Onabotulinumtoxin A Treatment of Drooling in Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Prospective, Longitudinal Open-Label Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Outcome Measures
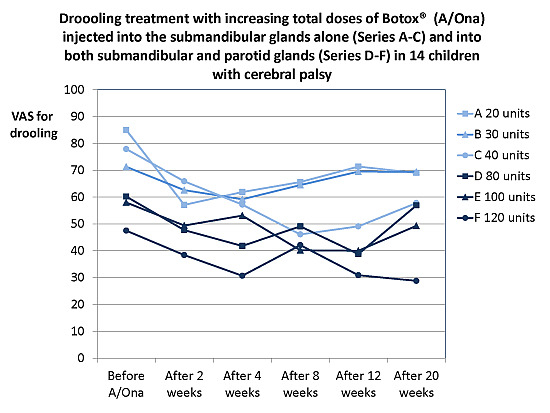
2.1.1. Treatment Effect, Drooling and Salivary Flow
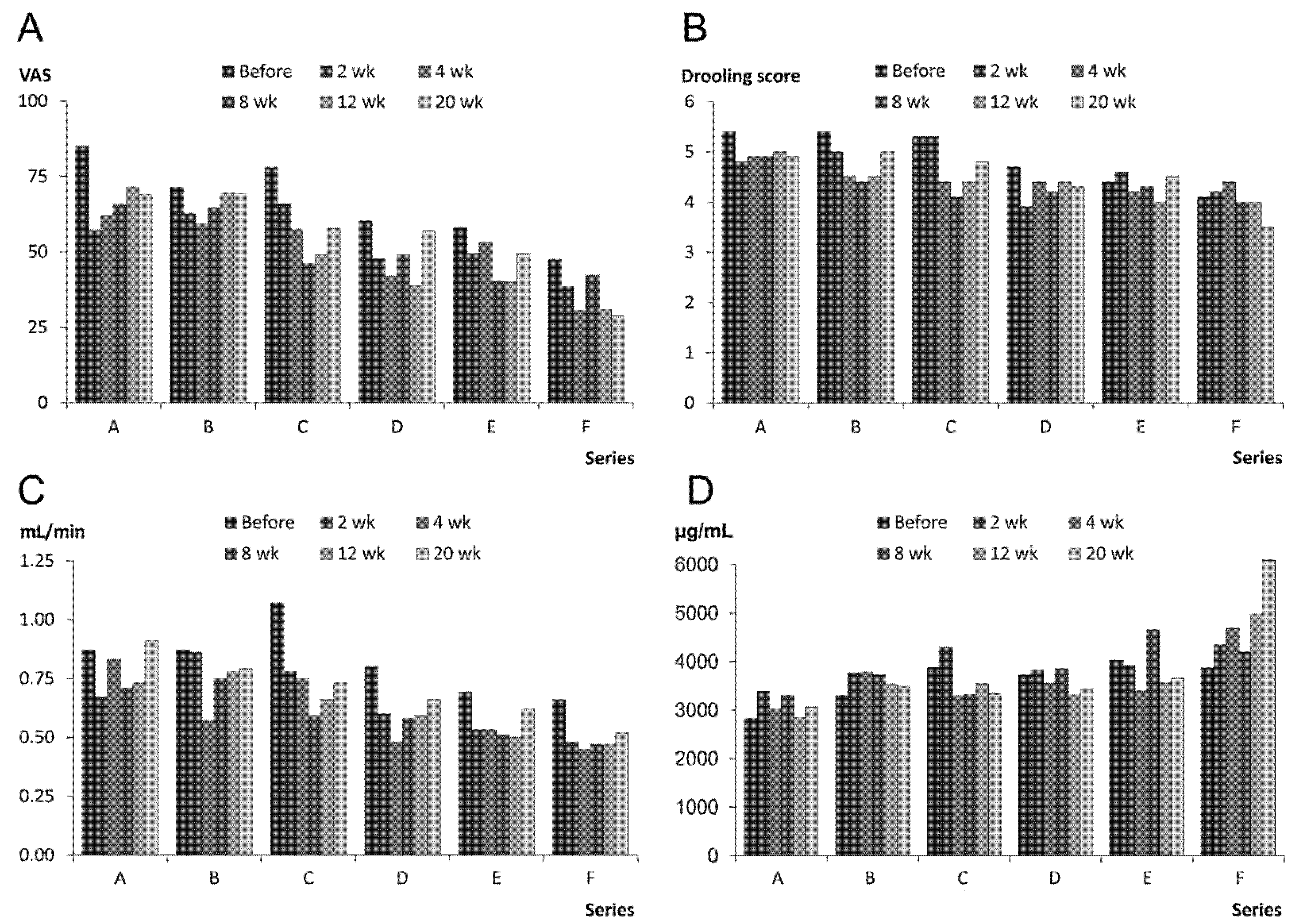
2.1.2. Prolonged Effect and Adverse Reactions
| Treatment Series | A | B | C | D | E | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment effect (0–5) a Mean (SD) of ratings (2, 4, 8, 12, 20 weeks) Median of ratings | 2.6 (0.1) 3.0 | 22.5 (0.2) 2.5 | 2.3 (0.2) 2.3 | 1.9 (0.1) 2.0 | 1.9 (0.2) 2.0 | 1.5 (0.1) 1.0 |
| Side effects (% of 14 treatments) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Immediate, short-lasting (less than 2 weeks after injection): Soreness, pain, swelling, dry mouth, viscous saliva | 14.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 7.1 | 0.0 | 28.6 |
| Long-term, longer lasting (up to 5 weeks after injection): Eating and swallowing problems (fluids and food) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 14.3 | 7.1 |
2.2. Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Design and Procedure
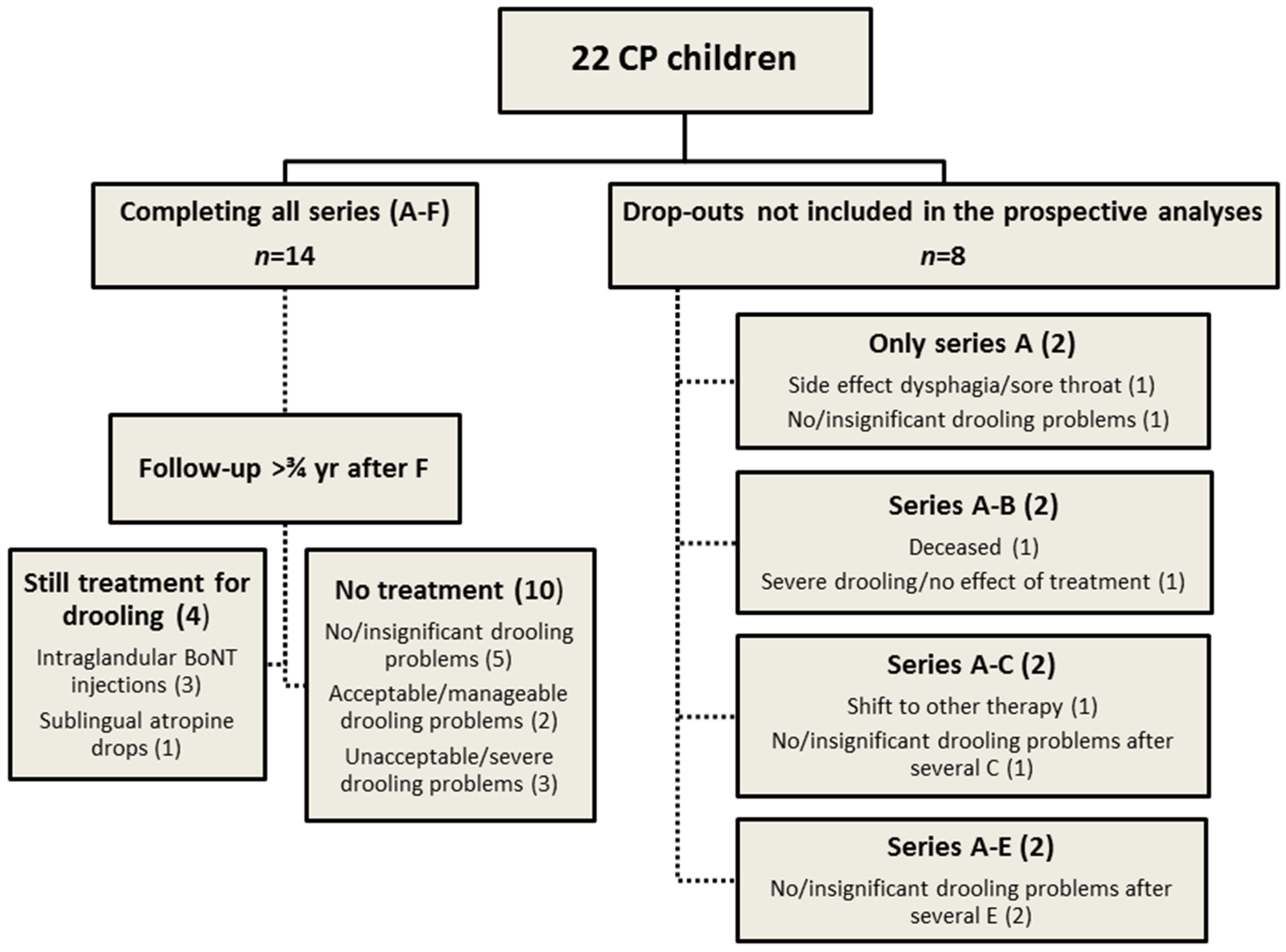
3.2. Participants
| No. | Age (year) | Sex (F/M) | Feeding (Oral/Tube) | GMFCS level (I–V) | CFCS level (1–5) | ID—Intellectual disability (1–4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 12 | M | Oral | II | 2 | 1 |
| 2 | 9 | F | Oral | V | 5 | 3 |
| 3 | 15 | F | Tube | V | 5 | 4 |
| 4 | 8 | F | Tube | V | 5 | 4 |
| 5 | 11 | M | Tube | V | 4 | 3 |
| 6 | 5 | M | Oral | IV | 3 | 2 |
| 7 | 5 | M | Oral | IV | 2 | 1 |
| 8 | 10 | M | Oral | IV | 4 | 3 |
| 9 | 9 | F | Oral | IV | 5 | 4 |
| 10 | 12 | F | Oral | IV | 2 | 2 |
| 11 | 15 | M | Tube | V | 4 | 4 |
| 12 | 16 | F | Tube | V | 5 | 4 |
| 13 | 7 | M | Oral | IV | 3 | 2 |
| 14 | 5 | M | Oral | IV | 3 | 1 |
| 15 | 7 | F | Oral | III | 2 | 2 |
| 16 | 12 | M | Oral | III | 2 | 1 |
| 17 | 5 | M | Oral | II | 2 | 2 |
| 18 | 10 | F | Oral | IV | 4 | 3 |
| 19 | 10 | M | Oral | IV | 3 | 3 |
| 20 | 11 | F | Tube | V | 5 | 3 |
| 21 | 13 | F | Tube | V | 4 | 4 |
| 22 | 15 | M | Oral | II | 2 | 1 |
| 14 children completing all treatment series: Mean (SD) | IV (I) | 4 (1) | 3 (1) | |||
| 8 children not completing all treatment series: Mean (SD) | IV (0) | 3 (1) | 2 (1) | |||
| All children: Mean (SD) | IV (I) | 4 (1) | 3 (1) | |||
| No. | Insufficient lip closure (Y/N) | Distinct malocclusion (Y/N) | Perioral dermatitis (Y/N) | Drooling problems (VAS 0–100) | Drooling impact score (0–7) | Saliva flow rate UWS (mL/min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | N | N | N | 100 | 5 | 0.90 |
| 2 | Y | Y a,e,g | N | 82 | 5 | 0.12 |
| 3 | Y | Y a,g | Y | 82 | 5 | 1.22 |
| 4 | Y | Y b | Y | 96 | 6 | 0.42 |
| 5 | Y | N | Y | 80 | 6 | 1.25 |
| 6 | Y | Y a | Y | 80 | 4 | 1.28 |
| 7 | Y | Y a,d–g | Y | 72 | 6 | 0.50 |
| 8 | N | N | N | 68 | 4 | 0.45 |
| 9 | Y | Y a,e | Y | 80 | 6 | 0.36 |
| 10 | Y | N | Y | 99 | 6 | 0.98 |
| 11 | Y | Y b,c | Y | 85 | 4 | 0.38 |
| 12 | Y | Y b,c | Y | 95 | 7 | 1.36 h |
| 13 | Y | N | Y | 95 | 6 | 0.92 |
| 14 | Y | N | Y | 76 | 5 | 2.05 h |
| 15 | Y | N | Y | 54 | 4 | 2.43 h |
| 16 | Y | Y a,g | Y | 52 | 4 | 0.63 |
| 17 | Y | Y a,e | Y | 51 | 6 | 0.73 |
| 18 | N | N | N | 63 | 6 | 0.63 |
| 19 | Y | Y b,c,f | Y | 99 | 5 | 0.76 |
| 20 | Y | N | Y | 84 | 7 | 1.10 |
| 21 | Y | Y a,d | Y | 84 | 6 | 1.09 |
| 22 | Y | Y b,c | Y | 99 | 7 | 3.91 h |
| 14 children completing all treatment series: Mean (SD) | 85 (10) | 5 (1) | 0.87 (0.53) | |||
| 8 children not completing all treatment series: Mean (SD) | 73 (19) | 6 (1) | 1.40 (1.10) | |||
| All children: Mean (SD) | 81 (15) | 6 (1) | 1.10 (0.80) | |||
3.3. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blasco, P.A.; Allaire, J.H. Drooling in developmentally disabled: Management practices and recommandations. Consortium on drooling. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 1992, 34, 849–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddihough, D.; Erasmus, C.E.; Johnson, H.; McKellar, G.M.W.; Jongerius, P.H. Botulinum toxin assessment, intervention and aftercare for paediatric and adult drooling: International consensus statement. Eur. J. Neurol. 2010, 17, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, S.M.; McCutcheon, J.; Reddihough, D.S.; Johnson, H. Prevalence and predictors of drooling in 7- to 14-year-old children with cerebral palsy: A population study. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2012, 54, 1032–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahmassebi, J.F.; Curzon, M.E. The cause of drooling in children with cerebral palsy—Hypersalivation or swallowing defect? Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2003, 13, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navazesh, M.; Christensen, C.M. A comparison of whole mouth resting and stimulated salivary measurement procedures. J. Dent. Res. 1982, 10, 1158–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotteveel, L.J.; Jongerius, P.H.; van Limbeek, J.; van den Hoogen, F.J. Salivation in healthy schoolchildren. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2004, 68, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walshe, M.; Smith, M.; Pennington, L. Interventions for drooling in children with cerebral palsy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 11, CD008624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naumann, M.; Dressler, D.; Hallett, M.; Jankovic, J.; Schiavo, G.; Segal, K.R.; Truong, D. Evidence-based review and assessment of botulinum neurotoxin for the treatment of secretory disorders. Toxicon 2013, 67, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tighe, A.P.; Schiavo, G. Botulinum neurotoxins: Mechanisms of action. Toxicon 2013, 67, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Møller, E.; Karlsborg, M.; Bardow, A.; Lykkeaa, J.; Nissen, F.H.; Bakke, M. Treatment of severe drooling with botulinum toxin in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and Parkinson’s disease: Efficacy and possible mechanisms. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2011, 69, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erasmus, C.E.; van Hulst, K.; van den Hoogen, F.J.A.; van Limbeek, J.; Roeleveld, N.; Veerman, E.C.; Rotteveel, J.J.; Jongererius, P.H. Thickened saliva after effective management of drooling with botulinum toxin A. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2010, 52, e114–e118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Møller, E.; Daugaard, D.; Holm, O.; Winge, K.; Bardow, A.; Lykkeaa, J.; Belhage, B.; Bakke, M. Repeated treatments of drooling with botulinum toxin B in neurology. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2015, 131, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodwell, K.; Edwards, P.; Ware, R.S.; Boyd, R. Salivary gland botulinum toxin injections for drooling in children with cerebral palsy and neurodevelopmental disability: A systematic review. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2012, 54, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, E.K. Botulinum toxin treatment of sialorrhoea: Comparing different therapeutic preparations. Eur. J. Neurol. 2006, 13, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakraj, A.A.; Moghimi, N.; Jabbari, B. Sialorrhea: Anatomy, pathophysiology and treatment with emphasis on the role of botulinum toxins. Toxins 2013, 5, 1010–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.P.; Ke, J.Y.; Chen, C.Y.; Chen, C.L.; Chou, M.Y.; Pei, Y.C. Botulinum toxin type A on oral health in treating sialorrhea in children with cerebral palsy: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J. Child. Neurol. 2011, 26, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basciani, M.; Di Rienzo, F.; Fontana, A.; Copetti, M.; Pellegrini, F.; Intiso, D. Botulinum toxin type B for sialorrhea in children with cerebral palsy: A randomized trial comparing three doses. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2011, 53, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilken, B.; Aslami, H.; Backes, H. Successful treatment of drooling in children with neurological disorders with botulinum toxin A or B. Neuropediatrics 2008, 39, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, A.S.; Kling, T.; Huss, K.; Borggraefe, I.; Koerte, I.K.; Blaschek, A.; Jahn, K.; Heinen, F.; Berweck, S. Botulinum toxin type A and B for the reduction of hypersalivation in children with neurological disorders: A focus on effectiveness and therapy adherence. Neuropediatrics 2012, 43, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas-Stonell, N.; Greenberg, J. Three treatment approaches and clinical factors in the reduction of drooling. Dysphagia 1988, 3, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porte, M.; Chaléat-Valayer, E.; Patte, K.; D’Anjou, M.C.; Boulay, C.; Laffont, I. Relevance of intraglandular injections of botulinum toxin for the treatment of sialorrhea in children with cerebral palsy: A review. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2014, 18, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jongerius, P.H.; van Limbeek, J.; Rotteveel, J.J. Assessment of salivary flow rate: Biologic variation and measure error. Laryngoscope 2004, 14, 1801–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, S.M.; Johnstone, B.R.; Westbury, C.; Rawicki, B.; Reddihough, D.S. Randomized trial of botulinum toxin injections into the salivary glands to reduce drooling in children with neurological disorders. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2008, 50, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, K.J.; Glasson, C.; O’Flaherty, S.J. Parotid and submandibular botulinum toxin A injections for sialorrhea in children with cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2006, 48, 883–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jongerius, P.H.; van den Hoogen, F.J.; van Limbeek, J.; Gabreëls, F.J.; van Hulst, K.; Rotteveel, J.J. Effect of botulinum toxin in the treatment of drooling: A controlled clinical trial. Pediatrics 2004, 114, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, L.C.; Wong, S.W.; Hamid, H.A. Treatment of drooling in children with cerebral palsy using ultrasound guided intraglandular injections of botulinum toxin A. J. Pediatr. Neurol. 2009, 7, 141–145. [Google Scholar]
- Scheffer, A.R.; Erasmus, C.; van Hulst, K.; van Limbeek, J.; Jongerius, P.H.; van den Hoogen, F.J. Efficacy and duration of botulinum toxin treatment for drooling in 131 children. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2010, 136, 873–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordgarden, H.; Østerhus, I.; Møystad, A.; Asten, P.; Johnsen, U.L.; Storhaug, K.; Loven, J.Ø. Drooling: Are botulinum toxin injections into the major salivary glands a good treatment option? J. Child. Neurol. 2012, 27, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erasmus, C.E.; Scheffer, A.R.; van Hulst, K.; van Limbeek, J.; van den Hoogen, F.J.; Rotteveel, J.J.; Jongerius, P.H. Does motor performance matter in botulinum toxin efficacy for drooling? Pediatr. Neurol. 2011, 45, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Møller, E.; Pedersen, S.A.; Vinicoff, P.G.; Bardow, A.; Lykkeaa, J.; Svendsen, P.; Bakke, M. Onabotulinumtoxin A Treatment of Drooling in Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Prospective, Longitudinal Open-Label Study. Toxins 2015, 7, 2481-2493. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7072481
Møller E, Pedersen SA, Vinicoff PG, Bardow A, Lykkeaa J, Svendsen P, Bakke M. Onabotulinumtoxin A Treatment of Drooling in Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Prospective, Longitudinal Open-Label Study. Toxins. 2015; 7(7):2481-2493. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7072481
Chicago/Turabian StyleMøller, Eigild, Søren Anker Pedersen, Pablo Gustavo Vinicoff, Allan Bardow, Joan Lykkeaa, Pia Svendsen, and Merete Bakke. 2015. "Onabotulinumtoxin A Treatment of Drooling in Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Prospective, Longitudinal Open-Label Study" Toxins 7, no. 7: 2481-2493. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7072481
APA StyleMøller, E., Pedersen, S. A., Vinicoff, P. G., Bardow, A., Lykkeaa, J., Svendsen, P., & Bakke, M. (2015). Onabotulinumtoxin A Treatment of Drooling in Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Prospective, Longitudinal Open-Label Study. Toxins, 7(7), 2481-2493. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7072481