Natural Occurrence of Alternaria Toxins in the 2015 Wheat from Anhui Province, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS) Method Validation
2.2. Natural Occurrence of the Four Alternaria Toxins in Chinese Wheat
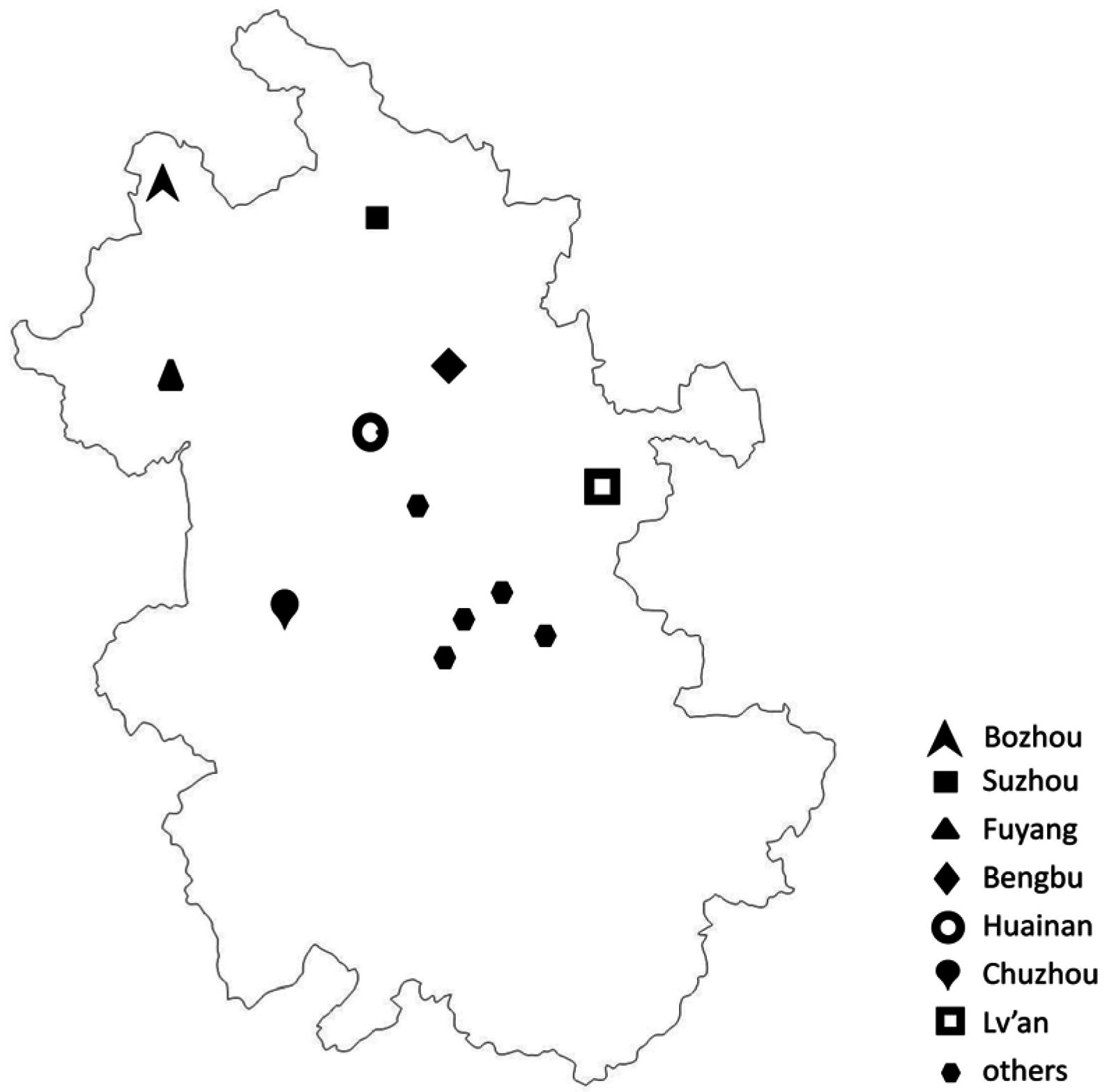
2.3. Geographical Distribution of the Four Alternaria Toxins in Anhui Province
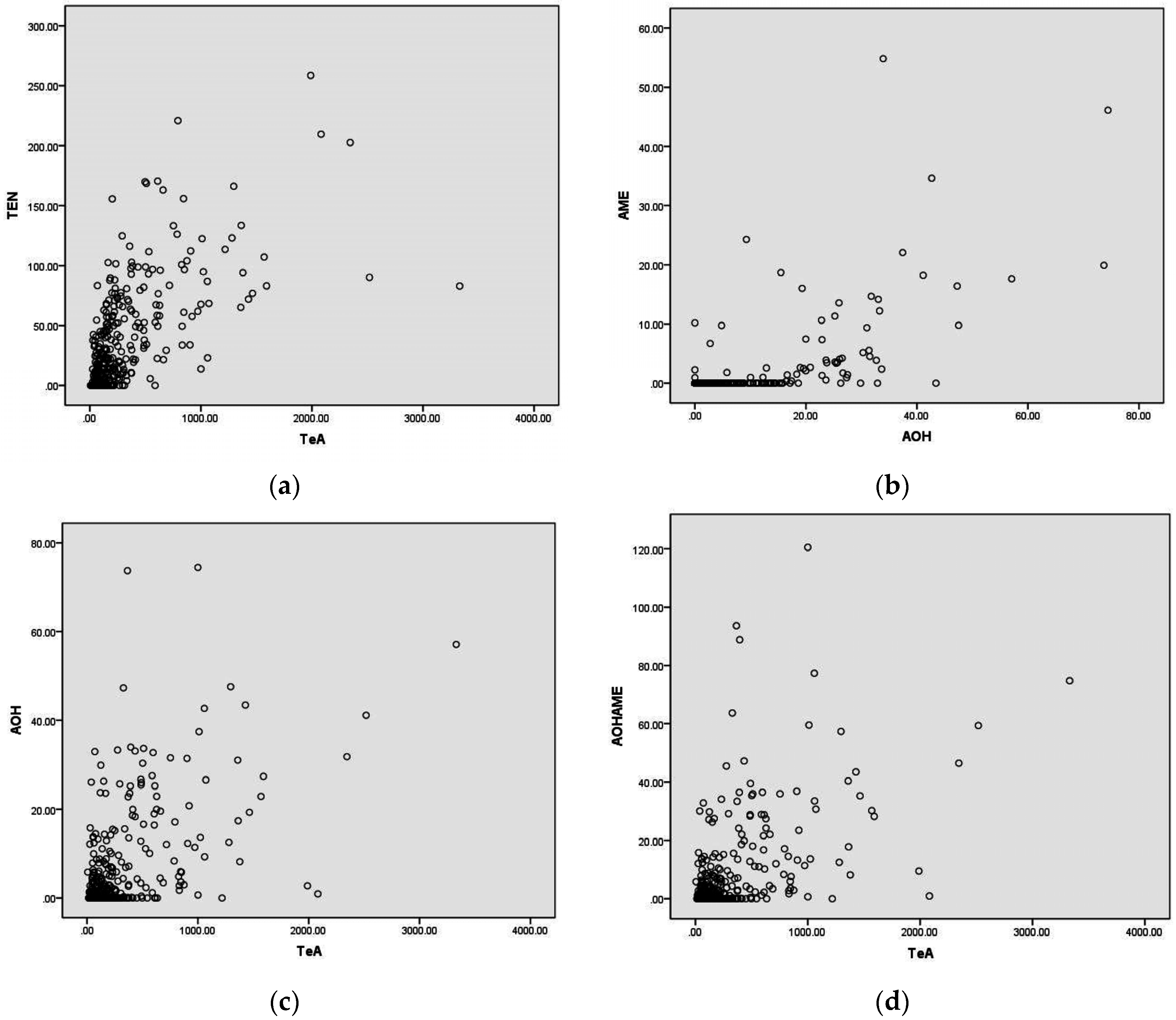
2.4. Co-Occurrence of the Four Alternaria Toxins in Wheat Kernels
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Samples Collection
4.3. Toxin Analysis
4.4. HPLC Conditions
4.5. MS/MS Conditions
4.6. Method Validation
4.7. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pavón Moreno, M.Á.; González Alonso, I.; Martín de Santos, Y.R.; García Lacarra, T. The importance of genus Alternaria in mycotoxins production and human diseases. Nutr. Hosp. 2012, 27, 1772–1781. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kosiak, W.; Torp, M.; Skjerve, E.; Andersen, B. Alternaria and Fusarium in Norwegain grains of reduced quality—A matched pair sample study. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 93, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, H. Alternaria mycotoxins in black rot lesion of tomato fruit: Conditions and regulation of their production. Mycopathologia 1995, 130, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Waals, J.E.; Korsten, L.; Slippers, B. Genetic diversity among Alternaria solani isolates from potatoes in South Africa. Plant Dis. 2004, 88, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akimitsu, K.; Peerver, T.L.; Timmer, L.W. Molecular, ecologocal and evolutionary approaches to understanding Alternaria diseases of citrus. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2003, 4, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rang, J.; Crous, P.W.; Mchau, G.R.A.; Serdani, M.; Song, S. Phylogenetic analysis of Alternaria spp. associated with apple core rot and citrus black rot in South Africa. Mycol. Res. 2002, 106, 1151–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, M.L. Epidemiology and yield losses associated with Alternaria blight of sunflower. Phytopathology 1985, 75, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostry, V. Alternaria mycotoxins: An overview of chemical characterization, producer, toxincity, analysis and occurrence in foodstuffs. World Mycotoxin J. 2008, 1, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottalico, A.; Logrieco, A. Alternaria plant diseases in Mediterranean countries and associated mycotoxins. In Alternaria: Biology, Plant Diseases and Metabolites; Chełkowski, J., Visconti, A., Eds.; Elsevier Science: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 209–232. [Google Scholar]
- Barkai-Golan, R. Alternaria mycotoxins. In Mycotoxins in Fruits and Vegetables; Barkai-Golan, R., Nachman, P., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2008; pp. 185–203. [Google Scholar]
- Visconti, A.; Sibilia, A. Alternaria toxins. In Mycotoxins in Grain: Compounds Other Than Aflatoxin; Miller, J.D., Trenholm, H.L., Eds.; Eagan Press: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1994; pp. 315–336. [Google Scholar]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Scientific opinion on the risks for animal and public health related to the presence of Alternaria toxins in feed and food. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 1–97. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.L.; Sun, J.M. Status and outlook of wheat consumption in China. J. Triticeae Crops 2015, 35, 655–661. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.Q.; Luo, X.Y.; Takumi, Y. Mycotoxins (trichothecenes, zearalenone and fumonisins) in cereals associated with human red-mold intoxications stored since 1989 and 1991 in China. Nat. Toxins 1999, 7, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.J.; Han, X.M.; Zhang, J.; Pan, Z.; Li, F.Q.; Zhang, L.S. Survey on fungi contamination of wheat harvested in 2015 from Anhui province of China. Health Sci. 2016, 54, 92–96. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.T.; Qian, Y.Z.; Zhang, P.; Dong, Z.M.; Shi, Z.Y.; Zhen, Y.Z.; Miao, J.; Xu, Y.M. Relationships between Alternaria alternata and oesophageal cancer. IARC Sci. Publ. 1991, 105, 258–262. [Google Scholar]
- European Union Decision 2002/657/EC. Commission Decision of 12 August 2002 implementing Council Directive 96/23/EC concerning the performance of analytical methods and the interpretation of results. Off. J. Eur. Common. 2001, L221, 8–36.
- European Commission. SANTE/11945/2015. Guidance Document on Analytical Quality Control and Method Validation Procedures for Pesticides Residues Analysis in Food and Feed. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/food/plant/docs/plant_pesticides_mrl_guidelines_wrkdoc_11945_en.pdf (accessed on 25 March 2016).
- Zhao, K.; Shao, B.; Yang, D.J.; Li, F.Q.; Zhu, J.H. Natural occurrence of Alternaria toxins in wheat-based products and their dietary exposure in China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotem, J. The genus Alternaria. In Biology, Epidemiology and Pathogenicity; APS Press: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1994; p. 326. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, M.E.H.; Korn, U. Alternaria mycotoxins in wheat—A 10 years survey in the Northeast of Germany. Food Control 2013, 34, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azcarate, M.P.; Patriarca, A.; Terminiello, L.; Fernandez Pinto, V. Alternaria toxins in wheat during the 2004 to 2005 Argentinean harvest. J. Food Prot. 2008, 71, 1262–1265. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, F.Q.; Yoshizawa, T. Alternaria mycotoxins in weathered wheat from China. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 2920–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oviedo, M.S.; Sturm, M.E.; Reynoso, M.M.; Chulze, S.N.; Ramirez, M.L. Toxigenic and AFLP variability of Alternaria alternata and Alternaria infectoria occurring on wheat. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2013, 44, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, M.E.; Urban, K.; Koppen, R.; Siegel, D.; Korn, U.; Koch, M. Mycotoxins as antagonistic or supporting agents in the interaction between phytopathogenic Fusarium and Alternaria fungi. World Mycotoxin J. 2015, 8, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magan, N.; Lacey, J. The phylloplane microflora of ripening wheat and effect of late fungicide appications. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1986, 109, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magan, N.; Lacey, J. Effect of water activity, temperature and substrate on interactions between field and storage fungi. Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 1984, 82, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Shao, B.; Yang, D.Y.; Li, F.Q. Natural occurrence of four Alternaria mycotoxins in tomato- and citrus-based foods in China. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
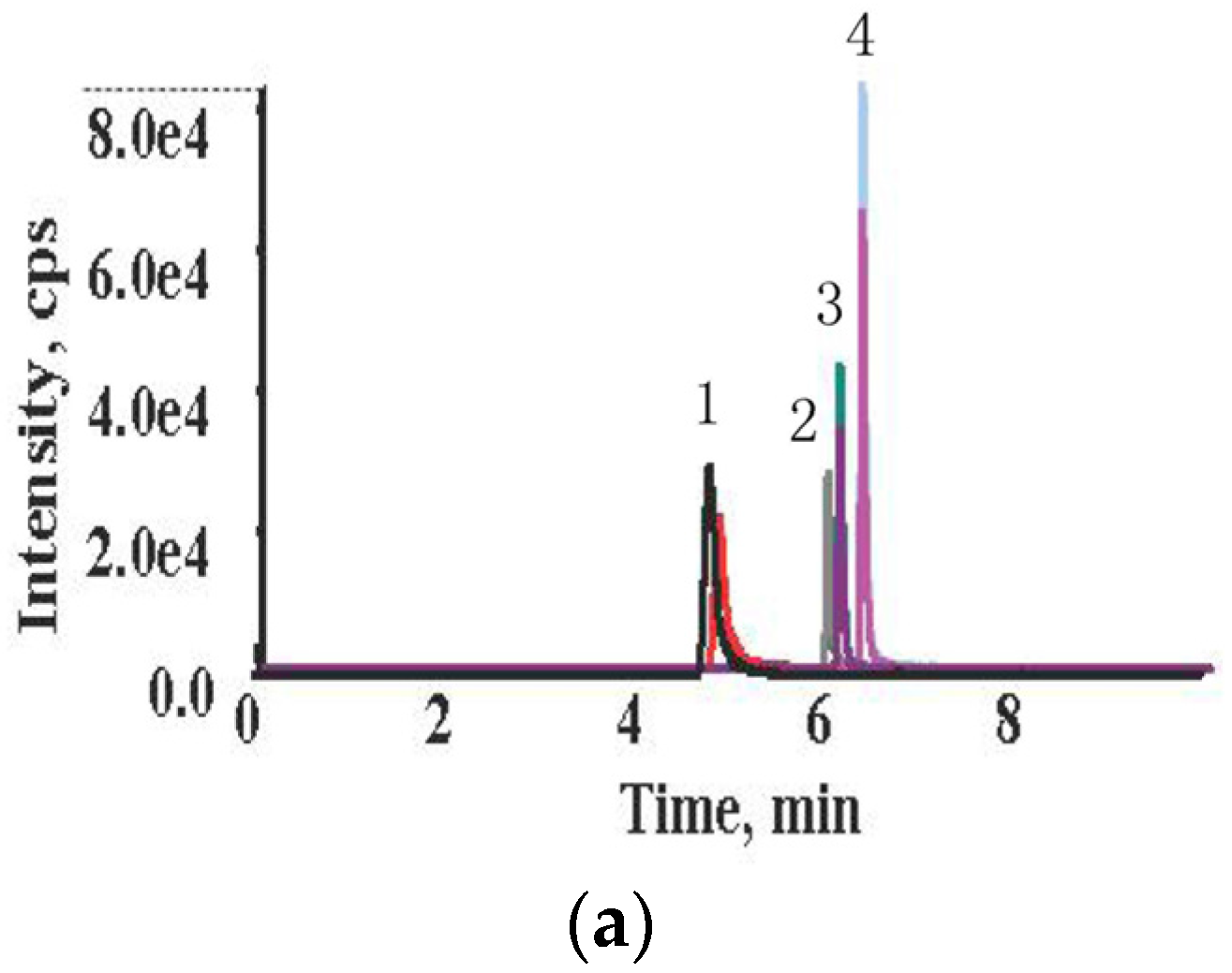
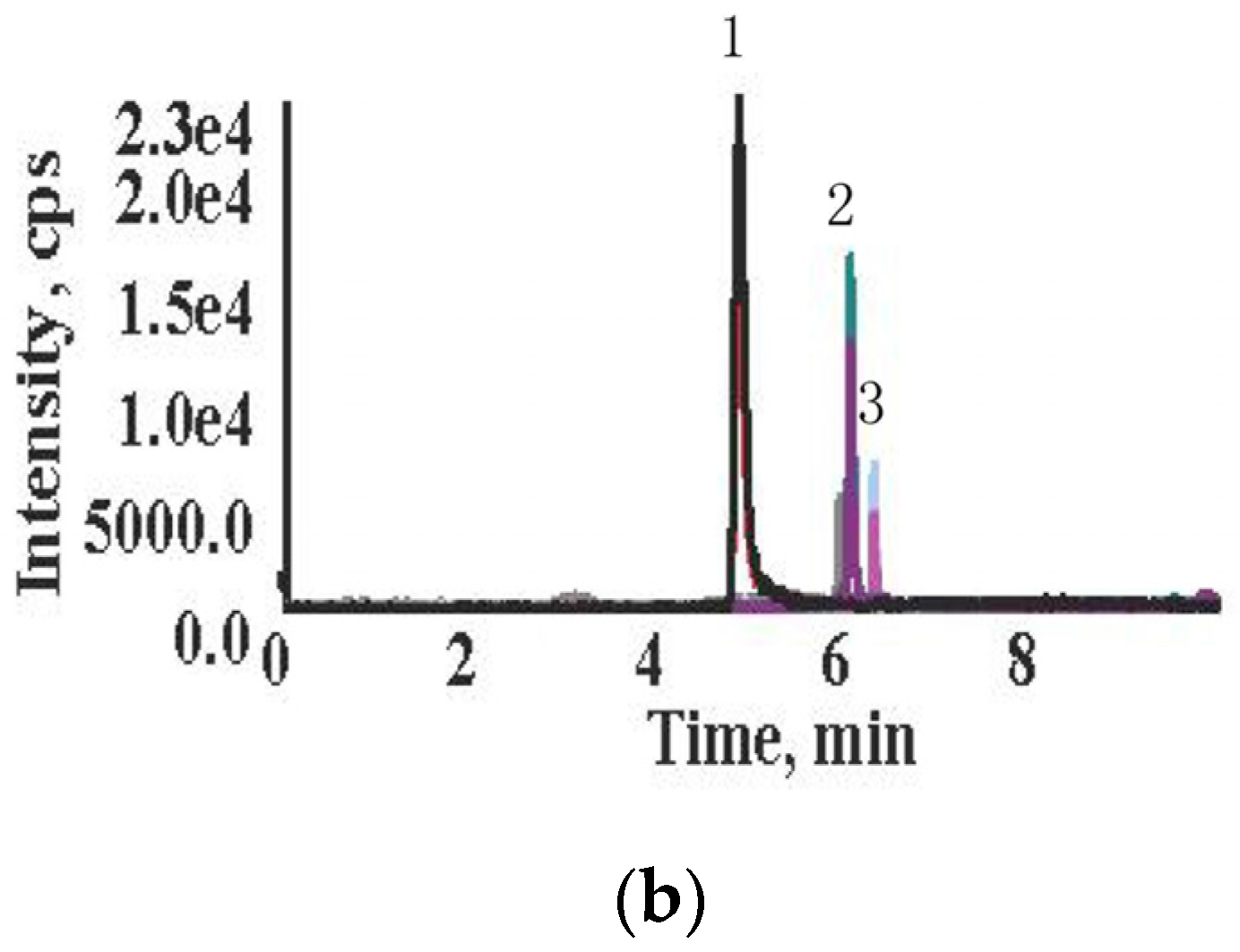
| Mycotoxin | Spiked Level (μg/kg) | Recovery (%, ) | RSD, % |
|---|---|---|---|
| TeA | 2 | 95.3 ± 8.1 | 8.5 |
| 10 | 95.8 ± 1.7 | 1.8 | |
| 20 | 98.9 ± 4.3 | 4.3 | |
| 40 | 96.3 ± 2.6 | 2.7 | |
| 100 | 99.3 ± 1.6 | 1.6 | |
| TEN | 5 | 101.2 ± 4.1 | 4.1 |
| 25 | 97.1 ± 5.4 | 5.6 | |
| 50 | 95.2 ± 3.4 | 3.6 | |
| 100 | 95.0 ± 4.7 | 4.9 | |
| 250 | 95.0 ± 2.6 | 2.7 | |
| AOH | 0.5 | 103.3 ± 8.4 | 8.1 |
| 2.5 | 95.3 ± 6.2 | 6.5 | |
| 5 | 97.6 ± 7.1 | 7.3 | |
| 10 | 98.1 ± 3.4 | 3.5 | |
| 25 | 96.2 ± 4.9 | 5.1 | |
| AME | 0.5 | 91.7 ± 5.0 | 5.5 |
| 1 | 87.0 ± 9.3 | 10.7 | |
| 2 | 100.3 ± 9.6 | 9.6 | |
| 5 | 94.0 ± 4.0 | 4.3 | |
| 10 | 98.1 ± 2.4 | 2.4 |
| Mycotoxin | Range (μg/kg) | Average (μg/kg) | Median (μg/kg) | Frequency, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TeA | 6.0–3330.7 | 289.0 | 150.0 | 100 |
| TEN | 0.4–258.6 | 43.8 | 29.7 | 77 |
| AOH | 1.3–74.4 | 12.9 | 7.9 | 47 |
| AME | 0.3–54.8 | 9.1 | 4.2 | 15 |
| Region | Mycotoxin | Range (μg/kg) | Average (μg/kg) | Median (μg/kg) | Frequency, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chuzhou (n = 53) | TeA | 6.0–3330.7 | 205.6 | 108.1 | 100 (53/53) |
| TEN * | 0.9–83.0 | 20.4 | 15.3 | 43 (23/53) | |
| AOH | 1.3–57.1 | 12.1 | 7.8 | 87 (46/53) | |
| AME | 2.1–17.6 | 6.2 | 3.9 | 9 (5/53) | |
| Fuyang (n = 93) | TeA | 53.7–2518.1 | 582.6 | 412.8 | 100 (93/93) |
| TEN * | 2.3–258.6 | 77.2 | 66.5 | 99 (92/93) | |
| AOH | 1.3–74.4 | 18.3 | 16.0 | 67 (62/93) | |
| AME | 0.3–46.1 | 8.5 | 4.2 | 38 (35/93) | |
| Huainan (n = 13) | TeA | 116.2–587.7 | 311.6 | 294.9 | 100 (13/13) |
| TEN * | 5.5–22.3 | 11.0 | 10.7 | 69 (9/13) | |
| AOH | 4.3–47.3 | 26.8 | 26.6 | 46 (6/13) | |
| AME | 1.4–16.4 | 8.8 | 10.6 | 38 (5/13) | |
| Suzhou (n = 86) | TeA | 13.2–832.3 | 125.0 | 86.5 | 100 (86/86) |
| TEN * | 0.4–76.7 | 14.2 | 8.7 | 58 (50/86) | |
| AOH | 1.3–15.5 | 3.9 | 2.8 | 23 (20/86) | |
| AME | 18.7 | 18.7 | 18.7 | 1 (1/86) | |
| Bozhou (n = 35) | TeA | 19.0–826.7 | 250.7 | 183.3 | 100 (35/35) |
| TEN * | 1.2–220.9 | 54.6 | 41.2 | 97 (34/35) | |
| AOH | 1.6–30.3 | 6.5 | 3.2 | 46 (16/35) | |
| AME | 0.9–9.8 | 4.2 | 3.1 | 11 (4/35) | |
| Lv’an (n = 22) | TeA | 21.1–1591.6 | 225.9 | 108.2 | 100 (22/22) |
| TEN * | 1.9–83.2 | 15.1 | 10.2 | 82 (18/22) | |
| AOH | 1.3–33.9 | 12.5 | 9.6 | 50 (11/22) | |
| AME | 0.9–54.8 | 20.7 | 13.4 | 18 (4/22) | |
| Bengbu (n = 41) | TeA | 21.2–616.2 | 131.1 | 93.4 | 100 (41/41) |
| TEN * | 0.5–101.5 | 21.6 | 14.1 | 80 (33/41) | |
| AOH | 1.7–9.9 | 4.1 | 2.8 | 12 (5/41) | |
| AME | 10.2 | 10.2 | 10.2 | 2 (1/41) | |
| Others (n = 27) | TeA | 47.3–1280.2 | 294.1 | 220.7 | 100 (27/27) |
| TEN * | 6.6–123.1 | 48.0 | 45.6 | 100 (27/27) | |
| AOH | 2.3–12.8 | 7.3 | 7.5 | 26 (7/27) | |
| AME | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 (0/27) |
| Contamination by | Toxin Combinations | Frequency, % |
|---|---|---|
| Two mycotoxins (46%, 170/370) | TeA-TEN | 35 (60/170) |
| TeA-AME | 21 (35/170) | |
| TEN-AME | 21 (35/170) | |
| TeA-AOH | 8 (14/170) | |
| AOH-TEN | 8 (13/170) | |
| AOH-AME | 8 (13/170) | |
| Three mycotoxins (30%, 110/370) | TeA-TEN-AME | 48 (53/110) |
| TeA-TEN-AOH | 18 (20/110) | |
| TeA-AOH-AME | 17 (19/110) | |
| TEN-AOH-AME | 16 (18/110) | |
| Four mycotoxins (19%, 72/370) | TeA-TEN-AOH-AME | 19 (72/370) |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, W.; Han, X.; Li, F.; Zhang, L. Natural Occurrence of Alternaria Toxins in the 2015 Wheat from Anhui Province, China. Toxins 2016, 8, 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8110308
Xu W, Han X, Li F, Zhang L. Natural Occurrence of Alternaria Toxins in the 2015 Wheat from Anhui Province, China. Toxins. 2016; 8(11):308. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8110308
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Wenjing, Xiaomin Han, Fengqin Li, and Lishi Zhang. 2016. "Natural Occurrence of Alternaria Toxins in the 2015 Wheat from Anhui Province, China" Toxins 8, no. 11: 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8110308
APA StyleXu, W., Han, X., Li, F., & Zhang, L. (2016). Natural Occurrence of Alternaria Toxins in the 2015 Wheat from Anhui Province, China. Toxins, 8(11), 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8110308






