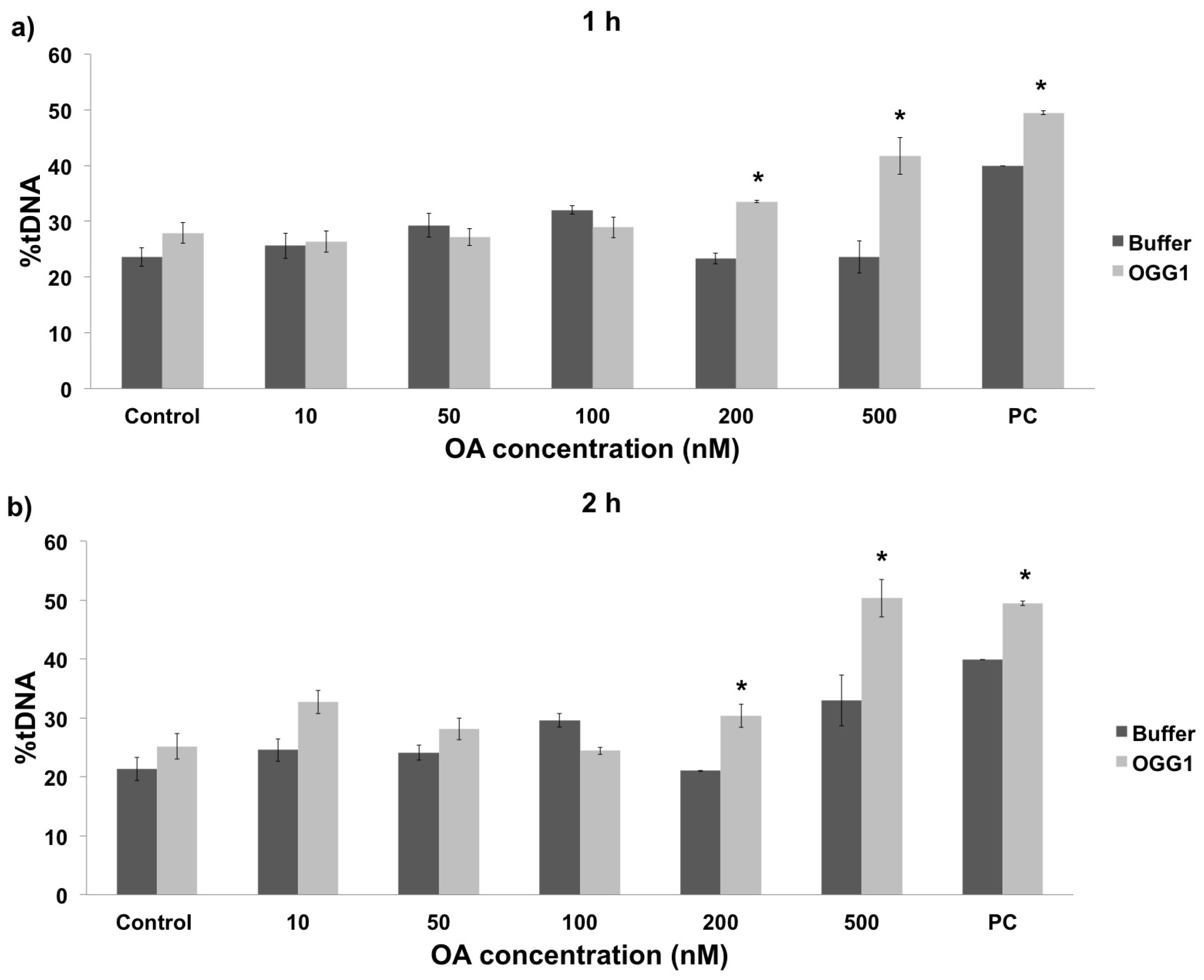
2.2. In Vivo vs. In Vitro Oxidative DNA Damage
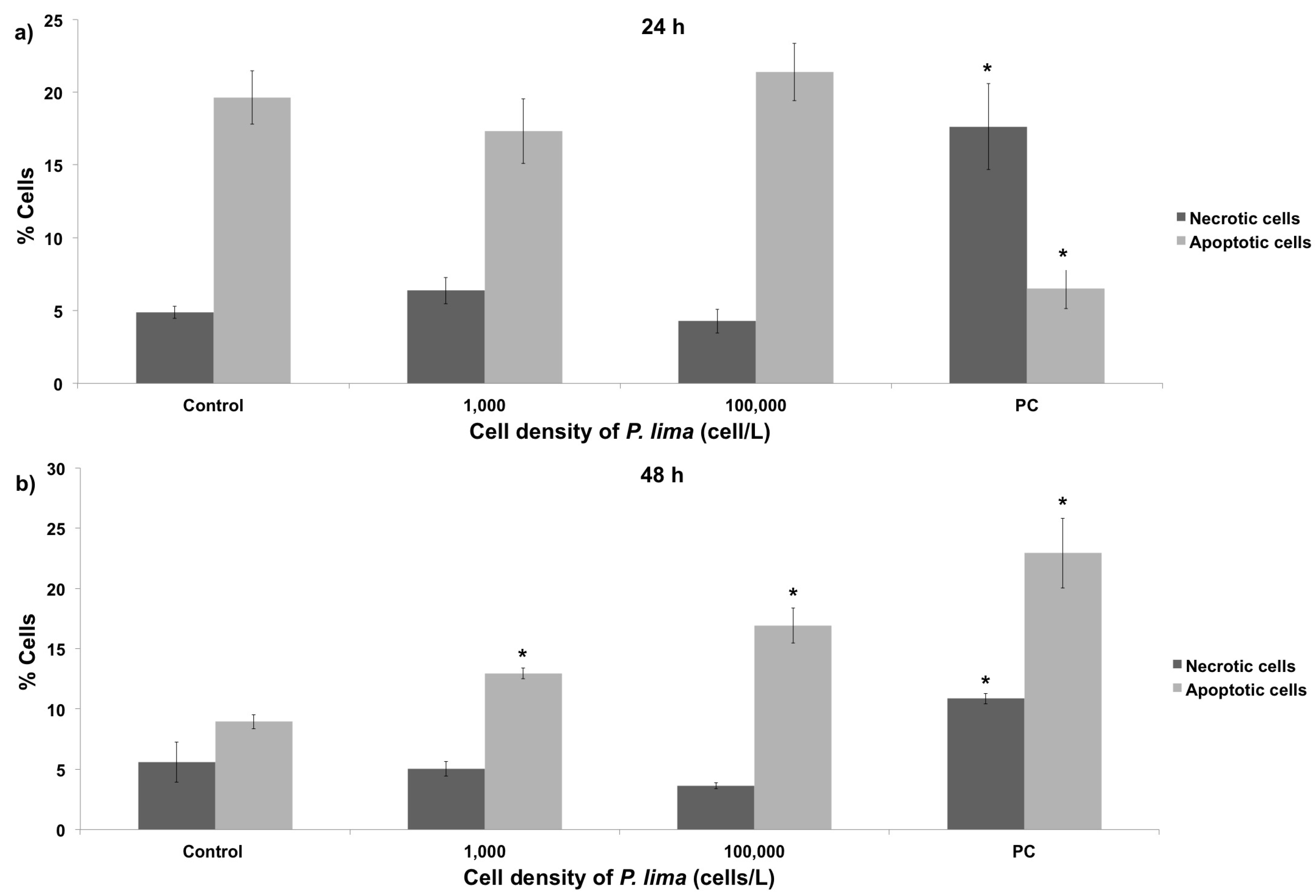
2.3. In Vivo Cytotoxic Damage After Exposure to P. lima
3. Discussion
3.1. Mussel Responses to the Toxic Dinoflagellate P. lima
3.2. Oxidative DNA Damage in Mussel Hemolymph
3.3. Cytotoxic Damage in Mussel Hemocytes
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Specimen Collection and Microalgae Cultures
5.2. Sample Preparation and HPLC/MS Analysis
5.3. In Vivo Exposure to P. lima
5.4. Isolation of Hemocytes and Gill Cells
5.5. In Vitro Exposure to OA
5.6. Alkaline Comet Assay
5.7. Modified Comet Assay with OGG1 Incubation
5.8. Flow Cytometry Cytotoxicity Assay
5.9. Statistical Analyses
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALS | Alkali Labile Site |
| DSB | Double-Stranded Breaks |
| HAB | Harmful Algal Bloom |
| HPLC/MS | High Performance Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry |
| IAP | Apoptosis Inhibitory Proteins |
| OA | Okadaic Acid |
| OGG1 | 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase |
| SSB | Single-Stranded Breaks |
References
- Díaz, P.A.; Reguera, B.; Ruiz-Villarreal, M.; Pazos, Y.; Velo-Suárez, L.; Berger, H.; Sourisseau, M. Climate variability and oceanographic settings associated with interannual variability in the initiation of dinophysis acuminata blooms. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2964–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reguera, B.; Riobó, P.; Rodríguez, F.; Díaz, P.A.; Pizarro, G.; Paz, B.; Franco, J.M.; Blanco, J. Dinophysis toxins: Causative organisms, distribution and fate in shellfish. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 394–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, L.P.; González, V.; Martínez, A.; Paz, B.; Lago, J.; Cordeiro, V.; Blanco, L.; Manuel Vieites, J.; Cabado, A.G. Occurrence of lipophilic marine toxins in shellfish from Galicia (NW of Spain) and synergies among them. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1666–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tubaro, A.; Sosa, S.; Bornancin, A.; Hungerford, J. Pharmacology and toxicology of diarrheic shellfish toxins. In Seafood and Freshwater Toxins Pharmacology, Physiology and Detection; Botana, L.M., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; pp. 229–253. [Google Scholar]
- Gestal-Otero, J.J. Epidemiology of marine toxins. In Seafood and Freshwater Toxins: Pharmacology, Physiology, and Detection; Botana, L.M., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; p. 123. [Google Scholar]
- Smaal, A.C. European mussel cultivation along the atlantic coast: Production status, problems and perspectives. Hydrobiologia 2002, 484, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Rodríguez, G.; Villasante, S.; García-Negro, M. Are red tides affecting economically the commercialization of the Galician (NW Spain) mussel farming? Mar. Policy 2011, 35, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialojan, C.; Takai, A. Inhibitory effect of a marine-sponge toxin, okadaic acid, on protein phosphatases. Specificity and kinetics. Biochem. J. 1988, 256, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konoki, K.; Onoda, T.; Watanabe, R.; Cho, Y.; Kaga, S.; Suzuki, T.; Yotsu-Yamashita, M. In vitro acylation of okadaic acid in the presence of various bivalves’ extracts. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 300–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdiglesias, V.; Prego-Faraldo, M.V.; Pásaro, E.; Méndez, J.; Laffon, B. Okadaic acid: More than a diarrheic toxin. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 4328–4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florez-Barros, F.; Prado-Alvarez, M.; Mendez, J.; Fernandez-Tajes, J. Evaluation of genotoxicity in gills and hemolymph of clam Ruditapes decussatus fed with the toxic dinoflagellate Prorocentrum lima. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2011, 74, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto-Silva, C.R.; Creppy, E.E.; Matias, W.G. Micronucleus test in mussels Perna perna fed with the toxic dinoflagellate Prorocentrum lima. Arch. Toxicol. 2005, 79, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prego-Faraldo, M.V.; Valdiglesias, V.; Laffon, B.; Eirin-Lopez, J.M.; Mendez, J. In vitro analysis of early genotoxic and cytotoxic effects of okadaic acid in different cell types of the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2015, 78, 814–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo, I.; Fernández, M.L.; Ramilo, I.; Martínez, A. Toxin composition of the toxic dinoflagellate prorocentrum lima isolated from different locations along the Galician coast (NW Spain). Toxicon 2001, 39, 1537–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernersson, A.-S.; Carere, M.; Maggi, C.; Tusil, P.; Soldan, P.; James, A.; Sanchez, W.; Dulio, V.; Broeg, K.; Reifferscheid, G.; et al. The european technical report on aquatic effect-based monitoring tools under the water framework directive. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2015, 27, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Geraldo, R.D.J.; García-Lagunas, N.; Hernández-Saavedra, N.Y. Effects of in vitro exposure to diarrheic toxin producer Prorocentrum lima on gene expressions related to cell cycle regulation and immune response in Crassostrea gigas. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97181. [Google Scholar]
- Kilemade, M.; Quinn, B. In vitro/in vivo bridging approaches-validating the relevance of in vitro techniques with references to the whole organism in the natural environment. In Vitro Met. Aquat. Toxicol. 2003, 377–393. [Google Scholar]
- Taju, G.; Majeed, S.A.; Nambi, K.S.N.; Babu, V.S.; Vimal, S.; Kamatchiammal, S.; Hameed, A.S.S. Comparison of in vitro and in vivo acute toxicity assays in Etroplus suratensis (Bloch, 1790) and its three cell lines in relation to tannery effluent. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garle, M.J.; Fentem, J.H.; Fry, J.R. In vitro cytotoxicity tests for the prediction of acute toxicity in vivo. Toxicol. In Vitro 1994, 8, 1303–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.C.; O’Donovan, M.R.; Martin, E.A. hOGG1 recognizes oxidative damage using the comet assay with greater specificity than FPG or ENDOIII. Mutagenesis 2006, 21, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, S.J.; Reutelingsperger, C.P.; McGahon, A.J.; Rader, J.A.; van Schie, R.C.; LaFace, D.M.; Green, D.R. Early redistribution of plasma membrane phosphatidylserine is a general feature of apoptosis regardless of the initiating stimulus: Inhibition by overexpression of Bcl-2 and Abl. J. Exp. Med. 1995, 182, 1545–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.F.; Steinert, S. Use of the single cell gel electrophoresis/comet assay for detecting DNA damage in aquatic (marine and freshwater) animals. Mutat. Res. 2003, 544, 43–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado-Alvarez, M.; Florez-Barros, F.; Sexto-Iglesias, A.; Mendez, J.; Fernandez-Tajes, J. Effects of okadaic acid on haemocytes from Mytilus galloprovincialis: A comparison between field and laboratory studies. Mar. Environ. Res. 2012, 81, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prado-Alvarez, M.; Florez-Barros, F.; Mendez, J.; Fernandez-Tajes, J. Effect of okadaic acid on carpet shell clam (Ruditapes decussatus) haemocytes by in vitro exposure and harmful algal bloom simulation assays. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2013, 29, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moroño, A.; Arévalo, F.; Fernández, M.L.; Maneiro, J.; Pazos, Y.; Salgado, C.; Blanco, J. Accumulation and transformation of DSP toxins in mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis during a toxic episode caused by Dinophysis acuminata. Aquat. Toxicol. 2003, 62, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, M.; O’Halloran, J.; O’Brien, N.M.; van Pelt, F.F.N.A.M. Does the marine biotoxin okadaic acid cause DNA fragmentation in the blue mussel and the pacific oyster? Mar. Environ. Res. 2014, 101, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallas, L.J.; Bean, T.P.; Turner, A.; Lyons, B.P.; Jha, A.N. Oxidative DNA damage may not mediate Ni-induced genotoxicity in marine mussels: Assessment of genotoxic biomarkers and transcriptional responses of key stress genes. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2013, 754, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocher, B.; Le Goff, J.; Peluhet, L.; Briand, M.; Manduzio, H.; Gallois, J.; Devier, M.H.; Geffard, O.; Gricourt, L.; Augagneur, S.; et al. Genotoxicant accumulation and cellular defence activation in bivalves chronically exposed to waterborne contaminants from the seine river. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 79, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fracasso, M.E.; Doria, D.; Franceschetti, P.; Perbellini, L.; Romeo, L. DNA damage and repair capacity by comet assay in lymphocytes of white-collar active smokers and passive smokers (non- and ex-smokers) at workplace. Toxicol. Lett. 2006, 167, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdiglesias, V.; Laffon, B.; Pasaro, E.; Mendez, J. Okadaic acid induces morphological changes, apoptosis and cell cycle alterations in different human cell types. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 1831–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lapuente, J.; Lourenço, J.; Mendo, S.A.; Borràs, M.; Martins, M.G.; Costa, P.M.; Pacheco, M. The comet assay and its applications in the field of ecotoxicology: A mature tool that continues to expand its perspectives. Front. Genet. 2015, 6, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, M.; Costa, P.M.; Ferreira, A.M.; Costa, M.H. Comparative DNA damage and oxidative effects of carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic sediment-bound PAHs in the gills of a bivalve. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 142, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noventa, S.; Pavoni, B.; Galloway, T.S. Periwinkle (Littorina littorea) as a sentinel species: A field study integrating chemical and biological analyses. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 2634–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, A.; Ruiz, Y.; Suárez, P.; Martinez, A.A.; Rossignoli, A.E.; Blanco, J.; Garcia, O.; San Juan, F. Accumulation of okadaic acid and detoxifying enzymes in the digestive gland of Mytilus galloprovincialis during exposure to DSP. In Molluscan Shellfish Safety; Springer: Berlin, Germany; Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 217–225. [Google Scholar]
- Levin, M.; Leibrecht, H.; Ryan, J.; Van Dolah, F.; De Guise, S. Immunomodulatory effects of domoic acid differ between in vivo and in vitro exposure in mice. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 636–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traoré, A.; Bonini, M.; Dano, S.D.; Creppy, E.E. Synergistic effects of some metals contaminating mussels on the cytotoxicity of the marine toxin okadaic acid. Arch. Toxicol. 1999, 73, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubiolo, J.A.; López-Alonso, H.; Vega, F.V.; Vieytes, M.R.; Botana, L.M. Okadaic acid and dinophysis toxin 2 have differential toxicological effects in hepatic cell lines inducing cell cycle arrest, at g0/g1 or g2/m with aberrant mitosis depending on the cell line. Arch. Toxicol. 2011, 85, 1541–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simões, E.; Vieira, R.C.; Schramm, M.A.; Mello, D.F.; Pontinha, V.D.A.; da Silva, P.M.; Barracco, M.A. Impact of harmful algal blooms (Dinophysis acuminata) on the immune system of oysters and mussels from Santa Catarina, Brazil. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2015, 95, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louzao, M.C.; Espina, B.; Cagide, E.; Ares, I.R.; Alfonso, A.; Vieytes, M.R.; Botana, L.M. Cytotoxic effect of palytoxin on mussel. Toxicon 2010, 56, 842–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galimany, E.; Sunila, I.; Hégaret, H.; Ramón, M.; Wikfors, G.H. Pathology and immune response of the blue mussel (Mytilus edulis L.) after an exposure to the harmful dinoflagellate Prorocentrum minimum. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto tecnoloxico para o control do medio mariño de galicia. Available online: http://www.intecmar.org/ (accessed on 13 March 2015).
- Community reference laboratory for marine biotoxins. Available online: http://www.aesan.msssi.gob.es/en/CRLMB/web/home.shtml (accessed on 28 April 2015).
- Pérez-Cadahía, B.; Laffon, B.; Pásaro, E.; Méndez, J. Evaluation of pah bioaccumulation and DNA damage in mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) exposed to spilled prestige crude oil. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2004, 138, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, J.T.; Pascoe, P.L.; Parry, J.M.; Dixon, D.R. Evaluation of the comet assay as a method for the detection of DNA damage in the cells of a marine invertebrate, Mytilus edulis L. (Mollusca: Pelecypoda). Mutat. Res. Fundam. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 1998, 399, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| P. lima (Cell/L) | Exposure Time (h) | Mean OA (ng/g Dry Weight) ± Standard Error |
|---|---|---|
| 1,000 | 24 | 28.35 ± 3.07 |
| 1,000 | 48 | 21.67 ± 2.02 |
| 100,000 | 24 | 64.77 ± 5.77 |
| 100,000 | 48 | 112.12 ± 7.78 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prego-Faraldo, M.V.; Valdiglesias, V.; Laffon, B.; Mendez, J.; Eirin-Lopez, J.M. Early Genotoxic and Cytotoxic Effects of the Toxic Dinoflagellate Prorocentrum lima in the Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Toxins 2016, 8, 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8060159
Prego-Faraldo MV, Valdiglesias V, Laffon B, Mendez J, Eirin-Lopez JM. Early Genotoxic and Cytotoxic Effects of the Toxic Dinoflagellate Prorocentrum lima in the Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Toxins. 2016; 8(6):159. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8060159
Chicago/Turabian StylePrego-Faraldo, María Verónica, Vanessa Valdiglesias, Blanca Laffon, Josefina Mendez, and Jose M. Eirin-Lopez. 2016. "Early Genotoxic and Cytotoxic Effects of the Toxic Dinoflagellate Prorocentrum lima in the Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis" Toxins 8, no. 6: 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8060159
APA StylePrego-Faraldo, M. V., Valdiglesias, V., Laffon, B., Mendez, J., & Eirin-Lopez, J. M. (2016). Early Genotoxic and Cytotoxic Effects of the Toxic Dinoflagellate Prorocentrum lima in the Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Toxins, 8(6), 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8060159