Determination of Gonyautoxin-4 in Echinoderms and Gastropod Matrices by Conversion to Neosaxitoxin Using 2-Mercaptoethanol and Post-Column Oxidation Liquid Chromatography with Fluorescence Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
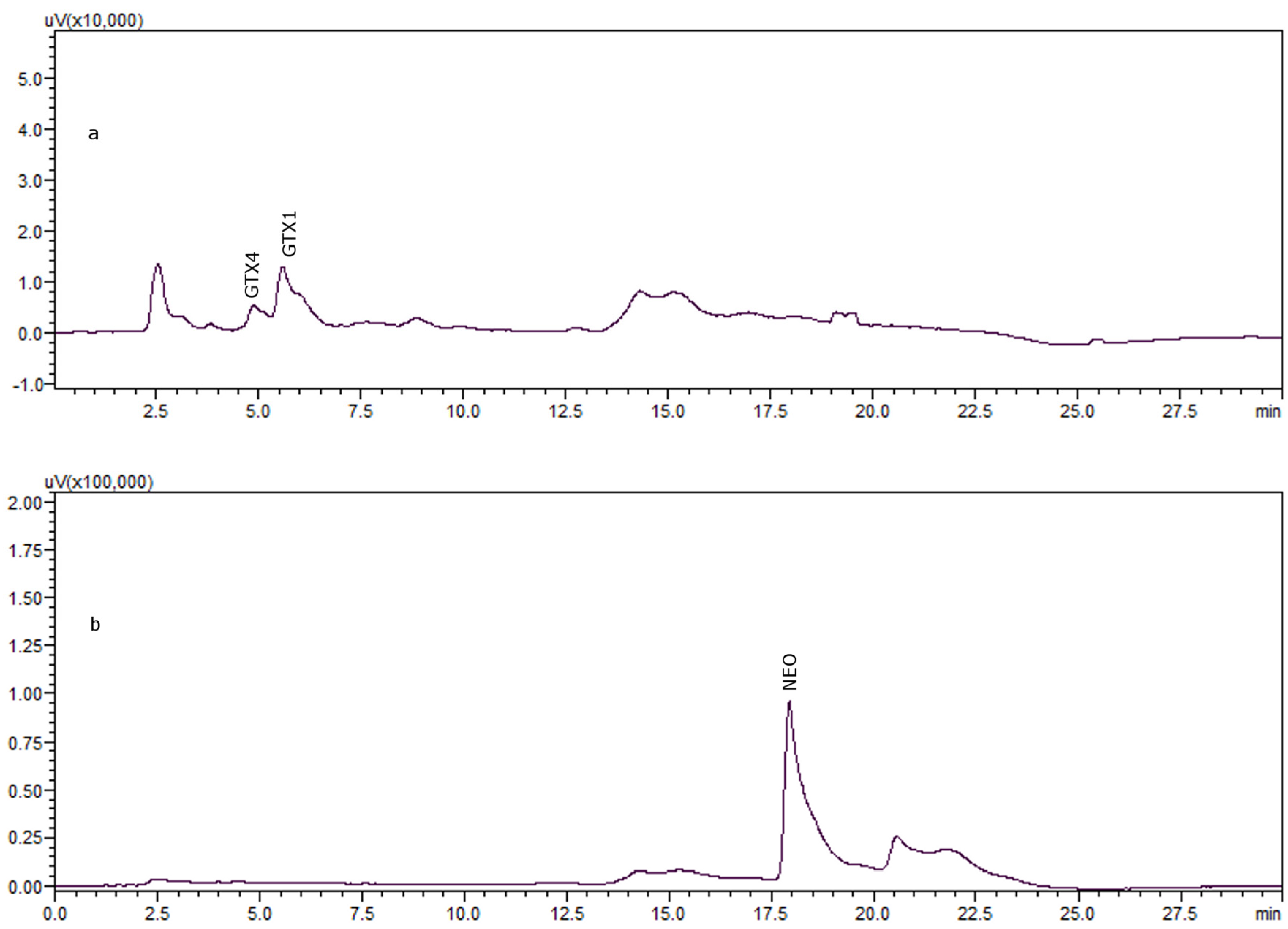
2. Results and Discussion
| Time (min) | 100 °C Water Bath | 100 °C Incubator | Gastropod Matrix | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average % | RSD % | Average % | RSD % | Average % | RSD % | |
| 10 | 59.5 | 0.8 | 64.5 | 2.8 | 62.2 | 1.2 |
| 15 | 55.3 | 0.3 | 58.4 | 1.7 | 69.7 | 1.5 |
| 20 | 62.6 | 1.0 | 58.9 | 1.0 | 71.9 | 1.1 |
| 25 | 81.1 | 1.2 | 61.4 | 1.0 | 80.2 | 1.5 |
| 30 | 82.2 | 1.1 | 50.5 | 1.4 | 84.3 | 1.3 |
| 35 | 65.8 | 1.8 | 47.7 | 1.0 | 71.1 | 1.4 |
| 40 | 64.8 | 1.3 | 31.0 | 2.4 | 68.0 | 1.8 |
| Code | Type of Organism | Species | Origin/Date of Collection | Before Transformation (μM) | After Transformation (μM) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GTX4 | GTX1 | NEO | GTX4 | ||||
| 351 | Gastropod | Umbraculum umbraculum | Madeira Island/September 2012 | 1.7 | 1.1 | 1.3 | 0.2 |
| 353 | Starfish | Echinaster sepositus | Madeira Island/September 2012 | 0.8 | 1.8 | 2.3 | 0.5 |
| 354 | Gastropod | Charonia lampas | Madeira Island/September 2012 | 90.5 | 3.8 | 29.3 | 25.5 |
| 412 | Starfish | Ophidiaster ophidianus | São Miguel Island, Azores/June 2013 | 17.3 | 3.7 | 4.4 | 0.7 |
| 424 | Starfish | O. ophidianus | São Miguel Island, Azores/June 2013 | 17.0 | - | 4.6 | 4.6 |
| 428 | Starfish | Marthaterias glacialis | São Miguel Island, Azores/June 2013 | 42.8 | 18.9 | 29.9 | 10.9 |
| 440 | Starfish | O. ophidianus | São Miguel Island, Azores/June 2013 | 26.4 | - | - | - |
| 443 | Gastropod | Stramonita haemostoma | Morocco/July 2013 | 428.6 | - | - | - |
| 454 | Gastropod | Cerithium vulgatum | Morocco/July 2013 | 121.6 | - | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| 470 | Gastropod | Monodonta lineata | Morocco/July 2013 | 3.9 | - | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| 474 | Gastropod | Onchidela celtica | Morocco/July 2013 | 6.9 | - | - | - |
| 475 | Gastropod | C. lampas | Morocco/July 2013 | 8.4 | - | - | - |
| 477 | Gastropod | Stramonita haemostoma | Morocco/July 2013 | 2.5 | - | - | - |
| 483 | Gastropod | Gibbula umbilicalis | Morocco/July 2013 | 13.3 | - | - | - |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Chemicals and Solutions
3.2. Sample Preparation and Transformation
3.3. HPLC Toxins Identification
3.4. Calculation of the Concentration of GTX4
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alexander, J.; Auðunsson, G.; Benford, D.; Cockburn, A.; Cravedi, J.; Dogliotti, E.; di Domenico, A.; Férnandez-Cruz, M.; Fürst, P.; Fink-Gremmels, J.; et al. Cross-contamination of non-target feedingstuffs by monensin authorised for use as a feed additive. EFSA J. 2008, 592, 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Rourke, W.A.; Murphy, C.J.; Pitcher, G.; van de Riet, J.M.; Burns, B.G.; Thomas, K.M.; Quilliam, M.A. Rapid postcolumn methodology for determination of paralytic shellfish toxins in shellfish tissue. J. AOAC Int. 2008, 91, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, S.M.; de Carvalho, M.; Mestre, T.; Ferreira, J.J.; Coelho, M.; Peralta, R.; Vale, P. Paralytic shellfish poisoning due to ingestion of gymnodinium catenatum contaminated cockles—Application of the AOAC HPLC official method. Toxicon 2012, 59, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, K.; Sommer, H.; Schoenholz, P. Shellfish poisoning. Medicine 1928, 2, 365–394. [Google Scholar]
- Bandem, D.; Trainer, V. Mode of action of toxins of seafood poisoning. In Algal Toxins in Seafood and Drinking Water; Falconer, I.R., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1993; p. 49. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, M.; Barreiro, A.; Rodriguez, P.; Otero, P.; Azevedo, J.; Alfonso, A.; Botana, L.M.; Vasconcelos, V. New invertebrate vectors for pst, spirolides and okadaic acid in the north atlantic. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1936–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anon, A. Official method 959.08. Paralytic shellfish poison. Biological method. Final action. AOAC Off. Methods Anal. 2005, 49, 79–80. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, J.; Benford, D.; Boobis, A.; Ceccatelli, S.; Cravedi, J.-P.; Di, A.; Domenico, D.D.; Dogliotti, E.; Edler, L.; Farmer, P.; et al. Marine biotoxins in shellfish—Summary on regulated marine biotoxins scientific opinion of the panel on contaminants in the food chain. EFSA J. 2009, 1306, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Anon, A. Official Method 2005.06 Quantitative Determination of Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning Toxins in Shellfish Using Pre-Chromatographic Oxidation and Liquid Chromatography with Fluorescence Detection; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Anon, A. Official Method 2011.02 Determination of Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning Toxins in Mussels, Clams, Oysters and Scallops; Post-column Oxidation Method (PCOX). First Action 2011; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- DeGrasse, S.L.; van de Riet, J.; Hatfield, R.; Turner, A. Pre-versus post-column oxidation liquid chromatography fluorescence detection of paralytic shellfish toxins. Toxicon 2011, 57, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rey, V.; Alfonso, A.; Botana, L.M.; Botana, A.M. Influence of different shellfish matrices on the separation of PSP toxins using a postcolumn oxidation liquid chromatography method. Toxins 2015, 7, 1324–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Riet, J.; Gibbs, R.S.; Muggah, P.M.; Rourke, W.A.; MacNeil, J.D.; Quilliam, M.A. Liquid chromatography post-column oxidation (PCOX) method for the determination of paralytic shellfish toxins in mussels, clams, oysters, and scallops: Collaborative study. J. AOAC Int. 2010, 94, 1154–1176. [Google Scholar]
- Li, A.; Ma, J.; Cao, J.; Wang, Q.; Yu, R.; Thomas, K.; Quilliam, M. Analysis of paralytic shellfish toxins and their metabolites in shellfish from the north yellow sea of china. Food Addit. Contam. A 2012, 29, 1455–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, T.R.; Doucette, G.J.; Powell, C.L.; Boyer, G.L.; Plumley, F.G. Gtx(4) imposters: Characterization of fluorescent compounds synthesized by pseudomonas stutzeri SF/PS and pseudomonas/alteromonas PTB-1, symbionts of saxitoxin-producing alexandrium spp. Toxicon 2003, 41, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Sakai, R.; Kodama, M. Identification of thioether intermediates in the reductive transformation of gonyautoxins into saxitoxins by thiols. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2000, 10, 1787–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, S.; Sato, S.; Ogata, T.; Kodama, M. Formation of intermediate conjugates in the reductive transformation of gonyautoxins to saxitoxins by thiol compounds. Fish. Sci. 2000, 66, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, Y. Chemical and enzymatic transformation of paralytic shellfish toxins in marine organisms. In Harmful Marine Algal Blooms; Lassus, P., Arzul, G., Eds.; Lavoisier Intercept Ltd.: Paris, France, 1995; p. 475. [Google Scholar]
- Asakawa, M.; Takagi, M.; Iida, A.; Oishi, K. Studies on the conversion of paralytic shellfish poison (PSP) components by biochemical reducing agents. Jpn. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 1987, 33, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, Y.; Yoshioka, M. Transformation of paralytic shellfish toxins as demonstrated in scallop homogenates. Science 1981, 212, 547–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vale, C.; Alfonso, A.; Vieytes, M.R.; Romarís, X.M.; Arévalo, F.; Botana, A.M.; Botana, L.M. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of paralytic shellfish poisoning toxin potency and the influence of the pH of extraction. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 1770–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, M.; Rey, V.; Botana, A.; Vasconcelos, V.; Botana, L. Determination of Gonyautoxin-4 in Echinoderms and Gastropod Matrices by Conversion to Neosaxitoxin Using 2-Mercaptoethanol and Post-Column Oxidation Liquid Chromatography with Fluorescence Detection. Toxins 2016, 8, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8010011
Silva M, Rey V, Botana A, Vasconcelos V, Botana L. Determination of Gonyautoxin-4 in Echinoderms and Gastropod Matrices by Conversion to Neosaxitoxin Using 2-Mercaptoethanol and Post-Column Oxidation Liquid Chromatography with Fluorescence Detection. Toxins. 2016; 8(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Marisa, Verónica Rey, Ana Botana, Vitor Vasconcelos, and Luis Botana. 2016. "Determination of Gonyautoxin-4 in Echinoderms and Gastropod Matrices by Conversion to Neosaxitoxin Using 2-Mercaptoethanol and Post-Column Oxidation Liquid Chromatography with Fluorescence Detection" Toxins 8, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8010011
APA StyleSilva, M., Rey, V., Botana, A., Vasconcelos, V., & Botana, L. (2016). Determination of Gonyautoxin-4 in Echinoderms and Gastropod Matrices by Conversion to Neosaxitoxin Using 2-Mercaptoethanol and Post-Column Oxidation Liquid Chromatography with Fluorescence Detection. Toxins, 8(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8010011