A Highly Specific Monoclonal Antibody for Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A-Cleaved SNAP25
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Western Blot Analysis
| Antibody | Specificity | Vendor | Species/Type | IgG-isotype | SNAP25197 antigen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMI-81R | SNAP25206/197 | Covance, Princeton, NJ | Murine/mAb | IgG1 | Uncleaved SNAP25 |
| MC-6050 | SNAP25206/197 | R&D Abs, LV, NV | Murine/mAb | n/a | 15-mer, COOH-term |
| MC-6053 | SNAP25197 | R&D Abs, LV, NV | Murine/mAb | n/a | 15-mer, COOH-term |
| Ab632 | SNAP25197 | Allergan | rHuman/rMAb | IgG1 | 12-mer, COOH-term |
| Ab635 | SNAP25197 | Allergan | rMurine/rMAb | IgG2A | 12-mer, COOH-term |
| RGT-1092 | SNAP25197 | Allergan | Rabbit/pAb | IgG | 7-mer, COOH-term |

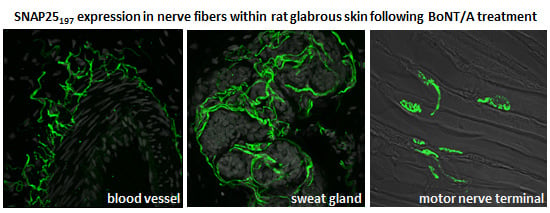
2.2. Immunohistochemistry
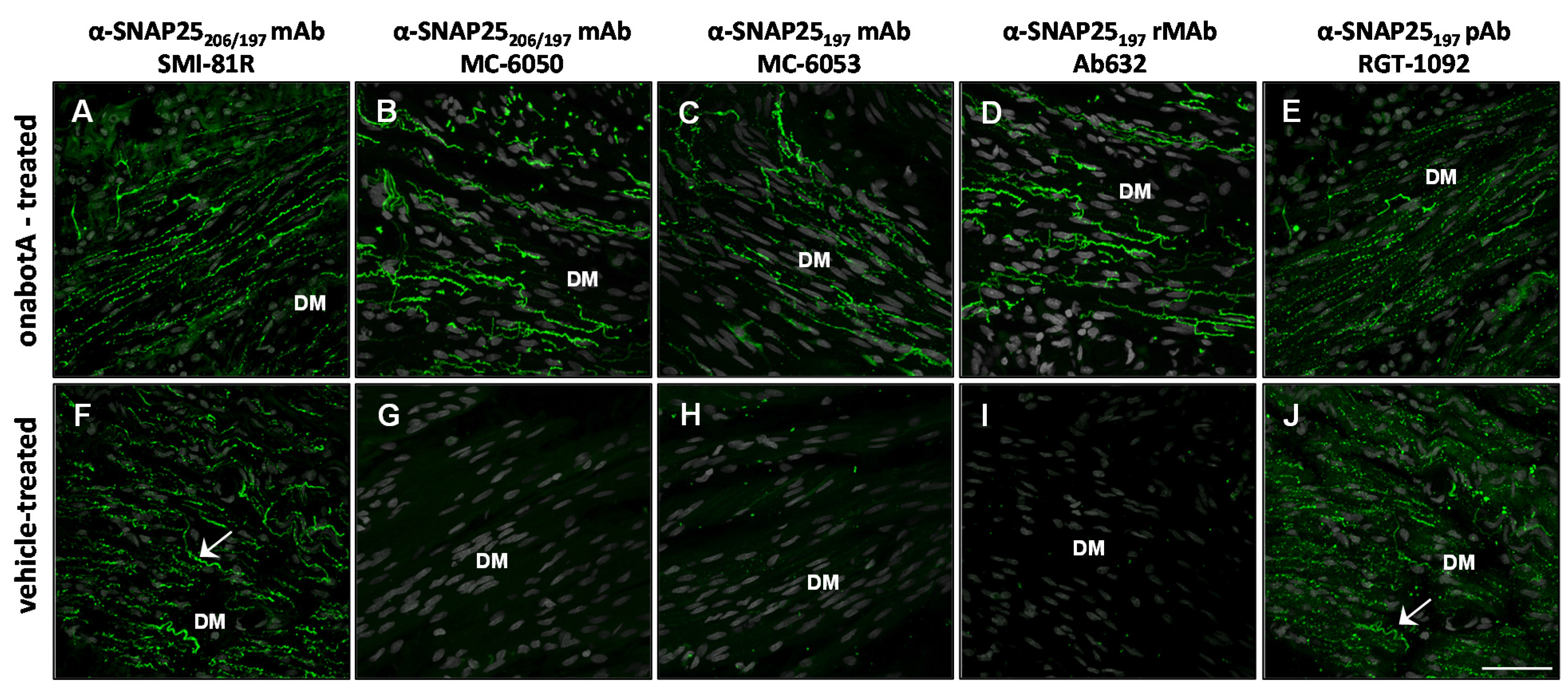
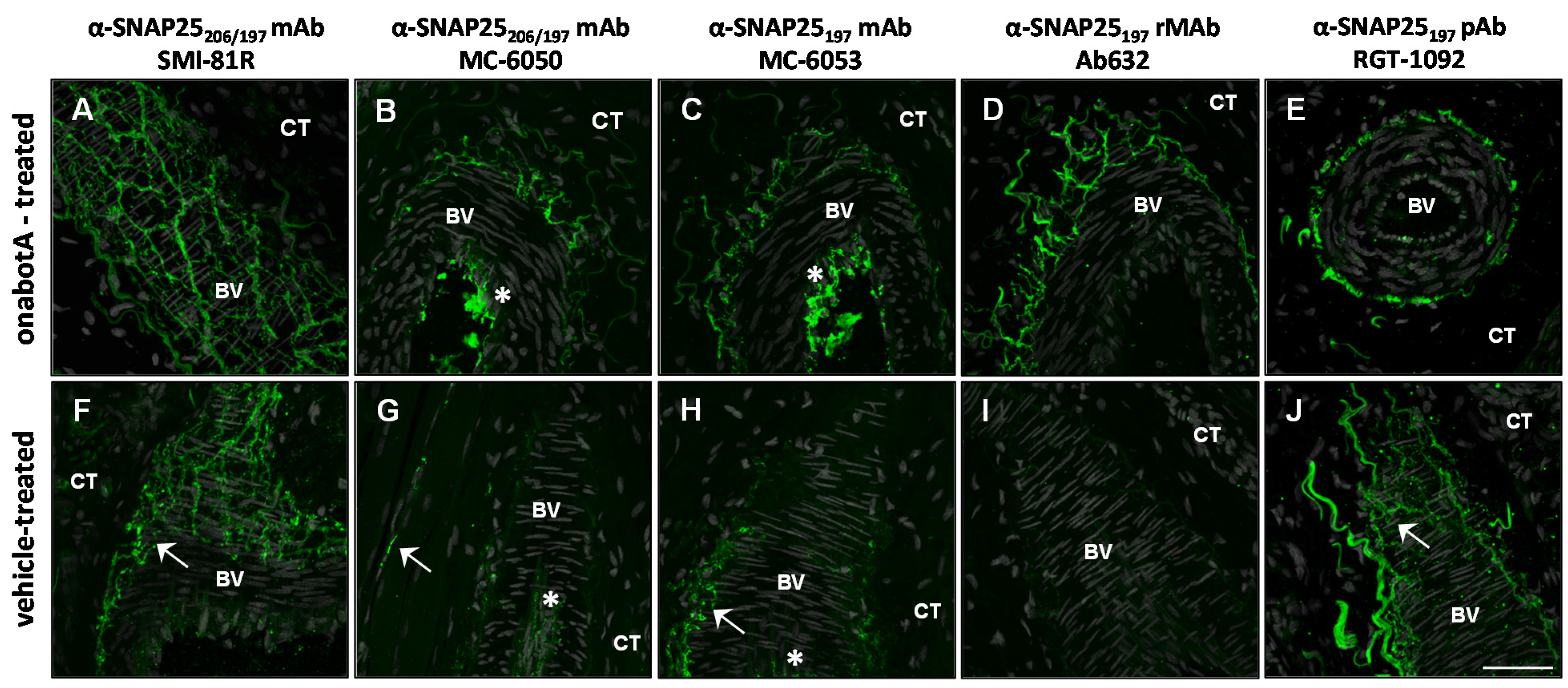
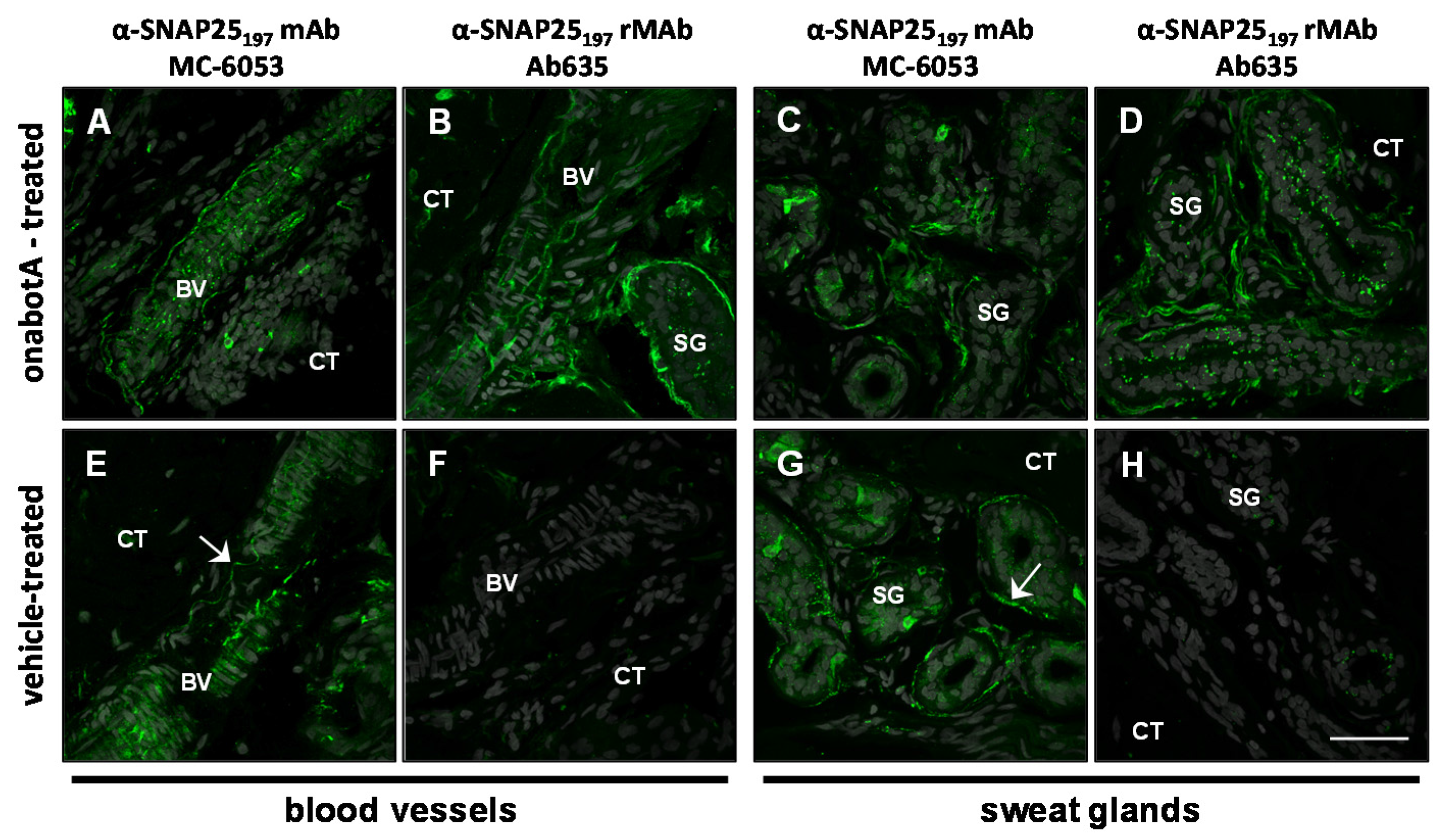
2.3. Immunocytochemistry

| Antibody | Specificity | Western blot | Rat bladder | Rat skin | Human skin | Rat DRG culture |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMI-81R | SNAP25206/197 | 206 + 197 | 206 + 197 | 206 + 197 | n/t | 206 + 197 |
| MC-6050 | SNAP25206/197 | 197 | 197 | 206 + 197 + b | n/t | n/t |
| MC-6053 | SNAP25197 | 197 | 197 | 206 + 197 + b | 206 + 197 | 197 + b |
| Ab632 | SNAP25197 | 197 | 197 | 197 | n/t | 197 |
| Ab635 | SNAP25197 | 197 | 197 | 197 | 197 | n/t |
| RGT-1092 | SNAP25197 | 197 | 206 + 197 | 206 + 197 | n/t | n/t |
3. Discussion
3.1. Anti-SNAP25197 Polyclonal Antibodies
3.2. Anti-SNAP25197 Monoclonal Antibodies
3.3. Conclusion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Antibodies
4.2. Cell cultures
4.3. Western Blot
4.4. Animals and Skin Biopsy Samples
4.5. BoNT/A Preparation and Injection Procedures
4.6. Tissue Preparation
4.7. Immunocyto/Histochemistry
4.8. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brin, M.F. Development of future indications for BOTOX. Toxicon 2009, 54, 668–674. [Google Scholar]
- Whitcup, S.M.; Turkel, C.C.; DeGryse, R.E.; Brin, M.F. Development of onabotulinumtoxinA for chronic migraine. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2014, 1329, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Castaneda, J.; Jankovic, J. Long-term efficacy, safety, and side effect profile of botulinum toxin in dystonia: A 20-year follow-up. Toxicon 2014, 90, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yablon, S.A.; Brin, M.F.; VanDenburgh, A.M.; Zhou, J.; Garabedian-Ruffalo, S.M.; Abu-Shakra, S.; Beddingfield, F.C., III. Dose response with onabotulinumtoxinA for post-stroke spasticity: A pooled data analysis. Mov. Disord. 2011, 26, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, F.; Nitti, V. Chapter 5: Clinical data in neurogenic detrusor overactivity (NDO) and overactive bladder (OAB). Neurourol. Urodyn. 2014, 33, S26–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellsworth, P.; Travis, M. Onabotulinum toxin A: A therapeutic option for refractory neurogenic detrusor overactivity and idiopathic overactive bladder. Urol. Nurs. 2014, 34, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grunfeld, A.; Murray, C.A.; Solish, N. Botulinum toxin for hyperhidrosis: A review. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2009, 10, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, K.R.; Francis, J. Updates on the antinociceptive mechanism hypothesis of botulinum toxin A. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2011, 17, S28–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burstein, R.; Zhang, X.; Levy, D.; Aoki, K.R.; Brin, M.F. Selective inhibition of meningeal nociceptors by botulinum neurotoxin type A: Therapeutic implications for migraine and other pains. Cephalalgia 2014, 34, 853–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binz, T.; Rummel, A. Cell entry strategy of clostridial neurotoxins. J. Neurochem. 2009, 109, 1584–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montal, M. Botulinum neurotoxin: A marvel of protein design. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2010, 79, 591–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolly, J.O.; Lawrence, G.W.; Meng, J.; Wang, J.; Ovsepian, S.V. Neuro-exocytosis: Botulinum toxins as inhibitory probes and versatile therapeutics. Curr. Opin Pharmacol. 2009, 9, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossetto, O.; Pirazzini, M.; Montecucco, C. Botulinum neurotoxins: Genetic, structural and mechanistic insights. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 535–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunger, A.T.; Rummel, A. Receptor and substrate interactions of clostridial neurotoxins. Toxicon 2009, 54, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humeau, Y.; Doussau, F.; Grant, N.J.; Poulain, B. How botulinum and tetanus neurotoxins block neurotransmitter release. Biochimie 2000, 82, 427–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mort, J.S.; Buttle, D.J. The use of cleavage site specific antibodies to delineate protein processing and breakdown pathways. Mol. Pathol. 1999, 52, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonucci, F.; Rossi, C.; Gianfranceschi, L.; Rossetto, O.; Caleo, M. Long-distance retrograde effects of botulinum neurotoxin A. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 3689–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matak, I.; Bach-Rojecky, L.; Filipovic, B.; Lackovic, Z. Behavioral and immunohistochemical evidence for central antinociceptive activity of botulinum toxin A. Neuroscience 2011, 186, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matak, I.; Riederer, P.; Lackovic, Z. Botulinum toxin’s axonal transport from periphery to the spinal cord. Neurochem. Int. 2012, 61, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Restani, L.; Antonucci, F.; Gianfranceschi, L.; Rossi, C.; Rossetto, O.; Caleo, M. Evidence for anterograde transport and transcytosis of botulinum neurotoxin A (BoNT/A). J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 15650–15659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Restani, L.; Novelli, E.; Bottari, D.; Leone, P.; Barone, I.; Galli-Resta, L.; Strettoi, E.; Caleo, M. Botulinum neurotoxin A impairs neurotransmission following retrograde transynaptic transport. Traffic 2012, 13, 1083–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, A.; Cruz, F.; Cruz, C.D.; Avelino, A. Spread of onabotulinumtoxinA after bladder injection. Experimental study using the distribution of cleaved SNAP-25 as the marker of the toxin action. Eur. Urol. 2012, 61, 1178–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, A.; Cruz, F.; Cruz, C.D.; Avelino, A. Effect of onabotulinumtoxinA on intramural parasympathetic ganglia: An experimental study in the guinea pig bladder. J. Urol. 2012, 187, 1121–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marini, P.; MacLeod, R.A.; Treuner, C.; Bruchelt, G.; Bohm, W.; Wolburg, H.; Schweizer, P.; Girgert, R. SiMa, a new neuroblastoma cell line combining poor prognostic cytogenetic markers with high adrenergic differentiation. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 1999, 112, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Salas, E.; Wang, J.; Molina, Y.; Nelson, J.B.; Jacky, B.P.; Aoki, K.R. Botulinum neurotoxin serotype A specific cell-based potency assay to replace the mouse bioassay. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacky, B.P.S.; Garay, P.E.; Dupuy, J.; Nelson, J.B.; Cai, B.; Molina, Y.; Wang, J.; Steward, L.E.; Broide, R.S.; Francis, J.; et al. Identification of Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 3 (FGFR3) as a Protein Receptor for Botulinum Neurotoxin Serotype A (BoNT/A). PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Salas, E.; Steward, L.E.; Ho, H.; Garay, P.E.; Sun, S.W.; Gilmore, M.A.; Ordas, J.V.; Wang, J.; Francis, J.; Aoki, K.R. Plasma membrane localization signals in the light chain of botulinum neurotoxin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 3208–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Research & Diagnostic Antibodies. Available online: http://www.rdabs.com/files/datasheets/MC-6050.pdf (accessed on 17 June 2015).
- Research & Diagnostic Antibodies. Available online: http://www.rdabs.com/files/datasheets/MC-6053.pdf (accessed on 17 June 2015).
- Bercsenyi, K.; Giribaldi, F.; Schiavo, G. The elusive compass of clostridial neurotoxins: Deciding when and where to go? Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 364, 91–113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mazzocchio, R.; Caleo, M. More than at the Neuromuscular Synapse: Actions of Botulinum Neurotoxin A in the Central Nervous System. Neuroscientist 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinelli, S.; Vacca, V.; Ricordy, R.; Uggenti, C.; Tata, A.M.; Luvisetto, S.; Pavone, F. The analgesic effect on neuropathic pain of retrogradely transported botulinum neurotoxin A involves Schwann cells and astrocytes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matak, I.; Rossetto, O.; Lackovic, Z. Botulinum toxin type A selectivity for certain types of pain is associated with capsaicin-sensitive neurons. Pain 2014, 155, 1516–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J. Personal communication. Allergan, Irvine, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mort, J.S.; Flannery, C.R.; Makkerh, J.; Krupa, J.C.; Lee, E.R. Use of anti-neoepitope antibodies for the analysis of degradative events in cartilage and the molecular basis for neoepitope specificity. Biochem. Soc. Symp. 2003, 107–114. [Google Scholar]
- Nagata, K.; Izawa, I.; Inagaki, M. A decade of site- and phosphorylation state-specific antibodies: Recent advances in studies of spatiotemporal protein phosphorylation. Genes Cells 2001, 6, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rhéaume, C.; Cai, B.B.; Wang, J.; Fernández-Salas, E.; Aoki, K.R.; Francis, J.; Broide, R.S. A Highly Specific Monoclonal Antibody for Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A-Cleaved SNAP25. Toxins 2015, 7, 2354-2370. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7072354
Rhéaume C, Cai BB, Wang J, Fernández-Salas E, Aoki KR, Francis J, Broide RS. A Highly Specific Monoclonal Antibody for Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A-Cleaved SNAP25. Toxins. 2015; 7(7):2354-2370. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7072354
Chicago/Turabian StyleRhéaume, Catherine, Brian B. Cai, Joanne Wang, Ester Fernández-Salas, K. Roger Aoki, Joseph Francis, and Ron S. Broide. 2015. "A Highly Specific Monoclonal Antibody for Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A-Cleaved SNAP25" Toxins 7, no. 7: 2354-2370. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7072354
APA StyleRhéaume, C., Cai, B. B., Wang, J., Fernández-Salas, E., Aoki, K. R., Francis, J., & Broide, R. S. (2015). A Highly Specific Monoclonal Antibody for Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A-Cleaved SNAP25. Toxins, 7(7), 2354-2370. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7072354