Occurrence and Seasonal Variations of Lipophilic Marine Toxins in Commercial Clam Species along the Coast of Jiangsu, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
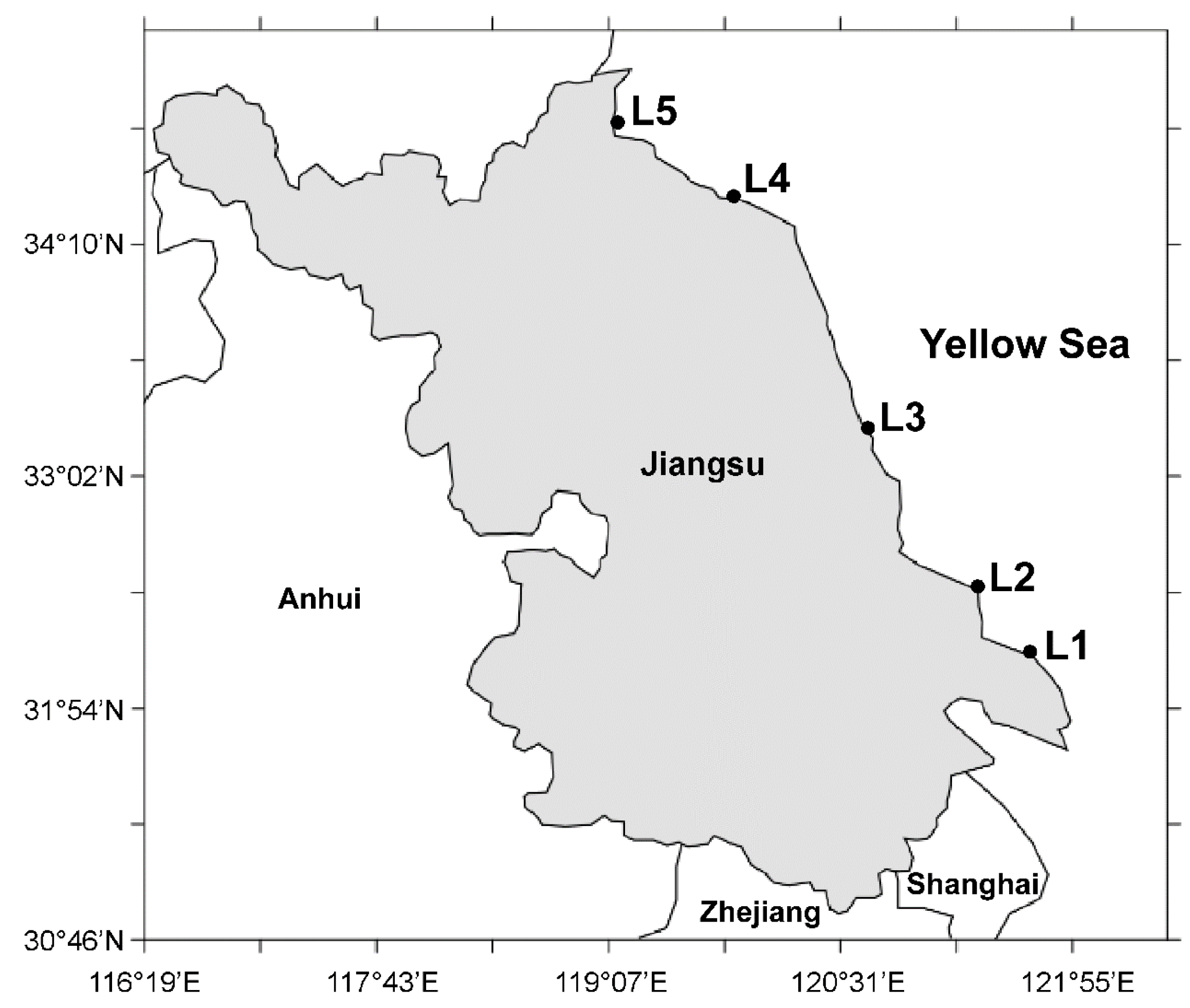
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. UFLC-MS/MS and Pre-Treatment Method Optimization
2.1.1. Optimization of Chromatographic Separation
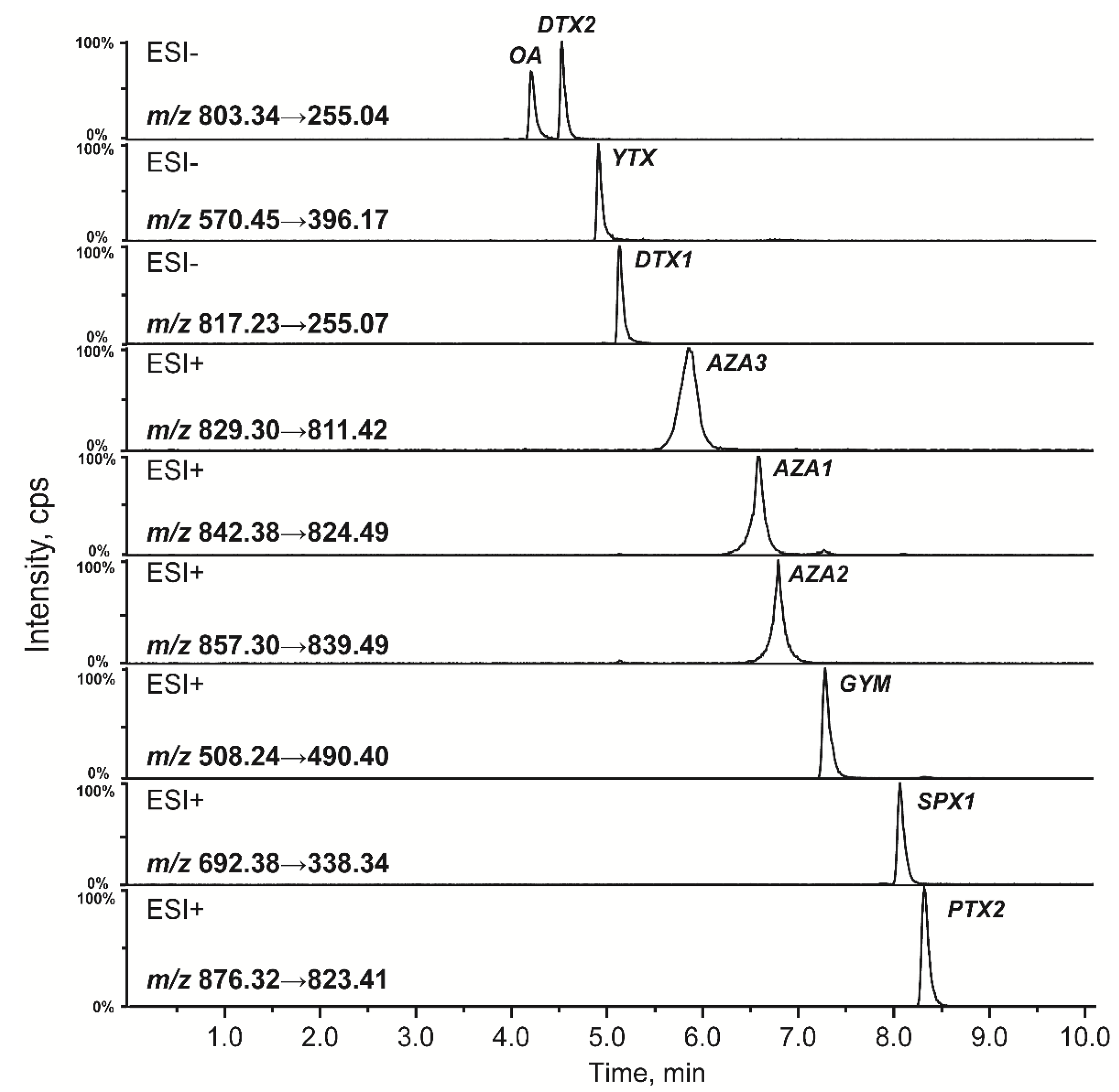
2.1.2. Optimization of MS/MS Parameters
| Toxins | ESI Mode | Precursor (m/z) | Product (m/z) | CE | DP | CXP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GYM | ESI+ | 508.24 | 490.40 | 33 | 206 | 42 |
| 160.2 | 55 | 206 | 20 | |||
| PTX2 | ESI+ | 876.32 | 823.41 | 33 | 36 | 34 |
| 213.1 | 45 | 36 | 12 | |||
| SPX1 | ESI+ | 692.38 | 338.34 | 25 | 41 | 36 |
| 164.2 | 56 | 41 | 32 | |||
| AZA1 | ESI+ | 842.4 | 824.49 | 41 | 81 | 34 |
| 672.4 | 68 | 81 | 45 | |||
| AZA2 | ESI+ | 857.3 | 839.49 | 42 | 21 | 34 |
| 673.5 | 65 | 21 | 52 | |||
| AZA3 | ESI+ | 829.3 | 811.42 | 39 | 11 | 34 |
| 659.4 | 61 | 11 | 39 | |||
| OA | ESI− | 803.5 | 255.04 | −62 | −30 | −17 |
| 112.80 | −67 | −30 | −15 | |||
| DTX1 | ESI− | 817.2 | 255.07 | −62 | −50 | −19 |
| 113.04 | −54 | −50 | −13 | |||
| DTX2 | ESI− | 803.5 | 255.09 | −58 | −45 | −21 |
| 113.08 | −30 | −45 | −15 | |||
| YTX | ESI− | 570.45 | 396.17 | −80 | −45 | −18 |
| 476.35 | −31 | −45 | −44 |
2.1.3. Optimization of the Sample Pre-Treatment Method
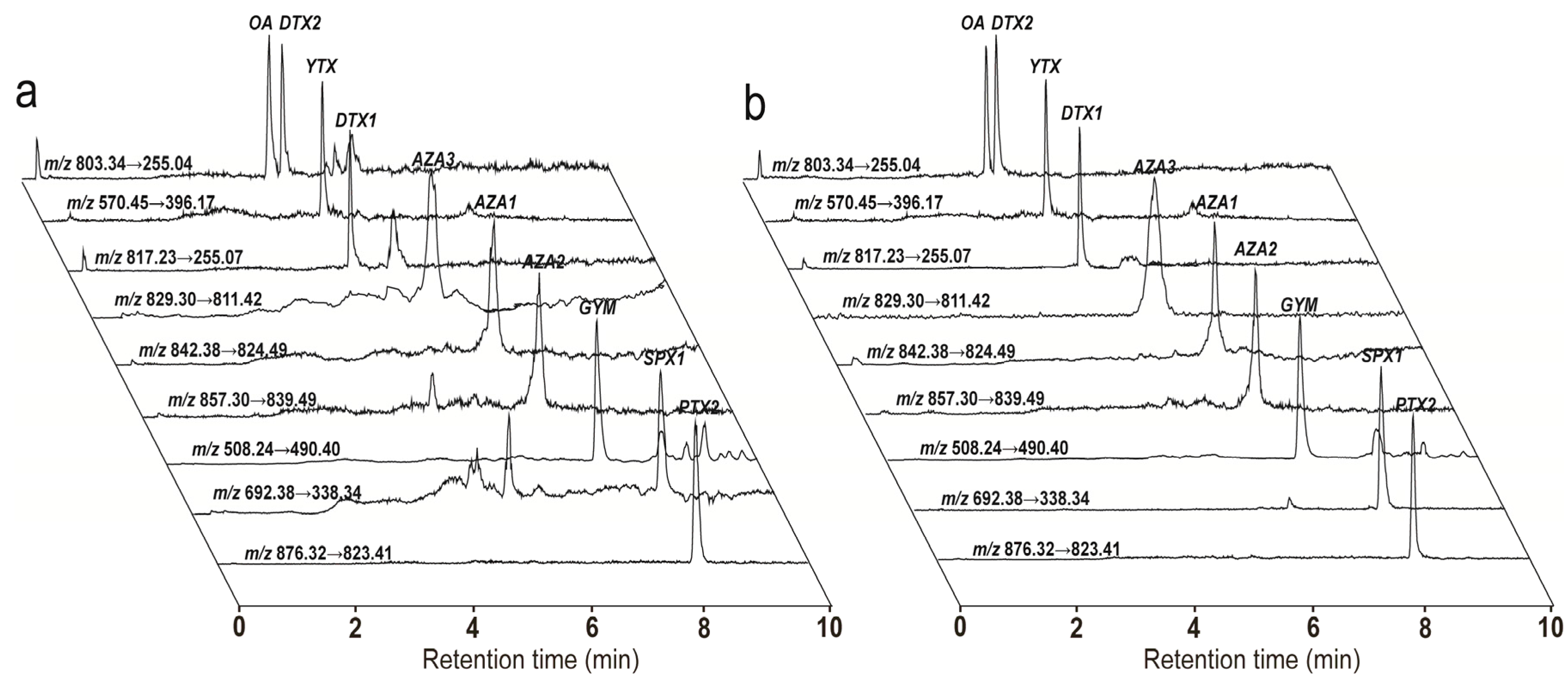
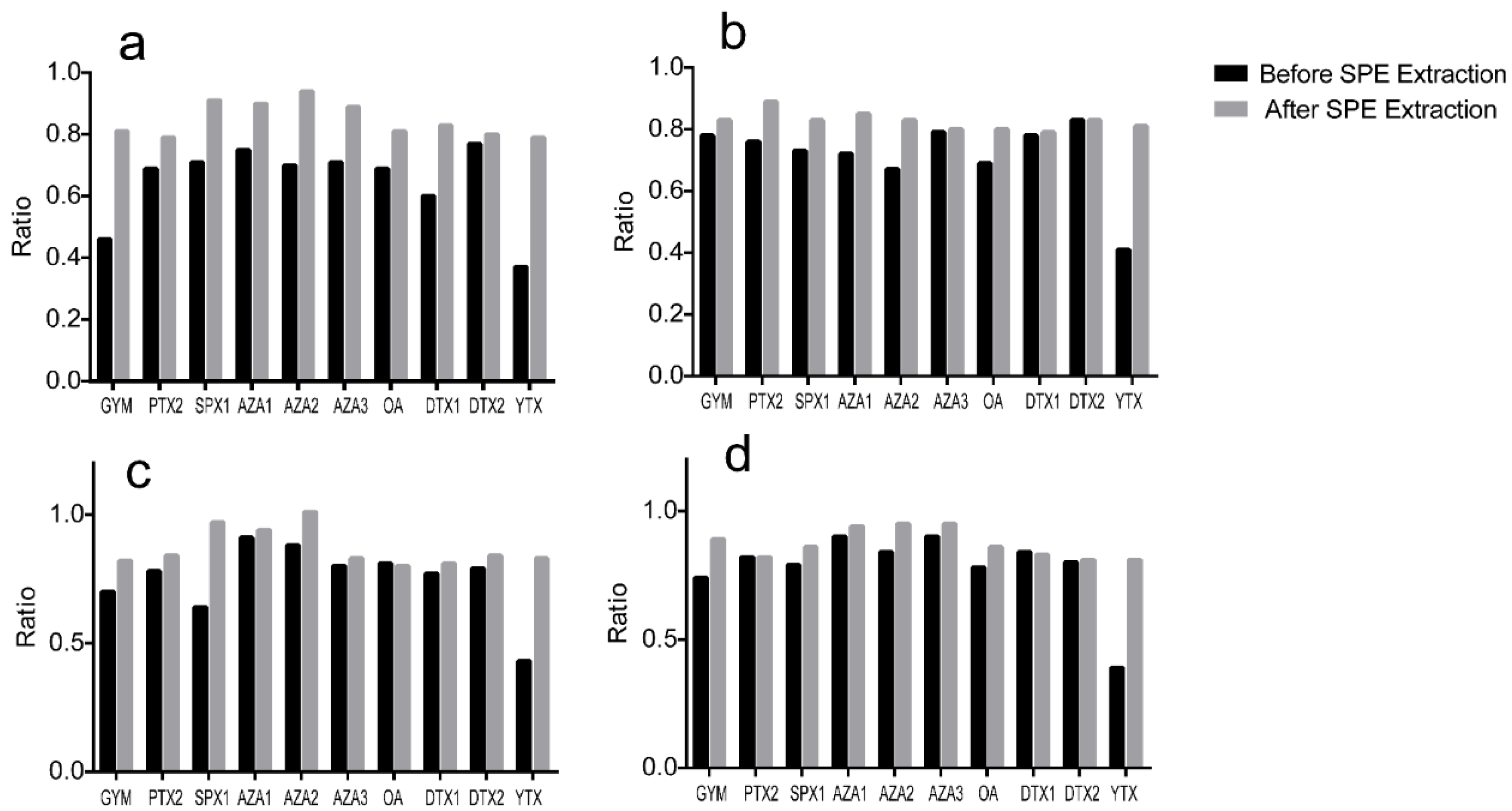
2.2. Method Performance
| Toxins | Solvent | M. meretrix | R. philippinarum | C. sinensis | M. meretrix | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Curve | R2 | LOD (μg/kg) | LOQ (μg/kg) | Curve | R2 | LOD (μg/kg) | LOQ (μg/kg) | Ratio a | Curve | R2 | LOD (μg/kg) | LOQ (μg/kg) | Ratio a | Curve | R2 | LOD (μg/kg) | LOQ (μg/kg) | Ratio a | Curve | R2 | LOD (μg/kg) | LOQ (μg/kg) | Ratio a | |
| GYM | y = 122254x + 33042 | 0.9969 | 0.01 | 0.02 | y = 99098x + 5125 | 0.9959 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.81 | y = 101305x + 24625 | 0.9987 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.83 | y = 99840x + 52125 | 0.9946 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.82 | y = 108656x − 24458 | 0.9935 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.89 |
| PTX2 | y = 33852x + 27875 | 0.9943 | 0.01 | 0.03 | y = 26711x + 10125 | 0.9975 | 0.10 | 0.34 | 0.79 | y = 30143x − 8254.2 | 0.999 | 0.04 | 0.15 | 0.89 | y = 28520x + 26017 | 0.9955 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.84 | y = 27772x + 38250 | 0.9949 | 0.07 | 0.21 | 0.82 |
| SPX1 | y = 34501x + 13083 | 0.9982 | 0.01 | 0.03 | y = 31367x + 139542 | 0.9974 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.91 | y = 28724x + 139250 | 0.9936 | 0.23 | 0.76 | 0.83 | y = 33315x + 66542 | 0.9981 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.97 | y = 29504x + 188000 | 0.9983 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.86 |
| AZA1 | y = 163976x + 18500 | 0.9946 | 0.01 | 0.02 | y = 147377x + 37208 | 0.9946 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.90 | y = 138922x + 241000 | 0.9961 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.85 | y = 153887x + 57458 | 0.995 | 0.04 | 0.12 | 0.94 | y = 154834x + 8333.3 | 0.9938 | 0.04 | 0.12 | 0.94 |
| AZA2 | y = 41999x + 4795.8 | 0.9948 | 0.01 | 0.02 | y = 39548x + 17808 | 0.9957 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.94 | y = 34863x + 20754 | 0.9956 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.83 | y = 42323x + 13600 | 0.9963 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 1.01 | y = 39863x − 270.83 | 0.9932 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.95 |
| AZA3 | y = 52647x + 5875 | 0.9959 | 0.01 | 0.04 | y = 47014x + 38983 | 0.9944 | 0.06 | 0.19 | 0.89 | y = 42359x + 9708.3 | 0.9996 | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.80 | y = 43498x − 2700 | 0.9964 | 0.06 | 0.20 | 0.83 | y = 49917x + 31592 | 0.9952 | 0.04 | 0.14 | 0.95 |
| OA | y = 21901x + 5875 | 0.9959 | 0.02 | 0.08 | y = 17703x + 9116.7 | 0.9974 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.81 | y = 17482x − 1487.5 | 0.9994 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.80 | y = 17613x − 2658.3 | 0.9994 | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.80 | y = 18871x − 11983 | 0.9988 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.86 |
| DTX1 | y = 40048x + 1545.8 | 0.9944 | 0.03 | 0.12 | y = 33291x + 6500 | 0.997 | 0.04 | 0.12 | 0.83 | y = 31723x − 1595.8 | 0.9971 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.79 | y = 32429x −1529.2 | 0.9931 | 0.08 | 0.27 | 0.81 | y = 33216x − 900 | 0.9964 | 0.04 | 0.12 | 0.83 |
| DTX2 | y = 9072.9x + 1250 | 0.9992 | 0.01 | 0.02 | y = 7286.3x + 10404 | 0.9974 | 0.11 | 0.34 | 0.80 | y = 7503.6x + 9516.7 | 0.9978 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.83 | y = 7656.1x + 14129 | 0.9978 | 0.04 | 0.14 | 0.84 | y = 7305.8x + 13629 | 0.9978 | 0.06 | 0.21 | 0.81 |
| YTX | y = 10246x − 8650 | 0.9974 | 0.02 | 0.07 | y = 8110.7x − 3329.2 | 0.9977 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.79 | y = 8262x − 8270.8 | 0.9981 | 0.06 | 0.20 | 0.81 | y = 8552.1x − 9491.7 | 0.9974 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.83 | y = 8303.7x + 4625 | 0.9987 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.81 |
2.3. Occurrence of LMTs in Clams Cultivated in Jiangsu
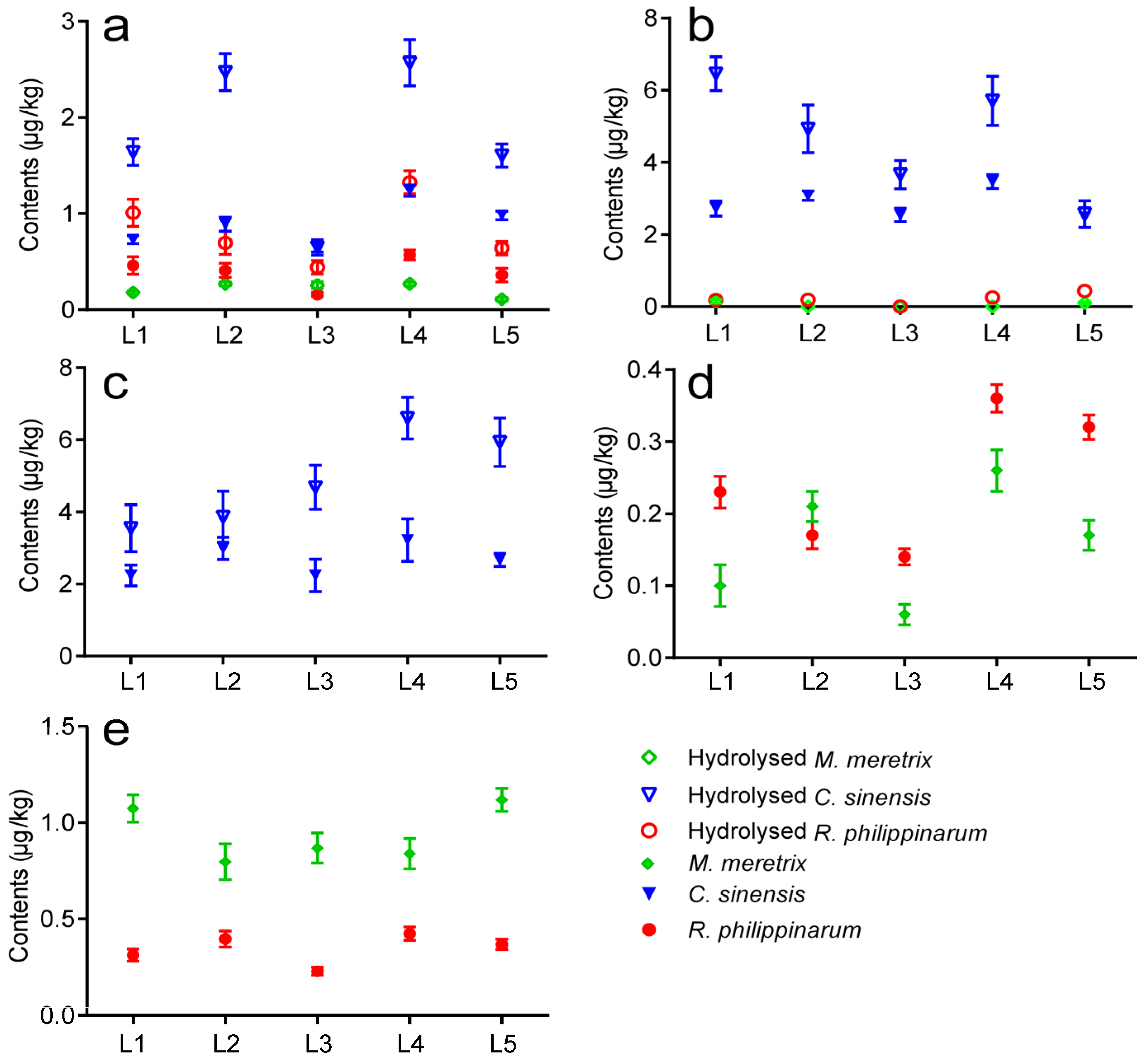
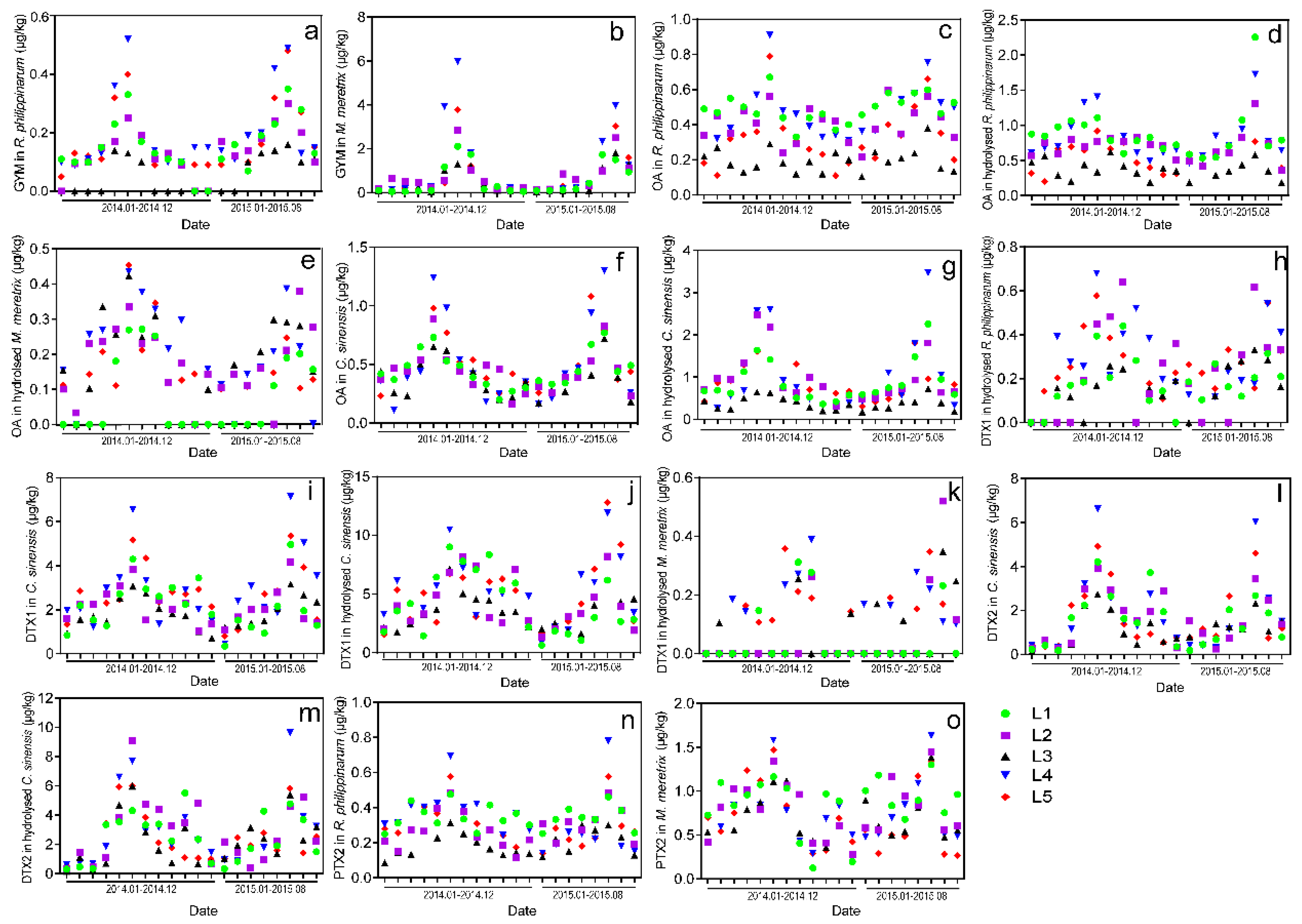
2.4. Monthly Variations of LMTs in Clams Cultivated in Jiangsu during 2014–2015
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Standards and Reagents
3.2. Sample Collections
3.3. Standards and Extracts Preparations
3.4. UFLC-MS/MS Method
3.5. Method Validation
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- An offline SPE coupled with the UFLC-MS/MS method was developed for the first time to determine the presence of 10 LMTs, including GYM, AZA1-3, DTX1&2, OA, PTX2, SPX1, and YTX in M. veneriformis, R. philippinarum, M. meretrix, and C. sinensis samples. This method is validated by precision, sensitivity, repeatability, recovery, and suitability for the routine monitoring of typical LMTs in clam samples.
- (2)
- The validated method was successfully applied to determine the presence of LMTs in clam samples collected from five aquaculture zones of Jiangsu Province. Results showed that GYM and PTX2 were found in R. philippinarum and M. meretrix samples, OA was observed in R. philippinarum and C. sinensis samples, and DTX1 and DTX2 were detected only in C. sinensis samples from all five locations in May 2014.
- (3)
- The monthly variations of LMTs (including GYM, PTX2, DTX1, DTX2, and OA) in different clam species were verified from January 2014 to August 2015, and the highest concentrations of the aforementioned LMTs were observed during May through August. Although the toxin levels of all samples were much lower than the EU regulatory limits, they might be underestimated due to the restricted toxin variety we detected.
- (4)
- The LMTs monitoring method we developed in this study could evaluate the potential risk and safety of clams for local consumers. The seasonal variation information we offered could guide local farmers or consumers to choose appropriate season or locations for clam harvesting. Further studies should focus on improving our current understanding of the distribution pattern and population dynamics of toxic algae in this area as well as the transportation and transformation of these toxins in the different clam species.
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ni, G. Phylogeography of Four Marine Bivalves along China’s Coastline, with Views into the Evolutionary Processes and Mechanisms. Ph.D. Thesis, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China, 28 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.Q.; Yuan, Q.; Wang, Y.L.; Jiang, M. Environmental quality evaluation on the mud-flat Meretrix meretrix aquaculture area in Rudong of Jiangsu Province, China. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2012, 31, 2480–2485. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Y. Environment Quality Assessment of the Shellfish Culture Area at Rudong, Jiangsu Province. Ph.D. Thesis, Ocean University of Shanghai, Shanghai, China, 20 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, A.H.; Yao, G.X. The breeding situation and countermeasures research of Jiangsu commercial shellfish. Sci. Fish. Farm. 2005, 3, 3–5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Jiang, M.; Shen, X.Q.; Wang, Y.L.; Yuan, Q. Culture capacity of Meretrix meretrix in mud flats of Rudong, Jiangsu province. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2014, 5, 754–756. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, M.R.; Shang, Z.T. Analysis of the climatic suitability for culturing seashell in the coastal areas of Jiangsu. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2008, 36, 14569–14572. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Wu, H.; Cheng, J.M.; Wang, X.Z.; Yang, X.L.; Qiu, Y.Y.; Wang, L.C. The status and prospect of comprehensive utilization of bivalve derived from Jiangsu coastal area. J. Nanjing Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2015, 31, 93–95. [Google Scholar]
- Shumway, S.E. A review of the effects of algal blooms on shellfish and aquaculture. J. World Aquacul. Soc. 1990, 21, 65–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerssen, A.; Pol-Hofstad, I.E.; Poelman, M.; Mulder, P.P.; van den Top, H.J.; de Boer, J. Marine toxins: Chemistry, toxicity, occurrence and detection, with special reference to the Dutch situation. Toxins 2010, 2, 878–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, K.J.; Carey, B.; O’Halloran, J.; van Pelt, F.N.; Skrabakova, Z. Shellfish toxicity: Human health implications of marine algal toxins. Epidemiol. Infect. 2010, 138, 927–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrouchi, R.; Rome, G.; Kharrat, R.; Molgo, J.; Benoit, E. Analysis of the action of gymnodimine-A and 13-desmethyl spirolide C on the mouse neuromuscular system in vivo. Toxicon 2013, 75, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tubaro, A.; Sosa, S.; Carbonatto, M.; Altinier, G.; Vita, F.; Melato, M.; Satake, M.; Yasumoto, T. Oral and intraperitoneal acute toxicity studies of yessotoxin and homoyessotoxins in mice. Toxicon 2003, 41, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, C.O.; Wilkins, A.L.; Munday, J.S.; Munday, R.; Hawkes, A.D.; Jensen, D.J.; Conney, J.M.; Beuzenberg, V. Production of 7-epi-pectenotoxin-2 seco acid and assessment of its acute toxicity to mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dolah, F.M. Marine algal toxins: Origins, health effects, and their increased occurrence. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahl, E.; Johannessen, T. Relationship between occurrence of Dinophysis species (Dinophyceae) and shellfish toxicity. Phycologia 2001, 40, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, E.; Yu, Q.; Eaglesham, G.; Connell, D.W.; McBroom, J.; Costanzo, S.; Shaw, G.R. Occurrence and seasonal variations of algal toxins in water, phytoplankton and shellfish from North Stradbroke Island, Queensland, Australia. Mar. Environ. Res. 2007, 64, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, L.P.; Gonzalez, V.; Martinez, A.; Paz, B.; Lago, J.; Cordeiro, V.; Blanco, L.; Vieites, J.M.; Cabado, A.G. Occurrence of lipophilic marine toxins in shellfish from Galicia (NW of Spain) and synergies among them. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1666–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mafra, L.L.; Lopes, D.; Bonilauri, V.C.; Uchida, H.; Suzuki, T. Persistent Contamination of octopuses and mussels with lipophilic shellfish toxins during spring dinophysis blooms in a Subtropical Estuary. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 3920–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerssen, A.; Mulder, P.P.; de Boer, J. Screening of lipophilic marine toxins in shellfish and algae: Development of a library using liquid chromatography coupled to orbitrap mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 685, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Mendoza, E.; Sanchez-Bravo, Y.A.; Turner, A.; Blanco, J.; O’Neil, A.; Mancera-Flores, J.; Perez-Brunius, P.; Rivas, D.; Almazan-Becerril, A.; Pena-Manjarrez, J.L. Lipophilic toxins in cultivated mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) from Baja California, Mexico. Toxicon 2014, 90, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fux, E.; Bire, R.; Hess, P. Comparative accumulation and composition of lipophilic marine biotoxins in passive samplers and in mussels (M. edulis) on the West Coast of Ireland. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 523–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duinker, A.; Bergslien, M.; Strand, Ø.; Olseng, C.D.; Svardal, A. The effect of size and age on depuration rates of diarrhetic shellfish toxins (DST) in mussels (Mytilus edulis L.). Harmful Algae 2007, 6, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, J.; Marino, C.; Martin, H.; Acosta, C.P. Anatomical distribution of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning (DSP) toxins in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Toxicon 2007, 50, 1011–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aasen, J.; Samdal, I.A.; Miles, C.O.; Dahl, E.; Briggs, L.R.; Aune, T. Yessotoxins in Norwegian blue mussels (Mytilus edulis): Uptake from Protoceratium reticulatum, metabolism and depuration. Toxicon 2005, 45, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, A.D.; Goya, A.B. Occurrence and profiles of lipophilic toxins in shellfish harvested from Argentina. Toxicon 2015, 102, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zingone, A.; Siano, R.; D’Alelio, D.; Sarno, D. Potentially toxic and harmful microalgae from coastal waters of the Campania region (Tyrrhenian Sea, Mediterranean Sea). Harmful Algae 2006, 5, 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, K.M.; Flewelling, L.J.; Byrd, M.; Nunez, A.; Villareal, T.A. The 2008 Texas Dinophysis ovum bloom: Distribution and toxicity. Harmful Algae 2010, 9, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana, G.; van Meulebroek, L.; van Vooren, S.; de Rijcke, M.; Vandegehuchte, M.; Janssen, C.R.; Vanhaecke, L. Quantification and profiling of lipophilic marine toxins in microalgae by UHPLC coupled to high-resolution orbitrap mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 6345–6356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Ma, J.; Cao, J.; McCarron, P. Toxins in mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) associated with diarrhetic shellfish poisoning episodes in China. Toxicon 2012, 60, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Sun, G.; Qiu, J.; Fan, L. Lipophilic shellfish toxins in Dinophysis caudata picked cells and in shellfish from the East China Sea. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 3116–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, R.; Wang, S.; Wang, X. Detection, occurrence and monthly variations of typical lipophilic marine toxins associated with diarrhetic shellfish poisoning in the coastal seawater of Qingdao City, China. Chemosphere 2014, 111, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Liu, Z.S.; Tan, C.Y.; Guo, Y.P.; Li, L.; Ren, H.L.; Li, Y.S.; Hu, P.; Gong, S.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Contamination of commercially available seafood by key diarrhetic shellfish poisons along the coast of China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 1545–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Liang, Y.; Wu, X.; Xu, D.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L. First report on the detection of pectenotoxin groups in Chinese shellfish by LC-MS/MS. Toxicon 2011, 57, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Yao, J.; Guo, M.; Tan, Z.; Zhou, D.; Zhai, Y. Distribution of marine lipophilic toxins in shellfish products collected from the Chinese market. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 4281–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Qi, Y.; Jiang, T.; Wu, F.; Zhang, F. Dinophysis caudata generated lipophilic shellfish toxins in bivalves from the Nanji Islands, East China Sea. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2014, 32, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Xu, X.; Wei, J.; Chen, J.; Miu, R.; Huang, L.; Zhou, X.; Fu, Y.; Yan, R.; Wang, Z.; et al. Food-borne disease outbreak of Diarrhetic shellfish poisoning due to toxic mussel consumption: The first recorded outbreak in China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of People’s Republic of China. Method for the Determination of Diarrhetic Shellfish Poison in Shellfish for Export by Mouse Bioassay. Patent SN0294-93, 1 May 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, T.; Yoshizawa, R.; Kawamura, T.; Yamasaki, M. Interference of free fatty acids from the hepatopancreas of mussels with the mouse bioassay for shellfish toxins. Lipids 1996, 31, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domenech, A.; Cortes-Francisco, N.; Palacios, O.; Franco, J.M.; Riobo, P.; Llerena, J.J.; Vichi, S.; Caixach, J. Determination of lipophilic marine toxins in mussels. Quantification and confirmation criteria using high resolution mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1328, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fux, E.; McMillan, D.; Bire, R.; Hess, P. Development of an ultra-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry method for the detection of lipophilic marine toxins. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1157, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerssen, A.; McElhinney, M.A.; Mulder, P.P.; Bire, R.; Hess, P.; de Boer, J. Solid phase extraction for removal of matrix effects in lipophilic marine toxin analysis by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 394, 1213–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerssen, A.; Mulder, P.P.; McElhinney, M.A.; de Boer, J. Liquid chromato graphy-tandem mass spectrometry method for the detection of marine lipophilic toxins under alkaline conditions. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerssen, A.; van Olst, E.H.; Mulder, P.P.; de Boer, J. In-house validation of a liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method for the analysis of lipophilic marine toxins in shellfish using matrix-matched calibration. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 3079–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regueiro, J.; Rossignoli, A.E.; Álvarez, G.; Blanco, J. Automated on-line solid-phase extraction coupled to liquid chromatography—Tandem mass spectrometry for determination of lipophilic marine toxins in shellfish. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serandour, A.L.; Ledreux, A.; Morin, B.; Derick, S.; Augier, E.; Lanceleur, R.; Hamlaoui, S.; Moukha, S.; Furger, C.; Bire, R.; et al. Collaborative study for the detection of toxic compounds in shellfish extracts using cell-based assays. Part I: Screening strategy and pre-validation study with lipophilic marine toxins. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 1983–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- These, A.; Scholz, J.; Preiss-Weigert, A. Sensitive method for the determination of lipophilic marine biotoxins in extracts of mussels and processed shellfish by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry based on enrichment by solid-phase extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 4529–4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Union Reference Laboratory for Marine Biotoxins. EU-Harmonised Standard Operating Procedure for Determination of Lipophilic Marine Biotoxins in Molluscs by LC-MS/MS. Available online: http://aesan.msssi.gob.es/CRLMB/docs/docs/metodos_analiticos_de_desarrollo/EU-Harmonised-SOP-LIPO-LCMSMS_Version5.pdf (accessed on 5 January 2015).
- Pihlstrom, T. Method Validation and Quality Control Procedures for Pesticide Residues Analysis in Food and Feed, Document No. SANCO/10684/2009. Available online: http://www.crl-pesticides.eu/docs/public/tmplt_article.asp?CntID=820&LabID=100&Lang=EN&Pdf=False&Theme_ID=1 (accessed on 1 January 2015).
- Li, C.S.; Liu, N.; Lu, S.Z.; Xu, F.; Liu, M.; Guo, W.C. Detection method of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning-okadaic acid by high performance liquid chromatography. Chin. J. Publ. Health 2009, 15, 447–448. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.Y.; Zhang, H.Y. Analysis and detection of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning in seafood market of Shanghai. J. Health Toxicol. 2005, 19, 320–321. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.Y.; Gao, C.L.; Liang, Y.B.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Y.J.; Xu, D.Y. First evidence of Gymnodimine in Dendostrea crenulifrea collected from the coast of Beihai, China. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2008, 30, 171–174. [Google Scholar]
- European Food Safety Authority. Scientific Opinion: Marine Biotoxins in shellfish—Summary on regulated marine biotoxins scientific opinion of the panel on contaminants in the food chain (Question No EFSA-Q-2009-00685). EFSA J. 2009, 1306, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- European Food Safety Authority. Marine Biotoxins in Shellfish-Azaspiracid Group Scientific Opinion of the Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain. Available online: http://www.gencat.cat/salut/acsa/html/ca/dir2949/pdf/contam_ej_723_aza_en,0.pdf (accessed on 9 June 2008).
- Yao, J.; Tan, Z.; Zhou, D.; Guo, M.; Xing, L.; Yang, S. Determination of azaspiracid-1 in shellfishes by liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. Se Pu 2010, 28, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X. Population Dynamics and Toxin Production of Dinophysis Species in the Coastal Waters of Qingdao. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Oceanology Chinese Academy of Science, Qingdao, China, 1 April 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Granby, K.; Adersen, J.H.; Christensen, H.B. Analysis of pesticides in fruit, vegetables and cereals using methanolic extraction and detection by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 520, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.-Z.; Cheng, Y.; Li, N.; Wen, H.-M.; Liu, R.; Shan, C.-X.; Chai, C.; Wu, H. Occurrence and Seasonal Variations of Lipophilic Marine Toxins in Commercial Clam Species along the Coast of Jiangsu, China. Toxins 2016, 8, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8010008
Wang X-Z, Cheng Y, Li N, Wen H-M, Liu R, Shan C-X, Chai C, Wu H. Occurrence and Seasonal Variations of Lipophilic Marine Toxins in Commercial Clam Species along the Coast of Jiangsu, China. Toxins. 2016; 8(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xin-Zhi, Ying Cheng, Na Li, Hong-Mei Wen, Rui Liu, Chen-Xiao Shan, Chuan Chai, and Hao Wu. 2016. "Occurrence and Seasonal Variations of Lipophilic Marine Toxins in Commercial Clam Species along the Coast of Jiangsu, China" Toxins 8, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8010008
APA StyleWang, X.-Z., Cheng, Y., Li, N., Wen, H.-M., Liu, R., Shan, C.-X., Chai, C., & Wu, H. (2016). Occurrence and Seasonal Variations of Lipophilic Marine Toxins in Commercial Clam Species along the Coast of Jiangsu, China. Toxins, 8(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8010008





