BmP02 Atypically Delays Kv4.2 Inactivation: Implication for a Unique Interaction between Scorpion Toxin and Potassium Channel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
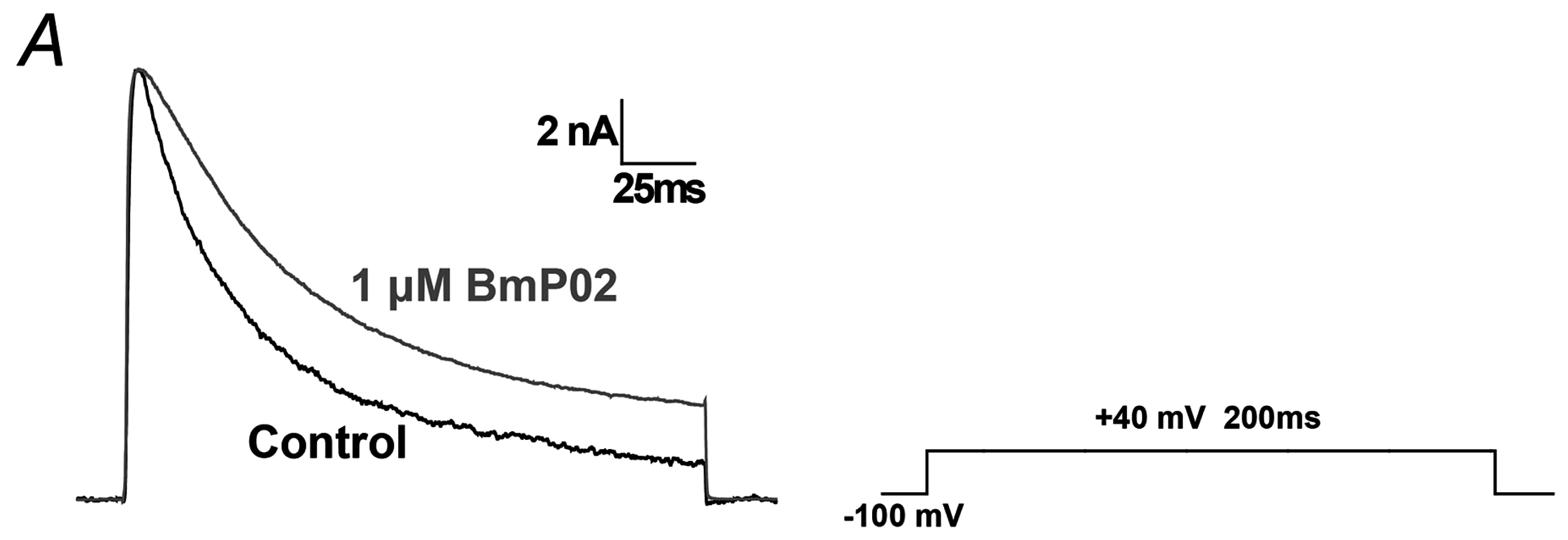
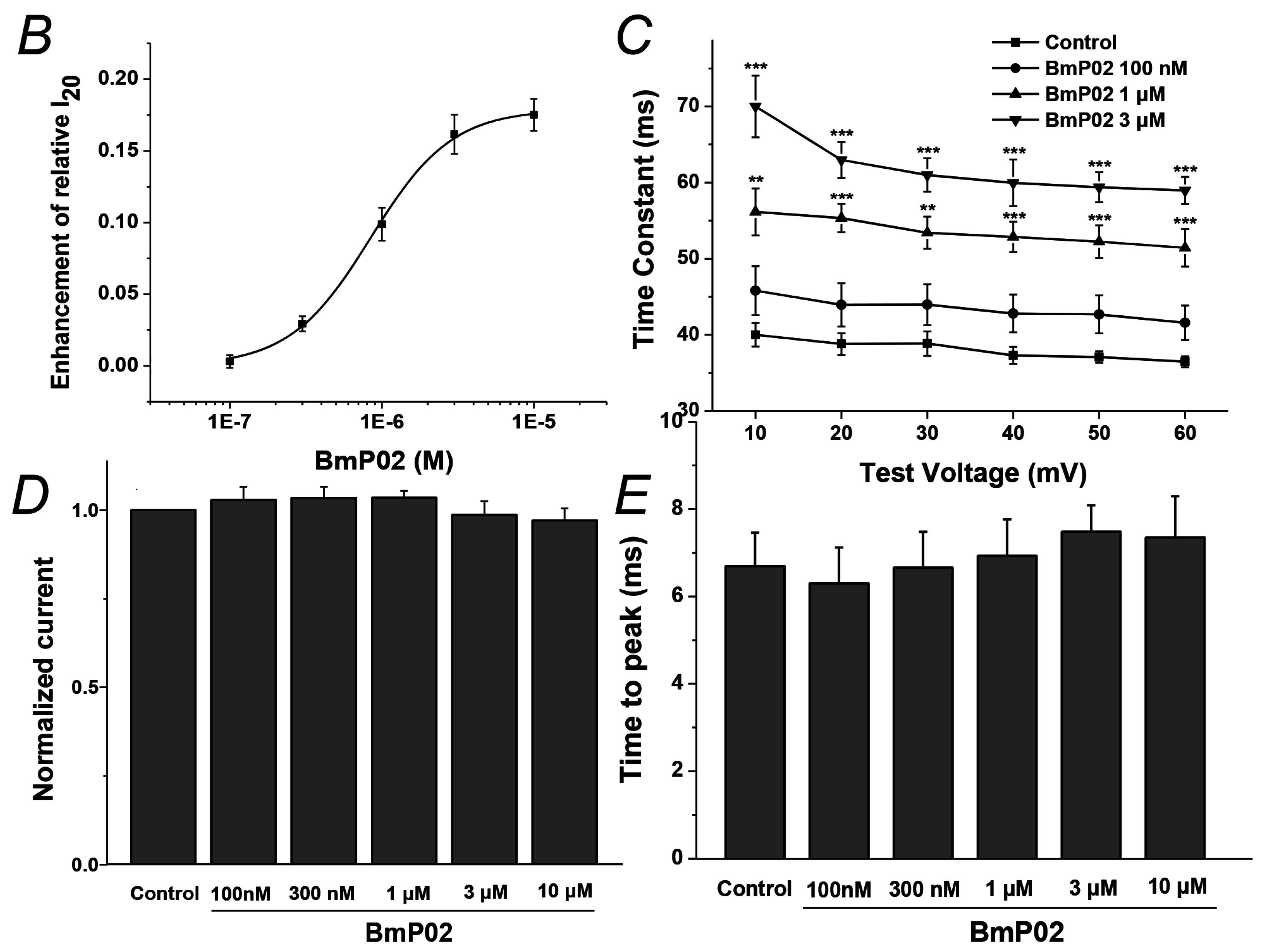
2.1. BmP02 Delayes the Inactivation of Kv4.2
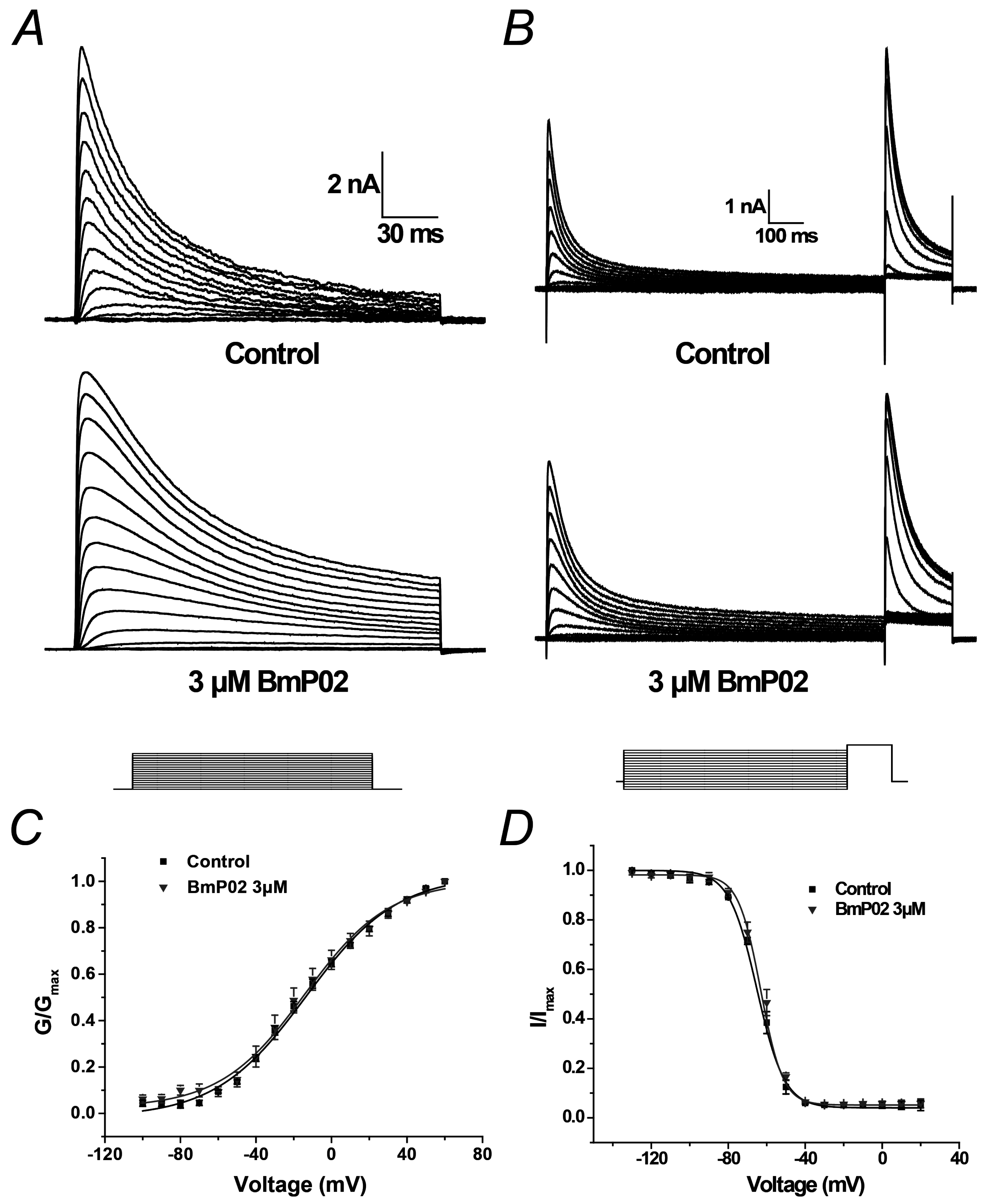
2.2. BmP02 Has No Effects on the Voltage-Dependence of Kv4.2 Activation and Inactivation
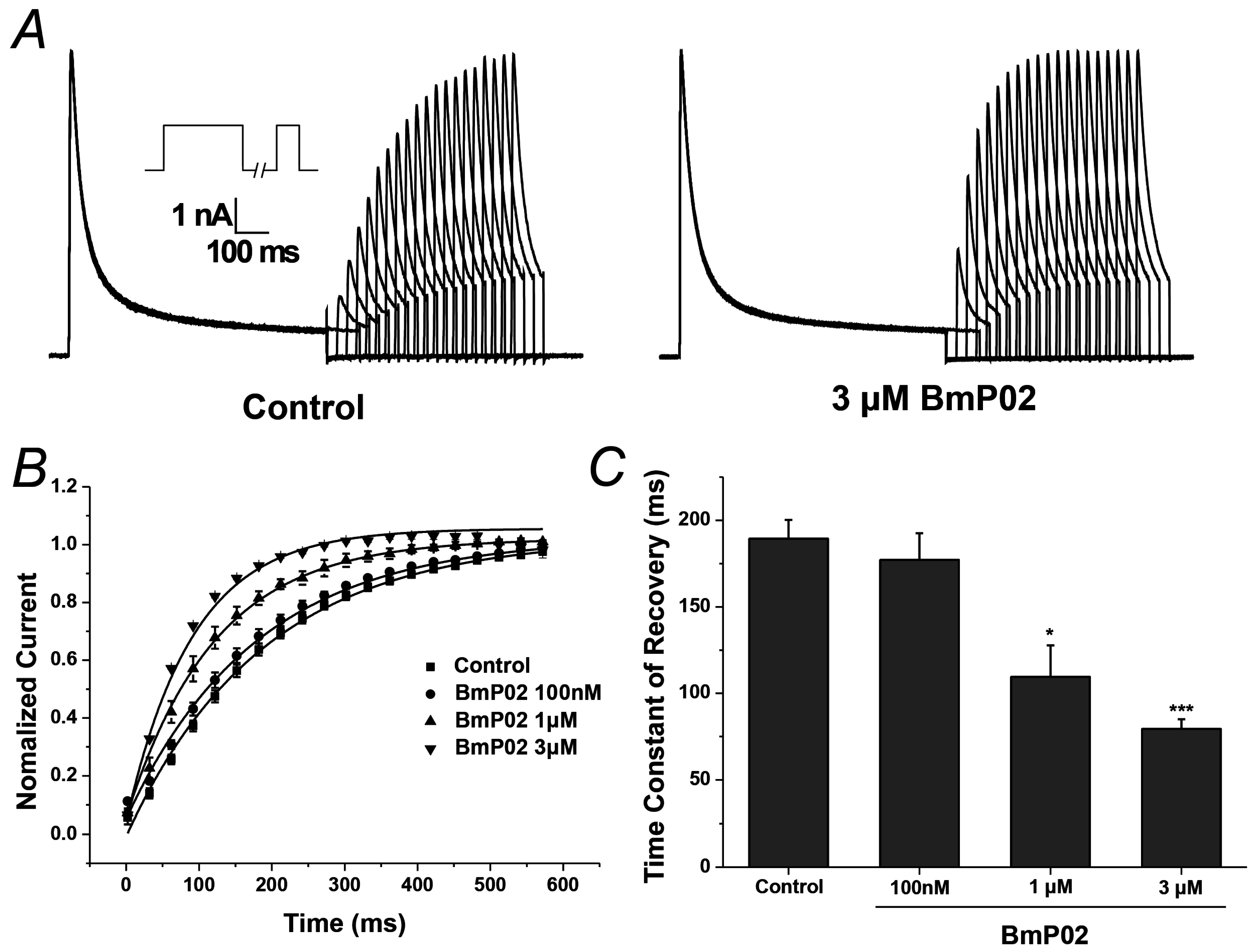
2.3. BmP02 Accelarates the Recovery of Kv4.2 Activity from Inactivation
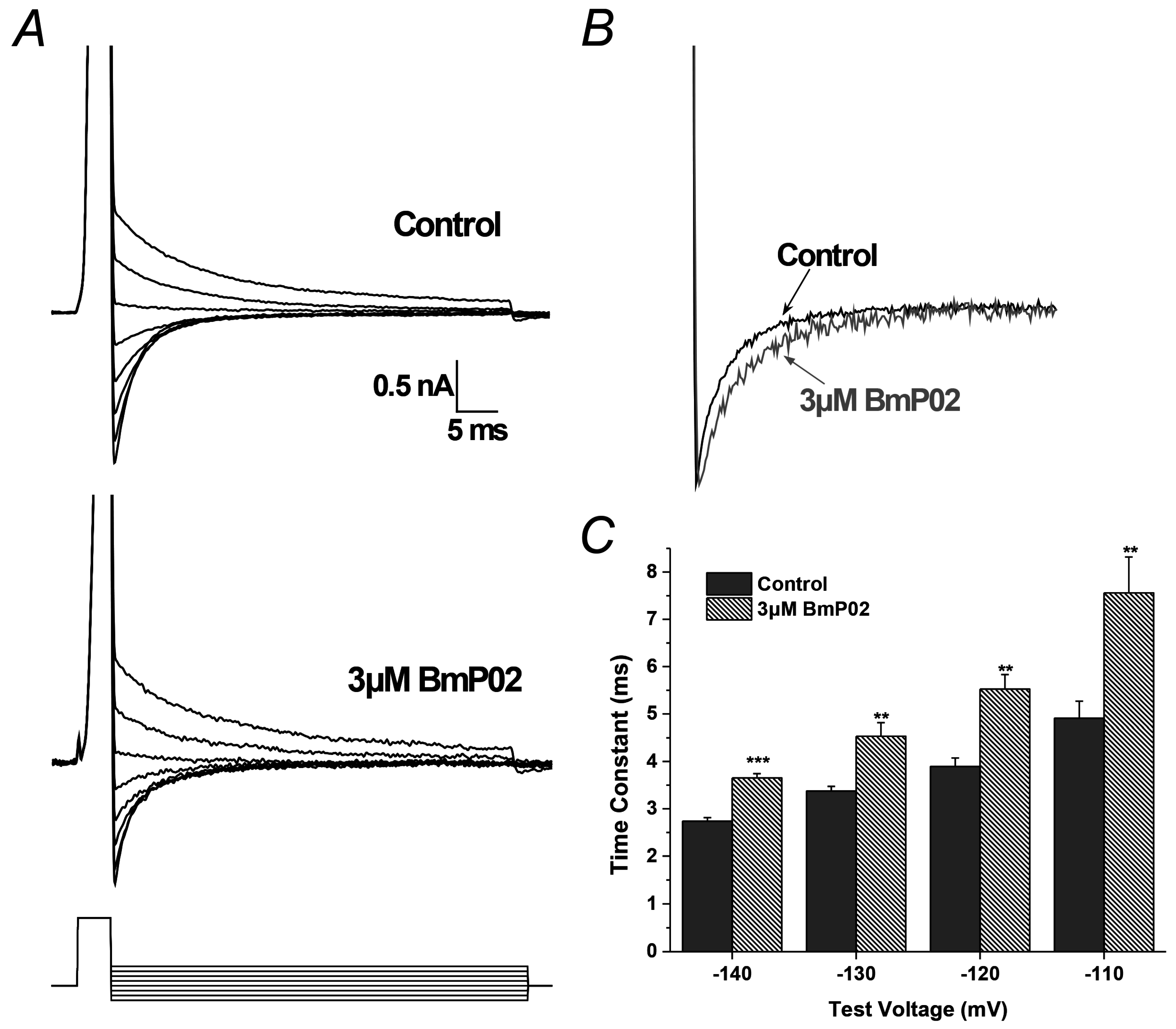
2.4. BmP02 Accelerated the Deactivation Process of Kv4.2
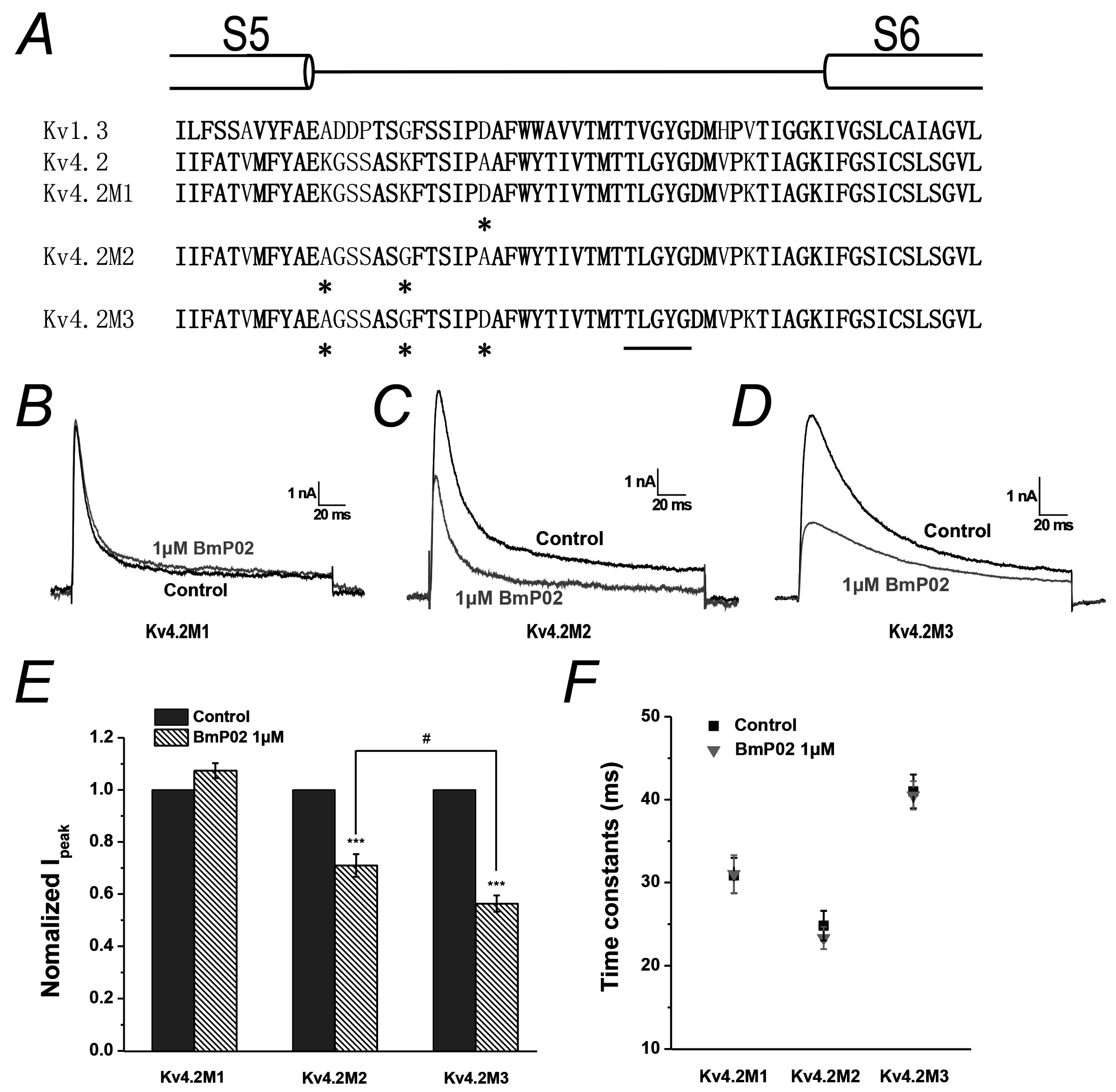
2.5. Amino Acid Residues Identified in Pore Region of Kv4.2 Mediate the Interaction between BmP02 and Kv4.2
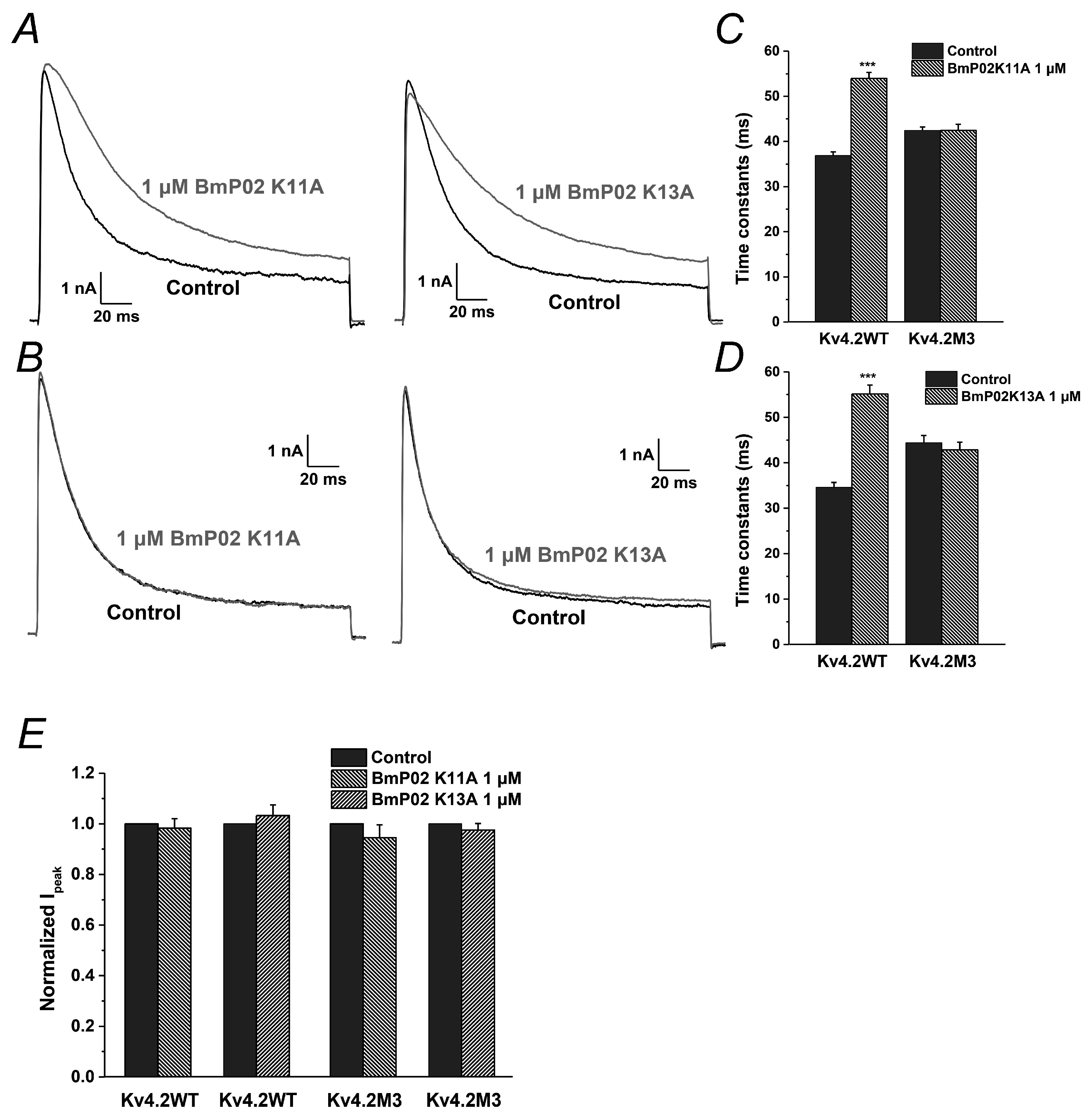
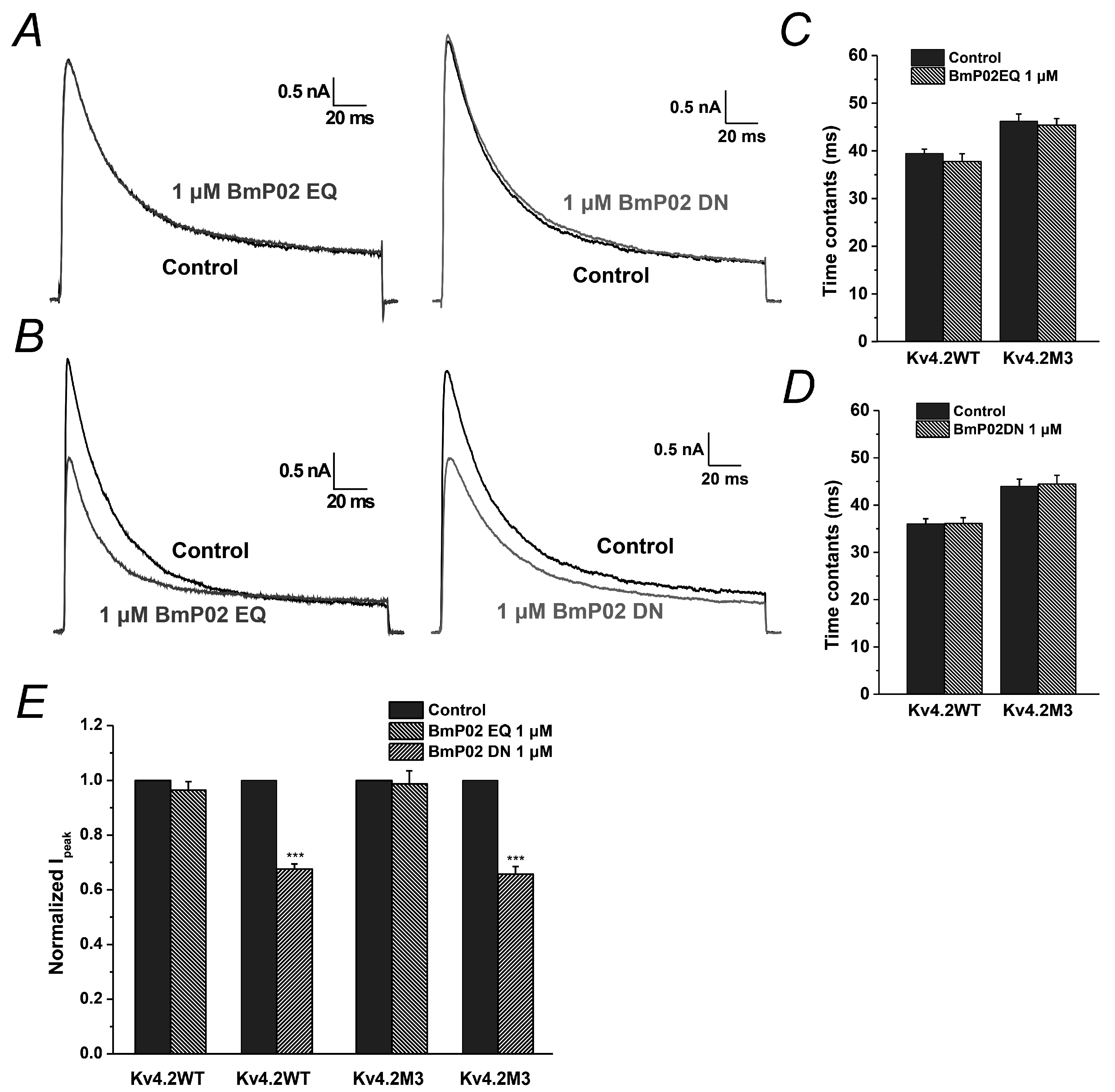
2.6. The Key Residues in BmP02 for Binding to Kv4.2 Are also Determined
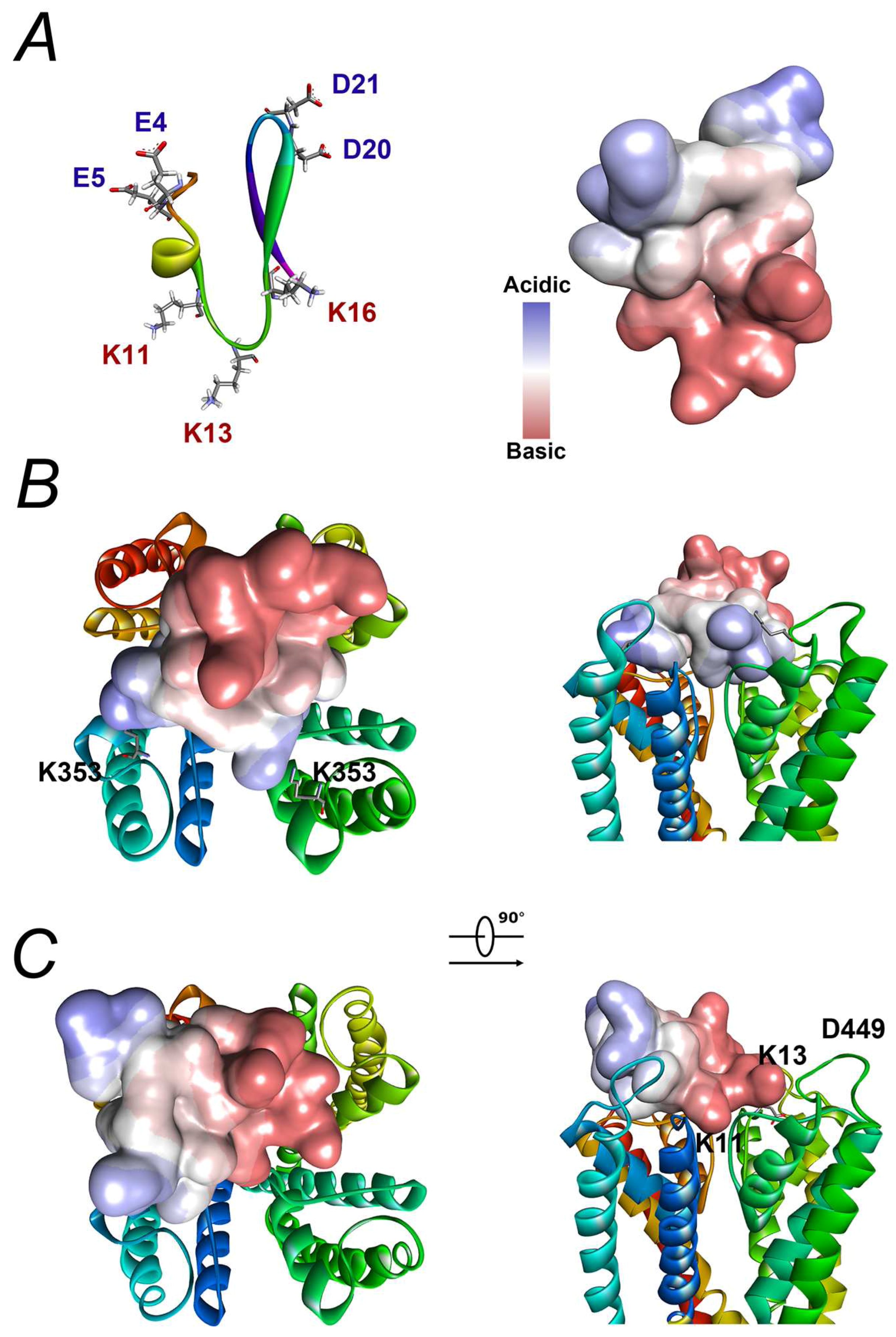
2.7. Modelling Reveals That the Interaction between BmP02 and Kv4.2 Is Unique
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plasmids and Cell Lines
4.2. Electrophysiological Recordings
4.3. Solutions and Drugs
- BmP02: VGCEECPMHCKGKNAKPTCDDGVCNCNV
- BmP02 K11A: VGCEECPMHCAGKNAKPTCDDGVCNCNV
- BmP02 K13A: VGCEECPMHCKGANAKPTCDDGVCNCNV
- BmP02EQ: VGCQQCPMHCKGKNAKPTCDDGVCNCNV
- BmP02DN: VGCEECPMHCKGKNAKPTCNNGVCNCNV.
4.4. 3D Modeling
4.5. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gutman, G.A.; Chandy, K.G.; Grissmer, S.; Lazdunski, M.; McKinnon, D.; Pardo, L.A.; Robertson, G.A.; Rudy, B.; Sanguinetti, M.C.; Stuhmer, W.; et al. International union of pharmacology. LIII. Nomenclature and molecular relationships of voltage-gated potassium channels. Pharmacol. Rev. 2005, 57, 473–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birnbaum, S.G.; Varga, A.W.; Yuan, L.L.; Anderson, A.E.; Sweatt, J.D.; Schrader, L.A. Structure and function of Kv4-family transient potassium channels. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 803–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rainnie, D.G.; Hazra, R.; Dabrowska, J.; Guo, J.D.; Li, C.C.; Dewitt, S.; Muly, E.C. Distribution and functional expression of Kv4 family alpha subunits and associated KChiP beta subunits in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. J. Comp. Neurol. 2014, 522, 609–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isbrandt, D.; Leicher, T.; Waldschutz, R.; Zhu, X.; Luhmann, U.; Michel, U.; Sauter, K.; Pongs, O. Gene structures and expression profiles of three human KCND (Kv4) potassium channels mediating A-type currents I(to) and I(sa). Genomics 2000, 64, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Wong, V.; Sihn, C.R.; Lv, P.; Perez Flores, M.C.; Mousavi-Nik, A.; Doyle, K.J.; Xu, Y.; et al. Functional significance of k+ channel beta-subunit KCNE3 in auditory neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 16802–16813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truchet, B.; Manrique, C.; Sreng, L.; Chaillan, F.A.; Roman, F.S.; Mourre, C. Kv4 potassium channels modulate hippocampal EPSP-spike potentiation and spatial memory in rats. Learn. Mem. 2012, 19, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- London, B.; Baker, L.C.; Petkova-Kirova, P.; Nerbonne, J.M.; Choi, B.R.; Salama, G. Dispersion of repolarization and refractoriness are determinants of arrhythmia phenotype in transgenic mice with long QT. J. Physiol. 2007, 578, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, R.P.; Kaur, K.; Hwang, E.; Ramirez, R.J.; Willis, B.C.; Filgueiras-Rama, D.; Ennis, S.R.; Takemoto, Y.; Ponce-Balbuena, D.; Zarzoso, M.; et al. Dominant frequency increase rate predicts transition from paroxysmal to long-term persistent atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2014, 129, 1472–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tytgat, J.; Chandy, K.G.; Garcia, M.L.; Gutman, G.A.; Martin-Eauclaire, M.F.; van der Walt, J.J.; Possani, L.D. A unified nomenclature for short-chain peptides isolated from scorpion venoms: Alpha-KTx molecular subfamilies. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1999, 20, 444–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez de la Vega, R.C.; Merino, E.; Becerril, B.; Possani, L.D. Novel interactions between k+ channels and scorpion toxins. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2003, 24, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, A.; Giller, K.; Hornig, S.; Martin-Eauclaire, M.F.; Pongs, O.; Becker, S.; Baldus, M. Toxin-induced conformational changes in a potassium channel revealed by solid-state nmr. Nature 2006, 440, 959–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, A.; Lee, A.; Campbell, E.; Mackinnon, R. Structure of a pore-blocking toxin in complex with a eukaryotic voltage-dependent k(+) channel. eLife 2013, 2, e00594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisciotta, M.; Coronas, F.I.; Bloch, C.; Prestipino, G.; Possani, L.D. Fast k(+) currents from cerebellum granular cells are completely blocked by a peptide purified from androctonus australis garzoni scorpion venom. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1468, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huys, I.; Xu, C.Q.; Wang, C.Z.; Vacher, H.; Martin-Eauclaire, M.F.; Chi, C.W.; Tytgat, J. BmTx3, a scorpion toxin with two putative functional faces separately active on A-type K+ and HERG currents. Biochem. J. 2004, 378, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Wu, J.; Pei, J.; Shi, Y.; Ji, Y.; Tong, Q. Solution structure of BmP02, a new potassium channel blocker from the venom of the chinese scorpion buthus martensi karsch. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 13669–13675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romi-Lebrun, R.; Martin-Eauclaire, M.F.; Escoubas, P.; Wu, F.Q.; Lebrun, B.; Hisada, M.; Nakajima, T. Characterization of four toxins from buthus martensi scorpion venom, which act on apamin-sensitive Ca2+-activated k+ channels. FEBS 1997, 245, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Gao, B.; Luo, L.; Zhu, S. Two dyad-free shaker-type k(+) channel blockers from scorpion venom. Toxicon 2012, 59, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Q.C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.P.; Zhou, Z.N.; Ji, Y.H. The blocking effect of BmP02, one novel short-chain scorpion peptide on transient outward k(+) channel of adult rat ventricular myocyte. Regul. Pept. 2000, 90, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Wu, B.F.; Feng, Y.J.; Tao, J.; Ji, Y.H. Mapping the Interaction Anatomy of BmP02 on Kv1.3 Channel. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.P.; Campbell, D.L. Transient outward potassium current, ‘Ito’, phenotypes in the mammalian left ventricle: Underlying molecular, cellular and biophysical mechanisms. J. Physiol. 2005, 569, 7–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ednie, A.R.; Bennett, E.S. Reduced sialylation impacts ventricular repolarization by modulating specific k+ channel isoforms distinctly. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 2769–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stehling, E.G.; Sforca, M.L.; Zanchin, N.I.; Oyama, S., Jr.; Pignatelli, A.; Belluzzi, O.; Polverini, E.; Corsini, R.; Spisni, A.; Pertinhez, T.A. Looking over toxin-k(+) channel interactions. Clues from the structural and functional characterization of alpha-KTx toxin Tc32, a Kv1.3 channel blocker. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 1885–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahjoubi-Boubaker, B.; Crest, M.; Khalifa, R.B.; El Ayeb, M.; Kharrat, R. Kbot1, a three disulfide bridges toxin from buthus occitanus tunetanus venom highly active on both SK and Kv channels. Peptides 2004, 25, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.H.; Li, Y.M.; Wu, G.; Cao, C.Y.; Wu, H.M. Three-dimensional structure of BmP03 from venom of scorpion buthus martensii Karsch. Acta Chim Sin. 2000, 58, 850–855. [Google Scholar]
- Pourrier, M.; Herrera, D.; Caballero, R.; Schram, G.; Wang, Z.; Nattel, S. The Kv4.2 N-terminal restores fast inactivation and confers KChlP2 modulatory effects on N-terminal-deleted Kv1.4 channels. Pflug. Arch. 2004, 449, 235–247. [Google Scholar]
- Zachariae, U.; Schneider, R.; Velisetty, P.; Lange, A.; Seeliger, D.; Wacker, S.J.; Karimi-Nejad, Y.; Vriend, G.; Becker, S.; Pongs, O.; et al. The molecular mechanism of toxin-induced conformational changes in a potassium channel: Relation to C-type inactivation. Structure 2008, 16, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barghaan, J.; Tozakidou, M.; Ehmke, H.; Bahring, R. Role of N-terminal domain and accessory subunits in controlling deactivation-inactivation coupling of Kv4.2 channels. Biophys. J. 2008, 94, 1276–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catterall, W.A. From ionic currents to molecular mechanisms: The structure and function of voltage-gated sodium channels. Neuron 2000, 26, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Liu, Z.; Dong, B.; Zhou, J.; Zhu, H.; Ji, Y. Molecular determination of selectivity of the site 3 modulator (BmK I) to sodium channels in the CNS: A clue to the importance of NAv1.6 in BmK I-induced neuronal hyperexcitability. Biochem. J. 2010, 431, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tejedor, F.J.; Catterall, W.A. Site of covalent attachment of alpha-scorpion toxin derivatives in domain I of the sodium channel alpha subunit. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 8742–8746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, W.J.; Catterall, W.A. Localization of the receptor site for alpha-scorpion toxins by antibody mapping: Implications for sodium channel topology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 10161–10165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, D.A.; Morais Cabral, J.; Pfuetzner, R.A.; Kuo, A.; Gulbis, J.M.; Cohen, S.L.; Chait, B.T.; MacKinnon, R. The structure of the potassium channel: Molecular basis of k+ conduction and selectivity. Science 1998, 280, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Group | Activation | Inactivation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V1/2 (mV) | k | n | V1/2 (mV) | k | n | |
| Control | −13.87 ± 1.61 | 23.88 ± 1.90 | 10 | −64.81 ± 1.73 | 6.86 ± 1.29 | 10 |
| BmP02 | −14.23 ± 1.76 | 23.07 ± 2.05 | 10 | −62.99 ± 1.81 | 5.93 ± 1.30 | 10 |
| Constants | Control | Concentration of BmP02 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 nM | 1 μM | 3 μM | ||
| τ (ms) | 189.35 ± 10.87 | 177.15 ± 15.41 | 109.58 ± 18.10 * | 79.45 ± 5.62 *** |
| n | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, B.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, J.; Tao, J.; Ji, Y. BmP02 Atypically Delays Kv4.2 Inactivation: Implication for a Unique Interaction between Scorpion Toxin and Potassium Channel. Toxins 2016, 8, 280. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8100280
Wu B, Zhu Y, Shi J, Tao J, Ji Y. BmP02 Atypically Delays Kv4.2 Inactivation: Implication for a Unique Interaction between Scorpion Toxin and Potassium Channel. Toxins. 2016; 8(10):280. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8100280
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Bin, Yan Zhu, Jian Shi, Jie Tao, and Yonghua Ji. 2016. "BmP02 Atypically Delays Kv4.2 Inactivation: Implication for a Unique Interaction between Scorpion Toxin and Potassium Channel" Toxins 8, no. 10: 280. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8100280
APA StyleWu, B., Zhu, Y., Shi, J., Tao, J., & Ji, Y. (2016). BmP02 Atypically Delays Kv4.2 Inactivation: Implication for a Unique Interaction between Scorpion Toxin and Potassium Channel. Toxins, 8(10), 280. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8100280





