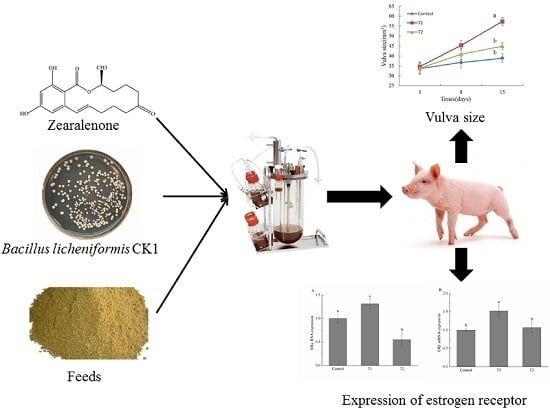
Effect of Degradation of Zearalenone-Contaminated Feed by Bacillus licheniformis CK1 on Postweaning Female Piglets
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Growth Performance
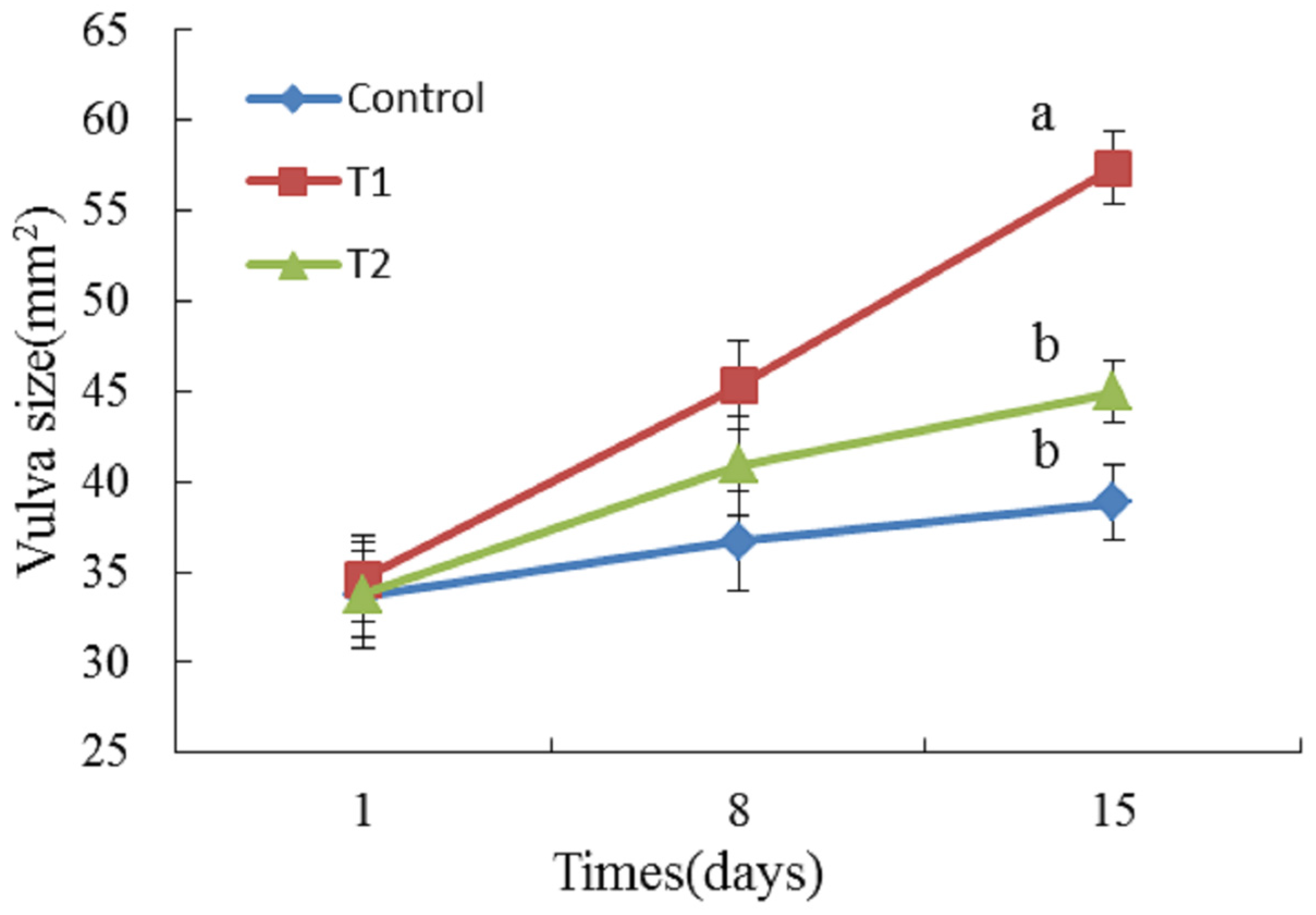
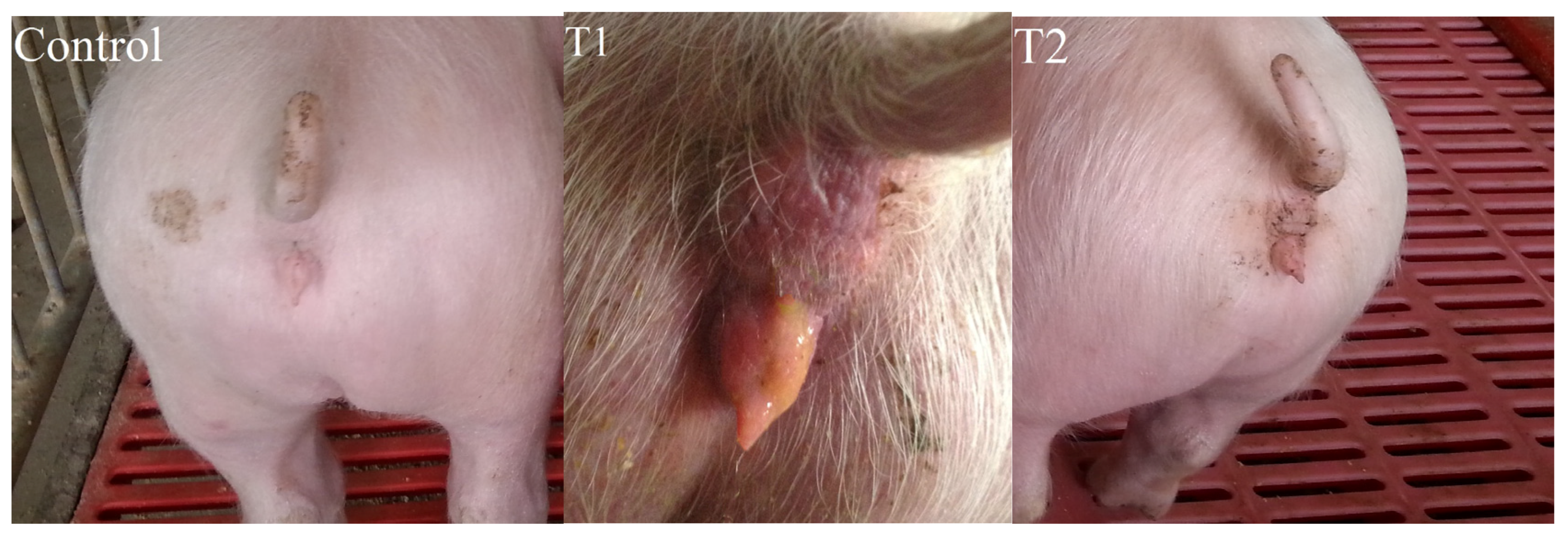
2.2. Vulva Size
2.3. Organ Weight
2.4. The Level of Serum Hormones
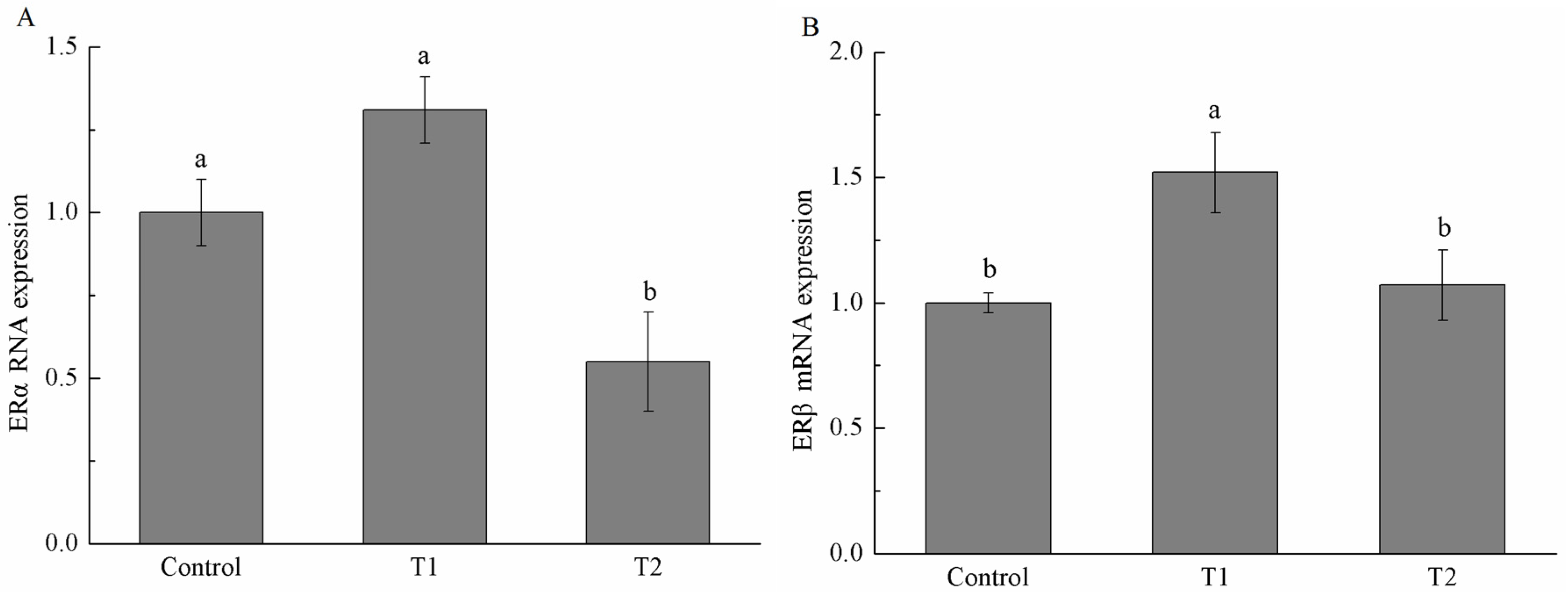
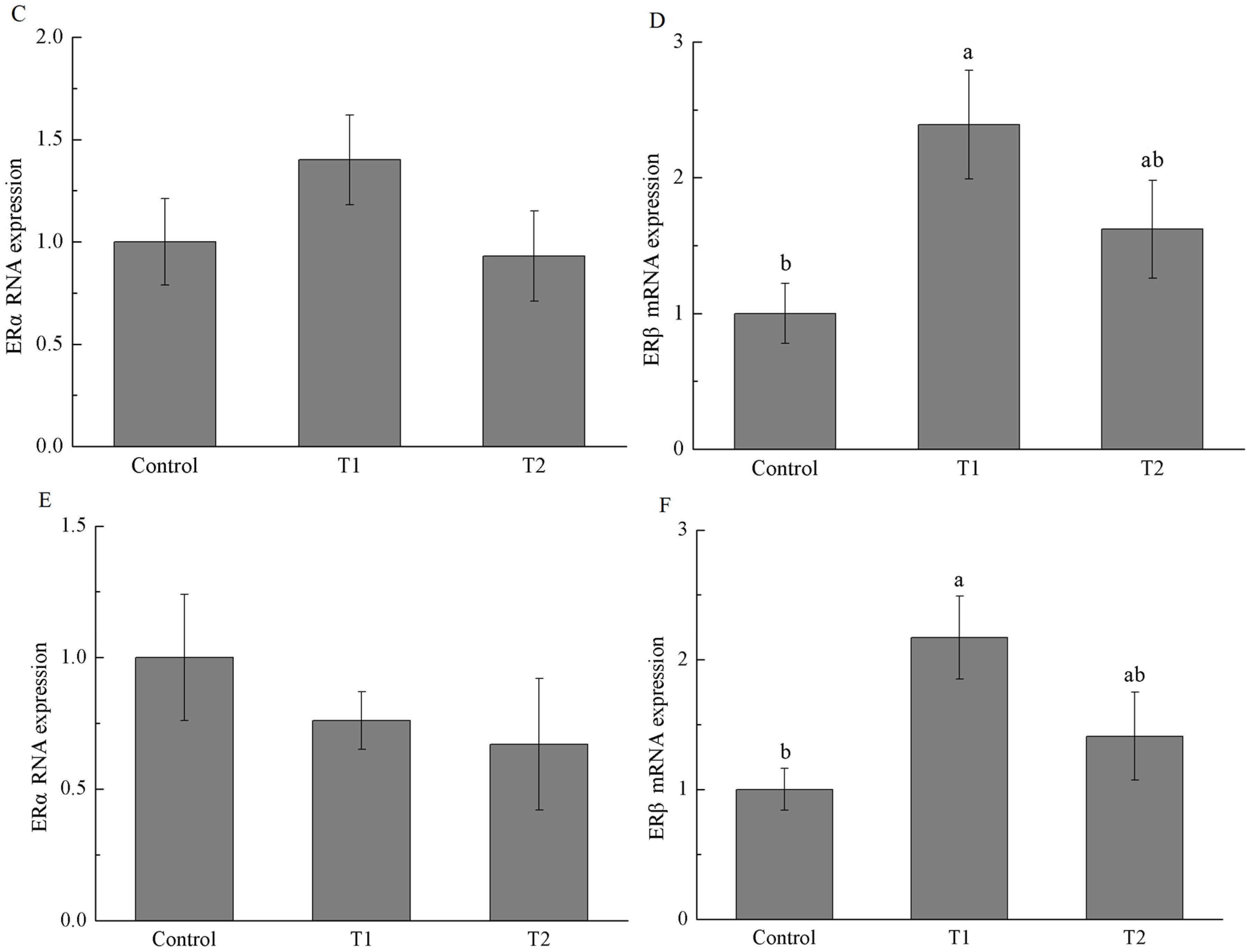
2.5. Estrogen Receptor α (ERα) and Estrogen Receptor β (ERβ) mRNA Expression
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Strains and Chemicals
4.2. Preparation of the Experimental Diets
4.3. Determination of ZEA in Feed by HPLC
4.4. Experimental Design and Animals
4.5. Sample Collection
4.6. Serum Hormone Analysis
4.7. Total RNA Extraction and Real-Time Quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR)
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reverberi, M.; Ricelli, A.; Zjalic, S.; Fabbri, A.A.; Fanelli, C. Natural functions of mycotoxins and control of their biosynthesis in fungi. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 87, 899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, S.; Ramos, A.J.; Cano-Sancho, G.; Sanchis, V. Mycotoxins: Occurrence, toxicology, and exposure assessment. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 60, 218–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terr, A.I. Sick building syndrome: Is mould the cause? Med. Mycol. 2009, 47, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardin, B.D.; Robbins, C.A.; Fallah, P.; Kelman, B.J. The concentration of no toxicologicconcen (CoNTC) and airborne mycotoxins. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2009, 72, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonen, J.; Malysheva, S.V.; Taevernier, L.; Di Mavungu, J.D.; De Saeger, S.; De Spiegeleer, B. Human skin penetration of selected model mycotoxins. Toxicology 2012, 301, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, K.F.; Smedsgaard, J. Fungal metabolite screening: Database of 474 mycotoxins and fungal metabolites for dereplication by standardised liquid chromatography-UV-mass spectrometry methodology. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 1002, 111–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taevernier, L.; Wynendaele, E.; De Vreese, L.; Burvenich, C.; De Spiegeleer, B. The mycotoxin definition reconsidered towards fungal cyclic depsipeptides. J. Environ. Sci. Health C 2016, 34, 114–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schatzmayr, G.; Streit, E. Global occurrence of mycotoxins in the food and feed chain: Facts and figures. World Mycotoxin J. 2013, 6, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jia, Z.; Yin, S.; Shan, A.; Gao, R.; Qu, Z.; Liu, M.; Nie, S. Toxic effects of maternal zearalenone exposure on uterine capacity and fetal development in gestation rats. Reprod. Sci. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koraichi, F.; Videmann, B.; Mazallon, M.; Benahmed, M.; Prouillac, C.; Lecoeur, S. Zearalenone exposure modulates the expression of ABC transporters and nuclear receptors in pregnant rats and fetal liver. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 211, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turcotte, J.C.; Hunt, P.J.; Blaustein, J.D. Estrogenic effects of zearalenone on the expression of progestin receptors and sexual behavior in female rats. Horm. Behav. 2005, 47, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Songsermsakul, P.; Böhm, J.; Aurich, C.; Zentek, J.; Razzazi-Fazeli, E. The levels of zearalenone and its metabolites in plasma, urine and faeces of horses fed with naturally, fusarium toxin-contaminated oats. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2013, 97, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mycotoxins. Available online: http://www.webcitation.org/6k9LUBU0l (accessed on 30 August 2016).
- Streit, E.; Naehrer, K.; Rodrigues, I.; Schatzmayr, G. Mycotoxin occurrence in feed and feed raw materials worldwide: Long-term analysis with special focus on Europe and Asia. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 2892–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinyiro, S.E.; Yao, W.R.; Sun, X.L.; Wokadala, C.; Wang, S.T. Scavenging of zearalenone by Bacillus strains-in vitro. Res. J. Microbiol. 2011, 6, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.J.; Kang, J.S.; Cho, W.T.; Lee, C.H.; Ha, J.K.; Song, K.B. In vitro degradation of zearalenone by Bacillus subtilis. Biotechnol. Lett. 2010, 32, 1921–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, P.J.; Pai, C.K.; Liu, J.R. Isolation and characterization of a Bacillus licheniformis strain capable of degrading zearalenone. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 27, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.H.; Lei, Y.P.; Bao, Y.H.; Jia, R.; Ma, Q.G.; Zhang, J.Y.; Chen, J.; Ji, C. Ameliorative effects of Bacillus subtilis ANSB01G on zearalenone toxicosis in pre-pubertal female gilts. Food Addit. Contam. A 2015, 32, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fink-Gremmels, J.; Malekinejad, H. Clinical effects and biochemical mechanisms associated with exposure to the mycoestrogen zearalenone. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2007, 137, 326–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shier, W.T.; Shier, A.C.; Xie, W.; Mirocha, C.J. Structure-activity relationships for human estrogenic activity in zearalenone mycotoxins. Toxicon 2001, 39, 1435–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaswamy, S.; Duan, S.X.; Von Moltke, L.L.; Greenblatt, D.J.; Sudmeier, J.L.; Bachovchin, W.W.; Court, M.H. Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine) glucuronidation in vitro: Assay development, human liver microsome activities and species differences. Xenobiotica 2003, 33, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.Z.; Yang, Z.B.; Yang, W.R.; Gao, J.; Liu, F.X.; Broomhead, J.; Chi, F. Effects of purified zearalenone on growth performance, organ size, serum metabolites, and oxidative stress in postweaning gilts. J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 89, 3008–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, W.T.; Miles, J.R.; Diaz, D.E.; Dibner, J.J.; Rottinghaus, G.E.; Harrell, R.J. Zearalenone enhances reproductive tract development, but does not alter skeletal muscle signaling in prepubertal gilts. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2012, 174, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.Z.; Yang, Z.B.; Yang, W.R.; Wang, S.J.; Liu, F.X.; Johnston, L.A.; Chi, F.; Wang, Y. Effect of purified zearalenone with or without modified montmorillonite on nutrient availability, genital organs and serum hormones in post-weaning piglets. Livest. Sci. 2012, 144, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.Z.; Yang, Z.B.; Yang, W.R.; Yao, B.Q.; Zhao, H.; Liu, F.X.; Chen, C.C.; Chi, F. Effects of feeding purified zearalenone contaminated diets with or without clay enterosorbent on growth, nutrient availability, and genital organs in post-weaning female pigs. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. 2010, 23, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denli, M.; Blandon, J.C.; Guynot, M.E.; Salado, S.; Pérez, J.F. Efficacy of activated diatomaceous clay in reducing the toxicity of zearalenone in rats and piglets. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 93, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.P.; Chi, F.; Kim, I.H. Effects of montmorillonite clay on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, vulva size, faecal microflora, and oxidative stress in weaning gilts challenged with zearalenone. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2012, 178, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.F.; Zhang, N.Y.; Peng, Y.Z.; Qi, D.S. Interaction of zearalenone and soybean isoflavone on the development of reproductive organs, reproductive hormones and estrogen receptor expression in prepubertal gilts. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2010, 122, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diekman, M.A.; Long, G.G. Blastocyst development on days 10 or 14 after consumption of zearalenone by sows on days 7 to 10 after breeding. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1989, 50, 1224–1227. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Green, M.L.; Diekman, M.A.; Malayer, J.R.; Scheidt, A.B.; Long, G.G. Effect of prepubertal consumption of zearalenone on puberty and subsequent reproduction of gilts. J. Anim. Sci. 1990, 68, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuiper, G.G.; Lemmen, J.G.; Carlsson, B.; Corton, J.C.; Safe, S.H.; van Der Saag, P.T.; van Der Burg, B.; Gustafsson, J.Å. Interaction of estrogenic chemicals and phytoestrogens with estrogen receptor β. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 4252–4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madak-Erdogan, Z.; Charn, T.H.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, E.T.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A.; Katzenellenbogen, B.S. Integrative genomics of gene and metabolic regulation by estrogen receptors α and β, and their coregulators. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2013, 9, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, M.; He, X.J.; Tulayakul, P.; Li, J.Y.; Dong, K.S.; Manabe, N.; Nakayama, H.; Kumagai, S. The toxic effects and fate of intravenously administered zearalenone in goats. Toxicon 2010, 55, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurd, R.N. Structure activity relationships in zearalenones. In Mycotoxins in Human and Animal Health; Rodricks, J.V., Hesseltine, C.W., Mehlman, M.A., Eds.; Pathotox Publishers: Park Forest South, IL, USA, 1977; pp. 379–391. [Google Scholar]
- Kiessling, K.H.; Pettersson, H.; Sandholm, K.; Olsen, M. Metabolism of aflatoxin, ochratoxin, zearalenone, and three trichothecenes by intact rumen fluid, rumen protozoa, and rumen bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microb. 1984, 47, 1070–1073. [Google Scholar]
- Kollarczik, B.; Gareis, M.; Hanelt, M. In vitro tranformation of the Fusarium mycotoxins deoxynivalenol and zearalenone by normal gut microflora of pigs. Nat. Toxins 1994, 2, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakeya, H.; Takahashi-Ando, N.; Kimura, M.; Onose, R.; Yamaguchi, I.; Osada, H. Biotransformation of the mycotoxin, zearalenone, to a non-estrogenic compound by a fungal strain of Clonostachys sp. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2002, 66, 2723–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnar, O.; Schatzmayr, G.; Fuchs, E.; Prillinger, H. Trichosporon mycotoxinivorans sp. nov., a new yeast species useful in biological detoxification of various mycotoxins. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 27, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schatzmayr, G.; Schatzmayr, D.; Pichler, E.; Taubel, M.; Loibner, A.P.; Binder, E.M. A novel approach to deactivate ochratoxin A. In Mycotoxins and Phycotoxins: Advances in Determination, Toxicology and Exposure Management; Njapau, H., Trujillo, S., van Egmond, H., Park, D., Eds.; Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 279–290. [Google Scholar]
- Kriszt, R.; Krifaton, C.; Szoboszlay, S.; Cserháti, M.; Kriszt, B.; Kukolya, J.; Czéh, Á.; Fehér-Tóth, S.; Török, L.; Szőke, Z.; et al. A new zearalenone biodegradation strategy using non-pathogenic Rhodococcus pyridinivorans K408 strain. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hathout, A.S.; Aly, S.E. Biological detoxification of mycotoxins: A review. Ann. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 905–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council. Nutrient Requirements of Swine, 10th ed.; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCt method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Groups | Average Daily Feed Intake (kg) | Average Day Gain (kg) | Feed Conversion Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 0.71 ± 0.01 | 0.40 ± 0.08 | 1.73 ± 0.09 |
| T1 | 0.68 ± 0.02 | 0.42 ± 0.05 | 1.63 ± 0.05 |
| T2 | 0.63 ± 0.04 | 0.39 ± 0.06 | 1.65 ± 0.09 |
| p value | 0.289 | 0.463 | 0.713 |
| Group | Relative Weight (g/kg) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heart | Liver | Spleen | Lung | Kidney | Reproductive Organs | |
| Control | 4.98 ± 0.24 | 27.51 ± 1.08 a | 2.09 ± 0.30 | 11.68 ± 0.77 | 5.32 ± 0.28 a | 0.47 ± 0.04 a |
| T1 | 4.87 ± 0.10 | 24.33 ± 0.85 b | 1.79 ± 0.07 | 10.38 ± 0.20 | 5.24 ± 0.26 a | 0.66 ± 0.06 b |
| T2 | 5.00 ± 0.17 | 25.53 ± 0.76 ab | 2.04 ± 0.19 | 11.16 ± 0.42 | 6.80 ± 0.52 b | 0.63 ± 0.04 b |
| p value | 0.888 | 0.048 | 0.559 | 0.243 | 0.015 | 0.006 |
| Group | Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH), mIU/mL | Luteinizing Hormone (LH), mIU/mL | Estradiol (E2), pg/mL | Prolactin (PRL), ng/mL | Progesterone (PRG), ng/mL | Testosterone (T), ng/dL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 13.33 ± 0.56 | 8.68 ± 0.11 a | 21.27 ± 1.18 | 12.64 ± 0.48 | 0.80 ± 0.14 | 32.07 ± 2.97 |
| T1 | 12.55 ± 0.56 | 8.02 ± 0.12 b | 24.38 ± 1.01 | 12.60 ± 0.72 | 0.91 ± 0.2 | 31.85 ± 3.59 |
| T2 | 12.76 ± 0.26 | 8.70 ± 0.13 a | 23.32 ± 1.57 | 11.09 ± 0.42 | 1.13 ± 0.32 | 31.85 ± 0.96 |
| p value | 0.521 | 0.002 | 0.256 | 0.124 | 0.635 | 0.998 |
| Ingredients | Percentage, % | Nutrients | Analyzed Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corn | 53.00 | Gross energy (MJ/kg) | 17.12 |
| Wheat middling | 5.00 | Crude protein (%) | 19.40 |
| Whey powder | 6.50 | Calcium (%) | 0.84 |
| Soybean oil | 2.50 | Total phosphorus (%) | 0.73 |
| Soybean meal | 24.76 | Lysine (%) | 1.36 |
| Fish meal | 5.50 | Methionine (%) | 0.46 |
| l-Lysine HCl | 0.30 | Sulfur amino acid (%) | 0.79 |
| dl-Methionine | 0.10 | Threonine (%) | 0.90 |
| l-Threonine | 0.04 | Tryptophan (%) | 0.25 |
| Calcium phosphate | 0.80 | - | - |
| Limestone, pulverized | 0.30 | - | - |
| Sodium chloride | 0.20 | - | - |
| Premix 1 | 1.00 | - | - |
| Total | 100 | - | - |
| Gene | Forward Primer and Reverse Primer (from 5′ to 3′) | Size (bp) | Genbank No. |
|---|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | CCTGGCCAAGGTCATCCATG | 500 | NM_214220.1 |
| CCACCACCCTGTTGCTGTAG | |||
| ERα | TTGCTTAATTCTGGAGGGTAC | 110 | EF195769.1 |
| AGGTGGATCAAGGTGTCTGTG | |||
| ERβ | GCTCAGCCTGTACGACCAAGTGC | 138 | NM_001001533.1 |
| CCTTCATCCCTGTCCAGAACGAG |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, G.; Ma, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhao, X. Effect of Degradation of Zearalenone-Contaminated Feed by Bacillus licheniformis CK1 on Postweaning Female Piglets. Toxins 2016, 8, 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8100300
Fu G, Ma J, Wang L, Yang X, Liu J, Zhao X. Effect of Degradation of Zearalenone-Contaminated Feed by Bacillus licheniformis CK1 on Postweaning Female Piglets. Toxins. 2016; 8(10):300. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8100300
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Guanhua, Junfei Ma, Lihong Wang, Xin Yang, Jeruei Liu, and Xin Zhao. 2016. "Effect of Degradation of Zearalenone-Contaminated Feed by Bacillus licheniformis CK1 on Postweaning Female Piglets" Toxins 8, no. 10: 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8100300
APA StyleFu, G., Ma, J., Wang, L., Yang, X., Liu, J., & Zhao, X. (2016). Effect of Degradation of Zearalenone-Contaminated Feed by Bacillus licheniformis CK1 on Postweaning Female Piglets. Toxins, 8(10), 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8100300